A Survey on Software Defined Network-Enabled Edge Cloud Networks: Challenges and Future Research Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Edge Cloud Deployment Areas and Use Cases
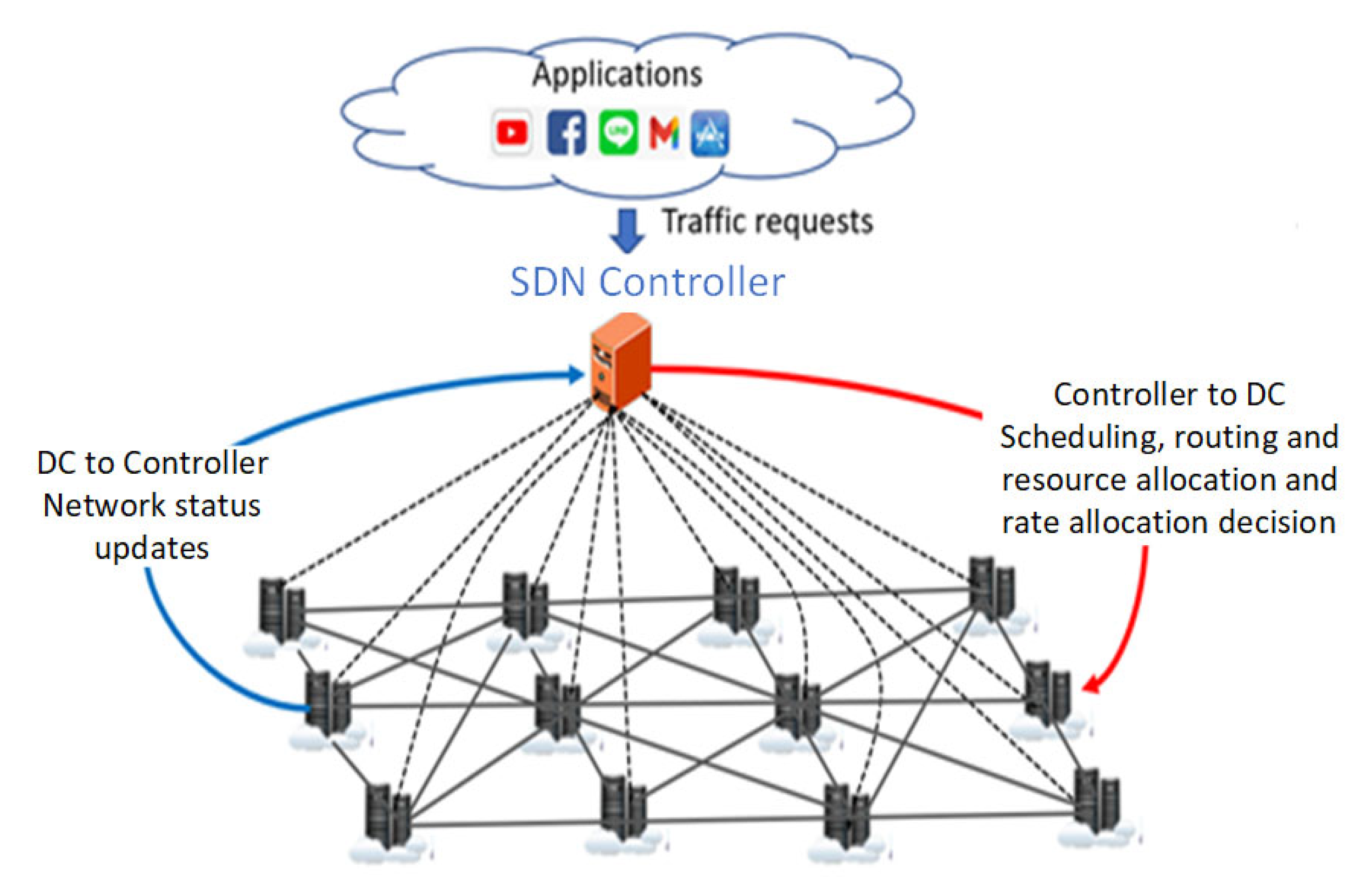
3. SDN-Enabled Edge Cloud Architecture
3.1. Mobile Edge Cloud
3.2. Fixed Edge Cloud
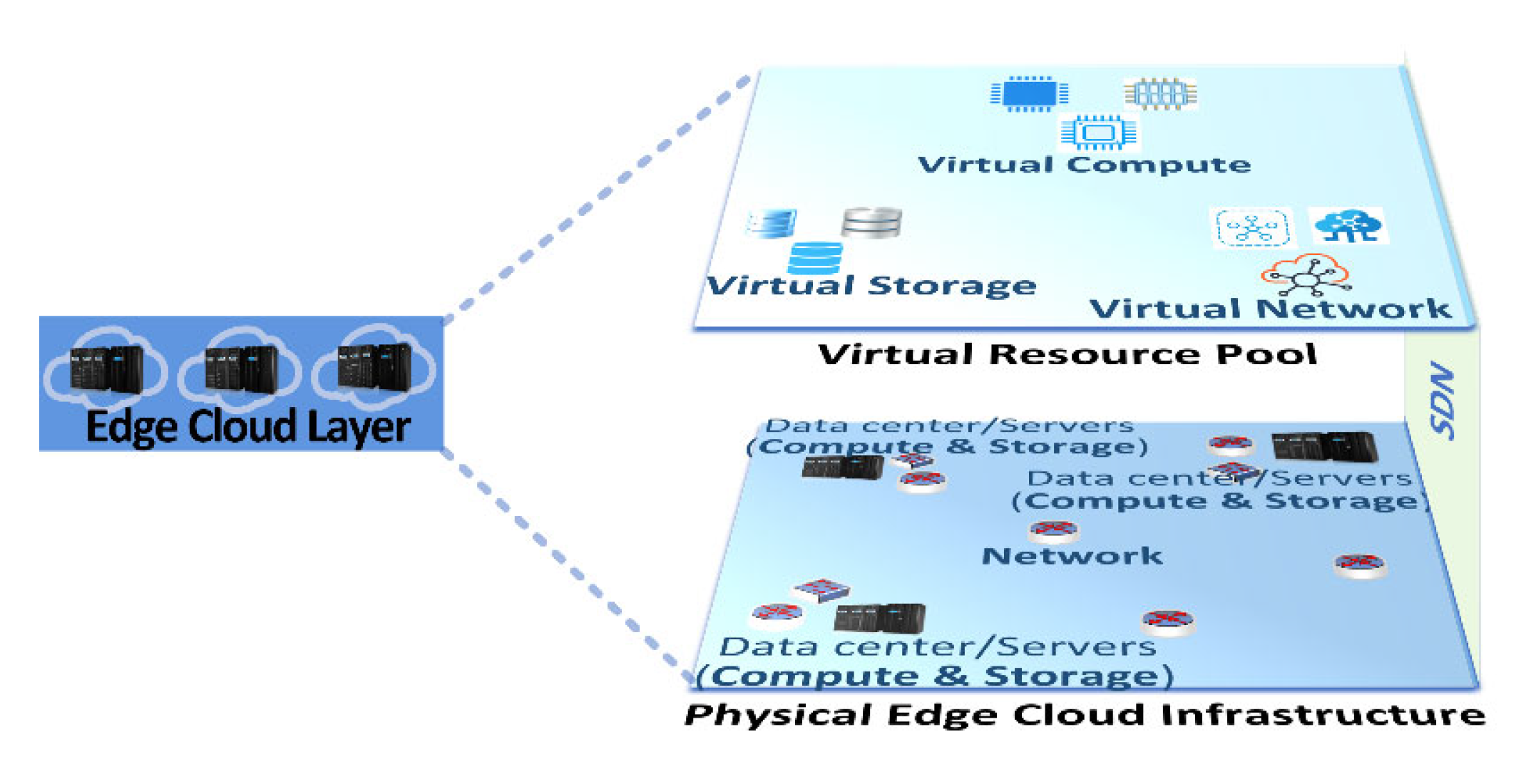
4. Edge Cloud Infrastructure
4.1. Storage
4.2. Computing
4.3. Networking
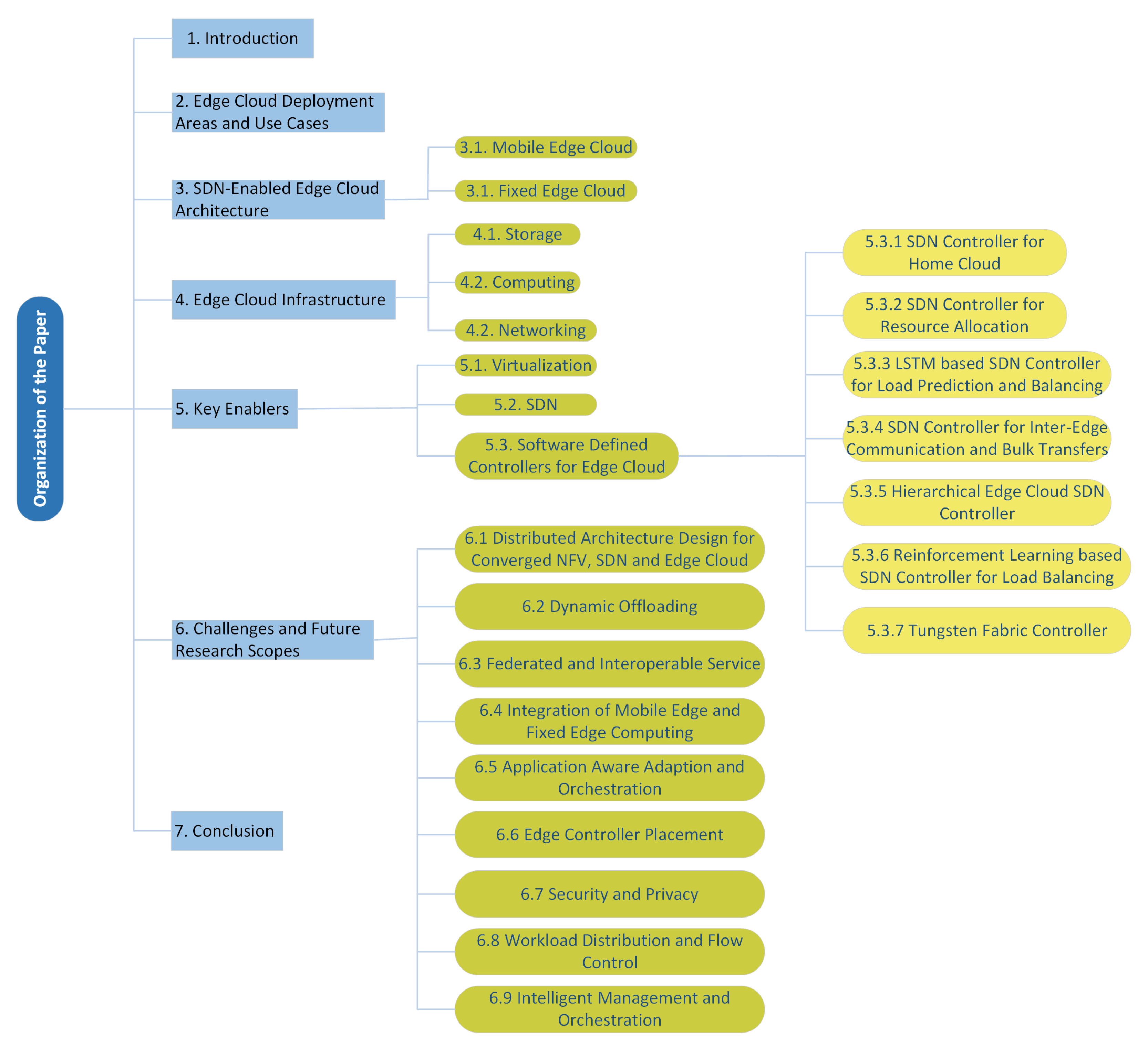
5. Key Enablers
5.1. Virtualization
5.2. Software Defined Networking
5.3. Software-Defined Controllers for Edge Cloud
5.3.1. SDN Controller for HomeCloud
5.3.2. SDN Controller for Resource Allocation
5.3.3. LSTM-Based SDN Controller for Load Prediction and Balancing
5.3.4. SDN Controller for Inter Edge Communication and Bulk Transfers
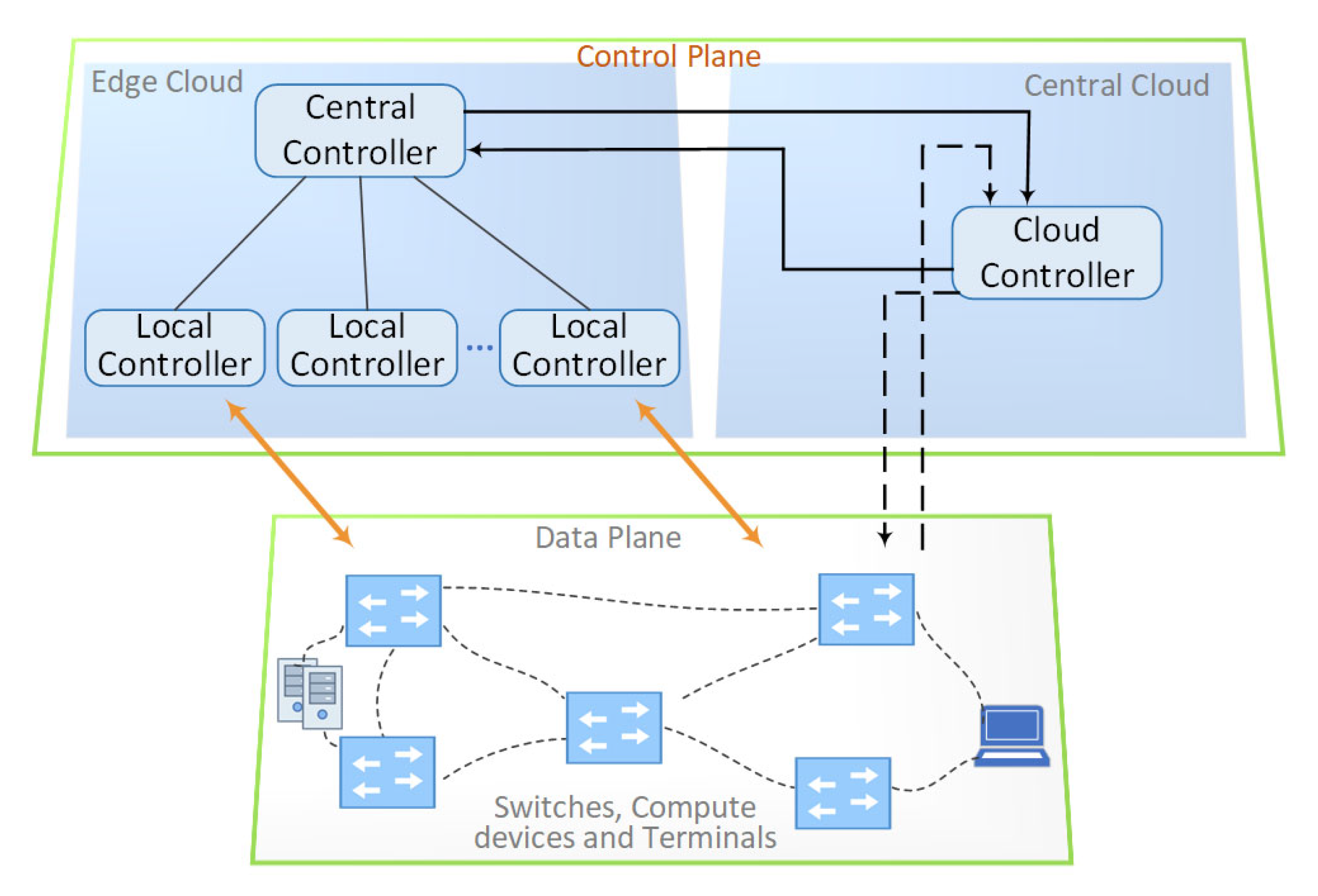
5.3.5. Hierarchical Edge Cloud SDN Controller
5.3.6. Reinforcement-Learning-Based SDN Controller for Load Balancing
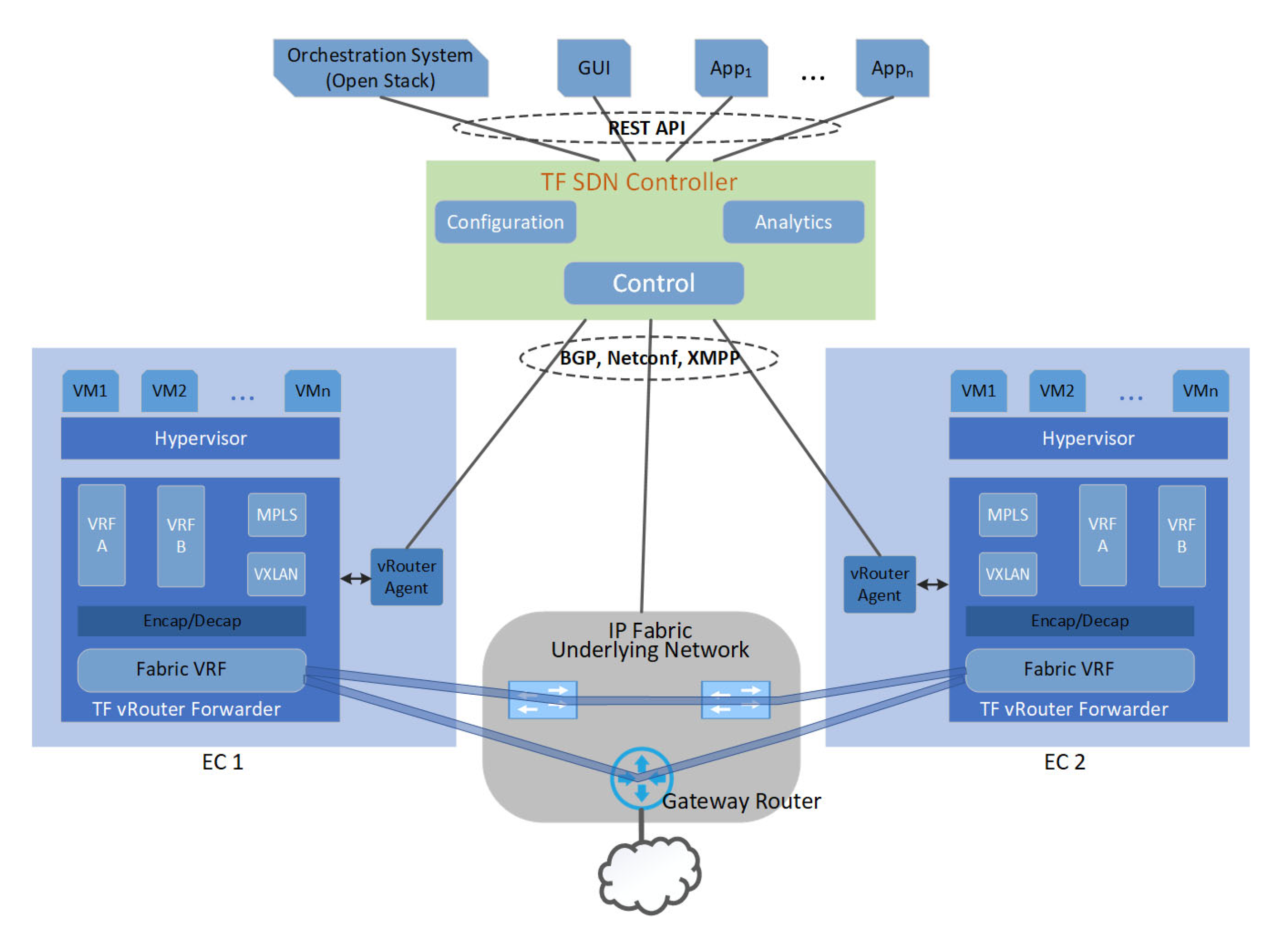
5.3.7. Tungsten Fabric Controller
6. Challenges and Future Research Scopes
6.1. Distributed Architecture Design for Converged NFV, SDNs, and Edge Cloud
6.2. Dynamic Offloading
6.3. Federated and Interoperable Service
6.4. Integration of Mobile Edge and Fixed Edge Computing
6.5. Application Aware Adaption and Orchestration
6.6. Edge Controller Placement
6.7. Security and Privacy
6.8. Workload Distribution and Flow Control
6.9. Intelligent Management and Orchestration
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Description |
| SDN | Software Defined Networking |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| NFV | Network Function Virtualization |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| PDA | Personal Digital Assistant |
| MEC | Mobile Edge Computing |
| MB-PB | Megabyte-Petabyte |
| LTE | Long Term Evolution |
| FEC | Fixed Edge Cloud |
| DC | Datacenter |
| RAN | Radio Access Network |
| VCF | Virtual Compute Function |
| VNF | Virtual Network Function |
| VSF | Virtual Storage Function |
| QOS | Quality of Service |
| VM | Virtual Machine |
| SFC | Service Function Chain |
| MANO | Management and Orchestration |
| IOT | Internet of Things |
| LAN | Local Area Network |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| OLSR | Optimized Link State Routing |
| LSTM | Long-Short-Term Memory |
| FL | Federated Learning |
| SW-WAN | Software Defined Wide Area Network |
| SBI | Southbound Interface |
| NBI | Northbound Interface |
| SLA | Service Level Agreement |
| RNN | Recurrent Neutral Network |
| WAN | Wide Area Network |
| HECSDN | Hierarchical Edge Cloud SDN |
| TF | Tungsten Fabric |
| REST API | Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| BGP | Border Gateway Protocol |
| XMPP | Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol |
| QOE | Quality of Experience |
| IEP | Internet Edge Protection |
| SDX | Software Defined Exchange |
| CFL | Continual Federated Learning |
| IDS | Intrusion Detection System |
| AE-MLP | Autoencoder Multi Layer Perceptron |
| DDOS | Distributed Denial of Service |
| WFL | Weighted Flow Length |
| FML | Federated Machine Learning |
| GCN | Graph Convolution Network |
| APT | Advanced Persistent Threat |
References
- Institute for the Future. The Hyperconnected World. 2020. Available online: https://legacy.iftf.org/fileadmin/user_upload/downloads/ourwork/IFTF_Hyperconnected_World_2020.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- The National Intelligence Council. Global Trends 2040 a More Connected World. March 2021. Available online: https://www.dni.gov/files/ODNI/documents/assessments/GlobalTrends_2040.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Wang, J.; Pan, J.; Esposito, F.; Calyam, P.; Yang, Z.; Mohapatra, P. Edge Cloud Offloading Algorithms: Issues, Methods, and Perspectives. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Internet of Things (IoT): An Overview. 15 October 2015. Available online: https://www.internetsociety.org/resources/doc/2015/iot-overview/ (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Al-Sarawi, S.; Anbar, M.; Abdullah, R.; Al Hawari, A.B. Internet of things market analysis forecasts, 2020–2030. In Proceedings of the Fourth World Conference on Smart Trends in Systems, Security and Sustainability (WorldS4), London, UK, 27–28 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Asim, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, P.Q. A review on computational intelligence techniques in cloud and edge computing. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2020, 4, 742–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Verma, V. Comparative study of cloud computing and edge computing: Three level architecture models and security challenges. Int. J. Distrib. Cloud Comput. 2021, 9, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, S.; Raychaudhuri, D.; Seskar, I.; Bronzino, F. Scalability and Performance Evaluation of Edge Cloud Systems for Latency Constrained Applications; IEEE Xplore: Seattle, WA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; You, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2322–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. A Survey on End-Edge-Cloud Orchestrated Network Computing Paradigms: Transparent Computing, Mobile Edge Computing, Fog Computing, and Cloudlet. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baktir, A.C.; Ozgovde, A.; Ersoy, C. How Can Edge Computing Benefit from Software-Defined Networking: A Survey, Use Cases, and Future Directions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2359–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porambage, P.; Okwuibe, J.; Liyanage, M.; Ylianttila, M.; Taleb, T. Survey on multi-access edge computing for internet of things realization. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2961–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; McElhannon, J. Future Edge Cloud and Edge Computing for Internet of Things Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.N.; Schelén, O.; Monrat, A.A.; Andersson, K. Enabling Industrial Internet of Things by Leveraging Distributed Edge-to-Cloud Computing: Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 127294–127308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Lan, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y. End-edge-cloud collaborative computing for deep learning: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 26, 2647–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkonis, P.; Giannopoulos, A.; Trakadas, P.; Masip-Bruin, X.; D’Andria, F. A survey on IoT-edge-cloud continuum systems: Status, challenges, use cases, and open issues. Future Internet 2023, 15, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, B.J.O.; Suárez, Á.; Pineda, V.G.; Jaimes, R.A.; Benitez, A.O.M.; Bustamante, J.D.G. Analysis of the use of artificial intelligence in software-defined intelligent networks: A survey. Technologies 2024, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilhore, U.K.; Simaiya, S.; Sharma, Y.K.; Rai, A.K.; Padmaja, S.M.; Nabilal, K.V.; Kumar, V.; Alroobaea, R.; Alsufyani, H. Cloud-edge hybrid deep learning framework for scalable IoT resource optimization. J. Cloud Comput. 2025, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noghabi, S.A.; Cox, L.; Agarwal, S.; Ananthanarayanam, G. The Emerging Landscape of Edge Computing. GetMobile Mob. Comput. Commun. 2019, 23, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthanarayanam, G.; Bahl, P.; Bodik, P.; Chintalapudi, K.; Philipose, M.; Ravindranath, L.; Sinha, S. Real-Time Video Analytics: The Killer App for Edge Computing. IEEE Comput. 2017, 50, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.A.; Munna, A.S.; Shaikh, M.S.I.; Kazi, B.U. Role of the Internet of Things (IoT) Applications in Business and Marketing. In Contemporary Approaches of Digital Marketing and the Role of Machine Intelligence; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://geekflare.com/?s=edge+computing+and+its+applications (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Duan, Q.; Wang, S.; Ansari, N. Convergence of networking and cloud/edge computing: Status, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneo, L.; Nitinder, M.; Aleksandr, Z.; Walter, W.; Christian, R.; Per, G.; Jussi, K. (How Much) Can Edge Computing Change Network Latency? In Proceedings of the 2021 IFIP Networking Conference (IFIP Networking), Espoo and Helsinki, Finland, 21–24 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, S. Mobile Edge Cloud Architecture for Future Low-Latency Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Rutgers The State University of New Jersey, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Meixner, C.C.; Tornatore, M.; Zhang, J. Edge Computing and Networking: A Survey on Infrastructures and Applications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 101213–101230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N. Edge Computing Platforms and Protocols. Ph.D. Thesis, Helsingin yliopisto, Helsinki, Finland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Han, Z.; Leung, V.C. Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning for Recommendation-Enabled Edge Caching in Mobile Edge-Cloud Computing Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, D.; Wu, H.; Lyu, F.; Shen, X.S. Cooperative edge-cloud caching for real-time sensing big data search in vehicular networks. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, W. A survey on Mobile Edge Networks: Convergence of computing, caching and communications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 6757–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, W.; Ha, K.; Amos, B.; Pillai, P.; Satyanarayanan, M. Are Cloudlets Necessary? School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestro, A.; Mohan, N.; Kangasharju, J.; Schneider, F.; Fu, X. Mute: Multi-tier edge networks. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on CrossCloud Infrastructures & Platforms, Porto, Portugal, 23–26 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, J.; Pignataro, C. RFC 7665—Service Function Chaining (SFC) Architecture; RFC Editor: Marina del Rey, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Shen, G.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.; Mukherjee, B. Service function chaining and embedding with heterogeneous faults tolerance in edge networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2022, 20, 2157–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinas, D.M.; Shami, A. The Need for Advanced Intelligence in NFV Management and Orchestration. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Bunyakitanon, M.; Da Silva, A.P.; Vasilakos, X.; Nejabati, R.; Simeonidou, D. Auto-3P: An autonomous VNF performance prediction & placement framework based on machine learning. Comput. Netw. 2020, 181, 107433. [Google Scholar]
- SDN Architecture; ONF TR-502. Open Networking Foundation: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2014; Available online: https://opennetworking.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/TR_SDN_ARCH_1.0_06062014.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- OpenFlow-Switch, version 1.5.1 (Protocol, version 0x06). ONF TS-025; The Open Networking Foundation: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2015; Available online: https://opennetworking.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/openflow-switch-v1.5.1.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Hu, F.; Bao, K. A Survey on Software-Defined Network and OpenFlow: From Concept to Implementation. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 2181–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Rajkumar, B. A taxonomy of software-defined networking (SDN)-enabled cloud computing. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2018, 51, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, A.; David, C.; Jennifer, R. A purpose-built global network: Google’s move to SDN. Commun. ACM 2016, 59, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Yatri, V.K.; Kapoor, C. Software defined networking: State-of-the-art. J. High Speed Netw. 2019, 25, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, A.H.; Subramaniam, S.K.; Samian, N.; Latip, R.; Zukarnain, Z. Towards Optimal Efficiencies in Software Defined Network SDN-Edge Cloud: Performance Evaluation of Load Balancing Algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1st International Conference on Advanced Engineering and Technologies (ICONNIC), Kediri, Indonesia, 14 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Boukraa, L.; Mahrach, S.; El Makkaoui, K.; Esbai, R. SDN southbound protocols: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Networking, Intelligent Systems and Security, Bandung, Indonesia, 30–31 March 2022; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Maashi, M.S.; Tanwar, S.; Badotra, S.; Aljebreen, M.; Bharany, S. A comparative study of software defined networking controllers using mininet. Electronics 2022, 11, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceselli, A.; Premoli, M.; Secci, S. Mobile Edge Cloud Network Design Optimization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2017, 25, 1818–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-M.; Chiang, M.-S.; Dao, D.-T.; Su, W.-L.; Xu, S.; Zhou, H. V2V Data Offloading for Cellular Network Based on the Software Defined Network (SDN) Inside Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) Architecture. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17741–17755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yu, H.; Forester, K.-T.; Noormohammadpour, M.; Schmid, S. Inter-Datacenter Bulk Transfers: Trends and Challenges. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakiri, A.; Sellami, B.; Patil, P.; Berthou, P.; Gokhale, A. Managing wireless fog networks using software-defined networking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACS 14th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Hammamet, Tunisia, 30 October–3 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Filali, A.; Mlika, Z.; Cherkaoui, S.; Kobbane, A. Preemptive SDN Load Balancing with Machine Learning for Delay Sensitive Applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 15947–15963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Roy, A.; Sairam, A.S. Optimizing SDN controller load balancing using online reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 131591–131604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, F.A.; Jarray, A.; Karmouch, A. Software Defined Network-Based Edge Cloud Resource Allocation Framework. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 10672–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlatch, S.; Humernbrum, T.; Glinka, F. Improving QoS in real-time internet applications: From best-effort to Software-Defined Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.; Yang, R.; Fang, C.; Yu, S. Deep reinforcement learning-based resource allocation for content distribution in IoT-edge-cloud computing environments. Symmetry 2023, 15, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Su, Z.; Li, R.; Yu, S. A Software-Defined-Networking-Enabled Approach for Edge-Cloud Computing in the Internet of Things. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lan, S.; Wang, L.; Shen, W.; Huang, G.G. Big data driven edge-cloud collaboration architecture for cloud manufacturing: A software defined perspective. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 2020–45950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thang, L.D.; Rafael, G.L.; Paolo, C.; Per-Olov, Ö. Machine Learning Methods for Reliable Resource Provisioning in Edge-Cloud Computing: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Oki, E. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for cooperative computing offloading and route optimization in multi cloud-edge networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2023, 20, 4416–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Duan, Q.; Li, J. A K-means-based network partition algorithm for controller placement in software defined network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–27 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Li, S.; Li, T. Load-aware dynamic controller placement based on deep reinforcement learning in SDN-enabled mobile cloud-edge computing networks. Comput. Netw. 2023, 234, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Wu, G.; Alzahrani, B.; Barnawi, A.; Alhindi, A.; Chen, M. Reinforcement learning for task placement in collaborative cloud-edge computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Madrid, Spain, 7–11 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chetouane, A.; Karoui, K. New Continual Federated Learning System for Intrusion Detection in SDN-Based Edge Computing. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2024, 37, e8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absardi, Z.N.; Javidan, R. IoT traffic management using deep learning based on osmotic cloud to edge computing. Telecommun. Syst. 2024, 87, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Lin, M.; Ravishankar, R.; Peyman, T. HomeCloud: An edge cloud framework and testbed for new application delivery. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT), Thessaloniki, Greece, 16–18 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Babou, C.S.M.; Fall, D.; Shigeru, K.; Yuzo, T.; Monowar, H.B.; Ibrahima, N.; Ibrahima, D.; Youki, K. D-LBAH: Dynamic Load Balancing Algorithm for HEC-SDN systems. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud (FiCloud), Rome, Italy, 23–25 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Kuang, Z.; Zhao, L. Multiuser computation offloading and resource allocation for cloud–edge heterogeneous network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 3799–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, J.; Luo, Y. Service cost-based resource optimization and load balancing for edge and cloud environment. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2020, 62, 2020–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Shao, J.; Liu, R.S.; Hu, W. Performance and cost of upstream resource allocation for inter-edge-datacenter bulk transfers. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Chongqing, China, 9–11 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, J.; Le, L.B.; Iosifidis, G.; Lee, K.; Kim, D.I. Collaboration of Network Operators and Cloud Providers in Software-Controlled Networks. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.P.-C.; Tsai, Z. Hierarchical Edge-Cloud SDN Controller System with Optimal Adaptive Resource Allocation for Load-Balancing. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, W. A hierarchical edge cloud architecture for mobile computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2016–The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tungsten Fabric Architecture. Available online: https://tungstenfabric.github.io/website/Tungsten-Fabric-Architecture.html (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Moledo, S.P.; Rawat, A.; Gurtov, A. Vendor-independent software-defined networking. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Signal, Control and Communication (SCC), Hammamet, Tunisia, 20–22 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Microsoft. Software Defined Networking (SDN) in Azure Local. 2025. Available online: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-local/concepts/software-defined-networking-23h2?view=azloc-2503 (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Microsoft. Introducing Azure Local: Cloud Infrastructure for Distributed Locations Enabled by Azure Arc. 2024. Available online: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/azurearcblog/introducing-azure-local-cloud-infrastructure-for-distributed-locations-enabled-b/4296017 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Microsoft. What Is Azure Private Multi-Access Edge Compute? 2024. Available online: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/azure/private-multi-access-edge-compute-mec/overview (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- AWS. New AWS Wavelength Zone in Toronto—The First in Canada. 2022. Available online: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/new-aws-wavelength-zone-in-toronto-the-first-in-canada/#:~:text=Wireless%20communication%20has%20put%20us,and%20in%2Dvehicle%20entertainment%20experiences (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Adamson, C. AWS Wavelength for Ultra-Low Latency Applications. 2024. Available online: https://medium.com/@christopheradamson253/aws-wavelength-for-ultra-low-latency-applications-f043ea2d3577#:~:text=AWS%20Wavelength%20allows%20you%20to,AR%2FVR%2C%20and%20more (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Nieto, G.; de la Iglesia, I.; Lopez-Novoa, U.; Perfecto, C. Deep Reinforcement Learning techniques for dynamic task offloading in the 5G edge-cloud continuum. J. Cloud Comput. 2024, 13, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, C.; Wu, F.; Xie, R. An Energy-Efficient Dynamic Offloading Algorithm for Edge Computing Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 127489–127506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandr, Z.; Nitinder, M.; Suzan, B.; Walter, W.; Kangasharju, J. ExEC: Elastic Extensible Edge Cloud. In Proceedings of the EdgeSys ’19: Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Edge Systems, Analytics and Networking, Dresden, Germany, 25 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kazi, B.U.; Wainer, G.A. Next generation wireless cellular networks: Ultra-dense multi-tier and multi-cell cooperation perspective. Wirel. Netw. 2019, 25, 2041–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymanifar, R.; Carolyn, B.A.S.; Srinivasa, S. A Clustering Approach to Edge Controller Placement in Software-Defined Networks with Cost Balancing. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 2642–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Jiang, L.; Jia, G. Deep reinforcement learning based controller placement and optimal edge selection in SDN-based multi-access edge computing environments. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2024, 193, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, G.; Florian, B.; Rolf, E.; Tim, G.; Max, M. What the Fog? Edge Computing Revisited: Promises, Applications and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 152847–152878. [Google Scholar]
- Adeniyi, O.; Sadiq, A.S.; Pillai, P.; Aljaidi, M.; Kaiwartya, O. Securing mobile edge computing using hybrid deep learning method. Computers 2024, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. AI-enabled blockchain and SDN-integrated IoT security architecture for cyber-physical systems. Adv. Control. Appl. Eng. Ind. Syst. 2024, 6, e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Zhe, P.; Bin, X.; Aiqun, H.; Kui, R. FloodDefender: Protecting data and control plane resources under SDN-aimed DoS attacks. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2017—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1–4 May 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.N.; Imran, M.; din, M.S.U.; Kim, B.S. Low rate DDoS detection using weighted federated learning in SDN control plane in IoT network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdinejad, A.; Parizi, R.M.; Dehghantanha, A.; Zhang, Q.; Choo, K.K.R. An energy-efficient SDN controller architecture for IoT networks with blockchain-based security. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2020, 13, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdinejad, A.; Parizi, R.M.; Dehghantanha, A.; Choo, K.K.R. P4-to-blockchain: A secure blockchain-enabled packet parser for software defined networking. Comput. Secur. 2020, 88, 101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, H.; Yazdinejad, A.; Dehghantanha, A.; Zarrinkalam, F.; Srivastava, N. P3GNN: A Privacy-Preserving Provenance Graph-Based Model for Autonomous APT Detection in Software Defined Networking. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Autonomous Cybersecurity, New York, NY, USA, 14–18 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Ouyang, X.; Chen, Y.; Townend, P.; Xu, J. Intelligent Resource Scheduling at Scale: A Machine Learning Perspective. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Service-Oriented System Engineering, Bamberg, Germany, 26–29 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Mostafa, G.-A. Joint computation offloading and resource provisioning for edge-cloud computing environment: A machine learning-based approach. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2020, 50, 2212–2230. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, R.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, B.; Li, Z. Preemptive Scheduling for Distributed Machine Learning Jobs in Edge-Cloud Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2022, 40, 2411–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoichi, S.; Yoshinobu, Y.; Takehiro, S. Flow control in SDN-Edge-Cloud cooperation system with machine learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 40th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Singapore, 29 November–1 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Qiu, X.; Li, W.; Guo, S. SFC Orchestration Method for Edge Cloud and Central Cloud Collaboration: QoS and Energy Consumption Joint Optimization Combined With Reputation Assessment. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2023, 34, 2735–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vozmediano, R.; Montero, R.S.; Huedo, E.; Llorente, I.M. Intelligent Resource Orchestration for 5G Edge Infrastructures. Future Internet 2024, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Features | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Centralized | Distributed |
| Latency | High | Low |
| Mobility | No | Yes |
| Computational capacity | High | Medium to low |
| Security | Less secure | More secure |
| Bandwidth usages | High network bandwidth uses | Lower network bandwidth uses |
| Scalability | Easy to scale | Less scalable than cloud |
| Data Processing | Through Internet | Near to the source of the data |
| Industry | Use Cases | Location | Killer Apps | Challenges | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Bw | L | St | Sa | Ra | ||||
| Restaurants | Forecast food preparation | Store | Video Analytics, Data Analysis | Y | Y | ||||
| Retail | Monitoring, tracking customers, and improving sales | Store | Video Analytics, Data Analysis | Y | Y | ||||
| Gas Station | Detect safety hazards | Gas Stations | Video Analytics | Y | Y | ||||
| Cities | Traffic administration and intelligent control | Intersections and City Clusters | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |
| Construction | Increase safety, efficiency, and productivity | Construction Site | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| Aviation | Analyze customers’ in-flight experience, monitoring and maintenance of aircraft operations | Plane | Video Analytics, Data Analysis | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |
| Railway | Monitoring freight cars, train tracks, and wheels for issues that could cause derailment | Train | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Road Control | Monitoring road quality and identify areas that require maintenance | Trucks | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | |||
| Self-Driving and Smart Cars | Robo-taxi such as Uber | Edge cloud | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| Oil Refinery | Predictive maintenance, workplace safety | Oil Rig or Pump | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |
| Manufacturing | Improve manufacturing yields, monitoring equipment and predicting maintance need | Factory | Video Analytics | Y | Y | ||||
| Manufacturing Robots | Managing a fleet of robots that assist in industy production pipeline | Factory | Video Analytics | Y | |||||
| Agriculture | Monitoring the quality of produce during harvest, storage, and processing. Observe and monitor using drone imagery | Field | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | |||
| Financial Services | Facial recognition, virtual tellers | Bank/Financial locations | Video Analytics, Machine Reading | Y | Y | ||||
| PDA | Facial recognition, gesture identification etc | Edge cloud | Video Analytics | Y | |||||
| AR | Holograms, recognize faces and people | Edge cloud | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | |||
| VR | Capture motions | Edge cloud | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | |||
| Voice Semantics | Voice AI such as Alexa | Edge cloud | Machine Reading | Y | Y | ||||
| Smart Health | Medical devices and applications at Hospitals | Hospitals | Video Analytics, Machine Reading | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| Gaming | Google’s Stadia, Microsoft’s xCloud support multiple gaming engines | Edge cloud | Video Analytics | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||
| Robotics | Restaurants, Industry, Rescue | Store/Industry | Video Analytics | Y | Y | ||||
| Reference | Work Area | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| [11] | Edge computing benefits from SDN | Latency, load balancing, and computation resources |
| [46] | MEC network design optimization | Latency, reliability, and resource Mobility |
| [47] | Data offloading in MEC using SDN | Centralized management, latency, and bandwidth |
| [48] | Inter-datacenter bulk transfers | Bandwidth, utilization, traffic exchanged overthe Wide-Area Networks (WANs) and SDN controller |
| [49] | SDN-enabled fog network | Latency, load balancing, hybrid SDN routing protocol combining the OLSR data forwarding, traffic engineering, and OpenFlow and SDN |
| [50,51] | SDN load balancing with deep learning | Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), reinforcement learning, latency, load balancing, Multi-access Edge Computing and SDN controller |
| [52] | SDN for edge cloud resources allocation | Node and link provisioning, latency, and bandwidth |
| [53,54] | Ensure high standard QoS and optimize resource allocation | Latency, Bandwidth, Throughput, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) |
| [55] | Secure and intelligent services in IoT | Architecture, Blockchain, and reinforcement learning |
| [56] | Edge cloud collaboration architecture | Data-driven architecture, latency, data analytics, SDNs, and cloud manufacturing. |
| [57,58] | Resource Provisioning in Edge Cloud Computing | Machine learning, RL, load balancing, placement of application, computation offloading, and route optimization |
| [59,60] | SDN controller placement | Machine learning, deep reinforcement learning, SDNs, network partitioning, latency, load balancing, and mobile edge cloud. |
| [61] | Controller-based edge cloud computing | Reinforcement learning, task placement and improve system utility. |
| [62] | Intrusion detection in SDN-based edge computing | Federated learning (FL), Intrusion Detection, and SDN-based edge computing. |
| [18,63] | IoT and edge cloud | Deep learning, adaptive resource management, traffic management, cloud-to-edge computing, and SD-WAN. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazi, B.U.; Islam, M.K.; Siddiqui, M.M.H.; Jaseemuddin, M. A Survey on Software Defined Network-Enabled Edge Cloud Networks: Challenges and Future Research Directions. Network 2025, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5020016
Kazi BU, Islam MK, Siddiqui MMH, Jaseemuddin M. A Survey on Software Defined Network-Enabled Edge Cloud Networks: Challenges and Future Research Directions. Network. 2025; 5(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazi, Baha Uddin, Md Kawsarul Islam, Muhammad Mahmudul Haque Siddiqui, and Muhammad Jaseemuddin. 2025. "A Survey on Software Defined Network-Enabled Edge Cloud Networks: Challenges and Future Research Directions" Network 5, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5020016
APA StyleKazi, B. U., Islam, M. K., Siddiqui, M. M. H., & Jaseemuddin, M. (2025). A Survey on Software Defined Network-Enabled Edge Cloud Networks: Challenges and Future Research Directions. Network, 5(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5020016