Environmentally Friendly and Cost-Effective Approaches to Reduce Toxin Content in Toxic Cyanobacterial Biomasses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Extraction of Cyanotoxins
2.4. Cyanotoxins Quantification by LC-ESI-MS
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
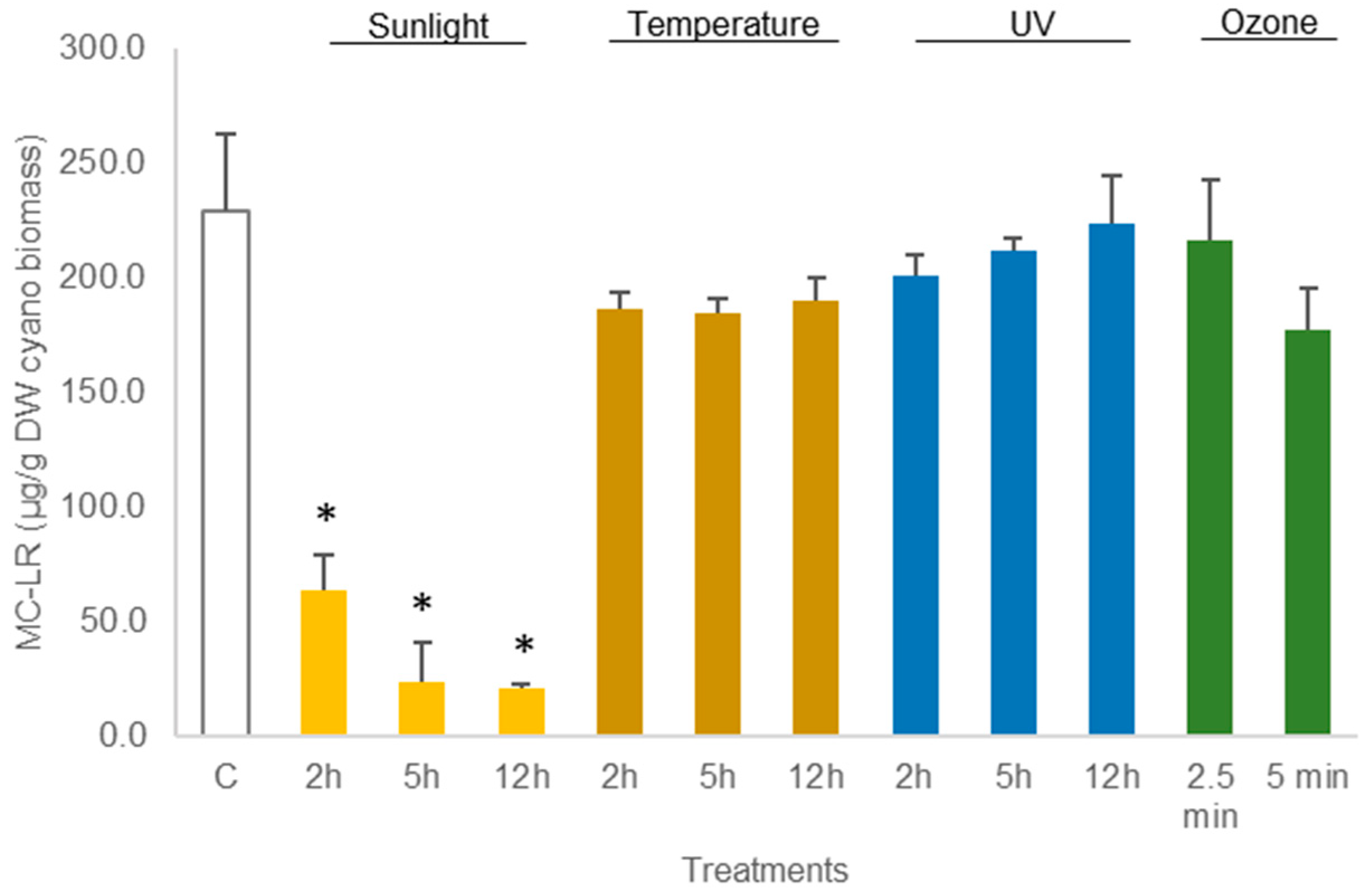
3.1. Experiments with M. aeruginosa Biomass
3.2. Experiments with C. ovalisporum Biomass
4. Discussion
4.1. Microcystin-LR Decomposition
4.2. CYN Decomposition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, B.; Fletcher, I.R.; Brocks, J.J.; Kilburn, M.R. LETTERS Reassessing the first appearance of eukaryotes and cyanobacteria. Nature 2008, 455, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, B.A. Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Seitzinger, S.; Heil, C.A.; Burkholder, J.M.; Parrow, M.W.; Codispoti, L.A.; Kelly, V. The role of eutrophication in the global proliferation of harmful algal blooms. Oceanography 2005, 18, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, L.; Mihali, T.; Moffitt, M.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B. On the Chemistry, Toxicology and Genetics of the Cyanobacterial Toxins, Microcystin, Nodularin, Saxitoxin and Cylindrospermopsin. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1650–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Molecular Mechanisms of Microcystin Toxicity in Animal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, Y.; Koiri, R.K.; Bhide, M. An overview of the toxic effect of potential human carcinogen Microcystin-LR on testis. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Díez-Quijada, L.; Puerto, M.; Gutiérrez-Praena, D.; Llana-Ruiz-Cabello, M.; Jos, A.; Cameán, A.M. Microcystin-RR: Occurrence, content in water and food and toxicological studies. A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, E.; Testai, E. Human Health Risk Assessment Related to Cyanotoxins Exposure. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.I.; Tsuji, K.; Watanabe, M.F.; Kondo, F. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria—III. Effect of pH and temperature. Phycologia 1996, 35, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, I.M.; Maraver, J.; Aguete, E.C.; Leao, M.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Cameán, A.M. Decomposition of Microcystin-LR, Microcystin-RR, and Microcystin-YR in Water Samples Submitted to in Vitro Dissolution Tests. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5933–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, I.; Moore, R.E.; Runnegar, M.T.C. Cylindrospermopsin: A Potent Hepatotoxin from the Blue-Green Alga Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 7941–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnear, S. Cylindrospermopsin: A Decade of Progress on Bioaccumulation Research. Mar. Drugs 1999, 8, 542–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, E.; Fewer, D.P.; Neilan, B.A. Cyanobacterial toxins: Biosynthetic routes and evolutionary roots. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Jiang, X. Cyanobacterial Toxins in Freshwater and Food: Important Sources of Exposure to Humans. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 281–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in water supplies: Cylindrospermopsins. Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 21, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kate, B.N.; Banecjee, U.C. Bioactive Compounds from Cyanobacteria and Microalgae: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.U.; Hussain, N.; Shahbaz, A.; Hameed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Bilal, M. Bioprospecting microalgae and cyanobacteria for biopharmaceutical applications. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022, 62, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsini, S.; Rosi, M.C.; Ravegnini, E.; Schiff, S.; Gonnelli, C.; Papini, A.; Adessi, A.; Urciuoli, S.; Ristori, S. Nanoformulations with exopolysaccharides from cyanobacteria: Enhancing the efficacy of bioactive molecules in the Mediterranean fruit fly control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 83760–83770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, J.; Pereira, S.; Ribeiro, T.; Plowman, J.E.; Thomas, A.; Clerens, S.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Almeida, J.R. A Multi-Bioassay Integrated Approach to Assess the Antifouling Potential of the Cyanobacterial Metabolites Portoamides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Redouane, E.M.; Freitas, M.; Amaral, S.; Azevedo, T.; Loss, L.; Máthé, C.; Mohamed, Z.A.; Oudra, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; et al. Impacts of Microcystins on Morphological and Physiological Parameters of Agricultural Plants: A Review. Plants 2021, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, R.; Kaur, T.; Kour, D.; Yadav, A.; Yadav, A.N.; Suman, A.; Ahluwalia, A.S.; Saxena, A.K. Minerals solubilizing and mobilizing microbiomes: A sustainable approach for managing minerals’ deficiency in agricultural soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhumalai, G.; Arun, M.; Manavalan, A.; Rajkumar, R.; Heese, K. A Holistic Approach to Circular Bioeconomy Through the Sustainable Utilization of Microalgal Biomass for Biofuel and Other Value-Added Products. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galetović, A.; Peña, G.; Fernández, N.; Urrutia, M.; Flores, N.; Gómez-Silva, B.; Di Ruggiero, J.; Shene, C.; Bustamante, M. Cellulose Synthase in Atacama Cyanobacteria and Bioethanol Production from Their Exopolysaccharides. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, L.; Miron, A.; Klímová, B.; Wan, D.; Kuča, K. The antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory activities of Spirulina: An overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1817–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nova, M.; Citterio, S.; Martegani, E.; Colombo, S. Unraveling the Anti-Aging Properties of Phycocyanin from the Cyanobacterium Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, V.; Morais, J.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Pinheiro, Â.; Martins, J.; Regueiras, A.; Pereira, A.L.; Lopes, V.R.; Frazão, B.; Gomes, D.; et al. Cyanobacterial diversity held in microbial biological resource centers as a biotechnological asset: The case study of the newly established LEGE culture collection. Arab Emir. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.; Diez-Quijada, L.; Turkina, M.V.; Morais, J.; Felpeto, A.B.; Azevedo, J.; Jos, A.; Camean, A.M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, J.C.; et al. Physiological and Metabolic Responses of Marine Mussels Exposed to Toxic Cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Chrysosporum ovalisporum. Toxins 2020, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Cyanobacterial Toxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management, 2nd ed.; Chorus, I., Welker, M., Eds.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 15–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Watanuki, T.; Kondo, F.; Watanabe, M.F.; Suzuki, S.; Nakazawa, H.; Suzuki, M.; Uchida, H.; Harada, K.I. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria—II. Effect of UV light on decomposition and isomerization. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Wu, C.; Xie, R.R.; Zheng, Y. Ultraviolet photosensitized transformation mechanism of microcystin-LR by natural organic matter in raw water. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumavalavan, M.; Hu, Y.L.; Lee, J.F. Effects of humic acid and suspended soils on adsorption and photo-degradation of microcystin-LR onto samples from Taiwan reservoirs and rivers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, L.X.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.M.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Decomposition of Microcystis aeruginosa and microcystin-LR by TiO 2 oxidation using artificial UV light or natural sunlight. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2012, 15, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, Z.; Kang, J.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, L.; Shen, J.M. Oxidation of microcystin-LR in water by ozone combined with UV radiation: The removal and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, Y. Photochemical Reactions of Microcystin-LR Following Irradiation with UV Light. Open J. Phys. Chem. 2016, 6, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawwa, A.R.; Smith, D.W. Kinetics of Microcystin-LR Oxidation by Ozone. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2001, 23, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merel, S.; LeBot, B.; Clément, M.; Seux, R.; Thomas, O. Ms identification of microcystin-LR chlorination by-products. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.I.; Tsuji, K. Persistence and Decomposition of Hepatotoxic Microcystins Produced by Cyanobacteria in Natural Environment. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1998, 17, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiswell, R.K.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.; Smith, M.J.; Norris, R.L.; Seawright, A.A.; Moore, M.R. Stability of cylindrospermopsin, the toxin from the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Effect of pH, temperature, and sunlight on decomposition. Env. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörmer, L.; Huerta-Fontela, M.; Cirés, S.; Carrasco, D.; Quesada, A. Natural photodegradation of the cyanobacterial toxins microcystin and cylindrospermopsin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3002–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, G.; De La Cruz, A.A.; O’Shea, K.E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation mechanism of cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin by hydroxyl radicals in homogeneous UV/H2O2 process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4495–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, A.I.; Guzmán-Guillén, R.; Valderrama-Fernández, R.; Jos, Á.; Cameán, A.M. Influence of Cooking (Microwaving and Broiling) on Cylindrospermopsin Concentration in Muscle of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Characterization of Decomposition Products. Toxins 2017, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senogles, P.; Shaw, G.; Smith, M.; Norris, R.; Chiswell, R.; Mueller, J.; Sadler, R.; Eaglesham, G. Degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin, from Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii, by chlorination. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Huang, W.J.; Ji, B.H. Degradation of cyanotoxin cylindrospermopsin by TiO2-assisted ozonation in water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Jia, A.; Merel, S.; Snyder, S.A.; O’Shea, K.E.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Song, W. Ozonation of Cylindrospermopsin (Cyanotoxin): Degradation Mechanisms and Cytotoxicity Assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, D.; Munoz, M.; Garcia, J.; Cirés, S.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Quesada, A.; Casas, J.A. Photo-Fenton oxidation of cylindrospermopsin at neutral pH with LEDs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 21598–21607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotiou, T.; Triantis, T.; Kaloudis, T.; Hiskia, A. Photocatalytic degradation of cylindrospermopsin under UV-A, solar and visible light using TiO2. Mineralization and intermediate products. Chemosphere 2015, 119, S89–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Days of Sampling | Temperature (°C) Min–Max | Average Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) Min–Max | Average Relative Humidity (%) | Max. Solar Radiation | Average Solar Radiation (KJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15-07-2021 | 24.1–32.7 | 29.7 | 26–53 | 35 | 34,743 | 21,815 |
| 16-07-2021 | 22.6–34.7 | 26.6 | 21–60 | 39 | 33,394 | 18,276 |
| 11-10-2021 | 18.8–27.5 | 23.6 | 34–50 | 42 | 23,697 | 15,138 |
| 12-10-2021 | 16.8–24.8 | 18.9 | 40–46 | 43 | 22,717 | 11,916 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loss, L.; Azevedo, J.; Azevedo, T.; Freitas, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Campos, A. Environmentally Friendly and Cost-Effective Approaches to Reduce Toxin Content in Toxic Cyanobacterial Biomasses. Biomass 2024, 4, 518-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4020027
Loss L, Azevedo J, Azevedo T, Freitas M, Vasconcelos V, Campos A. Environmentally Friendly and Cost-Effective Approaches to Reduce Toxin Content in Toxic Cyanobacterial Biomasses. Biomass. 2024; 4(2):518-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoss, Leticia, Joana Azevedo, Tomé Azevedo, Marisa Freitas, Vitor Vasconcelos, and Alexandre Campos. 2024. "Environmentally Friendly and Cost-Effective Approaches to Reduce Toxin Content in Toxic Cyanobacterial Biomasses" Biomass 4, no. 2: 518-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4020027
APA StyleLoss, L., Azevedo, J., Azevedo, T., Freitas, M., Vasconcelos, V., & Campos, A. (2024). Environmentally Friendly and Cost-Effective Approaches to Reduce Toxin Content in Toxic Cyanobacterial Biomasses. Biomass, 4(2), 518-529. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4020027








