Effect of Thickness Swelling and Termite Attack Resistance in Wood–Plastic Composites Produced with Pine Wood and Recycled Thermoplastics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Manufacture of the Particleboard
2.2. Thickness Swelling Test
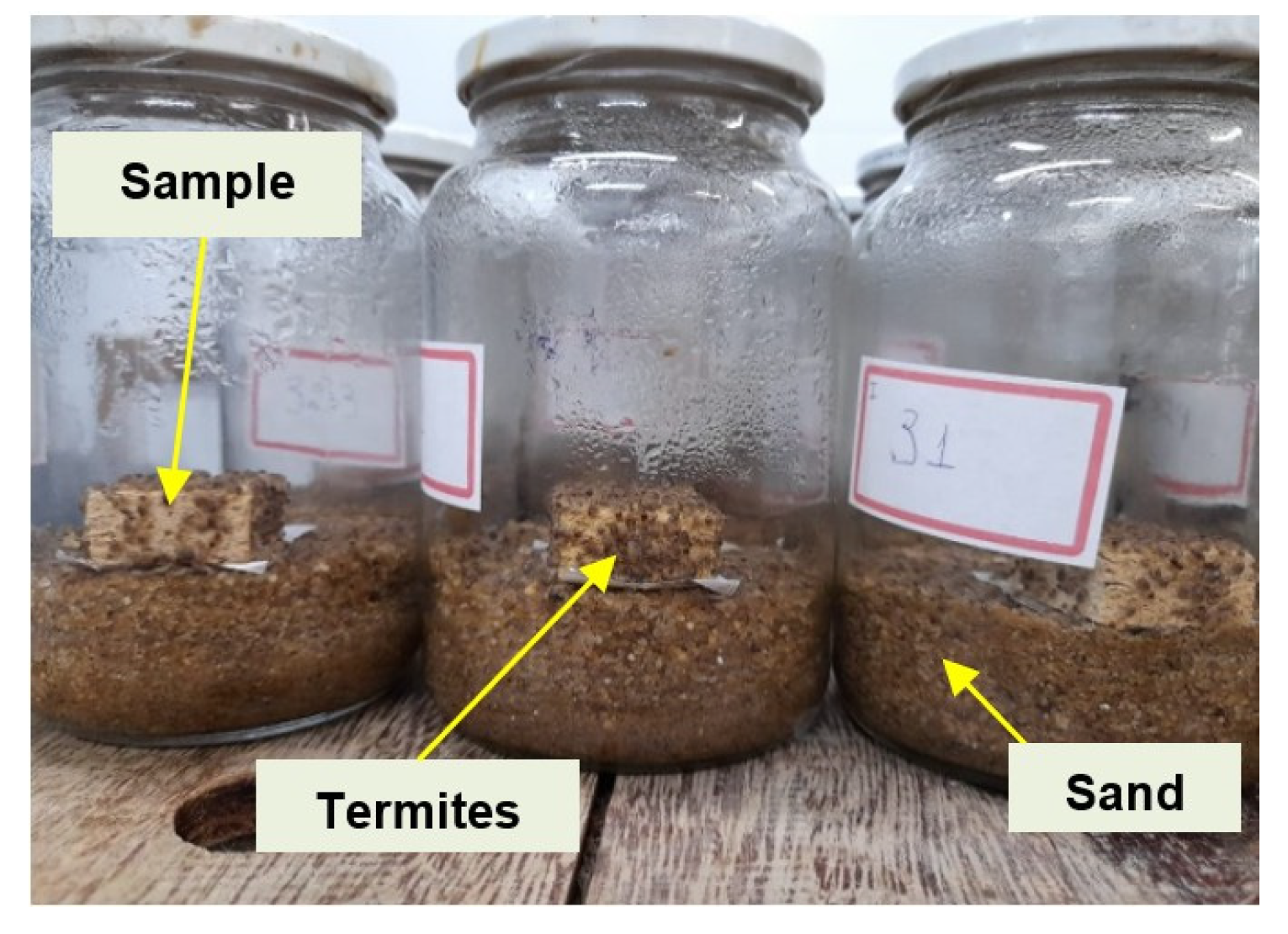
2.3. No-Choice Feeding Test with Nasutitermes corniger Termite
2.4. Drywood Termites Test with Cryptotermes brevis Termite
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
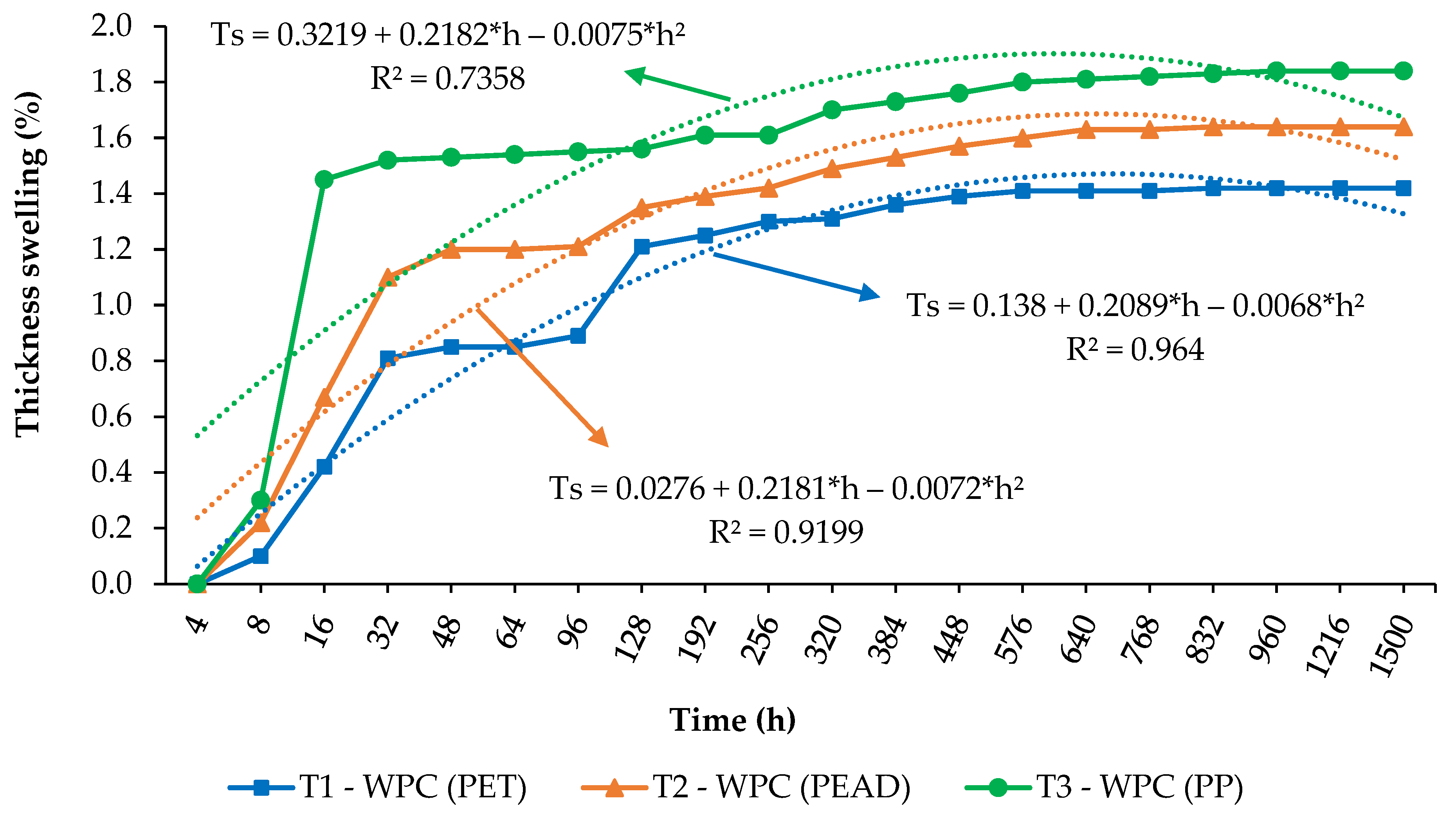
3.1. Wood–Plastic Composite on the Thickness Swelling During Water Immersion
3.2. Test with Soil or Arboreal Termites (Nasutitermes corniger)
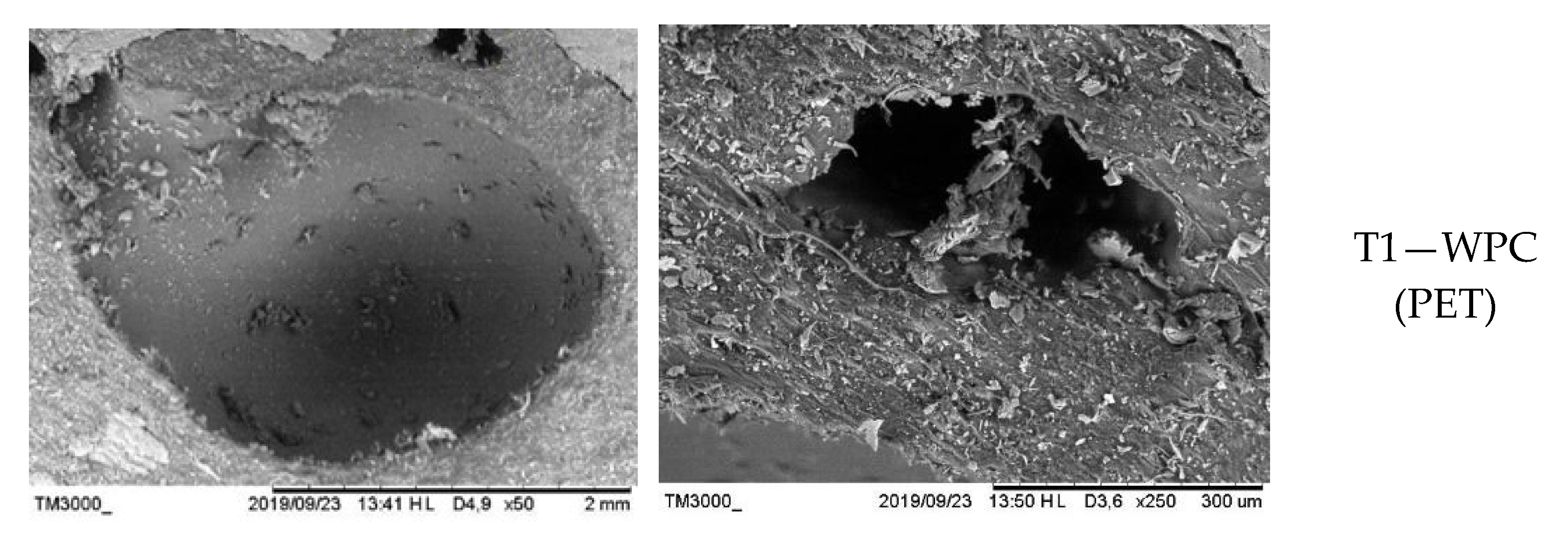
3.3. Test with Drywood Termites (Cryptotermes brevis)
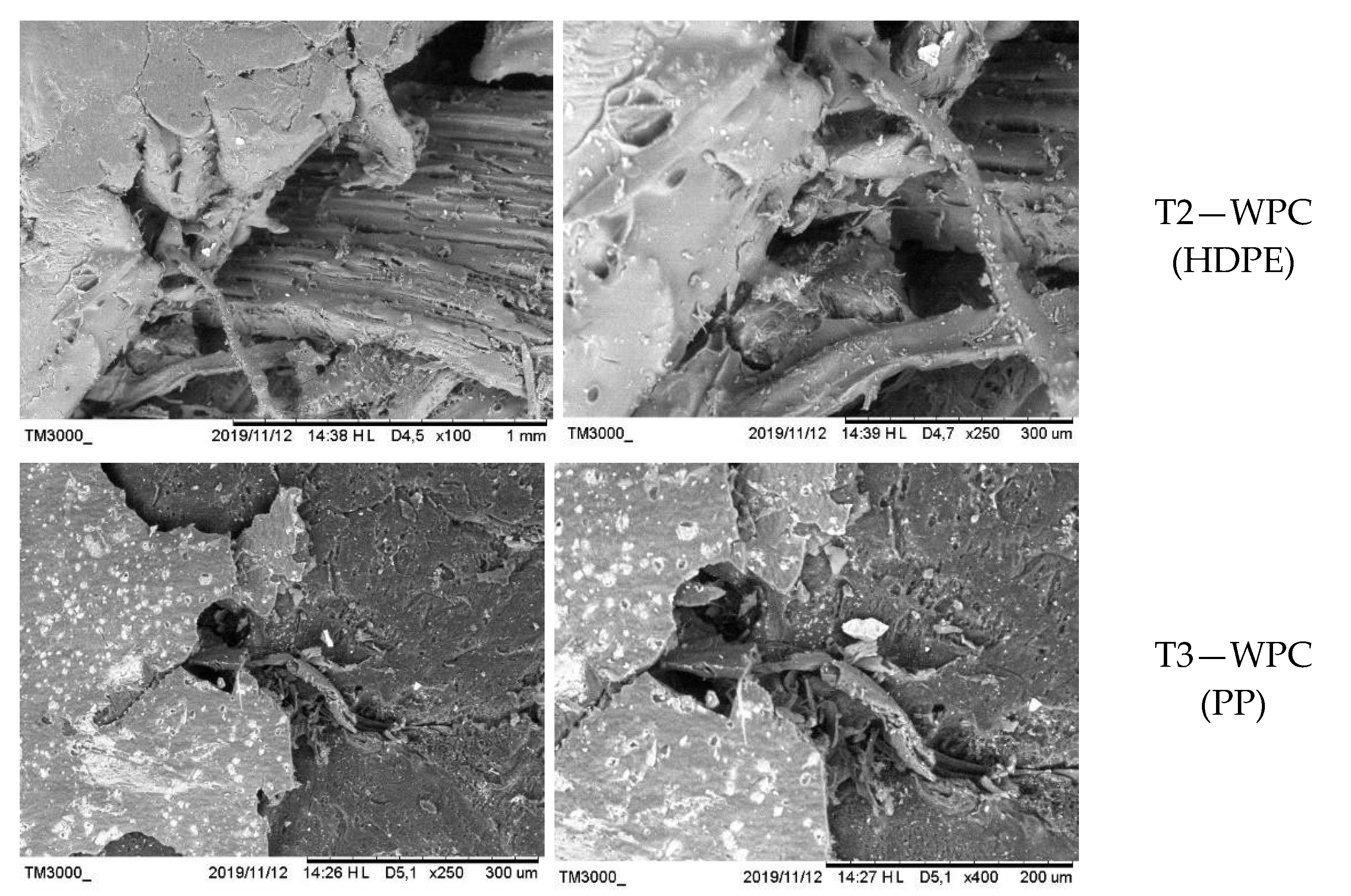
4. Discussion
4.1. Thickness Swelling of Wood–Plastic Composite by Water Immersion
4.2. Biological Resistance of Wood–Plastic Composite to Soil or Arboreal Termites
4.3. Biological Resistance of Wood–Plastic Composite to Drywood Termites
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PET | Polyethylene Terephthalate |
| HDPE | High-Density Polyethylene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| WPC | Wood–Plastic Composites |
References
- Kord, B.; Ghalehno, M.D.; Movahedi, F. Effect of immidazolium-based green solvents on the moisture absorption and thickness swelling behavior of wood flour/polyethylene composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2022, 35, 2162–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamperidou, V.; Ratajczak, I.; Perdoch, W.; Mazela, B. Impact of thermal modification combined with silicon compounds treatment on wood structure. Wood Res. 2022, 67, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turku, I.; Keskisaari, A.; Kärki, T.; Puurtinen, A.; Marttila, P. Characterization of wood plastic composites manufactured from recycled plastic blends. Compos. Struct. 2017, 161, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Araujo, E.; de Paula Protásio, T.; Barbosa, A.V.C.; Mendes, R.F.; Júnior, J.B.G.; Mendes, L.M.; da Silva, M.G. Variação das propriedades tecnológicas de painéis MDF em uma linha de produção industrial no Brasil. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e478101119951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanawilai, T.; Taneerat, K. Alternative polymeric matrices for wood-plastic composites: Effects on mechanical properties and resistance to natural weathering. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Youcai, Z.; Atta, E. Composite materials production using waste plastic taken from municipal solid waste and its landfill. In Resource Recovery Technology for Municipal and Rural Solid Waste; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, L.S.; Stolz, C.M.; Amario, M.; Silva, A.L.N.; Haddad, A.N. Use of post-consumer plastics in the production of wood-plastic composites for building components: A systematic review. Energies 2023, 16, 6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordà-Reolid, M.; Moreno, V.; Martínez-Garcia, A.; Covas, J.A.; Gomez-Caturla, J.; Ivorra-Martinez, J.; Quiles-Carrillo, L. Incorporation of argan shell flour in a biobased polypropylene matrix for the development of high environmentally friendly composites by injection molding. Polymers 2023, 15, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhoru, Y.U.; Tripathi, S.; Tripathi, S. Termite resistance of Pinus radiata D. Don wood after unified thermal and neem seed oil treatment. Indian For. 2016, 142, 882–890. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinihashemi, S.K.; Badritala, A. The influence of a treatment process on the reaction to water of durable and water resistant wood/plastic composites. Drewno 2017, 60, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosme, L.; Haro, M.M.; Guedes, N.M.P.; Della Lucia, T.M.C.; Guedes, R.N.C. Tropical wood resistance to the West Indian drywood termite Cryptotermes brevis: If termites can’t chew. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzi, E.; Kartal, S.N.; Muin, M.; Hassanin, A.H.; Hamouda, T.; Kilic, A.; Candan, Z. Biological performance of novel hybrid green composites produced from glass fibers and jute fabric skin by the VARTM process. BioResources 2018, 13, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.; Nanda, M.A. Detection and monitoring techniques of termites in buildings: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 195, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.; Fitzgerald, C. Potential of gas-propelled aerosol containing synergized pyrethrins for localized treatment of Cryptotermes brevis (Kalotermitidae: Blattodea). Insects 2023, 14, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.G.; Paes, J.B.; Lopez, Y.M.; de Alcântara Segundinho, P.G.; de Oliveira, R.G.E.; Fassarella, M.V.; Brito, A.S.; Chaves, I.L.S.; Martins, R.S.F. Resistance of particleboards produced with ligno-cellulosic agro-industrial wastes to fungi and termites. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 157, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, R.; Morrell, J.J. Ability of plant-derived oils to inhibit dampwood termite (Zootermopsis augusticollis) activity. Maderas Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2015, 17, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazal, V.; Bailez, O.; Viana-Bailez, A.M.; Menezes, E.D.L.A.; Menezes, E.B. Decayed wood affecting the attraction of the pest arboretum termite Nasutitermes corniger (Isoptera: Termitidae) to resource foods. Sociobiology 2014, 59, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Da Silva Lopes, R.; Barroso Martins, M.C.; De Lima, G.; Gonçalves De Oliveira, L.; Félix Da Costa, A.; Felipe Dos Santos, V.; Dos Santos Correia, M.T.; Da Silva, N.H.; Correia De Albuquerque, A.; De Luna Alves Lima, E.Á.; et al. Toxicity of Agave sisalana extracts on Cordyceps and their effect and the association with fungi on Nasutitermes corniger (Isoptera: Termitidae). Rev. Colomb. Entomol. 2022, 48, e11537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboorani, A. Characterizing water sorption and diffusion properties of wood/plastic composites as a function of formulation design. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Du, G.; Wang, S. Wood plastic composites: Their properties and applications. In Engineered Wood Products for Construction; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 317; Particleboards and Fibreboards: Determination of Swelling in Thickness After Immersion in Water. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 1999.
- D3345-22; Standard Test Method for Laboratory Evaluation of Wood for Resistance to Subterranean Termites. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022; p. 6.
- Brocco, V.F.; Paes, J.B.; Costa, L.G.; Kirker, G.T.; Brazolin, S. Wood color changes and termiticidal properties of teak heartwood extract used as a wood preservative. Holzforschung 2020, 74, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, J.B.; Maffioletti, F.D.; Silva, M.R.; Ramalho, A.H.C.; de Medeiros, J.R.; Lopez, Y.M.; Segundinho, P.G.D.A.; Rocco Lahr, F.A. Biological resistance of sandwich particleboard made with sugarcane, thermally-treated Pinus wood and malva fiber. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2022, 42, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPT. Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas. DIMAD 1157: Ensaio Acelerado da Resistência Natural ou de Madeira Preservada ao Ataque de Térmitas do Gênero Cryptotermes (Fam. Kalotermitidae); Publicação No 1157; IPT/DIMAD: São Paulo, Brazil, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Maistrello, L. Termites and standard norms in wood protection: A proposal targeting drywood termites. In Sustainability in Plant and Crop Protection, 2nd ed.; Khan, M.A., Ahmad, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2018; pp. 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, H.P.; Nee, L.A.; Meng, H.C. Physical and bending properties of injection molded wood plastic composites boards. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2008, 3, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Villablanca, C.M. Compuestos Lignocelulosico-Plástico Obtenidos a Partir de Harina de Madera o Corteza de Pinus radiata Y Polietileno Reciclado Fabricado Mediante Moldeo Por Inyección. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Concepción, Concepción, Chile, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikary, K.B.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P. Long-term moisture absorption and thickness swelling behaviour of recycled thermoplastics reinforced with Pinus radiata sawdust. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 142, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, Y.M.; Paes, J.B.; Gustave, D.; Gonçalves, F.G.; Méndez, F.C.; Nantet, A.C.T. Production of wood-plastic composites using Cedrela odorata sawdust waste and recycled thermoplastics mixture from post-consumer products—A sustainable approach for cleaner production in Cuba. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, C.M.; Wilson, H.P.; Hurtado, L.V. Propiedades físicas y mecánicas de compuestos de polietileno reciclado y harinas de corteza y madera de Pinus radiata fabricados mediante moldeo por inyección. Maderas Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2012, 14, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemons, C. Elastomer modified polypropylene-polyethylene blends as matrices for wood flour-plastic composites. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Cazella, P.H.; de Souza, M.V.; Rodrigues, F.R.; da Silva, S.A.M.; Bispo, R.A.; De Araujo, V.A.; Christoforo, A.L. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as a recycled raw material for particleboards produced from pinus wood and biopolymer resin. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, S.; Pizzi, A.; Köken, N.; Bengü, B. Tannin-based wood panel adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2024, 130, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magina, S.; Gama, N.; Carvalho, L.; Barros-Timmons, A.; Evtuguin, D.V. Lignosulfonate-based polyurethane adhesives. Materials 2021, 14, 7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, H.M.L.; Lelis, R.C.C.; Gomes, F.J.B.; Lopez, Y.M.; Gonçalves, F.G.; Chaves, I.L.S.; Brito, A.S. Effect of tannin and calcium lignosulfonate-based adhesives on particleboards production. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2024, 132, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesprini, E.; Causin, V.; De Iseppi, A.; Zanetti, M.; Marangon, M.; Barbu, M.C.; Tondi, G. Renewable tannin-based adhesive from quebracho extract and furfural for particleboards. Forests 2022, 13, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudemanche, S.; Perrot, A.; Pimbert, S.; Lecompte, T.; Faure, F. Properties of an industrial extruded HDPE-WPC: The effect of the size distribution of wood flour particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.T.S.; Paes, J.B.; Vidaurre, G.B. Biological resistance of eucalypt wood species to drywood termites. Sci. For. 2017, 45, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Hermawan, D.; Hadi, Y.S.; Fajriani, E.; Massijaya, M.Y.; Hadjib, N. Resistance of particleboards made fromfast-growing wood species to subterranean termite attack. Insects 2012, 3, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhasman, S.; Hadi, Y.S.; Massijaya, M.Y.; Santoso, A. Binderless particleboard resistance to termite attack. For. Prod. J. 2012, 62, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Estrada, R.H.; Guillén-Mallette, J.; López-Naranjo, E.J.; Zacarías-Calderón, E. Effect of teak wood on recycled HDPE/pine wood composites subjected to termite attack and accelerated weathering. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2024, 37, 1027–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, P.; Poonia, A. Biodegradation of plastic using termites and their gut microbiota: A mini review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1057, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskisaari, A.; Kärki, T. The use of waste materials in wood-plastic composites and their impact on the profitability of the product. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 134, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.-Z. Impact fracture toughness and flow properties of polypropylene composites. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, D.C.; Nisgoski, S.; Oliveira, J.T.S.; Muñiz, G.I.B.; Paes, J.B. Resistência da madeira modificada termicamente de Eucalyptus grandis W. Hill ex Maiden ao térmita de madeira seca Cryptotermes sp. Ciência Florest. 2016, 26, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
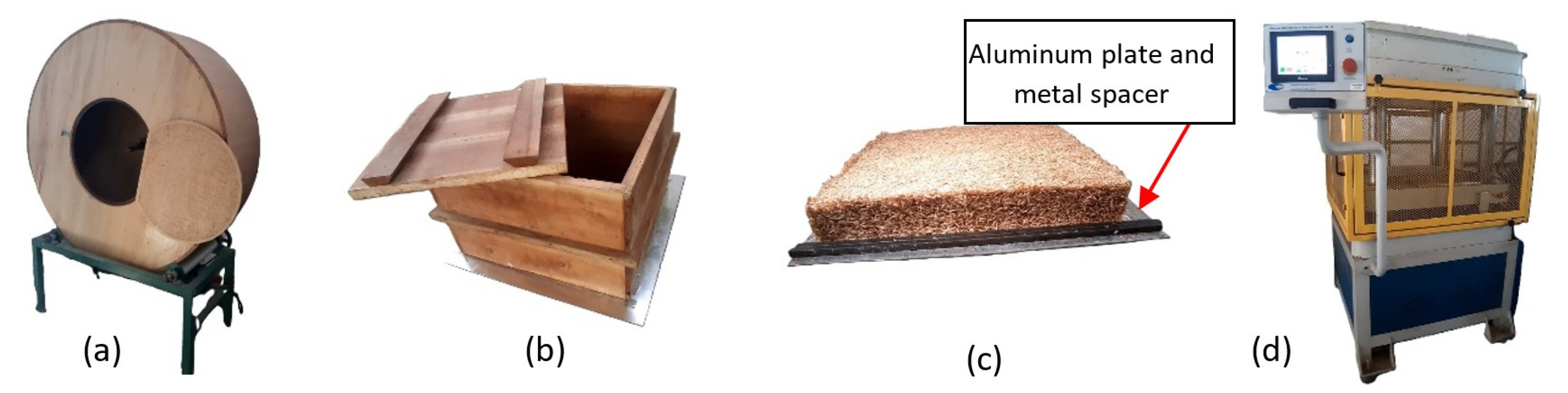



| Treatments | Sawdust Content (%) | Recycled Thermoplastics (%) | Density (Kg m−3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | HDPE | PP | |||
| T1—WPC (PET) * | 50 | 50 | - | - | 918.17 |
| T2—WPC (HDPE) | 50 | - | 50 | - | 964.33 |
| T3—WPC (PP) | 50 | - | - | 50 | 1097.33 |
| Control (pine particles) | 100 | - | - | - | 660.90 |
| Treatments | Wab (%) * | T0 (mm) | Tf (mm) | TSt (%) | Ksr (10−3 h−1) | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1—WPC (PET) | 0.60 | 16 | 17.90 | 11.90 | 0.82 | 0.95 |
| T2—WPC (HDPE) | 0.55 | 16 | 17.77 | 11.06 | 2.41 | 0.97 |
| T3—WPC (PP) | 0.40 | 16 | 16.66 | 4.13 | 5.00 | 0.98 |
| Treatments | Visual Damage (Score) | Mass Loss (%) | Mortality (%) | Classification (ASTM D3345-22) [22] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1—WPC (PET) | 6.4 (0.89) a * | 1.51 | 82.4 | Heavy |
| T2—WPC (HDPE) | 7.2 (1.02) a | 1.49 | 84.2 | Heavy |
| T3—WPC (PP) | 9.4 (1.09) a | 0.53 | 89.8 | Heavy |
| Control (pine particles) | 1.8 (0.84) b | 8.99 | 36.6 | Moderate |
| Treatments | Damage (Score) | Classification | Mass Loss (%) | Mortality (%) | Number of Days to Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1—WPC (PET) | 1.2 | Surface damage | 1.51 a * | 73 a | 27 |
| T2—WPC (HDPE) | 1.6 | Surface damage | 1.49 a | 76 a | 29 |
| T3—WPC (PP) | 0.4 | No damage | 0.53 b | 100 b | 12 |
| Control (pine particles) | 3.6 | Severe damage | 16.48 c | 40 c | 44 |
| Treatments | Density (kg m−3) | Survival of Termites (Day) | Percentage of Termite Survival (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1—WPC (PET) | 918.17 | 27 | 60 |
| T2—WPC (HDPE) | 964.33 | 29 | 64.4 |
| T3—WPC (PP) | 1097.33 | 12 | 26.7 |
| Control (pine particles) | 660.90 | 44 | 97.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, E.; Lopez, Y.; Paes, J.; Maffioletti, F.; Souza, G.; Gonçalves, F. Effect of Thickness Swelling and Termite Attack Resistance in Wood–Plastic Composites Produced with Pine Wood and Recycled Thermoplastics. Biomass 2025, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5030043
Silva E, Lopez Y, Paes J, Maffioletti F, Souza G, Gonçalves F. Effect of Thickness Swelling and Termite Attack Resistance in Wood–Plastic Composites Produced with Pine Wood and Recycled Thermoplastics. Biomass. 2025; 5(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Emilly, Yonny Lopez, Juarez Paes, Fernanda Maffioletti, Gabrielly Souza, and Fabricio Gonçalves. 2025. "Effect of Thickness Swelling and Termite Attack Resistance in Wood–Plastic Composites Produced with Pine Wood and Recycled Thermoplastics" Biomass 5, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5030043
APA StyleSilva, E., Lopez, Y., Paes, J., Maffioletti, F., Souza, G., & Gonçalves, F. (2025). Effect of Thickness Swelling and Termite Attack Resistance in Wood–Plastic Composites Produced with Pine Wood and Recycled Thermoplastics. Biomass, 5(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5030043







