Pineapple Waste Biorefinery: An Integrated System for Production of Biogas and Marketable Products in South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pineapple Waste Production in South Africa
3. Composition of Pineapple Waste
3.1. Lignocellulosic Composition
3.2. Proximate Composition
3.3. Ultimate Analysis
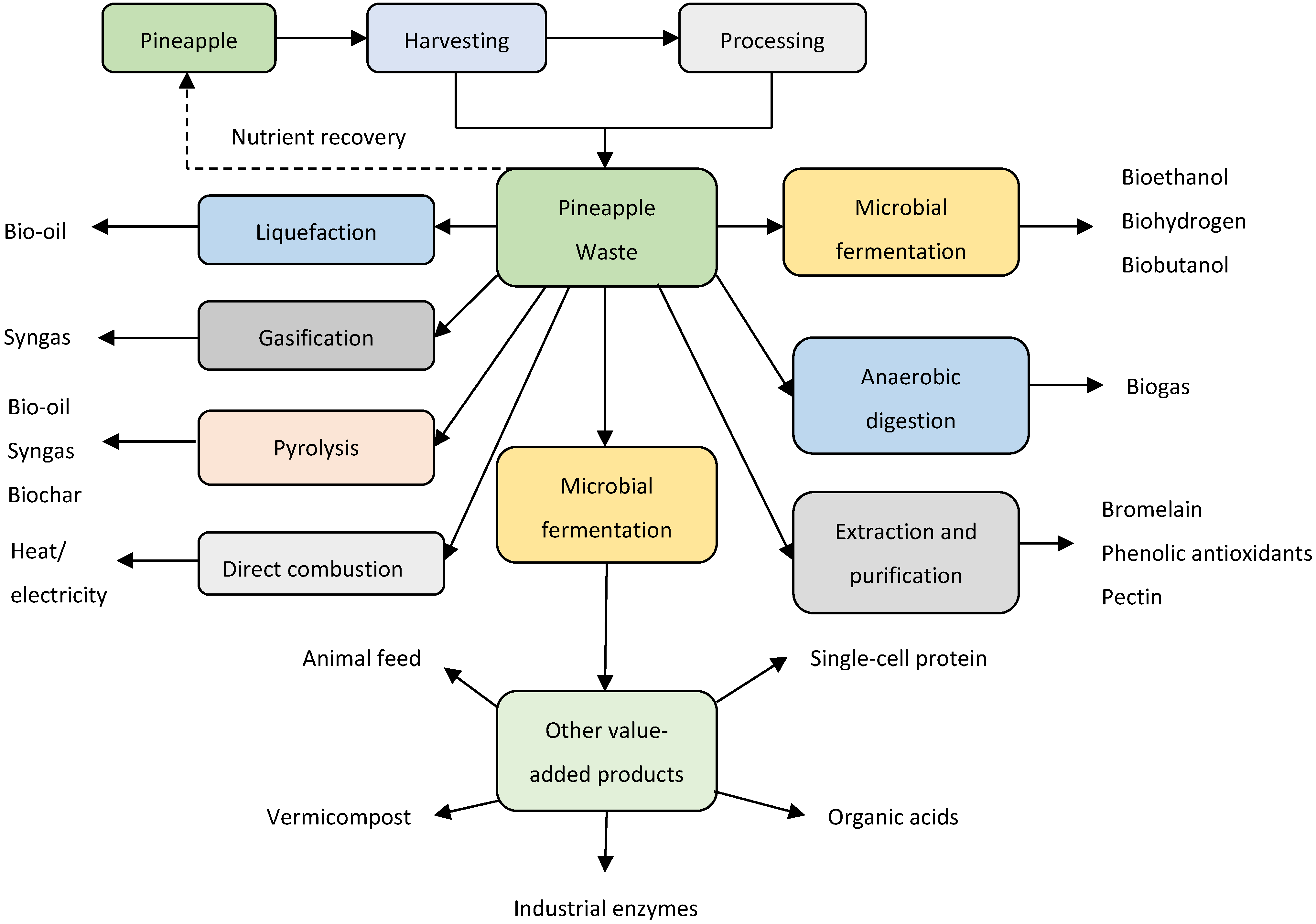
4. Pineapple Waste Biorefinery in South Africa
5. Energy Products from Pineapple Waste Biorefinery
5.1. Biogas
5.2. Biohythane
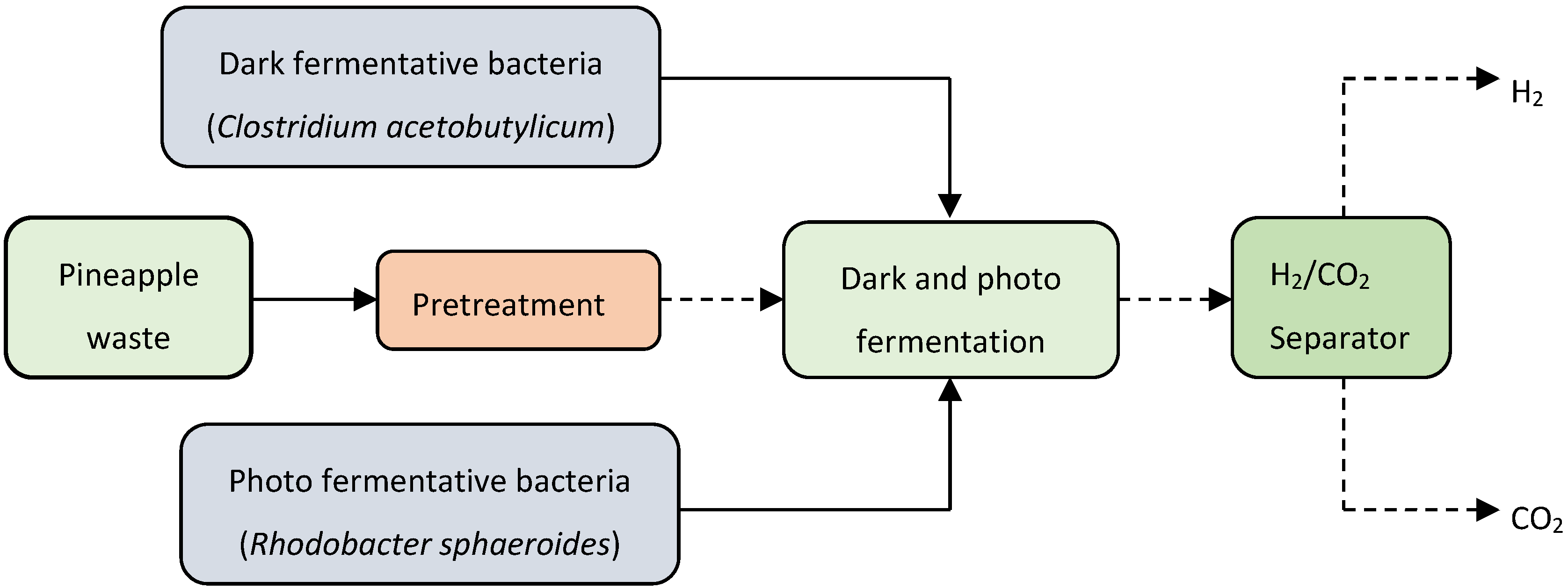
5.3. Biohydrogen
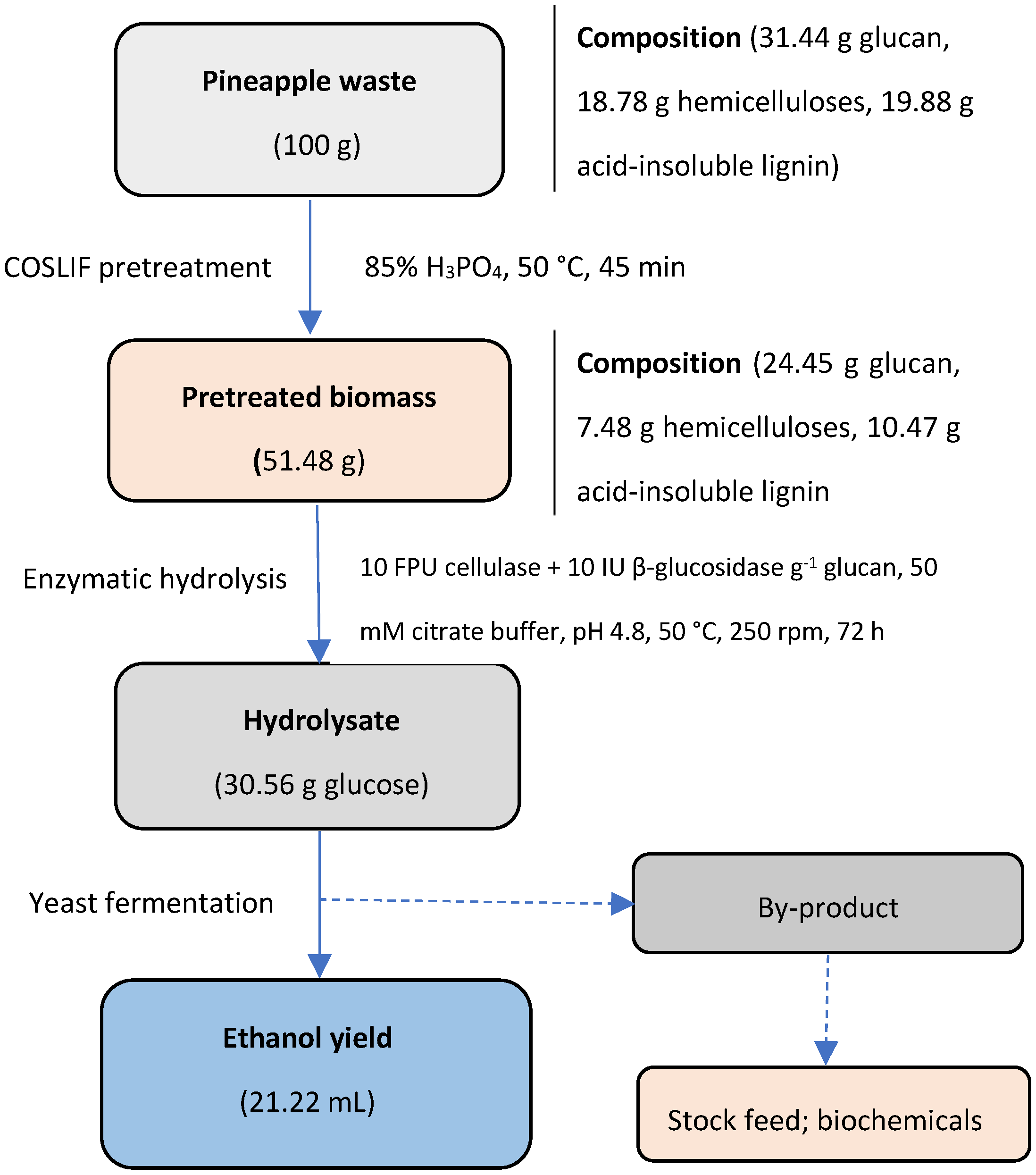
5.4. Bioethanol
5.5. Biobutanol
5.6. Pyrolytic Fuels
6. High-Value Products from Pineapple Waste Biorefining
6.1. Bioactive Compounds
6.2. Single-Cell Protein
6.3. Animal Feed
6.4. Vermicompost
7. Pretreatment of Pineapple Waste for Biochemical Platforms
8. Conclusions
9. Future Recommendations
- Formulate policies and regulations that influence the growth and development of biorefineries.
- Diversify feedstock streams for biorefinery systems.
- Develop scalable biorefinery platforms.
- Optimize process parameters and pretreatment conditions for bioconversion platforms.
- Life-cycle and environmental impact assessment of feedstocks for biorefineries.
- Establish competitive markets for bio-based products.
- Conduct pilot studies on scalable biorefinery technologies.
- Transform small-scale facilities into commercial enterprises.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABE | Acetone-butanol-ethanol |
| AD | Anaerobic digestion |
| BIDF | Biorefinery Industry Development Facility |
| ChCl-EG | Choline chloride: ethylene glycol |
| CHF | Consecutive hydrolysis and fermentation |
| COSLIF | Cellulose solvent and organic solvent lignocellulose fraction |
| CSIR | Council for Scientific and Industrial Research |
| DF | Direct fermentation |
| DF | Dietary fiber |
| DSI | Department of Science and Innovation |
| FAO | Food and Agricultural Organization |
| GRAS | Generally regarded as safe |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| LPSH | Low pressure steam heating |
| PAW | Pineapple waste |
| SCP | Single-cell protein |
| SSF | Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation |
| TS | Total solids |
| VFAs | Volatile fatty acids |
References
- Hamzah, A.F.A.; Hamzah, M.H.; Man, H.C.; Jamali, N.S.; Siajam, S.I.; Ismail, M.H. Recent updates on the conversion of pineapple waste (Ananas comosus) to value-added products, future perspectives and challenges. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Utilization of bioactive components present in pineapple waste: A review. The Pharm. Innov. J. 2021, 10, 954–961. [Google Scholar]
- Sarangi, P.K.; Singh, T.A.; Singh, N.G.; Shadangi, K.P.; Srivastava, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Chandel, A.K.; Pareek, N.; Vivekanand, V. Sustainable utilization of pineapple wastes for production of bioenergy, biochemicals and value-added products: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukirah, A.R.; Shuhaimi, M.; Uswatun, H.Z.; Koh, S.P.; Shukor, M.Y.A. Local pineapple waste as potential bio-ingredient. Food Res. 2023, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fouda-Mbanga, B.G.; Tyawabi, Z. Application of pineapple waste to the removal of toxic contaminants: A review. Toxics 2020, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statista. Global Pineapple Production 2002–2022. Statista. 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/298505/global-pineapple-production/ (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Tran, T.V.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, D.H.; Alhassan, M.; Jalil, A.A.; Waliabgan, W.; Lee, T. A critical review on pineapple (Ananas comosus) wastes for water treatment, challenges and future prospects towards circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Spike in Pineapple Consumption and Processing Amid Decline in Exports Due to COVID-19; Report No. SF2020-0044; USDA: Pretoria, South Africa, 2020.
- Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Food and Agricultural Commodities Production. FAOSTAT; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baidhe, E.; Kigozi, J.; Mukisa, I.; Muyanja, C.; Namubiru, L.; Kitarikawe, B. Unearthing the potential of solid waste generated along the pineapple drying process line in Uganda: A review. Environ. Chall. 2021, 2, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, L.; Sengar, A.C.; Neog, R.; Sunil, C.K. Pineapple processing waste (PPW): Bioactive compounds, their extraction, and utilisation: A review. J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4152–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichitsathian, B.; Yimrattanabavorn, J.; Wonglertarak, W. Enhancement of biogas production from pineapple waste by acid-alkaline pretreatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 471, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, E.O.; Kiplimo, R.; Mutwiwa, U. Optimization of anaerobic digestion parameters for biogas production from pineapple wastes codigested with livestock wastes. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Singh, B. Pineapple by-products utilization: Progress towards the circular economy. Food Humanit. 2024, 2, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, D.S.; Nand, K. Ensilage of pineapple processing waste for methane generation. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsree, P.; Suvajittanont, W.; Puttanlek, C.; Uttapap, D.; Rungsardthon, V. Anaerobic digestion of pineapple pulp and peel in a plug-flow reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherubini, F. The biorefinery concept: Using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Flores, F.G.; Martin-Martinez, F.J. Biorefineries: Achievements and challenges for a bio-based economy. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 973417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubando, A.T.; Ng, E.A.S.; Chen, W.; Culaba, A.B.; Kwon, E.E. Life cycle assessment of microalgal biorefinery: A state-of-the-art review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifan, F.; Broto, R.T.D.W.; Sumardiono, S.; Sutaryo; Dewi, A.L.; Yudanto, Y.A.; Sapatra, E.F. Effect of thermal pretreatment of pineapple peel waste in biogas production using response surface methodology. Int. J. Technol. 2022, 13, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekoai, P.T.; Chunilall, V.; Msele, K.; Buthelezi, L.; Johakimu, J.; Andrew, J.; Zungu, M.; Moloantoa, K.; Maningi, N.; Habimana, O.; et al. Biowaste biorefineries in South Africa: Current status, opportunities, and research and development needs. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2023, 188, 113870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firatoiu, A.; Chiurciu, I.; Marcuta, L.; Chereji, A.; Soare, E.; Voicu, V.; Marcuta, A. Study on the production and marketing of pineapples worldwide. In Proceedings of the 37th IBIMA Conference on Innovation Management and Information Technology Impact on Global Economy in the Era of Pandemic, Cordoba, Spain, 30–31 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Arteaga, S.L.; Cadena-Chamorro, E.; Goméz-García, R.; Serna-Cock, L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Torres-León, C. Unraveling the valorization potential of pineapple waste to obtain value-added products towards a sustainable circular bioeconomy. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.; Gominho, J.; Duarte, E. Performance of anaerobic codigestion of pig slurry with pineapple (Ananas comosus) bio-waste residues. Waste Biomass Valor. 2021, 12, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukruansuwan, V.; Napathorn, S.C. Use of agro-industrial residue from the canned pineapple industry for polyhydroxybutyrate production by Cupriavidus necator strain A-04. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabar, J.T.; Unpaprom, Y.; Ramaraj, R. Fermentation of pineapple fruit peel wastes for bioethanol production. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2019, 9, 761–765. [Google Scholar]
- Roda, A.; Faveri, D.M.; Dordon, R.; Lambri, M. Vinegar production from pineapple wastes-preliminary saccharification trials. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 37, 607–612. [Google Scholar]
- Khedkar, M.A.; Nimbalkar, P.R.; Gaikwad, S.G.; Chavan, P.V.; Bankar, S.B. Sustainable biobutanol production from pineapple waste by using Clostridium acetobutylicum B 527: Drying kinetic study. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 225, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jitpupakdee, J.; Pattharaprachayakul, N.; Rungsardthong, V.; Suvajittanont, W.; Uttapap, D. Enhancement of biogas production from industrial solid pineapple wastes by two-stage anaerobic digestion systems. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 3734–3746. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, M.E.S.; Cassellis, M.E.R.; Escobedo, R.M.; García, E.J. Chemical characterization of the industrial residues of the pineapple (Ananas comosus). J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2014, 3, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovich, V.A.; Linnenberg, C.; Theilen, U.; Weigand, H. Biogas production potential of mixed banana and pineapple waste as assessed by long-term laboratory-scale anaerobic digestion. Fermentation 2024, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Chintagunta, A.D.; Ray, S. A cleaner and eco-friendly bioprocess for enhancing reducing sugar production from pineapple leaf waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ofere, J.E.; Achube, F.I. Proximate composition, mineral content and phytochemical evaluation of different solvent extracts of pineapple (Ananas comosus) stalk. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2023, 27, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodagoda, K.; Marapana, R. Development of non-alcoholic wines from the wastes of Mauritius pineapple variety and its physicochemical properties. J. Phermacog. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 492–497. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Patti, A.F.; Ranganathan, V.; Arora, A. Hemicellulose based biorefinery from pineapple peel waste: Xylan extraction and its conversion into xylooligosaccharides. Food Bioprod. Process 2019, 117, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Shen, B.; Yang, J.; Xu, L. Pyrolysis of biomass pineapple residue and banana pseudo-stem: Kinetics, mechanism and valorization of bio-char. Catalysts 2022, 12, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Musa, N.F. Antioxidant property and chemical profile of pyroligneous acid from pineapple plant waste biomass. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kannah, R.K.; Merrylin, J.; Devi, T.P.; Kavitha, S.; Sivashanmugam, P.; Kumar, G.; Banu, J. Food waste valorization: Biofuels and value-added product recovery. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100524. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, B. Algal biorefinery: An integrated approach for sustainable biodiesel production. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 131, 105398. [Google Scholar]
- Kamusoko, R.; Jingura, R.M.; Chikwambi, Z.; Parawira, W. Strategies for valorization of crop residues into biofuels and other value-added products. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2021, 15, 1950–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, T.; Chowdhury, H.; Hossain, N.; Ahmed, A.; Hossen, M.S.; Chowdhury, P.; Thirugnanasambandam, M.; Saidur, R. Latest advancements on livestock waste management and biogas production: Bangladesh’s perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122818. [Google Scholar]
- Wagh, M.S.; Sowjanya, S.; Nath, P.C.; Chakraborty, A.; Amrit, R.; Mishra, B.; Mishra, A.K.; Mohanta, Y.K. Valorization of agro-industrial wastes: Circular bioeconomy and biorefinery process—A sustainable symphony. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 183, 708–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamusoko, R.; Mukumba, P. Potential of wheat straw for biogas production by anaerobic digestion in South Africa: A review. Energies 2024, 17, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, A.F.A.; Hamzah, M.H.; Mazlan, F.N.A.; Man, H.C.; Jamali, N.S.; Siajam, S.I. Anaerobic codigestion of pineapple wastes with cow dung: Effect of different total solid content on biomethane yield. Adv. Agric. Food Res. J. 2020, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chulalaksananukul, S.; Sinbuathong, N.; Chulalaksananukul, W. Bioconversation of pineapple solid waste under anaerobic condition through biogas production. KKU Res. J. 2012, 17, 734–742. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah, A.F.A.; Hamzah, M.H.; Mazlan, N.I.; Che Man, H.; Jamali, N.S.; Siajam, S.I.; Show, P.L. Optimization of subcritical water pretreatment for biogas enhancement on codigestion of pineapple waste and cow dung using the response surface methodology. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 98–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dahunsi, S.O.; Ogunwole, J.O.; Owoseni, A.A.; Olutona, G.O.; Nejo, Y.T.; Atobatele, O.E. Valorization of pineapple peel and poultry manure for clean energy generation. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e228. [Google Scholar]
- Avena, L.G.; Almendrala, M.; Marron, E.J.; Obille, J.A. Biogas production from the co- and tridigestion of pineapple wastes with food wastes and pig manure. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 521, 01004. [Google Scholar]
- Lamolinara, B.; Perez-Martinez, A.; Guardado-Yordi, E.; Fiallos, C.G.; Dieguez-Santana, K.; Ruiz-Mercado, G.J. Anaerobic digestate management, environmental impacts and techno-economic challenges. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jasinska, A.; Prasad, R.; Lisiecka, J.; Roszak, M.; Stoknes, K.; Mleczek, M.; Niedzielski, P. Combined dairy manure-food waste digestate as a medium for pleurotus djamor—Mineral composition in substrate and bioaccumulation of elements in fruiting bodies. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuffi, V.; Puliga, F.; Zambonelli, A.; Trincone, L.; Sanchez-Cortes, S.; Francioso, O. Sustainable management of anaerobic digestate: From biogas plant to full-scale cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus. Agronomy 2023, 13, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Tsai, M.L.; Dong, C.D.; Yadav, A.; Nargotra, P.; Sun, P.; Sharma, V. An innovative recyclable deep eutectic solvent-ultrasound pretreatment of pineapple leaf waste biomass for enhanced bioethanol production. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.D.L.; Sossa, J.P.R.; Roman, M.B. Techno-economic analysis of biogas production from pineapple leaves juice and chicken manure in anaerobic codigestion. Ing. Rev. 2024, 34, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.; Vo, T.; Chen, T. A novel of biohythane gaseous fuel production from pineapple peel waste juice in two-stage of continuously stirred anaerobic bioreactors. Fuel 2020, 279, 118526. [Google Scholar]
- Cavinato, C.; Giuliano, A.; Bolzonella, D.; Pavan, P.; Cecchi, F. Biohythane production from food waste by dark fermentation coupled with anaerobic digestion process: A long-term pilot scale experience. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 27, 11549–11555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Chu, C.; Ou, C. Pretreatment study on two-stage biohydrogen and biomethane productions in a continuous codigestion process from a mixture of swine manure and pineapple waste. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 11325–11336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopli, P.N.S.M.; Hassim, H.S.; Asli, U.A.; Wahab, F.A. Biohythane production from pineapple peel using Metharnosarcina maze enhanced with palm oil mill effluent (POME) sludge in single-stage anaerobic digestion. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2023, 33, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechery, J.; Kumar, C.S.P.; Ambily, V.; Varghese, A.; Sylas, V.P. Dark fermentation of pretreated hydrolysates of pineapple fruit waste for the production of biohydrogen using bacteria isolated from wastewater sources. Environ. Technol. 2023, 45, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reungsang, A.; Sreela-or, C. Biohydrogen production from pineapple waste extract by anaerobic mixed cultures. Energies 2013, 6, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyari, K.; Putri, A.M.; Oktaviani, E.D.; Hidayat, M.A.; Norajsha, J.D. Biohydrogen production from pineapple waste: Effect of substrate concentration and acid pretreatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 358, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onu, P.; Mbohwa, C. (Eds.) New approach and prospects of agrowaste resources conversion for energy systems performance and development. In Agricultural Waste Diversity and Sustainability Issues; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 97–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.I.; Rashid, R.; Hashim, Z.; Meng, C.C.; Lun, C.K.; Jumaatuden, D.M.H.; Yasin, N.A.; Jati, A.; Hassim, M.H. Economic study on biohydrogen production from liquid pineapple waste. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2023, 25, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, L.S.; Maupoey, P.F. An integrated approach for pineapple waste valorization. Bioethanol production and bromelain extraction from pineapple residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Salafia, F.; Ferracane, A.; Tropea, A. Pineapple waste cell wall sugar fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae for second generation bioethanol production. Fermentation 2022, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.K.; Anurag, R.K.; Arya, A.; Kumbhar, B.K.; Tewari, L. Optimization of saccharification of sweet sorghum bagasse using response surface methodology. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, A.; Wilson, D.; La Torre, L.G.; Lo Curto, R.B.; Saugman, B.; Troy-Davies, P.; Dugo, G.; Waldron, K.W. Bioethanol production from pineapple wastes. J. Food Res. 2014, 3, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Antonio, R.M.D.R.; dela Cruz, A.A.C.; Quinto, A.S., Jr.; Cordero, P.R.; Dimaano, M.N.R. Bioethanol production from pineapple (Ananas comosus) peelings using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as fermenting yeast with focus on fermentation pH. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Choonut, A.; Saejong, M.; Sangkharak, K. The production of ethanol and hydrogen from pineapple peel by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Enterobacter aerogenes. Energy Procedia 2014, 52, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, R.; Chen, C.W.; Patel, A.K.; Saini, J.K.; Dong, C.D.; Singhania, R.R. Valorization of pineapple leaves waste for the production of bioethanol. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mund, N.K.; Dash, D.; Mishra, P.; Nayak, N.R. Cellulose solvent–based pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of pineapple leaf waste biomass for efficient release of glucose towards biofuel production. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 12, 4117–4126. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.L.T.; Gheewala, S.H.; Garivait, S. Full chain energy analysis of fuel ethanol from cassava in Thailand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maiti, S.; Gallastegui, G.; Sarma, S.J.; Brar, S.K.; Bihan, Y.L.; Drogui, P.; Buelna, G.; Verma, M. A re-look at the biochemical strategies to enhance butanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 94, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabila, D.S.; Chan, R.; Syamsuri, R.R.P.; Nurlilasari, P.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ozturk, A.B.; Rossiana, N.; Doni, F. Biobutanol production from underutilized substrates using Clostridium: Unlocking untapped potential for sustainable energy development. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2024, 7, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, S.; Mazhar, S.; Abidi, S.H.; Syed, Q.; Abbas, N.; Nadeem, A.A.; Maryam, M.; Essa, R.; Ashfaq, S. Biobutanol production from sustainable biomass process of anaerobic ABE fermentation for industrial applications. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 672. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Cong, W.; Zhang, J. Biobutanol production from acetone–butanol–ethanol fermentation: Developments and prospects. Fermentation 2023, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaji, J.O.; Makut, M.D.; Ekeleme, I.K.; Owuna, J.; Abimiku, R.H. Biobutanol production from pineapple peels waste using single and coculture of Clostridium acetobutylicum and Clostridium beijerinckii isolated from Keffi Metropolis. S. Asian Res. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 4, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Alagumalai, A.; Devarajan, B.; Song, H. Unlocking the potential of catalysts in thermochemical energy conversion processes. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 5632. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Nam, H.; Seo, M.W.; Lee, S.H.; Tokmurzin, D.; Wang, S.; Park, Y. Recent progress in the catalytic thermochemical conversion process of biomass for biofuels. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 447, 137501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeramalai, S.; Ramlee, N.N.; Mahdi, H.I.; Manas, N.H.A.; Ramli, A.N.M.; Md Illias, R.; Azelee, N.I.W. Development of organic porous material from pineapple waste as a support for enzyme and dye adsorption. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 181, 114823. [Google Scholar]
- Dermawan, D.; Tsai, D.; Yudoyono, G.S.; You, S.; Hsieh, Y. Taguchi method optimization of syngas production via pineapple waste pyrolysis using atmospheric pressure microwave plasma. Renew. Energy 2024, 231, 120962. [Google Scholar]
- Hikal, W.; Mahmoud, A.; Said-Al Ahl, H.; Bratovcic, A.; Tkachenko, K.; Kačániová, M.; Rodriguez, R. Pineapple (Ananas comosus L. Merr.), waste streams, characterization and valorization: An overview. Open J. Ecol. 2021, 11, 610–634. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, R.; Uddin, M.B.; Jubayer, M.F. Optimization of pectin isolation method from pineapple (Ananas Comosus L.) waste. Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Rodsamran, P.; Sothornvit, R. Preparation and characterization of pectin fraction from pineapple peel as a natural plasticizer and material for biopolymer film. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 118, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Shivamathi, C.S.; Gunaseelan, S.; Soosai, M.R.; Vignesh, N.S.; Varalakshmi, P.; Kumar, R.S.; Karthikumar, S.; Kumar, R.V.; Baskar, R.; Rigby, S.P.; et al. Process optimization and characterization of pectin derived from underexploited pineapple peel biowaste as a value-added product. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107141. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, A.A.; Cobham, E.I.; Zeighami, M.; Ong, S.P. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Pineapple Fruit. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Processing and Drying of Foods, Vegetables and Fruits (ISPDFVF 2012), University of Nottingham, Malaysia Campus, 18–19 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, A.M.P.; Toro, C.R.; Londoño, L.; Boliver, G.; Ascacio, J.A.; Anguilar, C.N. Bioprocessing of pineapple waste biomass for sustainable production of bioactive compounds with high antioxidant activity. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 586–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhumeena, S.; Preetha, R.; Prasad, S. Effective utilization of pineapple waste. J. Phys. Confer. Ser. 2021, 1979, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampar, G.G.; Zampar, I.C.; de Souza, S.B.D.S.; da Silva, C.; Barros, B.C.B. Effect of solvent mixtures on the ultrasound-assisted extraction of compounds from pineapple by-product. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shen, P.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Liang, R.; Yan, N.; Chen, J. Major polyphenolics in pineapple peels and their antioxidant interactions. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, D.C.A.; de, S. Figueiredo, K.C. Bromelain separation and purification processes from pineapple extract. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.A.; Coscueta, E.R.; Valetti, N.W.; Pastrana-Castro, L.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Picó, G.A.; Pintado, M.M. Optimization of bromelain isolation from pineapple byproducts by polysaccharide complex formation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharge, V.; Ghutake, S.; Pawar, H. Valorization of pineapple waste for extraction and purification of bromelain enzyme. ACS Sustain. Resour. Manag. 2024, 1, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardawati, E.; Putri, S.H.; Fitriana, H.N.; Nurliasari, D.; Rahmah, D.M.; Rosanti; Maulana, I.; Dewantoro, A.I.; Hermiati, E.; Balia, R.L. Application of biorefinery concept to the production of bromelain, ethanol, and xylitol from pineapple plant waste. Fermentation 2023, 9, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.H.; Jenol, M.A.; Phang, L.Y.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Prasongsuk, S.; Bankeeree, W.; Punnapayak, H.; Lotrakul, P.; Abd-Aziz, S. Starch extracted from pineapple (Ananas comosus) plant stem as a source for amino acids production. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, R.A.; Jayasree, J.T.; Abdullah, S. A comprehensive review of pineapple processing and its by-product valorization in India. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, P.; Nickhil, C.; Pandiselvam, R.; Deka, S.C. Pineapple waste-based-biorefinery for sustainable generation of value-added products. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023, 14, 24927–24948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiviya, P.; Gamage, A.; Kapilan, R.; Merah, O.; Madhujith, T. Production of single-cell protein from fruit peel wastes using palmyrah toddy yeast. Fermentation 2022, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukoumaki, D.I.; Tsouko, E.; Papanikolaou, S.; Ioannou, Z.; Diamantopoulou, P.; Sarris, D. Recent advances in the production of single cell protein from renewable resources and applications. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2024, 7, 100195. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, P.N.; Nwokoro, O. Production of single cell protein from hydrolyzed pineapple (Ananas comosus) peel using fungi. Bio-Research 2017, 15, 961–971. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanasekarani, D.; Lawanya, S.; Saha, S.; Thajuddin, N.; Panneerselvam, A. Production of single-cell protein from pineapple waste using yeast. Innov. Rom. Food Biotechnol. 2011, 8, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Nigam, J. Single-cell protein from pineapple cannery effluent. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 14, 693–696. [Google Scholar]
- Mensah, J.K.M.; Twumasi, P. Use of pineapple waste for single-cell protein (SCP) production and the effect of substrate concentration on the yield. J. Food Process. 2017, 40, e12478. [Google Scholar]
- Sukri, S.A.M.; Andu, Y.; Sarijan, S.; Khalid, H.M.; Kari, Z.A.; Harun, H.C.; Rusli, N.D.; Mat, K.; Khalif, R.I.A.R.; Wei, L.S.; et al. Pineapple waste in animal feed: A review of nutritional potential, impact and prospects. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023, 23, 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Assumi, S.; Jha, S.; Kaur, C. Valorization of pineapple waste for development of animal feed block. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 3787–3795. [Google Scholar]
- Buliah, N.; Jamek, S.; Ajit, T.D.A.; Abu, R. Production of Dairy Cow Pellets from Pineapple Leaf Waste. In Proceedings of the AIP Proceedings of the International Conference on Materials, Manufacturing and Machining, Tamil Nadu, India, 8–9 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zainuddina, M.F.; Rosnaha, S.; Mohd Noriznana, M.; Dahlan, I. Effect of moisture content on physical properties of animal feed pellets from pineapple plant waste. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2014, 2, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, G.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Zou, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y. The effects of fermented pineapple residue on growth performance, meat quality, and rumen microbiota of fattening Simmental bull. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 942208. [Google Scholar]
- Chacón, S.A.R.G.; Araújo, T.L.A.C.; Pinedo, L.A.; Lima Junior, D.M.; Assis, L.C.S.L.C.; Pereira, M.W.F.; Lima, P.O. Effect of pineapple peel addition on sorghum ensilage. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 53, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zziwa, A.; Jjagwe, J.; Kizito, S.; Kabenge, I.; Komakech, A.J.; Kayondo, H. Nutrient recovery from pineapple waste through controlled batch and continuous vermicomposting systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainoo, N.O.K.; Barrington, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Sampedro, L. Pilot-scale vermicomposting of pineapple wastes with earthworms native to Accra, Ghana. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5872–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miito, G.; Komakech, A.; Zziwa, A.; Kiggundu, N.; Kambugu, R. Assessment of the suitability of pineapple waste as feedstock for vermicomposting. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2021, 23, 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Roda, R.; De Faveri, D.M.; Giacosa, S.; Dordoni, R.; Lambri, M. Effect of pretreatments on the saccharification of pineapple waste as a potential source for vinegar production. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, C.; Seguí, L.; Laguarda-Miró, N.; Fito, P. Microwaves as a pretreatment for enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis of pineapple industrial waste for bioethanol production. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, N.; Md Illias, R.; Manas, N.H.A.; Ramli, A.N.M.; Azelee, N.I.W. Efficient delignification of pineapple waste by low pressure steam heating pretreatment. Adv. Eng. Res. 2020, 200, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tanpichai, S.; Boonmahitthisud, A.; Witayakran, S. Use of steam explosion as a green alternative method to prepare pulp from pineapple leaves. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2019, 29, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Sharma, V.; Tsai, M.; Yadav, A.; Nargotra, P.; Sun, P.; Chen, C.; Dong, C. Improved xylooligosaccharides production from xylan extracted using ultrasound-assisted alcoholic deep eutectic solvent pretreatment of pineapple leaf waste. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 224, 120250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, A.N.A.; Ping, H.X.; Nordin, N.; Azelee, N.I.W. Screening of low-pressure steam heating pretreatment parameters for enhanced delignification of pineapple wastes. Bioprocess. Biomass Technol. 2022, 1, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, R.; Singhania, R.R.; Patel, A.M.; Chen, C.; Piechota, G.; Dong, C. Sustainable production of cellulose and hemicellulose-derived oligosaccharides from pineapple leaves: Impact of hydrothermal pretreatment and controlled enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 398, 130526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahunsi, S.O. Liquefaction of pineapple peel: Pretreatment and process optimization. Energy 2019, 185, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, L.B.T.; Carmob, S.K.S.; da S. Netob, J.M.; de Meloa, S.d.S.; da Silvac, F.L.H. Pretreatment strategies for optimizing the lignocellulosic fractionation of pineapple peel residual biomass for energy purposes. Quim. Nova 2025, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ariffin, K.K.; Masngut, N.; Seman, M.N.A.; Saufi, S.M.; Jamek, S.; Sueb, M.S.M. Dilute acid hydrolysis pretreatment for sugar and organic acid production from pineapple residues. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 991, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgeni, S.T.; Mtashobya, L.A.; Emmanuel, J.K. Bioethanol production from pineapple fruit waste juice using bakery yeast. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Chintagunta, A.D.; Ray, S. Laccase mediated delignification of pineapple leaf waste: An ecofriendly sustainable attempt towards valorization. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosdee, N.A.S.M.; Masngut, N.; Shaarani, S.M.; Jamek, S.; Sueb, M.S.M. Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass from pineapple leaves by using endo-1,4-xylanase: Effect of pH, temperature, enzyme loading and reaction time. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 736, 022095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Component | Cellulose (%) | Hemicelluloses (%) | Lignin (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peel | 19.8 | 11.7 | - | [3] |
| 11.2 | 7.0 | 11.52 | [15] | |
| 10.9 | 22.8 | 7.1 | [24] | |
| 22.9 | 36.8 | 5.12 | [25] | |
| 14.0 | 20.2 | 1.5 | [26] | |
| 35–50 | 20–35 | 5–30 | [27] | |
| 35 | 19 | 16 | [28] | |
| Mixed pulp and peel | 2.43 | 1.69 | 0.42 | [29] |
| Pulp | 14.3 | 22.1 | 2.3 | [3,26] |
| Core | 24.53 | 28.53 | 5.78 | [30] |
| 17.2 | 29.5 | 1.82 | [25] | |
| Cores and peelings | 11.2–19.8 | 7.0–11.7 | - | [31] |
| Shell | 40.55 | 28.69 | 10.01 | [30] |
| Crown | 41.15 | 21.02 | 13.05 | [32] |
| 43.53 | 21.88 | 13.88 | [30] | |
| 29.6 | 23.2 | 4.5 | [26] | |
| Whole | 19.4 | 22.4 | 4.7 | [26] |
| Component | Moisture (%) | Protein (%) | Fiber (%) | Fat (%) | Ash (%) | Carbohydrate (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peel | 82–88 | 5–9 | 1–6 | 2–3 | 4–6 | 50–80 | [10] |
| 6.22 | 5.14 | 17.4 | 1.14 | 2.42 | 85.07 | [4] | |
| Pomace | 7.79 | 6.34 | 19.3 | 1.09 | 2.04 | 82.75 | [4] |
| Stalk | 8.5 | 4.25 | 19.73 | - | 8.54 | - | [33] |
| Pulp | - | 1.58 | 24.14 | 3.19 | 3.0 | - | [30] |
| Crown | - | 0.7 | 62.5 | 3.5 | 7.37 | [30] | |
| Core | 84.9 | 3.6 | 9.14 | 2.35 | 1.7 | 83.03 | [34] |
| - | 0.85 | 47.6 | 3.17 | 1.3 | - | [30] | |
| Cores and peels | 71.1–92.2 | 3.1–5.0 | 5.0–42.0 | 2.4–4.8 | - | 35.0–83.0 | [31] |
| Shell | - | 0.75 | 65 | 2.0 | 1.5 | - | [30] |
| Fraction | Carbon (%) | Hydrogen (%) | Oxygen (%) | Nitrogen (%) | Sulfur (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peel | 49.3 | 5.7 | - | 0.6 | - | [35] |
| Crown leaf | 44.1 | 5.8 | 49.3 | 0.8 | - | [7] |
| Crown and peel | 44.95 | 5.5 | 47.65 | 1.68 | 0.22 | [36] |
| Peel | 47.39 | 6.13 | 40.64 | 1.08 | - | [7] |
| Root | 38.7 | 5.4 | 75.4 | 1.0 | 0.23 | [7] |
| Stem | 37.6 | 6.69 | 52.7 | 1.89 | 0.97 | [37] |
| Leaf | 40.5 | 6.91 | 50.3 | 1.78 | 0.36 | [37] |
| Crown leaf | 44.05 | 5.81 | 49.27 | 0.87 | - | [7] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamusoko, R.; Mukumba, P. Pineapple Waste Biorefinery: An Integrated System for Production of Biogas and Marketable Products in South Africa. Biomass 2025, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020017
Kamusoko R, Mukumba P. Pineapple Waste Biorefinery: An Integrated System for Production of Biogas and Marketable Products in South Africa. Biomass. 2025; 5(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamusoko, Reckson, and Patrick Mukumba. 2025. "Pineapple Waste Biorefinery: An Integrated System for Production of Biogas and Marketable Products in South Africa" Biomass 5, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020017
APA StyleKamusoko, R., & Mukumba, P. (2025). Pineapple Waste Biorefinery: An Integrated System for Production of Biogas and Marketable Products in South Africa. Biomass, 5(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020017