Expression and Purification of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Protein ORF7a and Functional Analysis of Its Role in Up-Regulating Cytokine Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
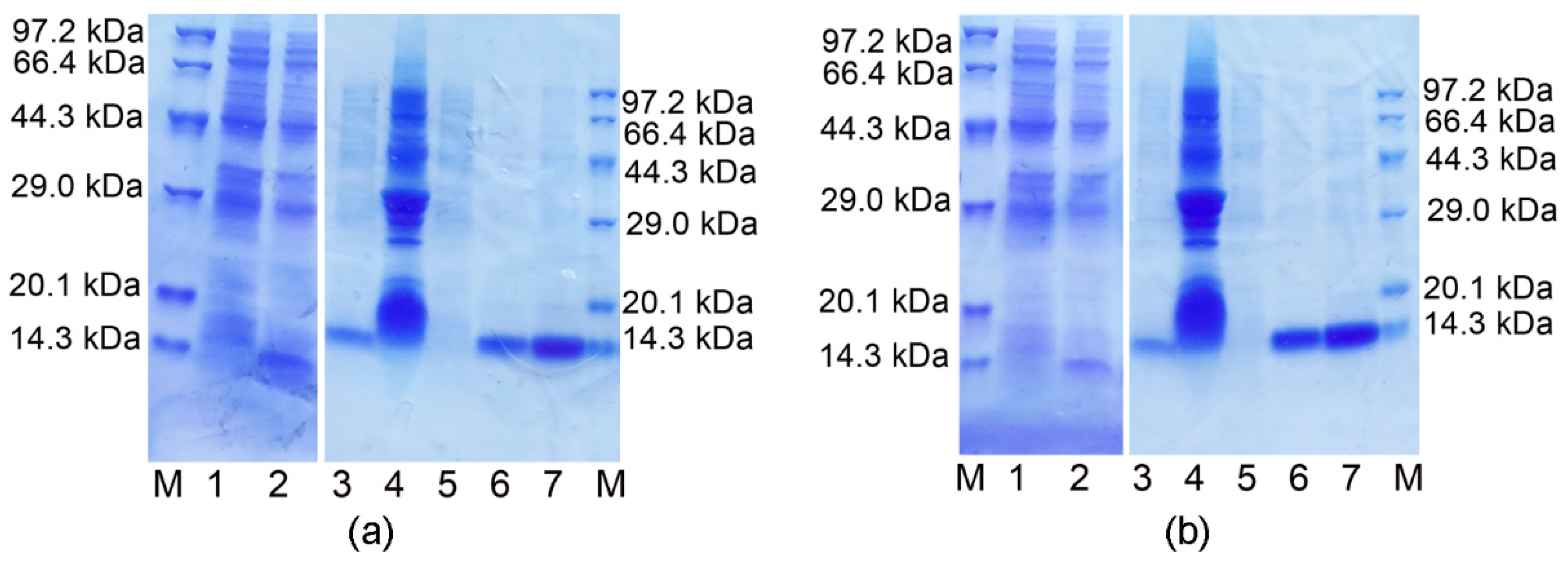
2.2.1. Expression and Purification of the Ectodomains of ORF7a-1 and ORF7a-2
2.2.2. Immunoblotting
2.2.3. Cell Experiments
2.2.4. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.2.5. ELISA Experiment
2.2.6. Amino Acid and Structural Alignments of ORF7a-1 and ORF7a-2
3. Results
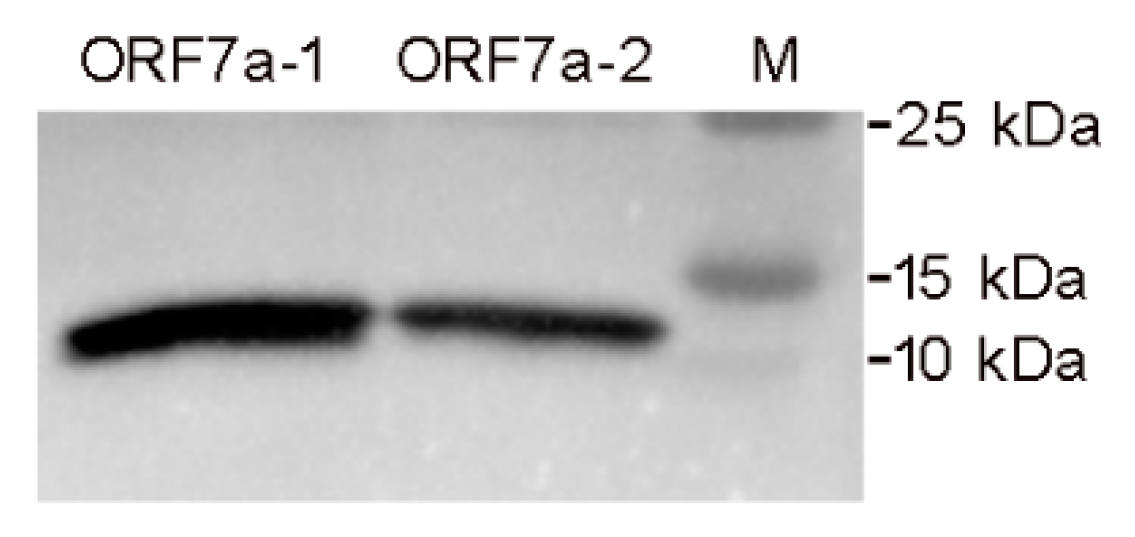
3.1. Expression, Purification and Identification of the Ectodomains of ORF7a-1 and ORF7a-2
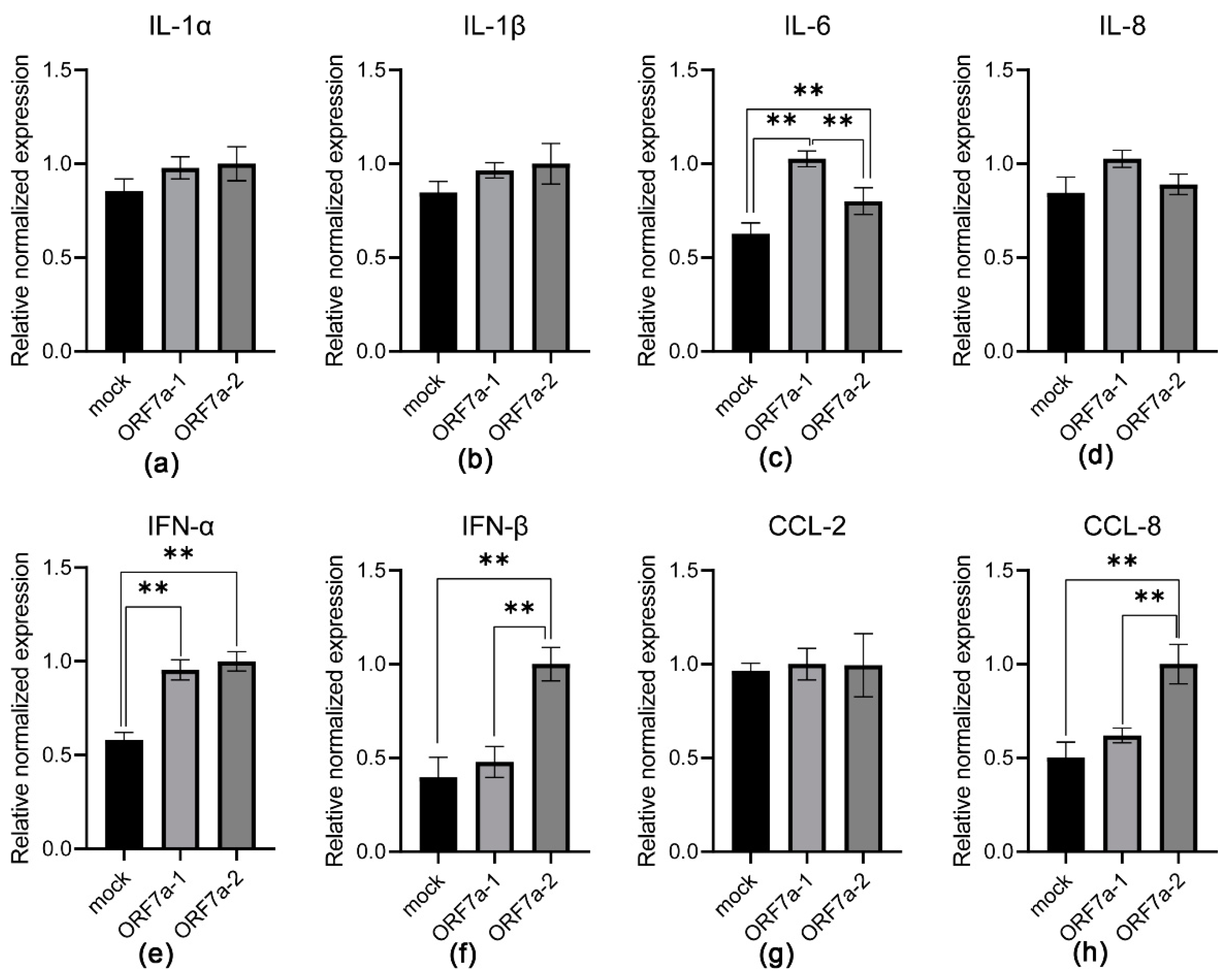
3.2. Induction of Proinflammatory Cytokine Transcription Mediated by Recombinant ORF7a-1 and ORF7a-2
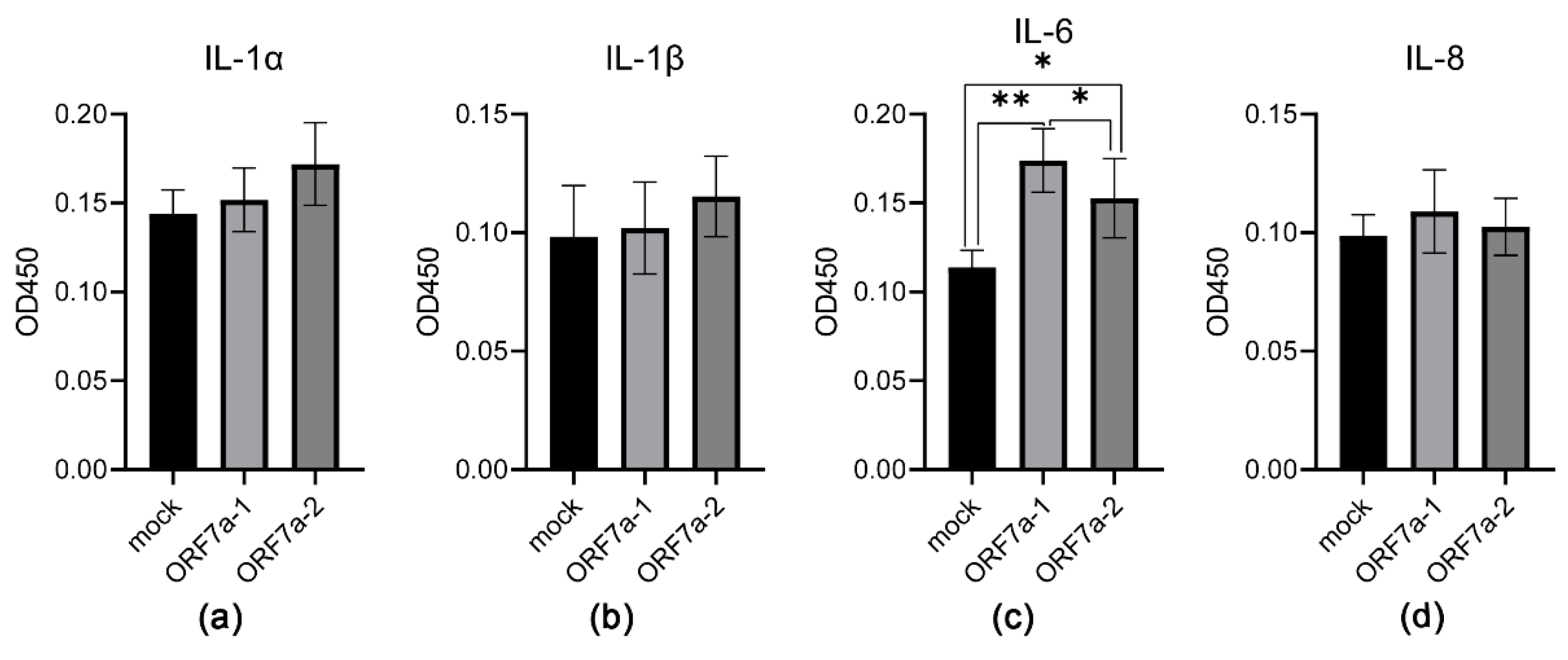
3.3. Induction of Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression Mediated by Recombinant ORF7a-1 and ORF7a-2
3.4. Amino Acid and Structural Comparisons of Ectodomains of ORF7a-1 and ORF7a-2
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meo, S.A.; Alhowikan, A.M.; Al-Khlaiwi, T.; Meo, I.M.; Halepoto, D.M.; Iqbal, M.; Usmani, A.M.; Hajjar, W.; Ahmed, N. Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: Prevalence, biological and clinical characteristics comparison with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2012–2019. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Feng, M.; Wen, Z.; He, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhang, M. Comparison of the characteristics of cytokine storm and immune response induced by SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 infections. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 5475–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisoncik, J.R.; Korth, M.J.; Simmons, C.P.; Farrar, J.; Martin, T.R.; Katze, M.G. Into the eye of the cytokine storm. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahallawi, W.H.; Khabour, O.F.; Zhang, Q.; Makhdoum, H.M.; Suliman, B.A. MERS-CoV infection in humans is associated with a pro-inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cytokine profile. Cytokine 2018, 104, 8–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yang, Z.Q. The cytokine storm of severe influenza and development of immunomodulatory therapy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Rothman, A.L.; Kurane, I.; Montoya, J.M.; Nolte, K.B.; Norman, J.E.; Waite, D.C.; Koster, F.T.; Ennis, F.A. High levels of cytokine-producing cells in the lung tissues of patients with fatal hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartee, E.; McFadden, G. Cytokine synergy: An underappreciated contributor to innate anti-viral immunity. Cytokine 2013, 63, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojyo, S.; Uchida, M.; Tanaka, K.; Hasebe, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Murakami, M.; Hirano, T. How COVID-19 induces cytokine storm with high mortality. Inflamm. Regen. 2020, 40, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Fatima, R.; Assaly, R. Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.M.; de Oliveira, M.H.S.; Benoit, S.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, C.; Han, J.; Yau, L.; Reiss, W.G.; Kramer, B.; Neidhart, J.D.; Criner, G.J.; Kaplan-Lewis, E.; Baden, R.; Pandit, L.; et al. Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with covid-19 pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.; Huang, C.; Makino, S. SARS coronavirus accessory proteins. Virus Res. 2008, 133, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.X.; Fung, T.S.; Chong, K.K.; Shukla, A.; Hilgenfeld, R. Accessory proteins of SARS-CoV and other coronaviruses. Antivir. Res. 2014, 109, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Zhong, Q.; Gao, G.F. Overview of SARS-CoV-2 genome-encoded proteins. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohaim, M.A.; El Naggar, R.F.; Clayton, E.; Munir, M. Structural and functional insights into non-structural proteins of coronaviruses. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, N.; Zaldívar-López, S.; Garrido, J.J.; Montoya, M. SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins in viral pathogenesis: Knowns and unknowns. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 708264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Chaudhary, J.K.; Jain, N.; Chaudhary, P.K.; Khanra, S.; Dhamija, P.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Handu, S. Role of structural and non-structural proteins and therapeutic targets of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzawa, N.; Nishigaki, K.; Hayashi, T.; Ishii, Y.; Furukawa, S.; Niiro, A.; Yasui, F.; Kohara, M.; Morita, K.; Matsushima, K.; et al. Augmentation of chemokine production by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3a/X1 and 7a/X4 proteins through NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6807–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.M.; Wang, L.; Yoo, D. Activation of NF-κB and induction of proinflammatory cytokine expressions mediated by ORF7a protein of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z.; Su, L.; Kang, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; He, S.; Rong, X.; et al. Structural insight reveals SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a as an immunomodulating factor for human CD14+ monocytes. iScience 2021, 24, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giard, D.J.; Aaronson, S.A.; Todaro, G.J.; Arnstein, P.; Kersey, J.H.; Dosik, H.; Parks, W.P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: Establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1973, 51, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studier, F.W. Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 41, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, T.O.; Ascoli, C.A. Immunometric double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2017, 2017, pdb.prot093724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundt, E.C.; Yu, L.; Park, E.; Lenardo, M.J.; Xu, X.N. Molecular determinants for subcellular localization of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus open reading frame 3b protein. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6631–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, Y.; Kimura, I.; Uriu, K.; Fukushi, M.; Irie, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Sauter, D.; Gifford, R.J. USFQ-COVID19 Consortium; Nakagawa, S.; Sato, K. SARS-CoV-2 ORF3b is a potent interferon antagonist whose activity is increased by a naturally occurring elongation variant. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecky-Bromberg, S.A.; Martínez-Sobrido, L.; Frieman, M.; Baric, R.A.; Palese, P. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus open reading frame (ORF) 3b, ORF 6, and nucleocapsid proteins function as interferon antagonists. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Liao, C.H.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.J.; Luo, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ge, X.Y. The ORF6, ORF8 and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 inhibit type I interferon signaling pathway. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Ito, N.; Tseng, C.T.; Makino, S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 7a accessory protein is a viral structural protein. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7287–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänel, K.; Stangler, T.; Stoldt, M.; Willbold, D. Solution structure of the X4 protein coded by the SARS related coronavirus reveals an immunoglobulin like fold and suggests a binding activity to integrin I domains. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänel, K.; Willbold, D. SARS-CoV accessory protein 7a directly interacts with human LFA-1. Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamudeen, Z.A.; Xu, E.R.; Karthik, V.; Halawa, M.; Arkill, K.P.; Jackson, A.M.; Bates, D.O.; Emsley, J. Structural assessment of SARS-CoV2 accessory protein ORF7a predicts LFA-1 and Mac-1 binding potential. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20203837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongaro, A.; Oselladore, E.; Memo, M.; Ribaud, G.; Gianoncelli, A. Insight into the LFA-1/SARS-CoV-2 Orf7a complex by protein-protein docking, molecular dynamics, and MM-GBSA calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 2780–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Schneider, T.; Leong, M.; Aravind, L.; Zhang, D. Novel immunoglobulin domain proteins provide insights into evolution and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2-related viruses. mBio 2020, 11, e00760-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, T.G.; Buffalo, C.Z.; Hooy, R.M.; Allaire, M.; Ren, X.; Hurley, J.H. Structure of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8, a rapidly evolving immune evasion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021785118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xia, T.; Shin, W.J.; Yu, K.M.; Jung, W.; Herrmann, A.; Foo, S.S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Viral mimicry of interleukin-17A by SARS-CoV-2 ORF8. mBio 2022, 13, e0040222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Arduini, A.; Bourassa, C.; Medjahed, H.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Richard, J.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liang, C.; Finzi, A. SARS-CoV-2 accessory protein ORF8 decreases antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Viruses 2022, 14, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Á.; Pongor, S.; Győrffy, B. Different mutations in SARS-CoV-2 associate with severe and mild outcome. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemudryi, A.; Nemudraia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Nichols, J.; Snyder, D.T.; Hedges, J.F.; Cicha, C.; Lee, H.; Vanderwood, K.K.; Bimczok, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance identifies naturally occurring truncation of ORF7a that limits immune suppression. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addetia, A.; Xie, H.; Roychoudhury, P.; Shrestha, L.; Loprieno, M.; Huang, M.L.; Jerome, K.R.; Greninger, A.L. Identification of multiple large deletions in ORF7a resulting in in-frame gene fusions in clinical SARS-CoV-2 isolates. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Zheng, Z.; Han, Z. Expression and Purification of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Protein ORF7a and Functional Analysis of Its Role in Up-Regulating Cytokine Production. COVID 2022, 2, 1449-1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2100104
Chen D, Zheng Z, Han Z. Expression and Purification of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Protein ORF7a and Functional Analysis of Its Role in Up-Regulating Cytokine Production. COVID. 2022; 2(10):1449-1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2100104
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dan, Zhenhua Zheng, and Zhenggang Han. 2022. "Expression and Purification of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Protein ORF7a and Functional Analysis of Its Role in Up-Regulating Cytokine Production" COVID 2, no. 10: 1449-1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2100104
APA StyleChen, D., Zheng, Z., & Han, Z. (2022). Expression and Purification of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Protein ORF7a and Functional Analysis of Its Role in Up-Regulating Cytokine Production. COVID, 2(10), 1449-1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2100104







