Abstract
In November of 2021, a recently evolved variant of SARS-CoV-2, omicron, was discovered. In just one month, omicron has spread to more than 89 countries resulting in a rapid rise in cases and a new wave of infections. With over 46 mutations, omicron brings concern to the public health and may be able to infect at a greater capacity than previous strains. Although able to infect double vaccinated and previously infected individuals, the booster vaccine may prove promising. However, more research is needed to fully elucidate the key function of each mutation and to better develop effective drugs. Marine resources may be a promising drug discovery avenue to investigate. For example, compounds such as natural bromotyrosines and inorganic polyphosphate have been shown to have multiple mechanisms of action against viruses, like SARS-CoV-2. Through viral entry blockade and preventing viral replication and protein synthesis, metabolites produced from marine organisms may be promising against the evolving SARS-CoV-2. The present review highlights key features of the omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant, summarizes key studies and reports on omicron viral infection and examines the potential for intervention using renewable marine resources.
1. Introduction
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) first emerged almost two years ago and has been ongoing since [1]. It is without a doubt that the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has led to frustration and prevalent negative effects on the mental wellbeing of individuals as well as the economy [2,3,4]. Vaccinations were effective at first, however, the solution was temporary, and the single-stranded SARS-CoV-2 virus is continuously evolving through mutations in key domains [5,6,7,8]. Several SARS-CoV-2 variants including the alpha, beta and delta strains were associated with new waves of COVID-19 infection [9,10]. The delta variant was shown to have a higher transmissible and infectious risk than other strains with reports of having a higher viral load and mutations granting a better immune response escape [11,12,13].
On 24 November 2021, a new SARS-CoV-2 variant, known as omicron (B.1.1.529) was reported to World Health Organization (WHO) [14]. The omicron variant was first reported on 11 November 2021, in Botswana and just a few days later, was identified in South Africa [15,16]. To date (January 2022), omicron has been reported in more than 57 countries, with South Korea reporting its highest number of COVID-19 cases in December 2021, since the start of the pandemic [17]. It has not been elucidated whether the transmissibility and severity status of the omicron variant is greater than the previous strains [18,19]. Over 45 mutations and several gene deletions have been identified, some in the same genes as the previous variants and others being novel (Figure 1) [20]. Together, these mutations in key regions give the omicron strain the ability to escape the host immune system, rendering vaccinations less effective [20,21]. Furthermore, it is not clear yet what the effects of several mutations are, and this serves as a barrier for developing new vaccinations or drugs for prevention and treatment of omicron viral infection [22,23].

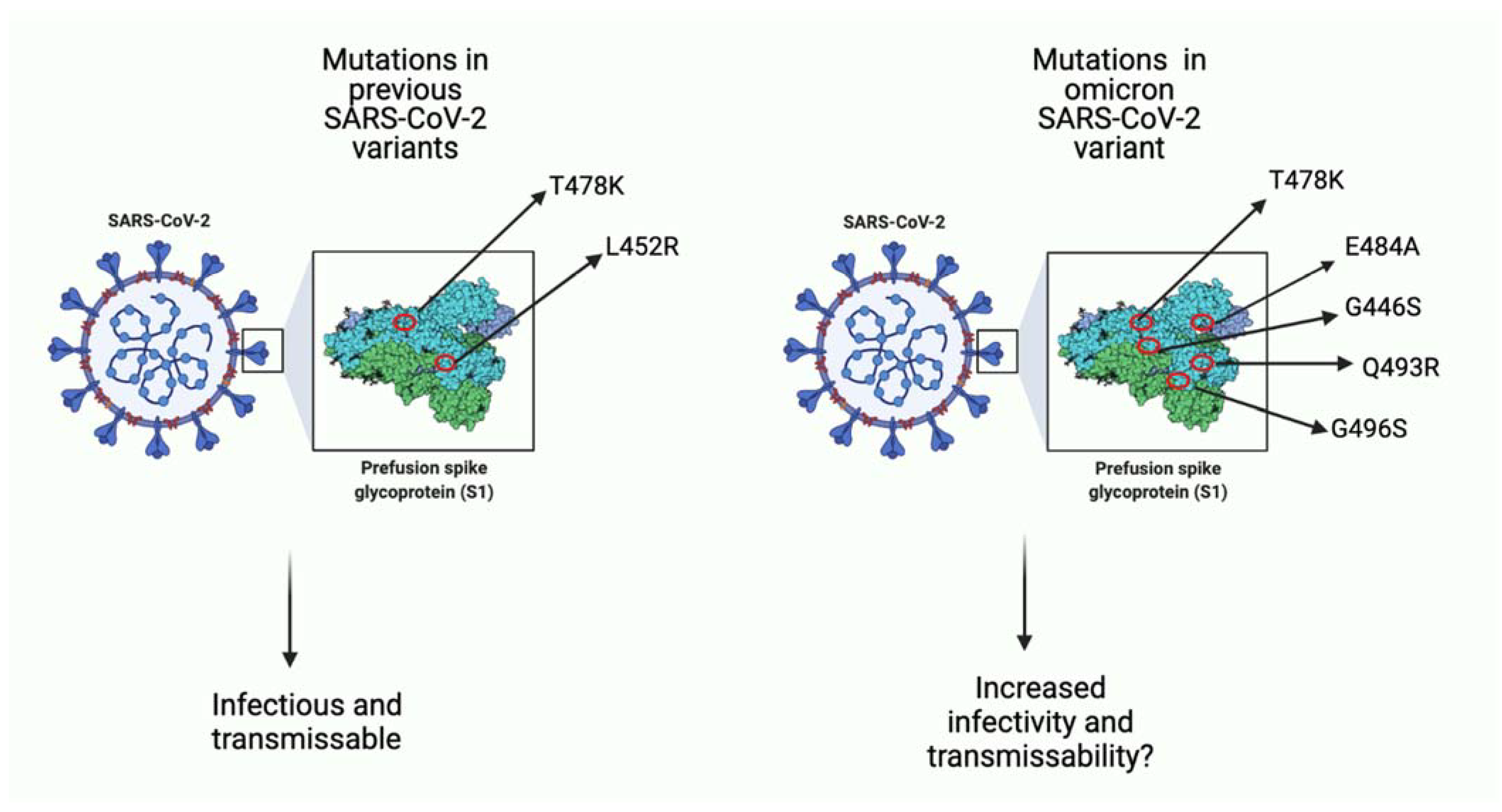
Figure 1.
A comparison of few key missense mutations in the spike protein of previous SARS-CoV-2 variants and the omicron variant. As seen in the image on the left, previous variants (i.e., delta variant) had few mutations that favored viral infection. Seen on the right, omicron has more mutations, many of which function to increase binding affinity to host ACE-2 receptor and potentially increase infectivity ability as well as transmissibility of viral particles. Some mutations such as T478K overlap with previous variants, and some (i.e., E484A) are unique to omicron. (Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 19 December 2021)).
Previous variants have shown to lower the efficacy of vaccinations. For example, the efficacy of the AstraZeneca ChAdOx1 vaccine decreased to 10% in South Africa because of the beta SARS-CoV-2 variant [19]. The re-purposing of drugs used for anti-bacterial infections or other anti-viral infections may be a promising avenue to investigate. Marine resources have a variety of molecules that have shown to have anti-viral abilities and their repurposing for treatment against omicron may be promising [24,25,26]. Specifically, inorganic polyphosphate has been shown to inhibit viral life cycle at several stages by blocking viral particle spike protein binding to host ACE-2 receptor and inhibiting viral protein synthesis once inside the cell [26,27]. Similarly, lambda-carrageenan isolated from marine algae have also been shown to inhibit viral protein transcription and translation [28]. Moreover, bromotyrosines have also been shown to have anti-bacterial and anti-viral activity, and have recently been isolated and purified for further research [24,29]. Although some challenges are ahead such as large-scale production and more in vivo studies necessary for further development, more research is warranted to determine the full potential of marine metabolites against SARS-CoV-2 variants. This review highlights the current understanding of the omicron variant and its features, depicts the potential for marine resource intervention and highlights some challenges faced ahead.
2. Key Features of the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant
Of the SARS-CoV-2 variants, omicron possesses the greatest number of mutations which grant the viral particles a greater ability to infect and transmit between hosts [20,30,31]. A study done by Kannan et al. identified 30 signature mutations in the spike protein of the omicron variant, with 23 being novel, and 7 overlapping with previously identified variants [20]. Additional mutations were found in other genes as well as totaling 46 genetic changes in the omicron variant. Several mutations such as residue changes like G446S and Q493R resulted in the inability of antibodies to bind due to steric interference and other mutations such as E484A and Y505H were reported to affect the neutralization ability of the antibodies (Figure 2) [20]. Kannan et al. reported that these mutations are reducing the affinity between the antibody and the spike protein resulting in the inability of present humoral immunity to protect against the omicron variant [20]. These results likely explain the recent (December 2021) rapid rise in SARS-CoV-2 infection, despite previous infection or vaccination.
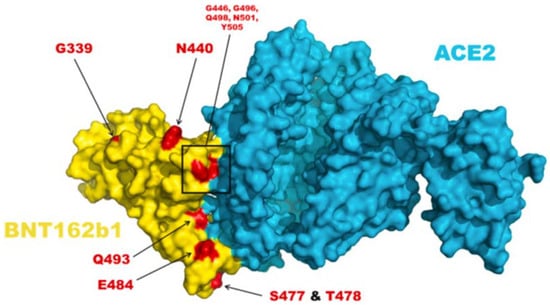
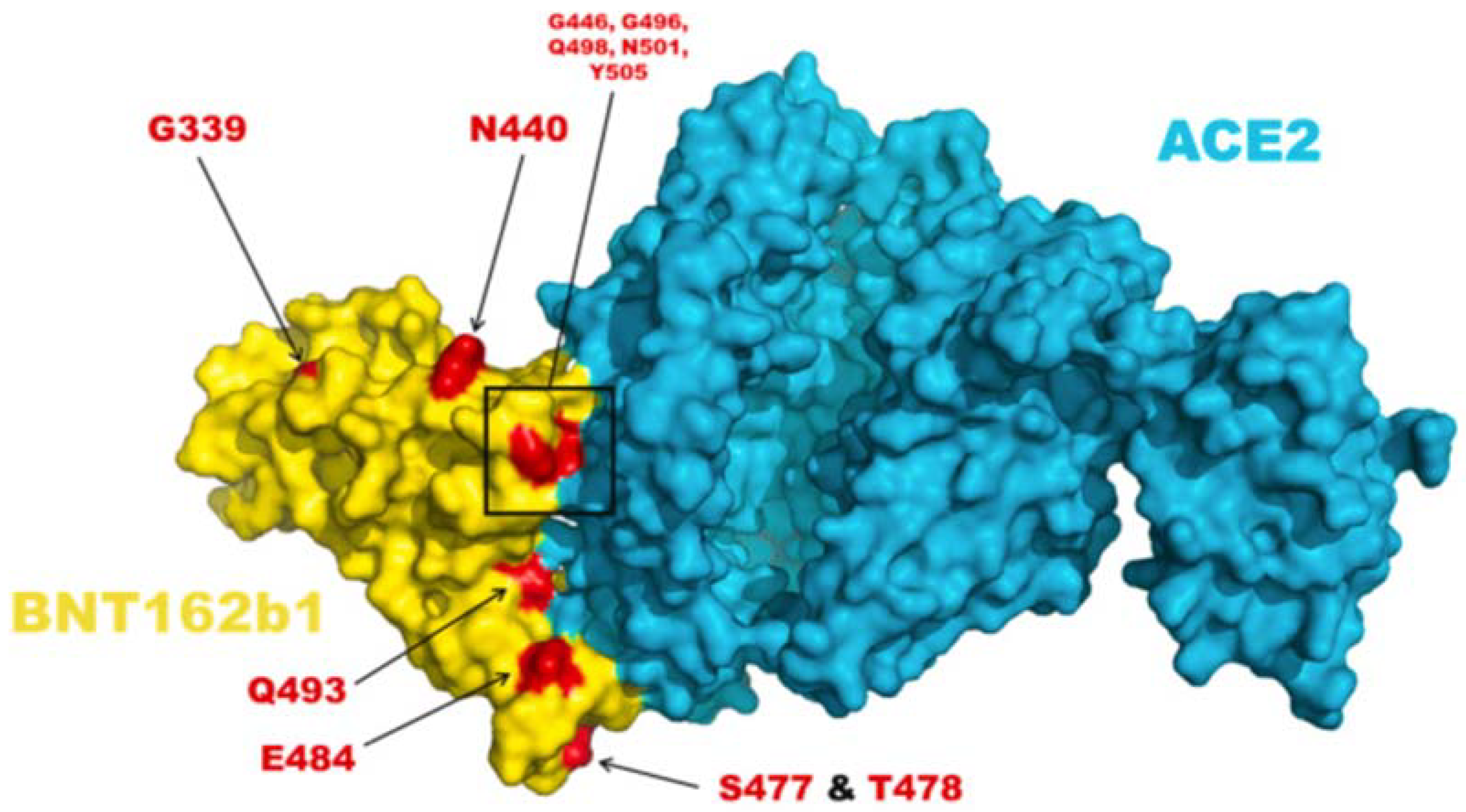
Figure 2.
The amino acid residue changes at the spike and ACE2 protein interface. The image above depicts the amino acid mutations in the omicron variant. BNT162b1 encodes for the spike-RBD region; the image displays the complex formed between spike protein and host ACE2 receptor [20].
Another finding of the Kannan et al. study was a deletion in the tyrosine residue at position 145 which further results in the reduced binding affinity of the antibodies [20]. Furthermore, a study done by Zhang et al. found that when a pseudotyped omicron virus was administered to convalescent serum from previous SARS-CoV-2 strain, the antibodies displayed a low ability to neutralize the omicron particles [32]. This suggests that the omicron variant can escape host humoral-antibody immune response which was initially protecting individuals who were either previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 or fully vaccinated [32]. This antibody neutralization evasion was in part attributed to a mutation from the residue glutamate at position 484 to alanine [32].
Moreover, HEK293T cells expressing ACE2 receptor were then infected with several strains of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, including omicron, beta, and delta. The study found that through the interaction of the viral spike protein and host ACE2 receptor, the omicron variant was significantly more able to enter and infect the cells compared to the beta or delta variants [32]. Knowing that the spike protein and ACE-2 interaction is necessary for infection is significant as it suggests that these proteins are potential targets for drug discovery and development against omicron and related variants [32]. To add, Zhang et al. reported that the omicron virus possesses 15 changes in genetic material at the RBD region of the spike protein spanning from Arg319 to Phe541, including G339D, S371L, S477N and several more. These mutations in the RBD did not alter the binding affinity of the spike protein, suggesting other mutations in the spike protein are responsible for increased cell entry [32].
A recent study by Venkatakrishnan et al. found that one of the mutations in the omicron variant is an insertion mutation (ins214EPE), which has not been identified in other strains of SARS-CoV-2 [33]. The insertion mutation is in a region of the viral particle recognized by human T cells, suggesting this mutation may help the virus escape cell-based host immunity, although evidence is not yet clear. Lau et al. have proposed that the insertion mutation may have originated from the human genome as several fragments of the human genome match the sequence of the gene that is inserted [34]. An in vitro study by Wilhelm et al. found that antibodies from double vaccinated sera were not effective at neutralizing omicron (effectiveness reduced by 32.8-fold) [35]. Furthermore, the monoclonal antibodies imdevimab and casirivimab that are currently used for treatment and prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection were effective at preventing delta variant infection yet were ineffective to prevent omicron variant infection [35]. Similarly, Kumar et al. reported that the numerous mutations in the spike proteins RBD area render the omicron variant resistant to host humoral immunity by antibodies [22]. The delta and the omicron variants share a T478K mutation in the RBD however, as seen in Figure 3, the omicron variant has several more mutations than the delta variant [22].

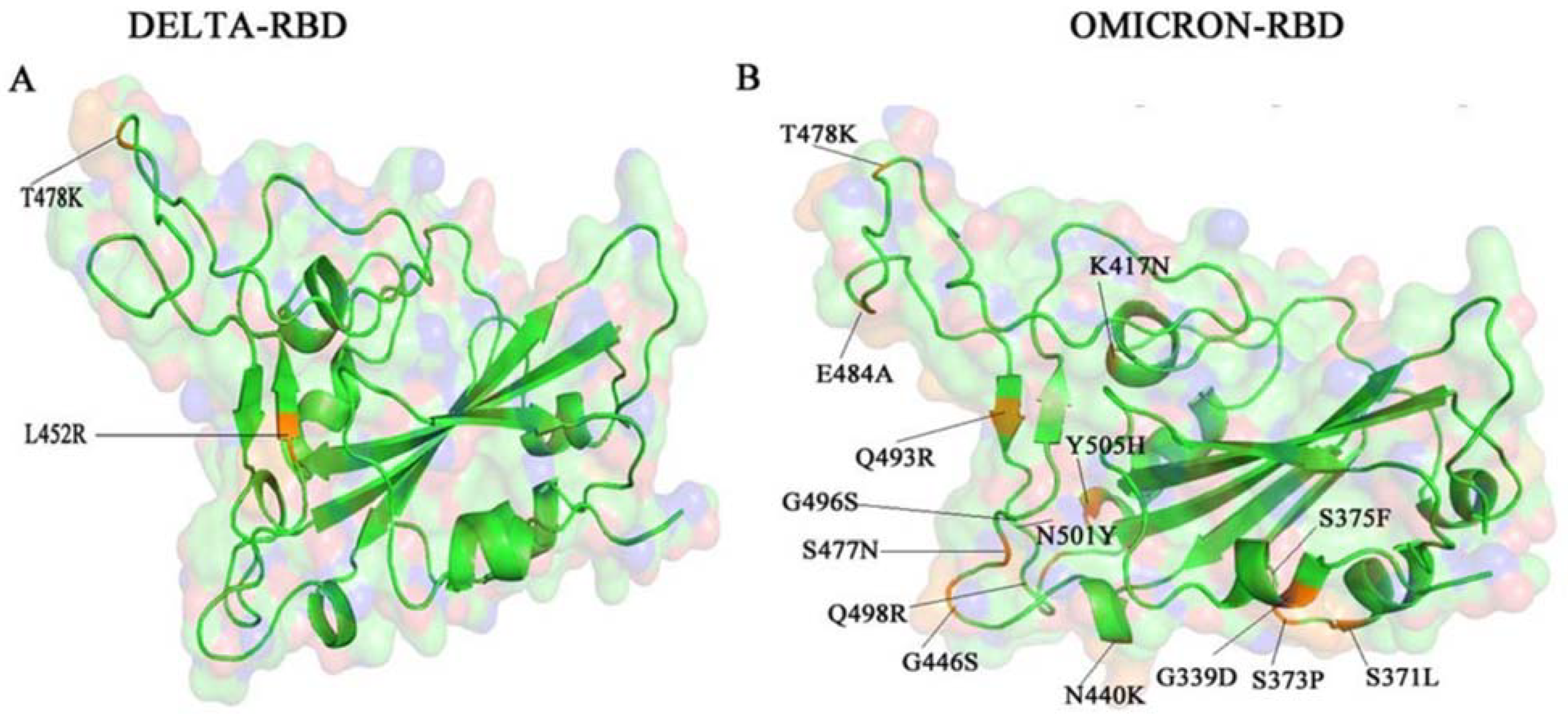
Figure 3.
The RBD of SARS-CoV-2 delta variant and omicron variant. Image depicts a comparison of the mutations present in the delta variant (A) and omicron variant (B), with a shared mutation at the 478-residue position [22].
Kumar and colleagues also reported that omicron variant proteins have a stability score of 32.81–34.69 suggesting that the spike proteins are highly thermostable [22]. Additionally, through computational primary structure analysis, the omicron variant had an increase in both positively (Arg, Lys) and negatively (Asp, Glu) charged residues which contribute formation of salt bridges compared to the delta variant. The spike protein of omicron had increased hydrophobic and non-polar residues and decreased polar amino acids compared to the delta variant. In addition, several mutations in the viral spike protein genes (i.e., G339D, T478K), decrease protein stability, and increase disease risk. When comparing human ACE2 receptor binding of the omicron and delta spike proteins, omicron displayed a higher docking score (−539.81) compared to the delta variant (−529.62) indicating that omicron variant is better able to infect [22]. In line with the studies above, Dejnirattisai et al. found that neutralization by antibodies of titers on sera from individuals how were previously infected dropped by a 29.8-fold in the omicron variant compared to previous strains [36]. These results suggest that previously infected patients and fully vaccinated patients are not fully protected from the omicron variant. Although disease severity is not yet known yet, the high ACE2 binding affinity makes the variant easily transmissible [36,37].
Conversely, one report by Schubert et al. found that the omicron RBD had the weakest binding and affinity to the host ACE2 receptor as depicted by the highest EC50 value of 150 ng/mL compared to the other strains such as the delta strain (EC50 = 89 ng/mL) [38]. These results suggest that omicron infectivity does not fully rely on RBD interaction with ACE2. Importantly, other factors involved in host cell entry such as processing of the viral spike protein, a fusion of the particles with the host cell membranes as well as RNA replication and translation efficacy play key roles during infection [38]. These results are in line with a study by Filip Fratev who identified several key missense mutations at residue positions 493, 417 and 478 that reduced the binding affinity of the RBD region to the ACE2 receptor [39]. Contrarily, missense mutations at positions 498, 505, 496 and 501 resulted in increased binding to the host ACE2 receptor [39]. These results suggest that omicron may have increased infectivity due to several mechanisms of action. Overall, an understanding of how and why the omicron variant has higher infectivity rates and transmissibility is key to the development of effective vaccinations and drugs against the virus.
3. The Potential for Prevention/Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Using Marine Resources
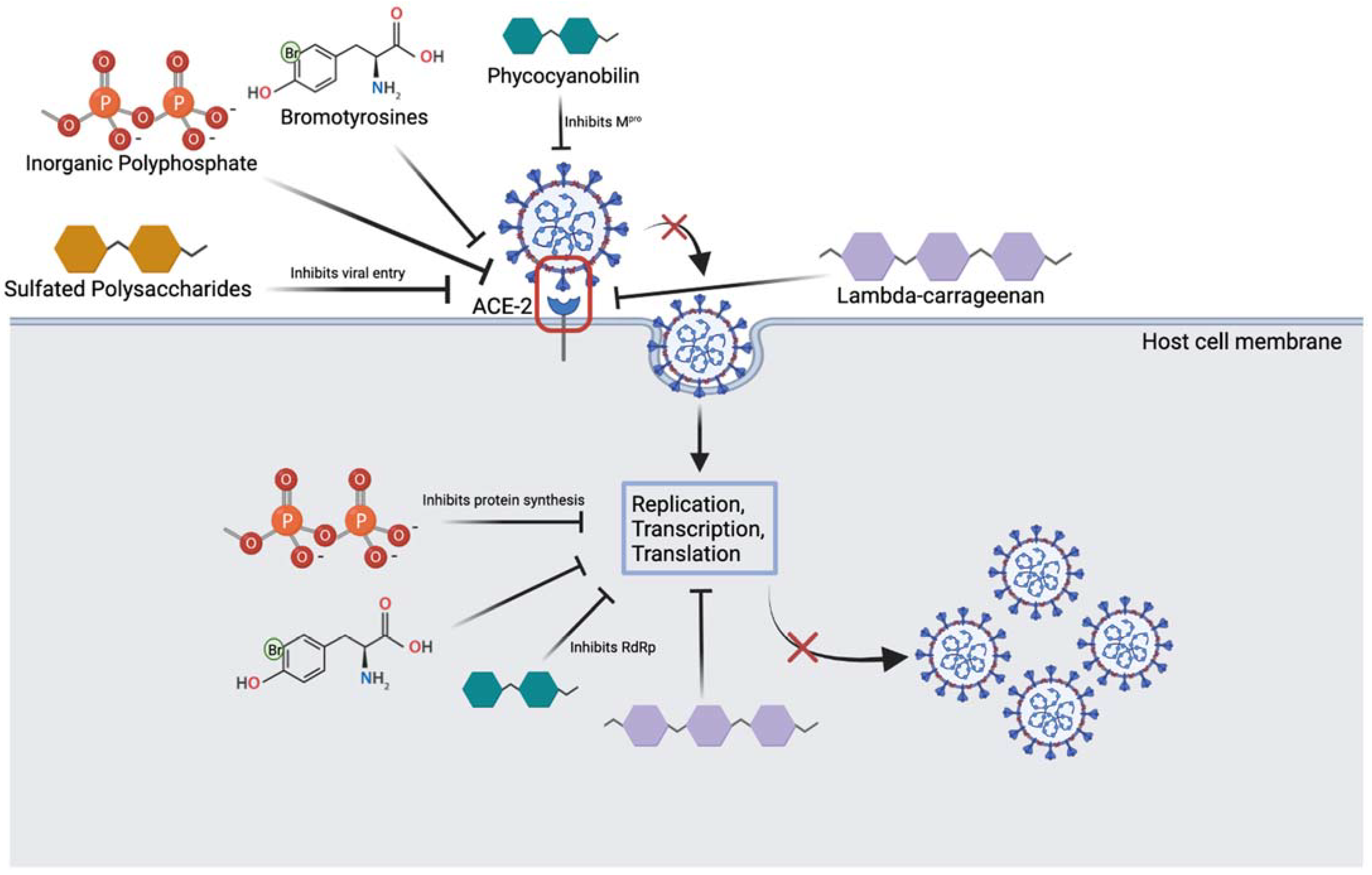
Considering the rapid rise in cases as well as the continuously evolving SARS-CoV-2 virus, there needs to be more effective vaccinations and drugs to prevent and treat not only the omicron variant but other future variants as well. One such drug discovery avenue to investigate is marine resources [40,41,42]. Marine resources harbor significant activity against cancer, viruses and bacteria, thus their ability to prevent or treat omicron viral infection should be investigated [29,43,44,45,46]. In fact, marine resources, which can be isolated from invertebrates and cultivated under farming conditions (i.e., sponges) [47,48], are highly advantageous over synthetic compounds as they lack religious constraints, have little to no toxins, are environmentally friendly and are metabolically compatible [24]. Furthermore, marine compounds isolated from a single organism can often combat several stages of the viral life cycle, including both viral entry and replication [49] (Figure 4).
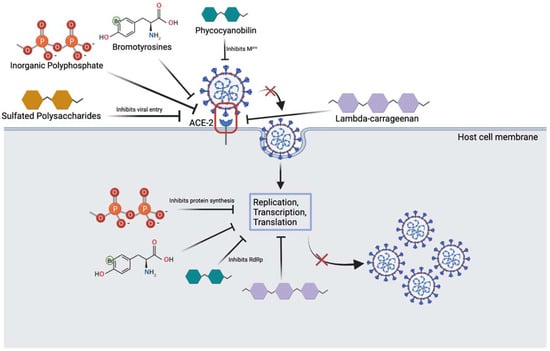
Figure 4.
Overview of marine compounds interfering with the SARS-CoV-2 viral life cycle. Image depicts several marine substances that can inhibit various steps of the life cycle which may be relevant to treatment. (Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 25 March 2022)).
Inorganic polyphosphate (polyP) are abundantly found in marine bacteria and sponges and have been shown to bind RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and prevent ACE-2 binding [27]. Several phosphate units of polyP are thought to interact with the spike protein through basic residues like Arginine, Lysine and Histidine [26,27]. Neuforth et al. found that polyP was able to inhibit the spike protein and ACE-2 interaction dose-dependently (up to 100 μg/mL) [26]. This inhibition was found to be 70% effective and during the 24 h incubation period, 100 μg/mL of polyP had no toxic effect on the cells. In addition, polyP is versatile in that it has also been shown to stimulate the innate antiviral immune system, by upregulating the mucin gene, MUC1 [26,27,46]. By boosting the innate immune response, polyP may serve a protective role as immunity plays an important role in the onset of COVID-19 symptoms and infection in patients. To add, Ferrucci et al. found that a long chain polyP is able to impair replication and transcription of viral particles, and this prevents the synthesis of viral proteins [26]. The study also found that polyP120 is able to bind to and downregulate the ACE-2 receptor by resulting in its degradation. It is clear that polyP may play a potential role in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection, however more studies investigating whether polyP interacts with spike protein on conserved or mutated residues is warranted to elucidate its usefulness against the omicron variant. This is important as the omicron variant differs from previous SARS-CoV-2 strains due to mutations in the spike protein, half of which are in the RBD. Thus, targeting stages in the latter portion of the viral life cycle, boosting the innate immune system or targeting the ACE-2 receptor interaction may together serve as competent methods to inhibit viral infection.
Moreover, lambda-carrageenan is a polysaccharide isolated from red algae and has been shown to inhibit influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2 viral replication dose-dependently [24,28]. Studies have found that like polyP, lambda-carrageenan is able to inhibit both viral entry and viral protein synthesis, by blocking transcription and translation of proteins. For example, in a study done by Jang et. al, SARS-CoV-2 viral protein and replication was suppressed dose-dependently in both Influenza A and SARS-CoV-2 viruses after lambda-carrageenan administration [28]. These multi-mechanisms of action likely serve beneficial not only for omicron variant treatment and prevention, but future and more aggressive variants as well. Another molecule of interest that may be redirected for different strains of SARS-CoV-2 viruses includes the pigment compounds phycocyanobilins (PCBs) [50]. In addition to their antioxidant properties, marine PCBs have been shown to inhibit a key conserved enzyme of the virus, main protease (Mpro) [51]. PCBs can also interfere with RNA dependant RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV-2 [50]. These findings are important as they are conserved enzymes among the various viral strains, and the design of drugs that can directly act on these molecules may serve as promising treatments. Similar to the above compounds, sulfated polysaccharides isolated from cyanobacteria and marine algae have been shown to bind to the SARS-CoV-2 viral spike protein and inhibit entry into cells [52]. One sulfated polysaccharide, iota-carrageenan, has been previously demonstrated to be effective against several respiratory virsuses, in vitro [53]. A recent study by Morokutti-Kurz et al. found that this molecule was able to inhibit the entry of a SARS-CoV-2 psudeotyped lentivirus dose-dependently with an IC50 of 2.6 µg/mL [54]. This is thought to be occurring through formation of a sulfated polysaccharide-ACE-2 complex which prevents the binding of the spike protein, and through the anionic sulfate groups interacting with the spike protein residues preventing ACE-2 interaction and thus, viral entry [54].
To add, marine sponges have been shown to rapidly filter out viruses and have highly specialized defense mechanisms against viral particles. One promising compound, bromotyrosine, is produced by the marine demosponges of Verongiida order in specialized spherulocyte cells and has been shown to have promising anti-viral effects [29,55,56,57]. These cells are sensitive to environmental stimuli and release bromotyrosine in response to damage. Muzychka et al. have recently isolated and purified a bromotyrosine derivative, 3,5-dibromoquinolacetic acid and found to have anti-bacterial capabilities [29]. Bromotyrosines have been shown to also have antiviral activity against HIV-1 retrovirus by inhibiting its entry into host cells as well as its replication inside the cell. Bromotyrosines are promising compounds to investigate for SARS-CoV-2 infection blockade. More research is needed to understand if bromotyrosines can target conserved residues on the spike protein, and whether they can inhibit viral proliferation once inside the host cell. Both bacterial and COVID-like viruses contain a lipid wall and cell adhesive proteins on their surface. While current drug development aims at targeting their surface proteins, their constant mutation significantly limits drug efficacy. The lipid wall or capsule is conserved in structure and does not mutate as frequently; this makes it a promising drug target. We suggest that bromotyrosines act through lipid surface of both bacterial and viruses protecting the sponges from such pathogens [29]. If so, bromotyrosines should be effective against any kind of viruses, including omicron.
Promisingly, a recent study by Bharathi et al. identified natural bioactive compounds isolated from various marine seaweed species, as inhibitors of the omicron variant [58]. Molecular docking analysis showed that two compounds, caffeic acid hexoside and phloretin isolated from Sargassum wightii were able to inhibit important residues necessary for ACE-2 interaction (ASN417, SER496, TYR501, and HIS505) [58]. This is significant as these 4 residues in the RBD of the omicron spike protein were found to most strongly bind ACE2 receptor. Phloretin has also been shown to activate transcription factors that can upregulate the expression of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase [59]. These enzymes play an important role in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients suggesting it has promising effects. Furthermore, several other compounds including cholestan-3-ol and 2-methylene from the Corallina officinalis were able to inhibit the novel mutated residues, LEU452 and ALA484 on the RBD of the spike protein [58]. This inhibition was found to be through hydrogen bonding and alkyl interactions. All together, it is clear that several seaweed compounds as well as compounds isolated from other marine organisms may be effective against omicron infection, however future experimental studies are warranted to support these findings (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of marine compounds and their mechanisms of action for potential omicron treatment.
Table 1.
Summary of marine compounds and their mechanisms of action for potential omicron treatment.
| Marine Compound | Sources | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Inorganic polyphosphate (polyP) [26,27] | Marine bacteria and sponges |
|
| Lambda-carrageenan [24,28] | Marine algae |
|
| Phycocyanobilins (PCB) [50,51] | Cyanobacteria and algae rhodophytes |
|
| Sulfated polysaccharides [52,53,54] | Cyanobacteria, sea cucumber, microalgae |
|
| Bromotyrosines [29,38,56,57] | Marine sponges |
|
| Caffeic acid hexoside, phloretin, cholestan-3-ol, 2-methylene [58,59] | Marine seaweed |
|
4. Current State and Challenges Faced Ahead
The development of drugs from marine resources is not without challenges. Although their use in small scale is environmentally friendly, large-scale production and the need for continuous supply of resources may harm the ecosystem [60]. Further, majority of research using marine resources for COVID-19 and other viral studies have been conducted in vitro, but their lacks in vivo efficacy and safety studies [60]. Although these may be ongoing, they are time consuming, which may limit their applications to current SARS-CoV-2 variants. Despite these challenges, marine resources remain a favorable area to investigate. Targeting conserved enzymes like RdRp and Mpro as well as conserved regions on the RBD of the viral spike protein are ways in which omicron and future variants can be tackled. Furthermore, combining anti-viral marine compounds with anti-oxidant or anti-inflammatory compounds may have promising synergistic effects in mitigating infection. The ability of each marine compound to inhibit and interfere with several stages of the viral life cycle is what makes them more advantageous over current drugs like remdesivir. For example, polyP is multifaceted in that it is not only able to prevent viral entry by binding to the spike protein but also downregulates ACE-2 by inducing its degradation. In the case that the viral load is high, or novel viral strains still enter the cell, polyP interferes with transcription and translation and stimulates the innate immune response [26,27,46]. Thus, in combination with other anti-viral agents, like remdesivir, polyP may be a promising pharmaceutical compound for further development. Thus, its investigation in vivo and in combination with other compounds is warranted for its development not only against omicron, but others strains of SARS-CoV-2. Notably, discovering anti-viral agents that are more potent and have less side effects than current marketed drugs is necessary. In a recent study, ElNaggar et al. found that the compound Aurasperone A, isolated from the marine fungus Aspergillus niger had greater potency against SARS-CoV-2 (IC50 = 12.25 µM) compared to remdesivir (IC50 = 10.11 µM) [61]. The compound was not only found to potently bind to and inhibit RdRp and Mpro, through hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions, but had a lower cytotoxicity index compared to remdesivir [61]. This suggests that marine resources have significant potential and should be further investigated for omicron and future variants.
There are several challenges faced when assessing omicron’s severity. First, omicron infection in South Africa has been reported to be mild, however, the population is high in young individuals in which many have been previously infected [62]. In addition, studies and reports are limited by small sample sizes and current omicron infections with limits the generalizability of data generated. To add, although several mutations in omicron have been identified and characterized, there remain some mutations of unknown effect, limiting the ability to generate effective drugs against the variant [18]. Understanding the link between the mutations and the clinical manifestations is significant in understanding infectivity and disease severity. Several confounding factors at the level of the patient and local population such as double dose vaccinations, booster shots, and age distribution may impact data on disease transmissibility and severity of omicron [62]. One study by Chen et al. conducted a quantitative analysis and found that the omicron variant might be ten times more contagious than the original strain [63]. Omicron was found to be about two times more infectious than the delta variant, and also twice as likely to escape vaccine immunity compared to the delta variant [63]. The mean neutralization ability of omicron decreased by more than 8-fold compared to the reference strain in patient samples that were previously infected with the original strain of SARS-CoV-2. Despite these findings, it is likely that an individual with a cocktail of different antibodies is more protected against the virus than the unvaccinated.
Promisingly, several studies have shown that booster immunizations will improve the host immune response against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant. Gruell et al. found that although double dose vaccinated individuals were not protected against omicron, the booster vaccine increased antibody neutralizing activity by 100-fold [64]. Furthermore, nine monoclonal antibodies currently used to treat COVID-19, such as imdevimab and casirivimab were tested for their neutralizing ability against omicron. However, only 2 of the 9 antibodies were found to be effective, limiting treatment for omicron infected patients [64]. Cameroni et al. found that monoclonal antibodies against conserved SARS-CoV-2 epitopes on omicron, retained virus neutralizing ability, suggesting that targeting conserved regions may provide protection against various newly evolving strains [65]. Like findings by Gruell et. al, Garcia-Beltran et al. found that booster vaccines enhanced the antibody responses against omicron variant by 19-fold, further highlighting the importance of booster vaccines [66]. Notably, it is difficult to characterize the true impact of the mutations in omicron on current vaccines. This is because different types of vaccines such as DNA/RNA or protein-based vaccines may result in different immune responses in the same individual. In addition, different people depending on differences in demographics like race and age or existing medical conditions may produce different antibodies against the same vaccines. Whether an individual with existing immunity is to develop an infection, and what the characteristics of that infection depend on the viral variant itself, as well as the host’s immune system.
More recent studies have shown that the omicron variant is less severe than previous strains with about a 15–80% decreased risk of hospital admission [67]. However, the emergence of other, potentially more infectious variants with their own characteristics, is expected. Thus, the rapid development of drugs and more effective vaccinations to protect vulnerable populations remains warranted.
5. Concluding Remarks
Although a significant amount of knowledge has been gained on how the omicron variant differs from other variants, there remains much unknown. The concern does not only stand with omicron but the emergence of other strains as well. The development of natural compounds from marine resources proves advantageous against the evolving SARS-CoV-2 variants due to their multifaceted mechanisms of action and their promising in vitro results. Developing compounds that target RdRp and Mpro as well as conserved residues in the RBD important for binding the ACE-2 receptor is where the focus of drug development should be. It is evident that booster vaccines are beneficial to combatting the omicron infection, although few studies have shown evidence that the evolving virus may escape the host immune response. Much remains unknown, but for now, individuals should comply with COVID-19 social restrictions to minimize risks for the spread of infection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R.; validation, A.R. and H.E.; resources, A.R. and S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R. and S.G.; writing—review and editing, A.R., S.G. and H.E.; visualization, A.R. and S.G.; supervision, A.R.; project administration, A.R.; funding acquisition, A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, X.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and Immunotherapeutics. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talevi, D.; Socci, V.; Carai, M.; Carnaghi, G.; Faleri, S.; Trebbi, E.; di Bernardo, A.; Capelli, F.; Pacitti, F. Mental Health Outcomes of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Riv. Psichiatr. 2020, 55, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, W.; Ye, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Pennington, M. Economic Burden of COVID-19, China, January–March, 2020: A Cost-of-Illness Study. Bull. World Health Organ. 2021, 99, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberndorfer, M.; Dorner, T.E.; Brunnmayr, M.; Berger, K.; Dugandzic, B.; Bach, M. Health-related and Socio-economic Burden of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Vienna. Health Soc. Care Commun. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Alam, A.S.M.R.U.; Islam, I.; Hoque, M.N.; Akter, S.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sultana, M.; Hossain, M.A. Evolutionary Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Consequences. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2177–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanetti, M.; Benedetti, F.; Campisi, G.; Ciccozzi, A.; Fabris, S.; Ceccarelli, G.; Tambone, V.; Caruso, A.; Angeletti, S.; Zella, D.; et al. Evolution Patterns of SARS-CoV-2: Snapshot on Its Genome Variants. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 538, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Woo, H.G. Omicron: A Heavily Mutated SARS-CoV-2 Variant Exhibits Stronger Binding to ACE2 and Potently Escape Approved COVID-19 Therapeutic Antibodies. Genomics 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, A.N.; Kannan, S.R.; Woods, L.T.; Weisman, G.A.; Quinn, T.P.; Lorson, C.L.; Sönnerborg, A.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Singh, K. Evolution, Correlation, Structural Impact and Dynamics of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 3799–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, D. Alpha, Beta, Delta, Gamma: What’s Important to Know about SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern? CMAJ 2021, 193, E1059–E1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cele, S.; Karim, F.; Lustig, G.; San, J.E.; Hermanus, T.; Tegally, H.; Snyman, J.; Moyo-Gwete, T.; Wilkinson, E.; Bernstein, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Evolved during Advanced HIV Disease Immunosuppression Has Beta-like Escape of Vaccine and Delta Infection Elicited Immunity. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Hu, F.; Lan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhan, C.; Shi, J.; Deng, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhong, S.; et al. Transmission, Viral Kinetics and Clinical Characteristics of the Emergent SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC in Guangzhou, China. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 40, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kampen, J.J.A.; van de Vijver, D.A.M.C.; Fraaij, P.L.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lamers, M.M.; Okba, N.; van den Akker, J.P.C.; Endeman, H.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Cornelissen, J.J.; et al. Duration and Key Determinants of Infectious Virus Shedding in Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19). Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farinholt, T.; Doddapaneni, H.; Qin, X.; Menon, V.; Meng, Q.; Metcalf, G.; Chao, H.; Gingras, M.-C.; Avadhanula, V.; Farinholt, P.; et al. Transmission Event of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant Reveals Multiple Vaccine Breakthrough Infections. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.1.529)-sars-cov-2-variant-of-concern (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Dyer, O. COVID-19: South Africa’s Surge in Cases Deepens Alarm over Omicron Variant. BMJ 2021, 375, n3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, G. Sequence Analysis of the Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variant Omicron in South Africa. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 94, 1728–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahase, E. COVID-19: Do Vaccines Work against Omicron—and Other Questions Answered. BMJ 2021, 375, n3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingraham, N.E.; Ingbar, D.H. The Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2: Understanding the Known and Living with Unknowns. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.S.A.; Karim, Q.A. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Variant: A New Chapter in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.R.; Spratt, A.N.; Sharma, K.; Chand, H.S.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Singh, K. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Variant: Unique Features and Their Impact on Pre-Existing Antibodies. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 126, 102779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. B.1.1.529 Escapes the Majority of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies of Diverse Epitopes. Immunology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Thambiraja, T.S.; Karuppanan, K.; Subramaniam, G. Omicron and Delta Variant of SARS-CoV-2: A Comparative Computational Study of Spike Protein. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevik, M.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Iwasaki, A.; Openshaw, P. COVID-19 Vaccines: Keeping Pace with SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Cell 2021, 184, 5077–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geahchan, S.; Ehrlich, H.; Rahman, M.A. The Anti-Viral Applications of Marine Resources for COVID-19 Treatment: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.T.; Ali, A.; Wang, Q.; Irfan, M.; Khan, A.; Zeb, M.T.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Chinnasamy, S.; Wei, D.-Q. Marine Natural Compounds as Potents Inhibitors against the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2—A Molecular Dynamic Study. J. Biomol. Struct. 2021, 39, 3627–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrucci, V.; Kong, D.-Y.; Asadzadeh, F.; Marrone, L.; Boccia, A.; Siciliano, R.; Criscuolo, G.; Anastasio, C.; Quarantelli, F.; Comegna, M.; et al. Long-Chain Polyphosphates Impair SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Replication. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eabe5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufurth, M.; Wang, X.; Tolba, E.; Lieberwirth, I.; Wang, S.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. The Inorganic Polymer, Polyphosphate, Blocks Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to ACE2 Receptor at Physiological Concentrations. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182, 114215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, M.K.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, H.-R.; Kim, M. Antiviral Activity of Lambda-Carrageenan against Influenza Viruses and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzychka, L.; Voronkina, A.; Kovalchuk, V.; Smolii, O.B.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Ehrlich, I.; Ehrlich, H. Marine Biomimetics: Bromotyrosines Loaded Chitinous Skeleton as Source of Antibacterial Agents. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golcuk, M.; Yildiz, A.; Gur, M. The Omicron Variant Increases the Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein with ACE2. Immunology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Ansari, S.; Paweska, J.T.; Maurya, V.K.; Tripathi, A.K.; Abdel-Moneim, A.S. Characterization of the Novel SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant of Concern and Its Global Perspective. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 94, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, B.; Yang, Q.; Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, T.; Zhang, H.; He, X. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Strain Exhibits Potent Capabilities for Immune Evasion and Viral Entrance. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatakrishnan, A.; Anand, P.; Lenehan, P.; Suratekar, R.; Raghunathan, B.; Niesen, M.J.M.; Soundararajan, V. Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2 Harbors a Unique Insertion Mutation of Putative Viral or Human Genomic Origin. Open Sci. Framew. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Lung, D.C.; Wong, E.Y.M.; Aw-Yong, K.L.; Wong, A.C.P.; Luk, H.K.H.; Li, K.S.M.; Fung, J.; Chan, T.T.Y.; Tang, J.Y.M.; et al. Molecular Evolution of Human Coronavirus 229E in Hong Kong and a Fatal COVID-19 Case Involving Coinfection with a Novel Human Coronavirus 229E Genogroup. MSphere 2021, 6, e00819–e00820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, A.; Widera, M.; Grikscheit, K.; Toptan, T.; Schenk, B.; Pallas, C.; Metzler, M.; Kohmer, N.; Hoehl, S.; Helfritz, F.A.; et al. Reduced Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant by Vaccine Sera and Monoclonal Antibodies. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejnirattisai, W.; Shaw, R. Reduced Neutralisation of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 Variant by Post-Immunisation Serum. Lancet 2021, 399, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rutte, E.A.; Shattock, A.J.; Chitnis, N.; Kelly, S.L.; Penny, M.A. Assessing Impact of Omicron on SARS-CoV-2 Dynamics and Public Health Burden. Public Glob. Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Bertoglio, F.; Steinke, S.; Heine, P.A.; Ynga-Durand, M.A.; Zuo, F.; Du, L.; Korn, J.; Milošević, M.; Wenzel, E.V.; et al. Human Serum from SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinated and COVID-19 Patients Shows Reduced Binding to the RBD of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratev, F. The High Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant Is Not Only Due to Its HACE2 Binding: A Free Energy of Perturbation Study. Biochemistry 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Saleem, M.; Yaseen, H.S.; Yehya, A.H.; Saadullah, M.; Zubair, H.M.; Oon, C.E.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Khalid, S.H.; Khan, I.U.; et al. Potential Role of Marine Species-Derived Bioactive Agents in the Management of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Future Microbiol. 2021, 16, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A.; Abdel-Aziz, T.M.; Elhady, S.S.; Darwish, K.M.; Hassan, A.H.E. Investigating the Structure–Activity Relationship of Marine Natural Polyketides as Promising SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 31339–31363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Chauhan, N.; Kuddus, M. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Marine-Derived Bioactive Compounds against COVID-19. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52798–52809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lira, S.P.D.; Seleghim, M.H.R.; Williams, D.E.; Marion, F.; Hamill, P.; Jean, F.; Andersen, R.J.; Hajdu, E.; Berlinck, R.G.S. A SARS-Coronovirus 3CL Protease Inhibitor Isolated from the Marine Sponge Axinella Cf. Corrugata: Structure Elucidation and Synthesis. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, A.; Helm, J.; Ehrlich, H.; Pantovic, S.; Bornstein, S.R.; Bechmann, N. Anti-Tumor Activity vs. Normal Cell Toxicity: Therapeutic Potential of the Bromotyrosines Aerothionin and Homoaerothionin In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianingsih, F. In Silico Analysis of Sponges Compound Against Mpro COVID-19: A Review. Proc. Int. Conf. Eng. 2021, 4, 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bechmann, N.; Ehrlich, H.; Eisenhofer, G.; Ehrlich, A.; Meschke, S.; Ziegler, C.; Bornstein, S. Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Voronkina, A.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Djurović, M.; Kovalchuk, V.; Tsurkan, M.; Martinovic, R.; et al. Marine Biomaterials: Biomimetic and Pharmacological Potential of Cultivated Aplysina Aerophoba Marine Demosponge. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Bazhenov, V.; Meschke, S.; Bürger, M.; Ehrlich, A.; Petovic, S.; Durovic, M. Marine Invertebrates of Boka Kotorska Bay Unique Sources for Bioinspired Materials Science. In The Boka Kotorska Bay Environment; Joksimović, A., Djurović, M., Semenov, A.V., Zonn, I.S., Kostianoy, A.G., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 54, pp. 313–334. ISBN 978-3-319-51613-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hamoda, A.M.; Fayed, B.; Ashmawy, N.S.; El-Shorbagi, A.-N.A.; Hamdy, R.; Soliman, S.S.M. Marine Sponge Is a Promising Natural Source of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Scaffold. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 666664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendyala, B.; Patras, A. In Silico Screening of Food Bioactive Compounds to Predict Potential Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro) and RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp). Chemistry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.; Vernès, L.; Cadoret, J.-P. Docking and in Silico Toxicity Assessment of Arthrospira Compounds as Potential Antiviral Agents against SARS-CoV-2. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 1579–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Peng, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Wen, C.; Ai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B. Inhibitory Activities of Marine Sulfated Polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7415–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassauer, A.; Weinmuellner, R.; Meier, C.; Pretsch, A.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E.; Unger, H. Iota-Carrageenan Is a Potent Inhibitor of Rhinovirus Infection. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morokutti-Kurz, M.; Fröba, M.; Graf, P.; Große, M.; Grassauer, A.; Auth, J.; Schubert, U.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E. Iota-Carrageenan Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 and Inhibits Viral Replication in Vitro. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0237480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.; Binnewerg, B.; Voronkina, A.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Kovalchuk, V.; Tsurkan, M.; Martinovic, R.; Bechmann, N.; et al. Naturally Prefabricated Marine Biomaterials: Isolation and Applications of Flat Chitinous 3D Scaffolds from Ianthella Labyrinthus (Demospongiae: Verongiida). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromont, J.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Galli, R.; Meissner, H.; Erpenbeck, D.; Vacelet, J.; Diaz, C.; Tsurkan, M.V.; Petrenko, I.; Youssef, D.T.A.; et al. New Family and Genus of a Dendrilla-like Sponge with Characters of Verongiida. Part II. Discovery of Chitin in the Skeleton of Ernstilla Lacunosa. Zool. Anz. 2019, 280, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, V.; Voronkina, A.; Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.V.; Bechmann, N.; Petrenko, I.; Fursov, A.; et al. Naturally Drug-Loaded Chitin: Isolation and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, M.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Thangaleela, S.; Chaiyasut, C. In Silico Screening of Bioactive Compounds of Representative Seaweeds to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 ACE2-Bound Omicron B.1.1.529 Spike Protein Trimer. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzad, S.; Sureda, A.; Barreca, D.; Nabavi, S.F.; Rastrelli, L.; Nabavi, S.M. Health Effects of Phloretin: From Chemistry to Medicine. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine Natural Products: A New Wave of Drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElNaggar, M.H.; Abdelwahab, G.M.; Kutkat, O.; GabAllah, M.; Ali, M.A.; El-Metwally, M.E.A.; Sayed, A.M.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Khalil, A.T. Aurasperone A Inhibits SARS CoV-2 In Vitro: An Integrated In Vitro and In Silico Study. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, E.; Ledford, H. How Bad Is Omicron? What Scientists Know so Far. Nature 2021, 600, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Gilby, N.B.; Wei, G.-W. Omicron Variant (B.1.1.529): Infectivity, Vaccine Breakthrough, and Antibody Resistance. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruell, H.; Vanshylla, K.; Tober-Lau, P.; Hillus, D.; Schommers, P.; Lehmann, C.; Kurth, F.; Sander, L.E.; Klein, F. MRNA Booster Immunization Elicits Potent Neutralizing Serum Activity against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameroni, E.; Saliba, C.; Bowen, J.E.; Rosen, L.E.; Culap, K.; Pinto, D.; De Marco, A.; Zepeda, S.K.; di Iulio, J.; Zatta, F.; et al. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Antigenic Shift. Nature 2022, 602, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; St. Denis, K.J.; Hoelzemer, A.; Lam, E.C.; Nitido, A.D.; Sheehan, M.L.; Berrios, C.; Ofoman, O.; Chang, C.C.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. MRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine Boosters Induce Neutralizing Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Cell 2022, 185, 457–466.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, B. COVID-19: Early Studies Give Hope Omicron Is Milder than Other Variants. BMJ 2021, 375, n3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).