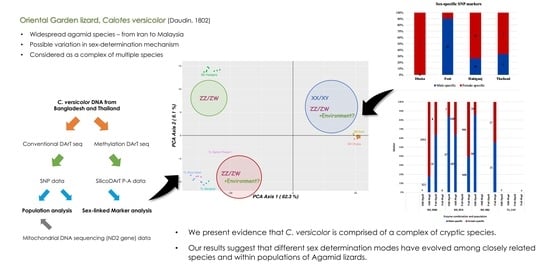
Sex-Determination Mechanisms among Populations within Cryptic Species Complex of Calotes (Squamata: Agamidae: Draconinae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
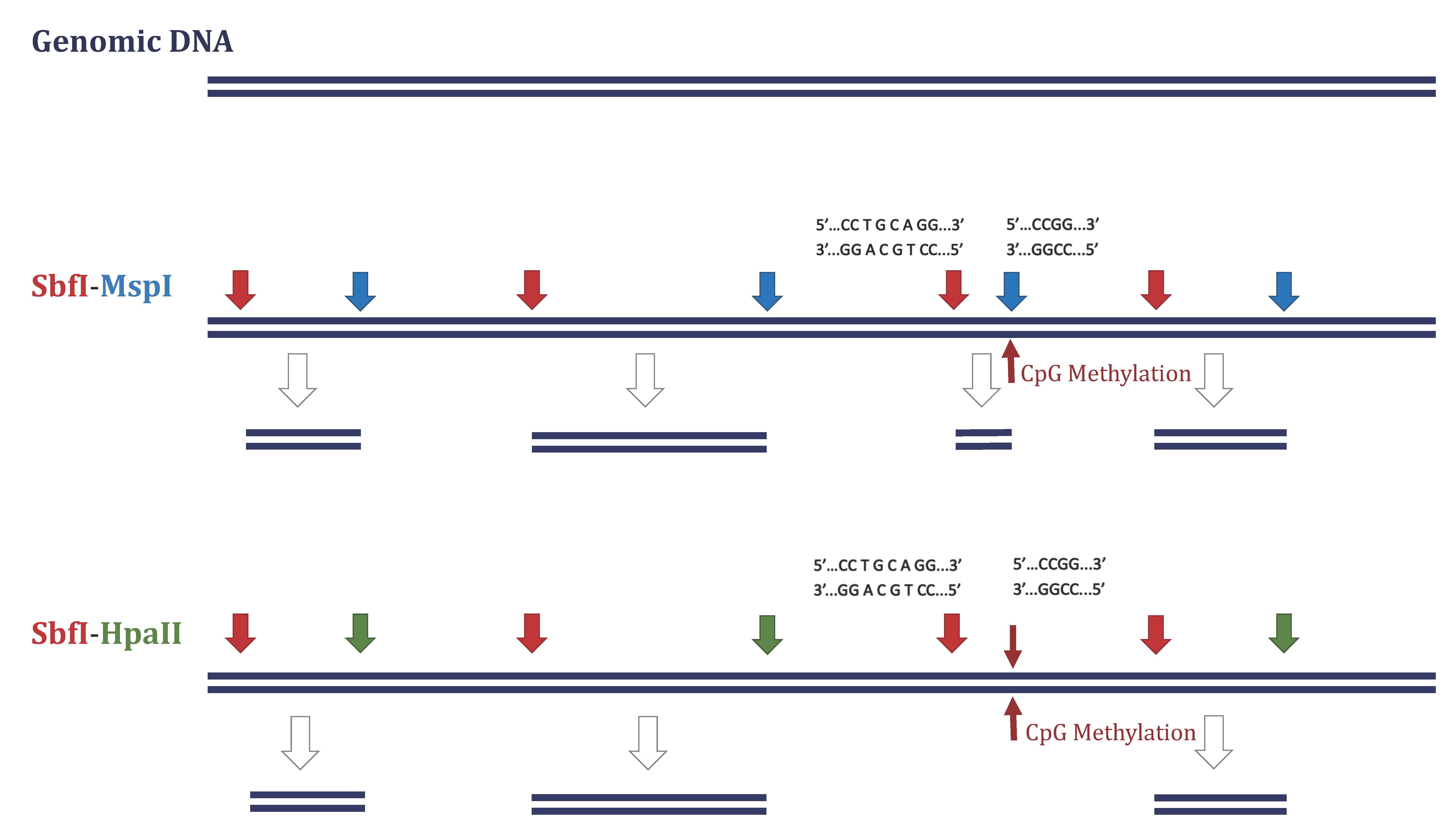
2.3. DArTseqMet—Methylation Analysis
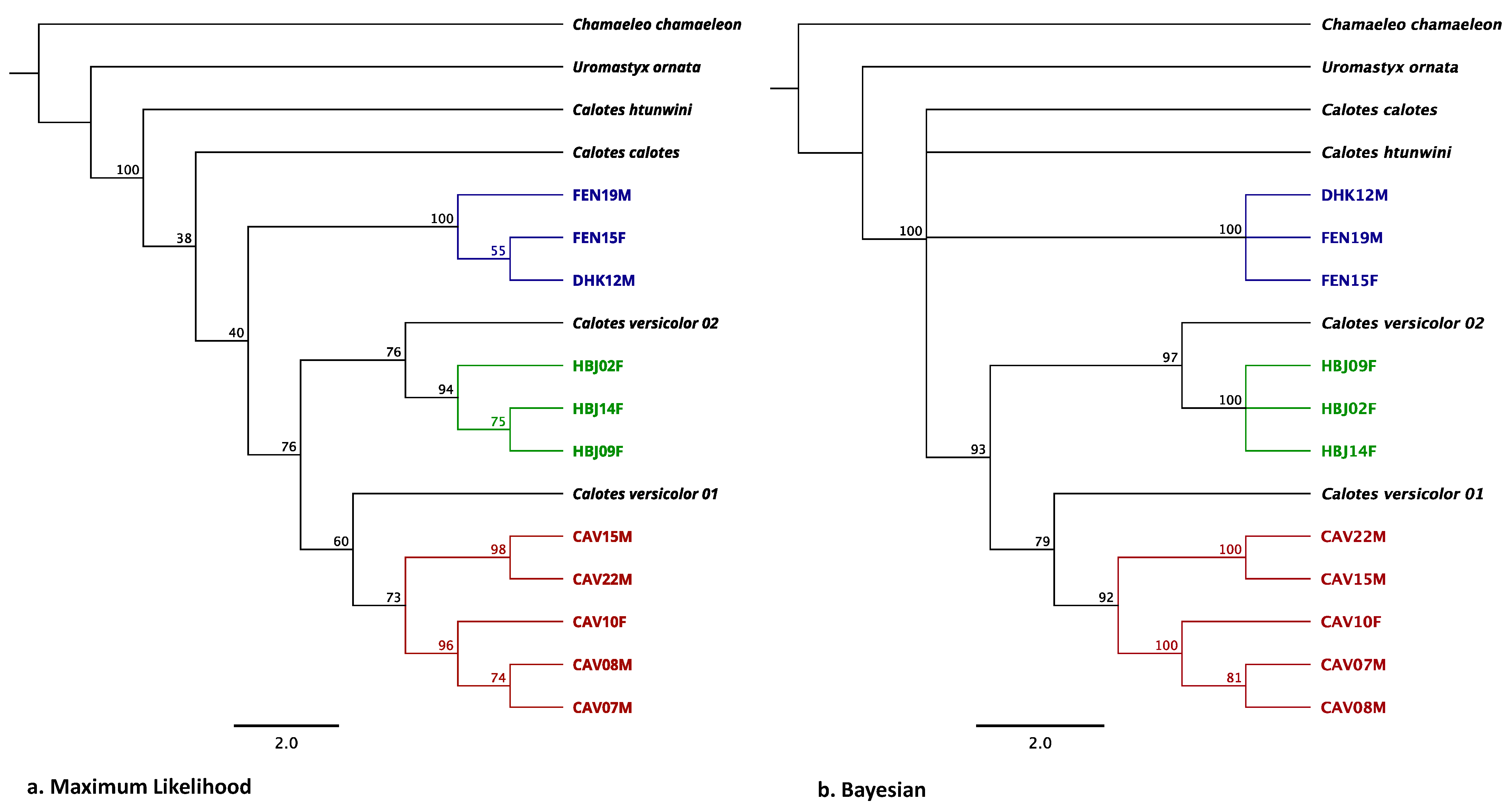
2.4. Population and Phylogenetic Analyses
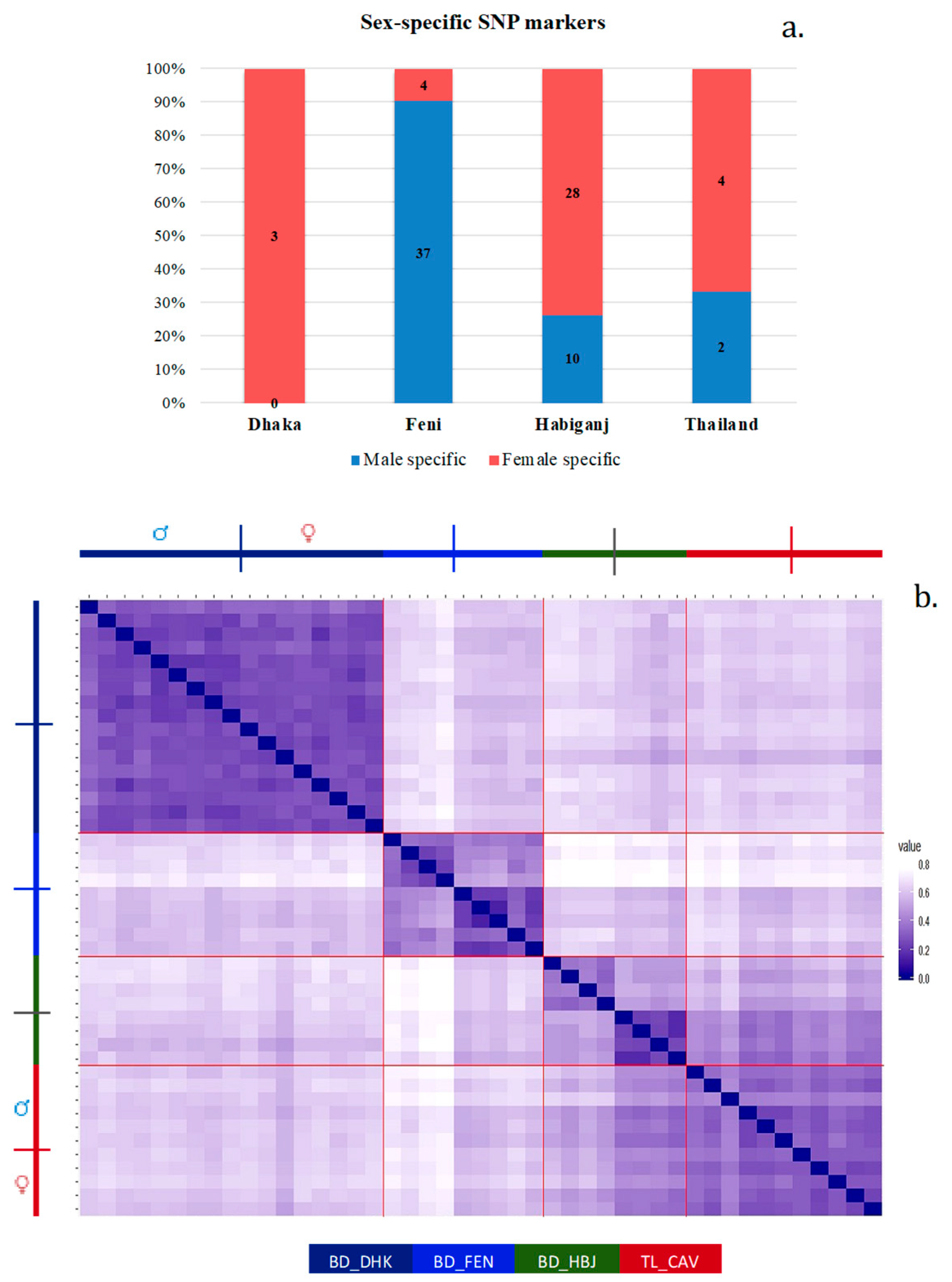
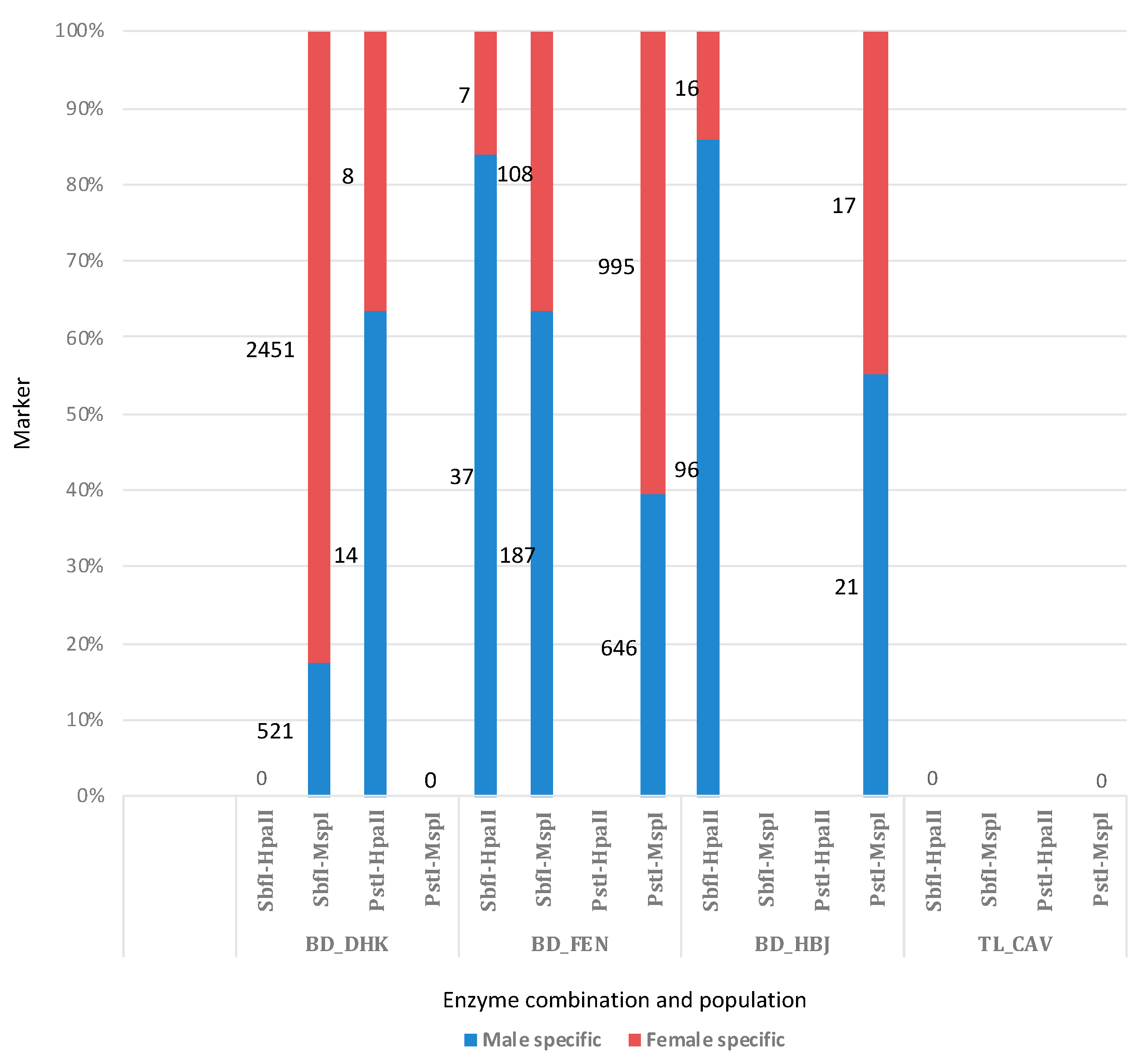
2.5. Sex-Linked Marker Analysis
3. Results
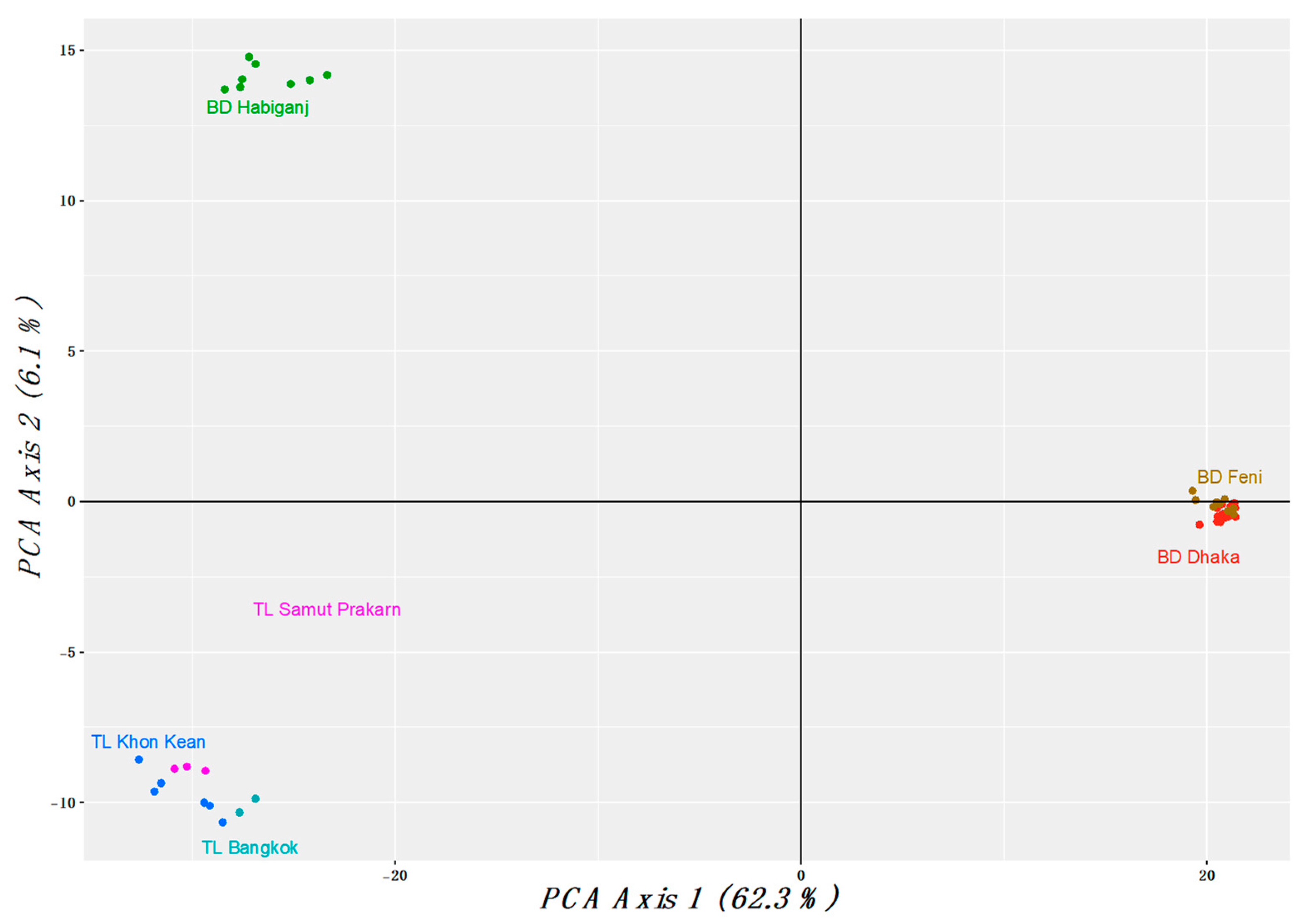
3.1. Population Analysis with DArTseq Results
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis with Sanger Sequencing Results
3.3. Sex-Linked Marker Analysis Using SNP Data
3.4. Sex-Linked Marker Analysis Using SilicoDArT Presence–Absence Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Population and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.2. Sex-Determination Modes across Calotes Species Complex
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bull, J.J. Evolution of Sex Determining Mechanisms; The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc.: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth, B. The evolution of chromosomal sex determination and dosage compensation. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, I. An evolutionary witness: The frog Rana rugosa underwent change of heterogametic sex from XY male to ZW female. Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, M.; Hanada, H.; Miura, I.; Ryuzaki, M. Four kinds of sex chromosomes in Rana rugosa. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphib. Biol. 1994, 13, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sreenivasulu, K.; Raman, R. Involvement of androgen receptor gene in male gonad differentiation in Indian garden lizard, Calotes versicolor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 303, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddamani, L.S.I.; Vani, V.; Seshagiri, P.B. A tropical oviparous lizard, Calotes versicolor, exhibiting a potentially novel FMFM pattern of temperature-dependent sex determination. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2012, 317, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, V.; Raman, R. Identification of Wnt4 as the ovary pathway gene and temporal disparity of its expression vis-a-vis testis genes in the garden lizard, Calotes versicolor. Gene 2010, 449, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, T.; Zarkower, D. Identification of sex-specific molecular markers using restriction site-associated DNA sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamble, T.; Coryell, J.; Ezaz, T.; Lynch, J.; Scantlebury, D.P.; Zarkower, D. Restriction Site-Associated DNA Sequencing (RAD-seq) Reveals an Extraordinary Number of Transitions among Gecko Sex-Determining Systems. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1296–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, M.R.; Skelly, D.K.; Ezaz, T. Sex-linked markers in the North American green frog (Rana clamitans) developed using DArTseq provide early insight into sex chromosome evolution. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamble, T.; Castoe, T.A.; Nielsen, S.V.; Banks, J.L.; Card, D.C.; Schield, D.R.; Schuett, G.W.; Booth, W. The Discovery of XY Sex Chromosomes in a Boa and Python. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2148–2153.e2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill, P.L.; Burridge, C.P.; Ezaz, T.; Wapstra, E. Conservation of sex-linked markers among conspecific populations of a viviparous skink, Niveoscincus ocellatus, exhibiting genetic and temperature-dependent sex determination. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, M.; Lambert, M.; Ezaz, T.; Miura, I. Reconstruction of female heterogamety from admixture of XX-XY and ZZ-ZW sex-chromosome systems within a frog species. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4078–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.V.; Pinto, B.J.; Guzmán-Méndez, I.n.A.; Gamble, T. First report of sex chromosomes in night lizards (Scincoidea: Xantusiidae). J. Hered. 2020, 111, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, A.E.; Radder, R.S.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Ezaz, T.; Shine, R. Isolation and development of a molecular sex marker for Bassiana duperreyi, a lizard with XX/XY sex chromosomes and temperature-induced sex reversal. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2009, 281, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Páramo, P.; Dissanayake, D.S.B.; Lira-Noriega, A.; Martínez-Pacheco, M.L.; Acosta, A.; Ramírez-Suástegui, C.; Méndez-de-la-Cruz, F.R.; Székely, T.; Urrutia, A.O.; Georges, A.; et al. Viviparous Reptile Regarded to Have Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination Has Old XY Chromosomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, D.S.; Holleley, C.; Hill, L.; O’Meally, D.; Deakin, J.; Georges, A. Identification of Y chromosome markers in the eastern three-lined skink (Bassiana duperreyi) using in-silico whole genome subtraction. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleley, C.E.; O’Meally, D.; Sarre, S.D.; Graves, J.A.M.; Ezaz, T.; Matsubara, K.; Azad, B.; Zhang, X.W.; Georges, A. Sex reversal triggers the rapid transition from genetic to temperature-dependent sex. Nature 2015, 523, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.A.; Georges, A.; Cherryh, C.; Rosauer, D.F.; Sarre, S.D.; Contador-Kelsall, I.; Holleley, C.E. Evolving thermal thresholds explain the distribution of temperature sex reversal in an Australian dragon lizard. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Ye, J.; Weber, C.; Sun, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, C.; Qian, G.; Capel, B. The histone demethylase KDM6B regulates temperature-dependent sex determination in a turtle species. Science 2018, 360, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, C.; Ye, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Sang, Y.; Capel, B.; Qian, G. Dmrt1 induces the male pathway in a turtle species with temperature-dependent sex determination. Development 2017, 144, 2222–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Deakin, J.E.; Domaschenz, R.; Lim, P.S.; Ezaz, T.; Rao, S. Comparative epigenomics: An emerging field with breakthrough potential to understand evolution of epigenetic regulation. AIMS Genet. 2014, 1, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Martín, L.; Viñas, J.; Ribas, L.; Díaz, N.; Gutiérrez, A.; Di Croce, L.; Piferrer, F. DNA methylation of the gonadal aromatase (cyp19a) promoter is involved in temperature-dependent sex ratio shifts in the European sea bass. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baroiller, J.F.; D’Cotta, H. The Reversible Sex of Gonochoristic Fish: Insights and Consequences. Sex. Dev. 2016, 10, 242–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, P.; Lian, J.; Hu, Q.; Sun, B.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. Epigenetic modification and inheritance in sexual reversal of fish. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramsey, M.; Shoemaker, C.; Crews, D. Gonadal expression of Sf1 and aromatase during sex determination in the red-eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta), a reptile with temperature-dependent sex determination. Differentiation 2007, 75, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Hannigan, B.; Crews, D. Temperature Shift Alters DNA Methylation and Histone Modification Patterns in Gonadal Aromatase (cyp19a1) Gene in Species with Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palaiokostas, C.; Bekaert, M.; Davie, A.; Cowan, M.E.; Oral, M.; Taggart, J.B.; Gharbi, K.; McAndrew, B.J.; Penman, D.J.; Migaud, H. Mapping the sex determination locus in the Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) using RAD sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, C.A.; High, S.K.; McCluskey, B.M.; Amores, A.; Yan, Y.-l.; Titus, T.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Batzel, P.; Carvan, M.J.; Schartl, M. Wild sex in zebrafish: Loss of the natural sex determinant in domesticated strains. Genetics 2014, 198, 1291–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brelsford, A.; Dufresnes, C.; Perrin, N. High-density sex-specific linkage maps of a European tree frog (Hyla arborea) identify the sex chromosome without information on offspring sex. Heredity 2016, 116, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsunomia, R.; Scacchetti, P.C.; Hermida, M.; Fernandez-Cebrian, R.; Taboada, X.; Fernandez, C.; Bekaert, M.; Mendes, N.J.; Robledo, D.; Mank, J.E. Evolution and conservation of Characidium sex chromosomes. Heredity 2017, 119, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sopniewski, J.; Shams, F.; Scheele, B.C.; Kefford, B.J.; Ezaz, T. Identifying sex-linked markers in Litoria aurea: A novel approach to understanding sex chromosome evolution in an amphibian. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koomgun, T.; Laopichienpong, N.; Singchat, W.; Panthum, T.; Phatcharakullawarawat, R.; Kraichak, E.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Ahmad, S.F.; Muangmai, N.; Peyachoknagul, S.; et al. Genome Complexity Reduction High-Throughput Genome Sequencing of Green Iguana (Iguana iguana) Reveal a Paradigm Shift in Understanding Sex-Chromosomal Linkages on Homomorphic X and Y Sex Chromosomes. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 556267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Hošek, J. The Reptile Database. Available online: http://reptile-database.org (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- Gowande, G.; Mishra, A.; Mirza, Z.A. Neotype designation for Calotes versicolor Daudin, 1802 (Sauria: Agamidae) with notes on its systematics. Zootaxa 2016, 4126, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Yan, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cai, B.; Jiang, N.; Huang, Y. Geographic variation in body size and its relationship with environmental gradients in the Oriental Garden Lizard, Calotes versicolor. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 4443–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zug, G.R.; Brown, H.H.; Schulte, J.A.; Vindum, J.V. Systematics of the garden lizards, Calotes versicolor group (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae), in Myanmar: Central dry zone populations. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 2006, 57, 35–68. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ho, S.Y.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Cai, B.; Wang, Y. Diversification and Demography of the Oriental Garden Lizard (Calotes versicolor) on Hainan Island and the Adjacent Mainland. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, V.; Raman, R. Conservation of Ovary-Specific Genes, Foxl2, Aromatase, and Rspo1, in the Common Indian Garden Lizard, Calotes versicolor, That Lacks Chromosomal or Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination. Sex. Dev. 2018, 12, 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, L. Study of mitotic and meiotic chromosomes in seven species of lizards. Proc. Zool. Soc. Calcutta 1974, 27, 57–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh, S.; Mohanty, J.; Raman, R. Male-biased distribution of the human Y chromosomal genes SRY and ZFY in the lizard Calotes versicolor, which lacks sex chromosomes and temperature-dependent sex determination. Chromosome Res. 1997, 5, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singchat, W.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Muangmai, N.; Baicharoen, S.; Indananda, C.; Duengkae, P.; Peyachoknagul, S.; O’Connor, R.E.; Griffin, D.K.; Srikulnath, K. Do sex chromosomes of snakes, monitor lizards, and iguanian lizards result from multiple fission of an “ancestral amniote super-sex chromosome”? Chromosome Res. 2020, 28, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, P. A harmless technique for sexing hatchiling lizards. Herpetol. Rev. 1996, 27, 71–72. [Google Scholar]
- Harlow, P. Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination in Lizards; Smithsonian Books: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Srikulnath, K.; Matsubara, K.; Uno, Y.; Thongpan, A.; Suputtitada, S.; Nishida, C.; Matsuda, Y.; Apisitwanich, S. Genetic relationship of three butterfly lizard species (Leiolepis reevesii rubritaeniata, Leiolepis belliana belliana, Leiolepis boehmei, Agamidae, Squamata) inferred from nuclear gene sequence analyses. Kasetsart J. Nat. Sci. 2010, 44, 424–435. [Google Scholar]
- Kilian, A.; Wenzl, P.; Huttner, E.; Carling, J.; Xia, L.; Blois, H.; Caig, V.; Heller-Uszynska, K.; Jaccoud, D.; Hopper, C. Diversity arrays technology: A generic genome profiling technology on open platforms. In Data Production and Analysis in Population Genomics; Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols); Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 888, pp. 67–89. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, B.; Unmack, P.J.; Berry, O.F.; Georges, A. dartr: An r package to facilitate analysis of SNP data generated from reduced representation genome sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, A.; Gruber, B.; Pauly, G.B.; White, D.; Adams, M.; Young, M.J.; Kilian, A.; Zhang, X.; Shaffer, H.B.; Unmack, P.J. Genomewide SNP markers breathe new life into phylogeography and species delimitation for the problematic short-necked turtles (Chelidae: Emydura) of eastern Australia. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 5195–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unmack, P.; Young, M.; Gruber, B.; White, D.; Kilian, A.; Zhang, X.; Georges, A. Phylogeography and species delimitation of Cherax destructor (Decapoda: Parastacidae) using genome-wide SNPs. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brelsford, A.; Lavanchy, G.; Sermier, R.; Rausch, A.; Perrin, N. Identifying homomorphic sex chromosomes from wild-caught adults with limited genomic resources. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 17, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macey, J.R.; Schulte, J.A.; Larson, A. Evolution and phylogenetic information content of mitochondrial genomic structural features illustrated with acrodont lizards. Syst. Biol. 2000, 49, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganesh, S.; Raman, R. Sex reversal by testosterone and not by estradiol or temperature in Calotes versicolor, the lizard lacking sex chromosomes. J. Exp. Zool. 1995, 271, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney-Melstad, E.; Gidiş, M.; Shaffer, H.B. Population genomic data reveal extreme geographic subdivision and novel conservation actions for the declining foothill yellow-legged frog. Heredity 2018, 121, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, S. Isolation by distance. Genetics 1943, 28, 114–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishat, A.; Huq, S.I.; Barua, S.P.; Reza, A.; Khan, A.M. Bio-Ecological Zones of Bangladesh; The World Conservation Union (IUCN): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2002; p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.R. The Geographical Distribution of Animals: With a Study of the Relations of Living and Extinct Faunas as Elucidating the Past Changes of the Earth’s Surface; Macmillan and Co.: London, UK, 1876; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Shanker, K.; Jayarajan, A.; Deepak, V. A systematic revision of Calotes Cuvier, 1817 (Squamata: Agamidae) from the Western Ghats adds two genera and reveals two new species. Zootaxa 2018, 4482, 401–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN Bangladesh. Red List of Bangladesh Volume 4: Reptiles and Amphibians; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Bangladesh Country Office: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2015; pp. xvi+320. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.A.; Priyanka; Titus, T.; Batzel, P.; Postlethwait, J.H.; Raman, R. A search for sex-linked loci in the agamid lizard, Calotes versicolor. Sex. Dev. 2019, 13, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, A.E.; Georges, A.; Sarre, S.D.; Guarino, F.; Ezaz, T.; Graves, J.A.M. Temperature sex reversal implies sex gene dosage in a reptile. Science 2007, 316, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holleley, C.E.; Sarre, S.D.; O’Meally, D.; Georges, A. Sex Reversal in Reptiles: Reproductive Oddity or Powerful Driver of Evolutionary Change? Sex. Dev. 2016, 10, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, A.; Georges, A.; Sarre, S.; Guarino, F.; Ezaz, T.; Graves, J. Sex Chromosomes and incubation temperature interact to determine sex of a reptile. IAHS Proc. Rep. 2007, 316, 411. [Google Scholar]
- Shine, R.; Elphick, M.; Donnellan, S. Co-occurrence of multiple, supposedly incompatible modes of sex determination in a lizard population. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patawang, I.; Tanomtong, A.; Chuaynkern, Y.; Chuaynkern, C.; Duengkae, P. Karyotype homology between Calotes versicolor and C. mystaceus (Squamata, Agamidae) from northeastern Thailand. Nucleus 2015, 58, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.J.; Fang, Z.L.; Wu, G.F. Karyotypes on nine species in the genus Phrynocephalus, with discussion of karyotypic evolution of Chinese Phrynocephalus. Acta Zool. Sin. 1997, 43, 399–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ezaz, T.; Quinn, A.E.; Miura, I.; Sarre, S.D.; Georges, A.; Marshall Graves, J.A. The dragon lizard Pogona vitticeps has ZZ/ZW micro-sex chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezaz, T.; Quinn, A.E.; Sarre, S.D.; O’Meally, D.; Georges, A.; Graves, J.A. Molecular marker suggests rapid changes of sex-determining mechanisms in Australian dragon lizards. Chromosome Res. 2009, 17, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
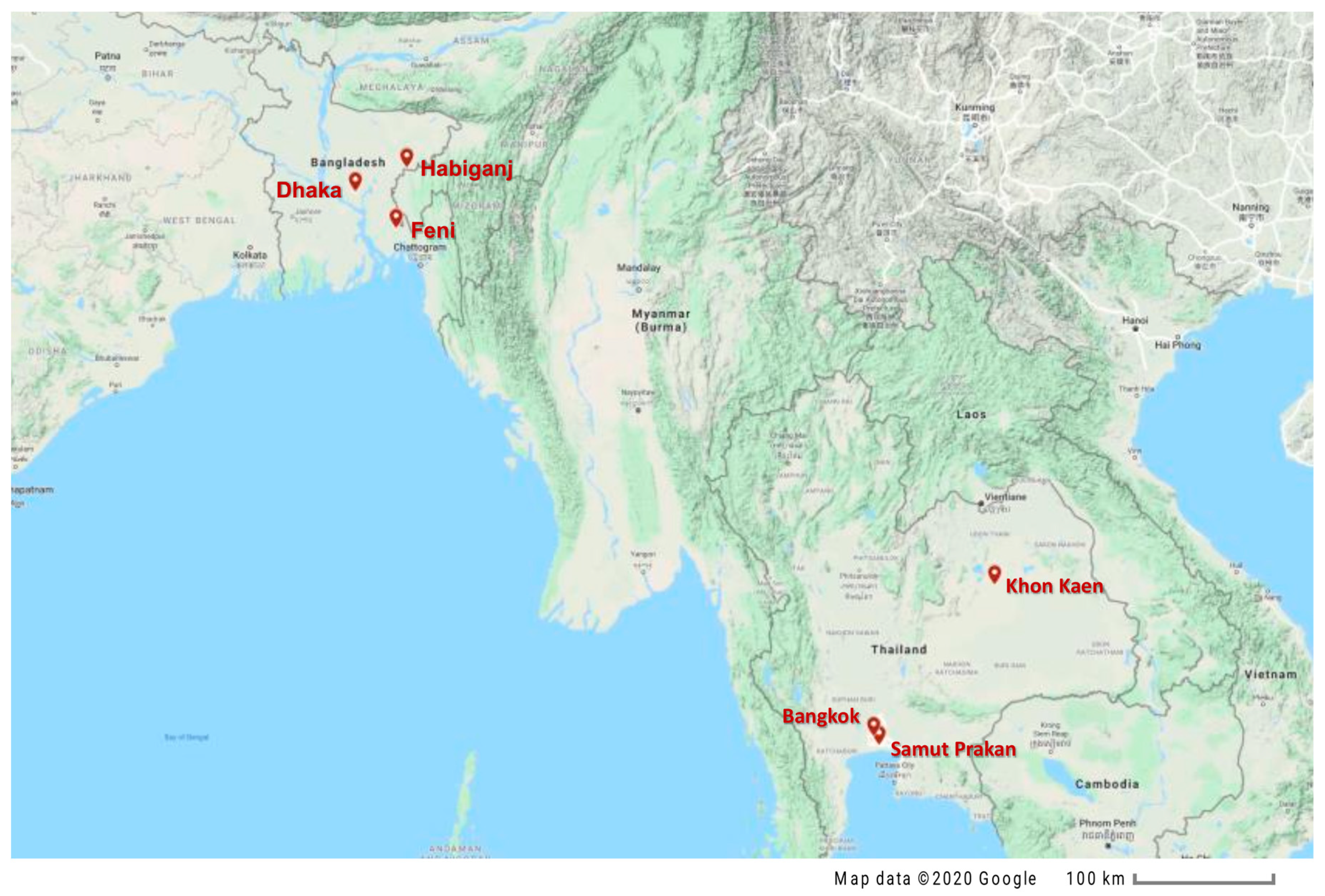
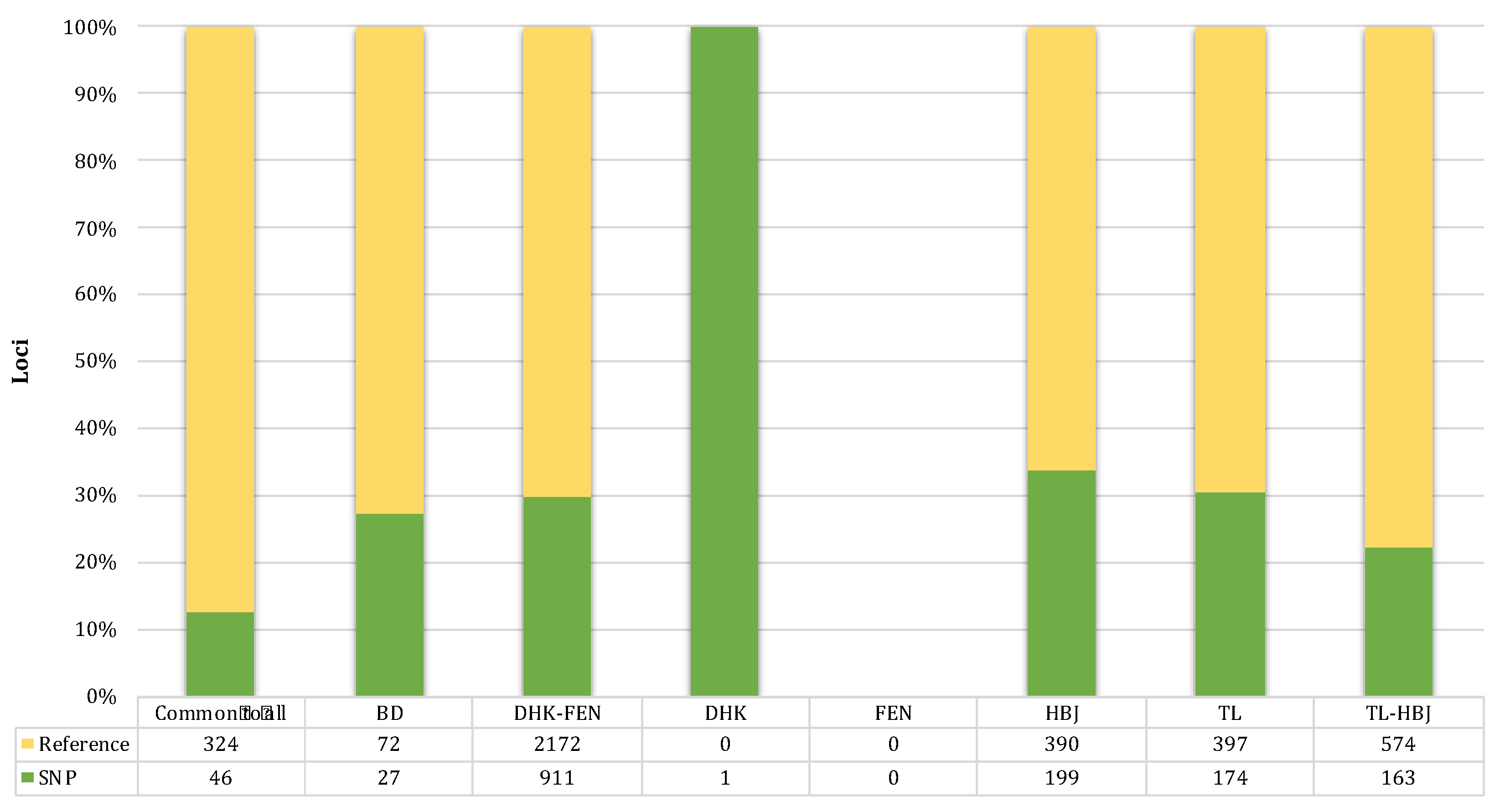
| Sl. No. | Sample ID | Location | Sex | Used for | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DArT Sequencing | Sanger Sequencing | ||||
| 1. | TL_CAV5 | Bangkok, Thailand | Female | X | |
| 2. | TL_CAV6 | Bangkok, Thailand | Male | X | |
| 3. | TL_CAV7 | Khon Kaen, Thailand | Male | X | X |
| 4. | TL_CAV8 | Khon Kaen, Thailand | Male | X | X |
| 5. | TL_CAV9 | Khon Kaen, Thailand | Female | X | |
| 6. | TL_CAV10 | Khon Kaen, Thailand | Female | X | X |
| 7. | TL_CAV11 | Khon Kaen, Thailand | Female | X | |
| 8. | TL_CAV12 | Khon Kaen, Thailand | Female | X | |
| 9. | TL_CAV13 | Samut Prakan, Thailand | Male | X | |
| 10. | TL_CAV15 | Samut Prakan, Thailand | Male | X | |
| 11. | TL_CAV17 | Samut Prakan, Thailand | Male | X | |
| 12. | TL_CAV19 | Samut Prakan, Thailand | Male | X | |
| 13. | TL_CAV20 | Samut Prakan, Thailand | Male | X | |
| 14. | TL_CAV22 | Samut Prakan, Thailand | Male | X | |
| 15. | BD_DHK01 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | X |
| 16. | BD_DHK02 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 17. | BD_DHK03 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 18. | BD_DHK04 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 19. | BD_DHK05 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 20. | BD_DHK06 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 21. | BD_DHK07 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 22. | BD_DHK08 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | X |
| 23. | BD_DHK09 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 24. | BD_DHK11 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 25. | BD_DHK12 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | X |
| 26. | BD_DHK13 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 27. | BD_DHK15 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 28. | BD_DHK16 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 29. | BD_DHK18 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 30. | BD_DHK19 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 31. | BD_DHK20 | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 32. | BD_FEN02 | Feni, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 33. | BD_FEN03 | Feni, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 34. | BD_FEN06 | Feni, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 35. | BD_FEN07 | Feni, Bangladesh | Female | X | X |
| 36. | BD_FEN10 | Feni, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 37. | BD_FEN15 | Feni, Bangladesh | Female | X | X |
| 38. | BD_FEN17 | Feni, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 39. | BD_FEN18 | Feni, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 40. | BD_FEN19 | Feni, Bangladesh | Male | X | X |
| 41. | BD_HBJ02 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 42. | BD_HBJ08 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 43. | BD_HBJ09 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Female | X | X |
| 44. | BD_HBJ10 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 45. | BD_HBJ11 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Female | X | |
| 46. | BD_HBJ14 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Female | X | X |
| 47. | BD_HBJ16 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 48. | BD_HBJ17 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| 49. | BD_HBJ20 | Habiganj, Bangladesh | Male | X | |
| Fst Values | Thailand | Bangladesh | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khon Kaen | Samut Prakan | Bangkok | Dhaka | Feni | Habiganj | ||
| Thailand | Khon Kaen | 0 | |||||
| Samut Prakan | 0.221 | 0 | |||||
| Bangkok | 0.201 | 0.0945 | 0 | ||||
| Bangladesh | Dhaka | 0.838 | 0.814 | 0.798 | 0 | ||
| Feni | 0.864 | 0.844 | 0.829 | 0.206 | 0 | ||
| Habiganj | 0.548 | 0.509 | 0.491 | 0.813 | 0.837 | 0 | |
| Fixed Differences | Thailand | Bangladesh | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khon Kaen | Samut Prakan | Bangkok | Dhaka | Feni | Habiganj | ||
| Thailand | Khon Kaen | 0 | |||||
| Samut Prakan | 439 | 0 | |||||
| Bangkok | 420 | 338 | 0 | ||||
| Bangladesh | Dhaka | 12,753 | 11,044 | 8889 | 0 | ||
| Feni | 12,606 | 10,923 | 8709 | 652 | 0 | ||
| Habiganj | 1974 | 1748 | 1544 | 13,895 | 13,900 | 0 | |
| Sample ID | Species | Accession No. | Total Score | Query Cover | E-Value | Percent Identity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bangladesh | BD_DHK 01M | C. calotes | AF128482.1 | 355 | 98% | 7 × 10−93 | 62.74% |
| BD_DHK 12M | C. calotes | AF128482.1 | 1273 | 100% | 0.0 | 87.86% | |
| BD_FEN 07F | C. calotes | AF128482.1 | 351 | 92% | 9 × 10−92 | 62.08% | |
| BD_FEN 15F | C. calotes | AF128482.1 | 1266 | 100% | 0.0 | 87.66% | |
| BD_FEN 19F | C. calotes | AF128482.1 | 1275 | 100% | 0.0 | 87.86% | |
| BD_HBJ 02F | C. versicolor | DQ289476.1 | 1739 | 100% | 0.0 | 98.03% | |
| BD_HBJ 09F | C. versicolor | DQ289476.1 | 1742 | 100% | 0.0 | 98.12% | |
| BD_HBJ 14F | C. versicolor | DQ289476.1 | 1737 | 100% | 0.0 | 98.03% | |
| Thailand | TL_CAV 07M | C. versicolor | DQ289474.1 | 1544 | 100% | 0.0 | 96.09% |
| TL_CAV 08M | C. versicolor | DQ289474.1 | 1643 | 100% | 0.0 | 95.95% | |
| TL_CAV 10F | C. versicolor | DQ289474.1 | 1656 | 100% | 0.0 | 96.25% | |
| TL_CAV 15M | C. versicolor | DQ289474.1 | 1646 | 100% | 0.0 | 95.95% | |
| TL_CAV 17M | C. versicolor | DQ289469.1 | 771 | 88% | 0.0 | 73.83 | |
| TL_CAV 22M | C. versicolor | DQ289474.1 | 1649 | 100% | 0.0 | 96.05% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, S.M.I.; Prasongmaneerut, T.; Gleeson, D.; Georges, A.; Sarre, S.D.; Srikulnath, K.; Ezaz, T. Sex-Determination Mechanisms among Populations within Cryptic Species Complex of Calotes (Squamata: Agamidae: Draconinae). DNA 2021, 1, 49-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna1020006
Alam SMI, Prasongmaneerut T, Gleeson D, Georges A, Sarre SD, Srikulnath K, Ezaz T. Sex-Determination Mechanisms among Populations within Cryptic Species Complex of Calotes (Squamata: Agamidae: Draconinae). DNA. 2021; 1(2):49-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna1020006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Shayer Mahmood Ibney, Tulyawat Prasongmaneerut, Dianne Gleeson, Arthur Georges, Stephen D. Sarre, Kornsorn Srikulnath, and Tariq Ezaz. 2021. "Sex-Determination Mechanisms among Populations within Cryptic Species Complex of Calotes (Squamata: Agamidae: Draconinae)" DNA 1, no. 2: 49-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna1020006
APA StyleAlam, S. M. I., Prasongmaneerut, T., Gleeson, D., Georges, A., Sarre, S. D., Srikulnath, K., & Ezaz, T. (2021). Sex-Determination Mechanisms among Populations within Cryptic Species Complex of Calotes (Squamata: Agamidae: Draconinae). DNA, 1(2), 49-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna1020006