Post-COVID-19 Condition and Health Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
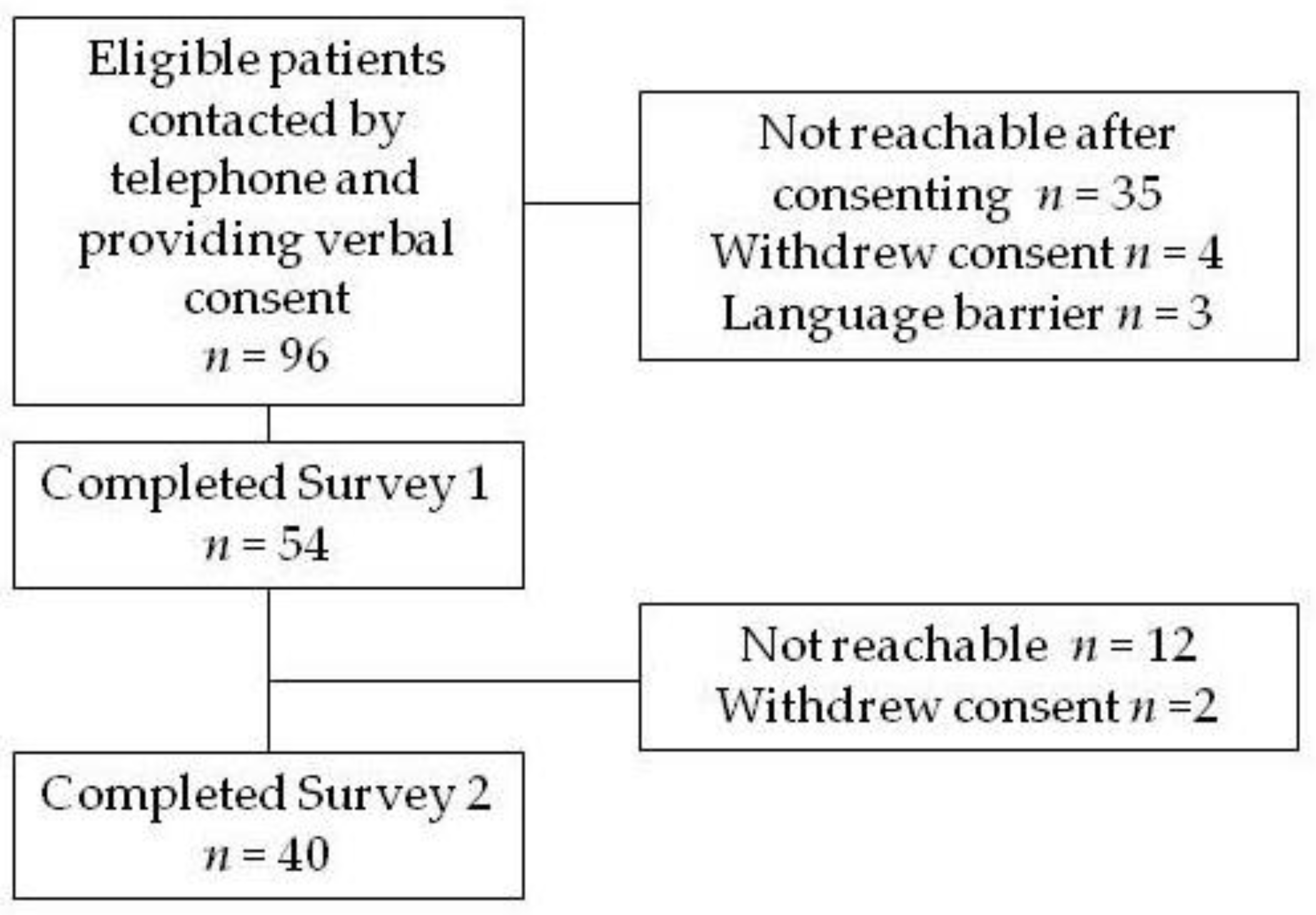
2. Methods
- The modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea questionnaire (0–4 scale) [7]. We considered an mMRC rating of 3 or 4 to indicate severe dyspnea.
- The Patient Health Questionnaire for Anxiety and Depression (PHQ-4). This screening instrument has 4 questions, 2 focusing on anxiety and 2 on depression symptoms, plus a composite score [8]. Severity scores of 3 or greater in either anxiety or depression subscales or a PHQ-4 composite score ≥ 6 were considered elevated.
- The Cognitive Change Questionnaire (CC8) [9] is a screening tool with 8 questions rating cognitive impairment. A score ≥ 2 was used as a marker for cognitive impairment.
- The Short Fatigue Questionnaire (SFQ) [10] rates fatigue using 4 questions, each rated on a 1–7-point scale. This is a visual scale with extremes and middle anchored by descriptors. Scores ≥ 18 were used to represent high levels of fatigue.
- The Medical Outcomes Study Short-Form General Health Survey (SF-20) [11]. This health status instrument has 20 questions summarized in 6 subscales: physical functioning, role functioning, social functioning, mental health, health perceptions, and pain. Scores are scaled to range from 0 (worst) to 100 (best). Since there are no thresholds indicating abnormality with this instrument, we included for comparison data from the closest cohort of individuals we could find in the medical literature [12].
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goërtz, Y.M.J.; Van Herck, M.; Delbressine, J.M.; Vaes, A.W.; Meys, R.; Machado, F.V.C.; Houben-Wilke, S.; Burtin, C.; Posthuma, R.; Franssen, F.M.E.; et al. Persistent symptoms 3 months after a SARS-CoV-2 infection: The post-COVID-19 syndrome? ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00542–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, J.K.; Franko, N.M.; McCulloch, D.J.; McDonald, D.; Magedson, A.; Wolf, C.R.; Chu, H.Y. Sequelae in Adults at 6 Months After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e210830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. More than 50 long-term effects of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V. Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition. A Clinical Case Definition of Post-COVID-19 Condition by a Delphi Consensus; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Guyatt, G.H. A taxonomy of health status instruments. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 22, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt, G.H. Measurement of health-related quality of life in heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 22, 185A–191A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, D.A.; Wells, C.K. Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest 1988, 93, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B.; Lowe, B. An ultra-brief screening scale for anxiety and depression: The PHQ-4. Psychosomatics 2009, 50, 613–621. [Google Scholar]
- Damin, A.E.; Nitrini, R.; Brucki, S.M.D. Cognitive Change Questionnaire as a method for cognitive impairment screening. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2015, 9, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Penson, A.; van Deuren, S.; Worm-Smeitink, M.; Bronkhorst, E.; Hoogen, F.H.V.D.; van Engelen, B.G.; Peters, M.; Bleijenberg, G.; Vercoulen, J.H.; Blijlevens, N.; et al. Short fatigue questionnaire: Screening for severe fatigue. J. Psychosom. Res. 2020, 137, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.L.; Hays, R.D.; Ware, J.E., Jr. The MOS short-form general health survey. Reliability and validity in a patient population. Med. Care 1988, 26, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, D.J.; Chapman, C.A.; Thomas, V.S.; Stadnyk, K.J.; Rockwood, K. Validity and reliability of the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-20 questionnaire as a measure of quality of life in elderly people living at home. Age Ageing 1999, 28, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.-M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and Validating the Charlson Comorbidity Index and Score for Risk Adjustment in Hospital Discharge Abstracts Using Data From 6 Countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, D.M.; Strange, J.E.; Gislason, G.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gerds, T.; Fosbøl, E.; Phelps, M.D. Charlson Comorbidity Index Score and Risk of Severe Outcome and Death in Danish COVID-19 Patients. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 2801–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.M.; Robinson, D.A.; Yang, L.; Williams, C.F.; Newman, L.M.; Breen, J.J.; Eisinger, R.W.; Schneider, J.S.; Adimora, A.A.; Erbelding, E.J. Toward Understanding COVID-19 Recovery: National Institutes of Health Workshop on Postacute COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center JHUCR. 2021. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/region/us/connecticut (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Bureau USC. QuickFacts, Hartford County, Connecticut. 2019. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/hartfordcountyconnecticut/PST045219 (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Connecticut COVID-19 Case Tracking. 202. Available online: https://public.tableau.com/app/profile/connecticut.state.data.center/viz/ConnecticutCOVID-19CaseTracking/CTdataCollaborativeCOVID-19 (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Karaca-Mandic, P.; Georgiou, A.; Sen, S. Assessment of COVID-19 Hospitalizations by Race/Ethnicity in 12 States. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.E.; Ashe, E.M.; Silverstein, M.; Hofman, M.; Lange, S.J.; Razzaghi, H.; Mishuris, R.G.; Davidoff, R.; Parker, E.M.; Penman-Aguilar, A.; et al. Race/Ethnicity, Underlying Medical Conditions, Homelessness, and Hospitalization Status of Adult Patients with COVID-19 at an Urban Safety-Net Medical Center—Boston, Massachusetts, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Davis, A.; Stanley, B.; Julious, S.; Ryan, D.; Jackson, D.J.; Halpin, D.M.; Hickman, K.; Pinnock, H.; Quint, J.K.; et al. Risk Predictors and Symptom Features of Long COVID Within a Broad Primary Care Patient Population Including Both Tested and Untested Patients. Pragmatic Obs. Res. 2021, 12, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Y.; Li, T.; Gong, F.H.; Zhang, J.S.; Li, X.K. Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life and Influencing Factors for COVID-19 Patients, a Follow-Up at One Month. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sar-van der Brugge, S.; Talman, S.; Winter, L.B.-D.; de Mol, M.; Hoefman, E.; van Etten, R.W.; De Backer, I.C. Pulmonary function and health-related quality of life after COVID-19 pneumonia. Respir. Med. 2021, 176, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, S.J. Long-Haul COVID-19: Putative Pathophysiology, Risk Factors, and Treatments. Preprints. 2020. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202012.0242/v1 (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- López-Sánchez, G.F.; López-Bueno, R.; Gil-Salmerón, A.; Zauder, R.; Skalska, M.; Jastrzębska, J.; Jastrzębski, Z.; Schuch, F.B.; Grabovac, I.; Tully, M.A.; et al. Comparison of physical activity levels in Spanish adults with chronic conditions before and during COVID-19 quarantine. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 31, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Que, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, L.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Meng, S.; et al. The impact of quarantine on mental health status among general population in China during the COVID-19 pandemic. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4813–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechili, E.A.; Saliaj, A.; Kamberi, F.; Girvalaki, C.; Peto, E.; Patelarou, A.E.; Bucaj, J.; Patelarou, E. Is the mental health of young students and their family members affected during the quarantine period? Evidence from the COVID-19 pandemic in Albania. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2021, 28, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.T.; Perrodeau, E.; Saldanha, J.; Pane, I.; Ravaud, P. Efficacy of COVID-19 vaccination on the symptoms of patients with long COVID: A target trial emulation using data from the ComPaRe e-Cohort in France. Lancet, 2021; Preprint. Posted 29 September. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worldometer. Daily New Deaths in Connecticut. 2021. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/usa/connecticut/ (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Antonelli, M.; Penfold, R.S.; Merino, J.; Sudre, C.H.; Molteni, E.; Berry, S.; Canas, L.S.; Graham, M.S.; Klaser, K.; Modat, M.; et al. Risk factors and disease profile of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID Symptom Study app: A prospective, community-based, nested, case-control study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nici, L.; ZuWallack, R.; Wouters, E.; Donner, C.F. On pulmonary rehabilitation and the flight of the bumblebee: The ATS/ERS Statement on Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nici, L.; ZuWallack, R. Integrated Care in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Rehabilitation. COPD 2018, 15, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynes, E.; Gerlis, C.; Singh, S.J. The demand for rehabilitation following COVID-19: A call to service providers. Physiotherapy 2021, 113, A1–A3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of Subjects | 40 |
| Age (years) (± SD) | 53 ± 8 |
| Obesity (clinical diagnosis) % | 70 |
| ED treatment only (%) | 13 |
| Female (%) | 50 |
| Race/Ethnicity | |
| Non-Hispanic Black (%) | 35.9 |
| Non-Hispanic White (%) | 35.9 |
| Non-Hispanic Other (%) | 7.7 |
| Hispanic ethnicity (%) | 20.5 |
| Low SES (%) | 40 |
| Acute severity score (± SD) | 3.2 ± 1.8 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index (± SD) | 1.0 ± 1.5 |
| ROS (baseline) (± SD) | 3.6 ± 2.3 |
| LOS of hospitalized patients (± SD) | 6.7 ± 5.6 |
| Severity Variable | % |
|---|---|
| Intravenous corticosteroid therapy for COVID-19 | 78 |
| Multilobar pneumonia | 73 |
| Peak oxygen requirement ≥4 L/min (or equivalent *) | 70 |
| Remdesivir treatment | 55 |
| Discharged home on supplemental oxygen | 35 |
| Non-invasive ventilation | 10 |
| Decompensated heart failure | 8 |
| Clinical cardiac ischemia | 8 |
| Shock | 3 |
| Endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation | 0 |
| Survey 1 | Survey 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| mMRC Dyspnea | 40 | 33 |
| SFQ Fatigue | 53 | 50 |
| PHQ-4 Anxiety | 33 | 18 |
| PHQ-4 Depression | 20 | 10 |
| PHQ-4 Total | 25 | 13 |
| CC8 Cognitive | 18 | 10 |
| Subscale | Comparison * | First Survey | Second Survey | Change | p. ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Functioning | 74 ± 23 | 66 ± 23 | 73 ± 26 | 7 ± 19 | 0.03 |
| Role Functioning | 70 ± 42 | 46 ± 43 | 61 ± 46 | 15 ± 40 | 0.02 |
| Social Functioning | 85 ± 27 | 49 ± 42 | 80 ± 33 | 31 ± 47 | <0.01 |
| Mental Health | 83 ± 15 | 69 ± 21 | 77 ± 21 | 8 ± 20 | 0.01 |
| Health Perceptions | 76 ± 23 | 46 ± 30 | 61 ± 32 | 15 ± 21 | <0.01 |
| Pain | 63 ± 39 | 62 ± 28 | 68 ± 32 | 7 ± 31 | 0.20 |
| SF-20 Subscale | Variable(s) | p | Model R2 * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survey 1 | |||
| Physical Function | High fatigue score | <0.01 | 0.44 |
| Role Functioning | High fatigue score | <0.01 | 0.44 |
| Low SES | <0.01 | ||
| Social Functioning | ROS summary score | <0.01 | 0.30 |
| Severity score | 0.04 | ||
| Mental Health | ROS summary score | <0.01 | |
| High depression score | <0.01 | 0.70 | |
| High anxiety score | 0.02 | ||
| Health Perception | ROS summary score | <0.01 | 0.70 |
| High fatigue score | <0.01 | ||
| High severity score | 0.02 | ||
| Charlson Index ≥ 1 | 0.03 | ||
| Pain | Elevated PHQ-4 total score | 0.04 | 0.32 |
| Survey 2 * | |||
| Physical Function | High dyspnea score 1 | 0.01 | 0.66 |
| Role Functioning | High dyspnea score 1 | 0.01 | 0.51 |
| Charlson Index > 1 | 0.04 | ||
| Social Functioning | Low SES | 0.01 | 0.28 |
| High dyspnea score 1 | 0.01 | ||
| Mental Health | High depression score 1 | <0.01 | 0.52 |
| High dyspnea score 1 | <0.01 | ||
| Health Perception | High dyspnea score 1 | <0.01 | 0.81 |
| Charlson Index > 1 | <0.01 | ||
| Low SES | 0.03 | ||
| Pain | High dyspnea score 1 | <0.01 | 0.45 |
| Variable | Survey 1 | Survey 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | Worse * | Present | Worse * | |
| Cough | 50 | 30 | 18 | 15 |
| Excessive Sleepiness | 33 | 23 | 38 | 23 |
| Chest Pain | 38 | 25 | 18 | 13 |
| Swelling of Ankles or Legs | 25 | 10 | 30 | 18 |
| Frequent Headaches | 45 | 15 | 23 | 18 |
| Numbness of Feet | 18 | 3 | 25 | 8 |
| Arthritis or Joint Pain | 40 | 13 | 48 | 23 |
| Difficulty Walking | 33 | 8 | 33 | 18 |
| Trouble sleeping | 55 | 23 | 45 | 28 |
| Loss or Decrease in Sense of Smell or Taste | 23 | 10 | 8 | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaur, A.; Michalopoulos, C.; Carpe, S.; Congrete, S.; Shahzad, H.; Reardon, J.; Wakefield, D.; Swart, C.; ZuWallack, R. Post-COVID-19 Condition and Health Status. COVID 2022, 2, 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2010006
Kaur A, Michalopoulos C, Carpe S, Congrete S, Shahzad H, Reardon J, Wakefield D, Swart C, ZuWallack R. Post-COVID-19 Condition and Health Status. COVID. 2022; 2(1):76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaur, Antarpreet, Chloe Michalopoulos, Suzanne Carpe, Soontharee Congrete, Hira Shahzad, Jane Reardon, Dorothy Wakefield, Charles Swart, and Richard ZuWallack. 2022. "Post-COVID-19 Condition and Health Status" COVID 2, no. 1: 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2010006
APA StyleKaur, A., Michalopoulos, C., Carpe, S., Congrete, S., Shahzad, H., Reardon, J., Wakefield, D., Swart, C., & ZuWallack, R. (2022). Post-COVID-19 Condition and Health Status. COVID, 2(1), 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/covid2010006






