Biofunctional Peptide FNIII14: Therapeutic Potential
Definition
1. Introduction
2. Peptide FNIII14 Derived from the FN Molecule
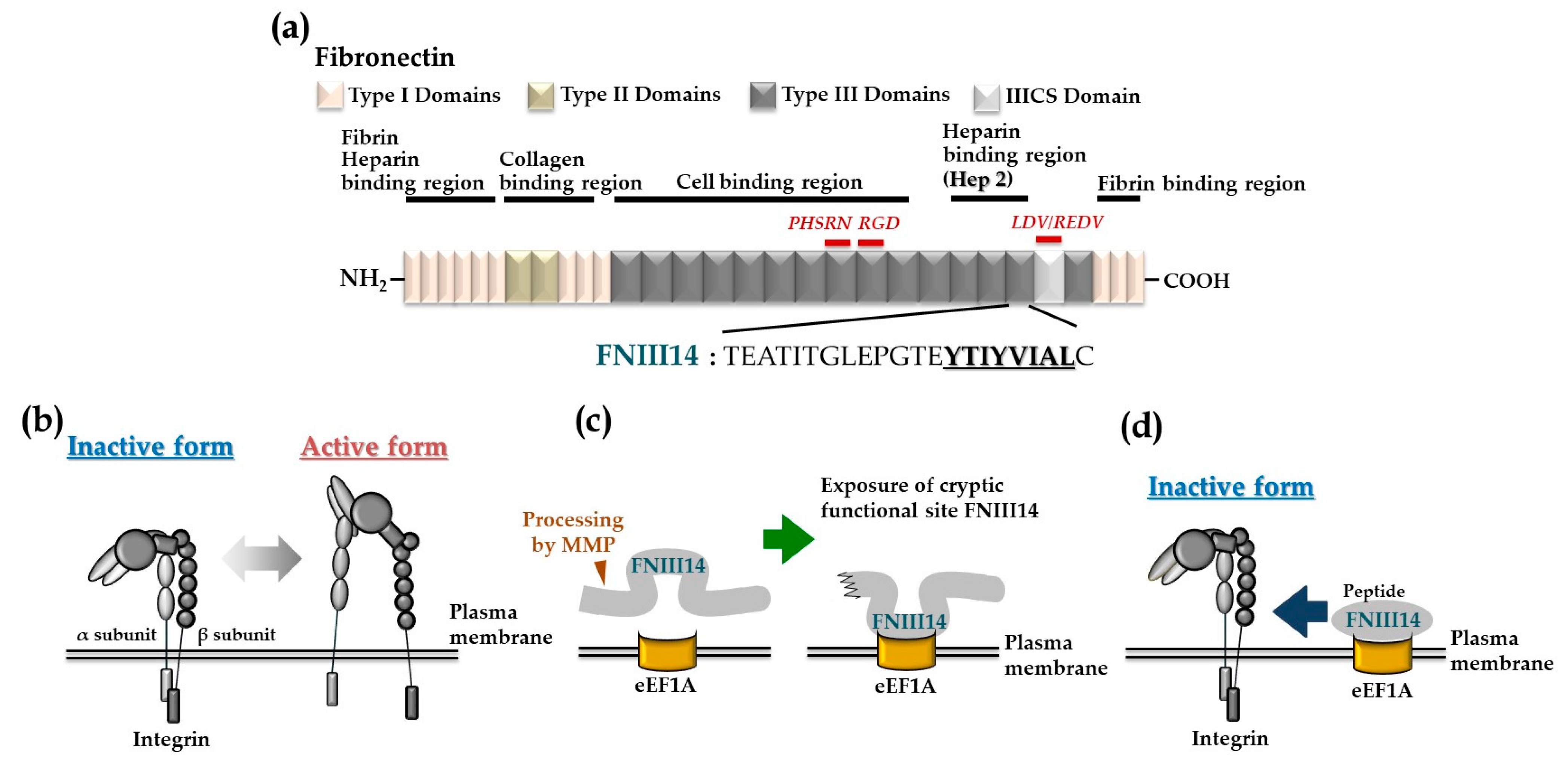
2.1. Anti-Adhesion Site of Fibronectin and Its Pepide FNIII14
2.2. Involvement of Integrin-Mediated Adhesion to the ECM in Adipocyte Differentiaion and Related Metabolic Disorder
2.3. Anti-Fibrotic Activity of Peptide FNIII14
2.4. Anti-Cancer Effects of Peptide FNIII14
| Cancer Type | Cells/Experimental Model | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suppression of survival/proliferation | |||
| In vitro | Glioma/Glioblastoma | T98G, 9L | [20] |
| Neuroblastoma | IMR-32 | [27] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | MIA-PaCa 2 | [27] | |
| Basophilic leukemia | RBL-2H3 | [33] | |
| In vivo | Glioma/Glioblastoma | Subcutaneous xenograft model | [20] |
| Neuroblastoma | Subcutaneous xenograft model | [27] | |
| Disruptionof anoikis resistance | |||
| In vitro | Glioma/Glioblastoma | T98G, 9L | [21] |
| Suppression of migration/invasion | |||
| In vitro | Glioma/Glioblastoma | T98G | [20] |
| Lymphoma | L5178Y-ML25 | [28] | |
| Neuroblastoma | IMR-32 | [27] | |
| Suppression of Myc expression | |||
| In vitro | Lung cancer | NCI-H82 (c-myc) | [27] |
| Pancreatic cancer | MIA-PaCa 2 (c-myc) | [27] | |
| Chronic myelogenous leukemia | K562 (c-myc) | [27] | |
| Neuroblastoma | IMR-32, NB-1, KELLY (N-myc) | [27] | |
| Potentiation of anti-cancer activity | |||
| In vitro | Glioma/Glioblastoma | T98G, 9L, U251 (cotreatment with temozolomide) | [8,20] |
| Oral squamous cell carcinoma | Ca9-22/FR2 (cotreatment with 5-fluorouracil) | [31] | |
| Breast cancer | 4T1 (cotreatment with doxorubicin) | [34] | |
| Melanoma | B16BL6 (cotreatment with aclarubicin, vinblastine, 5-fluorouracil, and dacarbazine) | [34] | |
| In vivo | Glioma/Glioblastoma | Subcutaneous xenograft model (cotreatment with temozolomide) | [20] |
| Inhibition of metastases | |||
| In vivo | Breast cancer (liver metastases) | Mouse model of experimental tumor metastasis | [34] |
| Lymphoma (liver and spleen metastases) | Mouse model of experimental tumor metastasis | [28] | |
| Disruption of cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance to cytosine arabinoside | |||
| In vitro | Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) | U937, HL-60, cells from AML patients | [30] |
| In vivo | AML | Mouse model of minimal residual disease in AML | [30] |
| Suppression of tumor onset | |||
| In vivo | Colitis-associated colorectal cancer | Azoxymethane-dextran sodium sulfate mouse model | [35] |
2.5. Perspectives
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
References
- de Castro Brás, L.E.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Extracellular Matrix-Derived Peptides in Tissue Remodeling and Fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2020, 91–92, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.M.; Pritchard, J.M.; Macdonald, S.J.F.; Jamieson, C.; Watson, A.J.B. Emergence of Small-Molecule Non-RGD-Mimetic Inhibitors for RGD Integrins. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.E.; Bayless, K.J.; Davis, M.J.; Meininger, G.A. Regulation of Tissue Injury Responses by the Exposure of Matricryptic Sites within Extracellular Matrix Molecules. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard-Blum, S.; Salza, R. Matricryptins and Matrikines: Biologically Active Fragments of the Extracellular Matrix. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankov, R.; Yamada, K.M. Fibronectin at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3861–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, S.; Svineng, G.; Wennerberg, K.; Armulik, A.; Lohikangas, L. Fibronectin-Integrin Interactions. Front. Biosci. J. Virtual Libr. 1997, 2, d126–d146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieberler, M.; Reuning, U.; Reichart, F.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.-J.; Schwaiger, M.; Weinmüller, M.; Räder, A.; Steiger, K.; Kessler, H. Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Sasada, M.; Iyoda, T.; Fukai, F. Involvement of Integrin-Activating Peptides Derived from Tenascin-C in Cancer Aggression and New Anticancer Strategy Using the Fibronectin-Derived Integrin-Inactivating Peptide. Molecules 2020, 25, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, F.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Tsugita, A.; Katayama, T. Rat Plasma Fibronectin Contains Two Distinct Chemotactic Domains for Fibroblastic Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 8807–8813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, F.; Takahashi, H.; Habu, Y.; Kubushiro, N.; Katayama, T. Fibronectin Harbors Anticell Adhesive Activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 220, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Takahashi, H.; Habu, Y.; Kamiya-Kubushiro, N.; Kamiya, S.; Nakamura, H.; Yajima, H.; Ishii, T.; Katayama, T.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. Interaction with Heparin and Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 Cleavage Expose a Cryptic Anti-Adhesive Site of Fibronectin. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 7138–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, F.; Hasebe, S.; Ueki, M.; Mutoh, M.; Ohgi, C.; Takahashi, H.; Takeda, K.; Katayama, T. Identification of the Anti-Adhesive Site Buried within the Heparin-Binding Domain of Fibronectin. J. Biochem. 1997, 121, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya, S.; Kato, R.; Wakabayashi, M.; Tohyama, T.; Enami, I.; Ueki, M.; Yajima, H.; Ishii, T.; Nakamura, H.; Katayama, T.; et al. Fibronectin Peptides Derived from Two Distinct Regions Stimulate Adipocyte Differentiation by Preventing Fibronectin Matrix Assembly. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3270–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itagaki, K.; Naito, T.; Iwakiri, R.; Haga, M.; Miura, S.; Saito, Y.; Owaki, T.; Kamiya, S.; Iyoda, T.; Yajima, H.; et al. Eukaryotic Translation Elongation Factor 1A Induces Anoikis by Triggering Cell Detachment. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16037–16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Fernández, J.L.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. Regulation of Fibronectin, Integrin and Cytoskeleton Expression in Differentiating Adipocytes: Inhibition by Extracellular Matrix and Polylysine. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 1989, 42, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; DeYoung, S.M.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, A.; Saltiel, A.R. Changes in Integrin Expression during Adipocyte Differentiation. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, N.; Sundberg, C.; Kveiborg, M.; Moghadaszadeh, B.; Asmar, M.; Dietrich, N.; Thodeti, C.K.; Nielsen, F.C.; Möller, P.; Mercurio, A.M.; et al. ADAM12 Induces Actin Cytoskeleton and Extracellular Matrix Reorganization during Early Adipocyte Differentiation by Regulating β1 Integrin Function. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, R.; Kamiya, S.; Ueki, M.; Yajima, H.; Ishii, T.; Nakamura, H.; Katayama, T.; Fukai, F. The Fibronectin-Derived Antiadhesive Peptides Suppress the Myofibroblastic Conversion of Rat Hepatic Stellate Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 265, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.; Pritchett, J.; Llewellyn, J.; Mullan, A.F.; Athwal, V.S.; Dobie, R.; Harvey, E.; Zeef, L.; Farrow, S.; Streuli, C.; et al. PAK Proteins and YAP-1 Signalling Downstream of Integrin Beta-1 in Myofibroblasts Promote Liver Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Iyoda, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Sasada, M.; Nagai, R.; Kudo, C.; Otsuka, K.; Kamiya, S.; Kodama, H.; et al. Aggressive Progression in Glioblastoma Cells through Potentiated Activation of Integrin α5β1 by the Tenascin-C-Derived Peptide TNIIIA2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Sasada, M.; Iyoda, T.; Nagai, R.; Kudo, C.; Yamamoto, T.; Osada, S.; Kodama, H.; Fukai, F. Anoikis Resistance Conferred by Tenascin-C-Derived Peptide TNIIIA2 and Its Disruption by Integrin Inactivation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 536, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janouskova, H.; Maglott, A.; Leger, D.Y.; Bossert, C.; Noulet, F.; Guerin, E.; Guenot, D.; Pinel, S.; Chastagner, P.; Plenat, F.; et al. Integrin α5β1 Plays a Critical Role in Resistance to Temozolomide by Interfering with the p53 Pathway in High-Grade Glioma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malric, L.; Monferran, S.; Gilhodes, J.; Boyrie, S.; Dahan, P.; Skuli, N.; Sesen, J.; Filleron, T.; Kowalski-Chauvel, A.; Cohen-Jonathan Moyal, E.; et al. Interest of Integrins Targeting in Glioblastoma According to Tumor Heterogeneity and Cancer Stem Cell Paradigm: An Update. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86947–86968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vehlow, A.; Klapproth, E.; Storch, K.; Dickreuter, E.; Seifert, M.; Dietrich, A.; Bütof, R.; Temme, A.; Cordes, N. Adhesion- and Stress-Related Adaptation of Glioma Radiochemoresistance Is Circumvented by β1 Integrin/JNK Co-Targeting. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49224–49237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordes, N.; Seidler, J.; Durzok, R.; Geinitz, H.; Brakebusch, C. Beta1-Integrin-Mediated Signaling Essentially Contributes to Cell Survival after Radiation-Induced Genotoxic Injury. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, W.S.; DeLay, M.; Jahangiri, A.; Park, C.C.; Aghi, M.K. β1 Integrin Targeting Potentiates Antiangiogenic Therapy and Inhibits the Growth of Bevacizumab-Resistant Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3145–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasada, M.; Iyoda, T.; Asayama, T.; Suenaga, Y.; Sakai, S.; Kase, N.; Kodama, H.; Yokoi, S.; Isohama, Y.; Fukai, F. Inactivation of Beta1 Integrin Induces Proteasomal Degradation of Myc Oncoproteins. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4960–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kato, R.; Ishikawa, T.; Kamiya, S.; Oguma, F.; Ueki, M.; Goto, S.; Nakamura, H.; Katayama, T.; Fukai, F. A New Type of Antimetastatic Peptide Derived from Fibronectin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Abdel-Ghany, M.; Pauli, B.U. A Novel Consensus Motif in Fibronectin Mediates Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Adhesion and Metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24600–24607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Fukai, F.; Miura, S.; Nakane, Y.; Owaki, T.; Kodama, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nagaya, T.; Takimoto, R.; Takayama, T.; et al. Combination Therapy of an Anticancer Drug with the FNIII14 Peptide of Fibronectin Effectively Overcomes Cell Adhesion-Mediated Drug Resistance of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Nagata, M.; Yoshida, R.; Kawahara, K.; Hirosue, A.; Tanaka, T.; Yuno, A.; Matsuoka, Y.; Kojima, T.; et al. Overexpression of Fibronectin Confers Cell Adhesion-Mediated Drug Resistance (CAM-DR) against 5-FU in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alday-Parejo, B.; Stupp, R.; Rüegg, C. Are Integrins Still Practicable Targets for Anti-Cancer Therapy? Cancers 2019, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hasebe, S.; Kamiya, N.; Saito, Y.; Miura, S.; Wada, S.; Yajima, H.; Katayama, T.; Fukai, F. A Fibronectin Fragment Induces Tumor Necrosis Factor Production of Rat Basophilic Leukemia Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1675, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyoda, T.; Nagamine, Y.; Nakane, Y.; Tokita, Y.; Akari, S.; Otsuka, K.; Fujita, M.; Itagaki, K.; Takizawa, Y.-I.; Orita, H.; et al. Coadministration of the FNIII14 Peptide Synergistically Augments the Anti-Cancer Activity of Chemotherapeutic Drugs by Activating Pro-Apoptotic Bim. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Ito-Fujita, Y.; Iyoda, T.; Sasada, M.; Okada, Y.; Ishibashi, K.; Osawa, T.; Kodama, H.; Fukai, F.; Suzuki, H. Peptide TNIIIA2 Derived from Tenascin-C Contributes to Malignant Progression in Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer via β1-Integrin Activation in Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.-L.; Harris, J.L.; Khanna, K.K.; Hong, J.-H. A Comprehensive Review on Current Advances in Peptide Drug Development and Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Abisoye-Ogunniyan, A.; Metcalf, K.J.; Werb, Z. Concepts of Extracellular Matrix Remodelling in Tumour Progression and Metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Lagares, D. Matrix Stiffness: The Conductor of Organ Fibrosis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschumperlin, D.J.; Lagares, D. Mechano-Therapeutics: Targeting Mechanical Signaling in Fibrosis and Tumor Stroma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 212, 107575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Fear, M.W.; Suk Choi, Y.; Wood, F.M.; Allahham, A.; Mutsaers, S.E.; Prêle, C.M. The Extracellular Matrix and Mechanotransduction in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 126, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnikova, Y.A.; Mouw, J.K.; Barnes, J.M.; Pickup, M.W.; Lakins, J.N.; Kim, Y.; Lobo, K.; Persson, A.I.; Reis, G.F.; McKnight, T.R.; et al. Tissue Mechanics Promote IDH1-Dependent HIF1α-Tenascin C Feedback to Regulate Glioblastoma Aggression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.M.; Kaushik, S.; Bainer, R.O.; Sa, J.K.; Woods, E.C.; Kai, F.; Przybyla, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, H.W.; Tung, J.C.; et al. A Tension-Mediated Glycocalyx-Integrin Feedback Loop Promotes Mesenchymal-like Glioblastoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wang, W.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Feng, G.; Wu, M.; Zhou, X.; Lafyatis, R.; Lee, J.; Hinchcliff, M.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; et al. Tenascin-C Drives Persistence of Organ Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Imazeki, H.; Miura, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Okutsu, H.; Harada, Y.; Ohwaki, T.; Nagao, O.; Kamiya, S.; Hayashi, R.; et al. A Peptide Derived from Tenascin-C Induces Beta1 Integrin Activation through Syndecan-4. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34929–34937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Seki, Y.; Saito, Y.; Kamiya, S.; Fujita, M.; Okutsu, H.; Iyoda, T.; Takai, T.; Owaki, T.; Yajima, H.; et al. Tenascin-C-Derived Peptide TNIIIA2 Highly Enhances Cell Survival and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)-Dependent Cell Proliferation through Potentiated and Sustained Activation of Integrin α5β1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17699–17708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Iyoda, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Nagai, R.; Kudo, C.; Sasada, M.; Kodama, H.; Fukai, F. Autocrine Production of PDGF Stimulated by the Tenascin-C-Derived Peptide TNIIIA2 Induces Hyper-Proliferation in Glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Sarkar, S.; Dzikowski, L.; Rawji, K.S.; Khan, L.; Faissner, A.; Bose, P.; Yong, V.W. Brain Tumor-Initiating Cells Export Tenascin-C Associated with Exosomes to Suppress T Cell Activity. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1478647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estany, S.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Llatjós, R.; Montes, A.; Penín, R.; Escobar, I.; Xaubet, A.; Santos, S.; Manresa, F.; Dorca, J.; et al. Lung Fibrotic Tenascin-C Upregulation Is Associated with Other Extracellular Matrix Proteins and Induced by TGFβ1. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujita, M.; Sasada, M.; Iyoda, T.; Osada, S.; Kodama, H.; Fukai, F. Biofunctional Peptide FNIII14: Therapeutic Potential. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 350-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020029
Fujita M, Sasada M, Iyoda T, Osada S, Kodama H, Fukai F. Biofunctional Peptide FNIII14: Therapeutic Potential. Encyclopedia. 2021; 1(2):350-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujita, Motomichi, Manabu Sasada, Takuya Iyoda, Satoshi Osada, Hiroaki Kodama, and Fumio Fukai. 2021. "Biofunctional Peptide FNIII14: Therapeutic Potential" Encyclopedia 1, no. 2: 350-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020029
APA StyleFujita, M., Sasada, M., Iyoda, T., Osada, S., Kodama, H., & Fukai, F. (2021). Biofunctional Peptide FNIII14: Therapeutic Potential. Encyclopedia, 1(2), 350-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020029







