Influence of Magnetic Field on Atrazine Adsorption and Degradation by Ferroxite and Hematite
Abstract
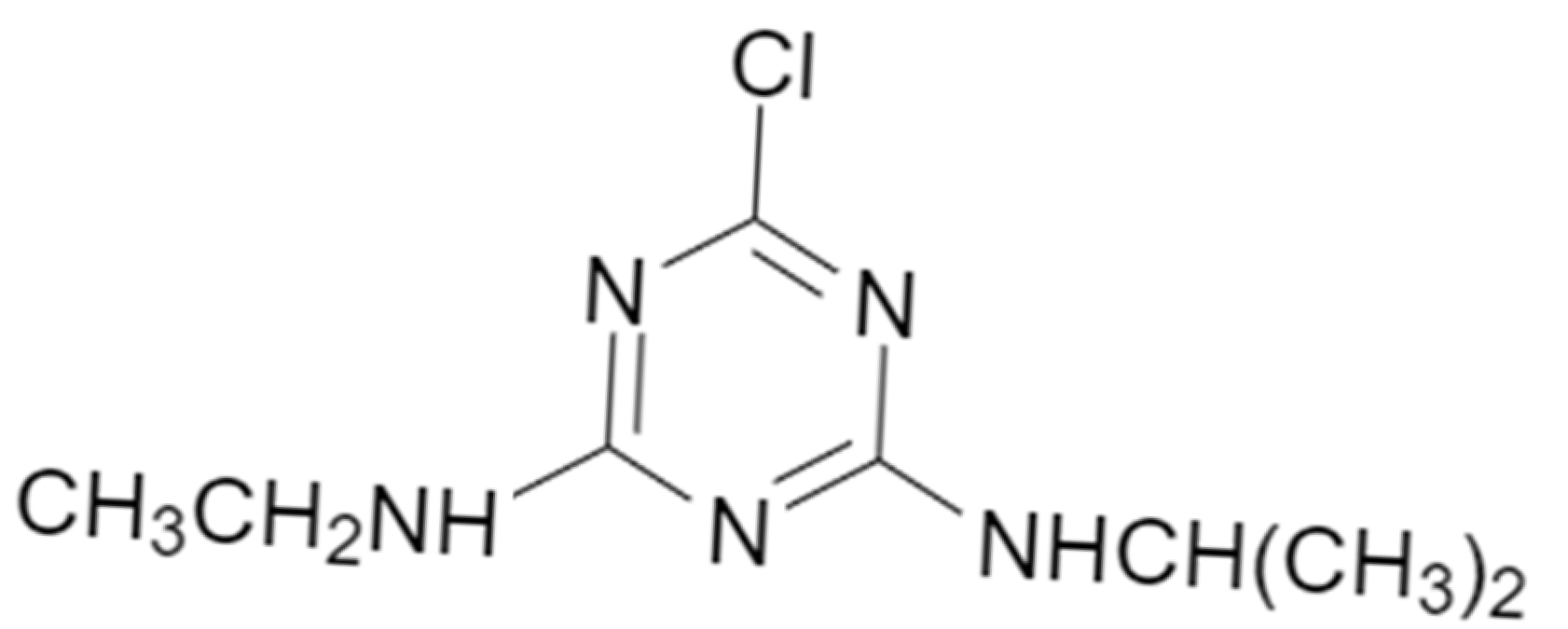
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Synthesis of Ferroxite
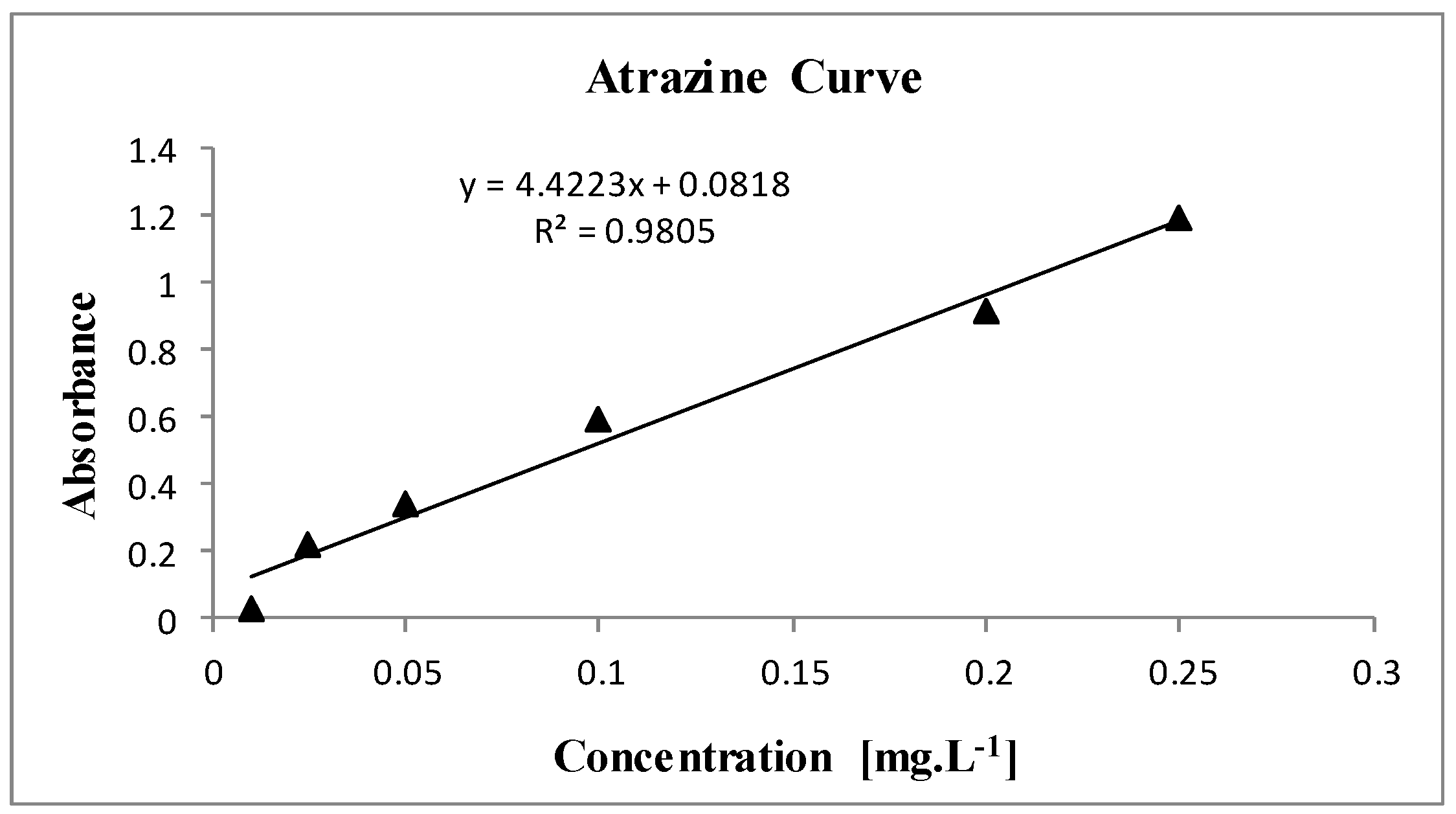
2.3. Standard Atrazine Curve for Analyses of Fenton
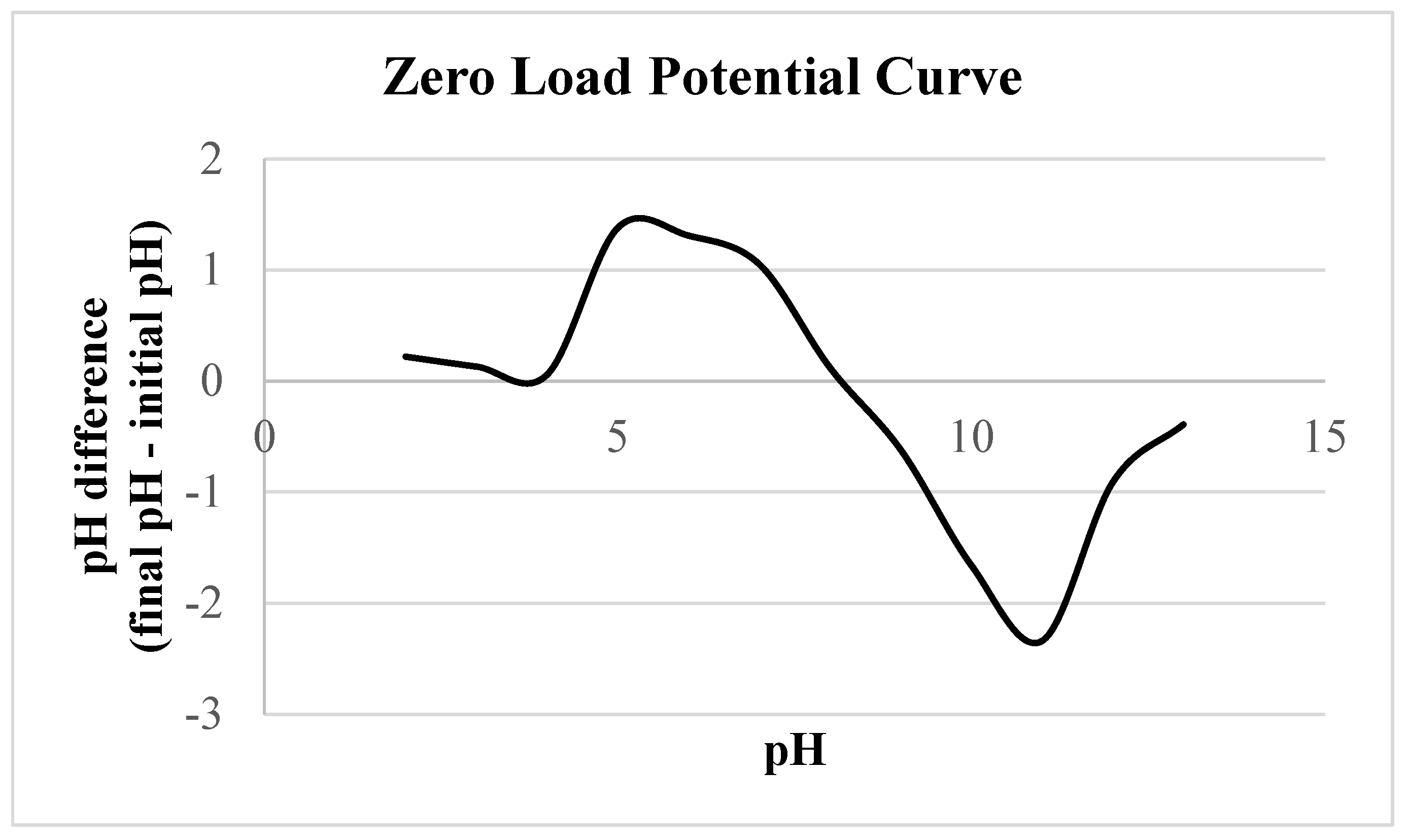
2.4. Obtaining of the Zero Load Potential
2.5. Mass of Ferroxite
2.6. Determination of Values for Fenton Analyses by Means of Removal by Adsorption
| Experimental Conditions A = Atrazine [mol·L−1] F = Ferroxite [g] | Adsorption Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample in the Absence of a Magnetic Field | Sample in the Presence of a Magnetic Field | |
| 1. A(0.01)/F(0.02)/pH(5)/1 h | 39.64 | 56.52 |
| 2. A(0.01)/F(0.02)/pH(5)/2 h | 63.03 | 5.95 |
| 3. A(0.01)/F(0.02)/pH(11)/1 h | 33.83 | 76.70 |
| 4. A(0.01)/F(0.02)/pH(11)/2 h | 33.56 | 76.82 |
| 5. A(0.01)/F(0.05)/pH(5)/1 h | 73.17 | 85.88 |
| 6. A(0.01)/F(0.05)/pH(5)/2 h | 81.05 | 77.10 |
| 7. A(0.01)/F(0.05)/pH(11)/1 h | 29.85 | 63.77 |
| 8. A(0.01)/F(0.05)/pH(11)/2 h | 50.39 | 0.00 |
| 9. A(0.2)/F(0.02)/pH(5)/1 h | 1.88 | 1.88 |
| 10. A(0.2)/F(0.02)/pH(5)/2 h | 3.25 | 3.25 |
| 11. A(0.2)/F(0.02)/pH(11)/1 h | 39.31 | 33.95 |
| 12. A(0.2)/F(0.02)/pH(11)/2 h | 39.31 | 43.06 |
| 13. A(0.2)/F(0.05)/pH(5)/1 h | 25.82 | 2.80 |
| 14. A(0.2)/F(0.05)/pH(5)/2 h | 52.69 | 2.85 |
| 15. A(0.2)/F(0.05)/pH(11)/1 h | 0.00 | 20.56 |
| 16. A(0.2)/F(0.05)/pH(11)/2 h | 0.00 | 4.98 |
| Experimental Conditions A = Atrazine [mol·L−1] H = Hematite [g] | Adsorption Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample in the Absence of a Magnetic Field | Sample in the Presence of a Magnetic Field | |
| 1. A(0.01)/H(0.02)/pH(5)/1 h | 19.24 | 31.34 |
| 2. A(0.01)/H(0.02)/pH(5)/2 h | 28.99 | 51.78 |
| 3. A(0.01)/H(0.02)/pH(11)/1 h | 29.23 | 0.00 |
| 4. A(0.01)/H(0.02)/pH(11)/2 h | 8.85 | 37.78 |
| 5. A(0.01)/H(0.05)/pH(5)/1 h | 10.96 | 53.49 |
| 6. A(0.01)/H(0.05)/pH(5)/2 h | 29.08 | 65.75 |
| 7. A(0.01)/H(0.05)/pH(11)/1 h | 53.18 | 29.67 |
| 8. A(0.01)/H(0.05)/pH(11)/2 h | 44.54 | 26.18 |
| 9. A(0.2)/H(0.02)/pH(5)/1 h | 18.06 | 25.90 |
| 10. A(0.2)/H(0.02)/pH(5)/2 h | 30.78 | 33.25 |
| 11. A(0.2)/H(0.02)/pH(11)/1 h | 0.00 | 10.28 |
| 12. A(0.2)/H(0.02)/pH(11)/2 h | 12.41 | 15.60 |
| 13. A(0.2)/H(0.05)/pH(5)/1 h | 26.07 | 45.87 |
| 14. A(0.2)/H(0.05)/pH(5)/2 h | 36.00 | 54.78 |
| 15. A(0.2)/H(0.05)/pH(11)/1 h | 9.23 | 0.53 |
| 16. A(0.2)/H(0.05)/pH(11)/2 h | 18.69 | 28.97 |
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Experimental Conditions
3.2. Influence of the Magnetic Field in the Adsorption Process
3.3. Influence of the Magnetic Field in the Degradation Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bailey, G.W.; White, J.L. Single Pesticide Volume: The Triazine Herbicides. In Pesticide Chemistry: The Model of the Triazine Herbicides; Gunther, F.A., Gunther, J.D., Eds.; Springer Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1970; pp. 29–92. [Google Scholar]
- Brigante, J.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Povinelli, J.; Nogueira, A.M.d.N. Environmental Evaluation of the Mogi-Guaçu River: Results of a Research with an Ecosystem Approach; Rima: São Carlos, Brazil, 2002; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, M.M. Environmental Impact of Pollution in the Mogi-Guaçu River. Cad. Saúde Pública 2006, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mehler, W.T.; Schuler, L.J.; Lydy, M.J. Pesticide Contamination and Its Effects on Aquatic Life. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Egler, M. Utilizing the Benthonic Macroinvertebrate Community of Evaluation of Degradation of Rivers Ecosystems in Agricultural Areas. Master’s Thesis, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2002; p. 147. [Google Scholar]
- Graymore, M.; Stagnitti, F.; Allinson, G. Toxicology and Ecotoxicology of Pesticides in River Systems. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Adams, C. Water Quality and Pollution in River Systems. Water Res. 2006, 40, 527–532. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, J.F. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Ecosystems: A Case Study in the Mogi-Guaçu River. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, E.J. Molecular Interactions of Herbicides in Aquatic Systems. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2009, 902, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Ketan, K.; Singh, J.K. Removal of Pesticides in Aquatic Systems: A Study on Adsorption Mechanisms. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W. Adsorption of Pollutants in Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5394–5401. [Google Scholar]
- Ozeki, S. Study of Surface Chemistry in Pollutant Adsorption on Nanomaterials. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 11843–11847. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, H.M.; Hassan, A.I. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanomaterials for Application in Cost-Effective Electrochemical Devices. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério Filho, A.; Xavaré Kulman, R.; Vaz Tholozan, L.; Felkl de Almeida, A.R.; Silveira da Rosa, G. Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon Obtained from Water Treatment Plant Sludge for Removal of Cationic Dye from Wastewater. Processes 2020, 8, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.S.; Torres, J.A.; Silva, M.C.; Nogueira, F.G.E.; da Silva, A.C.; Ramalho, T.C. Soybean peroxidase immobilized on δ-FeOOH as new magnetically recyclable biocatalyst for removal of ferulic acid. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wei, Y.; Yang, C.; He, Z. Interactions of microplastics and soil pollutants in soil-plant systems. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A. Oxidation Techniques for Water Purification. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2002, 5, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Acero, J.L.; Stemmler, K.; Von Gunten, U. Removal of Contaminants from Drinking Water: A Comparative Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4810–4816. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Graham, N.J.D. Study of Water Treatment Techniques for Pollution Control. Water Res. 2000, 34, 4754–4762. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, D.S.; Marquer, J., Jr.; Pereira, G.T. Geochemical Studies on the Contaminants in Soils. Geoderma 2010, 155, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y. Optical Properties of Contaminants and Their Effects on Water Quality. Optik 2019, 183, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Derco, J.; Žgajnar Gotvajn, A.; Čižmárová, O.; Dudáš, J.; Sumegová, L.; Šimovičová, K. Removal of Micropollutants by Ozone-Based Processes. Processes 2021, 9, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, J.; Regalbuto, J.R. The Engineering of Pt/Carbon Catalyst Preparation for Application on Proton Exchange Fuel Cell Membrane (PEFCM); University of Illinois: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Tireli, A.A.; Marcos, F.C.F.; Oliveira, L.F.; Guimarães, I.R.; Guerreiro, M.C.; Silva, J.P. Influence of Magnetic Field on the Adsorption of Organic Compound by Clays Modified with Iron. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97–98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.A. Influence of Magnetic Field on Adsorption and Degradation Processes of Atrazine with Ferroxite and Hematite. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Lavras, Lavras, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rajczykowski, K.; Loska, K. Stimulation of Heavy Metal Adsorption Process by Using a Strong Magnetic Field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Maksoud, M.I.A.; Fahim, R.A.; Bedir, A.G.; Osman, A.I.; Abouelela, M.M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Elkodous, M.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Rabee, M.M.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; et al. Engineered magnetic oxides nanoparticles as efficient sorbents for wastewater remediation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 519–562. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, X.; Quan, J.; Xing, G.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C.; Wu, P.; Zhao, F.; Hu, B.; Hu, Y. Application of magnetic fields to wastewater treatment and its mechanisms: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, D.; Utkarsh, U.; Ghosh, K.B. Spin-Controlled Electrocatalysis: An Out-of-the-Box Strategy for the Advancement of Electrochemical Water Splitting. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 6226–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Nazmutdinov, R.R.; Zairov, R.R.; Shao, Q.; Lu, J. Magnetic Field Enhanced Cobalt Iridium Alloy Catalyst for Acidic Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 6148–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yue, H.; Li, L.; Zou, J. Spin Effects in Electrocatalysis: Mechanisms, Catalyst Engineering, Modulation, and Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2025, 164, 100967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lv, H.; Yao, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C. Magnetic Field-Assisted Electrocatalysis: Mechanisms and Design Strategies. Carbon Energy 2024, 6, e575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; You, F.; Yao, J.; Yang, H.; Xia, B.Y. Magnetic Field-Assisted Construction and Enhancement of Electrocatalysts. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202201551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vensaus, P.; Liang, Y.; Ansermet, J.P.; Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A.; Lingenfelder, M. Enhancement of Electrocatalysis through Magnetic Field Effects on Mass Transport. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.-J.; Tao, K. Spin Selectivity Induced by the Interface Effect for Boosted Water Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 5685–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, D. Numerical Simulation for Magnetic Field Analysis and Magnetic Adsorption Behavior of Ellipse Magnetic Matrices in HGMS: Prediction Magnetic Adsorption Behavior via Numerical Simulation. Miner. Eng. 2021, 167, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, P. Recent Advances in Magnetic Field-Enhanced Electrocatalysis. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 11377–11395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y. Multiscale Catalysis Under Magnetic Fields: Methodologies, Advances, and Trends. ChemCatChem 2022, 14, e202200889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgami, M.A.; Patra, A.; Jeong, S.M.; Rout, C.S. Exploring the Synergy of Magnetism and Electrocatalysis: A Comprehensive Review on Mechanisms, Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 24005–24040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, L.F.O.; Hott, R.C.; Ladeira, P.C.C.; Batista, B.L.; Andrade, T.G.; Santos, M.S.; Faria, M.C.S.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Monteiro, D.S.; Pereira, M.C.; et al. Simple synthesis and characterization of l-Cystine functionalized δ-FeOOH for highly efficient Hg(II) removal from contaminated water and mining waste. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Mechanisms and Application of Magnetic Field Enhancing Pollutant Adsorption in Water: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.C.A.; Petkowicz, D.I.; Smaniotto, A.; Pergher, S.B.C. Magnetic Zeolites: A New Adsorbent for Removal of Metallic Contaminants from Water. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3699–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, A.; Yan, B.; Yoshimura, S.; Saito, H. Quantitatively Probing the Magnetic Behavior of Individual Nanoparticles by an AC Field-Modulated Magnetic Force Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, K.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, R.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Huang, M. Atrazine exposure induces TDP-43 protein translocation: A potential mechanism for prefrontal cortical neurodegeneration induced by environmental pollutants. Toxicology 2025, 515, 154128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrat, G.; De Bergevin, F.; Pernet, M.; Joubert, J.C. Structure Locale de δ-FeOOH. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1983, 39, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Experimental Conditions H2O2 [mL] | Degradation Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample in the Absence of a Magnetic Field | Sample in the Presence of a Magnetic Field | |
| 1. H2O2(0.1)/1 h | 3.12 | 0.00 |
| 2. H2O2(0.3)/1 h | 21.95 | 0.00 |
| 3. H2O2(0.5)/1 h | 36.43 | 14.41 |
| 4. H2O2(0.7)/1 h | 19.18 | 80.34 |
| 5. H2O2(0.9)/1 h | 46.42 | 87.53 |
| 6. H2O2(1.1)/1 h | 64.49 | 73.88 |
| 7. H2O2(1.3)/1 h | 58.03 | 48.53 |
| 8. H2O2(1.5)/1 h | 30.83 | 64.40 |
| Experimental Conditions H2O2 [mL] | Degradation Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample in the Absence of a Magnetic Field | Sample in the Presence of a Magnetic Field | |
| 1. H2O2(0.1)/1 h | 3.33 | 0.00 |
| 2. H2O2(0.3)/1 h | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 3. H2O2(0.5)/1 h | 18.34 | 56.35 |
| 4. H2O2(0.7)/1 h | 28.82 | 3.90 |
| 5. H2O2(0.9)/1 h | 25.60 | 24.11 |
| 6. H2O2(1.1)/1 h | 23.53 | 15.17 |
| 7. H2O2(1.3)/1 h | 12.66 | 13.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sousa, M.A.; Gonçalves, M.A.; Sales, T.A.; Lino, J.B.d.R.; de Moura, S.G.; da Silva, J.P.; Ramalho, T.C. Influence of Magnetic Field on Atrazine Adsorption and Degradation by Ferroxite and Hematite. Magnetism 2025, 5, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020011
Sousa MA, Gonçalves MA, Sales TA, Lino JBdR, de Moura SG, da Silva JP, Ramalho TC. Influence of Magnetic Field on Atrazine Adsorption and Degradation by Ferroxite and Hematite. Magnetism. 2025; 5(2):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSousa, Marcos Antônio, Mateus Aquino Gonçalves, Thais Aparecida Sales, Jessica Boreli dos Reis Lino, Stéfany Gonçalves de Moura, Joaquim Paulo da Silva, and Teodorico Castro Ramalho. 2025. "Influence of Magnetic Field on Atrazine Adsorption and Degradation by Ferroxite and Hematite" Magnetism 5, no. 2: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020011
APA StyleSousa, M. A., Gonçalves, M. A., Sales, T. A., Lino, J. B. d. R., de Moura, S. G., da Silva, J. P., & Ramalho, T. C. (2025). Influence of Magnetic Field on Atrazine Adsorption and Degradation by Ferroxite and Hematite. Magnetism, 5(2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetism5020011








