Performance of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Targeting the Nucleocapsid (N) Gene of SARS-CoV-2 for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
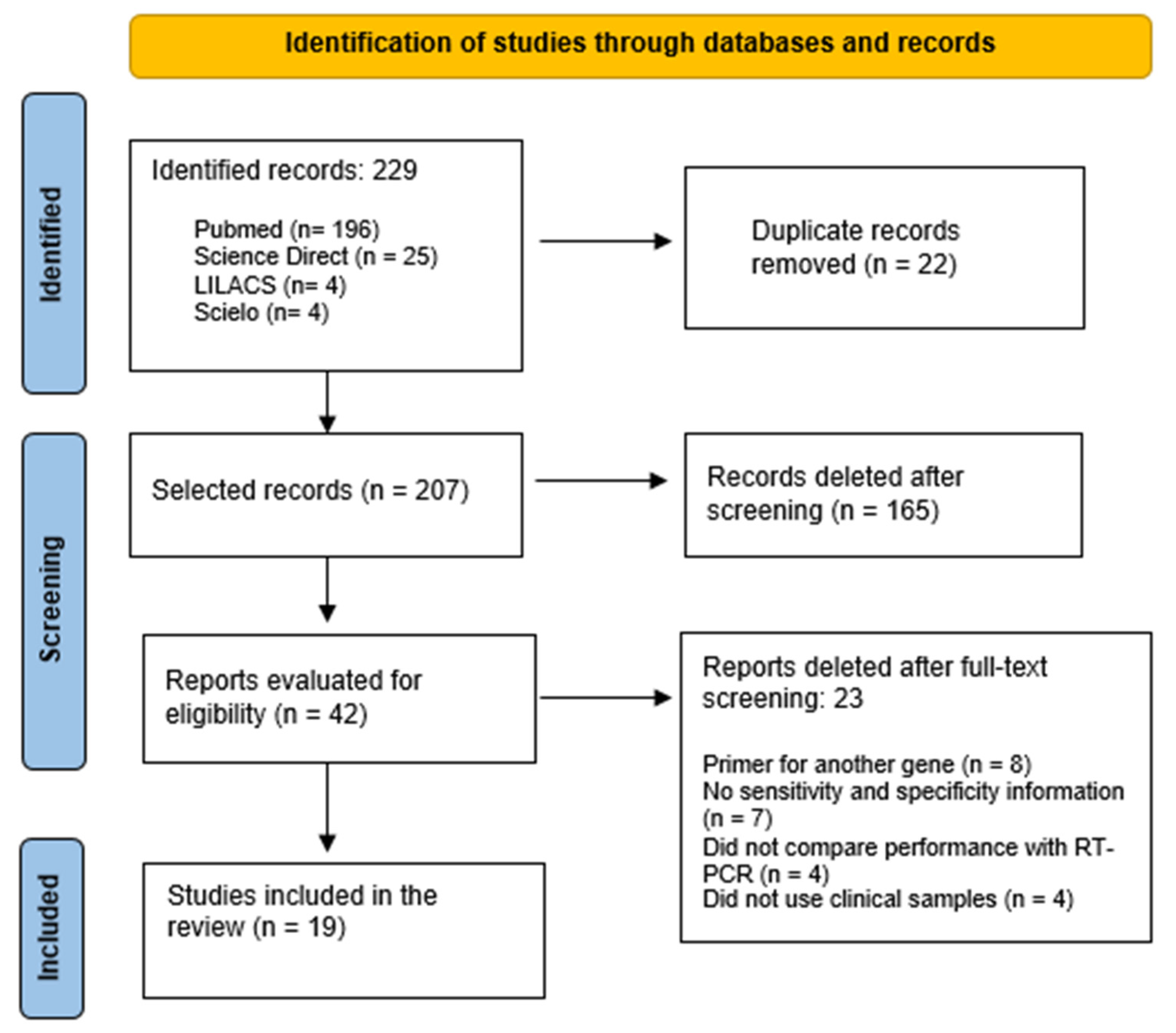
2.1. Article Search and Selection Strategy
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, R.; Wu, X.; Wan, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C. A Novel Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Histórico Da Pandemia de COVID-19—OPAS/OMS|Organização Pan-Americana Da Saúde. Available online: https://www.paho.org/pt/covid19/historico-da-pandemia-covid-19 (accessed on 26 June 2021).
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/naats.html (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Guidance for Antigen Testing for SARS-CoV-2 for Healthcare Providers Testing Individuals in the Community. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-guidelines.html (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Diagnostic Testing for SARS-CoV-2: Interim Guidance, 11 September 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Huang, W.E.; Lim, B.; Hsu, C.; Xiong, D.; Wu, W.; Yu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, M.; et al. RT-LAMP for Rapid Diagnosis of Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Notomi, T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomita, N.; Mori, Y.; Kanda, H.; Notomi, T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) of Gene Sequences and Simple Visual Detection of Products. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): A Rapid, Accurate, and Cost-Effective Diagnostic Method for Infectious Diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, I.; Kirstein, O.D.; Hailu, A.; Warburg, A. Optimization of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Assays for the Detection of Leishmania DNA in Human Blood Samples. Acta Trop. 2016, 162, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, M.; Park, E.; Chung, D.R.; Kim, J.; Hwang, E.S. A Simple and Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Assay for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV. BioChip. J. 2019, 13, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Soto, P.; Gandasegui Arahuetes, J.; Sánchez Hernández, A.; López Abán, J.; Vicente Santiago, B.; Muro, A. A Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Assay for Early Detection of Schistosoma Mansoni in Stool Samples: A Diagnostic Approach in a Murine Model. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer Program]. Version 5.4; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2020.
- Uribe-Alvarez, C.; Lam, Q.; Baldwin, D.A.; Chernoff, J. Low Saliva PH Can Yield False Positives Results in Simple RT-LAMP-Based SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostic Tests. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, Y.H.; Um, J.; Antigua, K.J.C.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y.; Choi, W.-S.; Kim, S.G.; Jeong, J.H.; et al. Development of a Reverse Transcription-Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification as a Rapid Early-Detection Method for Novel SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguli, A.; Mostafa, A.; Berger, J.; Aydin, M.Y.; Sun, F.; de Ramirez, S.A.S.; Valera, E.; Cunningham, B.T.; King, W.P.; Bashir, R. Rapid Isothermal Amplification and Portable Detection System for SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22727–22735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, F.; Sharif, S.; Khurshid, A.; Ikram, A.; Shabbir, I.; Salman, M.; Ahad, A.; Suleman Rana, M.; Raja, A.; Badar, N.; et al. Reverse Transcriptase Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP)-Based Diagnosis: A Potential Alternative to Quantitative Real-Time PCR Based Detection of the Novel SARS-COV-2 Virus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.S.; Lim, D.H.; Yoon, J.; Kim, A.; Lim, M.; Nam, J.; Yanagihara, R.; Ryu, S.-W.; Jung, B.K.; Ryoo, N.-H.; et al. Development of a Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Assay for on-Site Diagnosis of SARS CoV-2. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Pan, W.; Arasthfer, A.; Fang, W.; Ling, L.; Fang, H.; Daneshnia, F.; Yu, J.; Liao, W.; Pei, H.; et al. Development and Validation of a Rapid, Single-Step Reverse Transcriptase Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) System Potentially to Be Used for Reliable and High-Throughput Screening of COVID-19. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Orihara, Y.; Kawamura, R.; Imai, K.; Sakai, J.; Tarumoto, N.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, S.; Maesaki, S.; Maeda, T. Evaluation of Rapid Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, H.; Tamura, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kinoshita, H.; Katsuta, H.; Matsui, C.; Matsushita, A.; Arai, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Iuchi, A.; et al. Clinical COVID-19 Diagnostic Methods: Comparison of Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) and Quantitative RT-PCR (QRT-PCR). J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 139, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalli, M.A.; Langmade, J.S.; Chen, X.; Fronick, C.C.; Sawyer, C.S.; Burcea, L.C.; Wilkinson, M.N.; Fulton, R.S.; Heinz, M.; Buchser, W.J.; et al. Rapid and Extraction-Free Detection of SARS-CoV-2 from Saliva by Colorimetric Reverse-Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.H.; Best, N.; McAuley, J.; Porter, J.L.; Seemann, T.; Schultz, M.B.; Sait, M.; Orlando, N.; Mercoulia, K.; Ballard, S.A.; et al. Validation of a Single-Step, Single-Tube Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Hou, T.; Li, S. A Novel One-Pot Rapid Diagnostic Technology for COVID-19. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1154, 338310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Malpartida-Cardenas, K.; Moser, N.; Pennisi, I.; Cavuto, M.; Miglietta, L.; Moniri, A.; Penn, R.; Satta, G.; Randell, P.; et al. Handheld Point-of-Care System for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Extracted RNA in under 20 Min. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumani, F.; Azinheiro, S.; Sousa, H.; Sousa, A.; Timóteo, M.; Varandas, T.; Fonseca-Silva, D.; Baldaque, I.; Carvalho, J.; Prado, M.; et al. Optimization and Clinical Evaluation of a Multi-Target Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Nasopharyngeal Samples. Viruses 2021, 13, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rödel, J.; Egerer, R.; Suleyman, A.; Sommer-Schmid, B.; Baier, M.; Henke, A.; Edel, B.; Löffler, B. Use of the VariplexTM SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP as a Rapid Molecular Assay to Complement RT-PCR for COVID-19 Diagnosis. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 132, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellenberg, J.J.; Ormond, M.; Keynan, Y. Extraction-Free RT-LAMP to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Is Less Sensitive but Highly Specific Compared to Standard RT-PCR in 101 Samples. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 136, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Herbst, K.; Boerner, K.; Meurer, M.; Kremer, L.P.; Kirrmaier, D.; Freistaedter, A.; Papagiannidis, D.; Galmozzi, C.; Stanifer, M.L.; et al. A Colorimetric RT-LAMP Assay and LAMP-Sequencing for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Clinical Samples. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabc7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Meyerson, N.R.; Clark, S.K.; Paige, C.L.; Fattor, W.T.; Gilchrist, A.R.; Barbachano-Guerrero, A.; Healy, B.G.; Worden-Sapper, E.R.; Wu, S.S.; et al. Saliva TwoStep for Rapid Detection of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Carriers. Elife 2021, 10, e65113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Liang, J.; Qiu, L.; Han, D.; Tan, W. Rapid One-Pot Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on a Lateral Flow Assay in Clinical Samples. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3325–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Multiplex Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Combined with Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor for the Diagnosis of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.Y.; Cheung, P.P.H. Diagnostic Performances of Common Nucleic Acid Tests for SARS-CoV-2 in Hospitals and Clinics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e704–e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Target Gene | Nº of Samples | Type of Sample | Sample Pre-Treatment | Sensitivity % (CI:88. 0–92. 1) | Specificity % (CI:97. 9–99. 2) | Reading the Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alvarez, 2021 [15] | Orf1a, N, HMS Assay 1e | 59 (29+/30−) | Swab NP and saliva (with or without purification) | RNA extraction and direct assay | 93.1% (purified) 65.5% not purified | 100.0% | Colorimetric |
| Baek, 2020 [16] | N | 154 (14+/140−) | Swab NP, sputum and tears | RNA extraction | 100.0% | 98.7% | Colorimetric |
| Ganguli, 2021 [17] | Orf1a, S, Orf 8, N | 20 (10+/10−) | Swab NP | Without RNA extraction | 100.0% | 100.0% | Fluorescence |
| Haq, 2021 [18] | Orf-1ab, N, S | 297 (124+/173−) | Swab NP | RNA extraction | 91.5% | 90.0% | Colorimetric |
| Jang, 2021 [19] | RdRP, N, E | 292 (130+/162−) | Swab NP, oropharyngeal smears, sputum, saliva | RNA extraction | 93.9% | 100.0% | Fluorescence |
| Jiang, 2020 [20] | N | 260 (47+/213−) | Swab NP, sputum and tears | RNA extraction | 91.4% | 99.5% | Fluorescence |
| Kitagawa, 2020 [21] | N | 76 (30+/46−) | Swab NP | RNA extraction | 100.0% | 97.6% | Turbidimetry |
| Kitajima, 2021 [22] | N | 151 (79+/72−) | Swab NP and sputum | RNA extraction | 88.6% | 98.6% | Turbidimetry and Fluorescence |
| Lalli, 2021 [23] | N, E | 30 (20+/10−) | Saliva | Pre-treated without RNA extraction | 85.0% | 90.0% | Colorimetric |
| Lee, 2020 [24] | N | 157 (107+/50−) | Swab NP | RNA extraction | 87.0% | 100.0% | Fluorescence |
| Li, 2021 [25] | N | 45 (15+/30−) | Swab NP | Without RNA extraction | 100.0% | 100.0% | Colorimetric |
| Manzano, 2021 [26] | N | 183 (127+/56−) | Swab NP | RNA extraction | 91.0% | 100.0% | Fluorescence |
| Roumani, 2021 [27] | ORF8, N, ORF3a | 152 (49+/103−) | Swab NP | RNA extraction | 63.3% | 99.0% | Fluorescence |
| Rödel, 2020 [28] | RdRP M, E, N | 73 (38+/35−) | Respiratory Secretions | Without RNA extraction | 81.6 % | 100.0% | Fluorescence |
| Schellenberg, 2021 [29] | N | 101 (50+/51−) | Swab NP | Without RNA extraction | 77.0% | 100.0% | Colorimetric |
| Dao Thi, 2020 [30] | N | 235 (35+/200−) | Swab NP | Without RNA extraction | 86.0% | 99.5% | Colorimetric |
| Yang, 2021 [31] | N, AS1E | 573 (278 +/295−) | Saliva | Pre-treated without RNA extraction | 74.8% | 100.0% | Colorimetric |
| Zhang 2021 [32] | ORF1ab, N | 12 (8+/4−) | Swab NP | No RNA extraction (pre-treatment with NAOH solution) | 100.0% | 100.0% | Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) |
| Zhu, 2020 [33] | ORF1ab, N | 129 (33 +/96−) | Oropharyngeal smear | RNA extraction | 100.0% | 100.0% | Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor (LFB) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoffmann, E.d.R.; Dreifke, T.M.; Ghiotto, M.A.; Gaboardi, G.; Cantarelli, V.V. Performance of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Targeting the Nucleocapsid (N) Gene of SARS-CoV-2 for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. COVID 2022, 2, 759-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2060057
Hoffmann EdR, Dreifke TM, Ghiotto MA, Gaboardi G, Cantarelli VV. Performance of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Targeting the Nucleocapsid (N) Gene of SARS-CoV-2 for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. COVID. 2022; 2(6):759-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2060057
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoffmann, Elias da Rosa, Tatiane Marines Dreifke, Marco Antonio Ghiotto, Guilherme Gaboardi, and Vlademir Vicente Cantarelli. 2022. "Performance of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Targeting the Nucleocapsid (N) Gene of SARS-CoV-2 for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" COVID 2, no. 6: 759-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2060057
APA StyleHoffmann, E. d. R., Dreifke, T. M., Ghiotto, M. A., Gaboardi, G., & Cantarelli, V. V. (2022). Performance of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Targeting the Nucleocapsid (N) Gene of SARS-CoV-2 for Rapid Diagnosis of COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. COVID, 2(6), 759-766. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2060057






