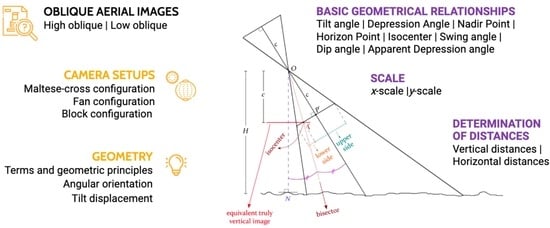
Oblique Aerial Images: Geometric Principles, Relationships and Definitions
Definition
1. Introduction
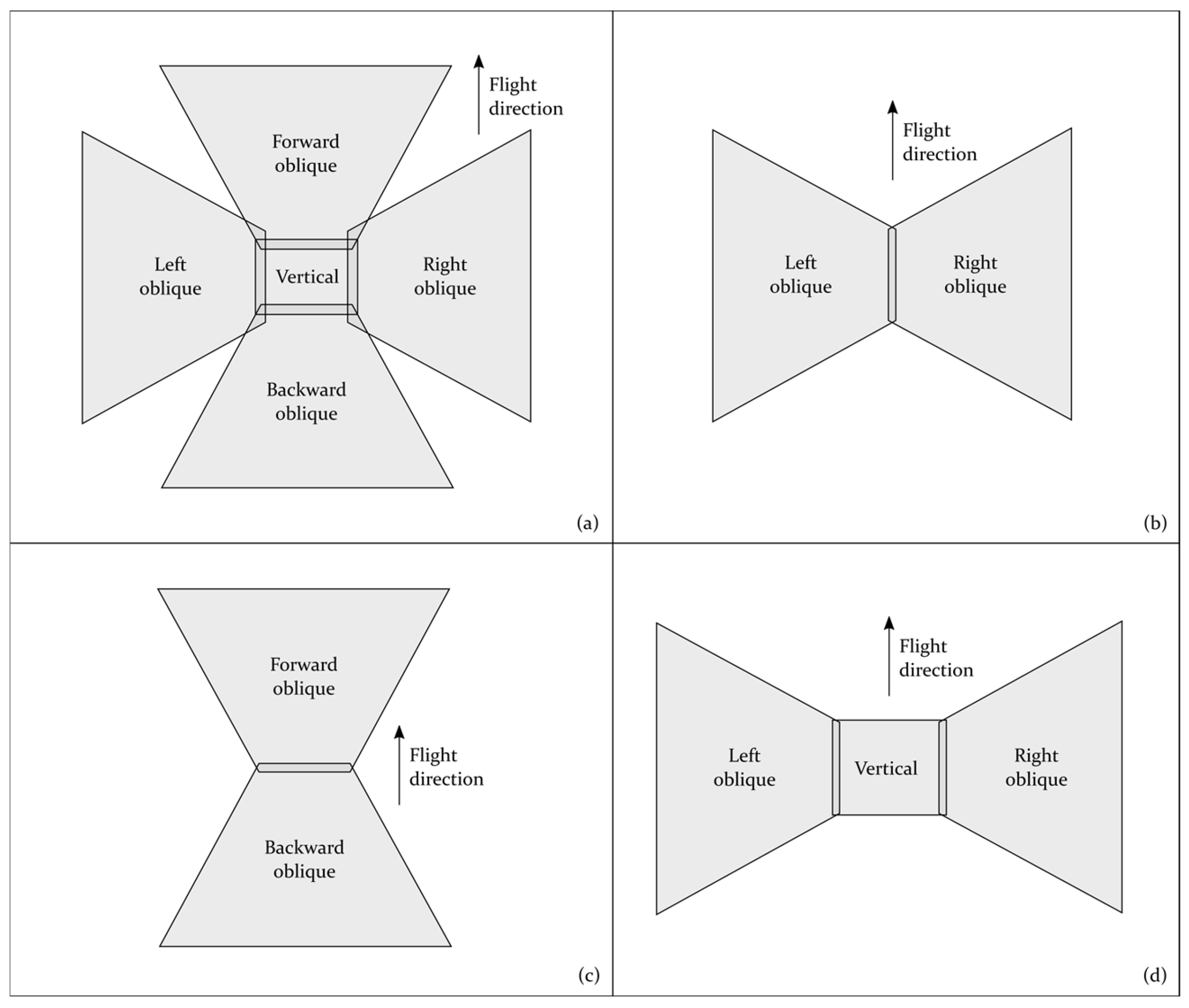
2. Types and Camera Setups
3. Geometry of Oblique Imagery
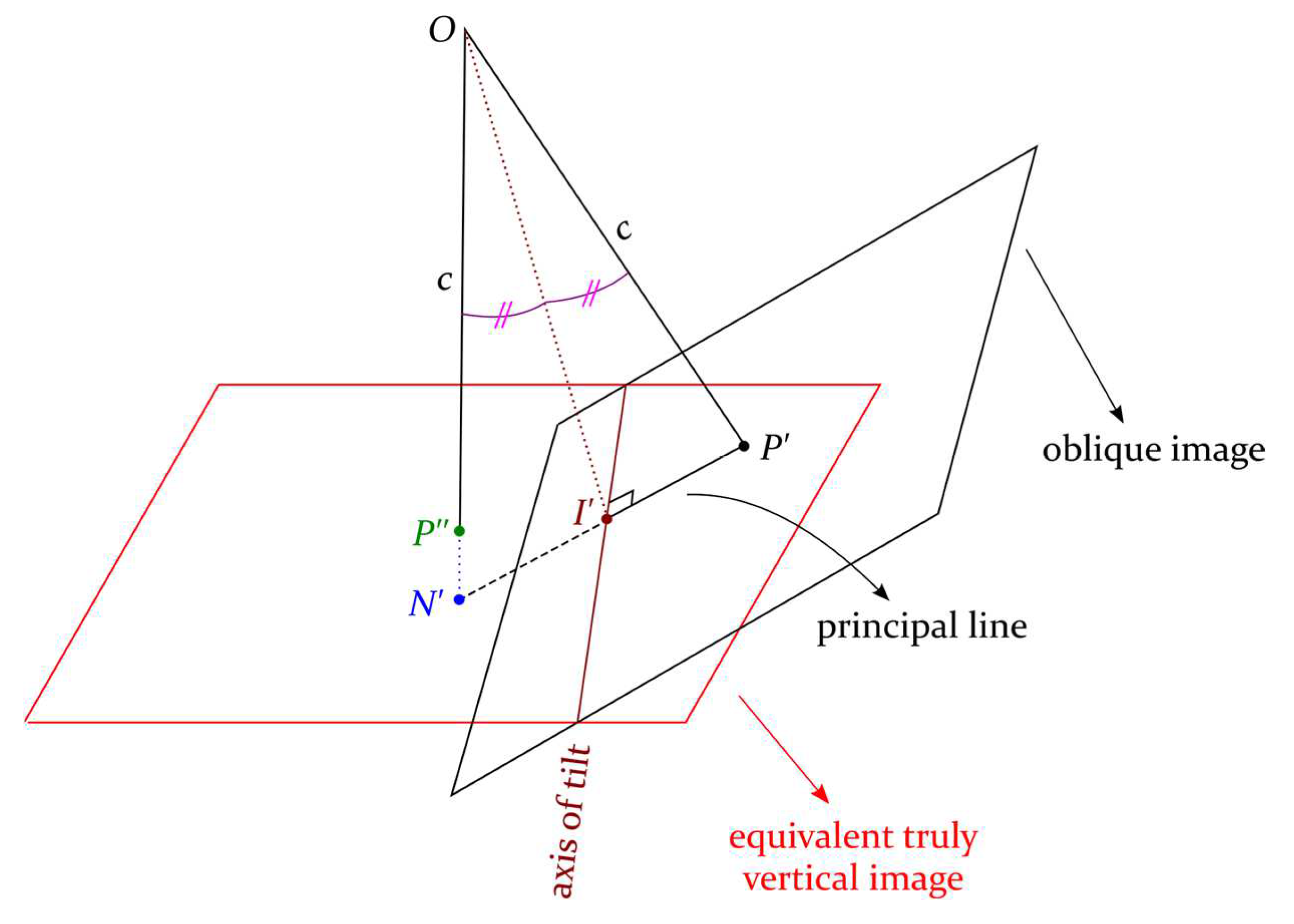
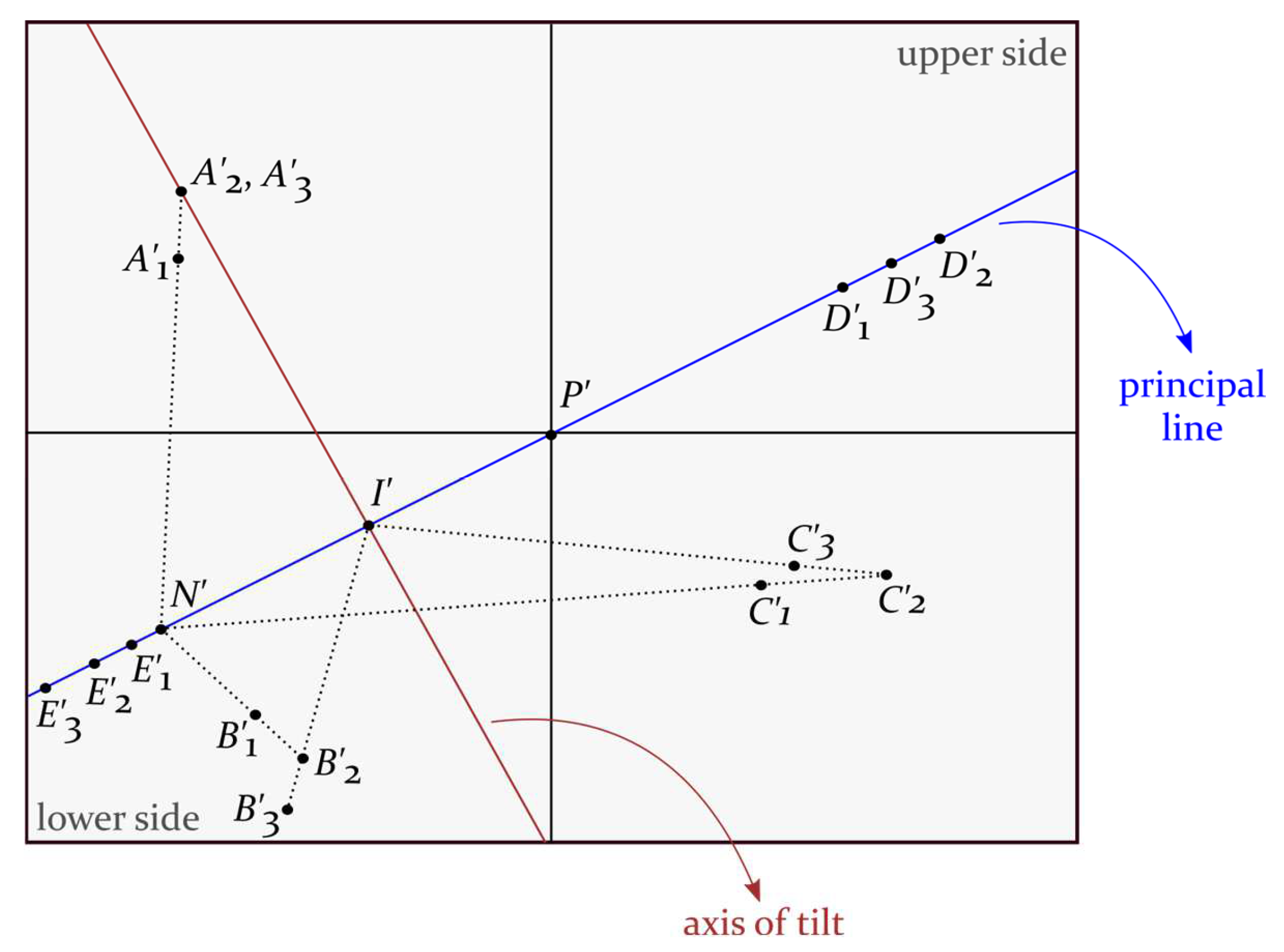
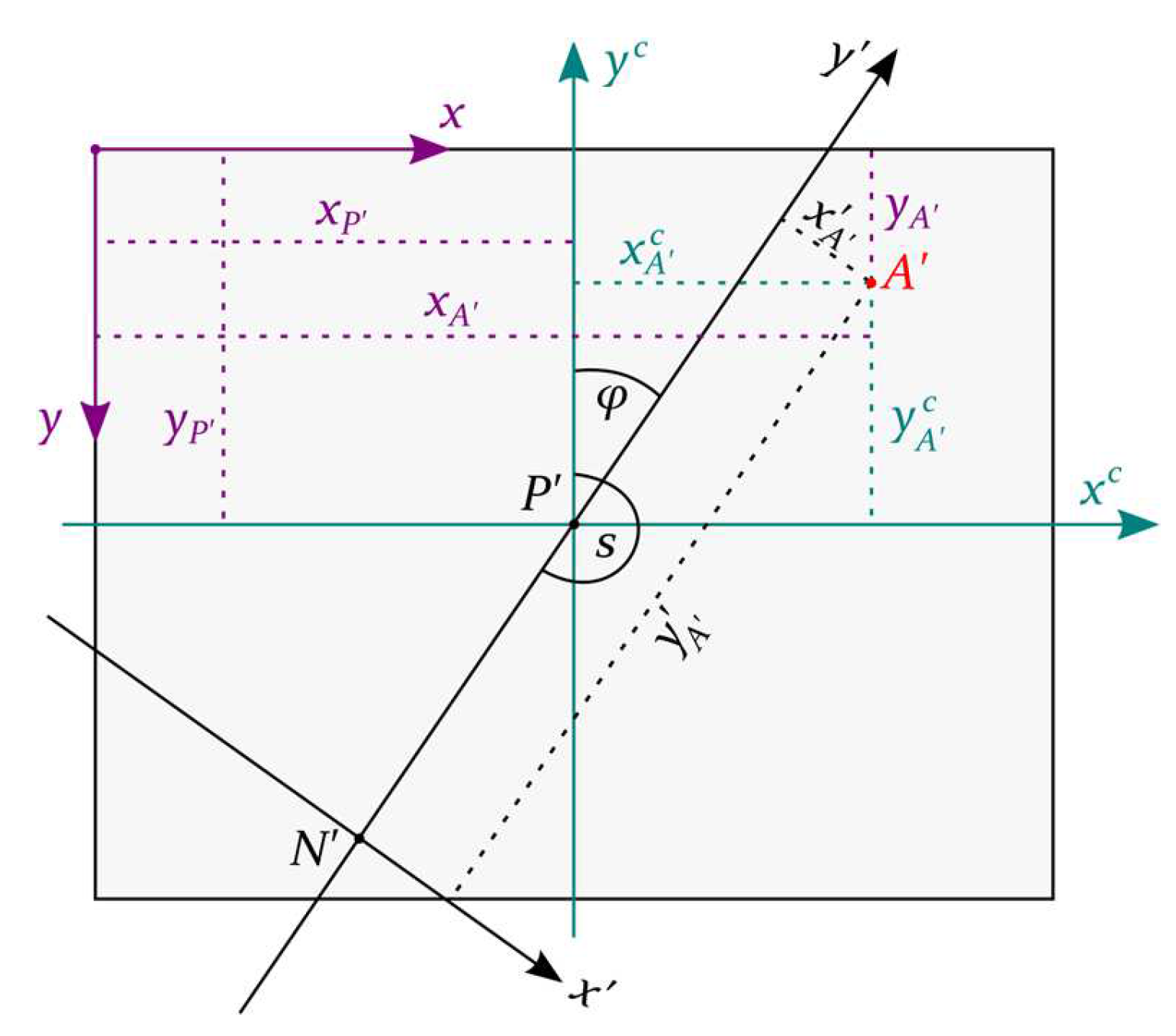
3.1. Terms and Geometric Properties
3.2. Angular Orientation in Azimuth-Tilt-Swing
3.3. Tilt Displacement
3.4. Scale
3.4.1. Scale of Lines Perpendicular to the Principal Line
3.4.2. Scale of Lines Parallel to the Principal Line
3.5. Basic Geometrical Relationships
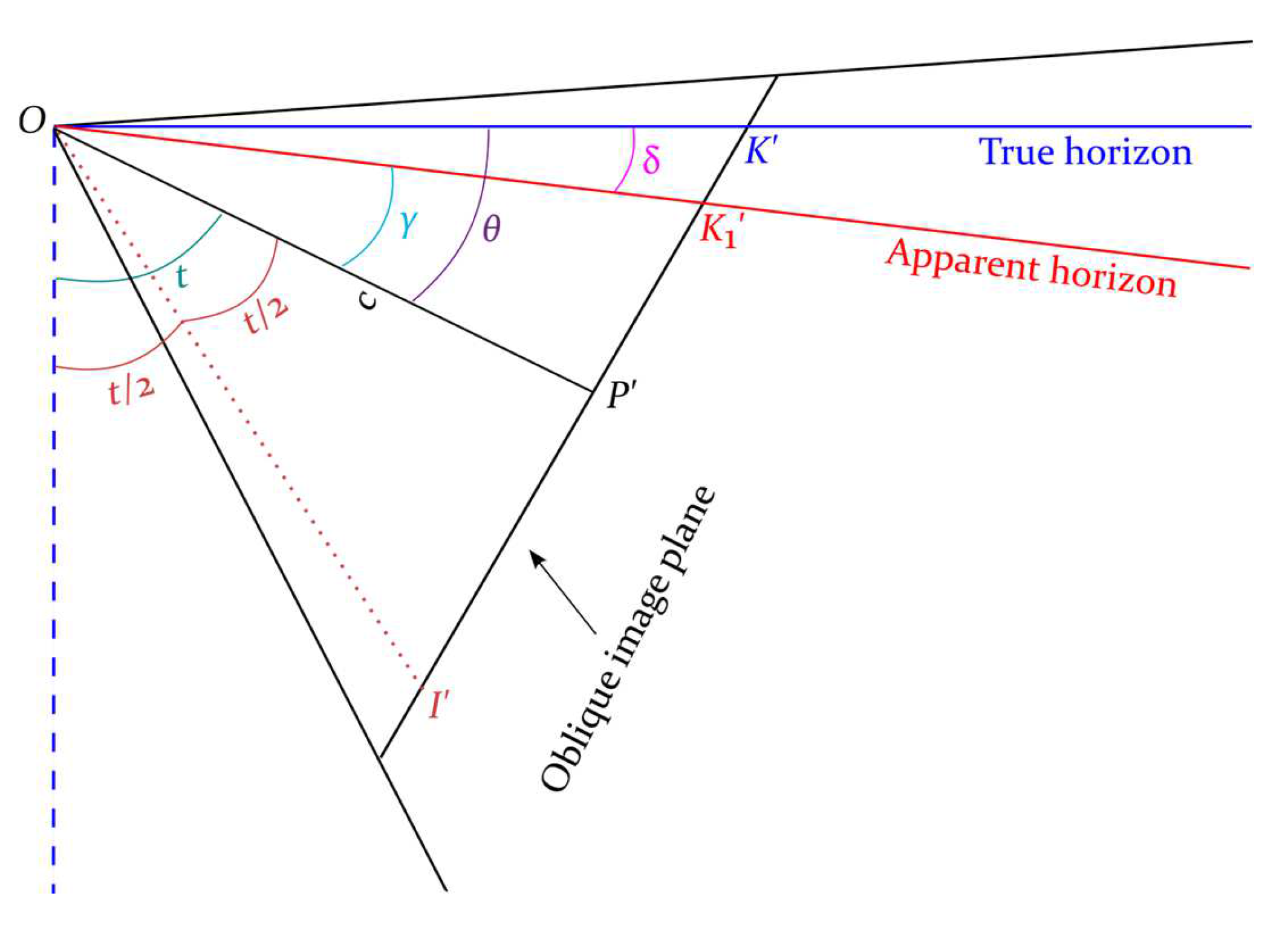
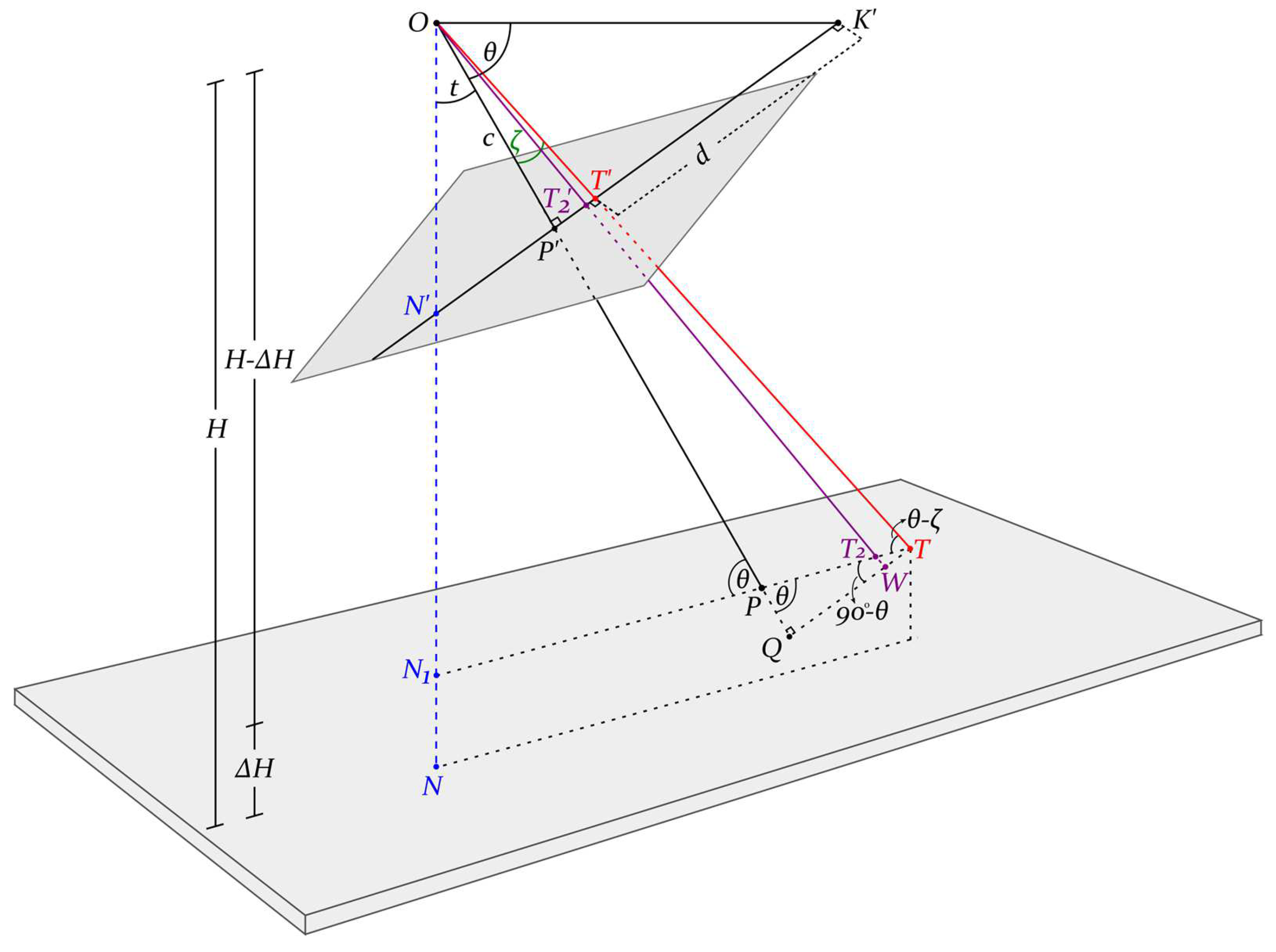
3.5.1. Tilt and Depression Angles, Nadir Point, and Horizon Point
3.5.2. Isocenter
3.5.3. Swing Angle
3.5.4. Dip Angle
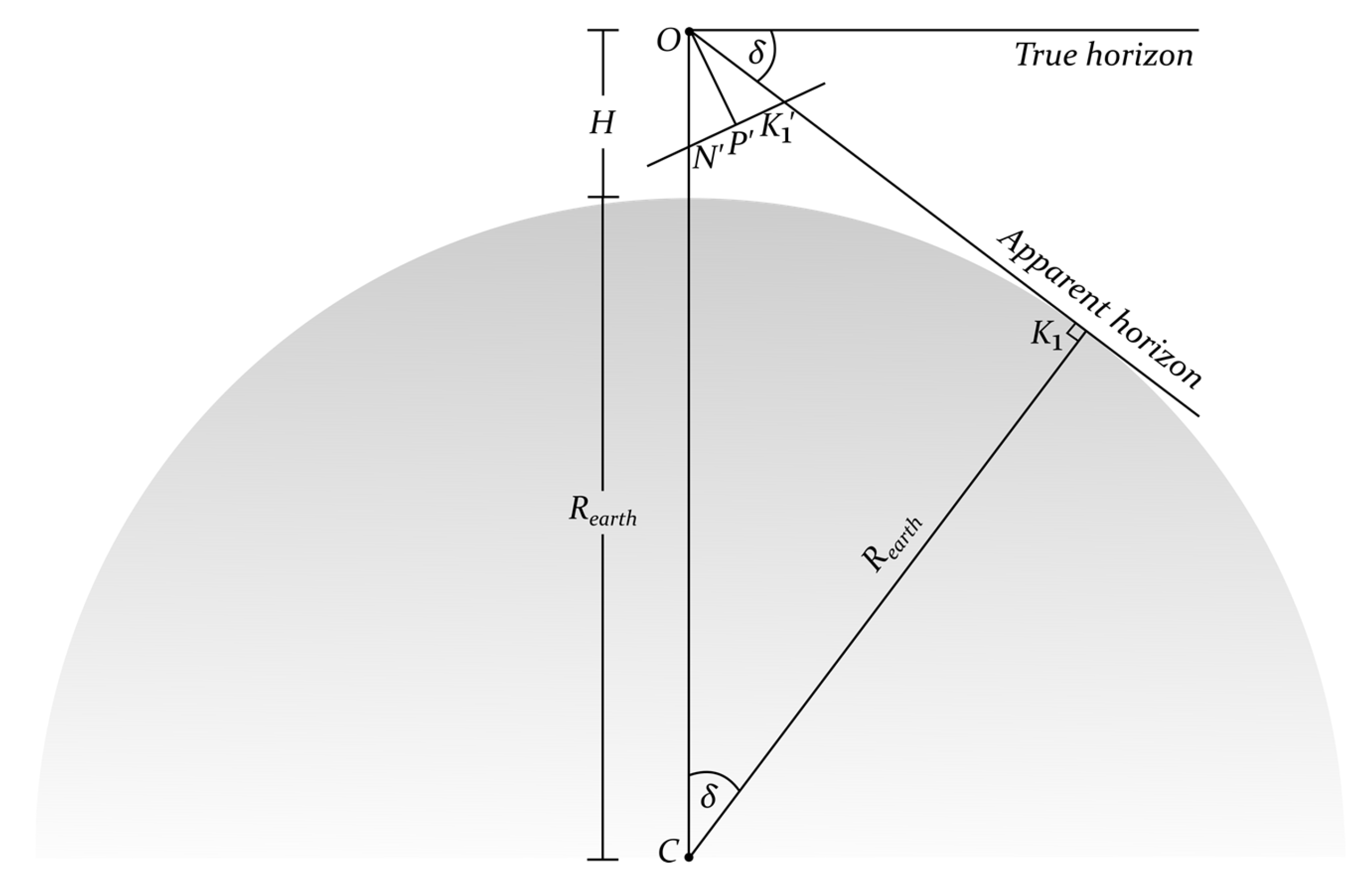
3.5.5. Apparent Depression Angle
4. Determination of Distances
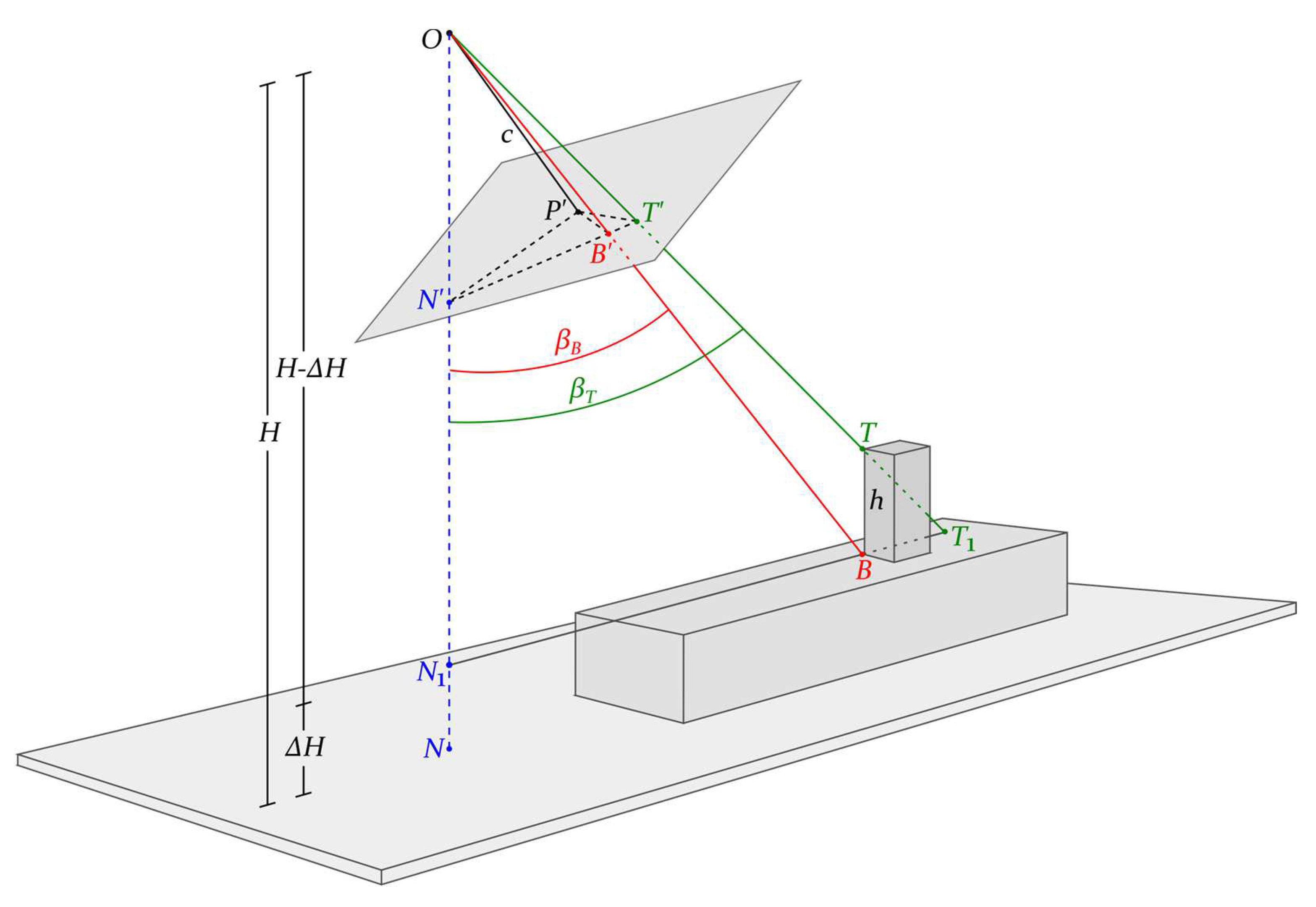
4.1. Vertical Distances
4.2. Horizontal Distances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. An Overview on Image-Based and Scanner-Based 3D Modeling Technologies. Sensors 2023, 23, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. Oblique Aerial Images: A Review Focusing on Georeferencing Procedures. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 3452–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verykokou, S.A. Georeferencing Procedures for Oblique Aerial Images. Ph.D. Thesis, National Technical University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, B.; Xie, L.; Chen, M. Stable Least-Squares Matching for Oblique Images Using Bound Constrained Optimization and a Robust Loss Function. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 118, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Yue, A.; He, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Oblique Image Registration Using an ASIFT-Based Matching Method. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, R. Efficient Large-Scale Oblique Image Matching Based on Cascade Hashing and Match Data Scheduling. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 138, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Bi, J. Direct Georeferencing of Oblique and Vertical Imagery in Different Coordinate Systems. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 95, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geniviva, A.; Faulring, J.; Salvaggio, C. Automatic Georeferencing of Imagery from High-Resolution, Low-Altitude, Low-Cost Aerial Platforms. In Proceedings of the Geospatial InfoFusion and Video Analytics IV; and Motion Imagery for ISR and Situational Awareness II, Baltimore, MD, USA, 19 June 2014; Volume 9089, pp. 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. Automatic Rough Georeferencing of Multiview Oblique and Vertical Aerial Image Datasets of Urban Scenes. Photogramm. Rec. 2016, 31, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, M. An Asymmetric Re-Weighting Method for the Precision Combined Bundle Adjustment of Aerial Oblique Images. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 117, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. A Photogrammetry-Based Structure from Motion Algorithm Using Robust Iterative Bundle Adjustment Techniques. Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. A Global Photogrammetry-Based Structure from Motion Framework: Application in Oblique Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the FIG Working Week 2019, Hanoi, Vietnam, 22–26 April 2019; FIG: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. Exterior Orientation Estimation of Oblique Aerial Images Using SfM-Based Robust Bundle Adjustment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 7233–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, W. Efficient Structure from Motion for Large-Scale UAV Images: A Review and a Comparison of SfM Tools. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Cui, T. Efficient and Accurate Hierarchical SfM Based on Adaptive Track Selection for Large-Scale Oblique Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xie, L.; Hu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Yau, E. Integration of Aerial Oblique Imagery and Terrestrial Imagery for Optimized 3D Modeling in Urban Areas. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbit, P.R.; Hugenholtz, C.H. Enhancing UAV–SfM 3D Model Accuracy in High-Relief Landscapes by Incorporating Oblique Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R. Dense Stereo Matching Strategy for Oblique Images That Considers the Plane Directions in Urban Areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5109–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.; Fregonese, L.; Crocetto, N. Use of SfM-MVS Approach to Nadir and Oblique Images Generated Throught Aerial Cameras to Build 2.5D Map and 3D Models in Urban Areas. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniga, V.-E.; Breaban, A.-I.; Pfeifer, N.; Diac, M. 3D Modeling of Urban Area Based on Oblique UAS Images—An End-to-End Pipeline. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommholz, D.; Linkiewicz, M.; Meissner, H.; Dahlke, D.; Poznanska, A. Extracting Semantically Annotated 3DBuilding Models with Textures from Oblique Aerial Imagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Deng, F.; Li, X.; Wan, F. Automatic Texture Reconstruction of 3D City Model from Oblique Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Bao, X.; Ye, S.; Wang, H.; Yan, H. Selection of Optimal Building Facade Texture Images From UAV-Based Multiple Oblique Image Flows. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1534–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Lin, D.; Song, T. Object Detection Deployed on UAVs for Oblique Images by Fusing IMU Information. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6505305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachar, P.; Kurczyński, Z.; Ostrowski, W. Application of Machine Learning for Object Detection in Oblique Aerial Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 43, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiu, J.; Liu, Z. Geo-Location Algorithm for Building Targets in Oblique Remote Sensing Images Based on Deep Learning and Height Estimation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, W. Automatic Identification of Building Structure Types Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Oblique Images and Deep Learning Considering Facade Prior Knowledge. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 3348–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Cui, T. Oblique View Selection for Efficient and Accurate Building Reconstruction in Rural Areas Using Large-Scale UAV Images. Drones 2022, 6, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, Ł.; Mielczarek, D.; Ostrowski, W.; Dominik, W.; Krawczyk, J. Semantic Urban Mesh Segmentation Based on Aerial Oblique Images and Point Clouds Using Deep Learning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 43, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshboresh-Masouleh, M.; Alidoost, F.; Arefi, H. Multiscale Building Segmentation Based on Deep Learning for Remote Sensing RGB Images from Different Sensors. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 034503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Huang, X.; Gong, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, F. A Dataset and Ensemble Model for Glass Façade Segmentation in Oblique Aerial Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6513305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Song, Y.; Ji, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, P.; Liu, S. Automatic Classification of Rural Building Characteristics Using Deep Learning Methods on Oblique Photography. Build. Simul. 2022, 15, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivel, A.; Gerke, M.; Kerle, N.; Vosselman, G. Identification of Structurally Damaged Areas in Airborne Oblique Images Using a Visual-Bag-of-Words Approach. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakooei, M.; Baleghi, Y. A Two-Level Fusion for Building Irregularity Detection in Post-Disaster VHR Oblique Images. Earth Sci. Inf. 2020, 13, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Duan, K.; You, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, F.; Hu, Y. Automatic Detection of Earthquake-Damaged Buildings by Integrating UAV Oblique Photography and Infrared Thermal Imaging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carricondo, P.; Carvajal-Ramírez, F.; Yero-Paneque, L.; Agüera-Vega, F. Combination of Nadiral and Oblique UAV Photogrammetry and HBIM for the Virtual Reconstruction of Cultural Heritage. Case Study of Cortijo Del Fraile in Níjar, Almería (Spain). Build. Res. Inf. 2020, 48, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, G.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Li, S.; Xie, J. Reconstruction of LoD-2 Building Models Guided by Façade Structures from Oblique Photogrammetric Point Cloud. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šafář, V.; Potůčková, M.; Karas, J.; Tlustý, J.; Štefanová, E.; Jančovič, M.; Cígler Žofková, D. The Use of UAV in Cadastral Mapping of the Czech Republic. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, G.M.; Mohr-Bell, D.; Garrett, M.; Muñoz, L.; Lencinas, J.D. Customizing Unmanned Aircraft Systems to Reduce Forest Inventory Costs: Can Oblique Images Substantially Improve the 3D Reconstruction of the Canopy? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 3480–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Schirrmann, M.; Weltzien, C.; Shafian, S.; Laursen, M.S. UAV Oblique Imagery with an Adaptive Micro-Terrain Model for Estimation of Leaf Area Index and Height of Maize Canopy from 3D Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Y.; Mao, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, X. Moving Car Recognition and Removal for 3D Urban Modelling Using Oblique Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprey, R.; Pope, F.; Ngene, S.; Norton-Griffiths, M.; Frederick, H.; Okita-Ouma, B.; Douglas-Hamilton, I. Comparing an Automated High-Definition Oblique Camera System to Rear-Seat-Observers in a Wildlife Survey in Tsavo, Kenya: Taking Multi-Species Aerial Counts to the next Level. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 241, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.; She, Y.; Loewen, M. Deep Learning Based River Surface Ice Quantification Using a Distant and Oblique-Viewed Public Camera. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 206, 103736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, F.H.; Mikhail, E.M. Photogrammetry; Harper & Row Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Trorey, L.G. Handbook of Aerial Mapping and Photogrammetry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Höhle, J. Photogrammetric Measurements in Oblique Aerial Images. Photogramm. Fernerkund. Geoinf. 2008, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shufelt, J.A. Performance Evaluation and Analysis of Monocular Building Extraction from Aerial Imagery. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, F.H. Elements of Photogrammetry; International Textbook Company: Scranton, PA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, P.R. Elements of Photogrammetry: With Air Photo Interpretation and Remote Sensing, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1983; ISBN 9780070713451. [Google Scholar]
- Petrie, G. Systematic Oblique Aerial Photography Using Multiple Digital Frame Cameras. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lemmens, M. Digital Oblique Aerial Cameras (1): A Survey of Features and Systems. GIM Int. 2014. Available online: https://repository.tudelft.nl/islandora/object/uuid:a2548e3d-2408-4eba-8e67-69c504d5cfec?collection=research (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Lemmens, M. Digital Oblique Aerial Cameras (2): A Survey of Features and Systems. GIM Int. 2014. Available online: http://www.gdmc.nl/publications/2014/Digital_Oblique_Aerial_Cameras_2.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Rupnik, E.; Nex, F.; Remondino, F. Oblique multi-camera systems—Orientation and dense matching issues. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 107114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Gerke, M. Oblique Aerial Imagery—A Review. In Proceedings of the Photogrammetric Week’15, Stuttgart, Germany, 7–11 September 2015; Wichmann/VDE Verlag: Belin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction to Oblique Photogrammetry; Hydrographic Office Navy Department & Photographic Intelligence Center—Division of Naval Intelligence—Navy Department: Arlington, VA, USA, 1945.
- Manual of Photogrammetry, 2nd ed.; American Society of Photogrammetry: Washington, DC, USA, 1952.
- Paine, D.P.; Kiser, J.D. Aerial Photography and Image Interpretation, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780470879382. [Google Scholar]
- Punmia, B.C.; Jain, A.K.; Jain, A.K. Higher Surveying, Surveying-III; Laxmi Publications Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2005; ISBN 9788170088257. [Google Scholar]
- Dewitt, B.A. Initial Approximations for the Three-Dimensional Conformal Coordinate Transformation. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1996, 62, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Misulia, M.G. A Derivation for the Image Displacement Due to Tilt. Photogramm. Eng. 1946, pp. 461–463. Available online: https://www.asprs.org/wp-content/uploads/pers/1946journal/dec/1946_dec_461-463.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Lane, B.B. Scales of Oblique Photographs. Photogramm. Eng. 1950, pp. 409–414. Available online: https://www.asprs.org/wp-content/uploads/pers/1950journal/jun/1950_jun_409-414.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Moffitt, F.H. Photogrammetry; International Textbook Company: Scranton, PA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, P.R. Elements of Photogrammetry; McGraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. Exterior orientation estimation of oblique aerial imagery using vanishing points. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; ISBN 9780521540513. [Google Scholar]
- Molinari, M.; Medda, S.; Villani, S. Vertical Measurements in Oblique Aerial Imagery. IJGI ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2014, 3, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verykokou, S.; Ioannidis, C. Oblique Aerial Images: Geometric Principles, Relationships and Definitions. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 234-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010019
Verykokou S, Ioannidis C. Oblique Aerial Images: Geometric Principles, Relationships and Definitions. Encyclopedia. 2024; 4(1):234-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerykokou, Styliani, and Charalabos Ioannidis. 2024. "Oblique Aerial Images: Geometric Principles, Relationships and Definitions" Encyclopedia 4, no. 1: 234-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010019
APA StyleVerykokou, S., & Ioannidis, C. (2024). Oblique Aerial Images: Geometric Principles, Relationships and Definitions. Encyclopedia, 4(1), 234-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010019