Abstract
A growing international consensus holds that science education must advance beyond content coverage to cultivate robust understanding of the Nature of Science (NoS)—how scientific knowledge is generated, justified, revised, and socially negotiated. Yet naïve conceptions persist among students and teachers, and effective, scalable classroom strategies remain contested. This narrative review synthesizes research and practice on games and playful activities that make epistemic features of science visible and discussable. We organize the repertoire into six families—(i) observation–inference and discrepant-event tasks; (ii) pattern discovery and rule-finding puzzles; (iii) black-box and model-based inquiry; (iv) activities that dramatize tentativeness and anomaly management; (v) deliberately underdetermined mysteries that cultivate warrant-based explanations; and (vi) moderately contextualized games. Across these designs, we analyze how specific mechanics afford core NoS dimensions (e.g., observation vs. inference, creativity, plurality of methods, theory-ladenness and subjectivity, tentativeness) and what scaffolds transform playful engagement into explicit, reflective learning. We conclude with pragmatic guidance for teacher education and curriculum design, highlighting the importance of language supports, structured debriefs, and calibrated contextualization, and outline priorities for future research on equity, assessment, and digital extensions.
1. Introduction
In the past decades, a broad international consensus has emerged around the need to move science education beyond rote content coverage and into the terrain of epistemic understanding: how scientific knowledge is generated, validated, revised, and situated within human communities. Major curricular reforms have foregrounded the Nature of Science (NoS)—which encompasses the epistemology, practices, social processes, and cultural values of science—as a central pillar for developing scientific literacy [1,2]. Scientific literacy for the twenty-first century demands not only familiarity with scientific facts and theories, but also an appreciation for the habits of mind and forms of reasoning that distinguish science from other ways of knowing [3,4,5].
Despite the rhetorical prominence of NoS in policy documents and teaching standards, research continues to show that both students and teachers often hold fragmented or naïve conceptions of what science is and how it operates. Multiple studies have documented persistent misconceptions about the tentativeness, creativity, and social dimensions of science among learners and educators, even after instruction [6,7,8]. Many view scientific progress as a linear, methodical pursuit of absolute truth, rather than as a dynamic, creative, and communal enterprise shaped by uncertainty, debate, and negotiation. These misconceptions persist even after traditional instruction, raising fundamental questions about the limitations of didactic, content-driven approaches to science education [9,10].
Parallel to this, a vibrant field of research and practice has explored the use of games and playful activities as vehicles for learning science. Recent reviews highlight the growing interest in game-based and playful learning as strategies to boost engagement and foster deeper understanding in science education [11,12]. The present review synthesizes current research and practical guidance on the use of games and playful activities to teach the NoS in ways that are explicit, reflective, and robustly aligned with the consensus principles outlined above. The review used purposive searching and iterative snowballing to identify classroom-ready games and playful activities that explicitly target NoS learning goals. Searches were conducted in Scopus, Web of Science Core Collection, ERIC, and Google Scholar and backward citation tracking, complemented by targeted browsing of professional association repositories and open curricular archives (gray literature). Core queries combined “nature of science” with terms such as “game,” “playful,” “simulation,” “card game,” “rule-finding,” “black box,” “observation–inference,” alongside specific titles (e.g., “Eleusis”, “Wason rule” “black-box modeling”). Inclusion prioritized explicit alignment with widely accepted NoS dimensions and replicability with typical school resources. Exclusions removed entertainment-only games lacking NoS alignment. The sources synthesized span from 1959 to 2025, covering both seminal foundational work and contemporary research. Selection prioritized activities with documented classroom implementation and explicit epistemic alignment. As a narrative review, this synthesis emphasizes critical interpretation, identification of patterns and gaps, and pragmatic guidance for practice, rather than exhaustive systematic coverage.
Ultimately, our aim is to clarify which playful strategies best serve particular epistemic goals, under what conditions, and with what forms of scaffolding. We argue that when designed and implemented with intention and reflection, games and playful activities have the power to transform science classrooms into genuine communities of inquiry—spaces in which students do not merely learn about science, but experience and internalize its foundational practices, values, and ways of thinking. The article concludes with a synthesis of how these activities map onto the key principles of the NoS, and with recommendations and prospects for sustaining innovation and equity in science education.
2. Theoretical Background
The NoS is a well-established area within science education, focusing on knowledge about what science is and how it operates. It represents a form of metaknowledge developed from multiple disciplines, emphasizing ontological, epistemological, and social aspects [6]. According to several authors [2,13], NoS topics are organized into two main dimensions: cognitive-epistemological and social-institutional. For the purposes of this review, the NoS is conceptualized in line with the synthesis proposed by Bell [14], who identifies a set of key principles widely endorsed in the literature. These include the tentativeness of scientific knowledge and its empirical grounding; the distinction between observation and inference; the recognition that scientific theories and laws are different types of knowledge, with neither subordinated to the other; the fact that science is not governed by a single, universal method, but rather encompasses a variety of approaches; the central role of creativity and imagination in scientific practice; and the understanding that, although science strives for objectivity, subjectivity—arising from individual backgrounds, perspectives, and social context—inevitably shapes scientific activity [5,14,15]. These principles provide a contemporary framework for addressing NoS in educational settings.
Despite broad agreement on the importance of NoS, the literature identifies several persistent challenges in its teaching and learning: the high cognitive demand involved, which requires the use of sophisticated thinking skills; the insufficient understanding of NoS among teachers, which is often linked to their own educational backgrounds; and the scarcity of effective didactic resources [16]. A particularly salient issue in science teacher education is that preservice teachers—both at the elementary and secondary levels—typically enter their training with naïve or mixed views of the NoS [17,18,19,20]. These initial perspectives commonly overemphasize factual knowledge and scientific procedures, and tend to adopt a positivist or realist stance, often underappreciating the tentative, creative, and social dimensions of science [21,22]. Common misconceptions include the belief in a universal scientific method, the expectation that theories eventually become laws, and a limited awareness of the sociocultural context of scientific activity [8,17,18]. Research has shown that explicit, reflective approaches to NoS instruction can foster significant improvements in preservice teachers’ conceptions [23,24,25]. Nevertheless, certain misunderstandings, especially regarding the distinction between scientific theories and laws or the institutional and social character of science, often persist even after targeted intervention [8,20,22]. Collectively, these findings highlight the ongoing need for sustained and targeted NoS education in teacher preparation programs, since the persistence of simplistic or fragmented views among future teachers risks perpetuating distorted images of science in subsequent generations of students [19,25].
Laboratory activities are traditionally used to address NoS [4]. However, some studies argue that such activities may not be effective, as they tend to generate only short-term interest [26]. Other conventional approaches, such as the integration of historical case studies [27], the analysis of socioscientific issues [28,29], newspaper articles [30], inquiry-based learning [31] or problem-based learning [32], have been proposed as alternative means to make NoS concepts explicit and meaningful to students. Yet, as highlighted in recent research, these approaches often face limitations regarding student engagement, depth of conceptual change, and their translation into classroom practice [10,30].
In response to these limitations, recent studies [11,33,34] suggest that games may provide a promising context for addressing NoS in science education, offering a more interactive and motivating framework for learning. A game can be defined as “an action or a set of actions, that includes one or more people, objects, or animals, usually in competition with others, that follow a specific set of rules, in order to achieve a goal” [35], p. 16. Various authors have argued that games, by their very nature, can foster environments in which students are invited to negotiate rules, explore alternative explanations, experience uncertainty, and engage collaboratively—features that mirror core aspects of scientific practice and the epistemology of science [33,34]. Nevertheless, systematic research on the actual mechanisms by which games facilitate epistemic learning remains scarce. For instance, Li and Tsai [36] analyzed thirty-one studies on digital science games and found that none addressed epistemic learning about scientific practice. Similarly, Arztmann et al. [37], in their review, did not identify a single epistemic game at any educational level, further underscoring the lack of resources specifically designed to teach NoS through games.
Game-based learning (GBL) can be defined as the use of digital or analog games for expected learning outcomes [38,39]. Whereas some authors argue that games are not superior to traditional methodologies in terms of learning outcomes [40,41], some others defend their potential to enhance learning and educational outcomes [42,43,44]. The use of games in education has been associated with increased motivation, engagement, adaptability, and the capacity for “graceful failure” [45,46], and this heightened excitement and motivation could translate into improved learning performance [38,47], learning persistence, and self-efficacy [48,49]. GBL has been shown to be particularly effective in developing skills such as critical thinking, creative thinking skills, interpersonal communication, and debating [50,51], while also fostering environments where failure is perceived as an opportunity, thus encouraging risk-taking and exploration [52]. Moreover, games provide an ideal setting for collaborative learning [53].
Despite these advantages, several barriers hinder the generalized implementation of GBL: behavioral and attitudinal obstacles, school policy limitations, material and technological restrictions, and issues related to game literacy [54]. Some teachers seldom incorporate games into their daily practice [55,56], which may be explained by their lack of skills and familiarity with this methodology [57,58]. Designing or using a game in an educational context is not a simple endeavor [59]. Educational games require careful planning to ensure effectiveness, balancing the need to achieve learning objectives while simultaneously providing a high-quality gameplay experience [60]. For this reason, adequate training in the use of this methodology is essential within teacher education programs. Connecting GBL to specific disciplines may also be necessary, as one of the main criticisms of this methodology is that it often lacks sufficient depth and adequacy in addressing content knowledge [61].
GBL offers a promising approach to improve both science teaching and learning [62,63,64]. Although GBL has been widely used to support science education [65,66], its mechanisms and effects are still not fully understood and this situation might lead to non-effective implementations [67,68]. Previous literature indicates that the initial interest in GBL’s potential to improve science education was centered on content acquisition [12,36], but in recent years this interest has expanded to include motivation and general perceptions, while topics such as cooperative learning, problem-solving skills, and communication skills have begun to gain prominence [12]. Several studies have reported positive effects of games in science education, including improvements in learning [63,69,70], motivation [71], attitudes [72], engagement [73], and self-efficacy [74]. One reason why the connection between science and games appears so natural is that both align with experiential learning theory [75], where learning is experiential, exploratory, and problem-based [76]. In their review, Cadiz et al. [11] noted that the most popular game-based approaches in science education are strategy games and role-playing. The same authors found that the most frequently studied outcomes of GBL in science were knowledge attainment and motivation, while skill attainment and reflection were much less frequently addressed. Given that critical thinking and problem-solving skills are essential for preparing students to face the challenges of the 21st century, innovative methodologies such as GBL should prioritize their contribution to the development of these competencies.
Beyond game-based learning, the broader concept of playful learning has gained prominence in educational research as an approach that deliberately incorporates elements of play to enhance engagement, motivation, and creativity in the learning process. The literature indicates that playfulness is assumed to have positive effects on learning [77], and recent work further clarifies that playful learning encompasses, but is not limited to, game-based environments—it also includes activities that integrate game-like features such as challenge, feedback, narrative, and positive framing of failure [45,78]. This expanded perspective recognizes that playful activities, even when not structured as complete games, can foster deeper learning and support the development of skills crucial for 21st-century science education.
Given the persistent challenges in NoS education—high cognitive demand, teacher misconceptions, and scarcity of effective resources—games and playful activities offer pedagogically aligned responses. By embedding epistemic reasoning in experiential, collaborative contexts, playful approaches can make abstract NoS principles concrete, discussable, and memorable. The following section presents six families of activities that operationalize this potential.
3. Games and Playful Activities to Learn About the Nature of Science
This section gathers a repertoire of classroom-ready games and playful tasks that make core NoS principles observable in action—from the empirical–inferential distinction and the role of evidence to creativity, tentativeness, methodological plurality, and the communal negotiation of claims (see [14]). The activities are organized by epistemic emphasis rather than difficulty or a recommended sequence: some surface how learners separate observation from inference; others foreground pattern seeking and rule discovery; still others center on modeling hidden mechanisms, coping with anomalies and unresolved cases, or working within moderately contextualized disciplinary settings. Across all families, structured debriefs are essential (as discussed in Section 2), transforming gameplay into a vehicle for naming the targeted NoS ideas and connecting them to students’ prior knowledge and to ongoing science units.
3.1. Playful Approaches to Observing and Inferring
A crucial entry point for NoS instruction is helping students distinguish between observation and inference [79]—a foundational skill for scientific thinking. This section presents a progression of playful, low-cost activities that are especially effective for introducing and reflecting on these concepts. By engaging with surprising demonstrations, indirect evidence puzzles, and role-played argumentation, learners confront the limits of perception, grapple with theory-laden explanations, and experience firsthand how scientific reasoning is built on the iterative interplay between what is observed and what is inferred.
Discrepant-event demonstrations [80] such as the “burning candle” [81] and “crazy ketchup” [81] offer memorable entry points. In the first, learners are invited to record “observations” about what appears to be a lit candle, only to discover at the reveal that it is actually a piece of string cheese with an almond sliver for a wick. In the second, a squeeze bottle rigged with hidden yarn creates the illusion of an erupting ketchup mess; students must reconsider which statements truly described what they saw versus what they inferred. Parallel logic is found in the “fake plant” activity [82], where a highly realistic silk plant prompts students to list characteristics, many of which—such as scent, photosynthesis, or the presence of roots—are revealed to be inferences after the plant is pulled from the pot. Similarly, in “raisidia” [82], students view raisins dancing in a clear, carbonated drink from a distance and are prompted to observe these mysterious “creatures”. Many students ascribe agency or intent—“diving,” “swimming”—that, upon closer inspection, turn out to be narrative inferences rather than direct observations. Each of these cases culminates in structured discussion about the empirical basis of claims, the theory-ladenness of perception, and the tentativeness of conclusions, making visible how easily inference masquerades as observation and highlighting the need for public criteria and reflective dialogue to discipline the observation–inference boundary.
Building on these concrete experiences, learners are prepared to grapple with more open-ended puzzles based on indirect evidence. The classic “track stories” sequence [83] presents three successive panels of fossil-like footprints (see image in [84]) and asks students to reconstruct what happened, updating their explanations as new but still incomplete evidence appears. The task is purposely designed to allow for several defensible hypotheses, and the iterative cycle of hypothesis, test, and revision echoes the logic of historical sciences, where only traces remain. Modern versions of this activity, such as “Tricky Tracks,” refs. [85,86] are specifically designed to also make students confront the difference between inference and observation. At the start of the activity, students are given only the first panel of animal footprints and are asked to write a brief account of what they think happened, thus encouraging them to propose an explanatory narrative based on incomplete evidence. As the activity progresses, students are then shown the second panel—so they now have access to both the first and second parts of the track sequence—and are prompted to describe what they can observe in the newly revealed section. This instruction often reveals their tendency to blend inference with observation. Finally, with all three panels visible, students are asked to distinguish between their direct observations and further inferences, and to consider whether any conclusion about what truly happened can ever be certain, or what further information might be needed. A recent gamified adaptation [87], situates the task within a narrative context to increase engagement and support collaborative argumentation about the meaning of evidence, all while preserving the epistemic rigor of the original activity. This carefully sequenced structure helps learners become aware of how scientists draw on indirect evidence, how multiple reasonable explanations can fit the same data, and why scientific conclusions remain tentative and subject to revision as new evidence becomes available [86,88].
As a culminating move in this strand, The Card Exchange is a negotiation-based learning game developed by Cobern [89] and further refined by Cobern and Loving [90,91], designed to introduce the diversity of perspectives on the NoS and to stimulate explicit debate around what counts as science. In this activity, participants circulate and trade cards containing concise, sometimes contrasting statements about science—spanning theoretical, empirical, scientistic, cultural, and pragmatic viewpoints—then negotiate in pairs and small groups to reach consensus, culminating in a collaboratively authored statement about the NoS and a whole-class discussion. The game’s deliberate inclusion of competing perspectives fosters awareness of diversity within scientific worldviews and encourages compromise and reflective argumentation, serving as a powerful set induction for deeper NoS instruction and often followed by analysis of historical case studies (e.g., Semmelweis, Newton) that anchor abstract claims in scientific practice [90,91]. However, research by Allaire [92] revealed that the density and vocabulary of the statements sometimes hinder participation, leading to the successful integration of literacy scaffolds such as statement previews, small-group paraphrasing, and class-wide negotiation of meanings. Allaire’s empirical study found that these strategies both enhanced engagement (over 80% of participants “strongly agreed” that the supports improved the experience) and preserved the game’s dialogic and reflective aims, making Card Exchange an even more effective and inclusive entry point for NoS exploration in teacher education.
Together, these activities move learners from controlled, memorable surprises to more complex reasoning with indirect evidence, laying a foundation for appreciating core dimensions of the NoS: the empirical–inferential distinction, the tentativeness and revisability of claims, the creative construction of explanations, and the need for public, communal negotiation of knowledge.
3.2. Discovering Patterns and Principles
Beyond tasks focused on observation and inference, another family of playful logic puzzles and games centers on the identification and testing of hidden patterns or “rules” within complex systems, illustrating how scientists move from isolated observations to generalizable principles.
Petals Around the Rose [93] is a classic inductive puzzle in which a facilitator repeatedly rolls five standard dice (physical or online [94]) and announces the result for each throw; players must infer the underlying rule without it being stated, with the hint that the name of the puzzle is significant (Figure 1). The answer for each roll is determined by counting only the dots (“petals”) that surround the central dot (“the rose”) on each die: dice showing 3 contribute two petals each (the dots adjacent to the center), dice showing 5 contribute four petals, and all other faces (1, 2, 4, 6) contribute zero petals—since either they lack a central dot or have no dots around “the rose”.

Figure 1.
Petals Around the Rose. Example dice roll for which the result is 6.
Traditionally, the activity is considered complete only when a participant is able to predict the correct answer on six consecutive rolls—a threshold that demonstrates genuine mastery of the underlying rule rather than accidental success. In classroom settings [95], this “six-in-a-row” criterion allows teachers to challenge participants to make public predictions while keeping their inferred rule private after success, thereby preserving the discovery experience for their peers. By ensuring that the solution is not immediately revealed, all participants remain engaged in hypothesis generation and testing until multiple students independently reach the solution.
The Wason rule discovery puzzle [96] presents learners with an apparently simple sequence—such as “2, 4, 6”—that obeys a hidden rule. Participants propose their own triples, receiving only yes/no feedback, and are invited to guess the rule once confident. The original study found that most participants, including highly intelligent adults, sought only to confirm their initial hypotheses (e.g., “numbers increasing by two”), rarely attempting to falsify them through counter-examples. This “confirmation bias” led many to incorrect or overly narrow solutions, and often to their astonishment, the actual rule may be far more general—for example, “any increasing sequence of numbers.” This outcome demonstrates how reliance on positive instances alone can impede genuine conceptual understanding. Instead, scientific progress relies on attempts to eliminate or falsify competing hypotheses, a logic mirrored in the task when participants test triples that might disconfirm their assumptions [96,97]. Recent empirical work [98] showed that when logic puzzles inspired by Wason’s task are embedded in explicit-reflective NoS programs, preservice teachers significantly improve their understanding of scientific reasoning and bias, especially regarding the importance of testing and revising claims.
Building on these logics, Eleusis is a card game invented by Robert Abbot in 1956 [99] and revised in 1977 [100], in which one player acts as “Nature” and secretly defines a rule that determines which card plays are accepted. Other players submit cards in turn, attempting to discover the rule by observing which plays are accepted onto the mainline and which are rejected to the sidelines. As illustrated in Figure 2, the mainline displays the sequence of cards that correctly follow the dealer’s hidden rule (in this example, alternating spades and hearts, each exactly two higher than the previous card), while cards placed below the mainline (sidelines) represent incorrect attempts that did not satisfy the secret pattern and were thus rejected, creating a transparent record of both supporting and contradicting cases. At any point, a player who believes they have discovered the rule may declare themselves “Prophet” and take over the role of judging subsequent plays [101]. The dynamics of play require participants to generate hypotheses, test predictions, revise their thinking in response to new evidence, and defend their reasoning. This process operationalizes a hypothetico-deductive approach, mirroring how scientific theories are articulated, tested, and revised within a community [102]. Eleusis Express (Figure 2)—developed by John Golden—distills the core mechanics by removing the Prophet and allowing any player to state the rule publicly immediately after a correct play; the dealer confirms or denies on the spot, and a correct conjecture ends the hand [103]. Speed Eleusis is a version that accelerates play and, distinctively, introduces the possibility for Research Teams to “publish” their proposed rules, “replicate” the published rules of other teams if they agree, or “retract” prior claims if subsequent evidence undermines them, thereby closely mirroring the communal, competitive, and self-correcting features of real scientific practice [104]. Classroom research shows that with Eleusis and its variants, learners can map game roles and moves onto features of scientific practice [105], report high engagement and measurable improvements in students’ abilities to formulate hypotheses, interpret evidence, and argue from data [16], and achieve gains in NoS dimensions related to subjectivity and communal knowledge building [106].
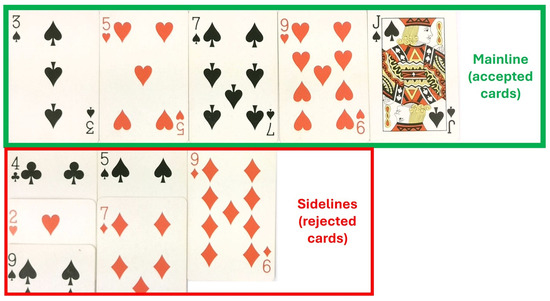
Figure 2.
Eleusis Express. Example from a round with the dealer’s secret rule: alternating spades and hearts, each exactly two higher than the previous card.
As digital technologies expand the landscape of playful science learning, digital games offer new opportunities to advance NoS instruction for younger learners. A notable example is Snatch and Hatch, a story-driven mobile application that immerses children in sensor-based inquiry and cultivates core scientific practices such as empirical testing, creativity, and collaborative model revision [107]. In the game, players help “Professor Yuni” capture and hatch virtual creatures using real-world sound amplitude, measured via the device’s microphone. Gameplay centers on hypothesis generation, empirical testing, and iterative model revision, with children using environmental sounds to trigger outcomes and reflecting on their discoveries. The design explicitly scaffolds NoS principles—emphasizing the empirical and tentative character of science, creativity, methodological plurality, and the social dimension of knowledge-building. A multi-day evaluation with children aged 8–12 [107] found that Snatch and Hatch was highly motivating, fostered sustained engagement, and improved attitudes toward science; children could articulate key scientific ideas such as the role of evidence and the tentativeness of results.
Taken together, this sequence of games and puzzles moves students from isolated pattern-seeking and confirmation bias toward increasingly sophisticated, collaborative, and reflective engagement with the processes of science. These playful tasks not only mirror key dimensions of scientific practice—hypothesis testing, evidence evaluation, theory revision, and communal argumentation—but also foster transferable habits of mind that underpin genuine NoS understanding.
3.3. Inferring the Invisible: Black-Box Activities and Model-Based Reasoning
Building on the logic of pattern-discovery games—which reveal how scientists formulate and test explicit rules—black-box (or mystery box) activities shift the epistemic challenge to inferring hidden mechanisms from observable outcomes. Instead of seeking a surface rule, learners are confronted with opaque systems whose internal workings cannot be directly observed. These hands-on tasks require students to generate, test, and revise models solely on the basis of indirect evidence, thereby foregrounding the role of modeling, the empirical–inferential distinction, the tentativeness of explanations, theory-laden observation, and the social negotiation of claims [15].
Canonical implementations demonstrate that progress depends on cycles of hypothesizing, testing, and model revision rather than on a single “scientific method,” and that more than one internally coherent model can fit the same data. Pragmatically, teachers can fabricate sturdy “inquiry boxes” from shoeboxes by gluing internal baffles and adding a marble—an inexpensive, PD-friendly build that centers indirect evidence and modeling [82,108] or can opt for commercial solutions such as the Lab-Aids’ Ob-Scertainer® (“A Better Black Box”, Figure 3a), which reproduces the shoebox logic in sealed black plastic Petri dishes, containing a small steel ball and dividers, and students tilt the dish from side to side to infer what the divider pattern is [109,110,111]. When these tasks are gamified or embedded in narrative-rich settings [87,112], black boxes shift from merely playful activities to gameful experiences (storyline, time pressure, competition) that heighten motivation and make public reasoning more salient. Recent work [113] has highlighted the epistemological value of explicitly discussing the explanatory limits of black boxes in the classroom, helping learners manage uncertainty and understand the inherent underdetermination of scientific inference. This versatility extends to professional development and all school levels, as teachers can adapt designs to their context and resources.

Figure 3.
Three types of black-box (mystery box) designs. (a) Commercial Ob-Scertainer® device, showing both the closed and open configurations. (b) Station-based mystery boxes with post-its. (c) A homemade mystery tube.
Two design norms are especially instructive: first, the box should remain closed—“answers” are neither revealed nor uniquely determined—so that students confront uncertainty and scope limits of models; second, as emphasized previously, guided reflection is required if NoS learning is to move beyond naïve or episodic understandings [15,114]. Further, portfolios that deliberately vary evidence types and access—such as station-based mystery boxes with post-its that scaffold phased clue-release and collaborative modeling (Figure 3b) [115] or advanced twists that add constraints and new probes in secondary settings [116]—show how instructional design can engineer anomalies and ambiguity to force model revision without ever opening the box. Extensions that add new forms of evidence (e.g., X-ray images of sealed boxes) clarify that novel instruments can both illuminate and complicate inference at once [117], fueling debate over how communities adjudicate competing models. At the primary level, lesson-study implementations of black-box games report high engagement and productive, evidence-based argumentation, underscoring feasibility for early NoS instruction [118].
A widely used entry point is the Mystery Tube (Figure 3c), where rope motions at the tube’s exterior are produced by a hidden internal linkage; students record observations, propose and test models (often building physical replicas), and publicly defend revisions in light of anomalies [15,81,114,119]. For more advanced learners, activities can incorporate added constraints and hidden elements, as in more challenging tube variants—which sustain iteration and underscore underdetermination, since multiple interior designs can reproduce the same behavior, and highlight the value of peer critique—and, notably, classes coupling this activity with explicit NoS discussion have outperformed comparison groups on standardized NoS measures [120].
Another effective approach is the Water Black Box [121,122], a process-rich modeling task with hidden tanks or siphons that yield non-obvious outputs—whether using physical apparatus or dedicated digital simulations [123]; this supports analysis of modeling strategies and produces measurable gains in meta-modeling knowledge when paired with reflection [121,122]. Recent research further deepens this line by unpacking alternative internal mechanisms and the mechanistic explanations they elicit, showing how students’ reasoning adapts as hydraulic system complexity scales [124].
Similarly, in the Cube activity, learners infer the hidden face of a six-sided dice from the visible pattern on the other five faces, publicly justifying competing models and revising them as counter-examples emerge [15,86,111]. Finally, another parallel epistemic challenge is posed by the Magic Glue activity [109,110], in which students observe a mysterious adhesive effect whose causal mechanism is concealed and must be inferred; using a CER (claim–evidence–reasoning) argumentation scaffold [125], teams advance rival mechanistic accounts, design discriminating tests, and argue why particular observations count as evidence for (or against) each claim.
Black-box activities powerfully demonstrate how scientists construct models from incomplete evidence. Together, these designs afford discussion of observation vs. inference, creativity in modeling, plurality of methods, tentativeness, and the communal character of validation—precisely the NoS dimensions emphasized in contemporary science-education frameworks.
3.4. Teaching Tentativeness
A foundational dimension of the NoS is the tentativeness of scientific knowledge: the recognition that explanations are always provisional and subject to change as new evidence emerges or unexpected results challenge prevailing models. The Extra Piece activity [126] offers a compelling analogy for the creative, tentative, and communal nature of scientific work. In this puzzle, each learner first arranges a set of tangram pieces (representing current scientific data) into a perfect square (Figure 4a). The facilitator then introduces an additional piece—framed as a new discovery—which prompts learners to reconstruct the square to accommodate the new piece (Figure 4b). Typically, students begin individually and then move to group collaboration as challenges arise, highlighting the role of dialogue, flexibility, and collective problem-solving. Throughout the process, assembling the square stands in for building scientific explanations, while the surprise piece dramatizes how science must adapt to new evidence, requiring trial-and-error, resilience, and open discussion. This sequence mirrors how scientific models are revised in response to new evidence.
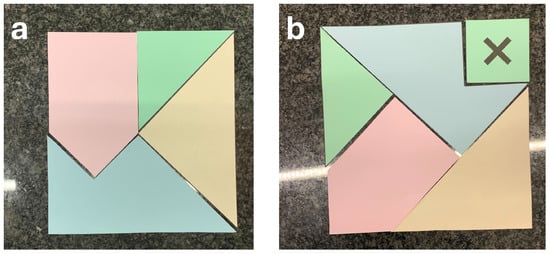
Figure 4.
The Extra Piece activity. (a) Initial solution with original tangram pieces; (b) revised solution when a new piece (marked X) is introduced.
Several instructional elaborations build on this core activity. For example, in one of these variations [127], groups receive different incomplete piece-sets and assumptions, attempt to build the most symmetric figure possible, and then face a mid-task change as a new piece is added. Groups must decide whether to assimilate, reorganize, or ignore the new data, then “publish” and compare their models—a direct parallel to scientific prediction, theory-ladenness, peer critique, and community validation. Another implementation [82] employs strict communication constraints and distributed tangram envelopes, foregrounding teamwork and the need to revise hypotheses for collective progress. Globally, the Extra Piece and its variants powerfully illustrate the interplay of observation and inference, the limits of empirical evidence, the plurality of scientific methods, creativity, theory-ladenness, tentativeness, and the vital role of consensus and critique in the scientific enterprise.
3.5. Unresolvable Mysteries
While the Extra Piece (and other tangram puzzles) underscores model revision in the face of new evidence, it carries a potential limitation: by design, all pieces ultimately fit to form a perfect square—potentially leaving learners with the misleading impression that scientific problems always yield complete, coherent solutions if only one searches long enough. This “closure bias” does not align with the NoS, where evidence is often incomplete, explanations remain open to revision, and some puzzles resist definitive resolution.
The Checks Lab activity [128] directly addresses this epistemic gap. Here, learners draw random batches of checks from a larger set, using these incomplete records to construct a plausible narrative about what occurred. As new checks are revealed, groups revise or sometimes abandon their initial hypotheses. The task cultivates skills in reasoning from indirect evidence [129]: claims are warranted not by eyewitness access to events but by traces whose probative force grows when multiple pieces of evidence cohere—while still falling short of certainty. Crucially, the set of available evidence is always insufficient to determine a single, correct story—different groups may select different checks and construct divergent but plausible explanations. The activity is framed as an analogue for historical sciences (e.g., geology, forensics), where only fragmentary traces remain and consensus emerges from debate over the “most warranted” explanation, not absolute truth.
Building on this design, The E-mail Lab [130] updates the medium: groups receive curated emails instead of checks. This format not only modernizes the artifact set but also further emphasizes skills such as evaluating source credibility, handling conflicting messages, and negotiating group interpretations as new information surfaces. Because interpreting indirect evidence is inevitably theory-laden, debriefing should make explicit the assumptions students bring to the records and how communities adjudicate among plausible narratives [129]. Instructors prompt students to “publish” their evolving hypotheses, critique others’ accounts, and iteratively adjust their conclusions as additional emails are disclosed—making the tentativeness and social negotiation of scientific knowledge explicit [130].
The Case of the Missing Computer Chip [131] takes this concept further by embedding it in a detective narrative, with layers of uncertainty and choice. Teams receive a map of the scene and a packet of 14 clues. In the first round, groups draw five clues at random, construct a tentative hypothesis, and record their reasoning. In subsequent rounds, they draw three more clues, prompting them to revisit and revise their explanation, always aware that different teams have access to different evidence subsets and will likely reach different conclusions. A key innovation is that, at a certain stage, groups are given the option (but not the obligation) to share clues with another team—a direct analogy to scientific collaboration and selective information sharing. The clues themselves vary in reliability: some are robust forensic reports, others are potentially unreliable witness statements or motives, and some are ambiguous. Students are challenged to debate the credibility and relevance of each clue, weighing how strongly each supports their hypothesis. Importantly, even after all rounds, not all clues are used and there is no solution key—the activity is deliberately underdetermined, and groups must justify the best-supported account possible with the available information. Empirical research with preservice teachers has shown the power and educational value of this approach. In one study [132], a recurrent pattern was premature closure: most groups ultimately indicted a suspect even while acknowledging that the evidence was insufficient or conflicting—an instructive manifestation of the closure bias discussed earlier. In another higher-education setting, the same mystery was adapted as part of a Harry Potter–themed course arc, further motivating reflection on scientific uncertainty and the handling of unresolved evidence [133].
Taken together, these games and playful activities vividly illustrate the theory-ladenness and subjectivity of scientific interpretation, as different teams often reach different conclusions from similar data [79]. The processes of clue sharing, argumentation, and public negotiation dramatize the communal and negotiated character of scientific knowledge. Most distinctively, by ensuring that some puzzles cannot be definitively solved—even after thorough investigation—these designs powerfully underscore the limits of science and highlight the centrality of seeking the “most warranted” explanation, rather than a single “final” answer.
3.6. The Power of Moderately Contextualized Playful Activities
The games and playful activities discussed in Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.3, Section 3.4, and Section 3.5 are, by design, largely decontextualized—they offer powerful simulations of reasoning, model construction, or argumentation, but are not anchored in specific disciplinary content or authentic scientific cases. This decontextualization is both a strength (allowing focus on core epistemic processes) and a limitation, as students may perceive them as “not real science” unless instructors scaffold explicit connections to scientific content or stories. Activities that are moderately contextualized—embedding epistemic reasoning within historical narratives or authentic practices—are especially effective for bridging this gap [134].
Extending the epistemic thread from Section 3.5—where the limits of evidence and the possibility of non-closure were foregrounded—while anchoring reasoning in disciplinary chemistry, a domain-authentic illustration is the classic mystery powders investigation. In its standard form [135,136], students analyze a set of common white powders (e.g., sodium bicarbonate, cornstarch, ascorbic acid, sodium chloride) using a magnifying glass to observe their physical properties, followed by systematic testing with three reagents: vinegar, iodine solution, and water (Figure 5). By carefully comparing the observable reactions of each known substance, learners establish diagnostic patterns. These tests are then repeated on an unknown white sample, which may correspond to one of the previously studied substances, a new substance, or a mixture. Students are thus challenged to identify unknown substances based on their observable properties and chemical reactivity, constructing evidence-based claims that mirror core scientific practices such as observation, inference, and argumentation from evidence [129,137]. Recent implementations convert this task into a competitive game or narrative-rich challenge [138,139], and some variants introduce a deliberate epistemic obstacle: after characterizing the reference powders, students are confronted with a “mystery” sample that may be or contain a substance not included in the initial set [140]. This design ensures that, even with systematic testing and careful argumentation, definitive identification is not always possible—forcing learners to grapple with uncertainty, acknowledge the limitations of empirical methods, and appreciate that some scientific questions may remain unresolved [14].
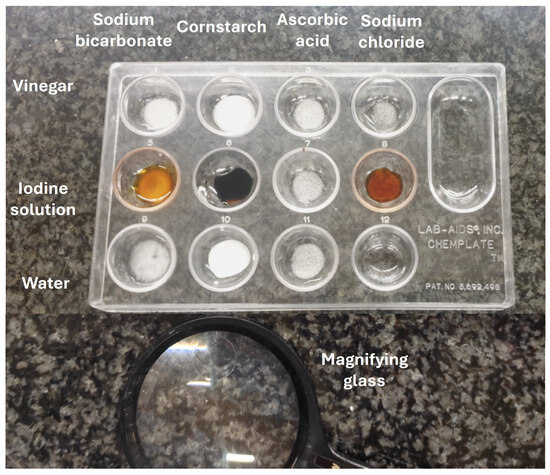
Figure 5.
Mystery powder investigation. Diagnostic reactions of four known white solids—sodium bicarbonate, cornstarch, ascorbic acid, and sodium chloride—are compared with those of an unknown sample.
The Periodic Patterns Puzzle [141] marks a departure from this trend, offering a moderately contextualized activity anchored in the genuine historical and conceptual challenge faced by Mendeleev in constructing the periodic table. Rather than simply sorting items by superficial attributes [142], students must discern multidimensional periodicity, justify leaving principled gaps, and use observed patterns to predict the properties of a missing or unknown element—mirroring the creativity and inferential reasoning at the heart of Mendeleev’s achievement. In this task, students work with cards (the deck can be downloaded from [143]) that are characterized by several independent features, including color, numbers at the top and bottom, a central star whose number varies from card to card, and a variable number of triangles on the right side and holes on the left side; the activity often includes a “misfit” card, compelling students to negotiate what counts as a regularity, and how to deal with apparent anomalies [144]. Instructors usually opt to remove a card from the deck (cards 14 or 19 work well [141,143]), challenging students to predict its properties based on the arrangement of the remaining cards—an explicit analogue to Mendeleev’s strategy of leaving gaps in his periodic table and predicting the existence and characteristics of unknown elements (Figure 6). This puzzle compels learners to coordinate multiple attributes, defend gap-based predictions, and justify why a particular card cannot fit, thus engaging them in complexity, communal negotiation, and the tentativeness and revisability of scientific knowledge—all qualities that align with the true intellectual achievement of Mendeleev and situate the task as a robust platform for NoS instruction [141,144].
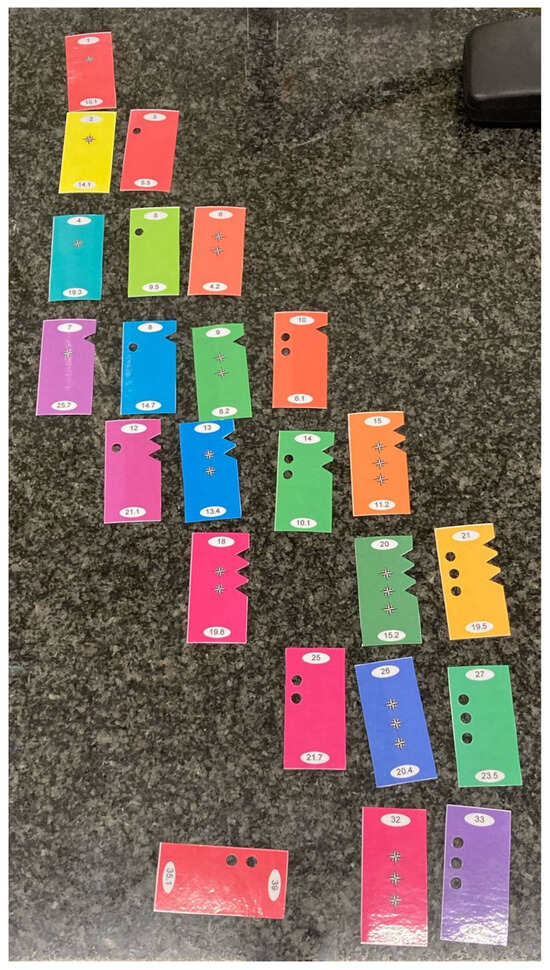

Figure 6.
Example of student work in the Periodic Patterns Puzzle activity. The empty space marks the position of card 19, whose properties must be deduced from its context within the “periodic table” constructed by the group. Card 39, which does not fit any pattern, is excluded.
Beyond its structural and epistemic sophistication, the Periodic Patterns Puzzle humanizes chemistry and brings to life the creative, situated, and social NoS. Instructors can draw on vivid historical narratives—including the journey of Mendeleev and his mother, who rode on horseback across Russia to ensure his education, and the now-classic story of Mendeleev’s inspiration for the periodic table during a long train journey, where his experience as a card player led him to arrange element “cards” to reveal hidden patterns [145,146]. Such stories not only illustrate resilience and serendipity, but also ground the lesson in the authentic, human dimensions of discovery, as emphasized by recent scholarship on the role of historical narrative in science education [147]. The puzzle also invites critical reflection on the status of “laws” in chemistry: while Mendeleev’s periodic law allowed for successful prediction and organization, it was, an interpretative and pattern-based regularity, not a deductive physical law—distinctions that become salient as students encounter exceptions or misfits in their own solutions [148,149,150]. The challenge of leaving gaps and predicting missing cards directly echoes Mendeleev’s strategy of forecasting undiscovered elements, as well as the scientific process of managing anomalies and recognizing when data do not fit a prevailing model [145,146].
Another example of a moderately contextualized game is a board game about the NoS set in the history of astronomy, developed for high school students in Taiwan [151]. In this activity, students take on the roles of scientists and “travel” through key episodes in astronomical history from the 5th century BCE to the 16th century, making and revising claims, interacting in a simulated community of scholars, and experiencing firsthand the process of scientific negotiation and model revision. The intervention, delivered over two hours within a single week to 149 high-school students, combined the board game with a companion app to facilitate gameplay and information sharing. Evaluation with pre–post tests showed a significant improvement in students’ recognition of the creative dimension of science [151].
Lastly, an innovative recent approach to addressing both the History and NoS in initial teacher education is the card game Cronociencia [152]. Adapted from the commercial game Timeline, this teaching sequence invites preservice elementary teachers to collaboratively build two decks of cards: one documenting the historical evolution of a chosen scientific concept and the other containing statements about various aspects of the NoS, each reflecting a range of naive, intermediate, or informed views. The didactic sequence unfolds over several sessions, combining small-group research, synthesis of historical information, and the creative design of playing cards, followed by gameplay in mixed teams. The gameplay centers on reconstructing a chronological sequence of scientific events and classifying NoS statements according to levels of epistemic adequacy, thus prompting discussion, negotiation, and explicit reflection on epistemological themes such as tentativeness, empirical evidence, model evolution, and the social and technological context of discovery. Empirical results indicate that participation in Cronociencia significantly exceeds student expectations, increases motivation and engagement, and is perceived as highly innovative and transferable to future teaching practice [152].
4. Conclusions and Prospects
This review has shown how games (e.g., Eleusis, Card Exchange, Petals Around the Rose, Cronociencia, Snatch & Hatch) and playful activities—when purposefully integrated into science education—can make the core principles of the NoS visible in practice. Across designs, learners are asked to generate and scrutinize observations, advance and defend claims, and revise explanations as new information emerges, experiencing science as an iterative, communal, and creative enterprise rather than a fixed procedure.
Distinguishing observation from inference is at the heart of discrepant-event demonstrations and open-ended modeling tasks. Activities like the burning candle, crazy ketchup, and the fake plant initially prompt students to describe what they see, only to reveal how much of their reasoning is colored by assumption or prior knowledge. In “raisidia”, what appears to be the behavior of living creatures is, upon closer analysis, a product of physical phenomena—provoking reconsideration of what counts as genuine observation. The Tricky Tracks sequence and the cube activity similarly force students to confront how often they infer “what happened” rather than report simply “what is seen,” a realization that becomes central in subsequent argumentation and modeling.
Creativity and imagination are unmistakable in games that require learners to construct, adapt, or invent explanatory models. The logic puzzles of Eleusis and its variants demand that students generate and test candidate rules, learning through failure as well as success. The Extra Piece tangram and the Periodic Patterns Puzzle go further, encouraging exploration of multiple solutions, defense of rival constructions, and even prediction of “missing” elements—recapitulating the imaginative leaps characteristic of discovery. Cronociencia and other timeline-based games place creative synthesis directly in students’ hands, who research and generate the cards that drive collaborative play.
Theory-ladenness and subjectivity emerge naturally as different groups, working with the same materials, arrive at contrasting interpretations. Whether sorting statement cards in Card Exchange, debating the best account for a set of clues in the Missing Computer Chip activity, or prioritizing different features in the Periodic Patterns Puzzle, learners experience first-hand how prior knowledge, perspective, and even preference shape scientific judgment. This diversity of interpretation is not a flaw but a feature of authentic science, which advances through public contestation and refinement of ideas.
The tentativeness of scientific knowledge becomes concrete in activities where new evidence or unexpected results force revision, abandonment, or defense of prior claims. In black-box investigations, students must be ready to discard favored models when new data undermine their fit. Rule-discovery games like Eleusis and its variants explicitly dramatize the provisional status of every claim. Even in contextualized tasks like the Periodic Patterns Puzzle, the deliberate inclusion of misfit cards or the need to leave gaps echoes real scientific practice in managing uncertainty and the limits of current understanding. Mystery powders tasks that incorporate unknowns which cannot be definitively identified reinforce the idea that some scientific problems remain unresolved and invite students to experience the genuine open-endedness and tentativeness that characterizes authentic inquiry.
A plurality of methods is evident across the corpus. Some tasks foreground empirical manipulation and repeated testing (e.g., mystery boxes); others rely on logical deduction and pattern recognition (Eleusis, Petals Around the Rose, Wason’s rule discovery); still others center on historical or creative synthesis (Cronociencia). This diversity helps students appreciate that there is no single “scientific method,” but rather a repertoire of strategies adapted to different questions, constraints, and contexts.
Empirical evidence is foregrounded wherever learners must collect, accumulate, and weigh data before advancing claims. In black-box investigations, Magic Glue and the Checks/E-mail/Chip sequence, students gather repeated observations, design tests, and compare multiple traces to reach defensible conclusions, highlighting that one result is never sufficient. Games like Eleusis and its variants model this principle through public records of trial and error, and the need for revision when counterexamples emerge. Even minimal puzzles, such as Petals Around the Rose and Wason’s rule discovery, reinforce the necessity of seeking disconfirmation across many trials, emphasizing evidence that is systematic, convergent, and open to revision.
The interplay among laws, theories, and models is dramatized in tasks that require students to propose, test, and revise representations of phenomena. Whether modeling the interior of a cube, finding the rule in Eleusis, or justifying a pattern-based “law” in the Periodic Patterns Puzzle, learners are encouraged to see regularities as provisional, subject to revision, and always contingent on available evidence and interpretation. The very structure of many games—requiring explanation, critique, and re-explanation—mirrors the living, evolving character of scientific models and theories.
While this review synthesizes a broad repertoire of classroom-ready activities for NoS instruction, it does not claim comprehensive coverage of all possible playful or game-based approaches, nor does it systematically evaluate their empirical impact across contexts. The selection of activities is based on documented epistemic alignment and practical feasibility, rather than exhaustive experimental evidence. As such, the effectiveness and transferability of each approach may vary depending on context, teacher expertise, and student characteristics. These limitations highlight the need for ongoing empirical investigation and critical evaluation of playful approaches in diverse educational settings.
Looking ahead, two priorities stand out for both practice and research. First, there is a need to calibrate contextualization: decontextualized puzzles can efficiently surface core reasoning, while moderately contextualized designs—anchored in historical cases or disciplinary content—deepen meaning and support transfer, provided cognitive load is well managed. Sequencing from observation–inference tasks to hidden-rule discovery, model-based black boxes, and then contextualized cases offers a pragmatic staircase that progressively increases demands on evidence coordination and social negotiation. The second priority is to make the explicit–reflective layer non-negotiable: short, named debrief routines (such as claim–evidence–reasoning, model-comparison protocols, or public criteria for “what counts as evidence”) should be deliberately planned with the targeted principle in mind, as learning gains consistently hinge on these moments of metacognitive consolidation.
Building on these priorities, future work should focus on refining principle-aligned assessments capable of capturing growth within specific NoS dimensions, as well as on developing accessible language scaffolds and logistical templates—such as station guides or clue-release scripts—to broaden uptake across diverse learners and settings. In addition, research should explore digital and narrative extensions not merely for engagement, but to simulate communal processes such as publication, replication, and the adjudication of competing claims. Finally, centering equity and inclusion is essential, ensuring that all students can participate in, and see themselves within, the communal enterprise of scientific knowledge building. Used intentionally, the designs reviewed here can do more than teach about the NoS; they can cultivate the habits of mind, resilience, and curiosity that sustain scientific inquiry.
Ultimately, these playful, principle-informed approaches do not merely enhance science lessons; they have the potential to foster a deeper scientific literacy—empowering future citizens to navigate a world shaped by evidence, uncertainty, and collective reasoning. When thoughtfully implemented, such experiences can transform science education from rote learning into an invitation to participate authentically in the ongoing human endeavor of making sense of the world.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.J.-V. and N.F.-M.; methodology, G.J.-V. and G.G.-B.; validation, G.J.-V., N.F.-M. and G.G.-B.; investigation, G.J.-V. and G.G.-B.; resources, G.J.-V., N.F.-M. and G.G.-B.; data curation, G.J.-V. and N.F.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, G.J.-V.; writing—review and editing, G.J.-V., N.F.-M. and G.G.-B.; supervision, G.J.-V.; project administration, G.J.-V. and N.F.-M.; funding acquisition, N.F.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research has been funded by the Institute of Professional Development (IDP) of Universitat de Barcelona, grant number REDICE24-3707, and the APC was partially funded by Universitat de Barcelona, through the Office of the Vice-Rector for Teaching Policy and the RIMDA program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BCE | Before Common Era |
| CER | Claim, Evidence, Reasoning |
| GBL | Game-Based Learning |
| NoS | Nature of Science |
| PD | Professional Development |
References
- Allchin, D. Evaluating knowledge of the nature of (whole) science. Sci. Educ. 2011, 95, 518–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erduran, S.; Dagher, Z.R. Reconceptualizing the Nature of Science for Science Education: Scientific Knowledge, Practices and Other Family Categories; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Bybee, R.W. Scientific Literacy, Science Literacy, and Science Education. In Handbook of Research on Science Education; Lederman, N.G., Abell, S.K., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume II, pp. 545–558. [Google Scholar]
- Lederman, N.G.; Lederman, J.S. Teaching and learning nature of scientific knowledge: Is it Déjà vu all over again? Discip. Interdiscip. Sci. Educ. Res. 2019, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.; Collins, S.; Ratcliffe, M.; Millar, R.; Duschl, R. What “ideas-about-science” should be taught in school science? A Delphi study of the expert community. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2003, 40, 692–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederman, N.G. Nature of science: Past, present, and future. In Handbook of Research on Science Education; Abell, S., Lederman, N.G., Eds.; Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 831–880. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Chen, D.-T.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chai, C.S. Students’ views of the nature of science: A critical review of research. Sci. Educ. 2011, 95, 961–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, V. Preservice science teachers’ science teaching orientations and beliefs about science. Sci. Educ. 2016, 100, 122–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComas, W.F.; Clough, M.P. Nature of Science in Science Instruction: Meaning, Advocacy, Rationales, and Recommendations. In Nature of Science in Science Instruction; McComas, W.F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Science: Philosophy, History and Education; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khishfe, R.; Lederman, N.G. Relationship between instructional context and views of nature of science. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2007, 29, 939–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadiz, G.S.; Lacre, G.J.R.; Delamente, R.L.; Diquito, T.J.A. Game-Based Learning Approach in Science Education: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Hum. Res. 2023, 6, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Hwang, G.J.; Yeh, S.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, T.W.; Chien, C.H. Three decades of game-based learning in science and mathematics education: An integrated bibliometric analysis and systematic review. J. Comput. Educ. 2021, 9, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manassero-Mas, M.A.; Vázquez-Alonso, Á. Conceptualización y taxonomía para estructurar los conocimientos acerca de la ciencia. Rev. Eureka Enseñ. Divulg. Cienc. 2019, 16, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.L. Teaching the Nature of Science: Three Critical Questions. In Best Practices in Science Education; National Geographic School Publishing: Carmel, CA, USA, 2009; Available online: https://ngl.cengage.com/assets/downloads/ngsci_pro0000000028/am_bell_teach_nat_sci_scl22-0449a_.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Lederman, N.G.; Abd-El-Khalick, F.; Bell, R.L.; Schwartz, R.S. Views of nature of science questionnaire: Toward valid and meaningful assessment of learners’ conceptions of nature of science. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2002, 39, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manassero-Mas, M.-A.; Vázquez-Alonso, Á. Enseñar y aprender a pensar sobre la naturaleza de la ciencia: Un juego de cartas como recurso en educación primaria. Rev. Eureka Enseñ. Divulg. Cienc. 2023, 20, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.L.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Kaya, O.N.; Adams, A.D.; Macklin, M.; Ebenezer, J. Preservice teachers’ views about nature of scientific knowledge development: An international collaborative study. Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 2009, 7, 987–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Valverde, G. ¿Cuáles son los perfiles de entrada sobre la naturaleza de la ciencia de los futuros docentes de física y química? In Educación Siglo XXI: Nuevos Retos, Nuevas Soluciones; Rodríguez Rodríguez, J.C., Ed.; Dykinson S.L.: Madrid, Spain, 2023; Volume 3, pp. 160–167. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2445/216280 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Abell, S.K.; Smith, D.C. What is science?: Preservice elementary teachers’ conceptions of the nature of science. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 1994, 16, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesci, G.; Schwartz, R.S. Changing preservice science teachers’ views of nature of science: Why some conceptions may be more easily altered than others. Res. Sci. Educ. 2017, 47, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takriti, R.; Tairab, H.; Alhosani, N.; Elhoweris, H.; Schofield, L.; Rabbani, L.; AlAmirah, I. Toward Understanding Science as a Whole. Sci. Educ. 2022, 32, 1321–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Valverde, G. Evaluación de la comprensión de la naturaleza de la ciencia en docentes de física y química en formación inicial. In Educar Para el Futuro: Claves Para Una Educación del Siglo XXI.; Rodríguez Góngora, J.C., Ed.; Dykinson S.L.: Madrid, Spain, 2024; pp. 640–655. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2445/217245 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Akerson, V.L.; Morrison, J.A.; McDuffie, A.R. One course is not enough: Preservice elementary teachers’ retention of improved views of nature of science. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2006, 43, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, S.; Kent-Schneider, I.; Kruse, J.; Daemicke, R. Investigating the development of preservice science teachers’ nature of science instructional views across rings of the family resemblance approach wheel. Sci. Educ. 2023, 32, 1363–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeghly, K.; Gao, S.; Kruse, J. Preservice secondary science teachers’ nature of science views, rationales, and teaching during a NOS course guided by RFN: A multiple case study. Sci. Educ. 2024, 34, 3155–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, I.; Reiss, M.J. Practical work: Its effectiveness in primary and secondary schools in England. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2012, 49, 1035–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, M.P. Using Stories Behind the Science to Improve Understanding of Nature of Science, Science Content, and Attitudes Toward Science. In Nature of Science in Science Instruction. Science: Philosophy, History and Education; McComas, W.F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.S.C. A practice-based approach to learning nature of science through socioscientific issues. Res. Sci. Educ. 2022, 52, 259–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, J.L.; Sadler, T.D.; Zeidler, D.L.; Lewis, A.; Amiri, L.; Applebaum, S. Contextualizing nature of science instruction in socioscientific issues. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2012, 34, 2289–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carmona, A.; Acevedo-Díaz, J.A. Learning About the Nature of Science Using Newspaper Articles with Scientific Content: A Study in Initial Primary Teacher Education. Sci. Educ. 2016, 25, 523–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safkolam, R.; Madahae, S.; Saleah, P. The effects of inquiry-based learning activities to understand the nature of science of science student teachers. Int. J. Instr. 2024, 17, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, S.; Torres, J.; Fernandes, I.; Vasconcelos, C. Problem-based learning and nature of science: A study with science teachers. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 191, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manassero-Mas, M.A.; Vázquez-Alonso, Á. El impacto de los juegos epistémicos para aprender sobre naturaleza de la ciencia en primaria. Ensen. Cienc. 2024, 42, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgari, I. Digital Games for Science Learning and Scientific Literacy. In Non-Formal and Informal Science Learning in the ICT Era; Giannakos, M., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Song, K.; Lockee, B.; Burton, J. What Is a Game? In Gamification in Learning and Education; Kim, S., Song, K., Lockee, B., Burton, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-C.; Tsai, C.-C. Game-based learning in science education: A review of relevant research. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2013, 22, 877–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arztmann, M.; Hornstra, L.; Jeuring, J.; Kester, L. Effects of games in STEM education: A meta-analysis on the moderating role of student background characteristics. Stud. Sci. Educ. 2022, 59, 109–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E. Game-Based Learning. In Encyclopedia of Education and Information Technologies; Tatnall, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, L. Doing Things with Games: Social Impact Through Play; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeote, D.F.; Legaki, N.Z.; Hamari, J. From traditional to game-based learning of climate change: A media comparison experiment. In Proceedings of the 2023 Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play (CHI PLAY 2023), Stratford, ON, Canada, 10–13 October 2023; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2023. Article 393. pp. 503–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, R.L.; Annetta, L.; Firestone, J.; Etopio, E. A meta-analysis with examination of moderators of student cognition, affect, and learning outcomes while using serious educational games, serious games, and simulations. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 80, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kula, S.S. Mind games with the views of classroom teachers. Int. J. Res. Educ. Sci. 2021, 7, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaim, M.N.M.; Karpudewan, M. STEM-PT Traveler, a game-based approach for learning elements of the periodic table: An approach for enhancing secondary school students’ motivation for learning chemistry. Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 2024, 25, 1251–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, G.W.; Flanagan, K.; Lee, J.; Cohen, A.; Krishnan, S.; Ward, C. A quasi-experimental study comparing learning gains associated with serious educational gameplay and hands-on science in elementary classrooms. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2020, 57, 1460–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plass, J.L.; Homer, B.D.; Kinzer, C.K. Foundations of game-based learning. Educ. Psychol. 2015, 50, 258–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, C.S.; Ryan, R.M. Glued to Games: How Video Games Draw Us in and Hold Us Spellbound; Praeger: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandria, L.N.; Bajenting, J.M.S.; Pacatan, M.A.L.D.; Diquito, T.J.A. The use of educational board game as a supplemental tool in learning periodic table of elements among senior high school students. Am. J. Educ. Technol. 2023, 2, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.D.; Negre, Y.; Casaca, J.; Patrício, R.; Tsvetcoff, R. The effect of game-based learning on the development of entrepreneurial competence among higher education students. Educ. Train. 2024, 66, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Setiani, I.; Darmawansah, D.; Yang, J.C. Effects of game-based learning integrated with the self-regulated learning strategy on nursing students’ entrustable professional activities: A quasi-experimental study. Nurse Educ. Today 2024, 139, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Tsai, J.-C.; Liu, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y. The effect of a scientific board game on improving creative problem solving skills. Think. Skills Creat. 2021, 41, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucher, T. Principles and best practices of designing digital game-based learning environments. Int. J. Technol. Educ. Sci. 2021, 5, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B.; Nadelson, L. Motivational engagement and video gaming: A mixed methods study. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2010, 58, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, I.; Caviedes, M.; Chantré, J.; Bernate, J. Gamification and Game-Based Learning as Cooperative Learning Tools: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2023, 18, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, H.; Sousa, C.; Neves, P.P.; Luz, F. Implementation of game-based learning in educational contexts: Challenges and intervention strategies. Electron. J. e-Learn. 2024, 22, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cès, P.; Doyen, A.-L.; Duflos, M.; Giraudeau, C. Board games in the elementary classroom: Teachers’ perspectives. Educ. Res. 2025, 67, 190–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byusa, E.; Kampire, E.; Mwesigye, A.R. Analysis of teaching techniques and scheme of work in teaching chemistry in Rwandan secondary schools. Eur. J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2020, 16, em1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesmin, T.; Osula, K.; Niglas, K.; Ley, T. A large-scale study to profile teachers’ use of games in the classrooms: From concerns to adoption. Tech. Knowl. Learn. 2025, 30, 483–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsop, Y.; Jessel, J. Teachers’ experience and reflections on game-based learning in the primary classroom: Views from England and Italy. Int. J. Game-Based Learn. 2015, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfisi-Schottman, I. Games in Higher Education. In Encyclopedia of Education and Information Technologies; Tatnall, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmpourtzis, G. Educational Game Design Fundamentals: A Journey to Creating Intrinsically Motivating Learning Experiences; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- van der Meij, H.; Albers, E.; Leemkuil, H. Learning from games: Does collaboration help? Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2011, 42, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, M.J. Video games: A route to large-scale STEM education? Science 2009, 323, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, X. Using game-based learning to support learning science: A study with middle school students. Asia-Pac. Educ. Res. 2021, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhou, S.N.; Hong, G.R.; Li, Q.Y.; Xu, S.Q. Evaluation of interactive game-based learning in physics domain. J. Balt. Sci. Educ. 2020, 19, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfer, E.; Thompson, M. Game-Based Learning in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. In Handbook of Game-Based Learning; Plass, J.L., Mayer, R.E., Homer, B.D., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 387–409. [Google Scholar]
- Nietfeld, J.L.; Shores, L.R.; Hoffmann, K.F. Self-regulation and gender within a game-based learning environment. J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 106, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.W.; Bunch, J.C.; Wallace, M.F.G. Agriscience teachers’ implementation of digital game-based learning in an introductory animal science course. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2015, 24, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.D.; Reichsman, F.; Mutch-Jones, K.; Gardner, A.; Marchi, L.; Kowalski, S.; Lord, T.; Dorsey, C. Teacher implementation and the impact of game-based science curriculum materials. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2018, 27, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plass, J.L.; Milne, C.; Homer, B.D.; Schwartz, R.N.; Hayward, E.O.; Jordan, T.; Verkuilen, J.; Ng, F.; Wang, Y.; Barrientos, J. Investigating the effectiveness of computer simulations for chemistry learning. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2012, 49, 394–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Chen, B.; Hwang, G.-J.; Guan, J.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Q. Effects of digital game-based STEM education on students’ learning achievement: A meta-analysis. Int. J. STEM Educ. 2022, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byusa, E.; Kampire, E.; Mwesigye, A.R. Game-based learning approach on students’ motivation and understanding of chemistry concepts: A systematic review of literature. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak Yallıhep, E.S.; Akcay, H.; Kapici, H.O. Impacts of serious games on middle school students’ science achievement and attitudes towards science. Int. J. Technol. Educ. Sci. 2021, 5, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, D.M.; Bodzin, A.M. A mixed methods assessment of students’ flow experiences during a mobile augmented reality science game. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2013, 29, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.Y.; Hwang, G.J. A collaborative game-based learning approach to improving students’ learning performance in science courses. Comput. Educ. 2013, 63, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, D.A. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Educational Game Design Based on Experiential Learning Theory. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Conference on Information and Education Technology (ICIET 2021), Kunming, China, 8–10 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.K. Educating for Innovation. Think. Skills Creat. 2006, 1, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari-Shahreza, M.A. Pedagogy of play: Insights from playful learning for language learning. Discov. Educ. 2024, 3, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinnesand, M.J. Observations v. assumptions. ChemMatters 2022, 40, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- González-Espada, W.J.; Birriel, J.; Birriel, I. Discrepant Events: A Challenge to Students’ Intuition. Phys. Teach. 2010, 48, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bell, R.L. Teaching the Nature of Science through Process Skills: Activities for Grades 3–8; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Herr, N. The Sourcebook for Teaching Science, Grades 6–12: Strategies, Activities, and Instructional Resources; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Harris, M.F.; Hisser, D.T.; Hynek, J.A.; Matthews, W.H., III; Roy, C.J.; Skehan, J.; Stevenson, R.E. Teacher’s Guide: Investigating the Earth, Revised ed.; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Tricky Tracks Overhead. Available online: http://fossilfinder.coe.uga.edu/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Tricky-Tracks-Overhead.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2025).[Green Version]
- Lederman, N.; Abd-El-Khalick, F. Avoiding De-Natured Science: Activities That Promote Understandings of the Nature of Science. In The Nature of Science in Science Education; McComas, W.F., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 83–126. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Warren, D. The Nature of Science; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Heras-Paniagua, C.; Jiménez-Valverde, G.; Calafell-Subirà, G. La necesidad de una narrativa en la gamificación estructural de una asignatura. In Narrativas y Usuarios de la Sociedad Transmedia; Anaya Benítez, F., Ed.; Dykinson S.L.: Madrid, España, 2022; pp. 73–94. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2445/215656 (accessed on 4 October 2025).[Green Version]
- McComas, W.F. (Ed.) Nature of Science in Science Instruction: Rationales and Strategies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobern, W.W. Introducing teachers to the philosophy of science: The card exchange. J. Sci. Teach. Educ. 1991, 2, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobern, W.W.; Loving, C.C. The card exchange: Introducing teachers to the philosophy of science. In The Nature of Science in Science Education: Rationales and Strategies; McComas, W.F., Ed.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cobern, W.W.; Loving, C. The Nature of Science Card Exchange: Introducing the Philosophy of Science. In Nature of Science in Science Instruction: Rationales and Strategies; McComas, W.F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, F.A. Cobern and Loving’s card exchange revisited: Using literacy strategies to support and enhance teacher candidates’ understanding of NOS. Innov. Sci. Teach. Educ. 2018, 3, 3. Available online: http://innovations.theaste.org/?p=3004 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Gilroy, H. Goodbye Old Paint: We’re A-Leavin’ Big D. Pers. Comput. 1977, 1, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Play Petals Around the Rose—JavaScript. Available online: https://www.borrett.id.au/computing/petals-j.htm (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Reichert, M.; Hawley, R. Reaching Boys, Teaching Boys: Strategies that Work—And Why; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wason, P.C. On the failure to eliminate hypotheses in a conceptual task. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 1960, 12, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Most Common Cognitive Bias. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vKA4w2O61Xo (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Kang, K. The influence of NOS learning program using board game to the perception of pre-service science teachers on the nature of science. Educ. Res. 2022, 85, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M. Mathematical games. Sci. Am. 1959, 200, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M. Mathematical games. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R. Abbott’s New Card Games; Funk and Wagnalls: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Romesburg, H.C. Simulating scientific inquiry with the card game eleusis. Sci. Educ. 1979, 63, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L. The Games Bible; Workman Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Walkup, J.R.; Key, R. Speed Eleusis: Variation on an old educational card game. Phys. Teach. 2020, 58, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Dias, G.; dos Santos, R.P. The game of Eleusis: An entertaining simulation of the research heuristic. Acta Sci. 2015, 17, 715–731. [Google Scholar]
- Hagège, H.; Dartnell, C.; Sallantin, J. Positivism Against Constructivism: A Network Game to Learn Epistemology. In Proceedings of the Discovery Science 2007 (DS’07), Sendai, Japan, 1–4 October 2007; Corruble, V., Takeda, M., Suzuki, E., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4755, pp. 91–103. Available online: https://hal-lirmm.ccsd.cnrs.fr/lirmm-00193672 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Qiao, H.; Suriyaarachchi, H.; Cooray, S.; Nanayakkara, S. Snatch and Hatch: Improving receptivity towards a Nature of Science with a playful mobile application. In Proceedings of the Interaction Design and Children (IDC ‘23), Chicago, IL, USA, 19–23 June 2023; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassard, J. The Art of Teaching Science; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn, D. Teaching High School Science Through Inquiry and Argumentation, 2nd ed.; Corwin: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn, D. Inquire Within: Implementing Inquiry- and Argument-Based Science Standards in Grades 3–8; Corwin: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Alonso, Á.; Manassero-Mas, M.A. Juegos para enseñar la naturaleza del conocimiento científico y tecnológico. Educar 2017, 53, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Valverde, G.; Fabre-Mitjans, N.; Guimerà-Ballesta, G. Narrative-Driven Digital Gamification for Motivation and Presence: Preservice Teachers’ Experiences in a Science Education Course. Computers 2025, 14, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskel-Ittah, M. Explanatory black boxes and mechanistic reasoning. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2023, 60, 915–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, T. Identification Detectives: Sounds and Smells of Science. In Brain-Powered Science: Teaching and Learning with Discrepant Events; National Science Teachers Association (NSTA): Arlington, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mystery Boxes. Available online: https://learning.sciencemuseumgroup.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/SMG-Academy-Mystery-Boxes.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Rau, G. A new twist on mystery boxes. Sci. Teach. 2009, 76, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- French, M. Using the Science Museum’s ‘Mystery Boxes’ as a model for science and ‘How science works’. Sch. Sci. Rev. 2012, 94, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Manassero-Mas, M.A.; Bennàssar-Roig, A.J.; Vázquez-Alonso, A. Formar, enseñar y aprender sobre la práctica científica en primaria con un juego de cajas negras. REIRE 2021, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S. Modeling the nature of science with the mystery tube. Phys. Teach. 2014, 52, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, M. A more challenging mystery tube for teaching the nature of science. Phys. Teach. 2019, 57, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krell, M.; Hergert, S. The Black Box Approach: Analyzing Modeling Strategies. In Towards a Competence-Based View on Models and Modeling in Science Education; Upmeier zu Belzen, A., Krüger, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 12, pp. 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruebush, L.; Sulikowski, M.; North, S. A simple exercise reveals the way students think about scientific modeling. J. Coll. Sci. Teach. 2009, 38, 18–22. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/42993571 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Modelle in der Biologie. Available online: https://tetfolio.fu-berlin.de/web/440484 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Ammoneit, R.; Göhner, M.F.; Bielik, T.; Krell, M. Why most definitions of modeling competence in science education fall short: Analyzing the relevance of volition for modeling. Sci. Educ. 2024, 108, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, K.L.; Krajcik, J. Supporting Grade 5–8 Students in Constructing Explanations in Science: The Claim, Evidence, and Reasoning Framework for Talk and Writing; Pearson Allyn & Bacon: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- “The Nature of Science”: An Activity for the First Day of Class 2004. Available online: https://www.scienceteacherprogram.org/genscience/Choi04.html (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Vesali, M.; Nouri, N.; Saberi, M. Promoting Understanding of Several Elements of Nature of Science Using an Analogy: A Tangram Activity. Innov. Sci. Teach. Educ. 2022, 7, 1–17. Available online: https://innovations.theaste.org/index.php/iste/article/view/366 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- The Checks Lab. Available online: https://evolution.berkeley.edu/ensi/ensi_checks_lab.html (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Colburn, A. Learning Science by Doing Science: 10 Classic Investigations Reimagined to Teach Kids How Science Really Works, Grades 3–8; Corwin, NSTA Press: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lederman, J.; Gnanakkan, D.; Bartels, S.; Lederman, N. The E-mail Lab: Teaching nature of science and science practices through story construction. Sci. Teach. 2015, 82, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Case of the Missing Computer Chip. ENSI—Evolution & the Nature of Science Institutes 1999. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20100211221949/http://www.indiana.edu/~ensiweb/lessons/crime.html (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Jimenez-Valverde, G.; Heras-Paniagua, C.; Fabre-Mitjans, N.; Calafell, G. Un chip-sterio intrigante: Abordando la Naturaleza de la Ciencia con un juego detectivesco. In Proceedings of the III International Conference on Innovation in Teaching and Research in Social and Legal Sciences (INNDOC), Online, 8–9 June 2023; Available online: https://2023.inndoc.org/ponencia/un-chip-sterio-intrigante-abordando-la-naturaleza-de-la-ciencia-con-un-juego-detectivesco/ (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Guimerà-Ballesta, G.; Jiménez-Valverde, G.; Fabre-Mitjans, N.; Heras-Paniagua, C. Integrant la naturalesa de la ciència en la formació inicial del professorat: Proposta narrativa i gamificada per promoure la comprensió científica. In Proceedings of the 13th CIDUI Congress 2025: Today’s Teachers for Tomorrow’s University, Barcelona, Spain, 9–11 July 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Clough, M.P. Learners’ Responses to the Demands of Conceptual Change: Considerations for Effective Nature of Science Instruction. Sci. Educ. 2006, 15, 463–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotar, M. Demystifying mystery powders. Sci. Child. 1989, 26, 25–28. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/43167067 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Oliver-Hoyo, M.; Allen, D.; Solomon, S.; Brook, B.; Ciraolo, J.; Daly, S.; Jackson, L. Qualitative analysis of fourteen white solids and two mixtures using household chemicals. J. Chem. Educ. 2001, 78, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Cite, S.; Hanuscin, D. Taking the “mystery” out of argumentation. Sci. Child. 2014, 52, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, D.M.; Bodzin, A.M. Investigating flow experience and scientific practices during a mobile serious educational game. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2016, 25, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, D.M.; Bodzin, A.M.; Eagan, B.; Tabatabai, S. Using epistemic network analysis to examine discourse and scientific practice during a collaborative game. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2019, 28, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contant, T.L.; Tweed, A.L.; Bass, J.E.; Carin, A.A. Teaching Science Through Inquiry-Based Instruction, 13th ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lederman, N.G.; Abd-El-Khalick, F.; Lederman, J.S. Avoiding De-Natured Science: Integrating Nature of Science into Science Instruction. In Nature of Science in Science Instruction; McComas, W.F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxer, A. Teaching Secondary Science: A Complete Guide; John Catt Educational Ltd.: Woodbridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Periodic Patterns Puzzle. Available online: https://www.wpi.edu/sites/default/files/docs/Events/Annual-Events/AweSTEM/puzzle_print.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- The Missing Piece. Available online: https://passionatelycurioussci.weebly.com/blog/the-missing-piece (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Hassard, J.; Dias, M. The Art of Teaching Science: Inquiry and Innovation in Middle School and High School; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, S.; Newton, D. Creative Chemists: Strategies for Teaching and Learning; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Valverde, G. Narrative Approaches in Science Education: From Conceptual Understanding to Applications in Chemistry and Gamification. Encyclopedia 2025, 5, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerri, E.R.; McIntyre, L. The Case for the Philosophy of Chemistry. Synthese 1997, 111, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, M.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Brito, A. An appraisal of Mendeleev’s contribution to the development of the periodic table. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. A 2004, 35, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, W.B. Mistake of Having Students Be Mendeleev for Just a Day. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-J. The Design and Effectiveness of Board Games about Nature of Science. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan, August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aragón, L.; Vicente, J.J. Abordar la Historia y la Naturaleza de la Ciencia en la Formación Inicial del Profesorado mediante una Secuencia Didáctica basada en un Juego de Cartas. Eur. Public Soc. Innov. Rev. 2024, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).