Fine-Tuning Flexographic Ink’s Surface Properties and Providing Anti-Counterfeit Potential via the Addition of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Used for Printing
2.2. Printing Process
2.3. Methods of Measurement and Analysis
2.3.1. Colorimetric Measurements
2.3.2. FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy
2.3.3. Analysis of Surface and Interfacial Properties
2.3.4. Microscopy and Image Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
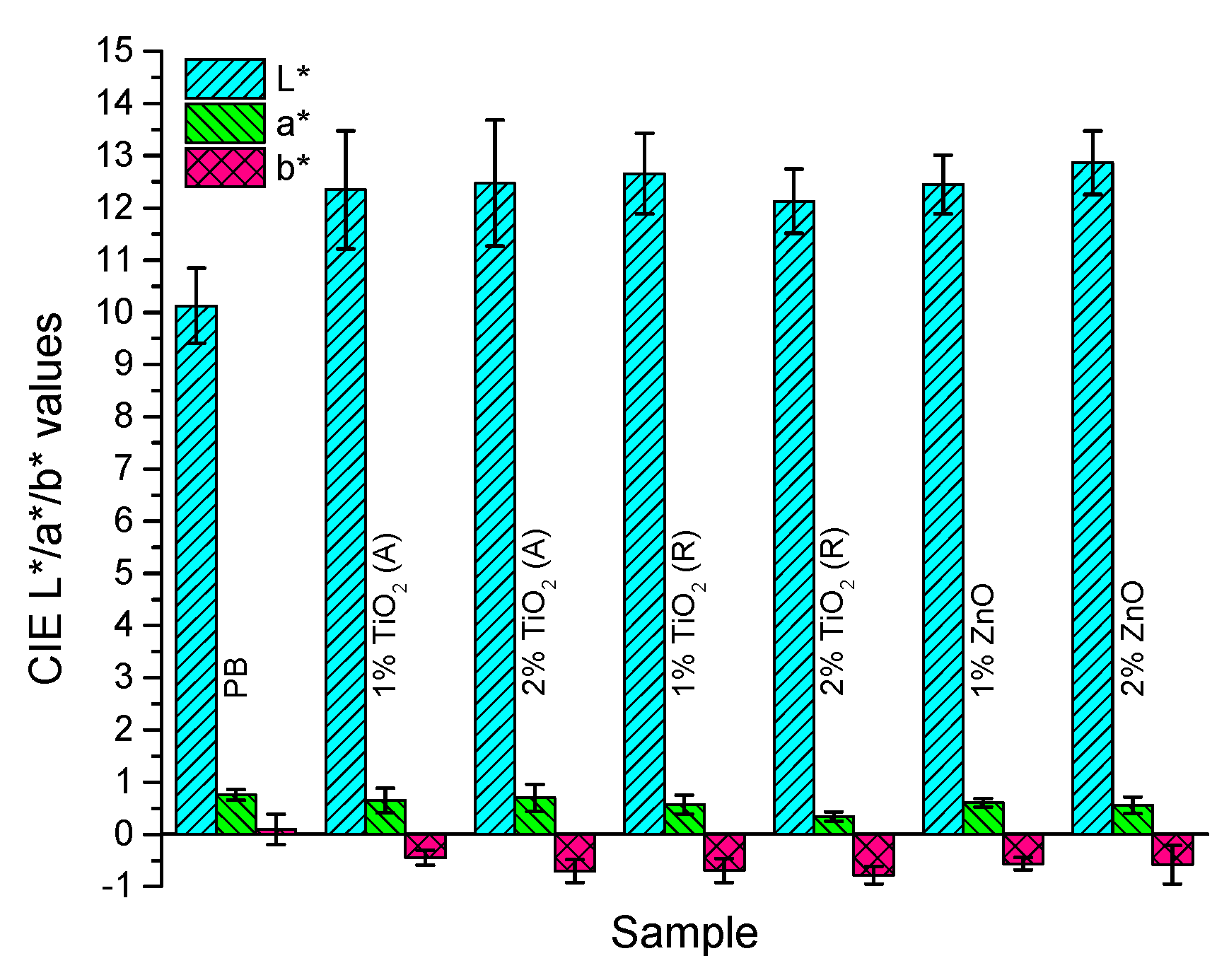
3.1. Colorimetric Properties of the Printed Layers
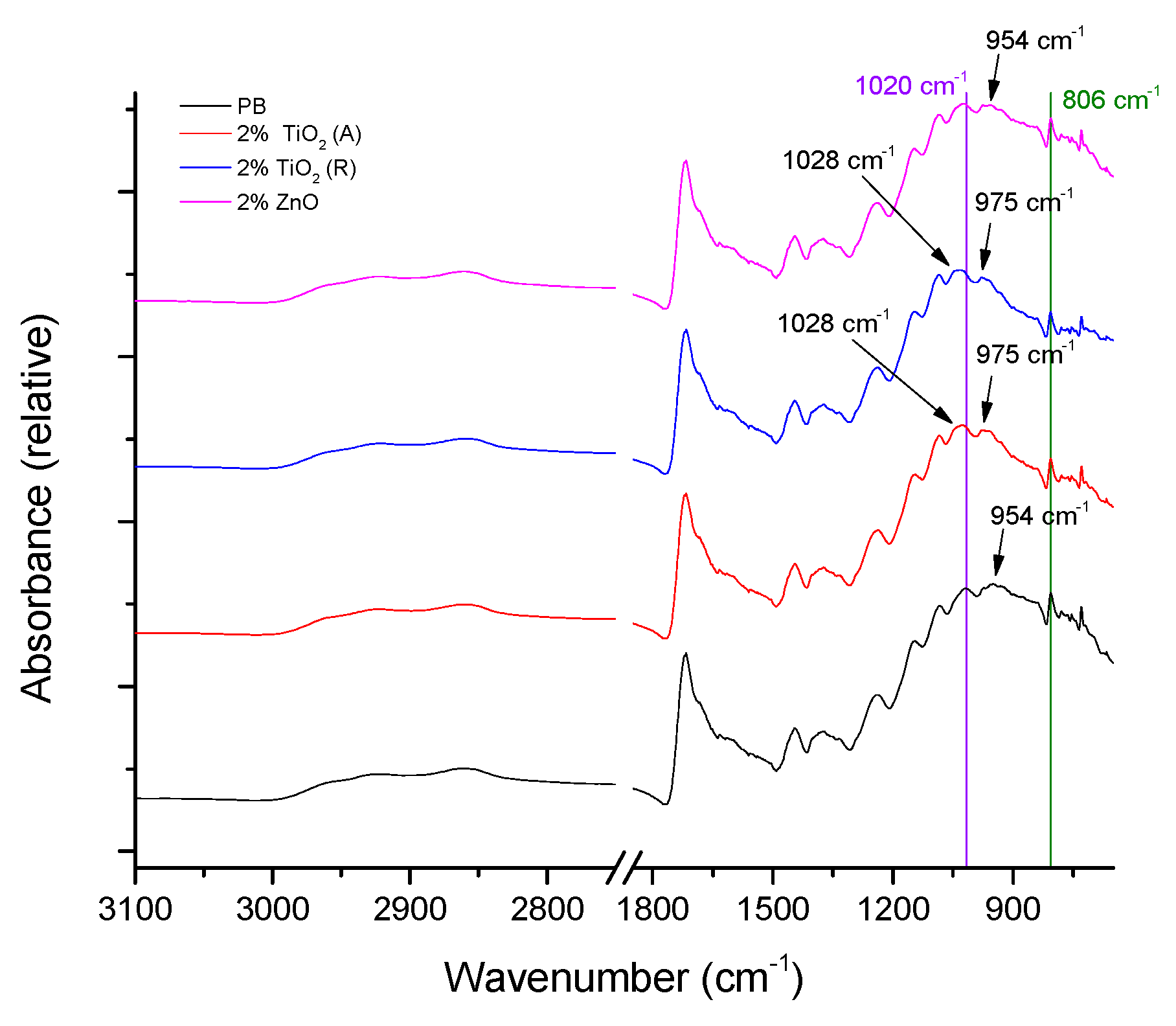
3.2. FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy
3.3. Surface and Interfacial Properties of the Prints
3.3.1. Contact Angle of Water
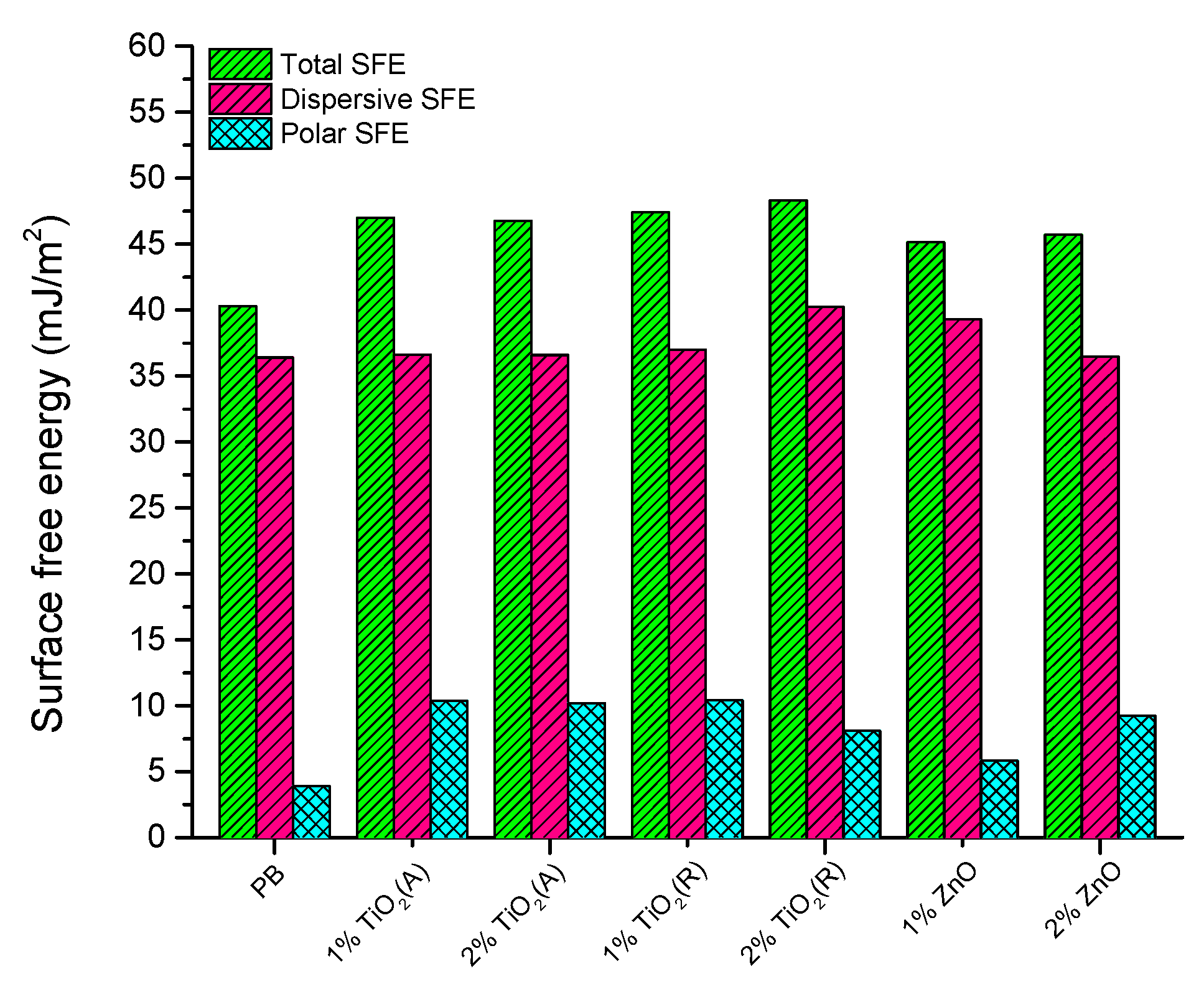
3.3.2. Surface Free Energy of Printed Layers
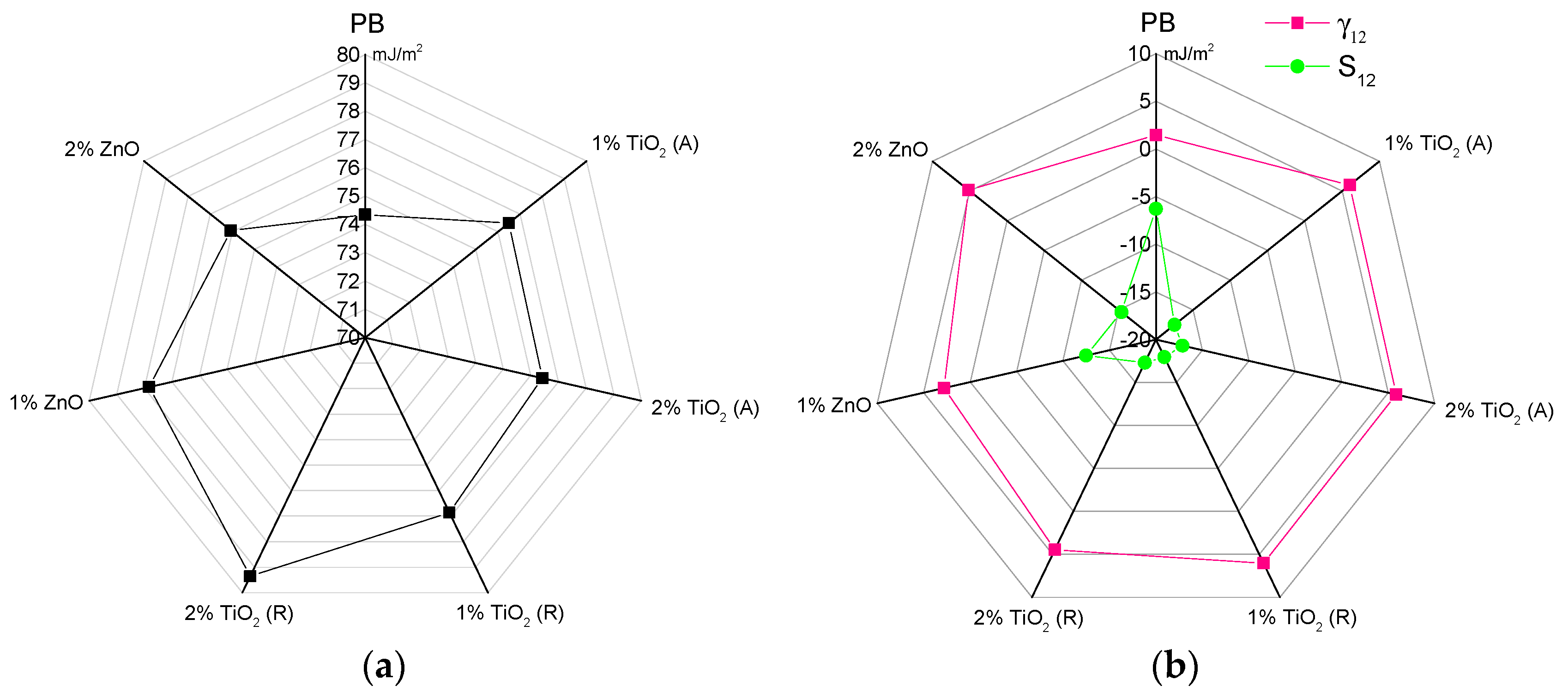
3.3.3. Adhesion Parameters
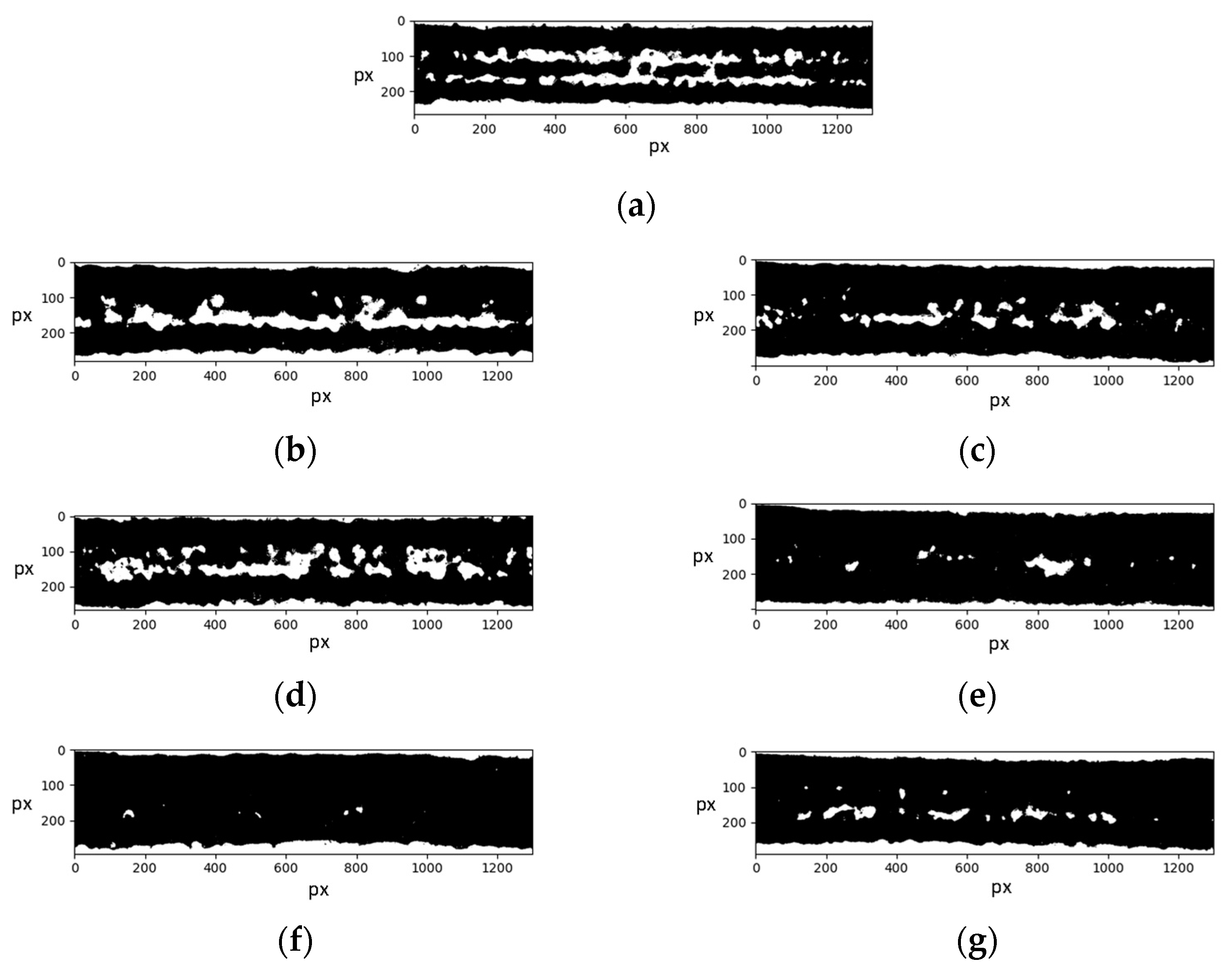
3.4. Microscopy and Image Analysis of the Printed Lines
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, Z.W.; Ee, J.H.; Chen, S.H.; Shan, X.C. Parametric investigation of flexographic printing processes for R2R printed electronics. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 35, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont, K.; Lipiak, J. The model of assessment for flexographic printing technology. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Pleiades Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 67–75. ISBN 9783319666969. [Google Scholar]
- Steadman, R. Handbook of Physical Testing of Paper; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T. Developing the use of cold foil imprinting as an added value and security Feature for printed materials using flexographic printing Plates. J. Herit. Des. 2024, 4, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddy, J.E.; Scheideler, W.J. Rapid 2D Patterning of High-Performance Perovskites Using Large Area Flexography. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elessawy, N.A.; Alhamzani, A.G.; Abou-Krisha, M.M.; Aljlil, S. Developing a new sustainable eco-adsorbent film from flexographic printing plate waste to remove cationic organic and inorganic pollutants. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 24373–24383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, G.R.; Anoop, M.S.; Jayadevan, P.C.; Kumar, R.A.; Nagarajan, K.J.; Muthukrishnan, D. Fabrication techniques for printed and wearable electronics. In Advances in Flexible and Printed Electronics Materials, Fabrication, and Applications; Inst of Physics Pub Inc.: Bristol, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, G.V. Printing inks for food contact packaging and articles. In Global Legislation Food Contact Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzhog, M. Water-Based Flexographic Printing on Polymer-Coated Board. Ph.D. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Muthamma, K.; Gouda, B.M.; Sunil, D.; Kulkarni, S.D.; Anand, P.J. Water-based fluorescent flexo-ink for security applications. Chem. Pap. 2023, 1, 4033–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keawkul, P.; Pachonklaew, P.; Waleetorncheepsawat, B. Optimization of Printing Conditions to Achieve Effective Ink Transfer in Flexographic Printing. J. Print. Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R.; Yang, L.; van Stam, J.; Lestelius, M. Effects on ink setting in flexographic printing: Coating polarity and dot gain. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2006, 21, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bould, D.C.; Claypole, T.C.; Bohan, M.F.J. An investigation into plate deformation in flexographic printing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2004, 218, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesan, N.; Sahinbaskan, T. Elimination of the Solid Graininess Issue with Different Micro-Pattern Structures at Flexo Printing. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.L.; Curtis, D.J.; Deganello, D. Control of morphological and electrical properties of flexographic printed electronics through tailored ink rheology. Org. Electron. 2019, 73, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašegović, T.; Beynon, D.; Claypole, T.; Mahović Poljaček, S. Tailoring the properties of deposited thin coating and print features in flexography by application of UV-ozone treatment. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahović Poljaček, S.; Tomašegović, T.; Leskovac, M.; Jakovljević, S. Neural network-based UV adjustment of the photopolymer surface for modification of coating properties printed in flexography. J. Coatings Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, S.; Salam, A.; Fleming, P.D.; Pekarovicova, A.; Wu, Q. Usability of cellulose-based binder in water-based flexographic ink. Color. Technol. 2023, 139, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, S.; Alsaid, D.; Pekarovicova, A.; Fleming, P.D.; Stoops, M.T. Effects on print quality of varying acrylic binder types in water-based flexographic ink formulations. Color. Technol. 2023, 139, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, S.; Li, K.; Marcello, C. Examination of the effects of using different crosslinkers in biodegradable coating formulation on printability properties of flexographic print system. Pigment Resin Technol. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.R.; Khan, F.S.; Syed, A.S.; Akhtar, J. Nano-inks and their applications in packaging industries. In Smart Multifunctional Nano-inks Fundamentals Emerging Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Nguyen, T.A.; Dao, P.H.; Mac, V.P.; Nguyen, A.H.; Do, M.T.; Nguyen, T.H. Effect of rutile titania dioxide nanoparticles on the mechanical property, thermal stability, weathering resistance and antibacterial property of styrene acrylic polyurethane coating. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafizas, A.; Kellici, S.; Darr, J.A.; Parkin, I.P. Titanium dioxide and composite metal/metal oxide titania thin films on glass: A comparative study of photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2009, 204, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, R.; Patiño-Ruiz, D.; Herrera, A. Preparation of modified paints with nano-structured additives and its potential applications. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2020, 10, 184798042090918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khir, H.; Pandey, A.K.; Saidur, R.; Ahmad, M.S.; Rahim, N.A.; Bhutto, Y.A.; Zaed, M.A.; Islam, A. TiO2-bismuth screen printing ink for flexible low temperature dye sensitized solar cells. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 488, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, R.; Bellè, U.; Brigatti, S.; Diamanti, M.V. 3D printing of photocatalytic nanocomposites containing titania nanoparticles. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 79, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Shan, M.; Lu, Y.; Abdalqadir, M.; Saeed, Z.; Azhdar, B.; Ali, S.S.; Abdel-moneam, Y.K.; Hegazy, M. Preparation and application of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in offset ink. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2305, 12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Majumder, D.; Rupa, P.K.P. Effect of Solid Loading of TiO2 on The Rheological Behaviour and Microstructure of Methyl Cellulose-TiO2 Inks by Direct Ink Writing. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2025, 78, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Priyadarshi, R.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.; Alekseev, D.G.; Rhim, J.W. 3D-Printed Pectin/Carboxymethyl Cellulose/ZnO Bio-Inks: Comparative Analysis with the Solution Casting Method. Polymers 2022, 14, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Han, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zha, W.; Fang, J.; Luo, Q.; Liu, L.; Ma, C.Q. Monodispersed ZnO nanoink and ultra-smooth large-area ZnO films for high performance and stable organic solar cells. Flex. Print. Electron. 2022, 7, 25013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyana, A.K.; Ganguly, P.; Beniwal, A.; Kumar, S.K.N.; Dahiya, R. Disposable pH Sensor on Paper Using Screen-Printed Graphene-Carbon Ink Modified Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 21049–21056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esa, Z.; Nauman, M.M.; Ullah, M.; Khalid, M.U.; Mehdi, M.; Abid, M.; Iqbal, A.; Zaini, J.H.; Ali, K. Compatibility and performance study of electrohydrodynamic printing using zinc oxide inkjet ink. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ye, J.; Mu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H. Improving the performance of polyacrylate latex binders for water-based inks through the application of reactive emulsifiers and nanosized zinc oxide. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 187, 108160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, S. Coagulation removal and recycling strategy of TiO2 nanoparticles based on Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharide application. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Xi, X.; Yang, Y.; Tian, W.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.-J. Sustainable Recycling of TiO2 Nanoparticles with High Photocatalytic Performance from Spent Selective Catalytic Reduction Catalysts. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaibes, R.M.; Arzehgar, Z.; Heydari, M.M.; Fatolahi, L. ZnO Nanoparticles: A Highly Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for Tandem Knoevenagel-Michael-Cyclocondensation Reaction. Asian J. Green Chem. 2023, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Sharma, A.L.; Mohanta, G.C.; Kumar, P.; Kim, K.H. A facile chemical route for recovery of high quality zinc oxide nanoparticles from spent alkaline batteries. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumah, E.A.; Fopa, R.D.; Harati, S.; Boadu, P.; Zohoori, F.V.; Pak, T. Human and environmental impacts of nanoparticles: A scoping review of the current literature. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuryadin, B.W.; Nurjanah, R.; Mahen, E.C.S.; Nuryantini, A.Y. Synthesis and characterization of carbon nanoparticle/PVA/ chitosan for security ink applications. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 34003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, A.; Gupta, R.R.; Mehta, S.K.; Sharma, S. An Overview of Security Materials in Banknotes and Analytical Techniques in Detecting Counterfeits. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 54, 2865–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.F.; Khan, Y.; Khan, M.I.; Abdullaeva, B.S.; Waqas, M. Exploring nanotechnology in forensic investigations: Techniques, innovations, and future prospects. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024, 45, 100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cviljušac, V.; Divjak, A.; Modrić, D.; Brkić, A.L. Utilizing standard high-resolution graphic computer-to-film process for computer-generated hologram printing. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, G143–G148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokazov, E.Y.; Kolyuchkin, V.V.; Lushnikov, D.S.; Smirnov, A.V. Computer-Generated Holograms Application in Security Printing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašegović, T.; Mahović Poljaček, S.; Strižić Jakovljević, M.; Marošević Dolovski, A. Properties and colorimetric performance of screen-printed thermochromic/uv-visible fluorescent hybrid ink systems. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE ΔE* (Color Difference) Equations, Techkon USA. Available online: https://techkonusa.com/cie-δe-color-difference-equations/ (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żenkiewicz, M. Methods for the calculation of surface free energy of solids. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 24, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular and Surface Forces. In Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.-S. Ultraviolet (UV) Curable Inks and Coatings; Satakunta University of Applied Sciences: Pori, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Hu, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, X. Novel Waterborne UV-Curable Hyperbranched Polyurethane Acrylate/Silica with Good Printability and Rheological Properties Applicable to Flexographic Ink. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolinário, L.D.; Colonetti, E.; Cercená, R.; da Silveira Santos, F.; Cargnin, M.; Dal-Bó, A.G. Partial substitution of nitrocellulose by polyurethane resins in flexographic ink concentrates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.H.R.; Wang, B. The Hidden Effect of Interface Energies in the Polymorphic Stability of Nanocrystalline Titanium Dioxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoud, M.; Trabelsi, F.; Kumari, P.; Merenda, A.; Dumée, L.F. Recrystallization and coalescence kinetics of TiO2 and ZnO nano-catalysts towards enhanced photocatalytic activity and colloidal stability within slurry reactors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 252, 123235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołek-Tryznowska, Z.; Prica, M.; Pavlović, Ž.; Cveticanin, L.; Annusik, T. The influence of aging on surface free energy of corona treated packaging films. Polym. Test. 2020, 89, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
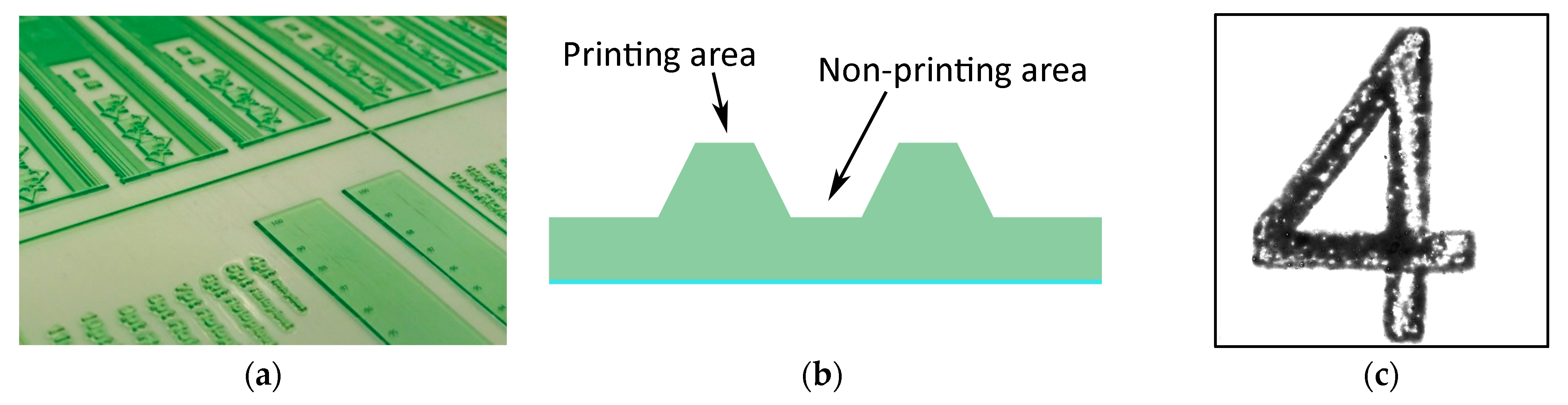


| Nanoparticle | Name | CAS Number | Average Nanoparticle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 (A) | Titanium (IV) oxide, anatase | 1317–70−0 | 15 |
| TiO2 (R) | Titanium (IV) oxide, rutile | 13463–67−7 | <100 |
| ZnO | Zinc oxide | 1314–13−2 | 40–100 |
| Probe Liquid | Total SFE (mJ/m2) | Dispersive SFE (mJ/m2) | Polar SFE (mJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 72.8 | 21.8 | 51.0 |
| Diiodomethane | 50.8 | 50.8 | 0.0 |
| Glycerol | 64.0 | 34.0 | 30.0 |
| Mass Concentration of Nanoparticles in the Ink (%) | Anatase TiO2 | Rutile TiO2 | ZnO |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | 2.29 | 2.48 | 2.53 |
| 2% | 2.66 | 2.23 | 2.83 |
| Printing Ink | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB | 2.36 | 79.05 | −1.57 |
| 1% TiO2 (A) | 0.40 | 87.69 | −6.30 |
| 2% TiO2 (A) | 0.41 | 87.47 | −6.09 |
| 1% TiO2 (R) | 0.44 | 88.07 | −6.75 |
| 2% TiO2 (R) | 1.11 | 88.32 | −8.34 |
| 1% ZnO | 1.64 | 84.61 | −5.69 |
| 2% ZnO | 0.48 | 86.34 | −5.10 |
| Ink | Measured Line Width—Positive (µm) | Measured Line Width—Negative (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| PB | 200.36 ± 4.79 | 191.33 ± 1.02 |
| PB + 1% TiO2 (A) | 177.31 ± 5.49 | 196.06 ± 2.53 |
| PB + 2% TiO2 (A) | 180.99 ± 2.49 | 195.95 ± 2.00 |
| PB + 1% TiO2 (R) | 183.51 ± 3.24 | 196.05 ± 1.21 |
| PB + 2% TiO2 (R) | 195.34 ± 2.64 | 193.56 ± 0.90 |
| PB + 1% ZnO | 199.66 ± 2.38 | 192.35 ± 1.03 |
| PB + 2% ZnO | 185.23 ± 3.95 | 195.57 ± 1.45 |
| Ink Used for Printing | Measured Line Segment Area (µm2) |
|---|---|
| PB | 429,401.02 |
| PB + 1% TiO2 (A) | 484,629.29 |
| PB + 2% TiO2 (A) | 566,771.37 |
| PB + 1% TiO2 (R) | 495,325.05 |
| PB + 2% TiO2 (R) | 600,903.94 |
| PB + 1% ZnO | 601,092.04 |
| PB + 2% ZnO | 552,346.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomašegović, T.; Mahović Poljaček, S.; Jurišić, I.; Donevski, D. Fine-Tuning Flexographic Ink’s Surface Properties and Providing Anti-Counterfeit Potential via the Addition of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles. Micro 2025, 5, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020020
Tomašegović T, Mahović Poljaček S, Jurišić I, Donevski D. Fine-Tuning Flexographic Ink’s Surface Properties and Providing Anti-Counterfeit Potential via the Addition of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles. Micro. 2025; 5(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomašegović, Tamara, Sanja Mahović Poljaček, Ivona Jurišić, and Davor Donevski. 2025. "Fine-Tuning Flexographic Ink’s Surface Properties and Providing Anti-Counterfeit Potential via the Addition of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles" Micro 5, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020020
APA StyleTomašegović, T., Mahović Poljaček, S., Jurišić, I., & Donevski, D. (2025). Fine-Tuning Flexographic Ink’s Surface Properties and Providing Anti-Counterfeit Potential via the Addition of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles. Micro, 5(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020020








