Abstract
Corn residues are an abundant and low-cost lignocellulosic feedstock that provides a renewable carbon platform for the production of biofuels, bioplastics, and high-value aromatic volatile compounds (AVCs). Isoamyl alcohol, an important AVC, has applications in the food, cosmetics, and biofuel industries. This study evaluated the bioconversion of corn cob acid hydrolysates by Meyerozyma guilliermondii into isoamyl alcohol and ethanol. Corn cob was selected as feedstock due to its high hemicellulose content. A Box–Behnken (BBD) design was used to optimize phosphoric acid hydrolysis. The optimal treatment (2.49% v/v H3PO4, 130 °C, 120 min, 1 mm particle size) generated 19.79 g L−1 xylose with 2.74 g L−1 acetic acid. Then, agitation speed and nitrogen concentration were optimized via a central composite design (CCD) in synthetic and hydrolysate-based media fermentations. Isoamyl alcohol specific yield after 48 h of fermentation was higher in hydrolysate medium (12.08 ± 0.67 mg·g−1) than in synthetic medium (8.274 ± 0.83 mg·g−1). Free amino nitrogen (FAN) and intracellular protein analyses revealed higher nitrogen consumption in synthetic media fermentation and greater biomass production in acid hydrolysate media. In addition to isoamyl alcohol (33 mg·L−1), and ethanol (10.18 g·L−1), 1-butanol (61.2 mg·L−1), 1-propanol (13.25 mg·L−1), and acetaldehyde (14.88 mg·L−1) were produced. These results demonstrate the potential of M. guilliermondii to convert corn cob into value-added products.
1. Introduction
Aromatic volatile compounds (AVCs), such as fusel alcohols, aldehydes, esters, and terpenes, are used in a variety of industries due to their ability to enhance product quality and sensory profiles [1,2]. Isoamyl alcohol, in particular, serves as a platform chemical for synthesizing isopentyl acetate, pharmaceuticals, sustainable aviation fuels and DNA extraction processes [3,4]. Microbial fermentation offers a sustainable approach for AVC production, particularly when lignocellulosic residues are used as feedstock, supporting a circular bioeconomy and the biorefinery concept [5,6].
Corn stover is an abundant byproduct with an annual global availability of 600 million tons [7] and over 11 million tons in Mexico [8,9]. However, its complex lignocellulosic structure requires pretreatment to release fermentable sugars like glucose and xylose [10]. During second-generation (2G) ethanol production, acid pretreatment is routinely applied to split lignocellulosic biomass into solid and liquid streams with distinct compositions and potential applications. The solid fraction, rich in cellulose, is commonly used in 2G bioethanol production, while the liquid fraction, rich in sugars (xylose, glucose and arabinose) is usually considered a byproduct. This liquid fraction, however, represents a valuable substrate for the microbial production of industrially and commercially relevant compounds, including aromatic volatile compounds [11].
Acid hydrolysis using sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is the most common acid treatment applied for corn cob valorization; at this stage of the pretreatment of the lignocellulosic biomass hemicellulose is obtained into the liquid fraction, while cellulose and lignin remain in the solid fraction. The hemicellulose is then depolymerized into simple sugars, mainly xylose. Nevertheless, alternative acids like phosphoric acid (H3PO4) offer advantages like lower environmental impact and reduced formation of microbial inhibitors [12]. Optimization strategies, such as response surface methodology, can improve sugar release while minimizing the generation of inhibitors like acetic acid, furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), which become cytotoxic to yeast metabolism at concentrations above 3 g·L−1 for acetic acid and 1 g·L−1 for furfural or HMF [13,14,15]. Despite these advantages, studies on H3PO4 pretreatment, specifically for corn cob, remain limited.
Recently, non-Saccharomyces yeasts gained attention for their ability to produce AVCs [16]. Species from the genera Brettanomyces, Candida, Hanseniaspora, and Kluyveromyces contribute to the sensory complexity of fermented products, producing over 1300 volatile compounds [17,18,19]. In particular, M. guilliermondii, has been associated with fruity and floral volatiles in mixed fermentations [20].
AVC biosynthesis in yeasts, primarily occurs via the Ehrlich pathway, where amino acids like valine, leucine, and phenylalanine are converted into α-keto acids, leading to higher alcohol production [21,22]. This process is influenced by multiple factors including yeast species, nitrogen availability, carbon source, oxygen levels, and fermentation conditions [18,23]. Several yeast species including Pichia anomala, Zygoascus meyerae, M. guilliermondii, Pichia kudriavzevii, Torulaspora delbrueckii, and Lachancea thermotolerans have been reported to produce higher alcohols, aldehydes, and other aromatic compounds from substrates as wort, apple pure and grape must. Production yields are strongly related to temperature (13–25 °C), agitation (0–100 rpm) and fermentation time (24–96 h) [20,24,25,26]. Non-Saccharomyces yeasts have demonstrated the ability to convert amino acids into volatile compounds, and nitrogen availability is a key factor influencing fermentation dynamics [27,28].
Although there have been advances in AVC production from synthetic media, the production of volatile aromatic compounds from the liquid fraction of pretreated corn residues or any lignocellulosic biomass remains unexplored. Previous studies have evaluated the biosynthesis of isoamyl alcohol and 2-phenylethanol from corn stover using engineered Kluyveromyces marxianus and Pseudomonas putida [29,30]. M. guilliermondii has been studied for its ability to produce AVCs during red wine fermentation and 2-phenylethanol (2-PE) from synthetic media, and for the conversion of corn residues into bioethanol and xylitol; however, its potential for converting corn stover into AVCs has not been studied yet [31,32]. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the potential of a native strain of M. guilliermondii, to grow on corn cob acid hydrolysates and produce aromatic volatile compounds. Corn residues were structurally characterized before pretreatment optimization. Acid hydrolysis using phosphoric acid led to the release of the highest concentration of fermentable sugars and a minimal concentration of acetic acid. Finally, the effect of agitation and yeast extract concentration on the production of aromatic volatile compounds was evaluated using this corn cob acid hydrolysate and a synthetic medium.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lignocellulosic Material, Reagent and Microorganism
Corn stover and corn cob, collected after harvest in Sinaloa, Mexico, were used as the lignocellulosic feedstock for the experimental work. Corn residues were ground to particles sizes of 1 mm and 4 mm (corresponding to 18-mesh and 5-mesh, as per ASTM standards) and subsequently stored in resealable bags at room temperature for future analysis. All reagents were analytical grade and purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The microbial isolate employed in this study was originally isolated from pineapple peels collected in northern Sinaloa, Mexico by Beltrán-Arredondo et al. [33]. The strain is maintained in the collection at the Laboratorio de Bioenergéticos of the Centro Interdisciplinario de Investigación para el Desarrollo Integral Regional (CIIDIR Unidad Sinaloa) of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional (IPN) and is capable of utilizing both hexose and pentose sugars from corn hydrolysates. The strain was cultured on agar plates containing (g·L−1): glucose (3), xylose (7), yeast extract (1), and agar (10). After incubation at 30 °C for 24 h, the plates were stored at 4 °C and periodically sub-cultured to ensure viability.
2.2. Yeast Identification by MALDI-TOF
MALDI-TOF identification of yeast was performed according to the methodology described by De la Torre-González et al. [34]. Yeast cells were reactivated on glucose-xylose agar for 24 h at 30 °C and sub-cultured twice. Fresh biomass was spotted on an MSP 96 target polished steel MALDI target plate and covered with 1 μL formic acid (70% v·v−1). After formic acid dried at room temperature, each spot was overlaid with 1 μL of a saturated HCCA (α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid) matrix solution in an organic solvent (50% acetonitrile and 2.5% trifluoroacetic acid) and allowed to completely dry before measurement. Independent biological replicates were analyzed on different days to evaluate strain purity.
Yeast fingerprints were acquired for each spot with the MBT_FC.par method, and 40 laser shots at six random positions within the spot were collected, automatically generating mass spectra in the mass range from 2000 to 20,000 Da. Prior to the analyses, calibration was performed with 1 μL of the protein calibration bacterial test standard (BTS; Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA, USA). MALDI Biotyper Compass Explorer v4.1 was used for taxonomic identification, comparing the spectral fingerprints to the Bruker BDAL database (Bruker Taxonomy Database). The latest BDAL database used was updated in 1 February 2022 [35]. Bruker log(score) classifies identification as follows: ≥2.30, highly probable species identification; range 2.00–2.29, secure genus identification, probable species identification; range 1.70–1.99, probable genus identification; <1.70, no reliable identification.
2.3. Characterization of Lignocellulosic Material
The analysis of the structural composition of corn residues (corn stover and corn cob) was carried out, in triplicate, using the methodology of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL/TP-510-42619) [36] to determine the content (% w·w−1) of the biomass main structural components: cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, ash and extractives.
2.4. Acid Hydrolysis
Multi-Response Optimization of Xylose and Acetic Acid Concentration
A Box–Behnken design (BBD) was used to optimize acid hydrolysis of corn cob, aiming to maximize xylose release while minimizing acetic acid concentration. The four independent variables were phosphoric acid concentration (0.5–5% v·v−1), temperature (80–130 °C), pretreatment time (30–120 min), and particle size (1 and 4 mm), with xylose and acetic acid concentrations as response variables. The experimental design consisted of 30 trials, including 12 factorial points and 3 central points for each particle size.
In order to reduce the presence of inhibitors such as furfural and HMF and remove impurities, all hydrolysates were detoxified with 3.2% (w·v−1) of activated carbon at 45 °C for 60 min (standardized before experimental design) [37]. After detoxification, the solution was filtered through a 5 µm membrane using a Millicup-FLEX™ Filtration Un (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany).
2.5. Aromatic Volatile Compound Production
2.5.1. Inoculum
The inoculum was prepared in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask with 50 mL of a medium containing (g·L−1): xylose (7) glucose (3) as carbon sources. After inoculation, the inoculum was incubated under aerobic conditions at 30 °C for 24 h at 150 rpm.
2.5.2. Fermentation in Synthetic Medium
Fermentation medium was formulated as follows (g·L−1): xylose (18), glucose (8), KH2PO4 (5), (NH4)2SO4 (2), Mg(SO4)2·7H2O (0.4), and yeast extract (3.2). The culture medium (50 mL) was adjusted to pH 4.5 with H3PO4, sterilized at 121 °C for 15 min. M. guilliermondii was inoculated at a concentration of 6 × 106 viable cells·mL−1, culture was incubated 30 °C for 72 h at 100 rpm in flasks under aerobic conditions.
2.5.3. Fermentation in Corn Cob Acid Hydrolysate
A two-variable central composite design (CCD) for response surface methodology was used to study the combined effect of agitation (100–200 rpm) and yeast extract concentration (0–5 g·L−1) on the specific yield of isoamyl alcohol produced by M. guilliermondii using corn cob acid hydrolysate. Each factor was evaluated at three levels, resulting in 11 experimental runs (8 factorial points, and 3 central points). Runs were inoculated with M. guilliermondii at a concentration of 6 × 106 viable cells·mL−1. The validation experiment was performed in triplicates using corn cob acid hydrolysates and synthetic medium.
Kinetic parameters determined were the specific growth rate μmax (h−1), specific yield Yp/x (mg of product·g−1 biomass) and volumetric productivity Qp (mg of product·(L·h)−1).
2.6. Analytical Methods
2.6.1. Biomass
Cell density was measured as optical density at 620 nm (OD620) and converted to dry biomass (g·L−1) using a calibration curve, all biomass values reported correspond to dry weight. Cell count was performed under the microscope using a Thoma Chamber Brand® (BRAND GMBH + CO KG, Wertheim, Germany). Cell viability percentage was determined using the methylene blue staining method [38].
2.6.2. Quantification of Sugars by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Sugars (xylose, glucose and arabinose) and acetic acid were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a Waters® HPLC (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) equipped with a refractive index detector (RID) and a Rezex ROA-Organic Acid H+ (8%) Ion-Exclusion Column. A mobile phase of 5 mM H2SO4 was used at a flow rate of 0.6 mL·min−1 with oven and detector temperatures of 60 °C and 40 °C, respectively. Analysis time per sample was 15 min. Compounds were identified and quantified by external calibration using pure standards.
2.6.3. Quantification of Volatile Compounds by Gas Chromatography (GC)
Volatile compounds produced during fermentation were quantified by gas chromatography coupled to a Head-Space Sampler (HSS Model 7694 E, Hewlett Packard, Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA) and a gas chromatograph (GC Hewlett Packard 6890, Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA) equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) and an HP-INNOWAX column (60 m × 0.32 mm × 0.25 µm). Chromatographic conditions used were those reported by Méndez-Zamora et al. [17] and compounds were identified and quantified using pure standards.
2.6.4. Free Amino Nitrogen and Protein Quantification
Free amino nitrogen (FAN) and intracellular protein concentrations (g·L−1) were determined following the methodology described by Campos-Valdez et al. [39]. FAN was quantified using a glycine standard solution (0–1.0 g·L−1), while a bovine serum albumin (BSA) standard (0–1.75 g·L−1) was used for intracellular protein quantification.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using Design Expert Software version 13. A Box–Behnken design (BBD) was used to optimize acid pretreatment conditions and a central composite design (CCD) for maximizing the specific yield of isoamyl alcohol (p < 0.05). Biological replicates at the central points of both designs assessed reproducibility and experimental variation within the statistical models. The mathematical models were generated and evaluated with an analysis of variance (ANOVA) at 95% confidence level. Model performance was determined based on the correlation coefficient (R2) and lack of fit test. In the resulting model equations, a positive sign in front of the terms indicates a synergistic effect. Kinetic experiments and model validations were performed in triplicate, and standard deviations were reported to ensure results reliability. The final models were used to identify optimal process conditions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition of Corn Residues
Corn residues are composed predominantly of cellulose and hemicellulose, making them a substantial source of fermentable sugars (Table 1). In this study, corn stover contained 33.48 ± 0.67% cellulose, 27.00 ± 2.29% hemicellulose, 19.90 ± 0.88% Klason lignin, 12.14 ± 0.84% extractives, and 7.48 ± 0.27% ashes. In contrast, hemicellulose (45.9 ± 1.2%) was the major constituent of corn cob, followed by cellulose (30.92 ± 0.61%) and lignin (15.68 ± 1.2%), extractives (5.88 ± 0.05%) and ash (1.61 ± 0.09%) content was lower than the observed in corn stover.

Table 1.
Lignocellulosic characterization of corn residues.
The composition of corn stover observed in this study is consistent with previous findings by Zhao et al. [40] and Yu et al. [41], who also reported higher cellulose content relative to hemicellulose. However, Hernández et al. [42] reported different structural carbohydrate proportions. Regarding corn cob, our results align with most studies indicating that corn cob contains more hemicellulose than cellulose [44,45]. An exception was reported by Ma et al. [43], who found similar levels of both (35.3% and 34.4%, respectively).
Cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin content variations can be attributed to factors like crop type, variety, and climatic conditions during cultivation [46]. The higher hemicellulose content in corn cob, compared to corn stover, makes it an ideal feedstock for dilute acid pretreatment, as this process effectively solubilizes pentose sugars in the liquid fraction, enabling their valorization as feedstock for the production of value-added compounds, including aromatic volatiles.
3.2. Optimization of Acid Pretreatment
The results of the BBD experiments evaluating the effects of phosphoric acid concentration, temperature, pretreatment time, and particle size on xylose and acetic acid concentrations after corn cob acid hydrolysis are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Experimental results of the multi-response BBD for xylose and acetic acid concentrations after corn cob acid hydrolysis.
Multi-response optimization was performed by overlapping contour plots for each response. The optimal point was determined by ensuring that the independent variables (acid concentration, temperature, time and particle size) allowed for maximizing xylose concentration, while keeping acetic acid concentration below 3 g/L, since higher values can be inhibitory to the xylose fermentation by several microorganism, as pointed out in the introduction.
The highest xylose concentration (19.89 g·L−1) was obtained using 2.75% (v·v−1) H3PO4 at 130 °C for 120 min, using a particle size of 1 mm. Under these conditions, acetic acid concentration was 2.64 g·L−1. Detoxification using activated carbon effectively reduced furfural concentration from 0.81 to 0.03 g·L−1 and completely removed HMF, thereby minimizing inhibitory effects during fermentation.
Regression analysis of the BBD data indicated that a second-order polynomial model accurately described the experimental data for both responses. Equations (1) and (2) represent the model predictions for xylose and acetic acid concentrations as functions of the process variables. The statistical significance of each factor was confirmed through ANOVA, with both models exhibiting strong predictive capacity with R2 values of 0.95 for xylose and 0.96 for acetic acid (Supplementary Table S1). The model equations for each response variable, including the statistically significant terms for xylose and acetic acid release, are presented below.
The response surface plots in Figure 1 illustrate the influence of H3PO4 concentration, temperature, and reaction time on xylose and acetic acid production and represent the optimal pretreatment conditions, using a particle size of 1 mm, which resulted in the highest xylose concentration. Increasing these variables enhanced xylose release beyond 20 g·L−1 but also led to high acetic acid concentrations. On the contrary, decreasing temperature and reaction time caused a drastic reduction of over 90% in xylose recovery.
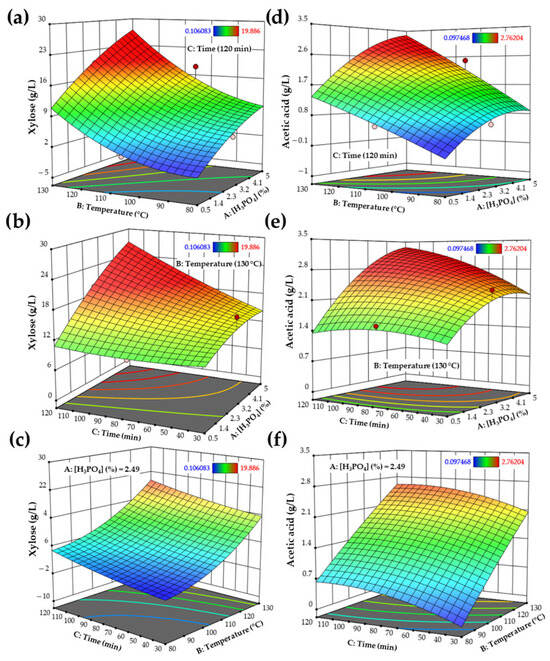
Figure 1.
Response surfaces for xylose and acetic acid concentrations: (a–c) shows the interactions of each variable on xylose production, and (d–f) shows the interactions of each variable on acetic acid production with a 1 mm particle size. (A red dot denotes design points above predicted values, and pink dots denote points below predicted values).
The significant p-values from the analysis of variance (Supplementary Table S1), along with low pure error and a non-significant lack of fit, confirm that the models adequately describe the hydrolysis process. For xylose release, H3PO4 concentration, temperature, reaction time, the interaction between H3PO4 concentration and reaction time, and the quadratic effect of temperature were statistically significant (p < 0.05). In the case of acetic acid, significant effects were observed for the interaction between H3PO4 concentration and temperature, and the quadratic term of H3PO4 concentration (p < 0.05), whereas the quadratic effect of temperature was not significant (p > 0.05).
The results of multi-response optimization showed 2.49% v·v−1 H3PO4, 130 °C, and 120 min as the optimal conditions, maximizing xylose recovery while keeping acetic acid below inhibitory levels. Validation under these parameters resulted in 19.79 ± 0.50 g·L−1 of xylose, 9.21 ± 0.35 g·L−1 of glucose, 4.08 ± 0.11 g·L−1 of arabinose and 2.74 ± 0.19 g·L−1 of acetic acid, demonstrating effective hemicellulose solubilization via the milder hydrolytic mechanism of phosphoric acid, which offers advantages over more toxic mineral acids such as sulfuric acid by cleaving β-(1→4) glycosidic bonds and deacetylating xylan while reducing dehydration reactions that generate furfural and HMF [47]. This milder effect minimizes inhibitor formation and enables residual biomass to be valorized as a phosphate fertilizer [48]. In this study, phosphoric acid pretreatment resulted in a xylose concentration comparable to the 26.64 g·L−1 reported for corn cob treated with a mixture of H2SO4 (0.5% v·v−1) and H3PO4 (1.5% v·v−1), and higher than the 11.03 g·L−1 obtained with 3% H3PO4 (v·v−1) in previous reports [45,49].
Nevertheless, acetic acid is still released from acetyl groups, and single response optimization focused solely on xylose can exceed inhibitory levels (1.5–5.8 g·L−1) [13,50]; therefore, multi-response optimization is essential to balance sugar recovery and inhibitor formation, ensuring effective fermentation of corn cob hydrolysates.
3.3. Yeast Strain Identification by MALDI-TOF MS
MALDI-TOF MS analysis was performed on three subcultures of the isolate to analyze their protein spectral fingerprints, identifying them as M. guilliermondii, with log score values of 2.37, exceeding the ≥2.30 threshold for highly reliable species-level identification. Accurate species identification of microorganisms is essential to ensure reproducibility and efficiency in fermentation processes, preventing contamination and optimizing the production of target compounds. The growing need for rapid yeast identification in industry has increased interest in MALDI-TOF MS, which offers species–specific spectral fingerprints that remain stable across geographic or culture condition variations [34,51]. Although this study identified only a single yeast species, MALDI-TOF MS can differentiate a wide range of isolates and assess taxonomic relationships at inter- and intra-species levels [52]. Its application in strain classification and microbial diversity studies improves precision of yeast selection for biotechnological applications, including volatile compound biosynthesis. It can also support rapid screening and identification of native yeast for lignocellulosic fermentation.
3.4. Optimization of Aromatic Volatile Compound Production Using Central Composite Design (CCD)
3.4.1. Effect of Agitation and Yeast Extract Concentration on Specific Yield of Isoamyl Alcohol
CCD was employed to study the effects of agitation and yeast extract concentration on the specific yield of isoamyl alcohol after 48 h of fermentation with M. guilliermondii using of corn cob acid hydrolysate obtained under optimal conditions (Table 3). The experimental data were adequately represented by a second order polynomial model with high coefficient of determination (R2 = 0.96), and adjusted R2 of 93.39%, indicating model reliability. The ANOVA analysis (Supplementary Table S2), confirmed that the model was statistically significant (0 = 0.001; F = 29.26), and the lack of fit test was non-significant (p = 0.47), validating the model accuracy and indicating that at least one independent variable significantly affects isoamyl alcohol yield. The mathematical model is described by the following equation:

Table 3.
Central composite design (CCD) and analysis with two variables and specific yield of isoamyl alcohol as response variable after 48 h of fermentation by M. guilliermondii using corn cob acid hydrolysate as substrate.
Among the factors, agitation and the quadratic term of yeast extract concentration had significant effects (p < 0.05), while the linear term of yeast extract and the interaction term with agitation were not significant (p > 0.05). The response surface plot (Figure 2) represents the optimal conditions for maximizing the specific yield of isoamyl alcohol. Agitation significantly influenced the response by improving oxygen transfer and favoring the Ehrlich pathway for higher alcohol production [53], whereas yeast extract showed a non-linear effect, indicating an optimal concentration beyond which excess nitrogen shifts metabolism toward biomass rather than isoamyl alcohol synthesis [54].
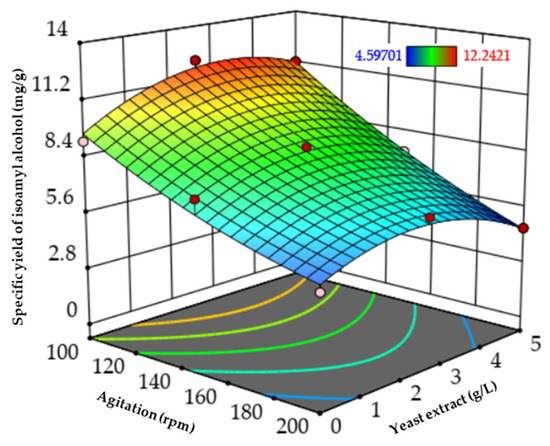
Figure 2.
Response surface plot of specific yield of isoamyl alcohol in corn cob acid hydrolysate. Effect of agitation and nitrogen concentration (yeast extract).
Under the optimal conditions predicted by the model for corn cob acid hydrolysate medium (3.2 g·L−1 of yeast extract and 100 rpm agitation), the maximum specific yield of isoamyl alcohol obtained was 12.08 ± 0.67 mg·g−1, which is close to the predicted value of 11.91 mg·g−1.
3.4.2. Comparative Analysis of M. guilliermondii Fermentation in Synthetic Media and Corn Cob Acid Hydrolysate
Under the optimal conditions predicted by the model (3.2 g·L−1 of yeast extract, 100 rpm), fermentations were carried out using corn cob hydrolysate and synthetic media to evaluate its metabolic performance and production of volatile compounds. Results showed that biomass production was higher in synthetic medium (8.38 ± 0.11 g·L−1) compared to hydrolysates (4.38 ± 0.29 g·L−1), likely due to the nutrient availability and lower inhibitory content [13,28]. Although the hydrolysate medium contained less than 3 g·L−1 of acetic and furfural (<1 g·L−1), the presence of this inhibitory compounds may still affect yeast metabolism [50]. Theoretical C/N ratios were comparable, at 35.52 for the synthetic medium and 36.86 for the hydrolysate, and this ratio is considered a condition of stress [55]. Although nitrogen was initially present in an assimilable form (as yeast extract), its availability decreased during fermentation, influencing growth and metabolite distribution. Therefore, the observed differences in performance are primarily attributed to medium stress and nutrient dynamics rather than differences in C/N ratio. Despite this, the specific yield of isoamyl alcohol was higher in the hydrolysates (12.08 ± 0.67 mg·g−1) than in synthetic medium (8.274 ± 0.83 mg·g−1) after 48 h of fermentation. This indicates that less biomass is required to produce isoamyl alcohol when using corn cob acid hydrolysates.
The fermentation kinetics showed glucose depletion in the synthetic medium at 24 h, whereas in the corn cob acid hydrolysate, glucose was completely consumed at 36 h (Figure 3). After 72 h of fermentation, M. guilliermondii was able to consume 80% of xylose in the synthetic medium, compared to 20% in corn cob acid hydrolysate, while cellular viability remained above 90% in both media. These differences may reflect limitations in nutrient accessibility or the presence of inhibitors in the corn cob hydrolysate, which can affect sugar transport and assimilation [56]. Yeasts as Candida tropicalis, Candida maltose, Debaromyces hansenii, and Meyerozyma caribbica can assimilate xylose; however, their ability to ferment it varies [57]. Tadioto et al. [58] reported that while four strains of M. caribbica metabolized glucose and xylose for ethanol and xylitol production in a synthetic medium, only one strain was able to consume 57% of the xylose in corn hydrolysates, whereas the remaining strains showed limited or no xylose consumption.
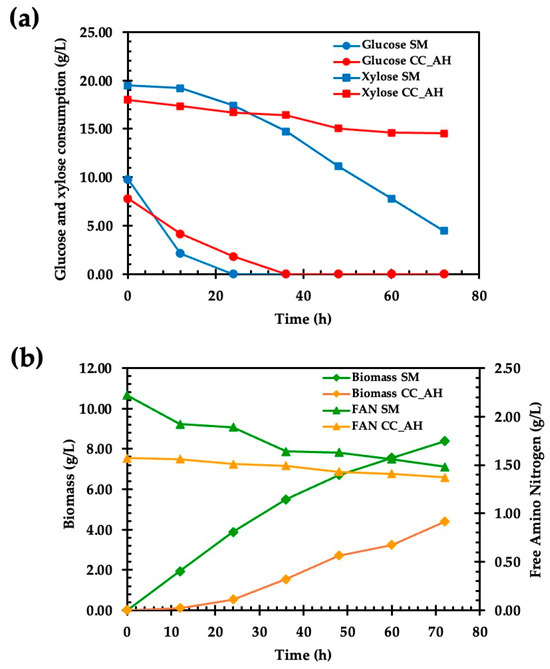
Figure 3.
Comparison of kinetic profiles of (a) substrate consumption (glucose and xylose), (b) biomass and free amino nitrogen (FAN) by M. guilliermondii in synthetic medium and corn cob acid hydrolysate. SM = synthetic medium, CC_AH = Corn cob acid hydrolysate.
Quantification of volatile compounds confirmed the production of other value-added metabolites in both media. In addition to the 32.7 ± 1.09 mg·L−1 of isoamyl alcohol produced after 48 h of corn cob acid hydrolysate fermentation, other volatile compounds were also detected, including 1-butanol (61.2 ± 2.61 mg·L−1), 1-propanol (13.25 ± 0.61 mg·L−1), acetaldehyde (14.88 ± 0.24 mg·L−1), and ethanol (10.18 ± 0.22 g·L−1) (Figure 4). Fermentation in synthetic medium resulted in higher isoamyl alcohol production (55.14 ± 2.63 mg·L−1), lower levels of acetaldehyde (7.54 ± 0.67 mg·L−1) and 1-butanol (41.87 ± 1.75 mg·L−1), and less than half regarding the ethanol concentration (4.41 ± 0.31 g·L−1), with no detectable 1-propanol. Similar trends have been reported in K. marxianus fermentations, where higher isoamyl alcohol (188 mg·L−1) and ethanol (30.21 g·L−1) concentrations were observed in agave juice compared to synthetic medium (70.6 mg·L−1 and 16.6 g·L−1) [59]. These differences are attributed to the greater content of assimilable nitrogen, mainly amino acids, in natural substrates, which act as available precursors that enhance yeast metabolism. Overall, these findings demonstrate that substrate composition influences the metabolic pathways of M. guilliermondii, with amino acids and ammonia promoting yeast growth and alcohol formation, and the nitrogen source potentially modulating ester synthesis [28,56]. In complex substrates, strain-to-strain variation may further affect aroma profiles, emphasizing the importance of both substrate and strain selection in optimizing volatile compound production [60].
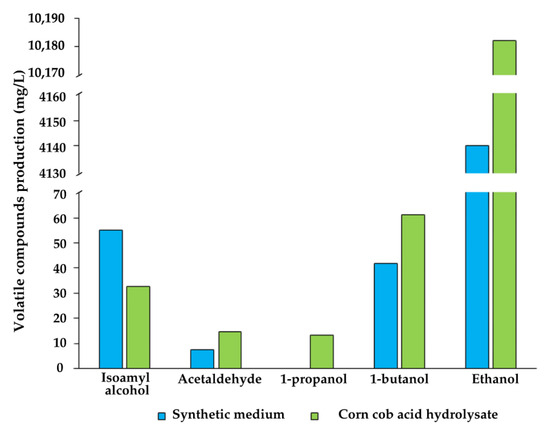
Figure 4.
Production of aromatic volatile compounds by M. guilliermondii in synthetic medium and corn cob acid hydrolysate after 48 h of fermentation.
The isoamyl alcohol concentration was also higher than the concentration reported for 21 Pichia kluyveri strains in agave juice (3.7–8.6 mg·L−1) after 8 days [18] and for K. marxianus from tomato pomace (1.5 mg·L−1) [1]. Liu et al. [61] reported isoamyl alcohol concentrations ranging from 10.61 to 30.44 mg·L−1 from the fermentation of yellow-fleshed peach wine using Hanseniaspora uvarum, Metschnikowia pulcherrima, L. thermotolerans, and T. delbrueckii. However, they found that a mixed fermentation of Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces could increase the isoamyl alcohol concentration to 44 mg·L−1. In comparison, in synthetic beer wort, P. anomala produced 31.48 mg·L−1 [24], and in brewing wort, M. guilliermondii and P. kudriavzevii yielded 65.0–75.6 mg·L−1 and 53.5 mg·L−1, respectively, [20]. Even higher concentrations (209.87–329.77 mg·L−1) were reported by Fejzullahu et al. [25] using L. thermotolerans and T. delbrueckii with S. cerevisiae in apple purée. Escribano et al. [26] obtained 4.3–124 mg·L−1 in wine fermented by non-Saccharomyces yeast species such as Debaryomyces hansenii, Candida zeylanoides, Cryptococcus uzbekistanensis, M. pulcherrima, T. delbrueckii, L. thermotolerans, Williopsis pratensis, and Zygosaccharomyces bailii. These variations highlight the influence of fermentation conditions, substrate composition and yeast strain on isoamyl alcohol production.
In this study, increased agitation enhanced biomass but did not improve isoamyl alcohol production. Previous studies on P. kluyveri reported that a 250 rpm agitation improved the production of alcohols and esters [18]. This suggests that fermentation conditions can be optimized to promote both alcohol and ester production. In particular, adjusting parameters to increase the levels of precursors such as ethanol and isoamyl alcohol would provide more precursors for subsequent ester formation. Gethins et al. [60] reported that at 120 rpm agitation, K. marxianus produced 0.87 mg/L isoamyl alcohol and 0.74 mg/L 2-phenylethanol, degradation products of leucine and phenylalanine, along with other volatile compounds such as ethyl acetate, isoamyl acetate, and phenylethyl propanoate.
Kinetic parameters demonstrated differences between the two fermentation media at 48 h (Table 4). The specific yield of isoamyl alcohol in corn cob acid hydrolysates (12.08 mg·g−1) indicated that this compound was synthesized using less biomass. Additionally, ethanol production in the corn cob acid hydrolysate was more than twice that observed in the synthetic medium, suggesting that M. guilliermondii adapted to the complexity of the substrate by redirecting its metabolism toward ethanol and other volatile compound production rather than biomass accumulation, as seen in the synthetic medium. This behavior aligns with findings in agave juice fermentation using K. marxianus where despite lower biomass concentration, higher production of amylic alcohols and ethanol was achieved, reflecting the influence of substrate composition in favoring metabolite biosynthesis over cell growth [59]. Although conventional second-generation bioethanol processes focus on the solid fraction, our findings support the use of the liquid fraction as a viable substrate for producing aromatic volatile compounds [11]. Sokan-Adeaga et al. [62] obtained 3.16 g·L−1 of ethanol from corn cob acid hydrolysates using S. cerevisiae and Bolzico et al. [63] reported ethanol concentrations of 1–5 g·L−1 after 24 h of fermentation using Scheffersomyces stipitis, Pachysolen tannophilus, and Spathaspora passalidarum, cultivated in synthetic medium (10 g·L−1 of xylose). Previous studies have used other residues, such as sugarcane bagasse hydrolysates, and reported 0.57 (g ethanol·g−1 biomass) after 144 h of fermentation with M. guilliermondii under acetic acid stress (5 g·L−1) [64]. This specific yield is lower than that obtained with corn cob acid hydrolysate (3.75 g ethanol·g−1 biomass) in the present study after 48 h of fermentation, which had a lower concentration acetic acid (2.7 g·L−1).

Table 4.
Kinetic parameters of M. guilliermondii isoamyl alcohol production from synthetic medium and corn cob acid hydrolysates after 48 h of fermentation.
After 48 h of fermentation using corn cob acid hydrolysates, M. guilliermondii produced 2.7 g·L−1 of biomass, 10.18 g·L−1 of ethanol, and several volatile aromatic compounds, including 32.7 mg·L−1 of isoamyl alcohol, 13 mg·L−1 of 1-propanol, and 61 mg·L−1 of 1-butanol. These quantified products represent a partial conversion of the available sugars, suggesting that the carbon flux may have been directed toward other metabolic pathways, which could be further explored to enhance product recovery. Although M. guilliermondii can metabolize xylose to produce xylitol [56], it did not achieve complete sugar consumption under the conditions tested. This behavior is consistent with the lower fermentative capacity characteristic of non-Saccharomyces yeast like H. uvarum and P. kluyveri [22]. The obtained products, residual sugars and solid residue from pretreatment can be recovered for further applications, highlighting the potential for resource optimization and their application into food, bioenergy, pharmaceuticals with a biorefinery approach [32].
3.4.3. Free Amino Nitrogen and Intracellular Protein Content
The initial concentration of FAN in the synthetic medium was higher compared to the corn cob hydrolysate. This difference is likely due to the presence of metal ions in the hydrolysate, which can form complexes with amino acids and reduce their bioavailability for yeast uptake. As a result, FAN consumption was higher in synthetic media (33.50% of the initial FAN), compared to 12.81% consumed in the hydrolysate. This suggests that M. guilliermondii may metabolize specific nitrogen sources more efficiently in the synthetic medium.
The complexity of lignocellulosic hydrolysates, particularly their nitrogen composition, makes the production of volatile aromatic compounds unpredictable [23]. These findings are consistent with Prior et al. [65], who reported that histidine assimilation is lower than other amino acids, highlighting the selective nature of nitrogen uptake in yeasts. In corn cob hydrolysates, lower nitrogen assimilation may result from differences in nutrient composition, as reported in other lignocellulosic hydrolysates, or by the presence of inhibitory compounds affecting uptake efficiency [66].
Higher nitrogen consumption in the synthetic medium corresponds with increased biomass production (8.38 g·L−1). In contrast, despite lower FAN assimilation in the corn cob hydrolysate, a higher specific yield of isoamyl alcohol was obtained, suggesting M. guilliermondii shifted from growth to secondary metabolites synthesis. This shift is consistent with nitrogen limiting conditions that activate the Ehrlich pathway. Nitrogen availability influences AVC production, and is affected not only by total nitrogen content but also by chemical nature and availability of nitrogen sources, particularly [67]. Therefore, evaluating VAC synthesis by non-Saccharomyces yeasts under varying nitrogen conditions is of considerable interest [28,68]. Gobert et al. [69], showed that non-Saccharomyces yeasts selectively metabolize specific nitrogen compounds, especially amino acids, which are considered “preferred” nitrogen sources. Understanding these preferences is essential for optimizing fermentation processes and maximizing AVC production, especially when using lignocellulosic derived hydrolysates [22].
The determination of intracellular protein showed that biomass obtained after 72 h of fermentation contained 11.0 ± 0.74% intracellular protein in corn cob hydrolysates and 7.3 ± 0.26% in the synthetic medium. This difference suggests that M. guilliermondii exhibits distinct metabolic responses depending on the culture medium. The higher protein content in the corn cob hydrolysate biomass may represent an adaptive mechanism to complex nutrient availability, as previously suggested for yeasts growing on lignocellulosic hydrolysates [39]. Beyond its physiological role, this protein could also be valorized as an ingredient for yeast extract, contributing to a biorefinery approach, where all biomass fractions are integrated in value-added applications.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the potential of M. guilliermondii to convert corn cob acid hydrolysates into isoamyl alcohol and other aromatic volatile compounds. Corn cob was selected due to its higher hemicellulose content compared to corn stover. Optimization of phosphoric acid hydrolysis via Box–Behnken design enabled high xylose release with minimal acetic acid formation, providing a less toxic fermentation medium. Central composite design evaluated conditions that enhanced the specific isoamyl alcohol yield. M. guilliermondii produced isoamyl alcohol (12.08 ± 0.67 mg·g−1) and other AVC such as 1-propanol and 1-butanol. These results demonstrated the relevance of nitrogen availability and substrate composition in modulating the metabolic performance of M. guilliermondii. The intracellular protein accumulation and incomplete sugar consumption suggest additional valorization pathways, including the recovery of residual sugars, yeast biomass, and solid fractions. Understanding the metabolism of non-Saccharomyces yeast is essential for optimizing fermentation strategies and their integration into biorefinery strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomass5030051/s1, Table S1: Analysis of variance for xylose and acetic acid production from corncob using H3PO4; Table S2: Analysis of variance for the specific yield of isoamyl alcohol produced by M. guilliermondii.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C.-M., C.R.-M. and L.C.-G.; methodology, N.E.P.-F., R.A.-T., C.C.-M. and L.C.-G.; validation, N.E.P.-F., C.C.-M. and L.C.-G.; formal analysis, N.E.P.-F. and C.C.-M.; investigation, N.E.P.-F., C.C.-M. and L.C.-G.; resources, C.C.-M. and L.C.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, N.E.P.-F. and R.A.-T.; writing—review and editing, C.C.-M., C.R.-M. and L.C.-G.; visualization and supervision, C.C.-M., C.R.-M. and L.C.-G.; project administration, C.C.-M. and C.R.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by SIP-IPN (20231627, 20240703, 20250313) and SECIHTI Ph.D. fellowship (CVU:987783).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AVCs | Aromatic volatile compounds |
| BBD | Box–Behnken design |
| CCD | Central composite design |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
References
- Kılmanoğlu, H.; İşleten Hoşoğlu, M.; Güneşer, O.; Karagül Yüceer, Y. Optimization of Pretreatment and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Conditions of Tomato Pomace for Production of Alcohols and Es-Ters by Kluyveromyces marxianus. LWT 2021, 138, 110728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, S.L.; Carvalho, L.C.; Romaní, A.; Domingues, L. Development of a Sustainable Bioprocess Based on Green Technologies for Xylitol Production from Corn Cob. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 156, 112867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahman, Y.; Syed, K.; Begum, S.; Roy, P.; Mohtasebi, B. 14—Biofuels: Their characteristics and analysis. In Biomass, Biopolymer-Based Materials, and Bioenergy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 277–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoumick, M.C.; Paul, S.; Roy, S.; Harvey, B.G.; Mitra, S. Recovery of Isoamyl Alcohol by Graphene Oxide Immobilized Membrane and Air-Sparged Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2024, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coma, M.; Chatzifragkou, A. Chemicals from Food Supply Chain By-Products and Waste Streams. Molecules 2019, 24, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, P.; Londo, M.; Junginger, M. The Circular Bioeconomy: Its Elements and Role in European Bioeconomy Clusters. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. X 2020, 6, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates; Interagency Commodity Estimates Committee Forecasts; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.usda.gov/sites/default/files/documents/november-2023-wasde-lockup-briefing.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Miranda, M.T.; Sepúlveda, F.J.; Arranz, J.I.; Montero, I.; Rojas, C.V. Analysis of Pelletizing from Corn Cob Waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIAP. Panorama Agroalimentario—La Ruta de La Transformación Agroalimentaria; Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera; Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural: Mexico City, Mexico, 2024.
- Gallego-García, M.; Moreno, A.D.; Manzanares, P.; Negro, M.J.; Duque, A. Recent Advances on Physical Technologies for the Pretreatment of Food Waste and Lignocellulosic Residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Bajar, S.; Kour, H.; Kothari, R.; Pant, D.; Singh, A. Lignocellulosic Biomass Valorization for Bioethanol Production: A Circular Bioeconomy Approach. Bioenerg. Res. 2022, 15, 1820–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, A.; Saha, B.C.; Kennedy, G.J.; Cotta, M.A. High Temperature Dilute Phosphoric Acid Pretreatment of Corn Stover for Furfural and Ethanol Production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-K.; Zhang, J.-A.; Ling, H.-Z.; Ping, W.-X.; Huang, W.; Ge, J.-P.; Xu, J.-M. Optimization of pH and Acetic Acid Concentration for Bioconversion of Hemicellulose from Corncobs to Xylitol by Candida tropicalis. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 43, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.K.; Sharma, S. Recent Updates on Different Methods of Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Feedstocks: A Review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.M.S.; Milan, T.M.; Tapia-Blácido, D.R. Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) to Optimize 2G Bioethanol Production: A Review. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 151, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Morales, P. Wine Secondary Aroma: Understanding Yeast Production of Higher Alcohols. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1449–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-T.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Lo, Y.-C.; Liou, B.-K.; Lin, H.-W.; Hou, C.-Y.; Cheng, K.-C. Isolation and Identification of Aroma-Producing Non-Saccharomyces Yeast Strains and the Enological Characteristic Comparison in Wine Making. LWT 2022, 154, 112653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Zamora, A.; Gutiérrez-Avendaño, D.O.; Arellano-Plaza, M.; De la Torre González, F.J.; Barrera-Martínez, I.; Gschaedler Mathis, A.; Casas-Godoy, L. The Non-Saccharomyces Yeast Pichia kluyveri for the Production of Aromatic Volatile Compounds in Alcoholic Fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res. 2021, 20, foaa067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.-L.; Li, A.-H.; Su, J.; Wang, X.-C.; Chen, C.-Q.; Tao, Y.-S. Flavor Modification of Dry Red Wine from Chinese Spine Grape by Mixed Fermentation with Pichia fermentans and S. cerevisiae. LWT 2019, 109, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaolesi, S.; Pérez-Través, L.; Pérez, D.; Roldán-López, D.; Briand, L.E.; Pérez-Torrado, R.; Querol, A. Identification and Assessment of Non-Conventional Yeasts in Mixed Fermentations for Brewing Bioflavored Beer. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 399, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzialo, M.C.; Park, R.; Steensels, J.; Lievens, B.; Verstrepen, K.J. Physiology, Ecology and Industrial Applications of Aroma Formation in Yeast. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41 (Suppl. 1), S95–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Li, A.; Yang, J.; Tao, Y. Utilization Efficiency of Ehrlich Pathway-Related Amino Acid Affected Higher Alcohol Acetate Production of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts during Alcoholic Fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbairn, S.; McKinnon, A.; Musarurwa, H.T.; Ferreira, A.C.; Bauer, F.F. The Impact of Single Amino Acids on Growth and Volatile Aroma Production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larroque, M.N.; Carrau, F.; Fariña, L.; Boido, E.; Dellacassa, E.; Medina, K. Effect of Saccharomyces and Non-Saccharomyces Native Yeasts on Beer Aroma Compounds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fejzullahu, F.; Kiss, Z.; Kun-Farkas, G.; Kun, S. Influence of Non-Saccharomyces Strains on Chemical Characteristics and Sensory Quality of Fruit Spirit. Foods 2021, 10, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, R.; González-Arenzana, L.; Portu, J.; Garijo, P.; López-Alfaro, I.; López, R.; Santamaría, P.; Gutiérrez, A.R. Wine Aromatic Compound Production and Fermentative Behaviour within Different Non-Saccharomyces Species and Clones. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrizon, J.; Gschaedler, A. Effects of the Addition of Different Nitrogen Sources in the Tequila Fermentation Process at High Sugar Concentration. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, M.; Meng, N.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Sun, B. Influence of Nitrogen Status on Fermentation Performances of Non-Saccharomyces yeasts: A Review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.; Udaondo, Z.; Duque, E.; Ramos, J.L. Biosynthesis of Fragrance 2-Phenylethanol from Sugars by Pseudomonas putida. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2024, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, E.T.; Li, M.; Hooker, C.A.; Englaender, J.A.; Wheeldon, I.; Solomon, K.V. Hydrolysis of Lignocellulose by Anaerobic Fungi Produces Free Sugars and Organic Acids for Two-stage Fine Chemical Production with Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2021, 37, e3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Application Potential of Native Meyerozyma guilliermondii in Pilot Production of Dry Red Wine. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Gao, H.; Qian, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, W.; Xin, F.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, M. Biotechnological Applications of the Non-Conventional Yeast Meyerozyma guilliermondii. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 46, 107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Arredondo, L.I.; Hernández-Leyva, S.R.; Maldonado-Mendoza, I.E.; Reyes-Moreno, C.; Contreras-Andrade, I.; Castro-Martínez, C. Valorisation of Agroindustrial Residues Acid Hydrolyzates as Carbon Sources for Ethanol Production by Native Yeast Strains with Different Fermentative Capabilities. Biotecnia 2020, 22, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre González, F.J.; Avendaño, D.O.G.; Mathis, A.C.G.; Kirchmayr, M.R. Evaluation of Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry for Differentiation of Pichia kluyveri Strains Isolated from Traditional Fermentation Processes. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinisterra-Sierra, M.C.; Campos-Valdez, A.; Pereira-Santana, A.; Zamora-Briseño, J.A.; Ramírez-Pérez, S.L.; González-Escobar, J.L.; Kirchmayr, M.R.; Barrera-Martínez, I.; Robles-Machuca, M.; Casas-Godoy, L. Microbial Diversity and Enzymatic Potential for Plastic Degradation in Contaminated Dumpsites in Mazamitla, Jalisco. Environ. Res. 2025, 283, 122170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); Issue Date: April 2008; Revision Date: July 2011 (Version 07-08-2011). Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008.
- Vallejos, M.E.; Chade, M.; Mereles, E.B.; Bengoechea, D.I.; Brizuela, J.G.; Felissia, F.E.; Area, M.C. Strategies of Detoxification and Fermentation for Biotechnological Production of Xylitol from Sugarcane Bagasse. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 91, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, H.; Bavouzet, J.M.; Talllandler, P.; Delorme, C. Systematic Error and Comparison of Four Methods for Assessing the Viability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Suspensions. Biotechnol. Tech. 1993, 7, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Valdez, A.; Kirchmayr, M.R.; Barrera-Martínez, I.; Casas-Godoy, L. Sustainable Production of Single-Cell Oil and Protein from Wastepaper Hydrolysate: Identification and Optimization of a Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Strain as a Promising Yeast. FEMS Yeast Res. 2023, 23, foad044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Damgaard, A.; Christensen, T.H. Bioethanol from Corn Stover—A Review and Technical Assessment of Alternative Biotechnologies. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 67, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Hou, J.; Ni, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Nie, S.; Wu, Q.; Wu, C. Efficient Fractionation of Corn Stover for Biorefinery Using a Sustainable Pathway. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3454–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, C.; Escamilla-Alvarado, C.; Sánchez, A.; Alarcón, E.; Ziarelli, F.; Musule, R.; Valdez-Vazquez, I. Wheat Straw, Corn Stover, Sugarcane, and Agave Biomasses: Chemical Properties, Availability, and Cellulosic-bioethanol Production Potential in Mexico. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2019, 13, 1143–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Du, L.; Cui, Y.; Song, P.; Jiang, F.; Ma, Q.; Xiao, D. Isolation and Structural Analysis of Hemicellulose from Corncobs after a Delignification Pretreatment. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7500–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Niu, R.; Minami, E.; Saka, S. Characterization of Three Tissue Fractions in Corn (Zea mays) Cob. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 115, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoh, B.N.; Onyelucheya, O.E.; Obijiaku, J.C. Kinetic Study of Acid Hydrolysis of Corn Cob to Xylose. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 2539–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Nieves, D.; Rostro Alanís, M.J.; de la Cruz Quiroz, R.; Ruiz, H.A.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Current Status and Future Trends of Bioethanol Production from Agro-Industrial Wastes in Mexico. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 102, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xiao, W.; Han, L.; Huang, G. Characterization of Mechanical Pulverization/Phosphoric Acid Pretreatment of Corn Stover for Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mekkawi, S.; Abou-Elseoud, W.; Fadel, S.; Hassan, E.; Hassan, M. Phosphoric Acid Pretreatment and Saccharification of Paper Sludge as a Renewable Material for Cellulosic Fibers. J. Renew. Mater. 2024, 12, 1573–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-K.; Wu, J.; Lin, Z.-N.; Zhang, J.-A. Aerobic and Sequential Anaerobic Fermentation to Produce Xylitol and Ethanol Using Non-Detoxified Acid Pretreated Corncob. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varilla-Mazaba, A.; Raggazo-Sánchez, J.A.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; del Moral, S.; Gómez-Rodríguez, J.; Aguilar-Uscanga, M.G. Multi-Response Optimization of Acid Hydrolysis in Sugarcane Bagasse to Obtain High Xylose Concentration. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drissner, D.; Freimoser, F.M. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy of Yeasts and Filamentous Fungi for Research and Diagnostics in the Agricultural Value Chain. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singhal, N.; Kumar, M.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Virdi, J.S. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: An Emerging Technology for Microbial Identification and Diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollero, S.; Roberts, S.; Bauer, F.F.; Divol, B. Agitation Impacts Fermentation Performance as Well as Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism inSaccharomyces Cerevisiae under Winemaking Conditions: Influence of Agitation on Yeast Metabolism. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2018, 24, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelwood, L.A.; Daran, J.-M.; Van Maris, A.J.A.; Pronk, J.T.; Dickinson, J.R. The Ehrlich Pathway for Fusel Alcohol Production: A Century of Research on Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.; Runge, D.; Marbà-Ardébol, A.-M.; Schmacht, M.; Stahl, U.; Senz, M. Systematic Development of a Two-Stage Fed-Batch Process for Lipid Accumulation in Rhodotorula Glutinis. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 246, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, F.A.; Fernandes, T.A.R.; Bragança, C.R.S.; Balbino, T.R.; Diniz, R.H.S.; Passos, F.M.L.; Da Silveira, W.B. Isolation of Xylose-Assimilating Yeasts and Optimization of Xylitol Production by a New Meyerozyma guilliermondii Strain. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Singh, E.; Shrivastava, S. Microbial Xylitol Production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadioto, V.; Milani, L.M.; Barrilli, É.T.; Baptista, C.W.; Bohn, L.; Dresch, A.; Harakava, R.; Fogolari, O.; Mibielli, G.M.; Bender, J.P.; et al. Analysis of Glucose and Xylose Metabolism in New Indigenous Meyerozyma caribbica Strains Isolated from Corn Residues. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-García, L.E.; Taillandier, P.; Brandam, C.; Gschaedler, A. Fermentative Capacity of Saccharomyces and Non-Saccharomyces in Agave Juice and Semi-Synthetic Medium. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gethins, L.; Guneser, O.; Demirkol, A.; Rea, M.C.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Karagul Yuceer, Y.; Morrissey, J.P. Influence of Carbon and Nitrogen Source on Production of Volatile Fragrance and Flavour Metabolites by the Yeast Kluyveromyces Marxianus: Nutrient Effects on Volatiles in K. Marxianus. Yeast 2014, 32, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, M.; Ren, T.; Wang, J.; Niu, C.; Zheng, F.; Li, Q. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Non-Saccharomyces Strains on Alcoholic Fermentation Behavior and Aroma Profile of Yellow-Fleshed Peach Wine. LWT 2022, 155, 112993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokan-Adeaga, A.A.; Salami, S.A.; Bolade, D.O.; Aledeh, M.; Sokan-Adeaga, M.A.; Amubieya, O.E.; Kehinde, S.A.; Farzadkia, M.; Ashraf, G.M.; Hoseinzadeh, E. Utilization of Local Corn (Zea mays) Wastes for Bioethanol Production by Separate Hydrolysis and Fermentation. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 15, 100447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzico, B.C.; Racca, S.; Khawam, J.N.; Leonardi, R.J.; Tomassi, A.H.; Benzzo, M.T.; Comelli, R.N. Exploring Xylose Metabolism in Non-Conventional Yeasts: Kinetic Characterization and Product Accumulation under Different Aeration Conditions. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 51, kuae023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, M.D.S.C.; Bastos, R.G.; Ceccato-Antonini, S.R. Single and Combined Effects of Acetic Acid, Furfural, and Sugars on the Growth of the Pentose-Fermenting Yeast Meyerozyma guilliermondii. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, K.J.; Bauer, F.F.; Divol, B. The Utilisation of Nitrogenous Compounds by Commercial Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts Associated with Wine. Food Microbiol. 2019, 79, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.-S.; Cate, J.H. Metabolic Engineering of Yeast for Lignocellulosic Biofuel Production. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 41, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Otero, P.; Nogueira, R.A.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Secondary Aroma: Influence of Wine Microorganisms in Their Aroma Profile. Foods 2020, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Miranda, L.A.; Zepeda-Peña, A.C.; Casas-Godoy, L.; Pereira-Santana, A.; Méndez-Zamora, A.; Barrera-Martínez, I.; Rodríguez-Zapata, L.; Gschaedler-Mathis, A.; Figueroa-Yañez, L.J. CRISPRi-Induced Transcriptional Regulation of IAH1 Gene and Its Influence on Volatile Compounds Profile in Kluyveromyces Marxianus DU3. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.; Tourdot-Maréchal, R.; Sparrow, C.; Morge, C.; Alexandre, H. Influence of Nitrogen Status in Wine Alcoholic Fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).