A Cost-Effective Saliva-Based Human Epigenetic Clock Using 10 CpG Sites Identified with the Illumina EPIC 850k Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Methylation Profiling
2.2. Identification of Age-Associated CpGs
2.3. Clock Construction
2.4. Performance Evaluation
2.5. Comparative Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selection of a 10-CpG Saliva Clock
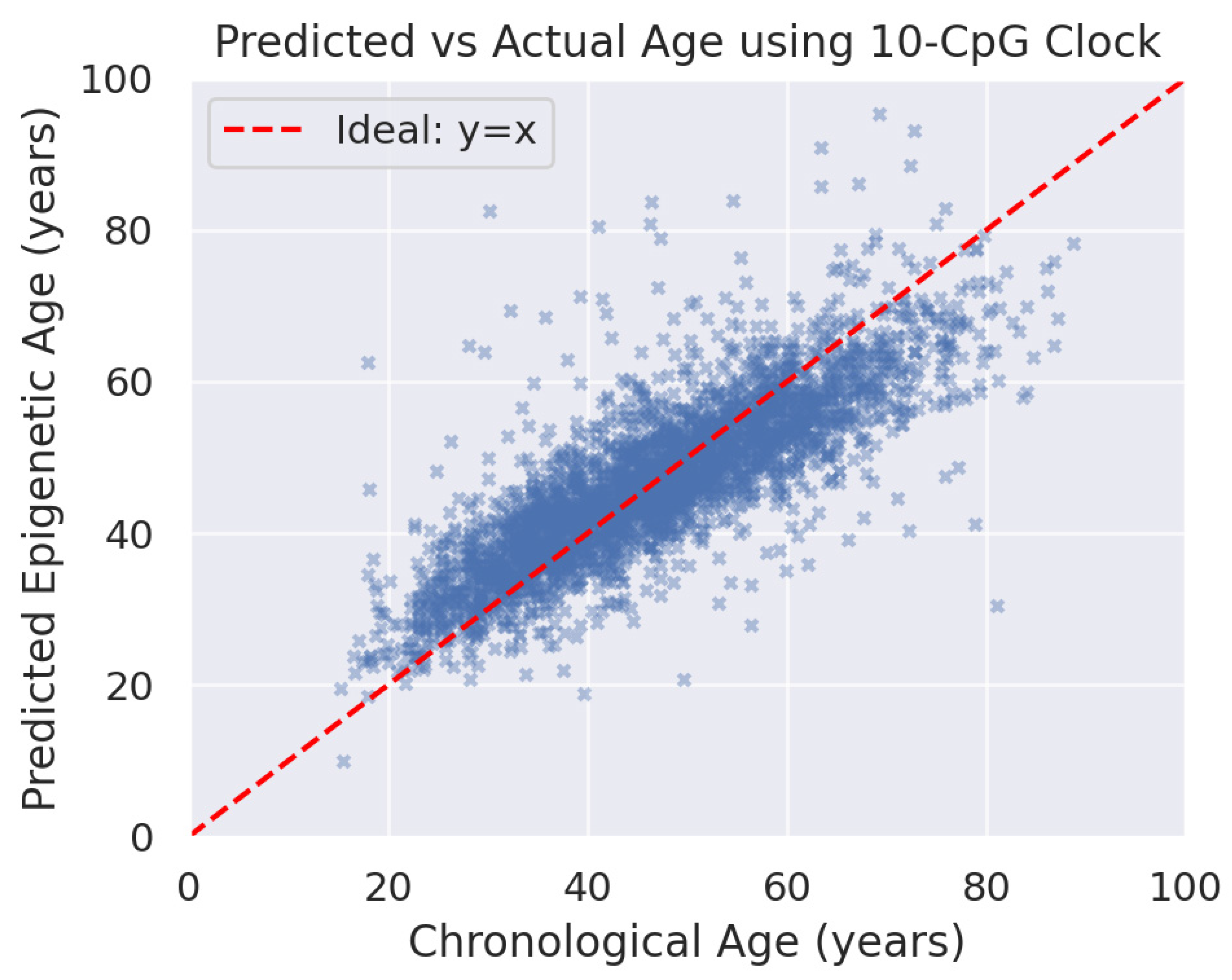
3.2. Epigenetic Age Prediction Accuracy
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Established Clocks
4.2. Biological Significance of Clock CpGs
4.3. Limitations
Convergence with Other Ageing Hallmarks
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, G.; Zou, J.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, C.; et al. Lipid metabolism dysfunction induced by age-dependent DNA methylation accelerates aging. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocklandt, S.; Lin, W.; Sehl, M.E.; Sánchez, F.J.; Sinsheimer, J.S.; Horvath, S.; Vilain, E. Epigenetic predictor of age. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shishtawy, N.M.; El Marzouky, F.M.; El-Hagrasy, H.A. DNA methylation of ELOVL2 gene as an epigenetic marker of age among Egyptian population. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2024, 25, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garagnani, P.; Bacalini, M.G.; Pirazzini, C.; Gori, D.; Giuliani, C.; Mari, D.; Passarino, G.; Di Blasio, A.M.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S. Methylation of ELOVL2 gene as a new epigenetic marker of age. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feil, R.; Fraga, M.F. Epigenetics and the environment: Emerging patterns and implications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, P.R.; Han, S.; Hing, B.; Nagahama, Y.; Gaul, L.N.; Heinzman, J.T.; Grossbach, A.J.; Close, L.; Dlouhy, B.J.; Howard, M.A., III; et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation comparison between live human brain and peripheral tissues within individuals. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajuddin, S.M.; Hernandez, D.G.; Chen, B.H.; Noren Hooten, N.; Mode, N.A.; Nalls, M.A.; Singleton, A.B.; Ejiogu, N.; Chitrala, K.N.; Zonderman, A.B.; et al. Novel age-associated DNA methylation changes and epigenetic age acceleration in middle-aged African Americans and whites. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, C.I.; Lin, Q.; Koch, C.M.; Eisele, L.; Beier, F.; Ziegler, P.; Bauerschlag, D.O.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Erbel, R.; Mühleisen, T.W.; et al. Aging of blood can be tracked by DNA methylation changes at just three CpG sites. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboute, T.; Zucca, S.; Holcomb, M.; Patil, D.N.; Garza, C.; Wheatley, B.A.; Roy, R.N.; Forli, S.; Martemyanov, K.A. Orphan receptor GPR158 serves as a metabotropic glycine receptor: mGlyR. Science 2023, 379, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, L.M.; Taylor, J.R.; Ding, J.; Lohman, K.; Johnson, C.; Siscovick, D.; Burke, G.; Post, W.; Shea, S.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; et al. Age-related variations in the methylome associated with gene expression in human monocytes and T cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pevsner, J.; Sabunciyan, S.; Yolken, R.H.; Webster, M.J.; Dinkins, T.; Callinan, P.A.; Fan, J.B.; Potash, J.B.; Feinberg, A.P. Functional annotation of the human brain methylome identifies tissue-specific epigenetic variation across brain and blood. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Chao, D.L.; Rocha, L.; Kolar, M.; Nguyen Huu, V.A.; Krawczyk, M.; Dasyani, M.; Wang, T.; Jafari, M.; Jabari, M.; et al. The lipid elongation enzyme ELOVL2 is a molecular regulator of aging in the retina. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dev, N.B.; Mir, S.A.; Gayen, J.R.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Mustapic, M.; Vaingankar, S.M. Cardiac electrical activity in a genomically “humanized” chromogranin a monogenic mouse model with hyperadrenergic hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2014, 7, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakyan, V.K.; Down, T.A.; Maslau, S.; Andrew, T.; Yang, T.P.; Beyan, H.; Whittaker, P.; McCann, O.T.; Finer, S.; Valdes, A.M.; et al. Human aging-associated DNA hypermethylation occurs preferentially at bivalent chromatin domains. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Mueller, A.; English, B.; Arena, A.; Vera, D.; Kane, A.E.; Sinclair, D.A. Novel feature selection methods for construction of accurate epigenetic clocks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florath, I.; Butterbach, K.; Müller, H.; Bewerunge-Hudler, M.; Brenner, H. Cross-sectional and longitudinal changes in DNA methylation with age: An epigenome-wide analysis revealing over 60 novel age-associated CpG sites. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1186–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Heijmans, B.T.; Hjelmborg, J.V.B.; Soerensen, M.; Christensen, K.; Christiansen, L. Epigenetic drift in the aging genome: A ten-year follow-up in an elderly twin cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Song, Z.; Wei, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ju, J.; Yao, P.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, H.; Chi, X.; Li, N. Expression mapping and functional analysis of orphan G-protein-coupled receptor GPR158 in the adult mouse brain using a GPR158 transgenic mouse. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, L.P.; Orlandi, C.; Song, C.; Oh, W.C.; Muntean, B.S.; Xie, K.; Filippini, A.; Xie, X.; Satterfield, R.; Yaeger, J.D.W.; et al. Orphan receptor GPR158 controls stress-induced depression. eLife 2018, 7, e33273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetereisi, D.; Kramvis, I.; Gebuis, T.; van der Loo, R.J.; Gouwenberg, Y.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Li, K.W.; Smit, A.B.; Spijker, S. Gpr158 Deficiency Impacts Hippocampal CA1 Neuronal Excitability, Dendritic Architecture, and Affects Spatial Learning. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaleh, H.; Haddrill, P.R. Identifying blood-specific age-related DNA methylation markers on the Illumina MethylationEPIC® BeadChip. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 303, 109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
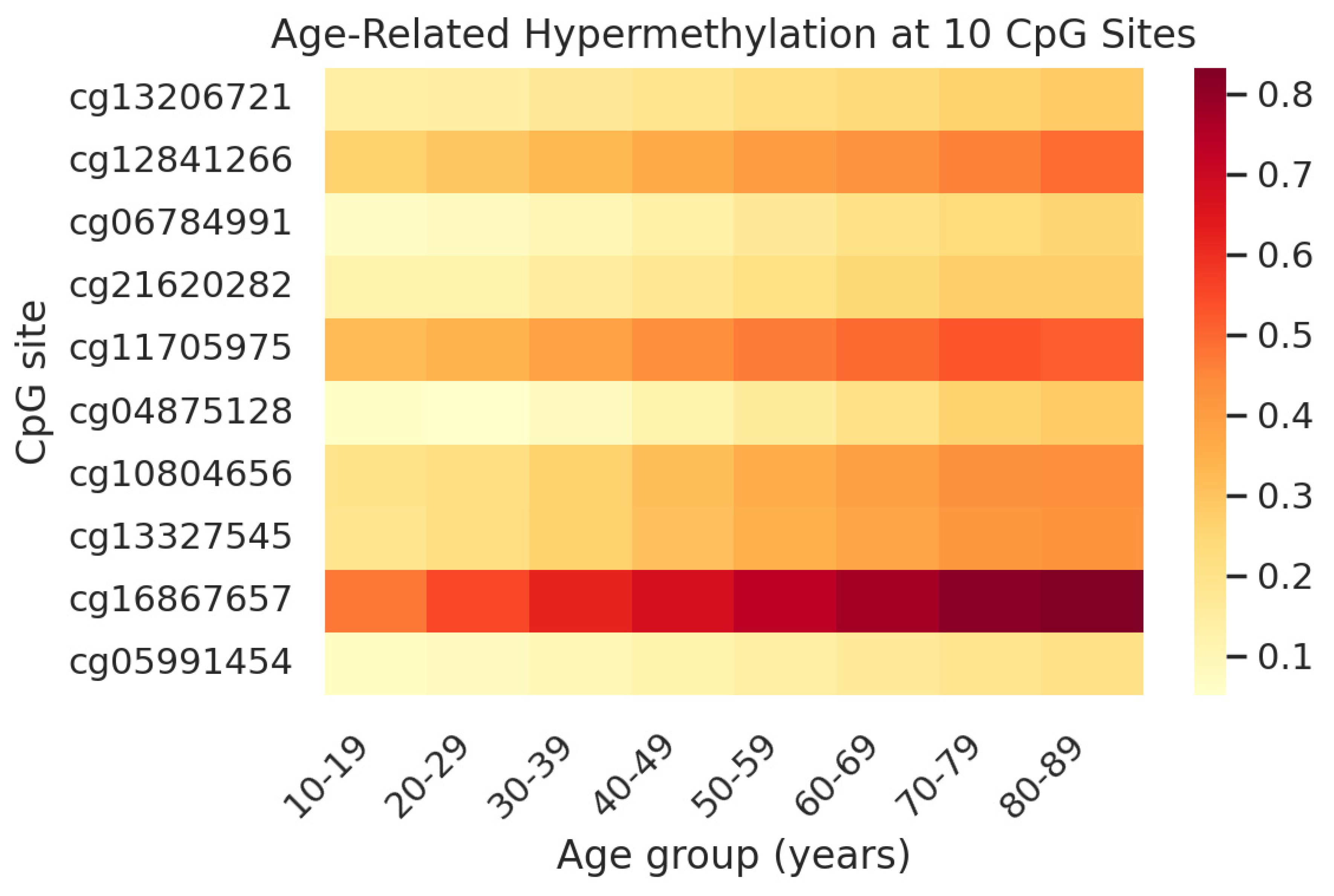
| CpG ID (Illumina) | Associated Gene(s) | Pearson r (with Age) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| cg16867657 | ELOVL2 | 0.66 | 3.39 × 10−73 |
| cg04875128 | OTUD7A | 0.61 | 5.02 × 10−73 |
| cg13327545 | (none) | 0.61 | 2.23 × 10−71 |
| cg12841266 | LHFPL4 | 0.56 | 4.5 × 10−71 |
| cg06784991 | ZYG11A | 0.56 | 5.39 × 10−71 |
| cg11705975 | PRLHR | 0.54 | 7.89 × 10−71 |
| cg13206721 | GPR158 (and GPR158-AS1) | 0.53 | 9.17 × 10−69 |
| cg10804656 | (none) | 0.52 | 1.83 × 10−66 |
| cg05991454 | (none) | 0.51 | 3.17 × 10−65 |
| cg21620282 | CHGA | 0.48 | 6.01 × 10−63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collins, C.; Brown, J.; Chung, H.C. A Cost-Effective Saliva-Based Human Epigenetic Clock Using 10 CpG Sites Identified with the Illumina EPIC 850k Array. DNA 2025, 5, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5020028
Collins C, Brown J, Chung HC. A Cost-Effective Saliva-Based Human Epigenetic Clock Using 10 CpG Sites Identified with the Illumina EPIC 850k Array. DNA. 2025; 5(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollins, Christopher, James Brown, and Henry C. Chung. 2025. "A Cost-Effective Saliva-Based Human Epigenetic Clock Using 10 CpG Sites Identified with the Illumina EPIC 850k Array" DNA 5, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5020028
APA StyleCollins, C., Brown, J., & Chung, H. C. (2025). A Cost-Effective Saliva-Based Human Epigenetic Clock Using 10 CpG Sites Identified with the Illumina EPIC 850k Array. DNA, 5(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5020028








