Wearable Electrospun Nanofibrous Sensors for Health Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Brief Overview of Electrospinning
2.1. Different Electrospinning Techniques
2.2. Different Fiber Orientations
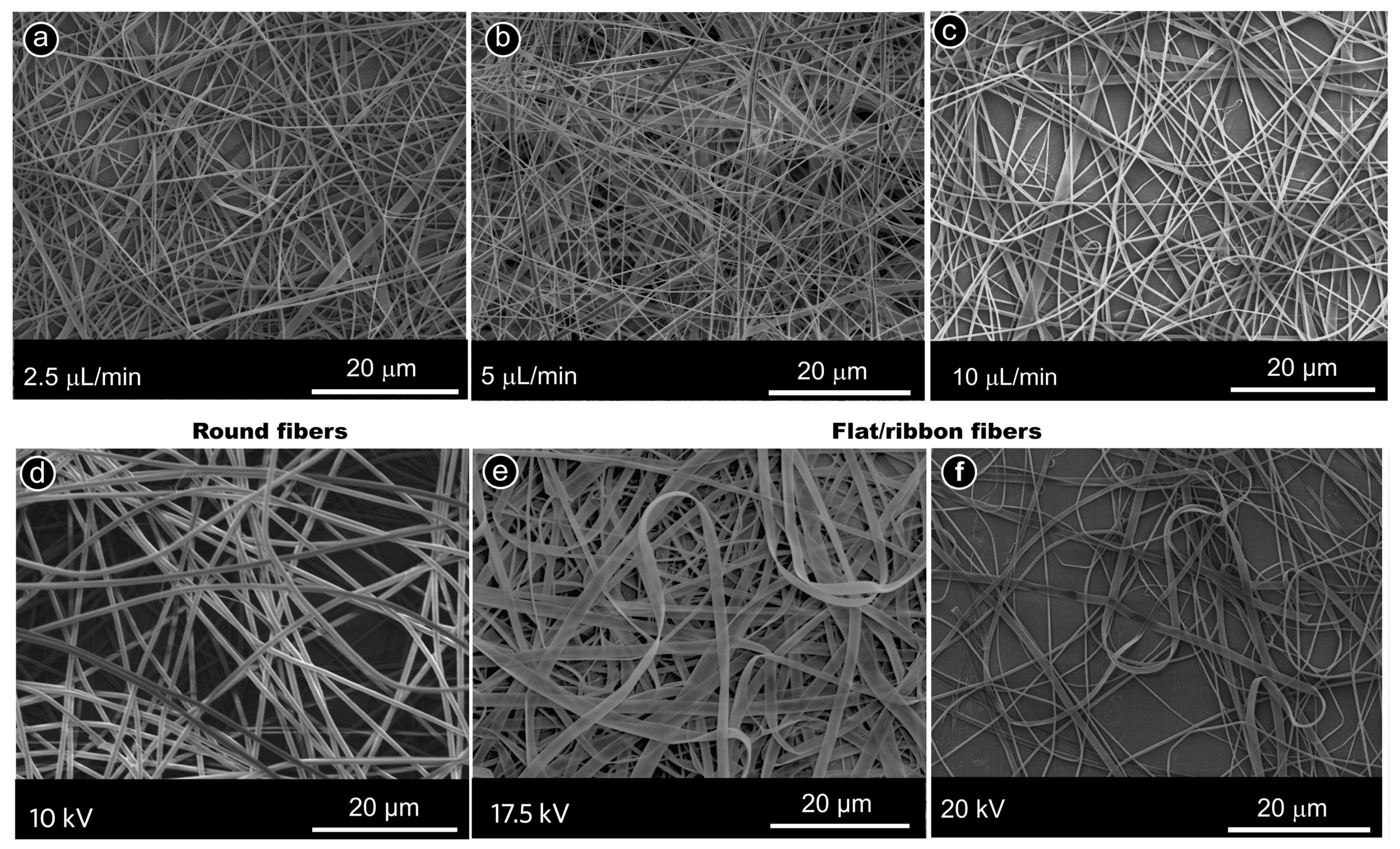
2.3. Different Fiber Cross-Sections
2.4. Different Materials
3. Making Nanofiber Mats Wearable
3.1. Embedding Nanofiber Mats in Smart Textiles
3.2. Gluing Nanofiber Mats on the Skin
3.3. Other Approaches to Integrating Nanofiber Mats into Wearable Textiles
4. Electrospun Wearable Sensors for Health Monitoring
4.1. ECG and Heartbeat
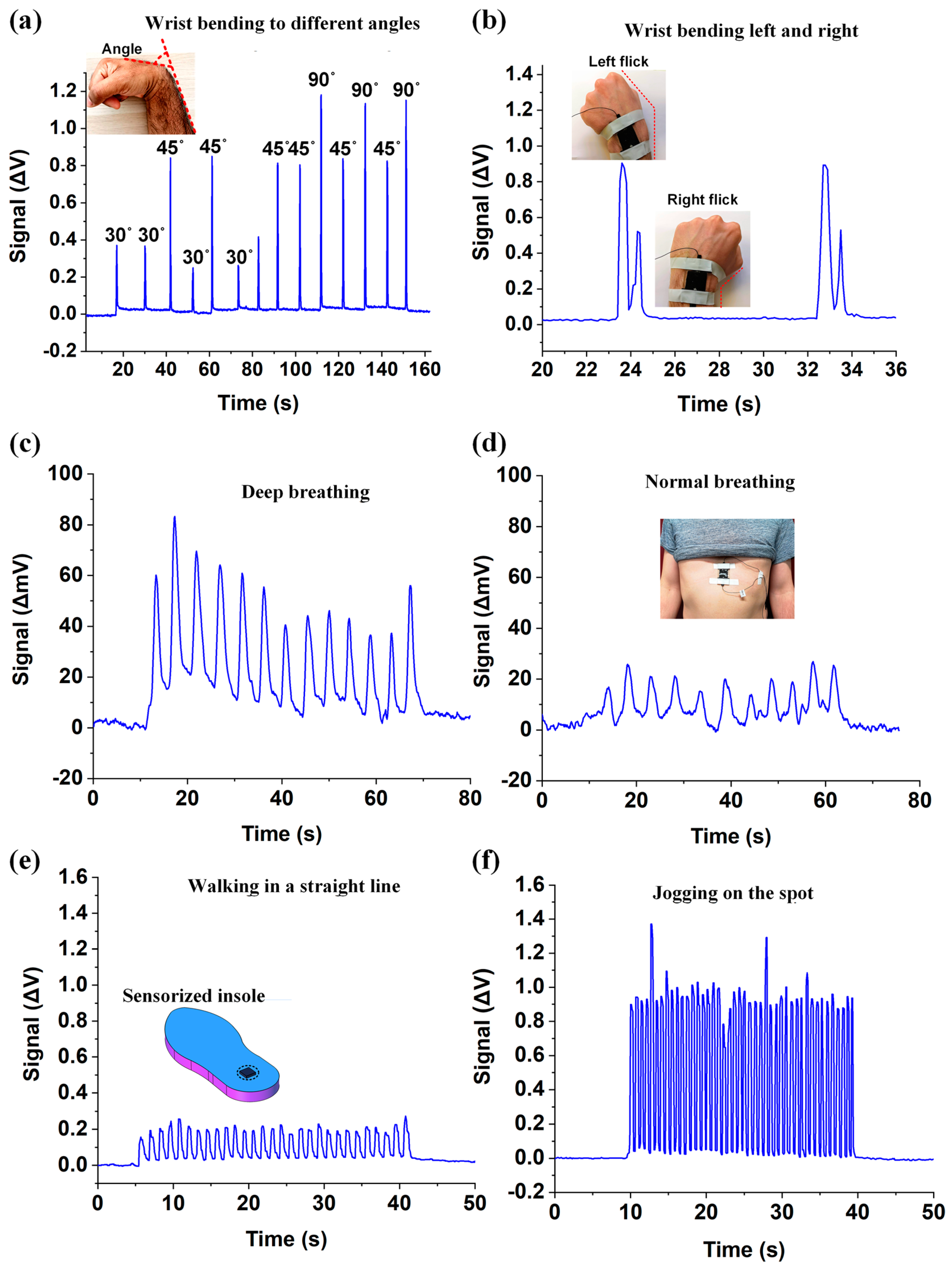
4.2. Respiration Rate
4.3. Movement Detection
4.4. Pressure Sensors
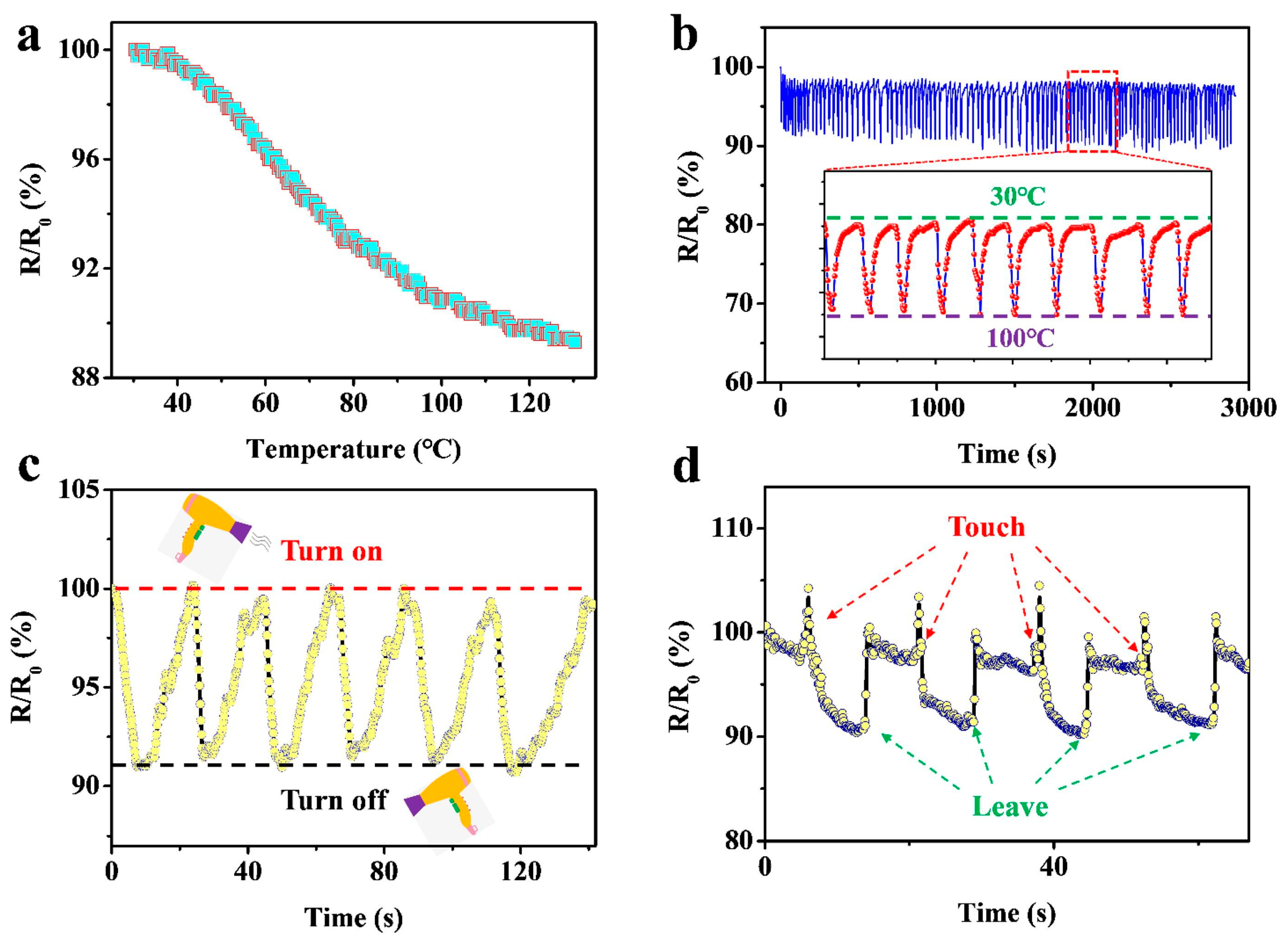
4.5. Temperature Sensors
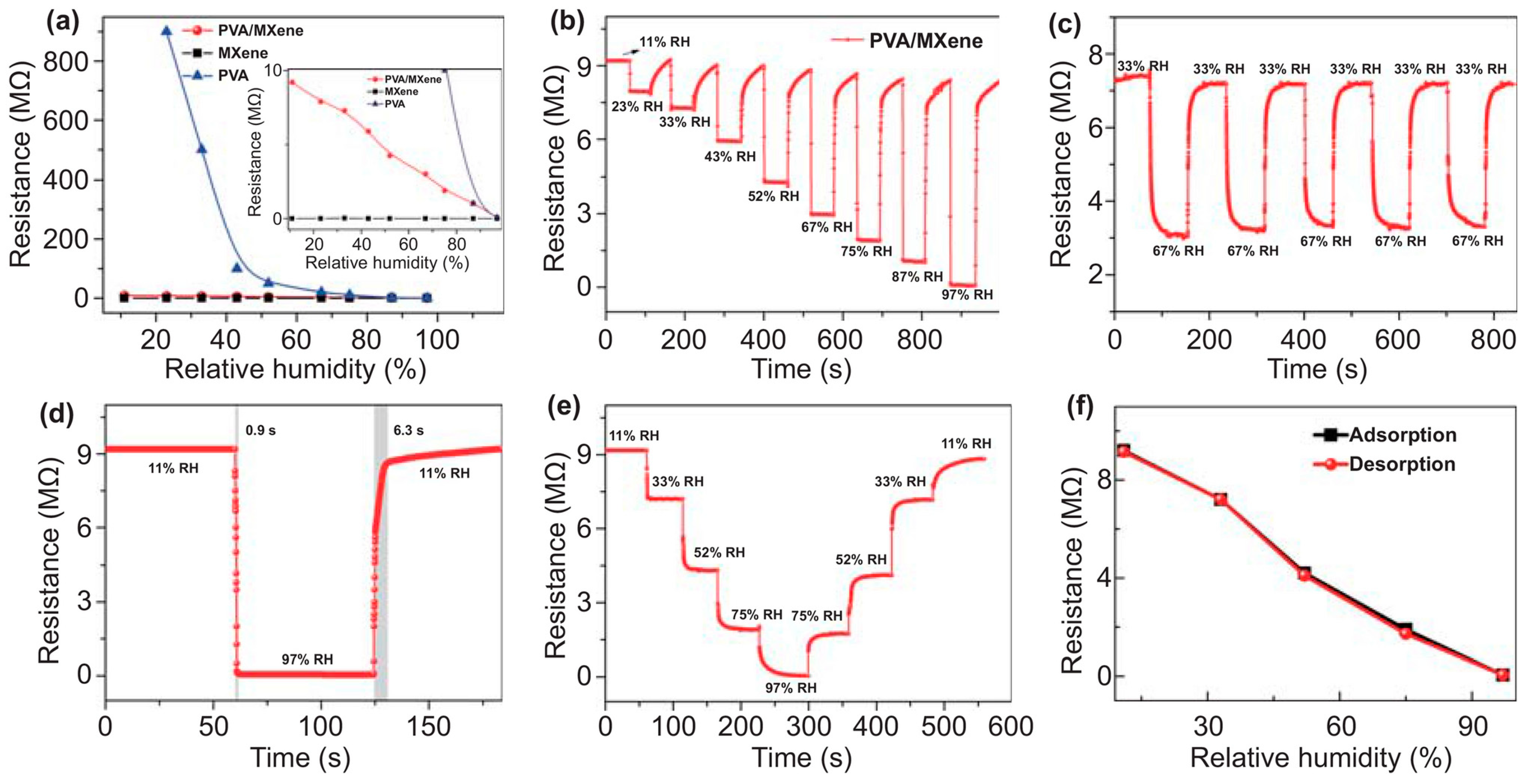
4.6. Humidity Sensors
5. Challenges and Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Klingner, A. A review on electrospun polymeric nanofibers: Production parameters and potential applications. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriello, M.; Afsari, M.; Shon, H.K.; Tijing, L.D. Progress on the fabrication and application of electrospun nanofiber composites. Membranes 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, W.-T.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, N.-H.; Jang, J.-S.; Kim, I.-D. Catalyst-decorated hollow WO3 nanotubes using layer-by-layer self-assembly on polymeric nanofiber templates and their application in exhaled breath sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Wu, S.S.; Wang, J.; Yu, A.; Wei, G. Carbon nanofiber-based functional nanomaterials for sensor applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeramuthu, L.; Venkatesan, M.; Benas, J.-S.; Cho, C.-J.; Lee, C.-C.; Lieu, F.-K.; Lin, J.-H.; Lee, R.-H.; Kuo, C.C. Recent Progress in Conducting Polymer Composite/Nanofiber-Based Strain and Pressure Sensors. Polymers 2021, 13, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, E.; Fonseca, H.; Diniz-Sousa, F.; Veras, L.; Boppre, G.; Oliveira, J.; Pinto, D.; Alves, A.J.; Barbosa, A.; Mendes, R.; et al. Wearable Devices for Physical Activity and Healthcare Monitoring in Elderly People: A Critical Review. Geriatrics 2021, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlShorman, O.; AlShorman, B.; Al-khassaweneh, M.; Alkahtani, F. A review of internet of medical things (IoMT)—Based remote health monitoring through wearable sensors: A case study for diabetic patients. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2020, 20, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujith, A.V.L.N.; Sajja, G.S.; Mahalakshmi, V.; Nuhmani, S.; Prasanalakshmi, B. Systematic review of smart health monitoring using deep learning and Artificial intelligence. Neurosci. Inform. 2022, 2, 1000028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Pin, K.Y.; Reddy, V.S.; Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Ji, D.X.; Serrano-García, W.; Bhargava, S.K.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chinnappan, A. Micro/nanofiber-based noninvasive devices for health monitoring diagnosis and rehabilitation. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 041309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shrestha, A.; Heidari, H.; Kernec, J.L.; Fioranelli, F. A Multisensory Approach for Remote Health Monitoring of Older People. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2018, 2, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Qi, J.M.; Fan, S.C.; Qiao, Z.; Yeo, J.C.; Lim, C.T. Flexible Wearable Sensors for Cardiovascular Health Monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Kola, I.; Ehrmann, A.; Guenther, K.; Ehrmann, G. Magnetic micro and nano sensors for continuous health monitoring. Micro 2024, 4, 206–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, T.S.; Liu, G.Z.; Liu, H.; Xie, X.Y.; Wie, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; He, Y.; Xu, F. Materials with Tunable Optical Properties for Wearable Epidermal Sensing in Health Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.; Condell, J.; Connolly, J.; Kelly, D.; Curran, K. Review of Wearable Sensor-Based Health Monitoring Glove Devices for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sensors 2021, 21, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anikwe, C.V.; Nweke, H.F.; Ikegwu, A.C.; Egwuonwu, C.A.; Onu, F.U.; Alo, U.R.; Teh, Y.W. Mobile and wearable sensors for data-driven health monitoring system: State-of-the-art and future prospect. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-D.; Ke, K.; Jia, J.; Pu, J.-H.; Zhao, X.; Bao, R.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M.-B.; et al. Recent Advances in Multiresponsive Flexible Sensors towards E-skin: A Delicate Design for Versatile Sensing. Small 2022, 18, 2103734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, J.; McLoughlin, L.; Bridgers, B.; Wujcik, E.K. Recent developments in nanofiber-based sensors for disease detection, immunosensing, and monitoring. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2020, 2, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, R.; Barhoum, A.; Bechelany, M.; Dufresne, A. Nanofibers for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1800256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.T.; Lu, L.J.; Pan, Z.F.; Mao, Y.C. Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Bioinspired Artificial Skins for Healthcare Monitoring and Human-Machine Interaction. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formhals, A. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. U.S. Patent No. 1,975,504, 2 October 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. Electrically Driven Jets. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1969, 313, 453–475. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.Y.; Wen, Y.; Dzenis, Y.; Leong, K.W. The role of electrospinning in the emerging field of nanomedicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4751–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sharma, G.; Rachel James, N. Electrospinning: The Technique and Applications. In Recent Developments in Nanofibers Research; Khan, M., Chelladurai, S.J.S., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrik, S.; Maly, M. Production Nozzle-Less Electrospinning Nanofiber Technology. MRS Proc. 2009, 1240, WW03–WW07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, F. A review on advanced nanofiber technology for membrane distillation. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 1558925018824901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morina, E.; Dotter, M.; Döpke, C.; Kola, I.; Spahiu, T.; Ehrmann, A. Homogeneity of needleless electrospun nanofiber mats. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teyeb, C.; Grothe, T.; Dotter, M.; Kola, I.; Ehrmann, A. Homogeneity of physical properties of electrospun gelatin nanofiber mats. Sustain. Green Mater. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Yang, X.; Shen, Y.J. Robot-aided electrospinning toward intelligent biomedical engineering. Robot. Biomim. 2017, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Salick, M.R.; Jing, X.; Crone, W.C.; Peng, X.-F.; Turng, L.-S. Electrospinning of unidirectionally and orthogonally aligned thermoplastic polyurethane nanofibers: Fiber orientation and cell migration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2015, 103, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y. Improving fiber alignment during electrospinning. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Li, L.M.; Hu, L.; Cui, X.J. Continuous aligned polymer fibers produced by a modified electrospinning method. Polymer 2006, 47, 4901–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.L.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospinning of Polymeric and Ceramic Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, H.; Ke, Q.; Chang, J. An anisotropically and heterogeneously aligned patterned electrospun scaffold with tailored mechanical property and improved bioactivity for vascular tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8706–8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, P.; Alessandro, M.; Ramsier, R.; Chase, G. Continuous electrospinning of aligned polymer nanofibers onto a wire drum collector. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, J.L.; Grothe, T.; Mamun, A.; Sabantina, L.; Klöcker, M.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Continuous electrospinning of aligned polymer nanofibers onto a wire drum collector. Materials 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellert, C.; Storck, J.L.; Grothe, T.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Hütten, A.; Ehrmann, A. Positioning and aligning electrospun PAN fibers by conductive and dielectric substrate patterns. Macromol. Symp. 2021, 395, 2000213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.; Büttner, U.; Sanderson, R.D. Continuous yarns from electrospun fibers. Polymer 2005, 46, 2419–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.H.; Bien, H.; Chung, C.Y.; Yin, L.H.; Fang, D.F.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Entcheva, E. Electrospun fine-textured scaffolds for heart tissue constructs. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5330–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, A.M.; Nakajima, H.; Yamane, H.; Kimura, Y.; Nakano, S. Fabrication of aligned poly(L-lactide) fibers by electrospinning and drawing. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2009, 294, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajao, J.A.; Abiona, A.A.; Chigome, S.; Fasasi, A.; Osinkolu, G.; Maaza, M. Electric-magnetic field-induced aligned electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2324–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnell, L.S.; Siochi, E.J.; Holloway, N.M.; Stephens, R.M.; Rhim, C.; Niklason, L.E.; Clark, R.L. Aligned mats from electrospun single fibers. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5345–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Jokisch, S.; Bargel, H.; Scheibel, T. Centrifugal Electrospinning Enables the Production of Meshes of Ultrathin Polymer Fibers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Z.X.; Li, C.X.; Lv, Y.R.; Hong, S.; Hu, P.; Liu, Y. Review of the Principles, Devices, Parameters, and Applications for Centrifugal Electrospinning. Macromol Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2200057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.E.; Bowlin, G.L. Near-Field Electrospinning and Melt Electrowriting of Biomedical Polymers—Progress and Limitations. Polymers 2021, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koombhongse, S.; Liu, W.X.; Reneker, D.H. Flat polymer ribbons and other shapes by electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiraliyan, N.; Nouri, M.; Kish, M.H. Effects of some electrospinning parameters on morphology of natural silk-based nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. 2009, 113, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Uyar, T. Electrospinning of gelatin with tunable fiber morphology from round to flat/ribbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Harding, D.R.; Yang, H. Helical peanut-shaped poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) ribbons generated by electrospinning. Polymer 2013, 54, 6752–6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzmeister, A.; Rudisile, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Structurally and chemically heterogeneous nanofibrous nonwovens via electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4859–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L. Coaxial electrospinning and emulsion electrospinning of core–shell fibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.G.; Zhao, Y.H.; Tang, G.W.; Yuan, X.Y. Electrospinning of ultrafine core/shell fibers for biomedical applications. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevsky, A.V.; Yarin, A.L.; Megaridis, C.M. Co-electrospinning of Core−Shell Fibers Using a Single-Nozzle Technique. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2311–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forward, K.M.; Flores, A.; Rutledge, G.C. Production of core/shell fibers by electrospinning from a free surface. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 104, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Hazar-Yavuz, A.N.; Tatar, E.; Haidari, M.M.; Ozcan, G.S.; Duruksu, G.; Graca, M.P.F.; Kalaskar, D.M.; Gunduz, O.; Cam, M.E. Oral empagliflozin-loaded tri-layer core-sheath fibers fabricated using tri-axial electrospinning: Enhanced in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.-Z.; Li, J.-J.; Yu, D.-G.; He, M.-F.; Yang, J.-H.; Williams, G.R. Nanosized sustained-release drug depots fabricated using modified tri-axial electrospinning. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yu, D.-G.; Pan, D.; Liu, X.-K.; Wang, X.; Bligh, S.W.A.; Williams, G.R. Electrospun pH-sensitive core–shell polymer nanocomposites fabricated using a tri-axial process. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, X.Y.; Jiang, L. Bio-mimic Multichannel Microtubes by a Facile Method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.Q.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, D.; Hong, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Qiu, S.; Wei, Y. Preparation and characterization of a PAN nanofibre containing Ag nanoparticles via electrospinning. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Science and Technology of Synthetic Metals (ICSM 2002), Shanghai, China, 29 June–5 July 2002; pp. 973–974. [Google Scholar]
- Cantu, T.; Walsh, K.; Pattani, V.P.; Moy, A.J.; Tunnell, J.W.; Irvin, J.A.; Betancourt, T. Conductive polymer-based nanoparticles for laser-mediated photothermal ablation of cancer: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Su, Z.; Wei, G. Electrostatic assembly of platinum nanoparticles along electrospun polymeric nanofibers for high performance electrochemical sensors. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; Tang, C. ZnO Nanofiber and Nanoparticle Synthesized Through Electrospinning and Their Photocatalytic Activity Under Visible Light. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zhou, W.; Fu, S.; Shao, C.; Liu, Y. Electrospun nanofibers of NiO/SiO2 composite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2009, 70, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graciano Alvarez, A.K.; Dotter, M.; Tuvshinbayar, K.; Bondzio, L.; Ennen, I.; Hütten, A.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning poly(acrylonitrile) containing magnetite nanoparticles: Influence of magnetite contents. Fibers 2024, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, N.; Yu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.-T.; Ding, B. From 1D Nanofibers to 3D Nanofibrous Aerogels: A Marvellous Evolution of Electrospun SiO2 Nanofibers for Emerging Applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, Z.B.; Yin, X.Q.; Lu, H.B.; Zhang, J.N.; Gao, J.Z.; Zhu, B.P. Amorphous SiO2-based all-inorganic self-supporting nanofiber membrane: A flexible and breathable sensing platform for NO2 detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 17432–17443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Liu, D.; Yu, B.; You, T.Y. A novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on electrospun nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles-embedded carbon nanofibers film. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2016, 224, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z. Developing Graphene-Based Nanohybrids for Electrochemical Sensing. Chem. Rec. 2019, 19, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Park, S.; Yu, K.; Ruoff, R.S.; Ocola, L.E.; Rosenmann, D.; Chen, J. Toward practical gas sensing with highly reduced graphene oxide: A new signal processing method to circumvent run-to-run and device-to-device variations. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercante, L.A.; Pavinatto, A.; Iwaki, L.E.; Scagion, V.P.; Zucolotto, V.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Mattoso, L.H.; Correa, D.S. Electrospun polyamide 6/poly(allylamine hydrochloride) nanofibers functionalized with carbon nanotubes for electrochemical detection of dopamine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4784–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabantina, L.; Klöcker, M.; Wortmann, M.; Rodríguez Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Moritzer, E.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Stabilization of polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats obtained by needleless electrospinning using dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 50, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.S.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.H.; Miao, P.; Liang, J.Y.; Wang, X.X. Effects of carbonization temperature on structure and mechanical strength of electrospun carbon nanofibrous mats. Mater. Lett. 2020, 273, 1277962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qanati, M.V.; Rasooli, A.; Rezvani, M. Main structural and mechanical properties of electrospun PAN-based carbon nanofibers as a function of carbonization maximum temperature. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 331–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, J.L.; Grothe, T.; Tuvshinbayar, K.; Diestelhorst, E.; Wehlage, D.; Brockhagen, B.; Wortmann, M.; Frese, N.; Ehrmann, A. Stabilization and carbonization of PAN nanofiber mats electrospun on metal substrates. Fibers 2020, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, J.L.; Brockhagen, B.; Grothe, T.; Sabantina, L.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Tuvshinbayar, K.; Braun, L.; Tanzli, E.; Hütten, A.; Ehrmann, A. Stabilization and carbonization of PAN nanofiber mats electrospun on metal substrates. C 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, M.A.; Ayoob, R.R.; Hameed, A.A. The effect of using two stabilization temperatures and fixation process on preparation of carbon nanofibers. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tang, Y.G.; Vlahovic, B.; Yan, F. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers Decorated with Noble Metal Nanoparticles for Chemical Sensing. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adabi, M.; Esnaashari, S.S.; Adabi, M. An electrochemical immunosensor based on electrospun carbon nanofiber mat decorated with gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes for the detection of breast cancer. J. Porous Mater. 2021, 28, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagoz, S.; Kiremitler, N.B.; Sarp, G.; Pekdemir, S.; Salem, S.; Goksu, A.G.; Onses, M.S.; Sozdutmaz, I.; Sahmetlioglu, E.; Ozkara, E.S.; et al. Antibacterial, Antiviral, and Self-Cleaning Mats with Sensing Capabilities Based on Electrospun Nanofibers Decorated with ZnO Nanorods and Ag Nanoparticles for Protective Clothing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5678–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolewe, K.W.; Dobosz, K.M.; Rieger, K.A.; Chang, C.-C.; Emrick, T.; Schiffman, J.D. Antifouling Electrospun Nanofiber Mats Functionalized with Polymer Zwitterions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27585–27593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaulsky, E.; Nejati, S.; Boo, C.H.; Perreault, F.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Post-fabrication modification of electrospun nanofiber mats with polymer coating for membrane distillation applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász Junger, I.; Wehlage, D.; Böttjer, R.; Grothe, T.; Juhász, L.; Grassmann, C.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Dye-sensitized solar cells with electrospun-nanofiber mat based counter electrodes. Materials 2018, 11, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hekmati, A.H.; Rashidi, A.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Drean, J.-Y. Effect of needle length, electrospinning distance, and solution concentration on morphological properties of polyamide-6 electrospun nanowebs. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Wehlage, D.; Böhm, T.; Remche, A.; Ehrmann, A. Needleless Electrospinning of PAN Nanofibre Mats. Tekstilec 2017, 60, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Großerhode, C.; Hauser, T.; Kern, P.; Stute, K.; Ehrmann, A. Needleless electrospinning of PEO nanofiber mats. Adv. Eng. Res. 2017, 102, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.J.; Kara, Y.H.; Molnar, K. Effect of needle characteristic on fibrous PEO produced by electrospinning. Resolut. Discov. 2019, 4, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Brikmann, J.; Meissner, H.; Ehrmann, A. Influence of Solution and Spinning Parameters on Nanofiber Mat Creation of Poly(ethylene oxide) by Needleless Electrospinning. Mater. Sci. 2017, 23, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angammana, C.J.; Jayaram, S.H. Investigation of the Optimum Electric Field for a Stable Electrospinning Process. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramariuc, B.; Cramariuc, R.; Scarlet, R.; Manea, L.R.; Lupu, I.G.; Cramariuc, O. Fiber diameter in electrospinning process. J. Electrost. 2013, 71, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Mirasol, J.R.; Cordero, T.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Investigation of Needleless Electrospun PAN Nanofiber Mats. AIP Conf. Ser. 2018, 1952, 020085. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Stachewicz, U. The impact of relative humidity on electrospun polymer fibers: From structural changes to fiber morphology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadevan, S.; Aliyana, A.K.; Stylios, G. An overview of advances and challenges in developing nanofiber yarns for wearable technology. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 110034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.L.; Guo, C.; Mu, Q.Q.; Yang, H.Y.; Chen, D.Y. Electrostatically spun nanofiber yarns for textile electronics. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2023, 56, 100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Liu, P.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.N.; Qin, X.H. Flexible and conductive nanofiber-structured single yarn sensor for smart wearable devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.L.; Xu, Z.; Chur, L.K.; Behroozfar, A.; Baniasadi, M.; Moreno, S.; Huang, J.C.; Gilligan, J.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Nanofibrous Smart Fabrics from Twisted Yarns of Electrospun Piezopolymer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24220–24229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, N.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, L.L.; Zhang, D.-A.; Wang, X.X.; Yan, X.; Long, Y.-Z. One-Step Preparation of a Core-Spun Cu/P(VDF-TrFE) Nanofibrous Yarn for Wearable Smart Textile to Monitor Human Movement. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 44234–44242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.L.; Qi, K.; Ou, K.K.; Song, Y.T.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhou, M.L.; Song, H.J.; He, J.X.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, R.W. Ag NW-Embedded Coaxial Nanofiber-Coated Yarns with High Stretchability and Sensitivity for Wearable Multi-Sensing Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 11244–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Wang, H.B.; You, X.L.; Tao, Y.J.; Li, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.M.; He, J.X.; Shao, W.L.; Cui, S.Z. Core-sheath nanofiber yarn for textile pressure sensor with high pressure sensitivity and spatial tactile acuity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, K.; Zhou, Y.M.; Ou, K.K.; Dai, Y.L.; You, X.L.; Wang, H.B.; He, J.X.; Qin, X.H.; Wang, R.W. Weavable and stretchable piezoresistive carbon nanotubes-embedded nanofiber sensing yarns for highly sensitive and multimodal wearable textile sensor. Carbon 2020, 170, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzabakiriho, P.C.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Ma, C.; Zhao, G. High-Strength and Extensible Electrospun Yarn for Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 46068–46076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.N.; Li, Y.R.; Xu, Z.J.; Li, W.F.; Xu, B.B.; Meng, H.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Guo, W.X. An integrated smart heating control system based on sandwich-structural textiles. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 325203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukali-Ozturk, M.; Ozden-Yenigun, E.; Nergis, B.; Candan, C. Nanofiber-enhanced lightweight composite textiles for acoustic applications. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 46, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsson, A.; Edvinsson, P.; Glantz, A.; Rodriguez, K.; Walkenström, P.; Gatenholm, P. Superhydrophobic behaviour of plasma modified electrospun cellulose nanofiber-coated microfibers. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, M.; Vaquero, C.; Amantia, D. Development of Protective Clothing against Nanoparticle Based on Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 892894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Liao, S.; He, L.M.; Lu, J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chan, C.K. Effects of Nanofiber/Stem Cell Composite on Wound Healing in Acute Full-Thickness Skin Wounds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, P.; Sadarani, B.; Majumdar, A.; Bullar, S. Nanofiber based drug delivery systems for skin: A promising therapeutic approach. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jian, M.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y. Carbonized Silk Nanofiber Membrane for Transparent and Sensitive Electronic Skin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qing, X.; Li, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. A nanofiber based artificial electronic skin with high pressure sensitivity and 3D conformability. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12105–12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; You, X.; Nan, N.; Shao, W.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.; Cui, S. A Highly Stretchable Nanofiber-Based Electronic Skin with Pressure-, Strain-, and Flexion-Sensitive Properties for Health and Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42951–42960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, H.; Jin, S.W.; Jeong, Y.R.; Yun, J.Y.; You, I.W.; Zi, G.S.; Ha, J.S. Stretchable Active Matrix Temperature Sensor Array of Polyaniline Nanofibers for Electronic Skin. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Wu, Y.C.; Gao, Y.X.; Su, Q.; Liu, Y.T.; Wu, H.D.; Zhang, H.C.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yao, H.; Huang, X.W.; et al. Nanofiber Composite Reinforced Organohydrogels for Multifunctional and Wearable Electronics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Adhikary, P.; Jana, S.; Biswas, A.; Sencadas, V.; Gupta, S.D.; Tudu, B.; Mandal, D. Electrospun gelatin nanofiber based self-powered bio-e-skin for health care monitoring. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Mastella, M.; Chicca, E.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Skin-Inspired Flexible and Stretchable Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Sensors for Neuromorphic Sensing. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Li, N.-W.; Zhao, S.Y.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Wang, J.N.; Du, X.Y.; Wang, B.; Cao, R.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, W.H.; et al. A Breathable and Screen-Printed Pressure Sensor Based on Nanofiber Membranes for Electronic Skins. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Z.; Bing, Y.; Li, F.; Mei, H.X.; Liu, S.; Fei, T.; Zhao, H.R.; Zhang, T. An All-Nanofiber-Based, Breathable, Ultralight Electronic Skin for Monitoring Physiological Signals. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, G.F.; Yu, W.; Li, G.X.; Meng, C.Z.; Guo, S.J. Wearable, ultrathin and breathable tactile sensors with an integrated all-nanofiber network structure for highly sensitive and reliable motion monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.S.; Lou, Y.Y.; Niu, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Jin, X.; Ma, J.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, X.Y. A Highly Sensitive, Breathable, and Biocompatible Wearable Sensor Based on Nanofiber Membrane for Pressure and Humidity Monitoring. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2200233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.Y.; Zheng, L.M.; Wang, G.R.; Gao, X.; Tan, Z.J.; Shan, J.Y.; Cui, L.Z.; Li, K.; Jian, M.Q.; Zhu, L.C.; et al. Transfer-Medium-Free Nanofiber-Reinforced Graphene Film and Applications in Wearable Transparent Pressure Sensors. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5541–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.F.; Chen, Y.Q.; Fu, B.F.; Li, K.J.; Huang, D.H.; Zheng, C.H.; Liu, M.H.; Yang, D.-P. Eggshell membrane-mimicking multifunctional nanofiber for in-situ skin wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 210, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.-F.; Liu, J.-J.; Wang, X.-X.; Xiang, H.-F.; Long, Y.-Z. Self-powered portable melt electrospinning for in situ wound dressing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrýsková, N.; Sourivong, P.; Babincová, M.; Simaljaková, M. Controlled Release of Tazarotene from Magnetically Responsive Nanofiber Patch: Towards More Efficient Topical Therapy of Psoriasis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.-C.; Bai, X.-H.; Cheng, G.-T.; Ding, Y.-N.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Wang, B.-C.; Xu, L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Zhang, J.; Long, Y.-Z. Icy core–shell composite nanofibers with cooling, antibacterial and healing properties for outdoor burns. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chiu, C.-W. Facile Fabrication of a Stretchable and Flexible Nanofiber Carbon Film-Sensing Electrode by Electrospinning and Its Application in Smart Clothing for ECG and EMG Monitoring. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, K.; Yang, Z.Y.; Hu, X.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, C.P.; Liu, Y. Electrospun Micro/Nanofiber-Based Biomechanical Sensors. ACS Apl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 6720–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-W.; Huang, B.-S.; Chang, C.-H.; Chiu, C.-W. Advanced electrospun AgNPs/rGO/PEDOT:PSS/TPU nanofiber electrodes: Stretchable, self-healing, and perspiration-resistant wearable devices for enhanced ECG and EMG monitoring. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, N. Low-Intensity Sensitive and High Stability Flexible Heart Sound Sensor Enabled by Hybrid Near-Field/Far-Field Electrospinning. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.S.; Jin, L.; Jeong, Y.J.; Oh, T.I.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, K.J. Electrospun Rubber Nanofiber Web-Based Dry Electrodes for Biopotential Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Li, J.-W.; Li, C.-L. Flexible Hybrid Electronics Nanofiber Electrodes with Excellent Stretchability and Highly Stable Electrical Conductivity for Smart Clothing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 42441–42453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Hao, S.W.; Yu, W.T.; Liu, X.D.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, N.; Bai, Y.X.; Xu, F.; et al. Compliant and breathable electrospun epidermal electrode towards artifact-free electrophysiological monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Zeng, W.X.; Asci, C.H.; Del-Rio-Ruiz, R.; Sonkusale, S. Recent progress in electrospun nanomaterials for wearables. APL Bioeng. 2022, 6, 021505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Wahab, M.A.; Will, G.; Karim, M.R.; Pan, T.S.; Gao, M.; Lai, D.K.; Lin, Y.; Miraz, M.H. Recent Advances in Stretchable and Wearable Capacitive Electrophysiological Sensors for Long-Term Health Monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, G.R.; Fang, Y.S.; Kurilova, O.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Chen, J. Advances in wearable respiration sensors. Mater. Today 2024, 72, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zhuang, Z.; Qi, D.; Zhao, C.J. High sensitive and fast response humidity sensor based on polymer composite nanofibers for breath monitoring and non-contact sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 330, 129239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.Z.; Duan, Z.H.; Yuan, Z.; Jiang, Y.D.; Tai, H.L. Electrospun nanofiber-based humidity sensors: Materials, devices, and emerging applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 27157–27179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Y.; Zhang, D.Z.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Kang, Z.J. Guar Gum/Ethyl Cellulose-Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone Composite-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Humidity Sensor for Human Respiration Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 31341–31353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Q.; Qu, D.Y.; Guo, L.H.; Zhou, G.D.; Zhang, G.J.; Du, T.; Wu, W.W. MXene/TPU Composite Film for Humidity Sensing and Human Respiration Monitoring. Adv. Sens. Res. 2024, 3, 2300014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Nguyen, T.; Dau, V.T.; Riduan, F.A.; Tran, C.-D.; Phan, H.-P. Flexible and Wearable Flow Sensor Using Spinnable Carbon Nanotube Nanofilm for Respiration Monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE 33rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–20 January 2020; pp. 634–637. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Dinh, T.; Dau, V.T.; Tran, C.-D.; Phan, H.-P.; Nguyen, T.-K. A Wearable, Bending-Insensitive Respiration Sensor Using Highly Oriented Carbon Nanotube Film. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 7308–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.F.; Hang, S.L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, P. Silk fibroin based flexible and self-powered sensor for real-time monitoring of abdominal respiration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Ning, C.; Chen, R.W.; Yi, J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Sheng, F.F.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.L. All-Nanofiber Self-Powered Skin-Interfaced Real-Time Respiratory Monitoring System for Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome Diagnosing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.A.; Patnam, H.; Manchi, P.; Paranjape, M.V.; Kurakula, A.; Yu, J.S. Biocompatible electrospun fibers-based triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and healthcare monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Long, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.D. Respiration-driven triboelectric nanogenerators for biomedical applications. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Xiao, X.; di Carlo, A.; Yin, J.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Huang, L.J.; Tang, J.G.; Chen, J. Advances in Wearable Strain Sensors Based on Electrospun Fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Q.S.; Schubert, D.W.; Liu, X.H. Review on Electrospun Conductive Polymer Composites Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; You, X.Y.; Fan, X.Y.; Wong, C.P.; Guo, P.; Zhao, N. Near-Field Electrospinning Enabled Highly Sensitive and Anisotropic Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.F.; Liu, X.G.; Zhang, C.H. Electrospinning of Highly Bi-Oriented Flexible Piezoelectric Nanofibers for Anisotropic-Responsive Intelligent Sensing. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2300701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, D.; Romano, J.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Electrospun bundled carbon nanofibers for skin-inspired tactile sensing, proprioception and gesture tracking applications. npj Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Shen, T.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Yin, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.T.; Shen, C.Y. Ultrasensitive electrospinning fibrous strain sensor with synergistic conductive network for human motion monitoring and human-computer interaction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 213, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-K.; Dutt, K.; Yao, Y.-S.; Wu, W.J.; Shiue, Y.-L.; Pan, C.-T.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, W.-F. Development of Flexible Biceps Tremors Sensing Chip of PVDF Fibers with Nano-Silver Particles by Near-Field Electrospinning. Polymers 2022, 14, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Nauman, S.; Khan, Z.M. Electrospun nanofibrous yarn based piezoresistive flexible strain sensor for human motion detection and speech recognition. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2023, 36, 2459–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, A.; Seyedin, S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Razal, J.M.; Dion, G.; Gogotsi, Y. Bath Electrospinning of Continuous and Scalable Multifunctional MXene-Infiltrated Nanoyarns. Small 2020, 16, 2002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadoss, T.S.; Ishii, Y.; Chinnappan, A.; Ang, M.H.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication of Pressure Sensor Using Electrospinning Method for Robotic Tactile Sensing Application. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Jen, Y.; Chen, R.; Aw, K.; Yamane, D.; Lo, C. Five-fold sensitivity enhancement in a capacitive tactile sensor by reducing material and structural rigidity. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 293, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.R.; Li, G.X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.X.; Meng, C.Z.; Guo, S.J. Recent Advances in Wearable Tactile Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofiber Platform. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2, 2200047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Russell, S.J.; Long, Y.Z. Advances in portable electrospinning devices for in situ delivery of personalized wound care. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19166–19178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Fu, J.T.; Liu, Z.X.; Li, P.; Tai, G.J.; Wang, P.S.; Xie, L.; Liu, X.Q.; He, X.M.; Wei, D.P.; et al. All-Fabric Capacitive Pressure Sensors with Piezoelectric Nanofibers for Wearable Electronics and Robotic Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 48683–48694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-F.; Cheng, C.; Yang, C.-C.; Hsiao, W.-T.; Yang, C.-R. A wearable and highly sensitive capacitive pressure sensor integrated a dual-layer dielectric layer of PDMS microcylinder array and PVDF electrospun fiber. Org. Electron. 2021, 98, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ding, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.Y.; Gong, H.L.; Shu, D.K.; Zhou, Z.; Jiao, L.; Cheng, B.W.; Ni, Y.H. Electrospun fiber-based high-performance flexible multi-level micro-structured pressure sensor: Design, development and modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Lou, Y.Y.; Ding, S.S.; Jin, X.; Liu, F.; Xu, Z.J.; Ma, J.Y.; Sun, Z.M.; Li, X.Y. Halloysite nanotubes strengthened electrospinning composite nanofiber membrane for on-skin flexible pressure sensor with high sensitivity, good breathability, and round-the-clock antibacterial activity. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 228, 106650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, T.J.; Cao, S.J.; Xia, X.; Bi, Y.; Xiao, Y.L. A novel flexible piezoresistive pressure sensor based on PVDF/PVA-CNTs electrospun composite film. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, F.L.; Wei, Q.F. All-Fiber-Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerator via One-Pot Electrospinning for Self-Powered Wearable Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 24774–24784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.K.; Zhou, Z.J.; Zhu, Q.X.; Lu, S.R.; Li, Y.Q.; Ionov, L. Electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibrous composites for multi-responsive shape memory actuators and self-powered pressure sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.S.; Bu, X.F.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.X.; Zhang, K.; Yao, Y.J.; Yang, L.Q.; Yang, R.R. The Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Dual Functions of Sensing and Power Generation Based on Electrospinning. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 8767–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, Z.J.; Wang, B.; Ding, S.S.; Ma, J.Y.; Cui, M.; Wang, C.C.; Jiang, Y.P.; Liu, J.L.; Zhang, X.Q. A highly sensitive and wide-range pressure sensor based on orientated and strengthened TPU nanofiber membranes fabricated by a conjugated electrospinning technology. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 14, 100491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Z.; Chen, G.; Pan, L.; Chen, D.S. Electrospun flexible PVDF/GO piezoelectric pressure sensor for human joint monitoring. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 129, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gong, H.; Li, W.P.; Gao, F.; Jiang, Q.S.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Han, Z.L.; Li, S.J. A flexible and highly sensitive pressure sensor based on three-dimensional electrospun carbon nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13898–13905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzubasoglu, B.A.; Bahadir, S.K. Flexible temperature sensors: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 315, 112282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roriz, P.; Silva, S.; Frazao, O.; Novais, S. Optical Fiber Temperature Sensors and Their Biomedical Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Chen, H.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Zhang, H.M.; Shen, X.; Zheng, Q.B.; Yang, J.L.; Jeon, S.W.; et al. Flexible temperature sensors made of aligned electrospun carbon nanofiber films with outstanding sensitivity and selectivity towards temperature. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.B.; Zhu, M.M.; Wie, X.D.; Yu, J.Y.; Li, Z.L.; Ding, B. A dual-mode electronic skin textile for pressure and temperature sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, W.; Li, G.X.; Meng, C.Z.; Guo, S.J. Printable, flexible, breathable and sweatproof bifunctional sensors based on an all-nanofiber platform for fully decoupled pressure–temperature sensing application. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Li, H.; Hu, D.W.; Xu, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.T.; Han, X.Y.; Zhao, G.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Chang, X.H.; et al. Stretchable strain and temperature sensor based on fibrous polyurethane film saturated with ionic liquid. Compos. Comm. 2021, 27, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.Y.; Xu, M.M.; Shi, J.D.; Zhu, J.F.; Li, Y.X. Highly temperature-sensitive and blue upconversion luminescence properties of Bi2Ti2O7:Tm3+/Yb3+ nanofibers by electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailley, D.; Hébraud, A.; Schlatter, G. A Review on the Impact of Humidity during Electrospinning: From the Nanofiber Structure Engineering to the Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Zhang, D.Z.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.M.; Mi, Q.; Yu, L.D. Electrospinning of Flexible Poly(vinyl alcohol)/MXene Nanofiber-Based Humidity Sensor Self-Powered by Monolayer Molybdenum Diselenide Piezoelectric Nanogenerator. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanty, B.; Ghosh, S.K.; Lee, D.-W. Advancements in polymer nanofiber-based piezoelectric nanogenerators: Revolutionizing self-powered wearable electronics and biomedical applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, S.; Singh, Z.; Sharma, A.K.; Kar, N.; Pati, P.K.; Mahajan, A. Electrospinning of Flexible Poly(vinyl alcohol)/MXene Nanofiber-Based Humidity Sensor Self-Powered by Monolayer Molybdenum Diselenide Piezoelectric Nanogenerator. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aguiar, M.F.; Leal, A.N.R.; de Melo, C.P.; Alves, K.G.B. Polypyrrole-coated electrospun polystyrene films as humidity sensors. Talanta 2021, 234, 122636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Chen, Y.; Abbel, R.; Visagie, I.; Parker, K. Flexible humidity sensors for wireless monitoring based on electrospun sulfonated polyether ether ketone (SPEEK) nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 324, 128704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Wang, X.K.; Wu, J.N.; Wang, X.G.; Lv, X.L.; Liu, G.; Li, B.S.; Zhou, J.Y.; Xie, E.Q.; Zhang, Z.X. Electrospun Nb-doped CeO2 nanofibers for humidity independent acetone sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 602, 154303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Q.; Han, W.J.; Jiang, B.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.F.; Wang, W.Y.; Lou, R.L.; Ci, H.D.; Zhang, H.; Lu, G.Y. Electrospinning Derived NiO/NiFe2O4 Fiber-in-Tube Composite for Fast Triethylamine Detection under Different Humidity. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Wang, X.K.; Wie, W.; Jiang, H.Q.; Li, X.J.; Liu, G.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Li, B.S.; Sheng, Y.B.; Zhou, J.Y.; et al. Humidity-resistant ethanol gas sensors based on electrospun tungsten-doped cerium oxide hollow nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
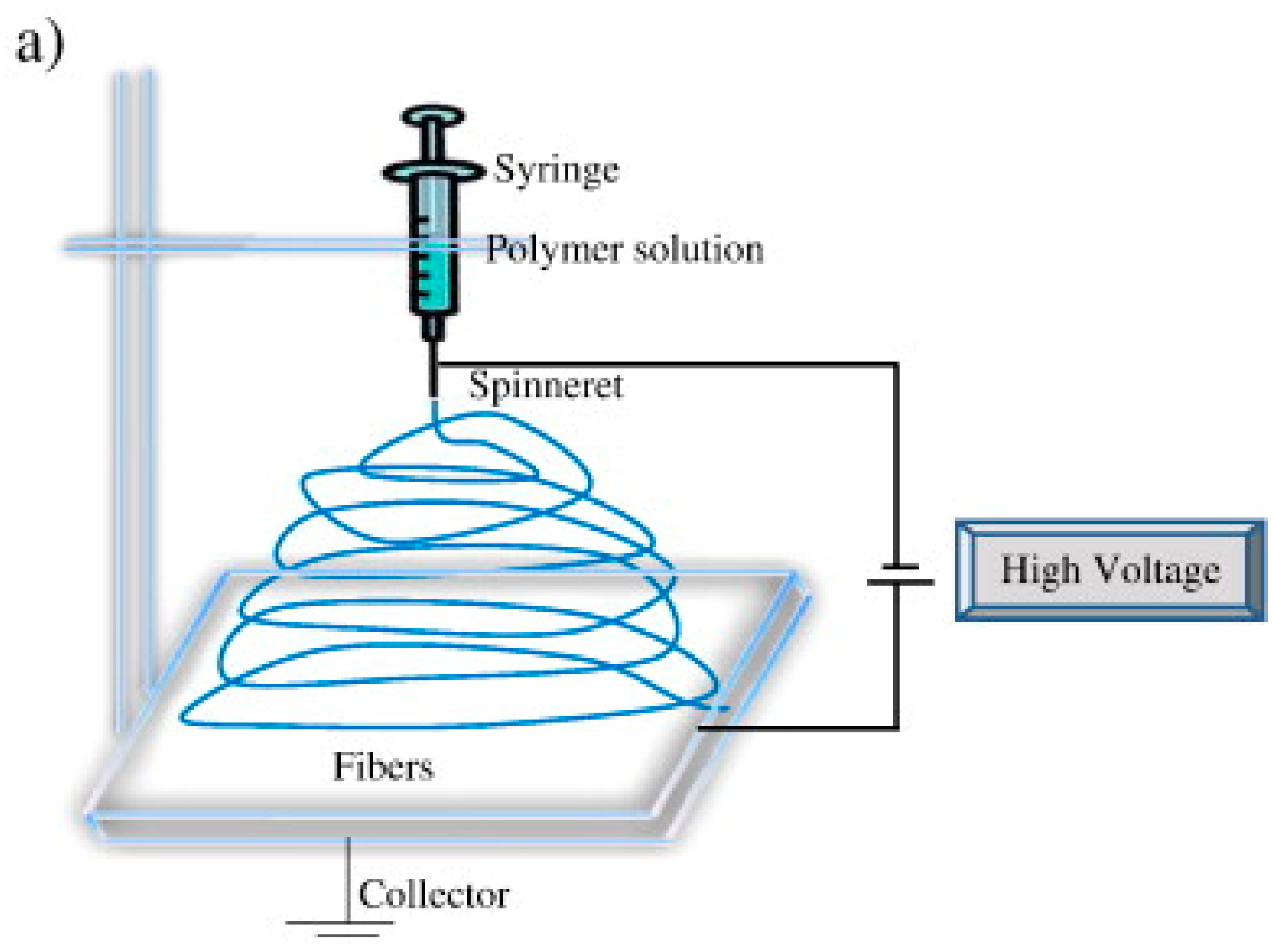

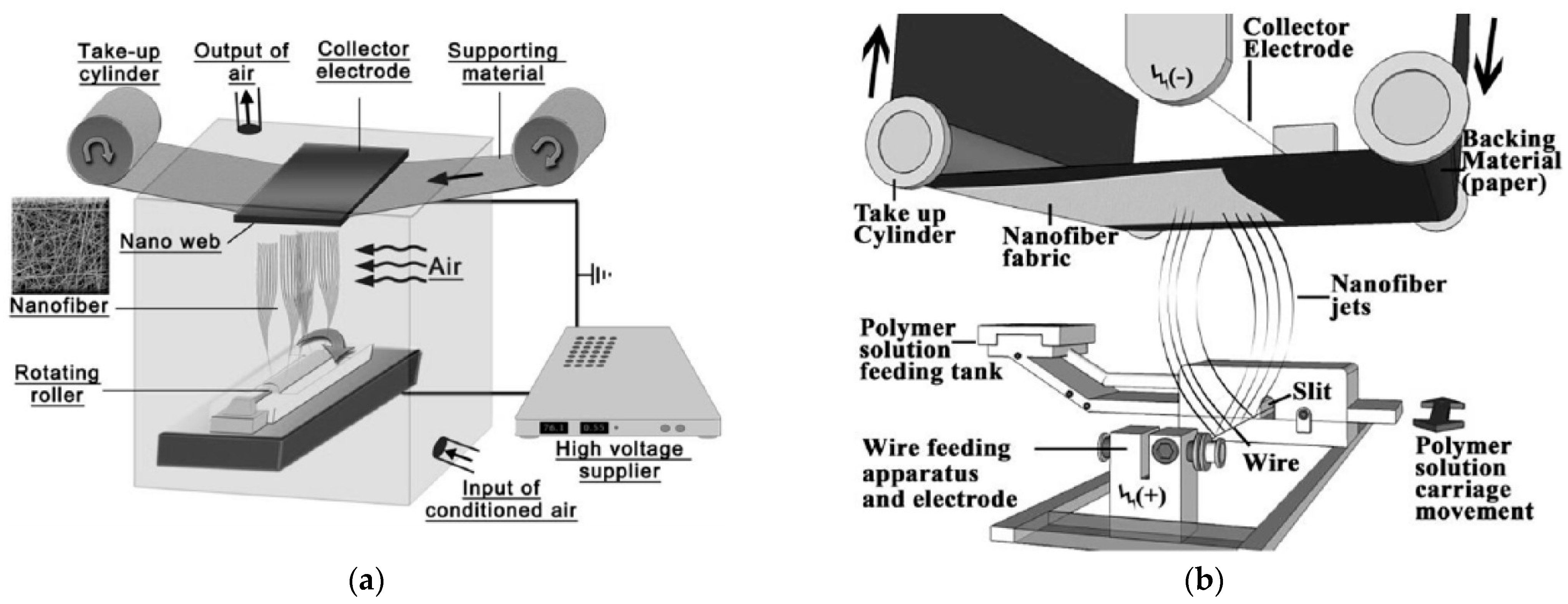
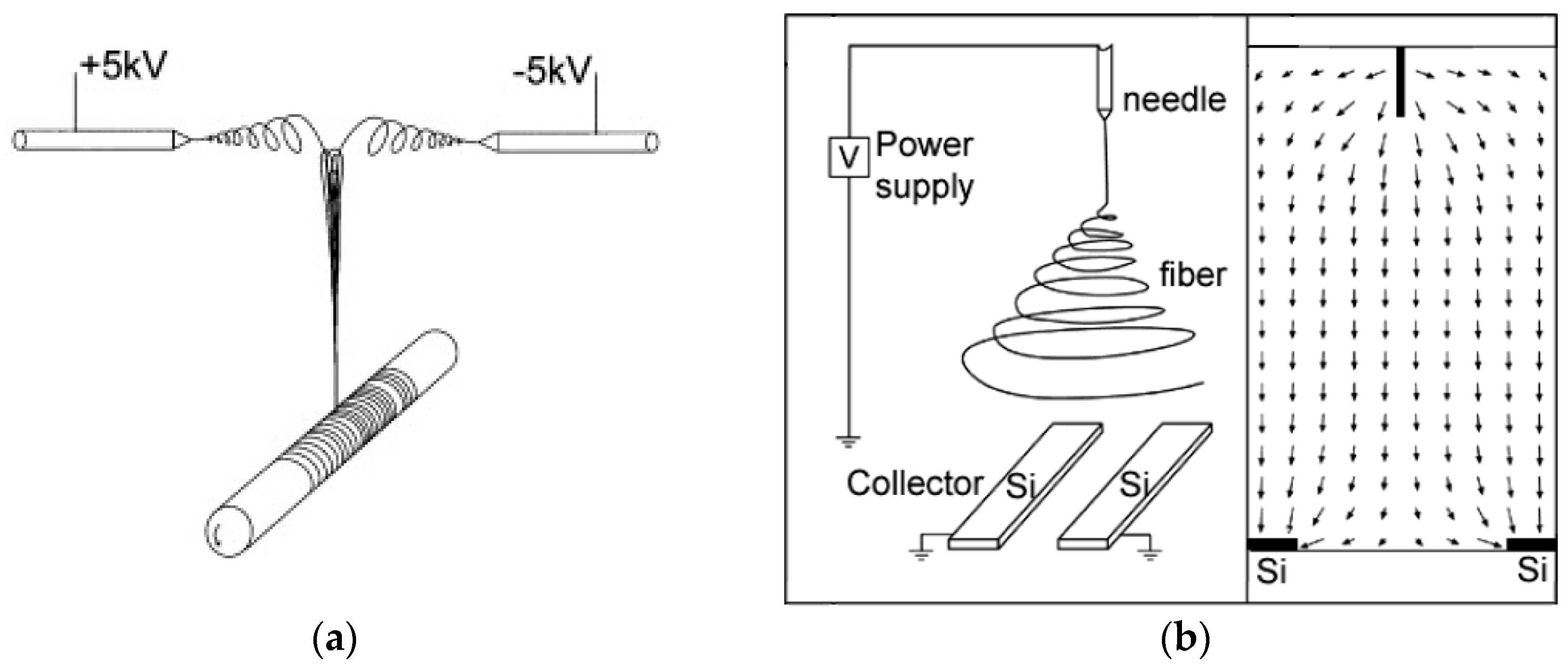

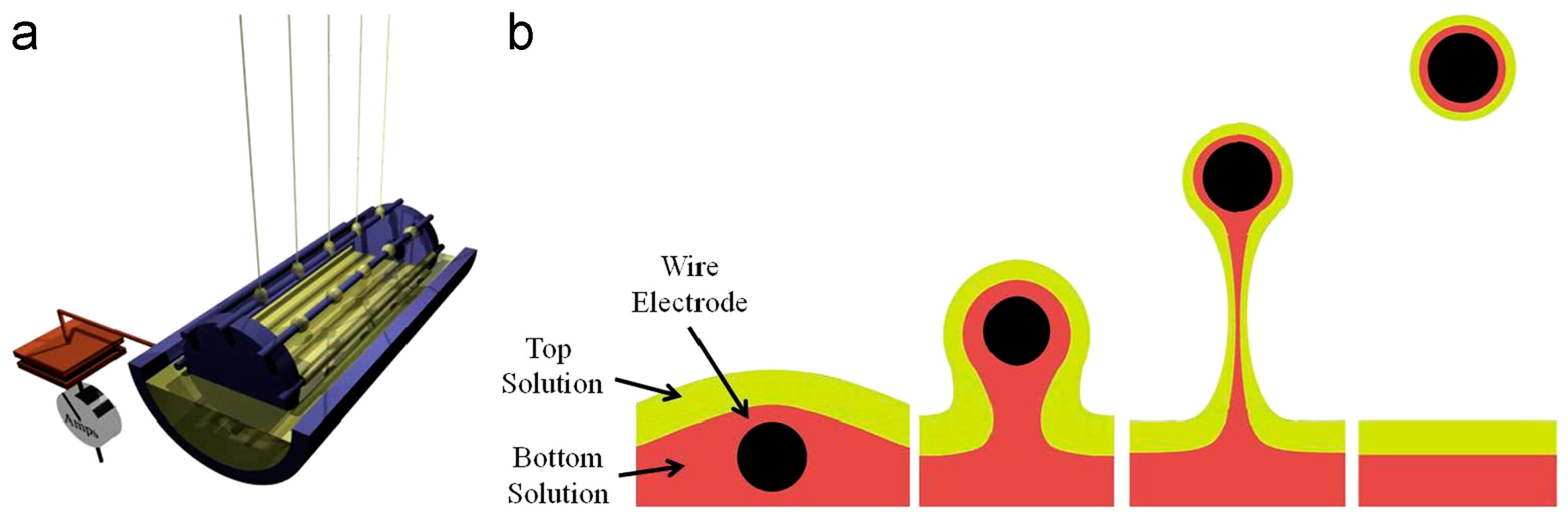

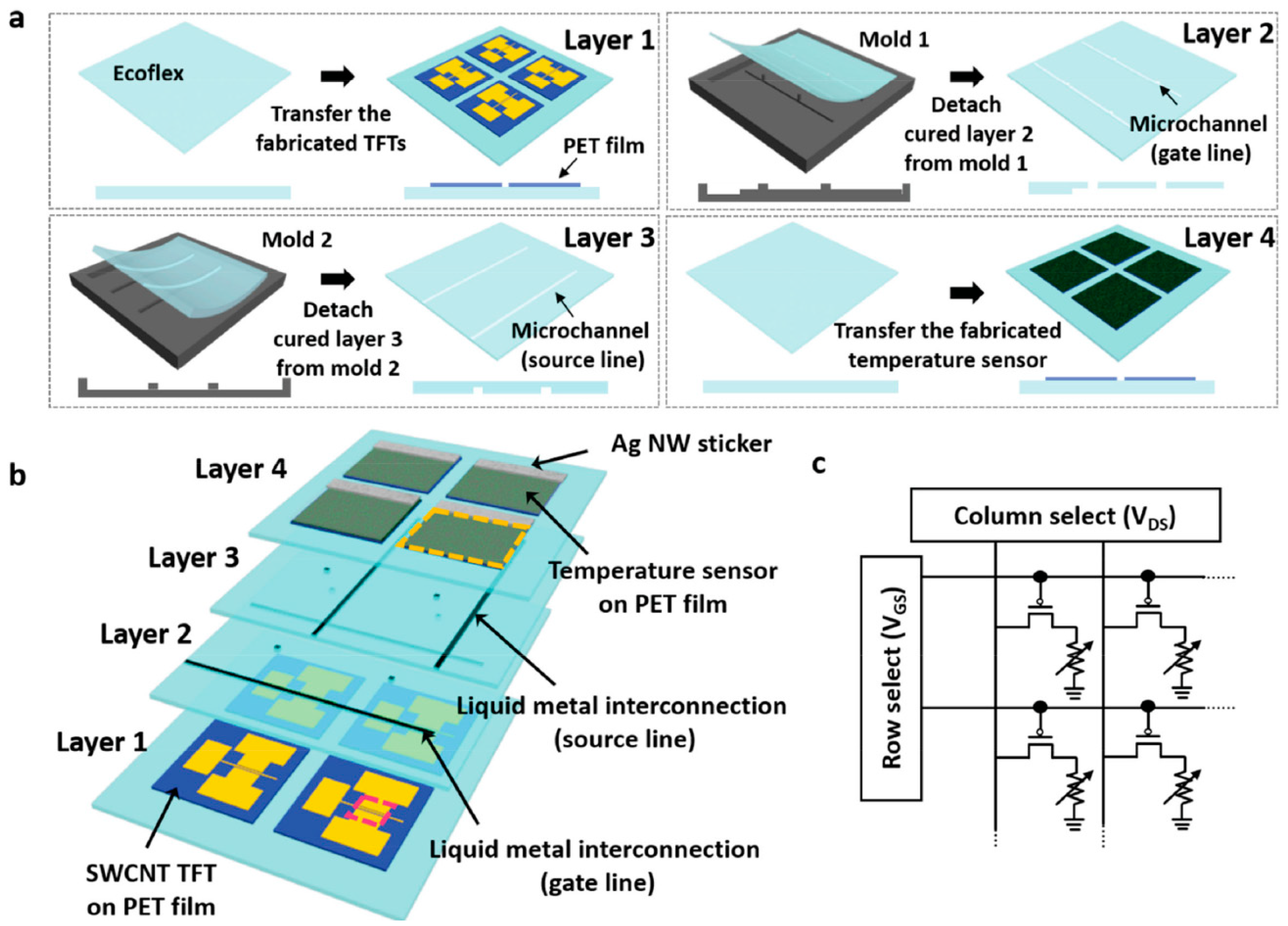

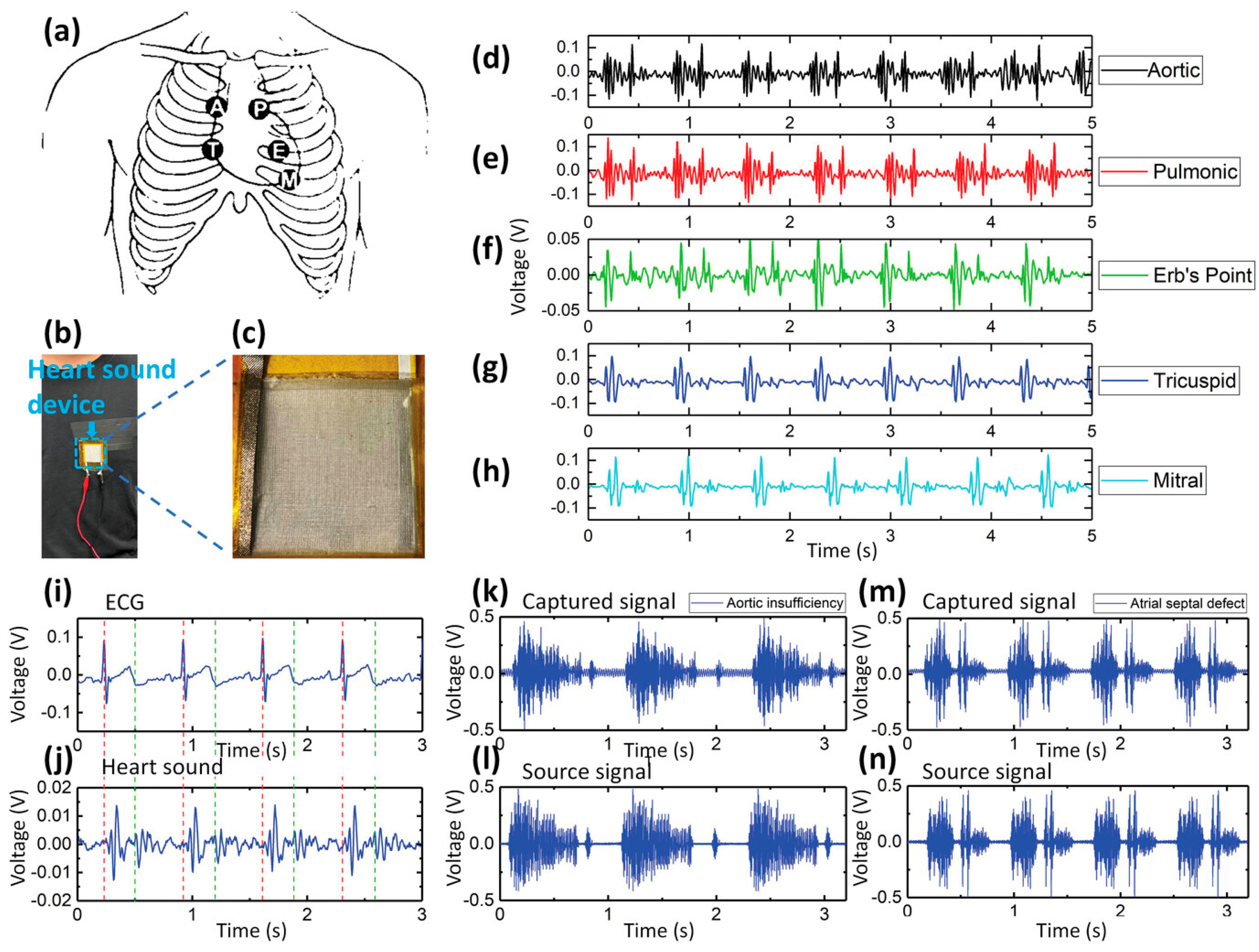
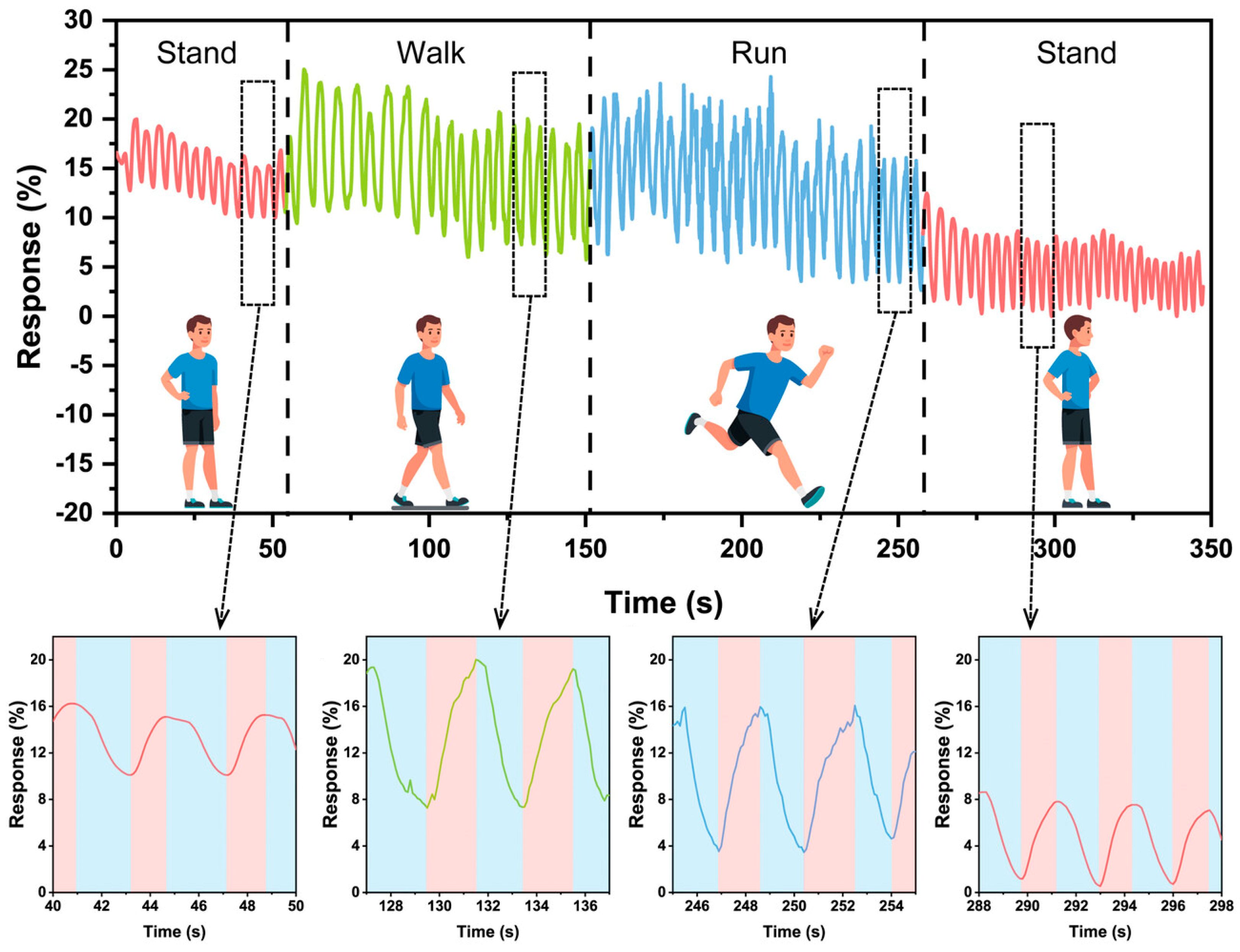

| Parameter | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Single-needle | Homogeneous nanofiber mat, well-controllable | Small area, low throughput |
| Multi-needle | Higher throughput → thicker or larger mats, alternatively combining different materials [25,26] | Risk of inhomogeneities, complicated electric field |
| Needleless electrospinning | Higher throughput → thicker or larger mats | Risk of inhomogeneities |
| Needle/fast rotating collector | Oriented fibers [32] | More complicated setup |
| Conjugate electrospinning/fast-rotating collector | Aligned fibers and long spinning durations since no charges are accumulated [33] | More complicated setup |
| Structured (drum) collector | Parallelized nanofibers [34,35,36,37,38] | More complicated setup |
| Water bath collector | Aligned nanofibers [39] | More complicated setup |
| Near-field electrospinning | Well-defined fiber positioning [46] | More complicated setup |
| Melt electrowriting | Well-defined fiber positioning [46] | More complicated setup |
| Coaxial electrospinning | Production of core-shell nanofibers [52,53] | More complicated process |
| Parameter | Influence on Electrospun Nanofiber Mat |
|---|---|
| Solid content in the solution | Reduces beads, only certain range spinnable [86,87] |
| Molecular weight of polymer | Reduces fiber diameter, only certain range spinnable [88] |
| Needle tip–collector distance | Decreases nanofiber diameter [86] |
| Wire–collector distance | Reduces nanofiber mat density [88] |
| Needle length (needle-based) | Increases nanofiber diameter [86] |
| Needle diameter (needle-based) | Increases nanofiber diameter [89] |
| Shape of the needle tip | Circular collection zone only for non-beveled needle [86] |
| Flow rate | Unstable spinning/no spinning at too low flow rates, defective fibers, and even electrospraying at too high flow rates [90,91] |
| Electric field strength | Increases or decreases fiber diameter, depending on needle–collector (wire–collector) distance [91,92,93,94] |
| Humidity | Reduces evaporation of solvent, eventually making spinning impossible or creating porous nanofibers [88,95] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mpofu, N.S.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A.; Ehrmann, G. Wearable Electrospun Nanofibrous Sensors for Health Monitoring. Micro 2024, 4, 798-822. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040049
Mpofu NS, Blachowicz T, Ehrmann A, Ehrmann G. Wearable Electrospun Nanofibrous Sensors for Health Monitoring. Micro. 2024; 4(4):798-822. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleMpofu, Nonsikelelo Sheron, Tomasz Blachowicz, Andrea Ehrmann, and Guido Ehrmann. 2024. "Wearable Electrospun Nanofibrous Sensors for Health Monitoring" Micro 4, no. 4: 798-822. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040049
APA StyleMpofu, N. S., Blachowicz, T., Ehrmann, A., & Ehrmann, G. (2024). Wearable Electrospun Nanofibrous Sensors for Health Monitoring. Micro, 4(4), 798-822. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040049








