Common Practices and Methodologies in Scientific Functional Characterization of Surface Topography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. State-of-the-Art
3. Methodology
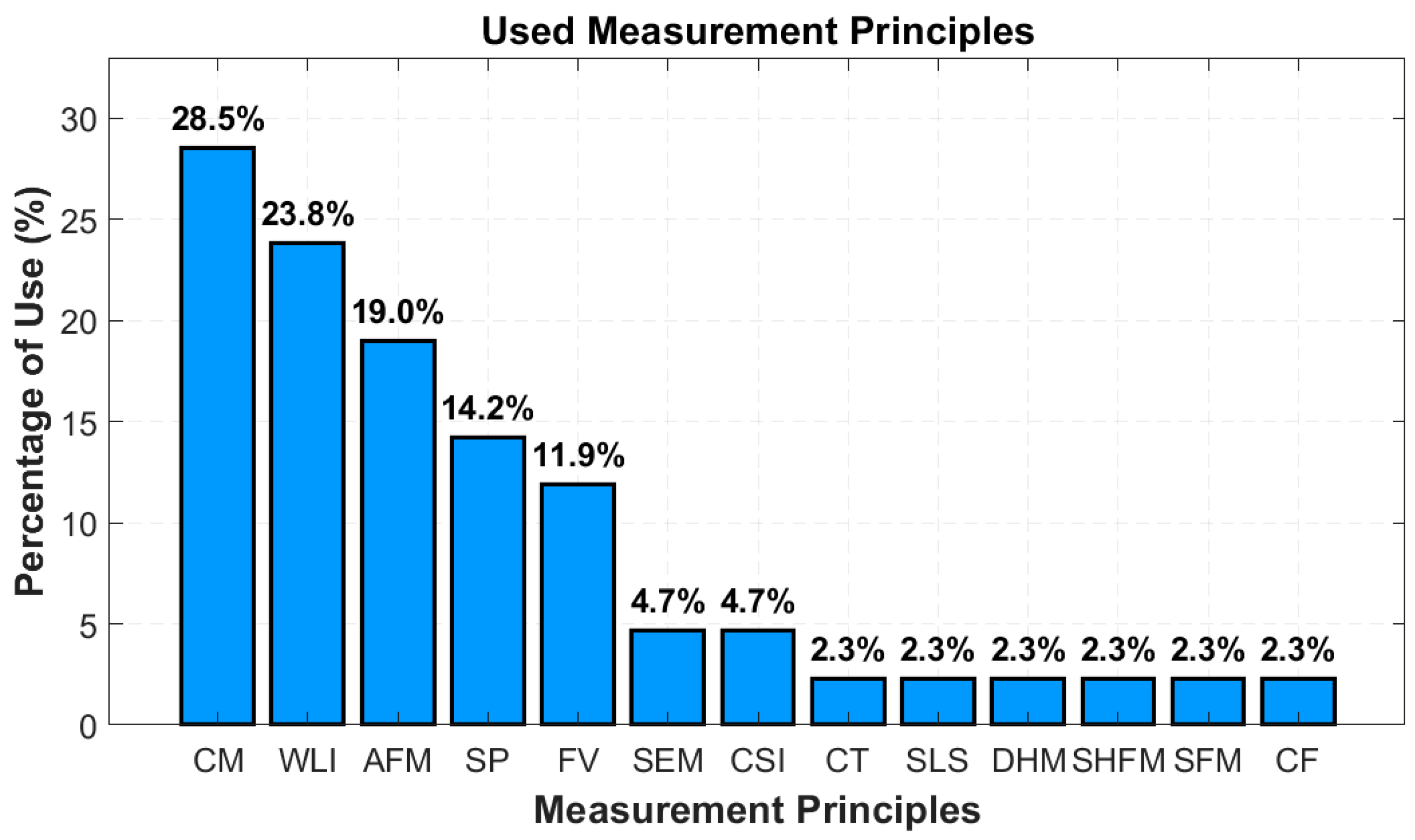
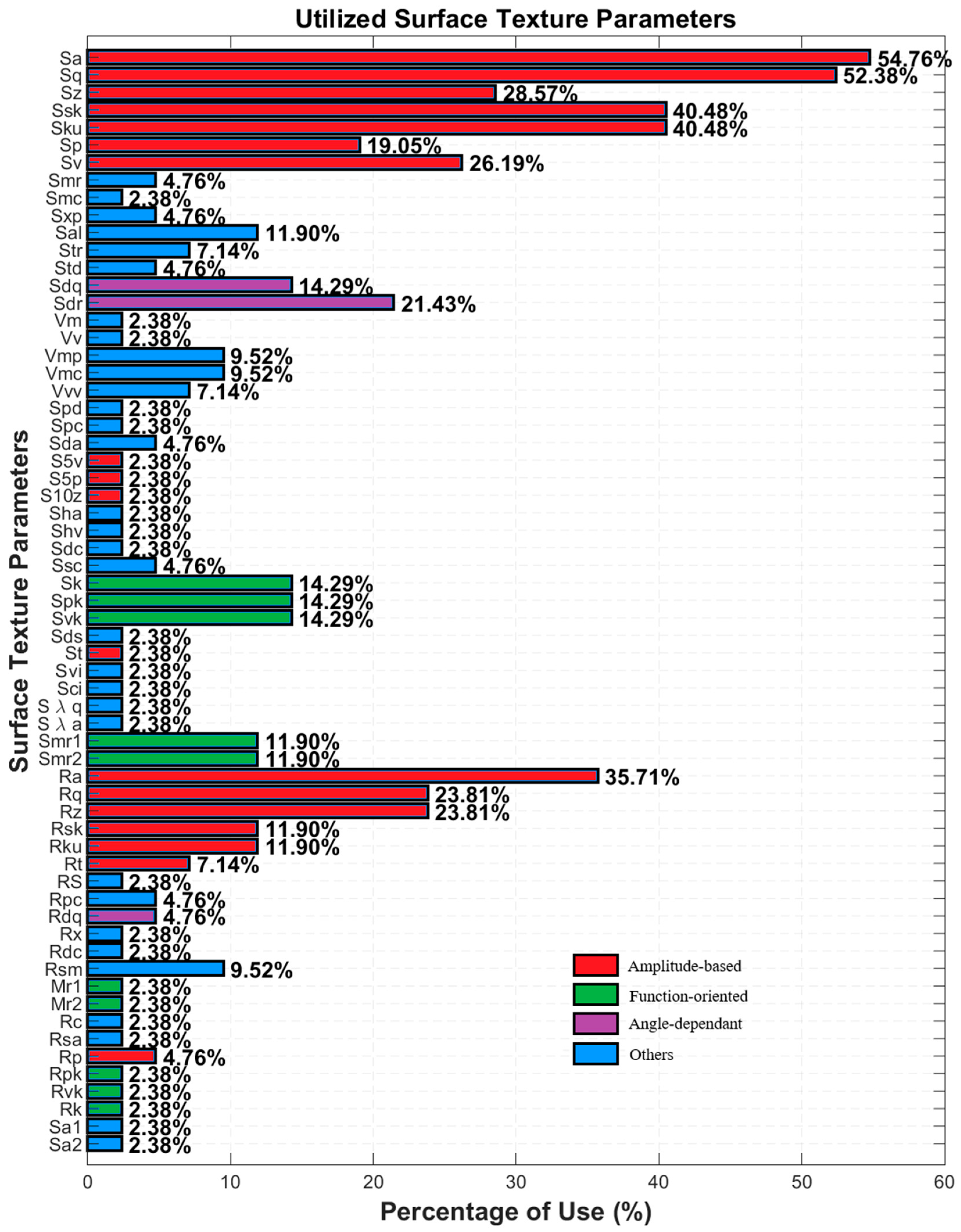
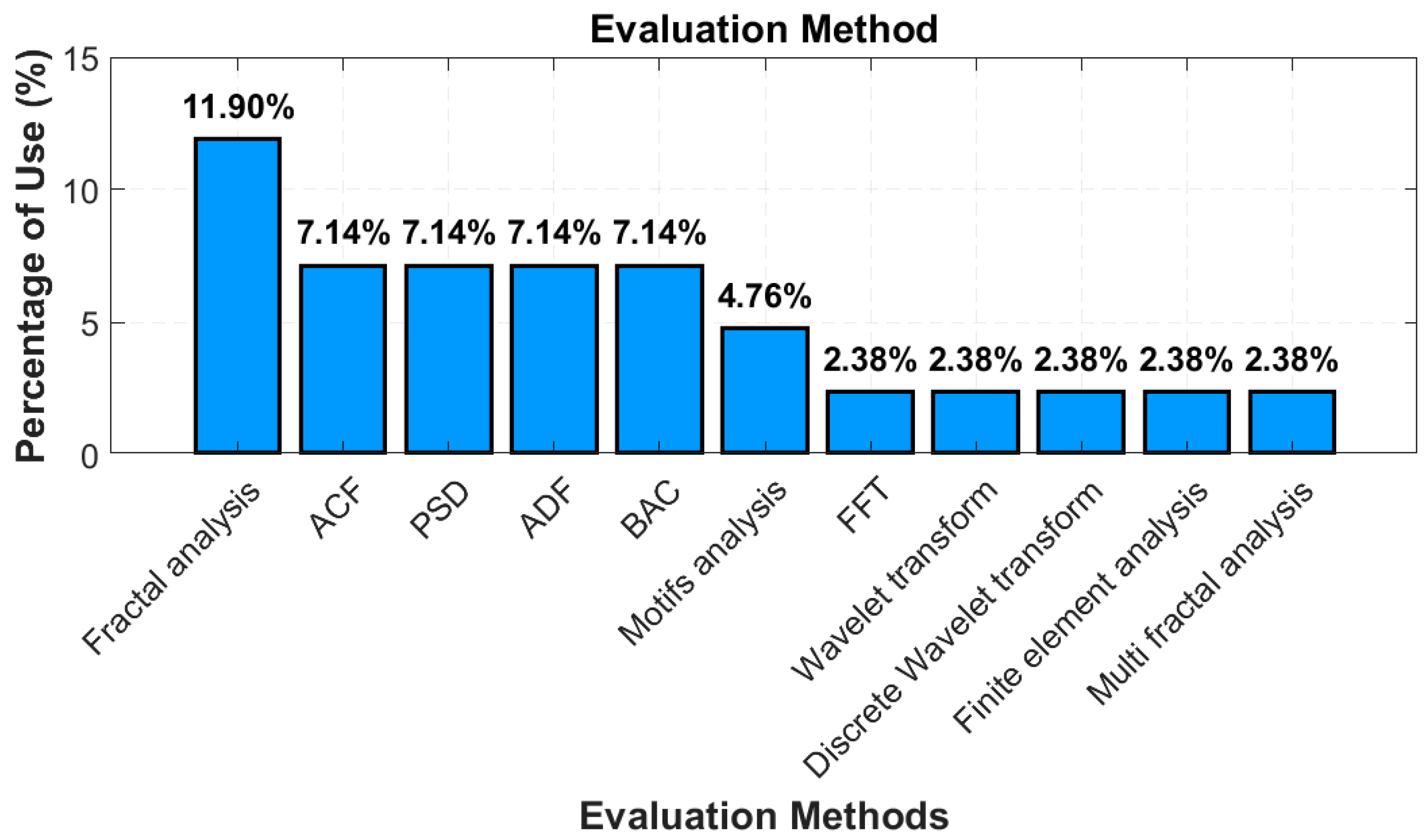
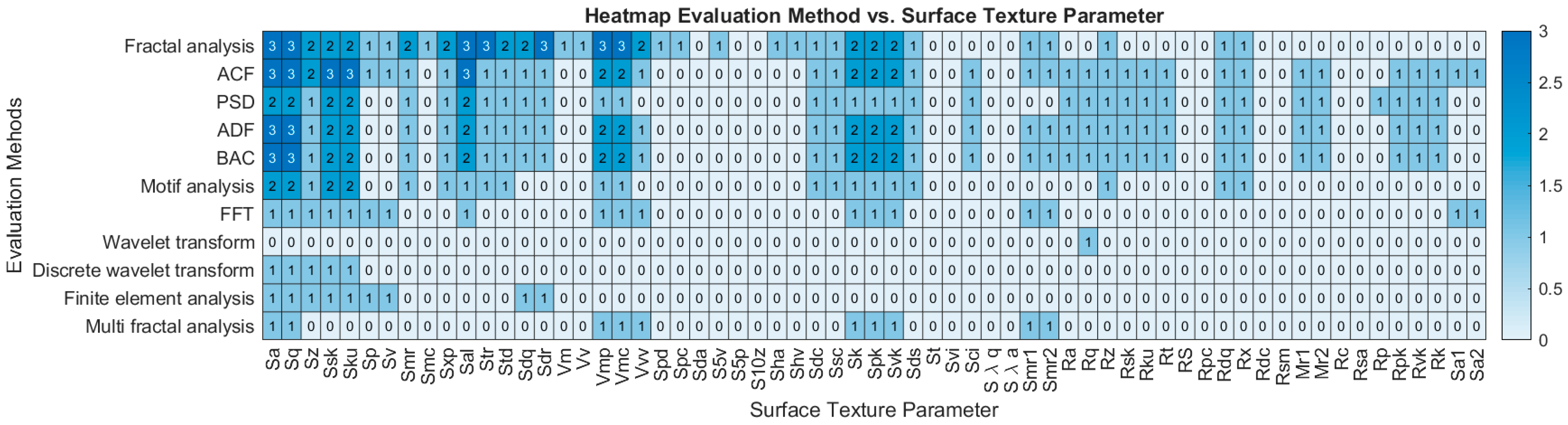
4. Results
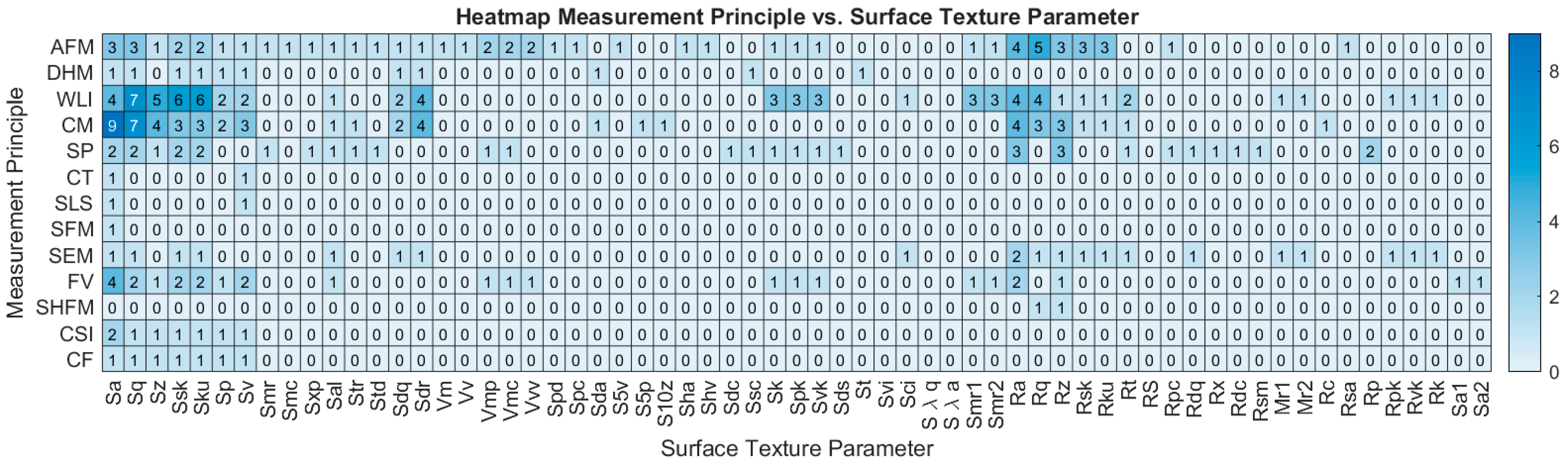
5. Correlation Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Study | Applied Measurement Principles | Parameters for Functional Surface Characterization | Additional Methods for Surface Characterization |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Abadías et al., 2015) [16] | AFM | Ra, Rq, Rsk, Rku | - |
| (Abbasian et al., 2017) [17] | DHM | Sa, Sq, Ssk, Sku, Sp, Sv, Sdq, Sdr, Sλq, Sλa, Sda, Ssc, St | - |
| (Alnoush et al., 2021) [18] | AFM, WLI | Rq | - |
| (Bellantone et al., 2022) [19] | CM | Sa, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Sp, Sv | - |
| (Berkmans et al., 2024) [20] | WLI | Sdr | Fractal analysis |
| (Gao et al., 2020) [21] | SP | Ra, Rz, Rt, RSm | - |
| (Gockel et al., 2019) [22] | CT, SLS | Sa, Sv | - |
| (Grimm et al., 2015) [23] | CM | Sal, Str, Sdq, Sdr | Fractal analysis |
| (Grover & Singh 2018) [24] | SP | Ra | - |
| (Grundke et al., 2014) [25] | SFM | Sa | - |
| (Grzesik & Żak 2016) [26] | SP | Sa, Sq, Sz/Rz, Ssk, Sku, Smr, Sxp, Sal, Str, Std, Rdq, Vmp, Vmc, Vvc, RSm, Rx, Spk, Sdc, Sk, Svk, Sds, Ssc | Fractal analysis, PSD, ACF, BAC, ADF, Motif analysis |
| (Guo et al., 2022) [27] | WLI | Sa, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku | Discrete wavelet transform |
| (Jiang et al., 2022) [28] | CM | Sa, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Sdq, Sdr | - |
| (Klink et al., 2017) [29] | SEM | Ra, Rz, Rdq, RSm | - |
| (Krishna et al., 2020) [30] | SP | Rp | PSD |
| (Krolczyk et al., 2018) [31] | FV | Sa, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Sp, Sv, Sal, Vmp, Vmc, Vvc, Vvv, Sa1, Sa2, Spk, Sk, Svk, Smr1, Smr2 | ACF, FFT |
| (Leksycki & Królczyk, 2020) [32] | CM, FV | Ra/Sa, Rz | - |
| (Leksycki et al., 2020) [33] | CM | Sa, Sq, Sz | - |
| (Li et al., 2023) [34] | WLI | Sa, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Sp, Sv, Sdq, Sdr | FEA |
| (Liu et al., 2021) [35] | WLI | Rq | Wavelet transform |
| (Merson et al., 2017) [14] | CM | Sa, Sq, Rs | - |
| (Moreau et al., 2024) [36] | CM, FV, CSI | Sa | - |
| (Newton et al., 2023) [37] | CM | Sa | - |
| (Niemczewska-Wójcik, 2017) [38] | WLI | Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Spk, Sk, Svk, Smr1, Smr2 | - |
| (Niemczewska-Wójcik et al., 2022) [39] | WLI | Ra, Sq, Ssk, Sku, Sp, Sv, Spk, Sk, Svk, Smr1, Smr2 | - |
| (Niemczewska-Wójcik & Wójcik, 2020) [40] | WLI | Ra, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Spk, Sk, Svk, Smr1, Smr2 | - |
| (Pakuła et al., 2019) [41] | AFM, CM | Ra, Rq, Rz | - |
| (Park et al., 2015) [42] | CM, WLI | Ra/Sa, Rq/Sq, Rz/Sz, Sdr, Rt | - |
| (Reddy et al., 2018) [43] | SP | Ra, Rz, Rp, Rv, Rpc, Rdc, Rsm | - |
| (Romoli et al., 2013) [44] | SHFM | Rq, Rz | - |
| (Sedlaček et al., 2016) [45] | SP | Sa, Sq, Ssk, Sku | - |
| (Sedlaček et al., 2020) [46] | FV | Ra | - |
| (Stach et al., 2019) [47] | AFM | Sa, Sq, Vmp, Vmc, Vvc, Vvv, Spk, Sk, Svk, Smr1, Smr2 | Fractal analysis, BAC, ADF, Multi fractal analysis |
| (Tălu et al., 2013) [48] | AFM | Sa, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Sp, Sv, Smr, Smc, Sxp, Sal, Str, Std, Sdq, Sdr, Vm, Vv, Vmp, Vmc, Vvc, Vvv, Spd, Spc, S5v, Sha, Shv | Fractal analysis |
| (Tălu, 2021) [49] | AFM | Sa, Sq, Ssk, Sku | Motif analysis |
| (Tian et al., 2012) [50] | CM | Sq, Sv, Sdr, Vvc, S5p, S10z, Sda | - |
| (Torrent-Burgués & Sanz, 2014) [51] | AFM | Ra, Rq, Rz, Rsk, Rku | - |
| (Walczak et al., 2023) [52] | CSI, CF | Sa, Sq, Sz, Ssk, Sku, Sp, Sv | - |
| (Wang et al., 2017) [53] | CM | Sa/Ra, Sq/Rq, Rc, Rsk/Ssk, Rku/Sku, Sp, Sv | - |
| (Webb et al., 2012) [54] | AFM | Ra, Rq, Rz, Rsk, Rku, Rpc, Rsa | - |
| (Zhu et al., 2020) [55] | FV | Sa, Sq, Ssk, Sku, Sv | - |
| (Zeng et al., 2018) [9] | SEM, WLI | Sa/Ra, Sq/Rq, Rt, Ssk/Rsk, Sku/Rku, Rpk, Rvk, Sal, Sdq, Sdr, Rk, Mr1, Mr2, Svi, Sci | PSD, ACF, BAC, ADF |
Appendix A.2
| Abbreviation | Full Form | Abbreviation | Full Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACF | Autocorrelation Function | Svi | Valley fluid retention index |
| ADF | Amplitude Density Function | Sda | Mean Pit Area |
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy | Sdc | Height difference of inverse Material Ratio |
| BAC | Bearing Area Curve | Sdq | Root Mean Square Gradient |
| CF | Confocal Fusion | Sdr | Developed Interfacial Area Ratio |
| CM | Confocal Microscopy | Sds | Peak/Summit Density |
| CSI | Coherence Scanning Interferometry | Sha | Mean Hill Area |
| CT | Computed Tomography | Shv | Mean Hill Volume |
| DHM | Digital Holographic Microscopy | Sk | Core Roughness Depth |
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis | Sku | Kurtosis |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform | Smc | Inverse Material Ratio |
| FV | Focus Variation | Smr | Material Ratio |
| PSD | Power Spectral Density | Smr1, Smr2 | Upper and Lower Material Ratio |
| Ra | Arithmetic Mean Roughness | Sp | Maximum Peak Height |
| Rdc | Material Ratio Height Difference | Spc | Mean Peak Curvature |
| Rdq | Root Mean Square Slope (profile) | Spd | Density of Peaks |
| Rk | Core Roughness depth (profile) | Spk | Reduced Peak Height |
| Rpc | Peak Count (profile) | Sq | Root Mean Square Height |
| Rpk | Reduced Peak Height (profile) | Ssc | Mean Summit Curvature |
| Rq | Root Mean Square Roughness | Ssk | Skewness |
| Rsk | Skewness (profile) | St | Total Height of the Areal Roughness |
| RSm | Mean Profile Element Spacing | Std | Texture Direction |
| Rt | Total Height of the Roughness Profile | Str | Texture Aspect Ratio |
| Rv | Mean Pit Depth (profile) | Sv | Maximum Pit Depth |
| Rvk | Reduced Pit Depth (profile) | Svk | Reduced Pit Depth |
| Rx | Largest Motif Height | Sxp | Extreme Peak Height |
| Rz | Maximum Height of the Profile | Sz | Maximum Height of the Surface |
| S10z | Ten-Point Height | Sλq | Root Mean Square of Spatial Wavelength |
| S5p | Five-Point Pit Height | Sλa | Spatial Average Wavelength |
| S5v | Five-Point Valley Depth | Vmc | Material Volume Core |
| Sa | Arithmetic Mean Height (areal) | Vmp | Material Volume Hill |
| Sa1, Sa2 | Hill / Dale areas of the Material Ratio Curve | Vvc | Void Volume Core |
| Sal | Autocorrelation Length | Vvv | Valley Void Volume |
| Sci | Core Fluid Retention Index | WLI | White Light Interferometry |
References
- Eifler, M.; Brodmann, B.; Hansen, P.E.; Seewig, J. Traceable functional characterization of surface topography with angular-resolved scattering light measurement. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2021, 9, 035042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, D. The parameter rash—Is there a cure? Wear 1982, 83, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Tang, J.; Xia, F.; Zhou, W. Rough surface characterization parameter set and redundant parameter set for surface modeling and performance research. Materials 2022, 15, 5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 13565-2; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Method—Surfaces Having Stratified Functional Properties—Part 2: Height Characterization Using the Linear Material Ratio Curve. DIN, Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1998.
- Klauer, K.; Eifler, M.; Seewig, J.; Kirsch, B.; Aurich, J. Application of function-oriented roughness parameters using confocal microscopy. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13565-3; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Method—Surfaces Having Stratified Functional Properties—Part 3: Height Characterization Using the Material Probability Curve. DIN, Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2000.
- ISO 21920-2; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. DIN, Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2022.
- ISO 25178-2; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Areal—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. DIN, Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2023.
- Zeng, Q.; Qin, Y.; Chang, W.; Luo, X. Correlating and evaluating the functionality-related properties with surface texture parameters and specific characteristics of machined components. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 149, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zong, W.; Zhang, J. Influencing factors and theoretical modeling methods of surface roughness in turning process: State-of-the-art. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2018, 129, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.; Senin, N.; Blunt, L.; Leach, R.; Taylor, J. Surface texture metrology for metal additive manufacturing: A review. Precis. Eng. 2016, 46, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, M.; Armstrong, J. A comparison of surface metrology techniques. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2005, 13, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Scott, P.; Whitehouse, D.; Blunt, L. Paradigm shifts in surface metrology. Part II. The current shift. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 463, 2071–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merson, E.; Danilov, V.; Merson, D.; Vinogradov, A. Confocal laser scanning microscopy: The technique for quantitative fractographic analysis. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 183, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todhunter, L.; Leach, R.; Lawes, S.; Blateyron, F. Industrial survey of ISO surface texture parameters. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadías, C.; Serés, C.; Torrent-Burgués, J. AFM in peak force mode applied to worn siloxane-hydrogel contact lenses. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasian, V.; Akhlaghi, E.A.; Charsooghi, M.A.; Bazzar, M.; Moradi, A. Digital holographic microscopy for 3D surface characterization of polymeric nanocomposites. Ultramicroscopy 2017, 185, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnoush, W.; Sayed, A.; Solling, T.I.; Alyafei, N. Impact of calcite surface roughness in wettability assessment: Interferometry and atomic force microscopy analysis. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellantone, V.; Surace, R.; Fassi, I. Quality definition in micro injection molding process by means of surface characterization parameters. Polymers 2022, 14, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkmans, F.; Lemesle, J.; Guibert, R.; Wieczorowski, M.; Brown, C.; Bigerelle, M. Two 3D Fractal-Based Approaches for Topographical Characterization: Richardson Patchwork versus Sdr. Materials 2024, 17, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Sun, Z.; Xue, H.; Bayraktar, E.; Qin, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, H. Effect of turning on the surface integrity and fatigue life of a TC11 alloy in very high cycle fatigue regime. Metals 2020, 10, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gockel, J.; Sheridan, L.; Koerper, B.; Whip, B. The influence of additive manufacturing processing parameters on surface roughness and fatigue life. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, T.; Wiora, G.; Witt, G. Characterization of typical surface effects in additive manufacturing with confocal microscopy. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 3, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.; Singh, A.K. Modelling of surface roughness in a new magnetorheological honing process for internal finishing of cylindrical workpieces. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 144, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundke, K.; Pöschel, K.; Synytska, A.; Frenzel, R.; Drechsler, A.; Nitschke, M.; Cordeiro, A.; Uhlmann, P.; Welzel, P. Experimental studies of contact angle hysteresis phenomena on polymer surfaces—Toward the understanding and control of wettability for different applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 222, 350–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzesik, W.; Żak, K. Comparison of precision hard turning and grinding operations in terms of the topographic analysis of machined surfaces. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Liu, M.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Xiong, Z.; Piano, S.; Zhang, S. Surface texture characterisation with reduced boundary effect for diamond-turned micro-structured surfaces. Precis. Eng. 2022, 79, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Yu, Z.; Yu, H.; Xu, J.; Feng, L. Evaluation of Three-Dimensional surface roughness in microgroove based on bidimensional empirical mode decomposition. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, A.; Holsten, M.; Hensgen, L. Crater morphology evaluation of contemporary advanced EDM generator technology. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.V.; Faulcon, M.; Timmers, B.; Reddy, V.V.; Barth, H.; Nilsson, G.; Rosén, B.G. Influence of different post-processing methods on surface topography of fused deposition modelling samples. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2020, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolczyk, G.; Maruda, R.; Krolczyk, J.; Nieslony, P.; Wojciechowski, S.; Legutko, S. Parametric and nonparametric description of the surface topography in the dry and MQCL cutting conditions. Measurement 2018, 121, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leksycki, K.; Królczyk, J.B. Comparative assessment of the surface topography for different optical profilometry techniques after dry turning of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Measurement 2020, 169, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leksycki, K.; Feldshtein, E.; Królczyk, G.M.; Legutko, S. On the Chip Shaping and Surface Topography When Finish Cutting 17-4 PH Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel under Near-Dry Cutting Conditions. Materials 2020, 13, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Ruan, X.; Li, L.; Xie, M. Multiscale characterization and contact performance analysis of machining surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Xu, G.; Wang, N. Analysis of surface morphology of TI-5553 based on WaVelet Transform. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2021, 217, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, C.; Bigerelle, M.; Marteau, J.; Lemesle, J.; Paez, D.; Guibert, R.; Blateyron, F.; Brown, C.A. A novel methodology to assess optical profilometer stability to discriminate surface roughness. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2024, 12, 025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, L.; Thanki, A.; Bermudez, C.; Artigas, R.; Thompson, A.; Haitjema, H.; Leach, R. Optimisation of imaging confocal microscopy for topography measurements of metal additive surfaces. Metrology 2023, 3, 186–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczewska-Wójcik, M. Wear mechanisms and surface topography of artificial hip joint components at the subsequent stages of tribological tests. Measurement 2017, 107, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczewska-Wójcik, M.; Pethuraj, M.; Uthayakumar, M.; Majid, M.S.A. Characteristics of the surface topography and tribological properties of reinforced aluminum matrix composite. Materials 2022, 15, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemczewska-Wójcik, M.; Wójcik, A. The multi-scale analysis of ceramic surface topography created in abrasive machining process. Measurement 2020, 166, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakuła, D.; Staszuk, M.; Dziekońska, M.; Kožmín, P.; Čermák, A. Laser Micro-Texturing of sintered tool Materials Surface. Materials 2019, 12, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yang, S.; Ko, Y. Evaluation of the surface characteristics of various implant abutment materials using confocal microscopy and white light interferometry. Implant Dent. 2015, 24, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Flys, O.; Chaparala, A.; Berrimi, C.E.; Rosen, B. Study on surface texture of Fused Deposition Modeling. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 25, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romoli, L.; Rashed, C.; Fiaschi, M. Experimental characterization of the inner surface in micro-drilling of spray holes: A comparison between ultrashort pulsed laser and EDM. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 56, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlaček, M.; Gregorčič, P.; Podgornik, B. Use of the Roughness Parameters SSK and SKU to control Friction—A method for designing surface texturing. Tribol. Trans. 2016, 60, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlaček, M.; Guštin, A.Z.; Žužek, B. Influence of laser surface texturing sequence on fatigue properties of coated cold work tool steel. Metals 2020, 10, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stach, S.; Ţălu, Ş.; Głuchaczka, A.; Siek, P.; Zając, J.; Tavazzi, S. Microscopic investigations of surface texture of siloxane-hydrogel contact lenses. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, E442–E451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţălu, Ş.; Ghazai, A.J.; Stach, S.; Hassan, A.; Hassan, Z.; Ţălu, M. Characterization of surface roughness of Pt Schottky contacts on quaternary n-Al0.08In0.08Ga0.84N thin film assessed by atomic force microscopy and fractal analysis. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 25, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţălu, Ş. Advanced morphological analysis of siloxane-hydrogel contact lenses. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 2702–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, X. A new approach to numerical characterisation of wear particle surfaces in three-dimensions for wear study. Wear 2012, 282–283, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent-Burgués, J.; Sanz, F. AFM in mode Peak Force applied to the study of un-worn contact lenses. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, D.; Krolczyk, J.; Chudy, R.; Gupta, M.K.; Pruncu, C.; Krolczyk, G. Role of optical measurement systems in analysing the surface topography of an industry standard component. Optik 2023, 283, 170919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, T.; Liao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, K. Using Wavelet Packet Transform for surface roughness evaluation and texture extraction. Sensors 2017, 17, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.K.; Truong, V.K.; Hasan, J.; Fluke, C.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Roughness Parameters for standard description of surface Nanoarchitecture. Scanning 2012, 34, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lou, S.; Majewski, C. Characterisation and correlation of areal surface texture with processing parameters and porosity of High Speed Sintered parts. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, R.K. Characterisation of Areal Surface Texture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.; Thorenz, B.; Schreiner, F.; Döpper, F. Comparison of areal and profile surface measurement methods for evaluating surface properties of machined components. Procedia CIRP 2021, 102, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorburger, T.V.; Rhee, H.; Renegar, T.B.; Song, J.; Zheng, A. Comparison of optical and stylus methods for measurement of surface texture. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 33, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, H. Parameters for evaluating the wearing behaviour of surfaces. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1992, 32, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, D.J. Handbook of Surface and Nanometrology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpuschewski, B.; Pieper, H.; Welzel, F.; Risse, K. Alternative strategies in finishing cylinder running surfaces. CIRP Ann. 2012, 61, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z. Neural networks modeling of honing surface roughness parameters defined by ISO 13565. J. Manuf. Syst. 2002, 21, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlus, P.; Cieslak, T.; Mathia, T. The study of cylinder liner plateau honing process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 6078–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, B.; Anderberg, C.; Ohlsson, R. Parameter correlation study of cylinder liner roughness for production and quality control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2008, 222, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüser, D.; Thomsen-Schmidt, P.; Meeß, R. Uncertainty of cutting edge roughness estimation depending on waviness filtration. Procedia CIRP 2016, 45, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigerelle, M.; Iost, A. A numerical method to calculate the Abbott parameters: A wear application. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eifler, M.; Brodmann, B.; Müller, A.; Seewig, J. Comprehensive analysis of surfaces featuring functional characteristics by angular-resolved scattering light measurement. In Proceedings of the Optical Manufacturing and Testing 2024, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–23 August 2024; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; p. 1313408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.L. What does friction really depend on? Robust governing parameters in contact mechanics and friction. Phys. Mesomech. 2016, 19, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walid, A.; Eifler, M. Common Practices and Methodologies in Scientific Functional Characterization of Surface Topography. Metrology 2025, 5, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020033
Walid A, Eifler M. Common Practices and Methodologies in Scientific Functional Characterization of Surface Topography. Metrology. 2025; 5(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalid, Abbass, and Matthias Eifler. 2025. "Common Practices and Methodologies in Scientific Functional Characterization of Surface Topography" Metrology 5, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020033
APA StyleWalid, A., & Eifler, M. (2025). Common Practices and Methodologies in Scientific Functional Characterization of Surface Topography. Metrology, 5(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5020033






