Definition
Wood decayed and colored by fungi, colloquially known as ‘spalted wood’, has been a source of art and folklore across numerous cultures. From intarsia and marquetry in Italy and Germany to woodturning in the U.S. and carving and mythology in Chile, the uses of, and stories about, spalted wood are explored, as well as how those have shaped their surrounding cultures as well as modern science.
1. History
A modern definition of spalting is as follows: any color in wood that has been produced as a fungal secondary metabolite [1]. Hence, spalting results from decayed fungi (brown rots, white rots, soft rots) that colonize wood and leave behind some sort of visible color. Spalting is generally broken down into three categories: large-scale pigment secretions, melanized or pigmented zone lines, and bleaching.
Pigment-type spalting often covers a large section of wood, in contrast to zone lines, which function more as fungal borders (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3). Spalting pigments span the entire color spectrum, from the bright turquoise of elf’s cup (Chlorociboria species) to the reds and oranges of flaming dragon fungus (Scytalidium cuboideum) to the rich brown found in English brown oak, which is secreted from the brown rotting fungus Fistulina hepatica (beefsteak fungus). Depending on growing conditions, spalting pigments can completely infiltrate downed, dead wood, leaving striking color across forest floors [1].
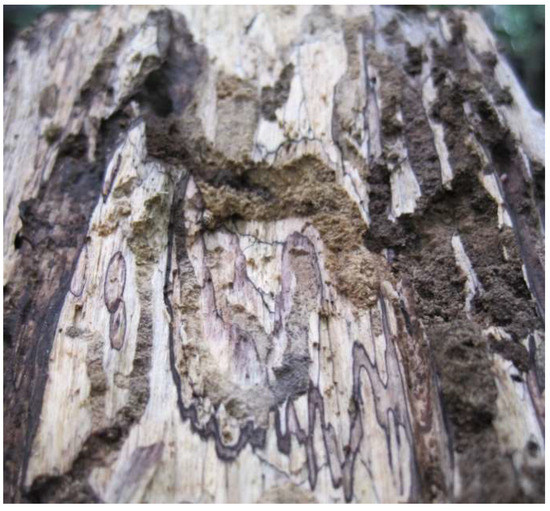

Figure 1.
Black zone lines on decayed wood from the Peruvian Amazon. The white areas surrounding the zone lines are from bleaching (white rotting) fungi.

Figure 2.
Orange zone lines on decayed wood from the Peruvian Amazon.

Figure 3.
Green zone lines on decayed wood from the Peruvian Amazon. The green is so concentrated in some areas that it appears black.
Zone lines occupy much less space on spalted wood, although their usual brown and black melanin is striking on white, rotted material. The winding, often narrow lines can also occur as lower-weight pigments, such as green, red, and orange, and are formed as territory boundaries within wood or can be produced as a response to environmental stressors (UV light, low water availability, a high amount of copper in the substrate, etc.). The third type of spalting is bleaching, which is caused as white, rotting fungi grow through wood and create lightened areas through their removal of lignin and from the mass of their white hyphae within the wood [1].
Cultures across the world, over the centuries, have focused on different aspects of spalting. Some have preferred the bright pigments and some have preferred the zone lines, while others have built folk tales to actively avoid the wood altogether. What is most interesting is the frequency with which spalting turns up in ancient and modern human history, and the different ways humans have reacted to and used it.
1.1. Western Europe
Although spalted wood was likely used well before, spalted wood became prominent in wood art around the late 1400s–early 1500s in Italy [1]. Influenced heavily by incrusted Islamic marble work, European medieval furniture began incorporating wood into its mosaics. The use of mosaics entered Italy in the fourteenth century on chests, small boxes, and cabinets, but included materials such as bone, ivory, mother-of-pearl, horn, and metals as well as wood. The middle of the fourteenth century saw the rise of intarsia in Italy—small cuts of wood made from 3–5 mm-thick veneer.
The small cuts of wood were laid out and glued together to create a larger image, often a panel. Perspectives, portraits, and landscapes were popular scenes. To the extent that they could, the woodcutters used natural wood-color variation—brown from walnut, red from cherry, blacks and greys from bog oak, etc., to give vibrancy to their work [1]. Ivory and horn were also occasionally dyed, however, wood itself, at this time, was seldom colored—primarily due to wood-dye technology being in its infancy (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7).
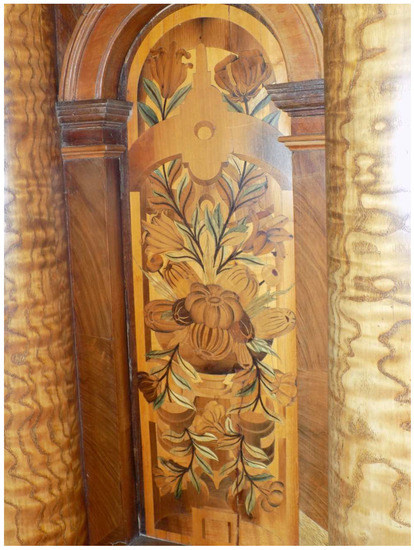

Figure 4.
Door detail from the Ambassador’s Room, Royal Monastery San Lorenzo de El Escorial, Spain, 1562–1570 [2]. Originally made in Augsburg by Bartholomew Weisshaupt. Image shows the use of Chlorociboria-stained wood (blue-green) in the leaves of the marquetry. Photo: Royal Sites Spain.
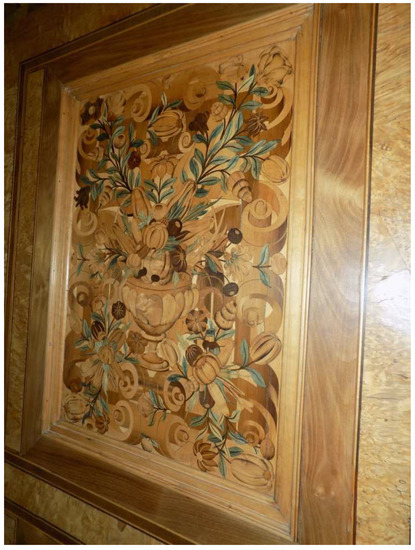

Figure 5.
Another detail panel from the Ambassador’s Room, Royal Monastery San Lorenzo de El Escorial, Spain, 1562–1570 [2]. Originally made in Augsburg by Bartholomew Weisshaupt. Image shows the use of Chlorociboria-stained wood (blue-green) in the leaves of the marquetry. Photo: Royal Sites Spain.
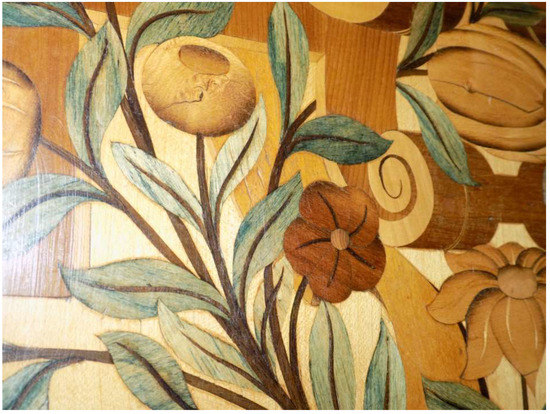

Figure 6.
Close up of the leaf detail from the Ambassador’s Room, Royal Monastery San Lorenzo de El Escorial, Spain, 1562–1570 [2]. Originally made in Augsburg by Bartholomew Weisshaupt. Image shows the use of Chlorociboria-stained wood (blue-green) in the leaves of the marquetry. Photo: Royal Sites Spain.
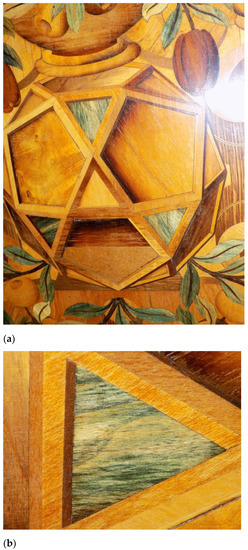
Figure 7.
Close up of geometric marquetry from the Ambassador’s Room, Royal Monastery San Lorenzo de El Escorial, Spain, 1562–1570 [2]. Originally made in Augsburg by Bartholomew Weisshaupt. Image shows the use of Chlorociboria-stained wood (blue-green) in the leaves (a) and interior triangles of the marquetry (b). Photo: Royal Sites Spain.
Most color in these panels were muted and dull. The one bright exception was a blue-green wood, shockingly distinct from its peers. The fungal pigment, known as xylindein, is produced by Chlorociboria species, a soft-rotting, cup-shaped fungus that grows throughout the world in wet, temperate forests. Chlorociboria stains wood as it decays, leaving behind a distinctive aquamarine hue. Wood stained by Chlorociboria was frequently used in these intarsia works, with the oldest known example being a Sicilian casket from the thirteenth century [1].
The use of blue-green wood (which falls under pigment-type spalting) became increasingly popular, and the mid-1400s through the late 1600s showed an explosion of blue-green wood in intarsiated and marquetry works. The wood was used for many applications, such as water, grass, clothing, book bindings, various types of vegetation, and animals such as parrots. The use of spalted wood (or collection of works that contained spalted wood) in intarsia and marquetry spread from Italy to Germany, Sweden, Spain, and later England (particularly Tunbridge Wells, London, UK) [1,2,3], with the skill and use of the spalted wood becoming increasingly complex. English brown oak also became a popular wood for contrasting and depth-based inlays during the Italian Renaissance, due to its uniform, rich brown color—courtesy of colonization by the brown rotting fungus Fistulina hepatica. Used to a lesser extent, but still popular, were grey stains produced by Ophiostomatoid fungi (‘blue stains’) to represent cloudy skies and occasionally water, and dark zone lines by a variety of white, rotting fungi, to give illusions of depth or to imitate marble. Blue-green wood was so popular, and microorganisms so poorly understood, that this specific type of spalting became known as ‘nature’s miracle’ [1]. It is unknown if artists at the time were able to induce spalting, or if there was merely an abundance of raw material that was harvested directly from the forest. Found bills of sale do indicate that Chlorociboria-stained wood was bought and sold, highly sought after, and valuable. Other types of spalting, which would have been easier to find and work with, were not used with any regularity. Zone-lined wood in particular, which is valuable in current markets, was not of as much interest to Renaissance woodworkers, as dye technology for stable blacks and browns was not limited, and there were plenty of wood species already in those colors to work with.
Unfortunately, the advancement of dye technology (particularly light, stable blue-green dyes that could be applied across substrates) and the Industrial Revolution in Europe left many guild traditions lost to time. Chlorociboria-stained wood did remain in use in English Tunbridge Ware boxes through the 20th century, but the distribution of these boxes, and the use of spalted wood on more middle-class offerings, did not lend to continued popularity. By the mid-seventeenth century, spalted wood had faded from the European marquetry landscape. The marquetry landscape changed as well, as handcrafts gave way to mass-produced, mechanized products. The existence of spalted wood and its use in grand marquetry and intarsia was forgotten until the early 1990s, when both German and U.S. researchers took samples of blue-green marquetry work and found they contained hyphae with blue-green pigment—indicating colonization by Chlorociboria species [4,5]. Until this discovery, museum curators had thought the blue-green color to be nothing more than the work of an oddly stable dye.
1.2. U.S.A
English brown oak moved heavily into U.S. furniture in the 1950s–1970s, again due to its unique, uniform brown color [1], which is caused by secretion of a brown pigment from beefsteak fungus, Fistulina hepatica. Interestingly, beefsteak fungus is one of the few brown, rotting fungi to be used for spalting, as most other species in the category turn the wood into cubic, cracked powder. Early-stage colonization by Fistulina hepatica results in an even brown pigment diffusing into the wood, and a subtle brittleness, but not whole-scale destruction.
More important to this region and time period, however, were zone lines. Zone lines (demarcation lines, usually composed of dark melanin, which delineate fungal boundaries), having played a limited role in Western European marquetry, were adopted independently by the U.S. Studio Woodturning Movement in the 1960s. Prior to this movement, woodworkers and consumers in the region strove for perfection and functionality in form. This meant useful items such as bowls, plates, and cups, made from wood free of knots, bark, and fungal colonization. Design was an allowed element, especially following the increasing influence of Bauhaus and the evolution of European woodturning. Of particular influence on the U.S. Studio Woodturning Movement was U.K. woodturner Maria Van Kesteren, who worked as well in glass and clay. Her work, along with many other U.K. woodturners, helped inform early U.S. studio woodturners, who were slowly moving into heavy design incorporation in their turned work.
The freedom of design lead to a broader inclusion of wood in woodturning, and birthed the U.S. Studio Woodturning Movement. This movement, like many studio movements of the time, attempted to redefine woodturning from craft and functionality into conceptual art (Figure 8). Early studio woodturning used spalted wood as the base material to make these statements—using a presumed ‘punky’ or otherwise ‘useless’ decayed wood for both sculptural and semi-functional purposes. Although all types of spalted wood were used, black zone-line-type spalting was the most popular and was, thereby, popularized along with the changing shapes popular with the studio woodturning through the 1980s. The term ‘spalting’ was coined during this time, although its full etiology remains unknown [6]. Some of the earliest use of turned spalted wood from this movement came from Rude Osolnik (1915–2001) and Osolnik Originals (the signature indicating his wife also contributed to the piece). Mel Lindquist (1911–2000) was also an early proponent of spalted wood for turning and together with his then-ceramicist son Mark, pushed U.S. woodturning into a studio movement. Spalted wood, spalted turnings, and, later, spalted sculpture went from tented craft shows to downtown galleries, to Fine Woodworking and the New York Times, to, finally, museums such as the Smithsonian’s Renwick.
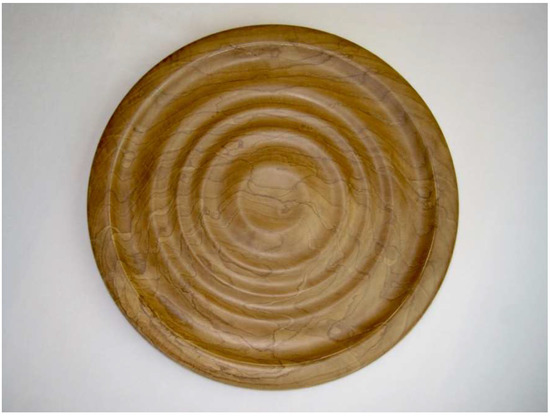

Figure 8.
Turned piece of oak stained brown by Fistulina hepatica, the fungus responsible for English Brown Oak. From the artwork Problematic Undercurrents by Seri Robinson.
Most of the spalted wood popularized during the U.S. Studio Woodturning Movememnt was zone-lined wood. This is likely due to the prevalence of zone-line spalting across temperate forests, and the better workability. Chlorociboria species, responsible for the previously popular blue-green spalting, frequently grow on already very decayed wood and hence, said wood is often, though not always, suitable for smaller applications, such as marquetry [1]. Zone lines, especially brown and black zone lines, are formed by a range of white rot and soft-rot fungi, most of which leave early-colonized wood suitable for woodturning and larger applications. Chlorociboria-stained wood is not rare in the U.S., however, it is uncommon and does not grow across all forest types. In contrast, zone lines are created by thousands of different fungi and occur with regularity on all hardwoods.
The 1990s brought the rediscovery of spalted wood in European marquetry—although pigment-type spalting did not move back into mainstream woodworking until the 2000s [1,4,5] and is still underutilized when compared to the popularity of zone line spalting. In the United States, many woodworkers and woodturners still only associate spalted wood with black zone lines and not pigment or bleaching. However, there is a growing use of spalting pigments in U.S. woodturning, particularly as dyes. The growth or harvesting of pigmenting fungi, extraction of the pigment into solvents such as acetone and dichloromethane, and then direct reapplication of the pigment back onto otherwise sound wood (or zone-lined wood) has taken the time and guesswork out of spalting. For many hobbyists and crafters, this processing has made spalted wood more accessible, faster, and more applicable to areas outside of woodturning.
As spalted wood gained popularity (and price) in the modern U.S., the culture and myth around spalting (and its cause) grew. Advanced processing, as mentioned above, continued to increase interest in having access to larger and larger amounts of spalted wood. No longer content with foraging, woodworkers developed methods to generate their own spalted wood. Urban legends sprung up, the most popular of which are spalting ‘recipes’, which abound on the Internet and attempt to teach the reader how to induce spalting in otherwise clear lumber. While Renaissance masters may have understood the concept that placing one piece of blue-green wood next to a clear piece of wood eventually generates more blue-green wood, U.S. woodworkers took spalting cultivation to new levels. The recipes vary by region, but most share the misconception that spalting is directly related to fungal growth. Hence, recipes advocate for additional resources to be added to wood, to help speed fungal growth. Additives such as beer and human urine are common.
Unfortunately, spalting is a product of fungal stress (hence, spalting pigments being secondary metabolites). Due to this misunderstanding of spalting mechanisms, most recipes cause the spalting to take longer than nature alone, as fungi preferentially utilize the free sugars available before expending resources to break down the wood cell wall (a required component to further penetrate wood). However, there is something deeply whimsical about instructions to slather wood with Miracle Grow, ground deer antlers, beer, and/or mayonnaise, that harkens back to earlier times and earlier understandings of spalting [7]. Is spalted wood a miracle from god, as in the Renaissance, or an artifact of modern, near-alchemical additives? Is it more important to drink the beer and then urinate on the wood, or simply to pour the beer over the wood and then, perhaps, mix in some mayonnaise? Does the type of leaves you bury your spalting pile in matter? Regardless, it is clear is that from the moment spalted wood hit the modern U.S. consciousness, artists and crafters were eager to try their hand, not only working with it but producing their own, even if they did not truly understand it.
1.3. Chile
While there are numerous examples of cultures that have embraced spalted wood as an art material, some cultures have evolved taboos around spalted wood that have kept the material from moving to mainstream use. One interesting example is Chlorociboria-stained wood in Chile (Figure 9 and Figure 10). In Chiloé, Chile, legend tells of a ‘trauco’, or little troll-like man, who is very ugly and walks on stumps as he has no feet. Women find him irresistible and upon seeing him, must immediately sleep with him (thus, the Chileans have an excellent method to explain unplanned pregnancies). In Chiloé, the blue-green Chlorociboria wood is said to be ‘trauco poop’, and is, therefore, taboo and not heavily used [7]. Modern woodworkers in the region do use spalted wood, including both Chlorociboria-stained wood and zone-lined wood, but not with regularity.
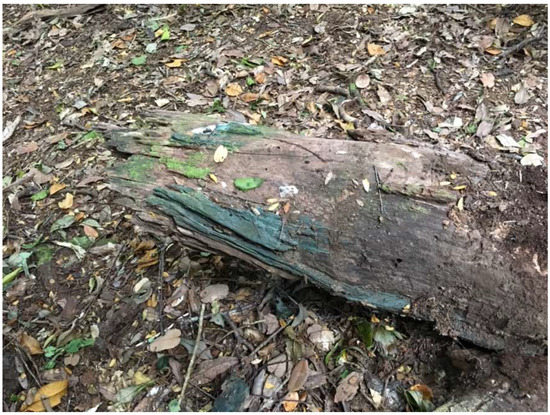

Figure 9.
Chlorociboria-stained wood from Valdivia, Chile.

Figure 10.
Chlorociboria-stained wood from Chiloé, Chile. Photo courtesy of Patricia Vega Gutierrez.
2. Modern Applications
Although traditionally used as a natural wood colorant in art, the last decade has seen an explosion of spalted wood use in the sciences. Scientists have been fascinated by Chlorociboria’s unique blue-green pigment, xylindein, since around 1812, when French chemist Eugéne Chevreul published about a greenish-blue color in wood [8]. Extraction of xylindein is believed to have begun around 1863, by French chemist M. Fordos [9]. The first known patent on spalted wood came in 1913, when Brooks sought to use xylindein as a natural fungicide [10].
The understanding of zone lines as melanized areas in wood that usually delineate fungal borders blossomed in the 1930s, through the works of scientists such as Alex Campbell [11,12,13]. The scientific literature on fungal interactions and fungal secondary metabolites continued to grow through the rest of the century, but spalting itself remained, mostly, a curiosity.
Within the last decade or so, however, non-artistic use of spalted wood—particularly the pigments extracted from spalted wood—has exploded (Figure 11). Spalting pigments, particularly xylindein from Chlorociboria, dramada from Scytalidium cuboideum, and the uncharacterized yellow pigment from Scytalidium ganodermophthorum, have been found to be exceptional textile dyes, being colorfast, and requiring no mordants, no rinsing, and no water carriers [14,15,16]. The pigments can be carried in many natural oils, making them applicable as colorants in artists’ paints and as oil-based textile dyes [17,18,19,20], although stabilization of the pigment is needed in some instances. Xylindein was found to have semiconductive properties and was investigated for use in photovoltaic cells [21,22,23,24,25], and the red crystal dramada, produced by the spalting fungus Scytalidium cuboideum, was successfully turned into an ink and used in a textile inkjet printer [26,27] (Figure 12). Dramada was also investigated for potential optoelectronic applications [28,29]. Spalting pigments have been used as a replacement for woodworkers’ synthetic aniline dyes [30], paper colorants [31] (Figure 13), and as UV-weathering protectants for wood decking [32]—the unique properties of xylindein make it an excellent UV retardant (Figure 14).
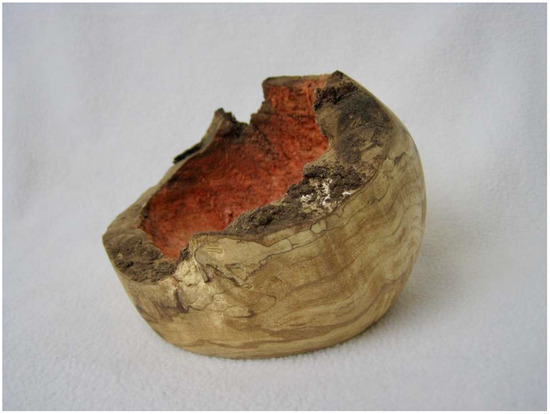

Figure 11.
Red stain from Scytalidium cuboideum on maple burl. Just a Little Tear, by Seri Robinson.
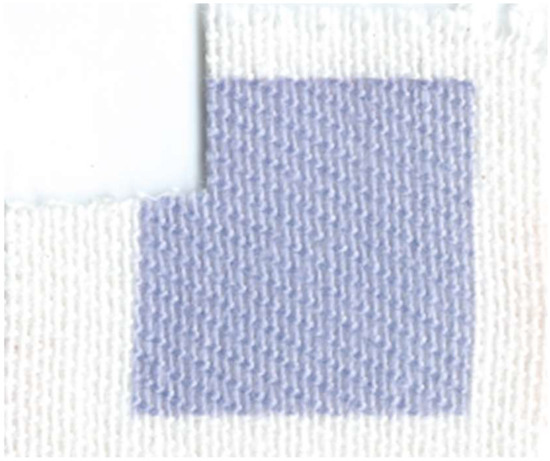

Figure 12.
Pigment Dramada on cotton, printed via inkjet printer. Photo courtesy of Sarath Vega Guteirrez.
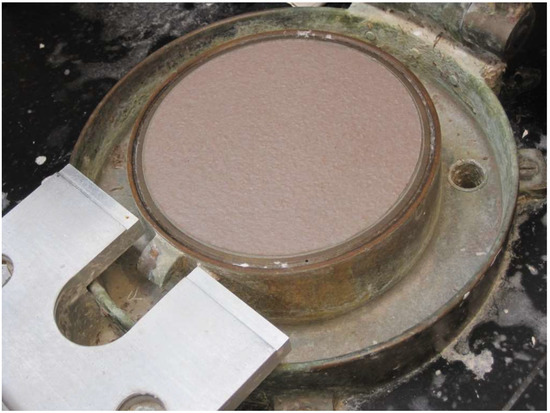

Figure 13.
Paper pressing with wet pulp and a blend of dramada from Scytalidium cuboideum. Photo courtesy of Sarath Vega Gutierrez.

Figure 14.
The full range of colors from Chlorociboria species, Scytalidium cuboideum, and Scytalidium ganodermophthorum.
3. Conclusions
Spalted wood has long occupied a place in the human imagination. Although historic use focused on wood art and mythology, the material is heavily used today in the sciences as a durable, UV-stable colorant and has potential applications in (opto)electronics. As understanding of spalting fungi and their pigments continues to evolve, there is likely to be considerable overlap between historic cultural uses and modern scientific curiosity. Cultures still rediscovering spalted wood are likely to find novel uses for the material, both in the arts and sciences.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Robinson, S.C.; Michaelsen, H.; Robinson, J. Spalted Wood: The History, Science, and Art of a Unique Material; Schiffer Publishing: Atglen, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vega Gutierrez, P.; Robinson, S.C. Determining the presence of spalted wood in Spanish marquetry woodworks of the 1500s through the 1800s. Coatings 2017, 7, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.A. British Fungi, Part 2; Jarrold & Sons: Norwich, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette, R.A.; Wilmering, A.M.; Baumeister, M. The use of green-stained wood caused by the fungus Chlorociboria in intarsia masterpieces from the 15th century. Holzforschung 1992, 46, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, H.; Unger, A.; Fischer, C.-H. Blaugrüne Färbung an Intarsienhölzern des 16. und 18. Jahrhunderts. Restauro 1992, 98, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.C. The Lindquist Legacy; Schiffer Publishing: Atglen, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.C. Spalting 101; Schiffer Publishing: Atglen, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Osann, G.W. Chevreul, Versuche mit dem Indig, Weid und Anil, bearbeitet von A.F. Gehlen. In Beiträge zur Chemie und Physik; Schweiger, J.S.C., Ed.; 1813; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Rommier, A. Über das Xylindein, einen aus abgestorbenem Holze dargestellten neuen Farbstoff: Übersetzung aus dem Comptes rendus, t. LXVI. Polytech. J. 1868, 188, 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, F.T. Improvements in or Relating to Colouring and/or Preserving Wood. UK Patent 24,595, 29 October 1914. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, A.H. Zone lines in Plant Tissues: I. The black lines formed by Xylaria polymorpha (Pers.) Grev. in hardwoods. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1933, 20, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.H. Zone lines in Plant Tissues: II. The black lines formed by Armillaria mellea (Vahi) Quel. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1934, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.H.; Munson, R.G. Zone lines in Plant Tissues. III. The black lines formed by Polyporus squamosus (Huds.) Fr. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1936, 23, 453–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Chen, H.-L.; Hinsch, E.; Freitas, S.; Robinson, S.C. Pigments extracted from the wood-staining fungi Chlorociboria aeruginosa, Scytalidium cuboideum, and S. ganodermophthorum show potential for use as textile dyes. Coloration Technol. 2014, 130, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsch, E.; Weber, G.; Chen, H.-L.; Robinson, S.C. Colorfastness of extracted wood-staining fungal pigments on fabrics—A new potential for textile dyes. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2015, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hinsch, E.; Robinson, S.C. Mechanical color reading of wood-stained fungal pigment textile dyes: An alternative method for determining colorfastness. Coatings 2016, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.C.; Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Cespedes, R.A.; Iroume, N.; Vorland, N.R.; McClelland, A.; Huber, M.; Stanton, S. Potential for carrying pigments derived from spalting fungi in natural oils. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino Agurto, M.E.; Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Chen, H.-L.; Robinson, S.C. Wood-rotting fungal pigments as colorant coatings in oil-based textile dyes. Coatings 2017, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.C.; Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Cespedes Garcia, R.A.; Iroume, N.; Vorland, N.R.; Andersen, C.; de Oliveira Xaxa, I.D.; Kramer, O.E.; Huber, M.E. Potential for fungal dyes as colorants in oil and acrylic paints. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino Agurto, M.E.; Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Van Court, R.C.; Chen, H.-L.; Robinson, S.C. Oil-based fungal pigments from Scytalidium cuboideum as a textile dye. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbers, G.; Van Schenck, J.; Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Robinson, S.C.; Ostroverkhova, O. Fungi-derived pigments for sustainable organic (opto)electronics. EP02: Excitonic Materials—Physics, Characterization and Devices. MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 3459–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbers, G.; Krueger, T.; Van Schenck, J.; Van Court, R.; Morré, J.; Fang, C.; Robinson, S.C.; Ostroverkhova, O. Fungi-derived xylindein: Effect of purity on optical and electronic properties. MRS Adv. 2019, 4, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbers, G.; Van Schenck, J.; Quinn, A.; Van Court, R.; Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Robinson, S.C.; Ostroverkhova, O. Xylindein: Naturally produced fungal compound for sustainable (opto)electronics. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13309–13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, T.D.; Geisbers, G.; Van Court, R.; Liangdong, Z.; Kim, R.; Beaudry, C.M.; Robinson, S.C.; Ostroverkova, O.; Fang, C. Ultrafast dynamics and photoresponse of a fungi-derived pigment xylindein from solution to thin films. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 5627–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbers, G.; Krueger, T.; Van Schenck, J.; Kim, G.; Van Court, R.; Robinson, S.C.; Beaudry, C.; Fang, C.; Ostroverkhova, O. The role of hydroxyl groups in the photophysics, photostability, and (opto)electronic properties of the fungi-derived pigment xylindein. J. Phys. Chem. 2021, 125, 6534–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; He, Y.; Cao, Y.; Stone, D.W.; Walsh, Z.M.; Malhotra, R.; Chen, H.-L.; Chang, C.-H.; Robinson, S.C. Feasibility and surface evaluation of the pigment from Scytalidium cuboideum for ink-jet printing on textiles. Coatings 2019, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hwang, H.-J.; Debarajb, H.; Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Chen, H.-L.; Robinson, S.C.; Malhotra, R.; Chang, C.-H. Inkjet printing and in-situ crystallization of biopigments for eco-friendly and energy-efficient fabric coloration. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2021, 9, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, T.D.; Tang, L.; Giesbers, G.; Van Court, R.; Zhu, L.; Robinson, S.C.; Ostroverkhova, O.; Fang, C. Ultrafast triplet state formation of a methylated fungi-derived pigment for sustainable optoelectronic materials. J. Phys. Chem. 2021, 125, 17565–17572. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, T.D.; Solaris, J.; Tang, L.; Zhu, L.; Van Court, R.C.; Robinson, S.C.; Ostroverkhova, O.; Fang, C. Illuminating excited state intramolecular proton transfer of a fungi-derived red pigment for sustainable optoelectronics. J. Phys. Chem. 2021, 126, 459–477. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, H.; Robinson, S.C.; Vega Gutierrez, P.; Stanton, S. Spalting pigments as colorants in wood stabilizers. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.W.; Vega Gutierrez, S.; Walsh, Z.M.; Robinson, S.C. Potential of the red pigment from Scytalidium cuboideum as a cellulosic pulp colorant. Challenges 2022, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Gutierrez, S.M.; Stone, D.W.; He, R.; Vega Gutierrez, P.T.; Walsh, Z.M.; Robinson, S.C. Red pigment from the fungus Scytalidium cuboideum helps prevent ‘greying’ in decking and other outdoor wood products. Coatings 2021, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).