Rapid Synthesis of Non-Toxic, Water-Stable Carbon Dots Using Microwave Irradiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis/Preparation of C-Dots
2.3. Characterization of C-Dots
2.4. Toxicity Test
3. Results and Discussion
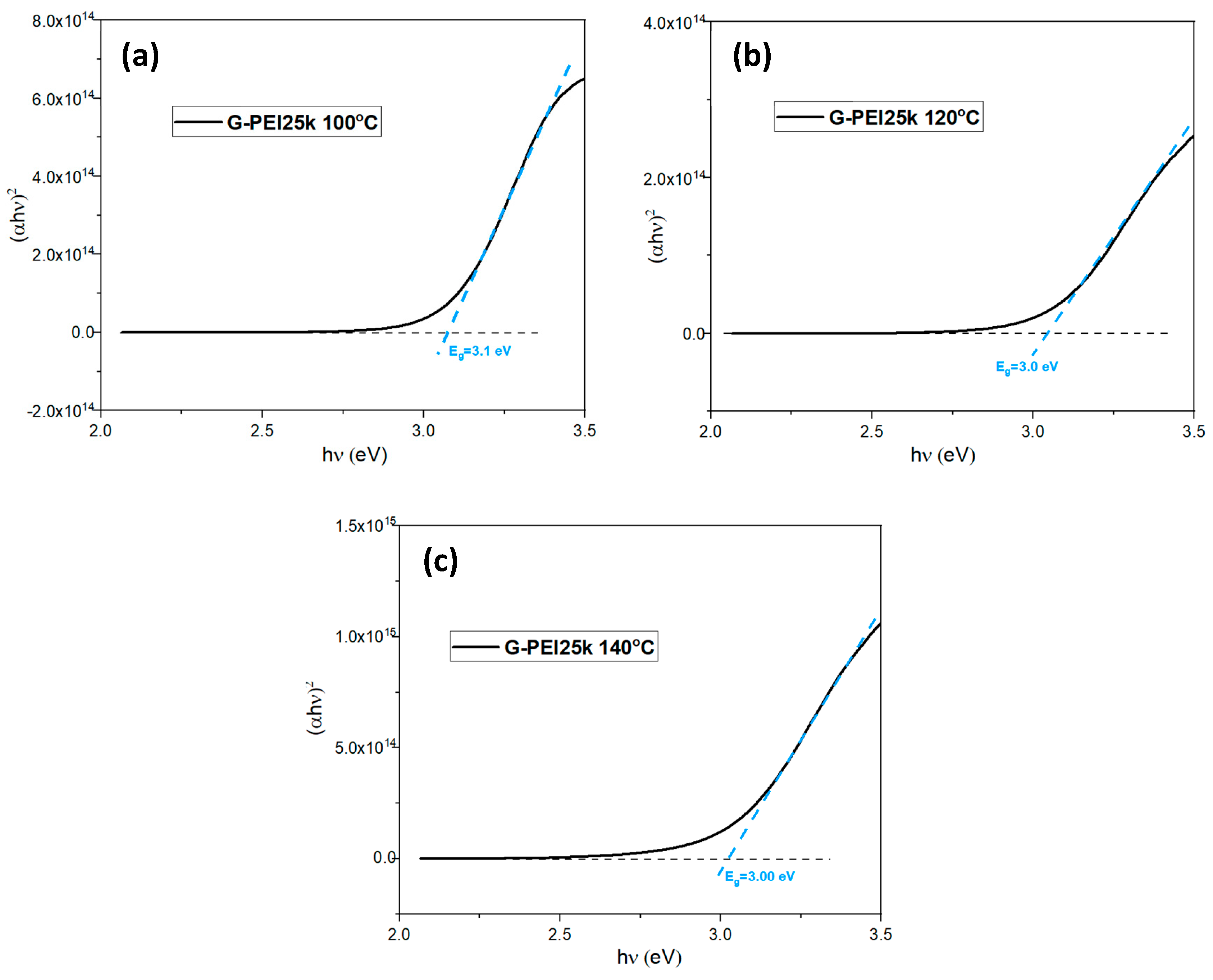
3.1. Morphological, Compositional, and Optical Characterization
3.2. Toxicity Test in Brine Shrimp
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Qi, W.; Sun, K. Luminescence of Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Application in Biochemistry. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raut, N.S.; Umekar, M.J.; Dhoble, S.J. Quantum Dots: Novel Approach for Biological Imaging. In Quantum Dots; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 477–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cai, W.; Li, W.; Sreeprasad, T.S.; He, Z.; Ong, W.-J.; Li, N. Two-Dimensional Quantum Dots: Fundamentals, Photoluminescence Mechanism and Their Energy and Environmental Applications. Mater. Today Energy 2018, 10, 222–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayen, B.; Palchoudhury, S.; Chowdhury, J. Carbon Dots: A Mystic Star in the World of Nanoscience. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 3451307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibhute, A.; Patil, T.; Gambhir, R.; Tiwari, A.P. Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis Methods, Functionalization and Biomedical Applications. Appl. Surf. Sci 2022, 11, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, P.; Chauhan, K.; Hirata, G.A. Progress on Carbon Dots and Hydroxyapatite Based Biocompatible Luminescent Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 101482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthupandi, M.; Varatharajan, P.; Shameem Banu, I.B.; Hafiz Mamat, M.; Vasimalai, N. White Light Emitting Diode and Anti-Counterfeiting Applications of Microwave Assisted Synthesized Green Fluorescent Carbon Dots Derived from Waste Curry Leaves. Results Opt. 2022, 8, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayal, A.; Dawane, V.; Yadav, V.K.; Yadav, K.K.; Khan, S.H. State of Art Technology: Synthesis of Carbon Dots and Their Potential Applications in Biomedical, Research and Environmental Remediation. Mater. Sci. 2021. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodhya, D. Recent Progress on Detection of Bivalent, Trivalent, and Hexavalent Toxic Heavy Metal Ions in Water Using Metallic Nanoparticles: A Review. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Li, J.-M.; Ji, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Miao, A.-J. Bioaccumulation Determines the Toxicity of Carbon Dots to Two Marine Dinoflagellates. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Molaei, R.; Alizadeh, A. Carbon Dots Embedded Bacterial Cellulose Membrane as Active Packaging: Toxicity, in Vitro Release and Application in Minced Beef Packaging. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, F.; Guo, R.; Ji, R.; Chen, J. Carbon Quantum Dot-Induced Developmental Toxicity in Daphnia Magna Involves Disturbance of Symbiotic Microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Song, L.; Li, S.; Tan, M. Carbon Quantum Dots from Roasted Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.): Formation, Biodistribution and Cytotoxicity. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Lv, X.; Zheng, G.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z. Effects of Carbon Quantum Dots on Aquatic Environments: Comparison of Toxicity to Organisms at Different Trophic Levels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14445–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, Y.; Na, X.; Bi, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Tan, M. Fluorescent Carbon Dots in Baked Lamb: Formation, Cytotoxicity and Scavenging Capability to Free Radicals. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, D.; Kobaisi, M.A.; Hocking, R.K.; Fox, B. Properties, Synthesis, and Applications of Carbon Dots: A Review. Carbon Trends 2023, 12, 100276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, A.M.A.; Piliang, A.F.R.; Goei, R.; Ramadhan, H.R.; Gea, S. Synthesis, Properties, and Utilization of Carbon Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts on Degradation of Organic Dyes: A Mini Review. Catal. Commun. 2024, 187, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.K.; Tripathi, A.; Taufeeq, A.; Dar, A.H.; Samrot, A.V.; Rustagi, S.; Malik, S.; Bhattacharya, T.; Kovacs, B.; Shaikh, A.M. Significance and Applications of Carbon Dots in Anti Cancerous Nanodrug Conjugate Development: A Review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 19, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansili, N. Review on Synthesis and Properties of Carbon Dots with Emphasis to Combat Environmental Toxins. Environ. Adv. 2024, 16, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Shibu, S.N.; Poelman, D.; Badyal, A.K.; Kunti, A.K.; Swart, H.C.; Menon, S.G. Recent Advances in Microwave Synthesis for Photoluminescence and Photocatalysis. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmandfard, M.; Kashani-Bozorg, S.F.; Barati, M.R.; Sarfarazijami, S. A Novel Strategy for Fast and Facile Synthesis of Bioactive Bredigite Nanoparticles Using Microwave-Assisted Method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Shelke, S.N.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Microwave-Assisted Chemistry: Synthetic Applications for Rapid Assembly of Nanomaterials and Organics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulvasu, C.; Jennifer, S.M.; Prabhu, D.; Chandhirasekar, D. Toxicity Effect of Silver Nanoparticles in Brine Shrimp Artemia. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 256919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varó, I.; Perini, A.; Torreblanca, A.; Garcia, Y.; Bergami, E.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Corsi, I. Time-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Nanoparticles in Brine Shrimp Artemia Franciscana at Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabi, S.; Ramazani, A.; Hamidi, M.; Naji, T. Artemia Salina as a Model Organism in Toxicity Assessment of Nanoparticles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Wang, W.; Wu, H.; Fang, F.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S. Polyethyleneimine Modified Fluorescent Carbon Dots and Their Application in Cell Labeling. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 100, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappe, C.O.; Dallinger, D. Microwaves in Organic and Medicinal Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Bai, H.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Yue, T. Fluorescent Detection of Tetracycline in Foods Based on Carbon Dots Derived from Natural Red Beet Pigment. LWT 2022, 157, 113100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, D. Green Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots Functionalized with Polyethyleneimine, and Their Application to Aptamer-Based Determination of Thrombin and ATP. Microchim Acta. 2019, 186, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wei, F.; Wu, X.; Zhou, P.; Chen, Q.; Cen, Y.; Xu, G.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, A.; Hu, Q. PEI Modified Orange Emissive Carbon Dots with Excitation-Independent Fluorescence Emission for Cellular Imaging and siRNA Delivery. Carbon 2021, 177, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, A.; Al-Qassar Bani Al-Marjeh, R.; Atassi, Y. Novel Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Prepared under Microwave-Irradiation for Highly Sensitive Detection of Mercury Ions. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramudita, R.; Marpongahtun; Gea, S.; Daulay, A.; Harahap, M.; Tan, Y.Z.; Goei, R.; Tok, A.I.Y. Synthesis of Fluorescent Citric Acid Carbon Dots Composites Derived from Empty Fruit Bunches of Palm Oil Tree and Its Anti-Bacterial Property. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, K.; Gaviria, M.I.; Arango, J.P.; Placido, J.; Bustamante, S.; Londoño, M.E.; Jaramillo, M. Synthesis, Characterization and Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Biochar-Derived Carbon Dots from Spruce Tree, Purple Moor-Grass and African Oil Palm. Processes 2021, 9, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubu, P.R.; Yam, F.K.; Igba, V.M.; Beh, K.P. Tauc-Plot Scale and Extrapolation Effect on Bandgap Estimation from UV–Vis–NIR Data—A Case Study of β-Ga2O3. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 290, 121576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.S.; Kim, J.M.; Jeong, S.; Ju, Y.; Won, S.J.; Choi, J.; Nam, S.; Molla, A.; Kim, J.; Song, J.K. Distinctive Optical Transitions of Tunable Multicolor Carbon Dots. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinterberger, V.; Damm, C.; Haines, P.; Guldi, D.M.; Peukert, W. Purification and Structural Elucidation of Carbon Dots by Column Chromatography. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8464–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Turnbull, M.J.; Nie, Y.; Sun, X.; Ding, Z. Band Structures of Blue Luminescent Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots by Synchrotron-Based XPS. Surf. Sci. 2018, 676, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Shi, H.; Yao, Z.; Liu, E.; Hu, X.; Guo, P.; Xue, W.; Fan, J. Carbon Quantum Dots Prepared by Pyrolysis: Investigation of the Luminescence Mechanism and Application as Fluorescent Probes. Dyes Pigment. 2022, 204, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shen, X.; Xing, D. Carbon Quantum Dots as ROS-Generator and -Scavenger: A Comprehensive Review. Dyes Pigment. 2023, 208, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Salazar, M.; Diaz-Sosa, V.R.; Cárdenas-Chávez, D.L. Toxicological Effect and Enzymatic Disorder of Non-Studied Emerging Contaminants in Artemia Salina Model. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.A.; Sorgeloos, P.; Trotman, C.N.A. (Eds.) Artemia Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soledad-Flores, O.; Bailón-Ruiz, S.J.; Román-Velázquez, F. Rapid Synthesis of Non-Toxic, Water-Stable Carbon Dots Using Microwave Irradiation. Micro 2024, 4, 659-669. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040040
Soledad-Flores O, Bailón-Ruiz SJ, Román-Velázquez F. Rapid Synthesis of Non-Toxic, Water-Stable Carbon Dots Using Microwave Irradiation. Micro. 2024; 4(4):659-669. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040040
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoledad-Flores, Olga, Sonia J. Bailón-Ruiz, and Félix Román-Velázquez. 2024. "Rapid Synthesis of Non-Toxic, Water-Stable Carbon Dots Using Microwave Irradiation" Micro 4, no. 4: 659-669. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040040
APA StyleSoledad-Flores, O., Bailón-Ruiz, S. J., & Román-Velázquez, F. (2024). Rapid Synthesis of Non-Toxic, Water-Stable Carbon Dots Using Microwave Irradiation. Micro, 4(4), 659-669. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4040040






