Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench Pod Extract Revealed Antagonistic Effect against the Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Metformin and Acarbose upon Concomitant Administration in Glucose-Induced Hyperglycemic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Collection of Materials
3.2. Preparation of Extract
3.3. Animal Experiment
3.3.1. Sample Size Calculation
3.3.2. Experimental Design
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes mellitus |
| NIDMI | Non-Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus |
| IDDM | Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
| NC | Negative (Fasting) Control |
| PC | Positive (Hyperglycemic) control |
| MET | Metformin only group |
| AE | Abelmoschus esculentus pod extract |
| ACR | Acarbose |
| MET + ACR | Metfomin + Acarbose group |
| MET + ACR + AEE | Metformin + Acarbose + Abelmoschus esculentus pod Extract group |
| p.o. | Per os |
| BW | Bodyweight |
References
- IDF. Diabetes around the world in 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- WHO. Improving Diabetes Outcomes for All, a Hundred Years on from the Discovery of Insulin: Report of the Global Diabetes Summit; World Health Organization and the Government of Canada: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Riddle, M.C. Oral pharmacologic management of type 2 diabetes. Am. Fam. Physician 1999, 60, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahman, K.M.H.; Hossain, M.S.; Haque, N.; Razak, T.B.A.; Ahmad, H. Apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism influenced glycemic status among Malaysians. Res. Ther. 2019, 6, 3307–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.W.; Hughey, C.C.; Lantier, L.; Sundelin, E.I.; Peggie, M.; Zeqiraj, E.; Sicheri, F.; Jessen, N.; Wasserman, D.H.; Sakamoto, K. Metformin reduces liver glucose production by inhibition of fructose-1-6-bisphosphatase. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hundal, R.S.; Krssak, M.; Dufour, S.; Laurent, D.; Lebon, V.; Chandramouli, V.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Schumann, W.C.; Petersen, K.F.; Landau, B.R.; et al. Mechanism by which metformin reduces glucose production in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 2063–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanefeld, M. Cardiovascular benefits and safety profile of acarbose therapy in prediabetes and established type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2007, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIver, L.A.; Tripp, J. Acarbose. StatPearls [Internet]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493214/ (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Kang, L. Metformin combined with acarbose vs. single medicine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Lou, Q.; Liu, J.; Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Lv, X.; Gu, M.; Guo, X. Comparative assessment of the efficacy and safety of acarbose and metformin combined with premixed insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicine 2017, 96, e7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.R.; Ramachandran, A.; Chadha, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Rathod, R.; Kalra, S. Acarbose plus metformin fixed-dose combination in the management of type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Huang, C.N.; Hung, Y.J.; Kwok, C.F.; Sun, J.H.; Pei, D.; Yang, C.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, C.L.; Sheu, W.H.; et al. Acarbose plus metformin fixed-dose combination outperforms acarbose monotherapy for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 102, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilun, Z. Application of acarbose combined with metformin in treatment of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients. Heilongjiang Med. J. 2011, 24, 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, N.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Mohd Mustafa, N.H.; Phang, I.C. Morpho-Physiological Characteristics, Selected Macronutrient Uptake, and Oxidative Stress Level of Andrographis paniculata Under Saline Condition. J. Teknol. 2015, 77, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, M.S.; Urbi, Z. Effect of Naphthalene Acetic Acid on the Adventitious Rooting in Shoot Cuttings ofAndrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees: An Important Therapeutical Herb. Int. J. Agron. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, M.S.; Urbi, Z.; Sule, A.; Rahman, K.M.H. Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Wall. ex Nees: A review of ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 274905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbi, Z.; Zainuddin, Z. Standardization of Surface Sterilization Protocol of Field Grown Stevia rebaudiana Prior to In Vitro Clonal Propagation. J. Teknol. 2015, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farooq, U.; Khan, T.; Shah, S.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Ali, Y.; Ullah, R.; Raziq, N.; Shahid, M.; Capasso, R. Isolation, Characterization and Neuroprotective Activity of Folecitin: An In Vivo Study. Life 2021, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Urbi, Z.; Karuniawati, H.; Mohiuddin, R.B.; Moh Qrimida, A.; Allzrag, A.M.M.; Ming, L.C.; Pagano, E.; Capasso, R. Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Wall. ex Nees: An Updated Review of Phytochemistry, Antimicrobial Pharmacology, and Clinical Safety and Efficacy. Life 2021, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S. The Effect of Salinity Stress on the Morpho-physiology and Protein Profile of Andrographis Paniculata. Master’s Thesis, International Islamic University Malaysia, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Urbi, Z.; Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, K.M.H.; Zayed, T.M. Grape: A medicinal fruit species in the holy Qur’an and its ethnomedicinal importance. World Appl. Sci. J. 2014, 30, 253–265. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Sharfaraz, A.; Dutta, A.; Ahsan, A.; Masud, M.A.; Ahmed, I.A.; Goh, B.H.; Urbi, Z.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Ming, L.C. A review of ethnobotany, phytochemistry, antimicrobial pharmacology and toxicology of Nigella sativa L. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 143, 112182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Novellino, E.; Souto, E.B.; Daliu, P.; Santini, A. Abelmoschus esculentus (L.): Bioactive Components’ Beneficial Properties-Focused on Antidiabetic Role-For Sustainable Health Applications. Molecules 2018, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dantas, T.L.; Alonso Buriti, F.C.; Florentino, E.R. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) as a Potential Functional Food Source of Mucilage and Bioactive Compounds with Technological Applications and Health Benefits. Plants 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpayam, O.; Safaei, E.; Bahreini, N.; Saghafi-Asl, M. The effects of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) products on glycemic control and lipid profile: A comprehensive systematic review. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doreddula, S.K.; Bonam, S.R.; Gaddam, D.P.; Desu, B.S.; Ramarao, N.; Pandy, V. Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant, antistress, and nootropic activities of aqueous and methanolic seed extracts of ladies finger (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) in mice. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 519848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabitha, V.; Ramachandran, S.; Naveen, K.R.; Panneerselvam, K. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic potential of Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhune, A.; Sharma, M.; Ojha, B. Abelmoschus esculentus (Okra) potential natural compound for prevention and management of diabetes and diabetic induced hyperglycemia. Tamil Nadu. Int. J. Herb. Med. 2017, 5, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Onuoha, N.O.; Iroegbu, L.U.; Uwaezuoke, N.J. Antidiabetic effects of okra [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench] fruits in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Biokemistri 2017, 29, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Aligita, W.; Muhsinin, S.; Susilawati, E.; Pratiwi, D.S.; Aprilliani, D.; Artarini, A.; Adnyana, I.K. Antidiabetic activity of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) fruit extract. Rasāyan J. Chem. 2019, 12, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, M.; Zheng, B.; Wu, X.; Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Huang, C. Extract of okra lowers blood glucose and serum lipids in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Demleitner, M.F.; Song, L.; Rychlik, M.; Huang, D. Oligomeric proanthocyanidins are the active compounds in Abelmoschus esculentus Moench for its α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition activity. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Afzal, M.; Kazmi, I.; Ahamd, I.; Ahmed, Z.; Ali, B.; Ahmad, S.; Anwar, F. Polypharmacy (herbal and synthetic drug combination): A novel approach in the treatment of type-2 diabetes and its complications in rats. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.C.; Chang, D.; Nammi, S.; Bensoussan, A.; Bilinski, K.; Roufogalis, B.D. Interactions between antidiabetic drugs and herbs: An overview of mechanisms of action and clinical implications. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Mixing Medications and Dietary Supplements Can Endanger Your Health. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/mixing-medications-and-dietary-supplements-can-endanger-your-health (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Peter, E.L.; Nagendrappa, P.B.; Ajayi, C.O.; Sesaazi, C.D. Total polyphenols and antihyperglycemic activity of aqueous fruits extract of Abelmoschus esculentus: Modeling and optimization of extraction conditions. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Shrivastava, S.L.; Mandal, S.M. Functional properties of Okra Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Moench): Traditional claims and scientific evidences. Plant Sci. Today 2014, 1, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Al-Shammari, E.; Adnan, M.; Alcantara, J.C.; Mehmood, K.; Eltoum, N.E.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Khan, M.A.; Ashraf, S.A. Development and Characterization of Novel Biopolymer Derived from Abelmoschus esculentus L. Extract and Its Antidiabetic Potential. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, V.; Panneerselvam, K.; Ramachandran, S. In vitro α–glucosidase and α–amylase enzyme inhibitory effects in aqueous extracts of Abelmoscus esculentus (L.) Moench. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, S162–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliu, P.; Annunziata, G.; Tenore, G.C.; Santini, A. Abscisic acid identification in Okra, Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Moench): Perspective nutraceutical use for the treatment of diabetes. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husen, S.A.; Winarni, D.; Wahyuningsih, S.P.A.; Ansori, A.N.M.; Hayaza, S.; Susilo, R.J.K.; Doong, R.A.; Darmanto, W. Antioxidant potency of various fractions of okra pods extract to ameliorate liver structure and function in diabetic mice. Ann. Biol. 2020, 36, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, H.; Rahman, A.; Biswas, M.; Islam, A.U. Water-soluble Fraction of Abelmoschus esculentus L. Interacts with Glucose and Metformin Hydrochloride and Alters Their Absorption Kinetics after Coadministration in Rats. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 260537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekin, E.; Beppler, C.; White, C.; Mao, Z.; Savage, V.M.; Yeh, P.J. Enhanced identification of synergistic and antagonistic emergent interactions among three or more drugs. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20160332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-N.; Wang, C.-J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Peng, C.-H. Active subfractions of Abelmoschus esculentus substantially prevent free fatty acid-induced β cell apoptosis via inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase-4. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arapitsas, P. Identification and quantification of polyphenolic compounds from okra seeds and skins. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Jain, B.; Jain, V.K. Phytochemical evaluation and characterization of hypoglycemic activity of various extracts of Abelmoschus esculentus Linn. fruit. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 183–185. [Google Scholar]
- Agnes Jenitha, X.; Kanimozhi, R. Evaluation of phytochemicals and antidiabetic activity of abelmoschus esculentus. Int. J. Res. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2021, 5, 142–152. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.-D.; Li, X.; Qin, Y.-L.; Li, M.-T.; Han, Q.-H.; Zhou, J.; Lin, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, W. Physicochemical properties, phenolic profiles, antioxidant capacities, and inhibitory effects on digestive enzymes of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) fruit at different maturation stages. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.M.; Tzeng, T.-F.; Liou, S.-S.; Lan, T.-W. Improvement of insulin sensitivity in obese Zucker rats by myricetin extracted from Abelmoschus moschatus. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Merino, J.; Sun, Q.; Fitó, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary polyphenols, Mediterranean diet, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes: A narrative review of the evidence. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 6723931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Yan, T.; Xu, F.; Xiao, F.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Polysaccharide from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) Improves Antioxidant Capacity via PI3K/AKT Pathways and Nrf2 Translocation in a Type 2 Diabetes Model. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krinsky, N.I. Carotenoids as antioxidants. Nutrition 2001, 17, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petznick, A. Insulin management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 84, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Genuth, S.; Alberti, K.G.; Bennett, P.; Buse, J.; Defronzo, R.; Kahn, R.; Kitzmiller, J.; Knowler, W.C.; Lebovitz, H.; Lernmark, A.; et al. Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 3160–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, S.; Shi, J.; Tang, Z.; Sawhney, M.; Hu, H.; Shi, L.; Fonseca, V.; Dong, H. Comparison of glucose lowering effect of metformin and acarbose in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, Q.; McCowen, K.C.; Xiong, W.; Liu, J.; Jiang, W.; Thomas, R.L.; Hepokoski, M.; He, M.; Shyy, J.Y.J.; et al. Inpatient use of metformin and acarbose is associated with reduced mortality of COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 5, e00301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.M.; Liou, S.-S.; Lan, T.-W.; Hsu, F.-L.; Cheng, J.-T. Myricetin as the Active Principle of Abelmoschus moschatus to Lower Plasma Glucose in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, O.; Eck, P.; Chen, S.; Corpe, C.P.; Lee, J.H.; Kruhlak, M.; Levine, M. Inhibition of the intestinal glucose transporter GLUT2 by flavonoids. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaradua, I.; Ibrahim, M.; Matazu, K.I.; Nasir, A.; Matazu, N.U.; Zainab, A.S.; Abdul Rahman, M.B.; Bilbis, L.; Abbas, A.Y. Antidiabetic activity of Abelmoschus esculentus (Ex-Maradi Okra) fruit in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Niger. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 32, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Charan, J.; Kantharia, N.D. How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hubrecht, R.C.; Carter, E. The 3Rs and Humane Experimental Technique: Implementing Change. Animals 2019, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arifin, W.N.; Zahiruddin, W.M. Sample Size Calculation in Animal Studies Using Resource Equation Approach. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 24, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

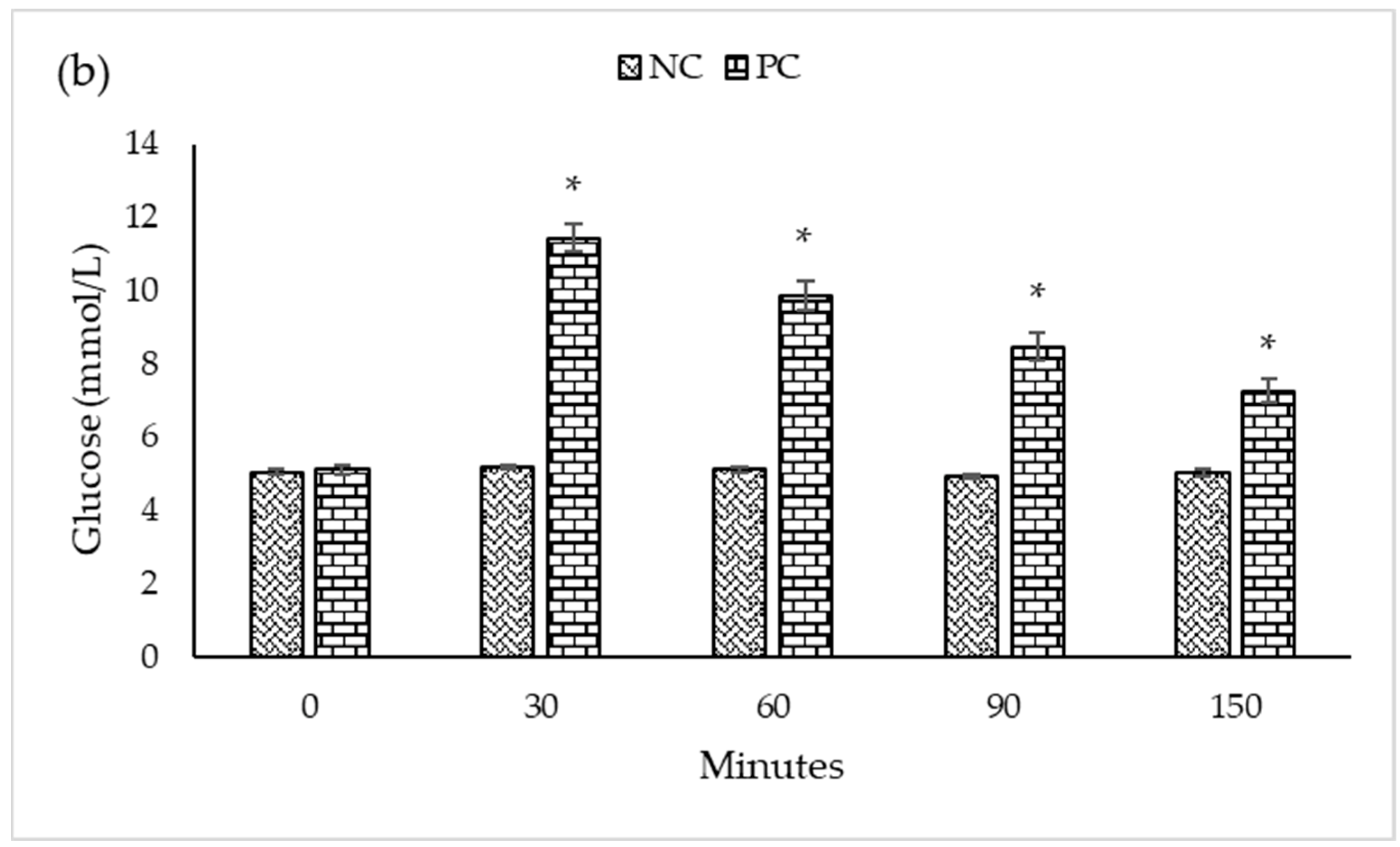

| Experimental Groups | n | Blood Glucose Levels (mmol/L) at a Different Time (Minutes) Intervals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 150 | ||
| Mean ± SEM | ||||||
| PC | 5 | 5.10 ± 0.105 a | 11.44 ± 0.387 a | 9.86 ± 0.408 a | 8.46 ± 0.387 a | 7.26 ± 0.311 a |
| MET | 5 | 5.12 ± 0.066 a | 9.64 ± 0.227 b | 8.54 ± 0.172 b | 7.32 ± 0.139 b | 5.32 ± 0.102 b |
| MET + ACR | 5 | 4.92 ± 0.058 a | 9.04 ± 0.178 b | 7.82 ± 0.188 b | 6.36 ± 0.154 c | 4.50 ± 0.095 c |
| MET + ACR + AEE | 5 | 5.10 ± 0.084 a | 9.28 ± 0.128 b | 8.60 ± 0.089 b | 7.76 ± 0.121 ab | 6.58 ± 0.086 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Sayed, N.M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Khan, M.R.; Ahmmed, F.; Zohora, F.T.; Ağagündüz, D.; Ming, L.C.; Capasso, R. Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench Pod Extract Revealed Antagonistic Effect against the Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Metformin and Acarbose upon Concomitant Administration in Glucose-Induced Hyperglycemic Mice. Biologics 2022, 2, 128-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2020010
Haque MA, Hossain MS, Sayed NMA, Islam MT, Khan MR, Ahmmed F, Zohora FT, Ağagündüz D, Ming LC, Capasso R. Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench Pod Extract Revealed Antagonistic Effect against the Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Metformin and Acarbose upon Concomitant Administration in Glucose-Induced Hyperglycemic Mice. Biologics. 2022; 2(2):128-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Md. Anamul, Md. Sanower Hossain, Nur Muhammad Abu Sayed, Mohammad Touhidul Islam, Md. Robin Khan, Foyez Ahmmed, Fatama Tous Zohora, Duygu Ağagündüz, Long Chiau Ming, and Raffaele Capasso. 2022. "Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench Pod Extract Revealed Antagonistic Effect against the Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Metformin and Acarbose upon Concomitant Administration in Glucose-Induced Hyperglycemic Mice" Biologics 2, no. 2: 128-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2020010
APA StyleHaque, M. A., Hossain, M. S., Sayed, N. M. A., Islam, M. T., Khan, M. R., Ahmmed, F., Zohora, F. T., Ağagündüz, D., Ming, L. C., & Capasso, R. (2022). Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench Pod Extract Revealed Antagonistic Effect against the Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Metformin and Acarbose upon Concomitant Administration in Glucose-Induced Hyperglycemic Mice. Biologics, 2(2), 128-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics2020010










