Definition
Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides mainly consist of characteristic TFF domains, which contain about 40 amino acid residues, including 6 conserved cysteine residues. TFF peptides possess a single (mammalian TFF1 and TFF3), two (mammalian TFF2, Xenopus laevis xP2) or four TFF domains (X. laevis xP4). They exhibit lectin activities and are characteristic exocrine products of the mucous epithelia. Here, they play different roles for mucosal protection and the innate immune defense: TFF1 is a gastric tumor suppressor; TFF2 builds a lectin complex with the mucin MUC6, physically stabilizing the inner gastric mucus layer; and TFF3 forms a disulfide-linked heterodimer with IgG Fc binding protein (FCGBP), probably preventing the infiltration of microorganisms. Minor amounts of TFF peptides are endocrine products of the immune and nervous systems. Pathologically, TFF peptides are linked to inflammation. There are increasing indications that TFF peptides can antagonize cytokine receptors, such as receptors for IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα (thereby acting as anti-inflammatory peptides). TFF peptides can probably also activate a variety of receptors, such as CXCR4. The TFF domain is a unique shuffled module which is also present in a number of mosaic proteins, such as zona pellucida proteins, sugar degrading enzymes and frog skin mucins. Here, their function seems to be defined by a lectin activity, which might even allow a role in fertilization.
1. Introduction or History
Members of the trefoil factor family, i.e., mammalian TFF1, TFF2, and TFF3, are primarily considered secretory peptides involved in mucosal protection and defense (reviews: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]). Furthermore, they are synthesized in the immune and nervous systems, and probably also blood vessels. They share a common cysteine-rich structural motif, the TFF domain (formerly: trefoil domain [1], P-domain [3]).
Historically, human TFF1 (formerly “pS2”) was discovered in 1982 as an estrogen responsive transcript [15]. TFF2 (formerly “pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide”) was detected independently at the same time [16], and a first sequence appeared in 1985. The similarity of TFF1 and TFF2 was only recognized in 1988 when TFF domains were detected in the frog integumentary mucin FIM-A.1 (formerly “spasmolysin”) [17]. TFF3 (formerly “intestinal trefoil factor” or “hP1.B”) was described in 1991 in the rat [18] and in 1993 in humans [19,20]. Thus, the discovery was a result of four independent groups working in different fields (review: [21]). The present nomenclature is based upon an agreement reached at the Conférence Philippe Laudat in Aix-les-Bains in 1996 in order to avoid the single term “trefoil” because of its manifold meanings [22].
Thus far, TFF peptides have been characterized from amphibia to mammals. TFF modules already arose before amphibian evolution, i.e., in a tunicate and a nematode [21,23]). Furthermore, there is a number of mosaic proteins known which contain TFF domains, such as the human zona pellucida proteins ZP1 and ZPB, the sugar-degrading enzymes sucrose-isomaltase, α-glucosidase, and maltase-glucoamylase, the frog skin proteins APEG, “βγ-crystallin and trefoil factor” (βγ-CAT), and the frog integumentary mucins FIM-A.1 and FIM-C.1 (reviews: [12,21]).
Within the last four decades, our understanding concerning the biosynthesis and function of these peptides changed dramatically and only within the last years has a somewhat clearer picture emerged.
2. Structure and Expression
2.1. Genomic Organization, Structure and Natural Forms of TFF Peptides
In humans, all three TFF genes are clustered on chromosome 21q22.3 in a head-to-tail arrangement in the order telomer-TFF1-TFF2-TFF3-centromer (review: [24]). In the mouse, a syntenic region is located on chromosome 17q. Of note, all TFF domains are encoded by separate exons, as is typical of shuffled modules.
As a hallmark, the TFF domain contains six conserved cysteine residues, creating a disulfide-linked, three-looped structure (Figure 1) [3,5]. TFF1 and TFF3 show high similarity, as both consist of a TFF domain and an additional seventh cysteine residue near the C-terminal (CysVII). A major difference between TFF1 and TFF3 is probably the nucleophilicity of CysVII, which seems to be enhanced in TFF1 due to steric exposure by neighboring proline residues (Figure 1). Furthermore, the pKa of CysVII is probably different in TFF1 and TFF3 because of the multiple flanking acidic residues, particularly in TFF1 (Figure 1). In contrast, TFF2 consists of two TFF domains arranged in tandem; the N- and the C-terminals are linked via two additional cysteine residues (Figure 1). This gives rise to a circular structure, which probably can adopt different conformations [25,26]. Notably, human TFF2 is N-glycosylated, and the glycosylation probably differs in the stomach when compared with the duodenum; gastric TFF2 contains an unusual fucosylated LacdiNAc oligosaccharide (Figure 1) [27]. In contrast, murine and porcine TFF2 lack N-glycosylation sites.
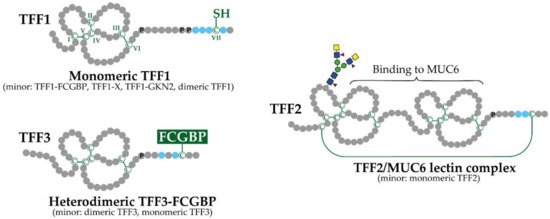
Figure 1.
Schematic structures of human TFF1, TFF2, and TFF3 and their major natural forms (minor forms are mentioned in parentheses). Cysteine residues (C; numbering in Roman numerals) and disulfide bridges are shown in green. Proline residues (P) at the C-terminal outside the TFF domains are indicated. Acidic residues in proximity to the C-terminal cysteine residues are shown in blue. Additionally, the N-linked carbohydrate moiety in gastric TFF2 is illustrated.
The secondary and tertiary structures of recombinant TFF peptides (TFF1 and TFF3 homodimers) and purified porcine pancreatic TFF2 were studied by the use of X-ray crystallography as well as two-dimensional 1H NMR spectroscopy (review: [9]). Generally, the TFF domains show very similar folds. The 3D structures are available from the Protein Data Bank (PDB; https://rcsb.org/, accessed on 7 September 2021). There is a pronounced groove between the ends of the second and third loops, and this has been discussed as a potential binding site for either an oligosaccharide or an aromatic amino acid side chain. Conserved residues are placed around this groove.
Of special note, TFF1 and TFF3 contain an odd number of cysteine residues, which is unusual for secretory proteins because disulfide formation is enforced in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Normally, such free thiol groups act as a three-way switch, mediating assembly, retention, or degradation in the ER, but they are not secreted.
Only long-lasting systematic studies have revealed that TFF peptides appear in unexpected different molecular forms (Figure 1), indicative of diverse molecular functions (see Section 3.2; reviews: [12,14]).
Surprisingly, TFF1 occurs predominantly in a monomeric form, probably with an unusual free thiol group (Figure 1). This has been demonstrated for X. laevis (ortholog xP1), mouse and human [26,28,29]. The reason is probably the cluster of acidic residues as well as the proline residues before (Figure 1), which would allow TFF1 to escape ER retention, as has been similarly described for Ig light chains [26,28,29]. Minor forms of TFF1 are disulfide-linked heterodimers with IgG Fc binding protein (FCGBP), a yet-unknown protein X with a Mr of 60 k (TFF1-X), and gastrokine 2 (GKN2), as well as a homodimer [12,26,29,30,31].
Gastric TFF2 mainly exists in a high molecular mass form associated with the mucin MUC6 (TFF2/MUC6 complex; Figure 1) [12,25,31,32,33,34], whereas porcine pancreatic TFF2 mainly forms a non-covalently linked homodimer [32].
TFF3 mainly forms a disulfide-linked heterodimer with FCGBP, as shown for the intestine and the saliva (Figure 1) [35,36]. Minor forms are a monomer and a homodimer. There are indications that the homodimer spontaneously forms only after secretion.
In the frog X. laevis, the TFF1 ortholog is termed xP1, whereas xP4.1 and xP4.2 are the X. laevis orthologs of mammalian TFF2 [28,37,38]. As a special feature, xP4.1 and xP4.2 contain four TFF domains arranged in tandem. In xP4.1, exon shuffling of TFF modules has also been documented [39]). Thus, the TFF domain is a unique shuffled module encoded by a single exon belonging to class 1-1 (review: [24]).
2.2. Mosaic Proteins Containing TFF Domains
As is typical of shuffled modules, TFF domains also occur in a number of mosaic proteins: zona pellucida proteins from humans (ZP1 and ZPB) and teleost fish, sugar-degrading enzymes (sucrose-isomaltase, α-glucosidase, and maltase-glucoamylase), frog skin proteins (APEG, which is a splice variant of xP2; βγ-CAT), as well as the frog integumentary mucins FIM-A.1 and FIM-C.1 [12,21,23]). Generally, many of these proteins are associated with carbohydrate moieties.
2.3. Exocrine Secretion of TFF Peptides in Mucous Epithelia
The majority of TFF peptides are secreted from mucous epithelia, where they are released together with mucins in an exocrine manner (reviews: [2,7,21,40,41]. TFF1 is mainly expressed in gastric surface mucous cells (together with the mucin MUC5AC). TFF2—together with MUC6—is restricted to gastric mucous neck cells, antral gland cells and duodenal Brunner’s glands, whereas TFF3 is a typical product of intestinal goblet cells as well as most other mucous epithelia and their glands. Consequently, TFFs are constituents of mucus barriers and appear also in the corresponding exocrine body fluids, such as saliva, gastric juice, urine, tears and breast milk [10].
2.4. Endocrine Secretion of TFF Peptides
Tiny amounts of TFF peptides also undergo endocrine secretion (for reviews, see [12,13]), such as in lymphoid organs and tissues (thymus, bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, gut-associated lymphatic tissue, etc. [42,43,44]), the brain [45], the thyroid, the pancreas, and probably also blood vessels. For example, TFF2 (and to some extent also TFF3) is synthesized in peritoneal macrophages and memory T-cells; cerebral TFF3 is particularly synthesized in neurons and activated microglial cells. As a consequence, TFFs are detectable in normal human serum [10,12].
2.5. Pathological Expression of TFF Peptides: Links to Inflammation and Cancer
Based upon histopathological evaluation (immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, in situ hybridization), the ectopic expression of TFF peptides was detected in pathological conditions, particularly during chronic inflammation (for reviews, see [7,10,13,14,21]). Typical examples are gastro-esophageal reflux disease, Barrett’s esophagus, gastric and duodenal ulcers, diverticulitis, inflammatory bowel disease, pancreatitis, hepatolithiasis, cholecystitis, salpingitis, inflammatory nasal polypi, and chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD). In many cases, a glandular structure termed “ulcer-associated cell lineage” (UACL, also known as pyloric or pseudo-pyloric metaplasia) was the prominent site of TFF peptide synthesis [46]. After mucosal injury/ulceration, TFF2 was characterized as an early response gene, and TFF3 as a late response gene [47].
TFF expression is also dysregulated in various metaplasias [48,49], as well as in tumors (for compilations, see: [7,10,21,24]). The potential roles of TFF peptides for tumor progression have not been clarified conclusively [6,50,51,52,53,54].
Regulation of TFF gene expression is complex, and the three TFF genes share several cis-acting elements in their promoter regions [55]. Regulatory signals reported include estrogen, transforming growth factor α (TGFα), fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), gastrin, TFF peptides (interregulation), pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, prostaglandins, arachidonic acid, indomethacin, aspirin, omeprazole, butyrate, hydrogen peroxide, osmotic stress, hypoxia, X-ray irradiation, and pathogens (reviews: [21,51,52,56,57]). Stimulation by omeprazole and FGFs could be secondary effects due to gastrin.
Numerous studies have analyzed the regulation of TFF expression during inflammation in particular, and the three TFF genes have been shown to often respond differently to inflammatory mediators (for review, see [13]). Generally, the links between TFF peptides and inflammation are rather complex. On the one hand, inflammatory signals regulate TFF expression. On the other hand, TFF peptides influence inflammatory processes, which also enables complex feedback loops with inflammatory signals.
3. Functional Aspects
Primarily, TFF peptides play different roles in the mucosal protection and defense, such as being part of the innate immune system (for reviews, see [12,14]). There is also a broad range of literature describing (relatively weak) protective effects in various animal models (for reviews, see [10,21]). Furthermore, TFF peptides also seem to modulate immune responses (see Section 3.5), and they have enigmatic functions in the nervous system, such as fear-modulating activities and a role in motoric coordination (for reviews, see [12,21]).
3.1. TFF Domains Have Different Lectin Activities
All three TFF peptides are sugar-binding proteins, i.e., they have lectin activities [58], but to different extents and with different specificities (for reviews, see [13,14]). Dimeric TFF1 binds to the core oligosaccharide of the Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide, while TFF3 binds with lesser affinity [59,60]. Studies with glycosylation-defective H. pylori mutants point to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) as being part of the carbohydrate structure recognized by TFF1 [61]. Dimeric TFF1 also interacts weakly with the carbohydrate moiety of the gastric mucin MUC6 in vitro [29]. Binding is conserved from X. laevis to humans and probably occurs at the conserved O-linked GlcNAcα1→4Galβ1→R moiety [61].
TFF2 strongly binds to the evolutionary conserved O-linked GlcNAcα1→4Galβ1→R moiety of the mucin MUC6, and both the αGlcNAc as well as the βGal residues are essential for binding [25,28,33,34,62]. TFF2 binding is dependent on the pH and is modulated by Ca2+ [25,33]. A prerequisite for the biosynthesis of the unusual terminal αGlcNAc residue is α1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (A4GNT), which is mainly restricted to TFF2/MUC6 secreting cells, such as mucous neck and antral gland cells in the stomach and Brunner’s gland cells in the duodenum (see also Section 3.4.).
Furthermore, TFF domains occur as shuffled modules in sugar-degrading enzymes (sucrose-isomaltase, α-glucosidase, and maltase-glucoamylase), pointing also to a lectin activity. Shuffled TFF modules are also integral parts of the frog integumentary mucins FIM-A.1 and FIM-C.1 from X. laevis, which form high molecular mass complexes, probably via lectin activities of the TFF modules [63].
3.2. Exocrine TFF Peptides Occur in Different Molecular Forms and Have Diverse Molecular Functions
Under normal conditions, TFF peptides are mainly secreted by mucous epithelia and occur in different molecular forms (Section 2.1., Figure 1). Here they play different roles mainly in the mucosal innate immune defense (for reviews, see [12,14].
Due to its free thiol group, monomeric TFF1 (Figure 1; and the X. laevis ortholog xP1) is perfectly designed to act as an extracellular scavenger for reactive oxygen/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) [26,28,29]. This predominant form would particularly protect the gastric surface from damage by the ROS H2O2 and O2− (Figure 2A) [12]. Gastric juice is also a rich source of peroxynitrite (ONOO−), the prototype of a toxic RNS, which is formed from HO-NO after disproportionation and reaction with O2− [12]. Heterodimeric TFF1-GKN2 mainly occurs in the antrum, is hardly soluble and seems to be a constituent of the firmly adherent inner layer of the gastric mucus barrier [12,29]. In contrast, TFF1-FCGBP is probably located in the outer layer of the gastric mucus barrier and might be involved in the clearing of microorganisms [12,14,26,29].
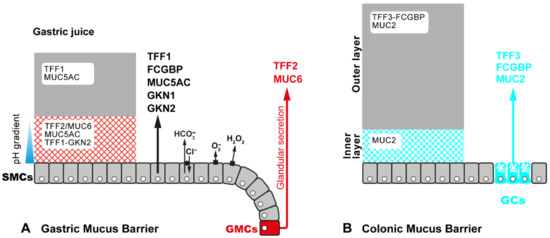
Figure 2.
Schematic model of the gastric mucus-bicarbonate barrier (A) and the colonic mucus barrier (B), respectively. Both barriers consist of a loose outer layer (grey) and a firmly attached inner layer (hatched). (A) The gastric mucus originates from different cell types, i.e., surface mucous cells (SMCs) and glandular mucous cells (GMCs, i.e., fundic mucous neck cells and antral gland cells, respectively). SMCs secrete TFF1, gastrokines GKN1 and GKN2, FCGBP and the mucin MUC5AC, whereas GMCs secrete TFF2 and the mucin MUC6. SMCs also secrete bicarbonate (HCO3−) in exchange with Cl−, creating a pH gradient along the inner layer. Furthermore, as part of the innate immune defense, they generate H2O2 and O2− via dual oxidase (DUOX) and NADPH oxidase (NOX), respectively. Monomeric TFF1, which is the predominant soluble form of TFF1, appears also in the gastric juice. The TFF2/MUC6 complex seems to be concentrated in the inner mucus layer. (B) TFF3, together with FCGBP and the mucin MUC2, is secreted from goblet cells (GCs). The heterodimer TFF3-FCGBP is easily soluble and seems to be concentrated in the outer layer.
TFF2 and the X. laevis orthologs xP4.1 and xP4.2 are lectins tightly bound to the mucin MUC6 (TFF2/MUC6 complex, Figure 1), where they physically stabilize the water-insoluble inner layer of the gastric mucus barrier (Figure 2A) [25,28]. In porcine gastric mucus, TFF2 is more strongly bound than in human mucus [25,32]. The stabilizing effect is even detectable at the electron microscopic level, were the X. lavis ortholog of TFF2, i.e., xP4, prevents shrinking of mucous granules during sample processing [64]. The physical interaction of TFF2 and MUC6 also alters the viscoelastic properties of gastric mucous gels [65]. Thus, TFF2, together with MUC6, contributes to the gastric mucosal innate immune defense (for reviews, see [12,14]).
TFF3 mainly occurs as a disulfide-linked heterodimer with FCGBP (TFF3-FCGBP; Figure 1) [35,36]. FCGBP is a large repetitive cysteine-rich glycoprotein which consists of nearly 5400 amino acid residues. It is widely secreted, together with TFF3, by most mucous epithelia, and there are multiple indications that it plays a role in the innate immune defense (Figure 2B) [66]. Generally, FCGBP is an early response gene after microbial infections and might regulate pathogen attachment and disease progression (for reviews, see [12,14]). For example, it could bind IgG after its transcytosis via the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), and this complex could trap microbia, including viruses [67,68]. Alternatively, FCGBP could directly bind to microbia. Currently, the hypothetical function of TFF3 is not known in TFF3-FCGBP, but TFF3 could specifically modulate the binding to microbia by a lectin activity [12,14,26]. A similar function could arise in TFF1-FCGBP [26,29]. In addition, recombinant dimeric TFF3 also binds to the secreted form of Deleted in Malignant Brain Tumors/gp340 (DMBT1gp340), a repetitive cysteine-rich glycoprotein, which is identical to salivary agglutinin and aggregates, e.g., Streptococuccus mutans [69]. Generally, DMBT1gp340 is a pattern recognition receptor particularly involved in innate mucosal immune defense [70]. Thus, TFF3 might have a role in mucosal innate immunity by enhancing binding of FCGBP and DMBT1gp340 to microbia, maybe together with galectins [12,14].
3.3. Tff-Deficient (TffKO) Mice Have Different Phenotypes: Functional Implications
Mice deficient in TFF1, TFF2 and TFF3 have been investigated partly for more than two decades now (for reviews, see [12,13]). The most prominent phenotype is observed in TFF1KO mice [71].
3.3.1. TFF1 Is a Gastric Tumor Suppressor
TFF1KO mice generally develop adenomas in the gastric antrum, and about 30% progress to carcinomas [72]. Of note, TFF2 expression is drastically reduced in these mice, particularly in the gastric corpus, but hardly in the pancreas [26,72]. TFF1 loss is accompanied by NF-κB activation, chronic antral inflammation, and multi-step carcinogenesis [73]. The dysplastic lesions could be significantly reduced by a selective Cox-2 inhibitor [74]. Thus, TFF1 is a gastric tumor suppressor in mice, and TFF1KO animals are a recognized model for gastric carcinogenesis [71]. Of note, TFF1 expression is lost in approximately 50% of human gastric carcinomas [71].
Elegant lineage tracing studies with TFF1-CreERT2 and TFF1-Cre mice revealed that TFF1 is expressed already in antral Lgr5+ (and maybe also in Cckbr+) progenitor cells, but not in fundic Troy+ progenitor cells [75]. This would explain why inflammation and carcinogenesis in TFF1KO mice is restricted to the antrum (for review, see [13]).
Currently, it is not clear how a loss of TFF1 triggers inflammation and carcinogenesis at the molecular level. There are at least four hypothetical models (or a combination of these) open for discussion (for review, see [13]). First, TFF1 could act as an intracellular chaperone in the ER for, e.g., secretory cysteine-rich glycoproteins, such as the mucin MUC5AC. There are multiple results favoring this hypothesis, such as activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) in TFF1KO mice [13,76]. Second, TFF1 could act as a scavenger for ROS/RNS, in particular to protect highly sensitive stem and precursor cells [26,28,29]. Third, TFF1 could serve as a lectin ligand, which activates or inhibits transmembrane proteins, triggering correct self-renewal of antral units (see also Section 3.4 and Section 3.5) [13]. Fourth, a Gkn2 homodimer detected only in TFF1KO mice (particularly in the antrum) may impact the inflammatory process in the antrum [26].
3.3.2. TFF2: Component of the Gastric Mucus Barrier, Anti-Inflammatory Peptide, and Induction of IL-33 (Promotion of Th2 Immunity)
TFF2KO mice did not show a striking phenotype [77]. They have a highly increased antral TFF3 expression [43] and exhibited accelerated progression of Helicobacter-induced gastritis to dysplasia [78]. The latter is in agreement with a hypothetical function of TFF2 in the gastric mucosal innate immune defense by physically stabilizing the inner mucus layer (Figure 2A) [12,14,25,34].
Furthermore, TFF2KO mice have also a dysregulated expression of immune response-related genes, and their macrophages are hyperresponsive to interleukin (IL)-1β stimulation concerning the secretion of IL-6 [43,44]. There are also multiple studies on TFF2KO mice using different infection models (e.g., Toxoplasma gondii, Yersinia enterocolitica, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis), which showed significant changes in the immune/inflammatory response when compared with the wild type animals (for review, see [13]). This is in line with the observation that TFF2KO mice have a compromised immune system [43]. On the one hand, TFF2 seems to inhibit the immune response; i.e., TFF2 is an anti-inflammatory peptide antagonizing, e.g., the IL-1β-induced expression of IL-6 or the Toll-like receptor (TLR)-driven IL-12 synthesis in macrophages and dendritic cells [44,79]. On the other hand, TFF2 triggers the induction of IL-33 synthesis, probably via the receptor CXCR4 [80,81]; IL-33 is an alarmin promoting Th2 immunity.
3.3.3. TFF3: Component of the Intestinal Mucus Barrier
Under normal conditions, TFF3KO mice are grossly indistinguishable from their wild type littermates [82]. They only show minor motoric deficits and morphological differences in the cerebellum (for review, see [12]). In contrast, in the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis model, TFF3KO mice exhibited a much stronger inflammatory response when compared with the wild type animals [82]. Furthermore, TFF3KO mice were more sensitive to chemotherapy- and radiation-induced intestinal damage [83].
The murine colonic mucus is a two-layered structure with a firmly attached inner layer and a loose outer layer (Figure 2B). Normally, the inner layer is devoid of bacteria. When DSS is given in the drinking water, the inner layer becomes more permeable, and bacteria can reach the epithelial cells leading to inflammation [84]. Thus, the loss of TFF3 seems to weaken the intestinal barrier so that more bacteria can reach the epithelial cells. This would be in line with the assumption that TFF3-FCGBP regulates the attachment and/or infiltration of microbia, e.g., in the intestine [12,14]. There are indications that TFF3-FCGBP is located in the outer mucus layer (Figure 2B), where it also could interact with DMBT1gp340. Together with galectins, these proteins may form an anti-microbial defense complex as part of the innate immune system [12,14].
3.4. TFF Peptides Weakly Enhance Cell Migration: TFF Binding Sites and Hypothetical Lectin-Triggered Activation of Transmembrane Glycoproteins
In the past, as a paradigm TFF peptides were primarily considered as a family of motogenic peptides, which stimulate the rapid repair of mucous epithelia by a process called “restitution” (for reviews, see [12,13,21,85]). All three TFF peptides show comparable chemotactic activities. Furthermore, anti- as well as pro-apoptotic effects were also reported (for review, see [12]). Particularly, the anti-apoptotic effect is in line with the motogenic activity, as cell migration and cell survival are coordinately regulated [86]. However, the effects were rather weak, hardly detectable in vitro and occurred at concentrations of 10−6 to 10−7 M or even above. This concentration range is atypical of classical high-affinity receptor/peptide ligand interactions and is in agreement with a failure to detect high-affinity TFF receptors/binding proteins [87]. Rather, low-affinity binding can be expected, which could be based upon the lectin activities of TFF peptides (see Section 3.1). Thus, a lectin-triggered activation of glycosylated transmembrane proteins has already been proposed in the past for TFF peptides [34]. Such a mechanism could be also highly cell specific, as glycosylation patterns can vary widely between different cells. In addition, binding of TFF peptides to the carbohydrate moiety of certain receptors could also change the transcriptional program triggered by this receptor. Such a case has recently been described for the epidermal growth factor receptor [88].
In an early attempt to search for TFF binding sites (“TFF receptors”), 125I-labeled TFF1, TFF2 or TFF3 were intravenously injected into rats and localized via autoradiography [89,90]. Surprisingly, all three TFF peptides accumulated at the same sites, and silver grains were localized at TFF2/MUC6-producing glandular cells only, i.e., mucous neck and antral gland cells in the stomach as well as duodenal Brunner’s gland cells [89,90]. This clearly is an indication for TFF-binding sites at the basolateral side of these cells (Figure 3). Nowadays, it is tempting to speculate that this specific TFF binding is due to a lectin interaction with glycosylated transmembrane proteins (e.g., various receptors) harboring a terminal GlcNAcα1→4Galβ epitope at their carbohydrate moiety (see Section 3.1). The terminal αGlcNAc residue is generated by the glycosyltransferase A4GNT, which is unique for these cells (for review, see [91]).
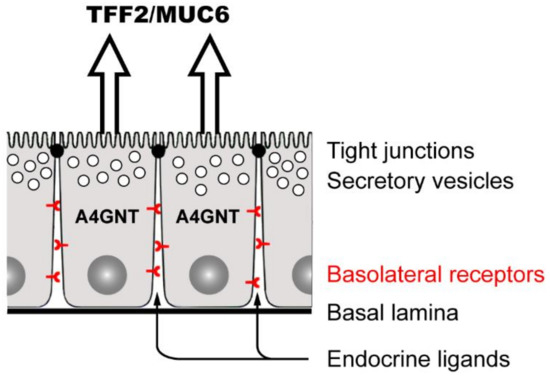
Figure 3.
TFF2/MUC6-secreting mucous cells (i.e., mucous neck cells, antral gland cells, and Brunner’s gland cells) and their basolateral receptors. These glandular epithelial cells also specifically synthesize the glycosyltransferase A4GNT [91] responsible for a post-translational modification of certain glycoproteins by a terminal αGlcNAc residue. Targets of A4GNT are MUC6 and likely also various glycosylated basolateral transmembrane proteins (receptors). Generally, these receptors are subject to ligation by numerous endocrine ligands. Furthermore, after a mucosal barrier defect and damage of tight junctionsm exocrine peptides, such TFF2, can also ligate these receptors.
Unfortunately, the postulated glycosylated transmembrane protein(s) responsible for TFF binding in A4GNT-positive cells have not been identified yet. However, the terminal αGlcNAc residue in glycosylated transmembrane proteins synthesized by A4GNT seems to be of major functional importance, as A4GntKO mice develop adenocarcinomas in the gastric antrum (for review, see [91]. Thus, A4GNT is a tumor suppressor in the gastric antrum, such as TFF1 [72]. One possible explanation for this astonishing similar phenotype could be that binding of TFF1 to a glycosylated transmembrane protein modified by A4GNT serves as a signal for the correct self-renewal of antral units (see also Section 3.3.1) [13].
Thus far, the following transmembrane proteins were reported to bind TFF peptides (for reviews and references, see [12,13,92]: β1 integrin, CRP-ductin/DMBT1gp340, CXCR4 and CXCR7, PAR2, PAR4, LINGO2, and LINGO3. Remarkably, many of these transmembrane proteins support cell migration processes. CXCR4 seems to play a special role (for reviews, see [13,93]), but not only for cell migration [80,81,94]. It can be expected that this rather diverse list will be continuously extended in the future (e.g., by transmembrane mucins and other cluster of differentiation/CD molecules, and TLRs). Generally, TFF peptides share similarities with galectins, which also act as modulators of glycosylated receptors [95].
Currently, there is an absolute need to characterize the potential ligand binding in detail and on a molecular level (e.g., dose-response curves for different forms of TFF peptides; binding via lectin or protein-protein interactions; signaling cascades triggered). A fundamental question also arises regarding the physiological function of such interactions. As the concentrations of TFF peptides in mucous epithelia (exocrine secretion) are rather high, it seems unlikely that they predominantly act as receptor-activating ligands enhancing restitution. This view is strongly supported by systematic studies characterizing the natural forms of TFF peptides in mucous epithelia [29,31,32,33,35]. As a surprise, TFF peptides were recognized to appear in different molecular forms (Figure 1), indicating novel and diverse molecular functions. This changed the paradigm concerning their roles in healthy mucous epithelia (see Section 3.2) [12].
3.5. Lectin-Triggered Receptor Blocking Hypothesis (Anti-Inflammatory Action)
There are multiple reports that TFF peptides block the activation of various receptors and might be used as anti-inflammatory peptides (for review, see [13]). For example, TFF2 blocks activation of the IL-1β receptor [44]; TFF1 interacts with IL6Rα-gp80 (the IL-6 binding chain), blocking the interaction with gp130 (signal-transducing chain) [96]; TFF1 also suppresses activation of the tumor necrosis factor α receptor (TNFR1) [73]. These blocking events were detected because expression of response genes were suppressed. A similar mechanism might be responsible for the TLR-driven suppression of IL-12 expression by TFF2 [79]. Thus, it was hypothesized that receptor inactivation could occur via lectin binding of TFF peptides to the carbohydrate moieties of receptors (Figure 4) [13].
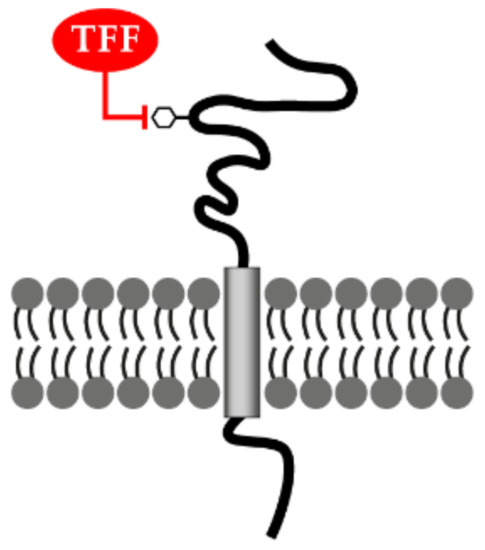
Figure 4.
Lectin-triggered receptor blocking hypothesis. TFF peptides could negatively interfere with the binding of the natural ligand(s) after binding as lectins to the carbohydrate moiety (hexagon) of various glycosylated transmembrane receptors.
Such inhibitory mechanisms were already developed during evolution and are also exploited pharmacologically. For example, TFF1 as a natural antagonist of the IL-6 receptor system would be comparable with the action of tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor antibody used clinically to treat rheumatoid arthritis, cytokine release syndrome and even COVID-19 [97]. Blockage of the IL-1 receptor system by TFF2 is reminiscent of the natural receptor antagonist anakinra, which is also clinically used for treating rheumatoid arthritis.
4. Medical Perspectives
Currently, TFF peptides are still considered primarily as players in mucosal protection and repair. Thus, they have been used in few clinical trials to prevent, in particular, oral mucositis after different regimes of chemotherapy (for reviews, see [12,98]). For the future, TFF1-FCGBP or TFF3-FCGBP in particular could be components of new anti-microbial formulations, e.g., used as artificial saliva. Furthermore, a synthetic small molecule (AMPC) was used as an inhibitor of TFF3 homodimerization enhancing the sensitivity of colorectal carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil [99].
Future attempts are expected to deal again with the interaction of TFF peptides and transmembrane proteins/receptors. Here, their potential anti-inflammatory actions are most promising (for review, see [13]). However, as a prerequisite for clinical applications, there is a need to clarify unambiguously the type of interaction with the various transmembrane proteins/receptors; particularly, the possibility of lectin interactions has to be tested rigorously. Furthermore, it will be very important to define the cells, other than epithelial cells, which synthesize TFF peptides in minute amounts. Certainly, most interesting are immune cells, but vascular and neural cells are also of interest.
Another promising area with clinical potential would be mosaic proteins, which contain TFF modules. Of particular interest would be zona pellucida proteins, where TFF modules might have a function for fertilization. In the future, this might also allow to influence this process specifically.
Finally, it would be challenging to create a series of mutant TFF peptides and test their binding characteristics, particularly to different carbohydrate moieties. This could result in new TFF forms, particularly those with different lectin activities. Such an approach could also be extended to mosaic proteins containing TFF modules. Here, novel sugar degrading enzymes could be created. New mucins, analogous to FIM-A.1 and FIM-C.1, could also be created, which could have highly selective binding characteristics and could be used as glues, e.g., for intelligent biomaterials [100]. Generally, the creation of a wide range of mutant TFF modules with different lectin activities could be highly innovative and open many possibilities, particularly as glycosylation patterns are cell specific. However, there is much basic research to be done before innovative clinical applications are within reach.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The 3D structures of TFF peptides are available from the Protein Data Bank (PDB; https://rcsb.org/, accessed on 7 September 2021).
Acknowledgments
I thank Daniela Lorenz (Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg) for her help with the illustrations, and Jonathan A. Lindquist (Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg) for his comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
Abbreviations
| A4GNT | α1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FCGBP | IgG Fc binding protein |
| IL | Interleukin |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TFF | Trefoil factor family |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
References
- Thim, L. A new family of growth factor-like peptides. ‘Trefoil’ disulphide loop structures as a common feature in breast cancer associated peptide (pS2), pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP), and frog skin peptides (spasmolysins). FEBS Lett. 1989, 250, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsom, R.; Wright, N.A. Trefoil peptides: A newly recognized family of epithelial mucin-associated molecules. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1993, 265, G205–G213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W.; Hauser, F. The P-domain or trefoil motif: A role in renewal and pathology of mucous epithelia? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993, 18, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, B.E.; Podolsky, D.K. The trefoil peptide family. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1996, 58, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thim, L. Trefoil peptides: From structure to function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribieras, S.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. The pS2/TFF1 trefoil factor, from basic research to clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1378, F61–F77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.M.; Poulsom, R.; Wright, N.A. Trefoil peptides. Gut 1999, 44, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taupin, D.; Podolsky, D.K. Trefoil factors: Initiators of mucosal healing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thim, L.; May, F.E.B. Structure of mammalian trefoil factors and functional insights. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2956–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellev, S. The trefoil factor family—Small peptides with multiple functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 66, 1350–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, E.; Engevik, K.A.; Montrose, M.H. Trefoil factor peptides and gastrointestinal function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 357–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and their diverse molecular functions in mucus barrier protection and more: Changing the paradigm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and their links to inflammation: A re-evaluation and new medical perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and their different roles in the mucosal innate immune defense and more: An update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiakowski, P.; Breathnach, R.; Bloch, J.; Gannon, F.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P. Cloning of cDNA sequences of hor-mone-regulated genes from the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982, 10, 7895–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, K.H.; Thim, L.; Jacobsen, H.E. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): I. Preparation and initial chemical char-acterization of a new polypeptide from porcine pancreas. Regul. Pept. 1982, 3, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. A new repetitive protein from Xenopus laevis skin highly homologous to pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 7686–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemori, S.; Lynch-Devaney, K.; Podolsky, D.K. Identification and characterization of rat intestinal trefoil factor: Tissue and cell-specific member of the trefoil protein family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11017–11021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, F.; Poulsom, R.; Chinery, R.; Rogers, L.A.; Hanby, A.M.; Wright, N.; Hoffmann, W. hP1.B, a human P-domain peptide homologous with rat intestinal trefoil factor, is expressed also in the ulcer-associated cell lineage and the uterus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6961–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, D.; Lynch-Devaney, K.; Stow, J.; Oates, P.; Murgue, B.; DeBeaumont, M.; Sands, B.; Mahida, Y. Identification of human intestinal trefoil factor. Goblet cell-specific expression of a peptide targeted for apical secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 6694–6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W.; Jagla, W. Cell type specific expression of secretory TFF peptides: Colocalization with mucins and synthesis in the brain. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 147–181, 182e–188e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.; Hoffmann, W.; Otto, W.; Rio, M.-C.; Thim, L. Rolling in the clover: Trefoil factor family (TFF)-domain peptides, cell migration and cancer. FEBS Lett. 1997, 408, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, P.; Blin, N.; Gött, P. Tracing the evolutionary origin of the TFF-domain, an ancient motif at mucous surfaces. Gene 1999, 236, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF Peptides. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 2nd ed.; Karstin, A.J., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1338–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Heuer, F.; Stürmer, R.; Heuer, J.; Kalinski, T.; Lemke, A.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Different Forms of TFF2, A Lectin of the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: In vitro binding studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Salm, F.; Hoffmann, W. Molecular alterations in the stomach of Tff1-deficient mice: Early steps in antral carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisch, F.-G.; Ragge, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Human gastric TFF2 peptide contains an N-linked fucosylated N,N’-diacetyllactosediamine (LacdiNAc) oligosaccharide. Glycobiology 2012, 23, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stürmer, R.; Reising, J.; Hoffmann, W. The TFF peptides xP1 and xP4 appear in distinctive forms in the Xenopus laevis gastric mucosa: Indications for different protective functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, J.; Heuer, F.; Stürmer, R.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Emidio, N.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Jechorek, D.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. The tumor suppressor TFF1 occurs in different forms and interacts with multiple partners in the human gastric mucus barrier: Indications for diverse protective functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westley, B.R.; Griffin, S.M.; May, F.E.B. Interaction between TFF1, a gastric tumor suppressor trefoil protein, and TFIZ1, a brichos domain-containing protein with homology to SP-C. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7967–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Laubinger, W.; Kalbacher, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W. Biosynthesis of gastrokine-2 in the human gastric mucosa: Restricted spatial expression along the antral gland axis and differential interaction with TFF1, TFF2 and mucins. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.-G.; Hoffmann, W. Porcine gastric TFF2 is a mucus constituent and differs from pancreatic TFF2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Hoffmann, W. Commercial porcine gastric mucin preparations, also used as artificial saliva, are a rich source for the lectin TFF2: In vitro binding studies. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF2, a MUC6-binding lectin stabilizing the gastric mucus barrier and more (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, T.K.; Laubinger, W.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.-G.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Human Intestinal TFF3 Forms disulfide-linked heteromers with the mucus-associated FCGBP protein and is released by hydrogen sulfide. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, T.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Different forms of TFF3 in the human saliva: Heterodi-merization with IgG Fc binding protein (FCGBP). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, F.; Hoffmann, W. xP1 and xPP-domain peptides expressed in Xenopus laevis stomach mucosa. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 21306–21309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagla, W.; Wiede, A.; Hoffmann, W.; Kölle, S. Differential expression of the TFF-peptides xP1 and xP4 in the gastrointestinal tract of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res. 1997, 291, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzler, C.; Oertel, M.; Hinz, M.; Hoffmann, W. Structure of the Xenopus laevis TFF-gene xP4.1, differentially expressed to its duplicated homolog xP4. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Struct. Expr. 1999, 1489, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W.; Jagla, W.; Wiede, A. Molecular medicine of TFF-peptides: From gut to brain. Histol. Histopathol. 2001, 16, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madsen, J.; Nielsen, O.; Tornøe, I.; Thim, L.; Holmskov, U. Tissue localization of human trefoil factors 1, 2, and 3. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, G.; Familari, M.; Thim, L.; Giraud, A. The trefoil peptides TFF2 and TFF3 are expressed in rat lymphoid tissues and participate in the immune response. FEBS Lett. 1999, 456, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baus-Loncar, M.; Kayademir, T.; Takaishi, S.; Wang, T. Trefoil factor family 2 deficiency and immune response. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Cao, L.; Sandor, F.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Nambiar, P.R.; Cerny, A.; Bowen, G.; Yan, J.; Takaishi, S.; et al. Trefoil family factor 2 is expressed in murine gastric and immune cells and controls both gastrointestinal inflammation and systemic immune responses. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probst, J.C.; Skutella, T.; Müller-Schmid, A.; Jirikowski, G.F.; Hoffmann, W. Molecular and cellular analysis of rP1.B in the rat hypothalamus: In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry of a new P-domain neuropeptide. Mol. Brain Res. 1995, 33, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.A. Trefoil peptides and the gut. Gut 1993, 34, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wong, W.M.; Playford, R.J.; Wright, N.A. Peptide gene expression in gastrointestinal mucosal ulceration: Ordered sequence or redundancy? Gut 2000, 46, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF (trefoil factor family) peptides and their potential roles for differentiation processes during airway remod-eling. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2716–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenring, J.R.; Nam, K.T.; Wang, T.C.; Mills, J.C.; Wright, N. Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia and intestinal metaplasia: Time for reevaluation of metaplasias and the origins of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2207–2210.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, F.E.; Westley, B.R. Trefoil proteins: Their role in normal and malignant cells. J. Pathol. 1997, 183, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M. Trefoil factors and human gastric cancer (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 12, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Rodrigues, S.; Rodrigue, C.M.; Le Floch, N.; Rivat, C.; Attoub, S.; Bruyneel, E.; Gespach, C. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and cancer progression. Peptides 2004, 25, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regalo, G.; Wright, N.A.; Machado, J.C. Trefoil factors: From ulceration to neoplasia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2910–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.K.; Kannan, N.; Grandison, P.M.; Mitchell, M.D.; Lobie, P.E. Are trefoil factors oncogenic? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 19, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.; Sommer, P.; Blin, N.; Gött, P. 5′-flanking motifs control cell-specific expression of trefoil factor genes (TFF). Int. J. Mol. Med. 1998, 2, 353–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baus-Loncar, M.; Giraud, A.S. Multiple regulatory pathways for trefoil factor (TFF) genes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2921–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, A.S.; Jackson, C.; Menheniott, T.R.; Judd, L.M. Differentiation of the gastric mucosa IV. Role of trefoil peptides and IL-6 cytokine family signaling in gastric homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1–G5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvå, M.A.; Lingford, J.; John, A.; Soler, N.M.; Scott, N.E.; Goddard-Borger, E.D. Trefoil factors share a lectin activity that defines their role in mucus. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, E.P.; Ali, T.; Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; O’Kennedy, R.; May, F.E.B.; Westley, B.R.; Josenhans, C.; Rust, M.; Suerbaum, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide interacts with TFF1 in a pH-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, M.; May, F.E.B. The interaction of helicobacter pylori with TFF1 and its role in mediating the tropism of the bacteria within the stomach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emidio, N.B.; Baik, H.; Lee, D.; Stuermer, R.; Heuer, J.; Elliott, A.G.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Haupenthal, K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Hoffmann, W.; et al. Chemical synthesis of human trefoil factor 1 (TFF1) and its homodimer provides novel insights into their mechanisms of action. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6420–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisch, F.-G.; Bonar, D.; Schloerer, N.; Schroten, H. Human trefoil factor 2 is a lectin that binds α-GlcNAc-capped mucin glycans with antibiotic activity against Helicobacter pylori. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 289, 27363–27375. [Google Scholar]
- Stürmer, R.; Reising, J.; Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) modules are characteristic constituents of separate mucin complexes in the xenopus laevis integumentary mucus: In vitro binding studies with FIM-A. 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, H.; Hoffmann, W. Subcellular localization of the TFF peptides xP1 and xP4 in the Xenopus laevis gastric/esophageal mucosa: Different secretion modes reflecting diverse protective functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thim, L.; Madsen, F.; Poulsen, S.S. Effect of trefoil factors on the viscoelastic properties of mucus gels. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.; Klasson, S.; Larsson, E.; Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C.; Samuelsson, T. Searching the evolutionary origin of epi-thelial mucus protein components-mucins and FCGBP. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencer, W.I.; Blumberg, R.S. A passionate kiss, then run: Exocytosis and recycling of IgG by FcRn. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.L. Fcgbp—A potential viral trap in RV144. Open AIDS J. 2014, 8, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.; Sørensen, G.L.; Nielsen, O.S.; Tornøe, I.; Thim, L.; Fenger, C.; Mollenhauer, J.; Holmskov, U. A variant form of the human deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 (DMBT1) gene shows increased expression in inflammatory bowel diseases and interacts with dimeric trefoil factor 3 (TFF3). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.; Mollenhauer, J.; Holmskov, U. Review: Gp-340/DMBT1 in mucosal innate immunity. Innate Immun. 2010, 16, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Pleiotropic effects of Trefoil Factor 1 deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, O.; Chenard, M.-P.; Masson, R.; Linares, J.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Wendling, C.; Tomasetto, C.; Chambon, P.; Rio, M.-C. Gastric mucosa abnormalities and tumorigenesis in mice lacking the pS2 trefoil protein. Science 1996, 274, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutto, M.; Belkhiri, A.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Schneider, B.G.; Peng, D.; Jiang, A.; Washington, M.K.; Kokoye, Y.; Crowe, S.E.; Zaika, A.; et al. Loss of TFF1 is associated with activation of NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation and gastric neoplasia in mice and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saukkonen, K.; Tomasetto, C.; Narko, K.; Rio, M.-C.; Ristimäki, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and effect of celecoxib in gastric adenomas of trefoil factor 1-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3032–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Thiem, S.; Eissmann, M.F.; Elzer, J.; Jonas, A.; Putoczki, T.L.; Poh, A.; Nguyen, P.; Preaudet, A.; Flanagan, D.; Vincan, E.; et al. Stomach-specific activation of oncogenic KRAS and STAT3-dependent in-flammation cooperatively promote gastric tumorigenesis in a preclinical model. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, L.-F.; Karam, S.M.; Wendling, C.; Chenard, M.-P.; Kershenobich, D.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. TreFoil factor 1 (TFF1/pS2) deficiency activates the unfolded protein response. Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.J.; Taupin, D.; Koh, T.J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C.M.; Podolsky, D.K.; Wang, T.C. TFF2/SP-deficient mice show decreased gastric proliferation, increased acid secretion, and increased susceptibility to NSAID injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Ge, Z.; Ohtani, M.; Jones, E.K.; Wang, T.C. Accelerated progression of gastritis to dysplasia in the pyloric antrum of TFF2-/-C57BL6 x Sv129 Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBerry, C.; Egan, C.E.; Rani, R.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Boespflug, N.; Boon, L.; Butcher, B.; Mirpuri, J.; Hogan, S.P.; et al. Trefoil Factor 2 negatively regulates Type 1 immunity against toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3078–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M.; Rani, R.; Dienger, K.; Lewkowich, I.; Fox, J.G.; Perkins, C.; Lewis, L.; Finkelman, F.D.; Smith, D.E.; Bryce, P.J.; et al. Trefoil factor 2 rapidly induces interleukin 33 to promote type 2 immunity during allergic asthma and hookworm infection. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzelli, J.N.; Chalinor, H.V.; Pavlic, D.I.; Sutton, P.; Menheniott, T.R.; Giraud, A.S.; Judd, L.M. IL33 is a stomach alarmin that initiates a skewed Th2 response to injury and infection. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 203–221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, H.; Wu, D.-C.; Podolsky, D.K.; Fishman, M.C. Impaired defense of intestinal mucosa in mice lacking intestinal trefoil factor. Science 1996, 274, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.L.; Wong, J.F.; Li, Y.; Swaminathan, S.; Xavier, R.J.; Devaney, K.L.; Podolsky, D.K. Chemotherapy-and radiothera-py-induced intestinal damage is regulated by intestinal trefoil factor. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Sjöberg, K.E.; Petersson, J.; Holm, L.; Sjövall, H.; Hansson, G.C. Bacteria penetrate the inner mucus layer before inflammation in the dextran sulfate colitis model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF (trefoil factor family) peptide-triggered signals promoting mucosal restitution. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Klemke, R.L. Extracellular-regulated kinase activation and Cas/Crk coupling regulate cell migration and suppress apoptosis during invasion of the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, W.R.; Thim, L. Trefoil factor family-interacting proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajadura-Ortega, V.; Gambardella, G.; Skinner, A.; Halim, A.; Coillie, J.V.; Schjoldager, K.T.-B.G.; Beatson, R.; Graham, R.; Achkova, D.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; et al. O-linked mucin-type glycosylation regulates the tran-scriptional programme downstream of EGFR. Glycobiology 2021, 31, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, S.S.; Thulesen, J.; Nexø, E.; Thim, L. Distribution and metabolism of intravenously administered trefoil factor 2/porcine spasmolytic polypeptide in the rat. Gut 1998, 43, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Poulsen, S.S.; Thulesen, J.; Hartmann, B.; Kissow, H.; Nexø, E.; Thim, L. Injected TFF1 and TFF3 bind to TFF2-immunoreactive cells in the gastrointestinal tract in rats. Regul. Pept. 2003, 115, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J. Dual roles of gastric gland mucin-specific o-glycans in prevention of gastric cancer. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Emidio, N.B.; Brierley, S.M.; Schroeder, C.I.; Muttenthaler, M. Structure, function, and therapeutic potential of the trefoil factor family in the gastrointestinal tract. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and chemokine receptors: A promising relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6505–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubeykovskaya, Z.; Si, Y.; Chen, X.; Worthley, D.L.; Renz, B.W.; Urbanska, A.M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Xu, T.; Westphalen, C.B.; Dubeykovskiy, A.; et al. Neural innervation stimulates splenic TFF2 to arrest myeloid cell expansion and cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porębska, N.; Poźniak, M.; Matynia, A.; Żukowska, D.; Zakrzewska, M.; Otlewski, J.; Opaliński, Ł. Galectins as modulators of receptor tyrosine kinases signaling in health and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 60, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutto, M.; Chen, Z.; Bhat, A.A.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S.; Gomaa, A.; Bates, A.; Bhat, N.S.; Peng, D.; Belkhiri, A.; et al. Activation of STAT3 signaling is mediated by TFF1 silencing in gastric neoplasia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meanwatthana, J.; Majam, T. Interleukin-6 antagonists: Lessons from cytokine release syndrome to the therapeutic application in severe COVID-19 infection. J. Pharm. Pract. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emidio, N.B.; Hoffmann, W.; Brierley, S.; Muttenthaler, M. Trefoil factor family: Unresolved questions and clinical perspectives. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-M.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Chong, Q.-Y.; Poh, H.-M.; Tan, T.-Z.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, T.; Pandey, V.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of TFF3 enhances sensitivity of CMS4 colorectal carcinoma to 5-fluorouracil through inhibition of p44/42 MAPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolle, T.; Meyer, F.; Walcher, F.; Lohmann, C.; Jockenhövel, S.; Gries, T.; Hoffmann, W. Materials/biomaterials in clinical practice—A short review and current trends. Zentralbl. Chir. 2017, 142, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).