Nano-Materials-Based Printed Glucose Sensor for Use in Incontinence Products for Health-Care Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
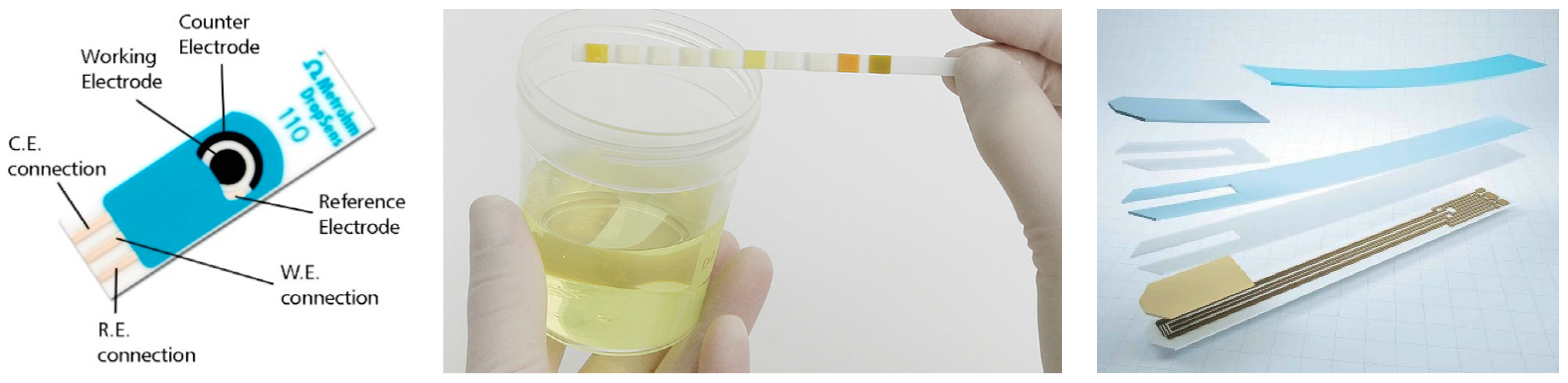
2. The State-of-the-Art Glucose Sensors
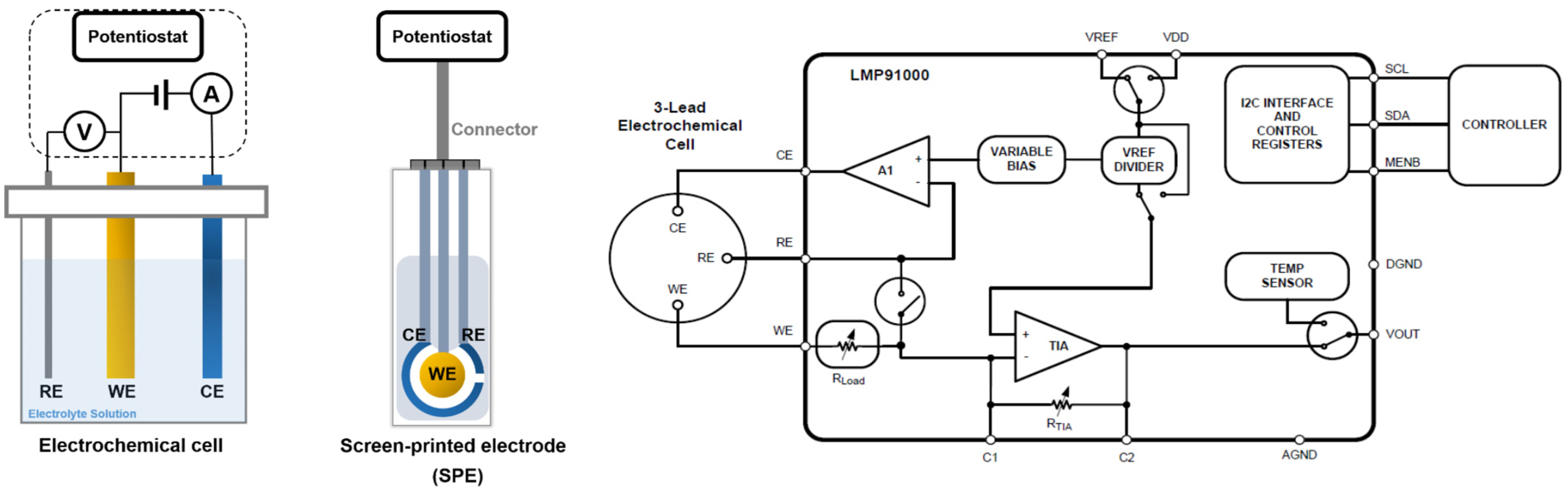
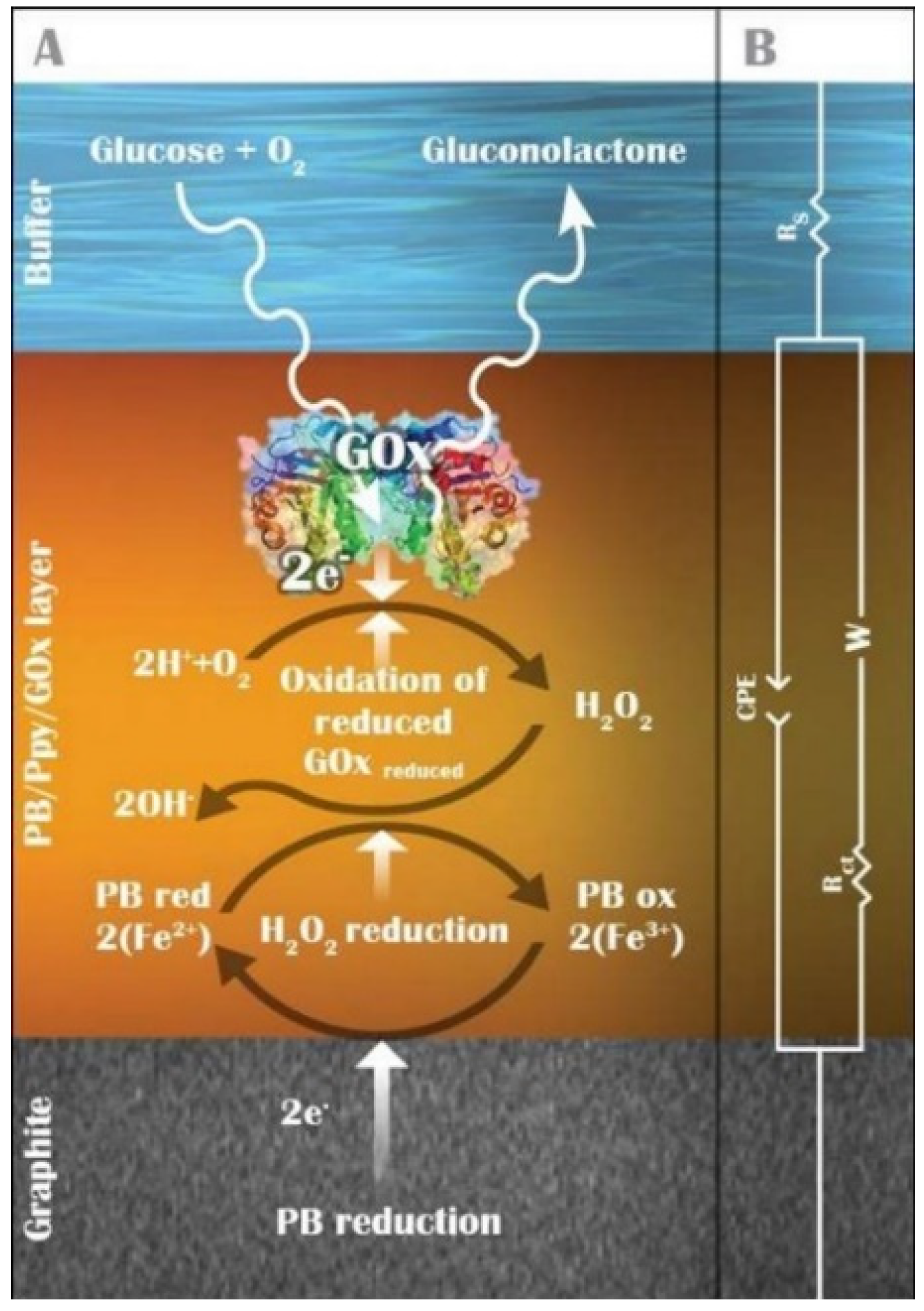
3. Electrochemical Detection of Glucose
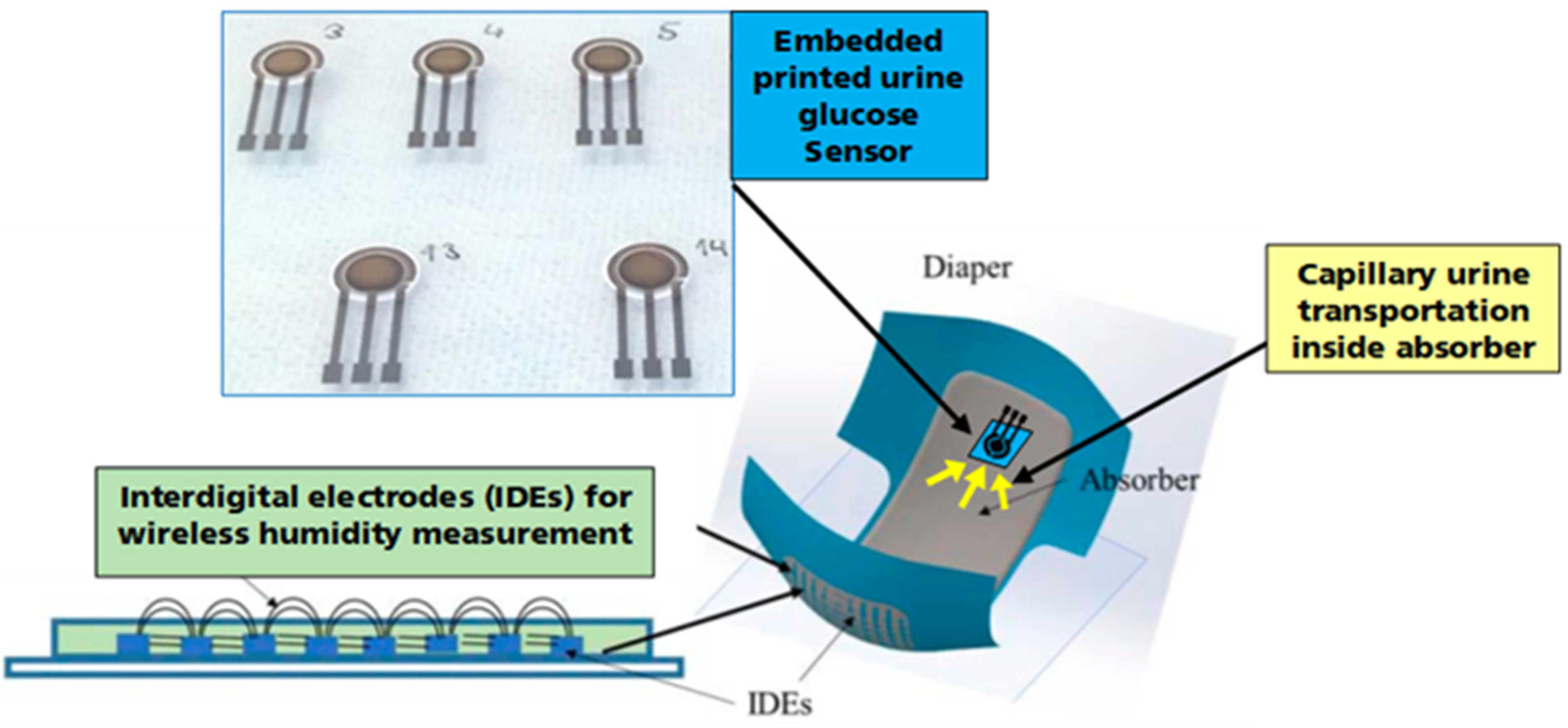
4. Embedded Urine Glucose Sensor
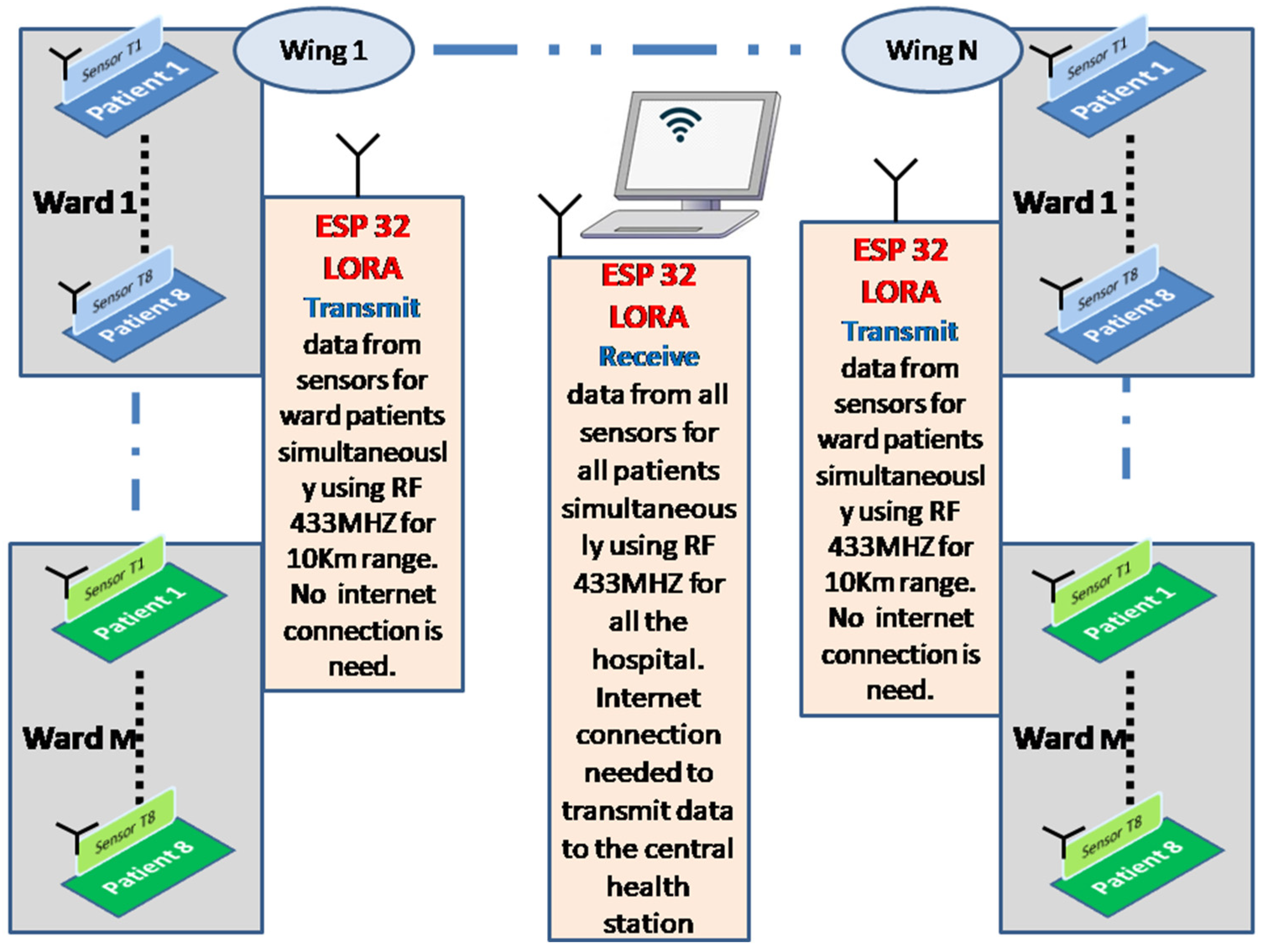
5. Readout and Data Acquisition Circuits
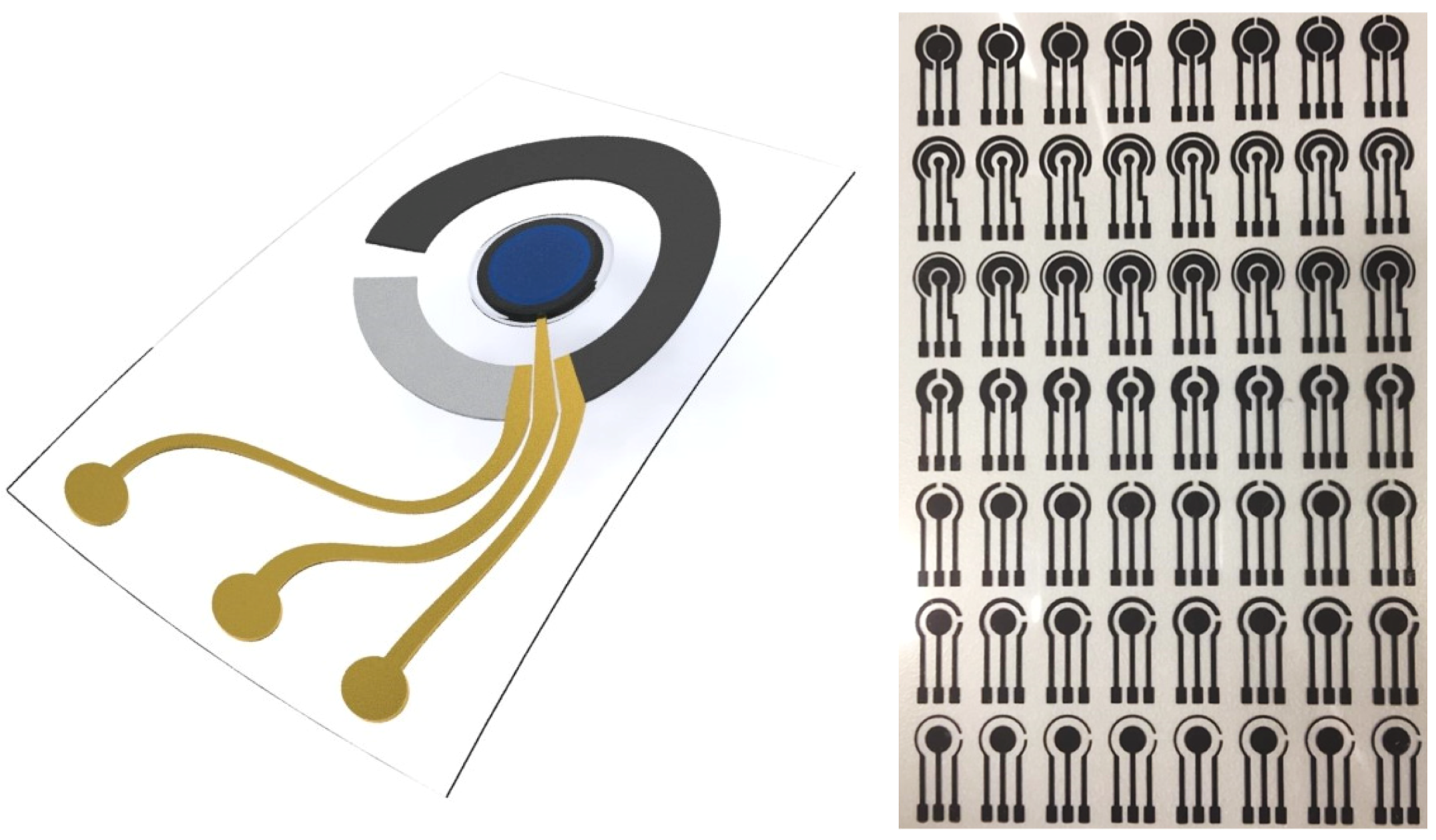
6. Fabrication of Printed Urine Glucose Sensor
6.1. Screen-Printed Electrodes
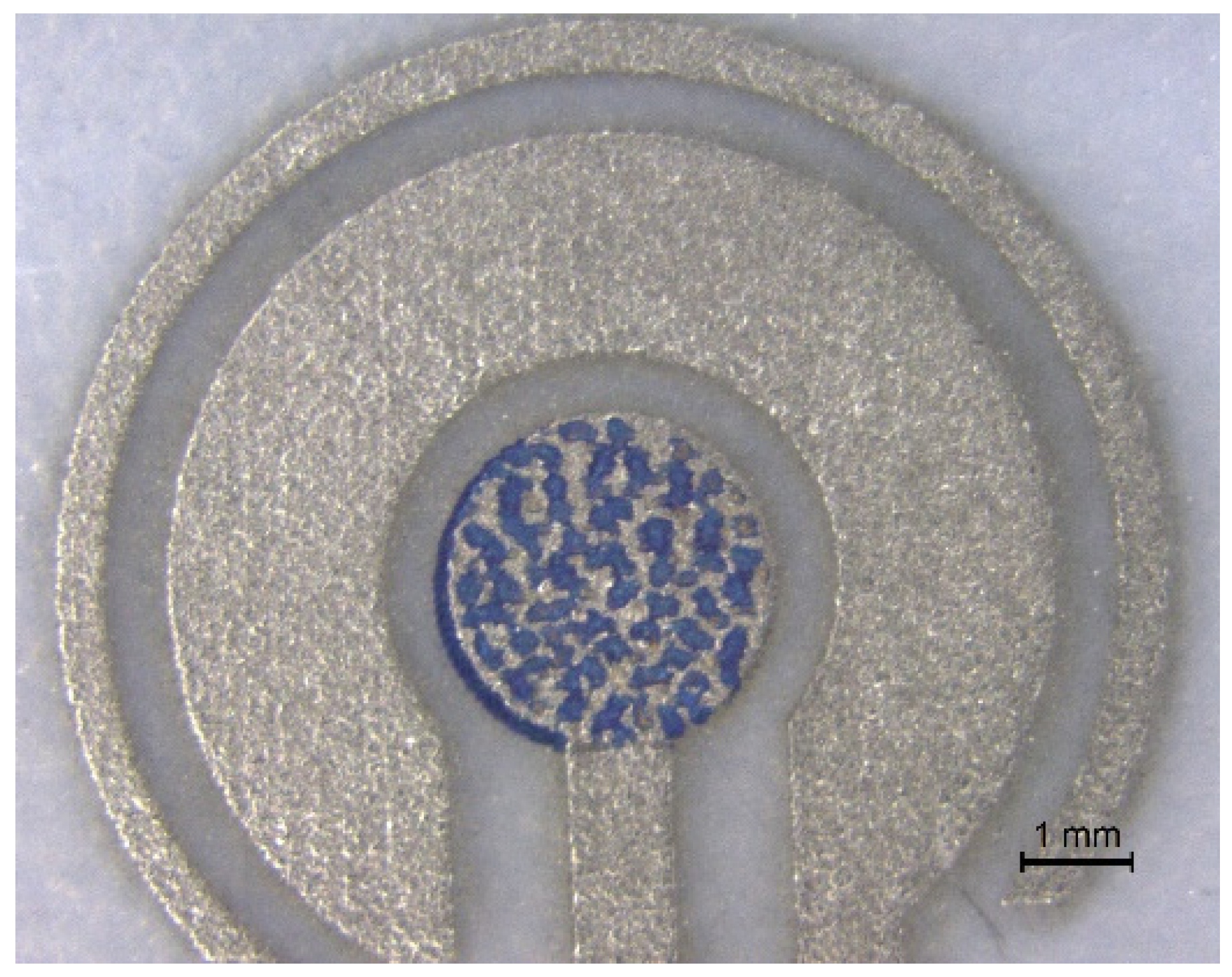
6.2. Enhancement of Sensor Performance Using a Printed Mediator
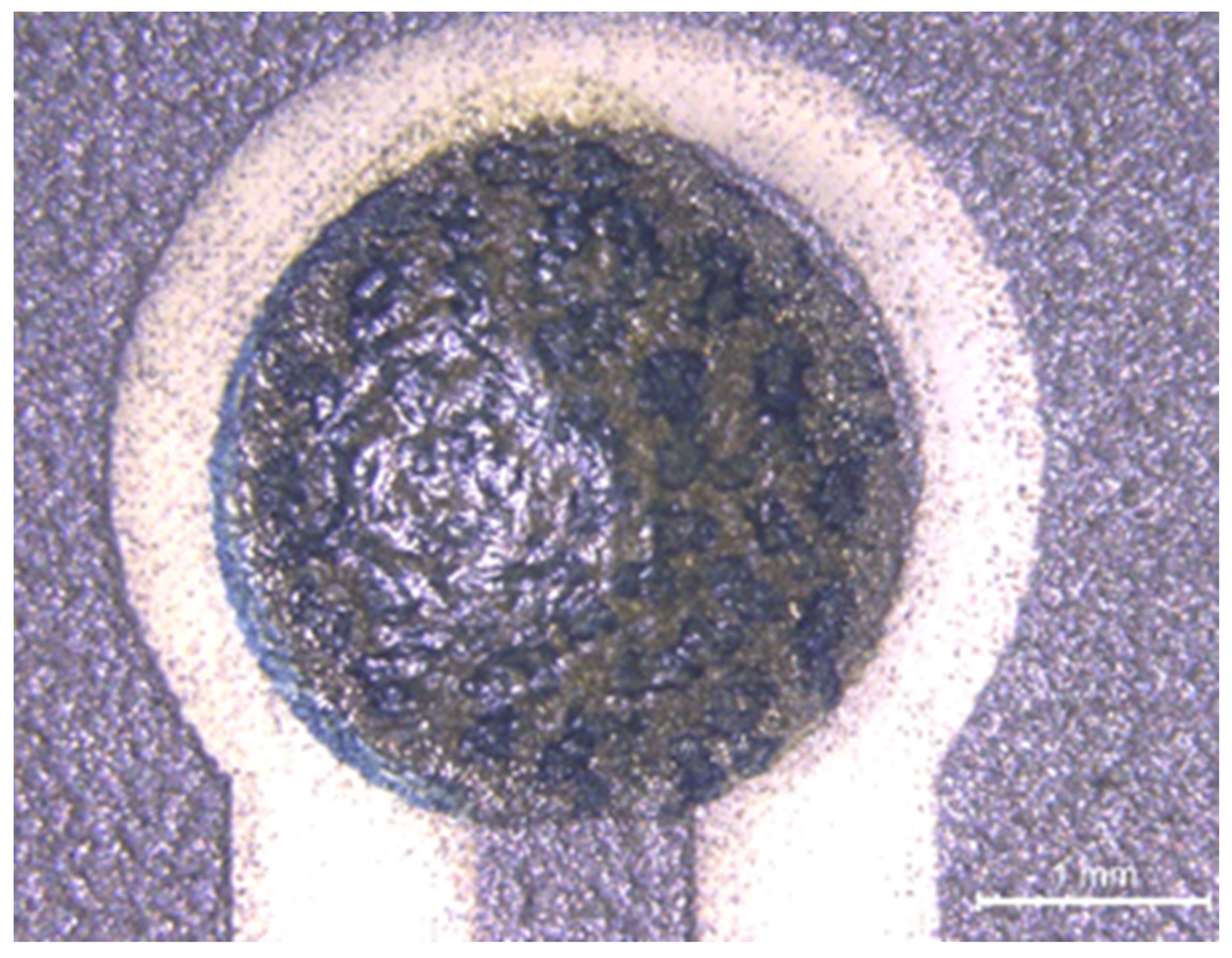
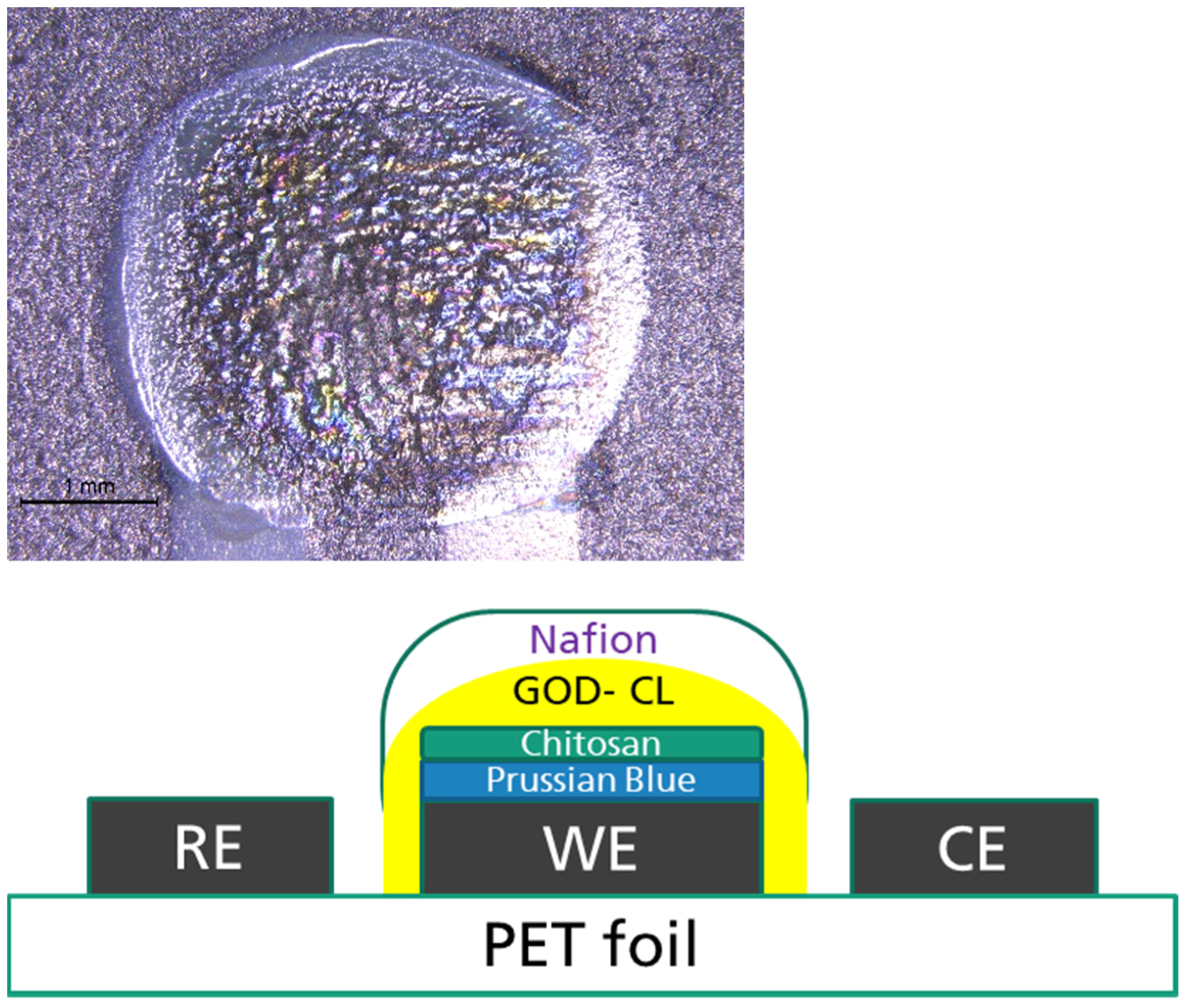
6.3. Biofunctionalization via Drop Casting
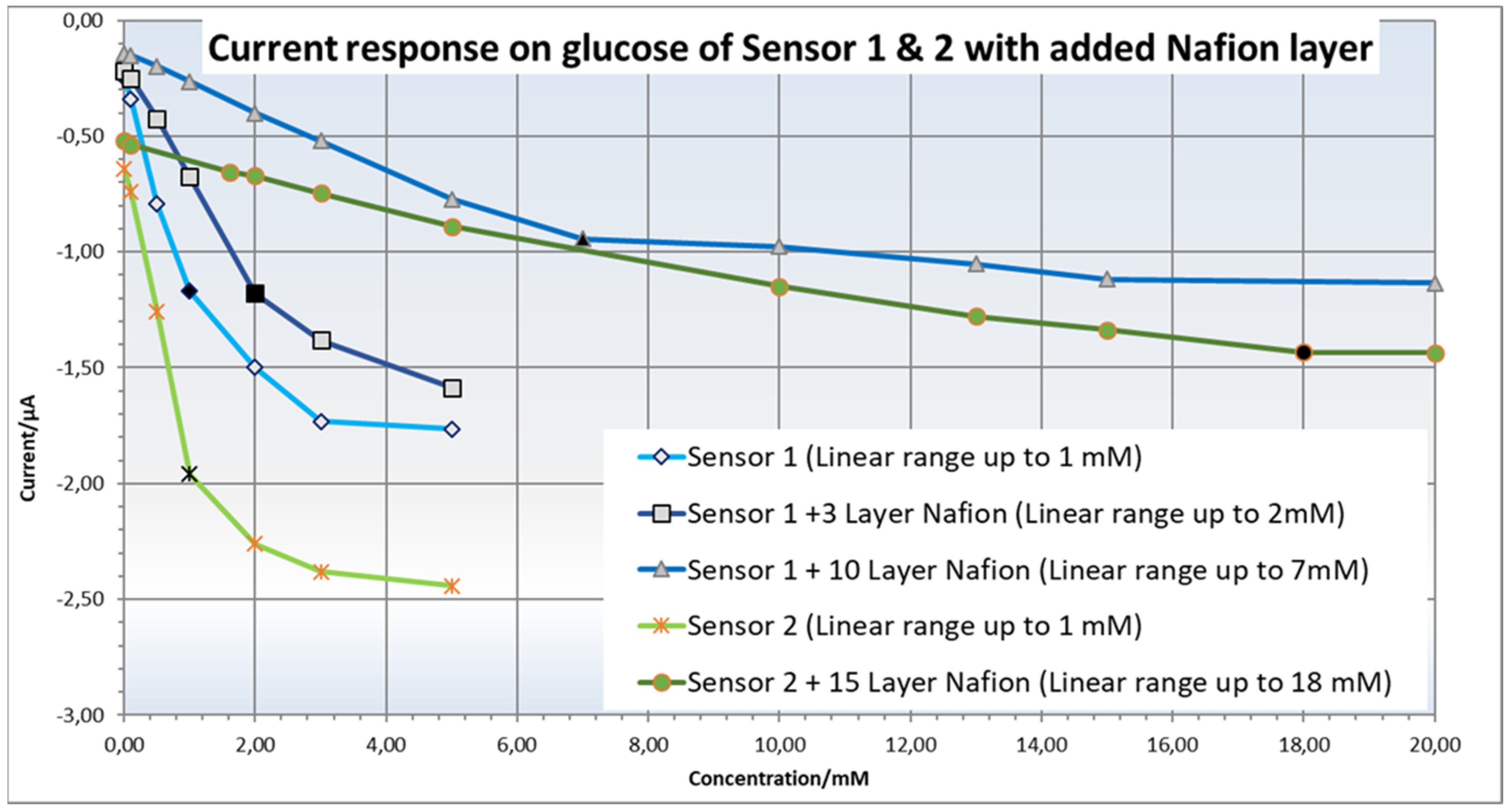
6.4. Printing of a Barrier Membrane against Interfering Substances and Working Range Adjustment
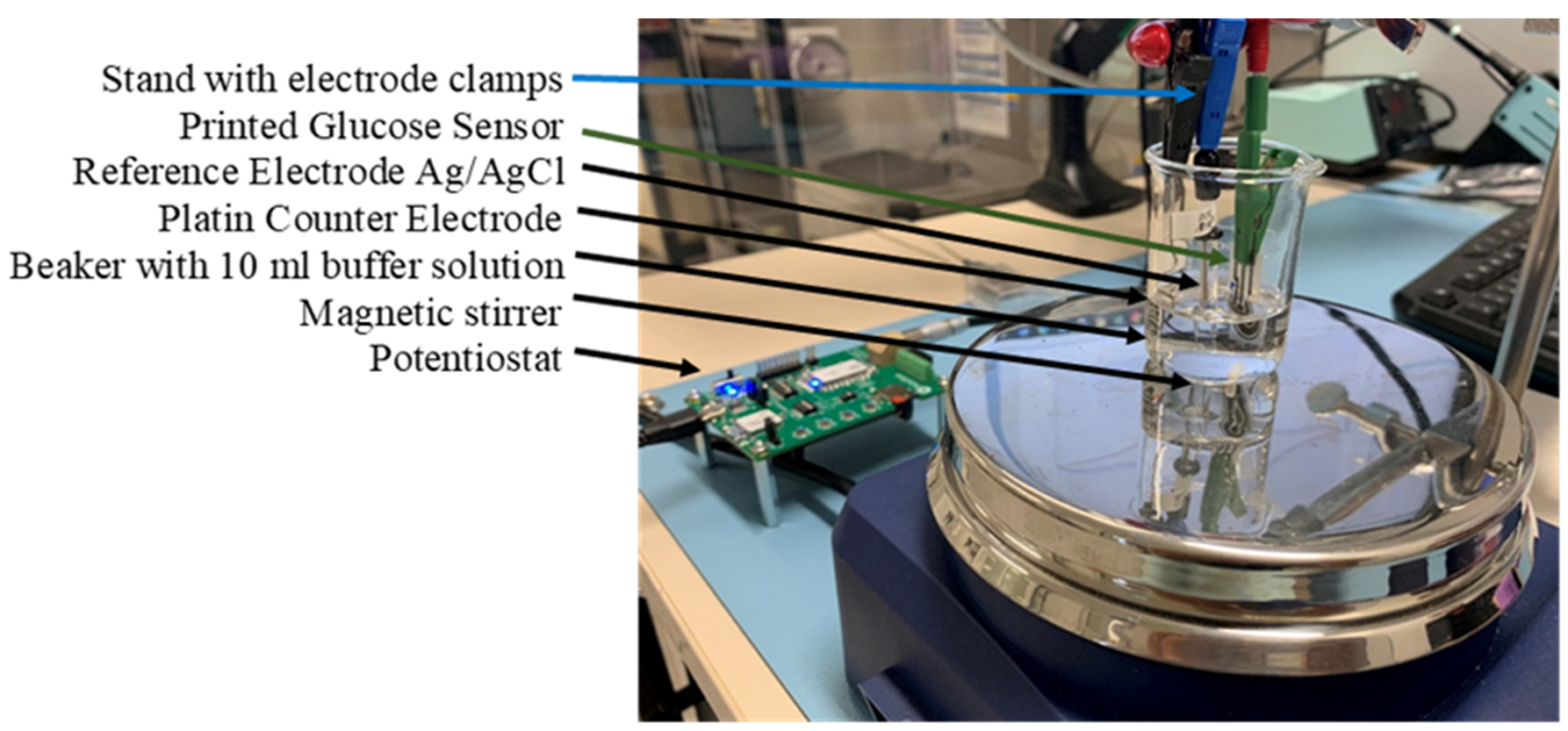
7. Experimental Setup
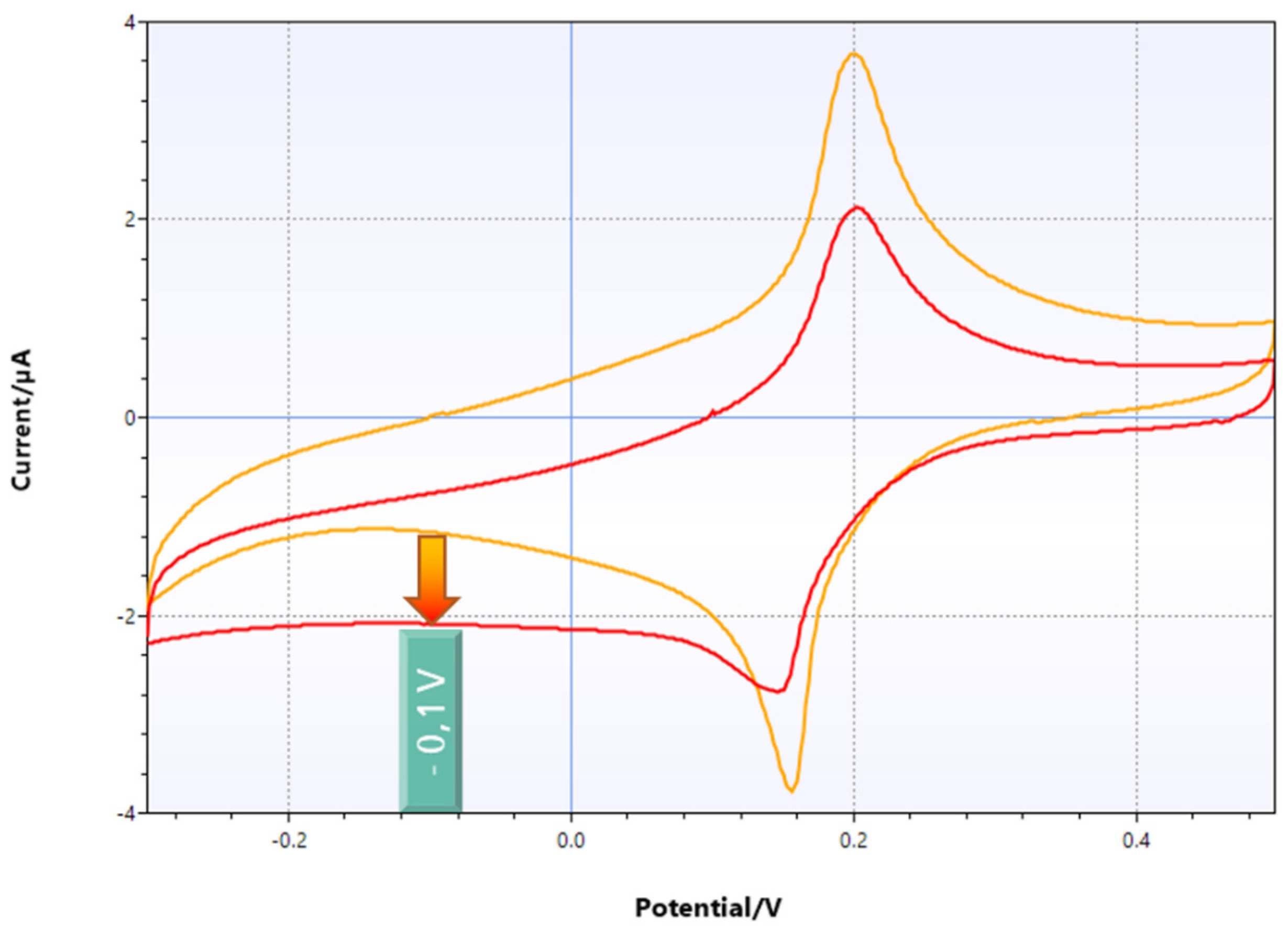
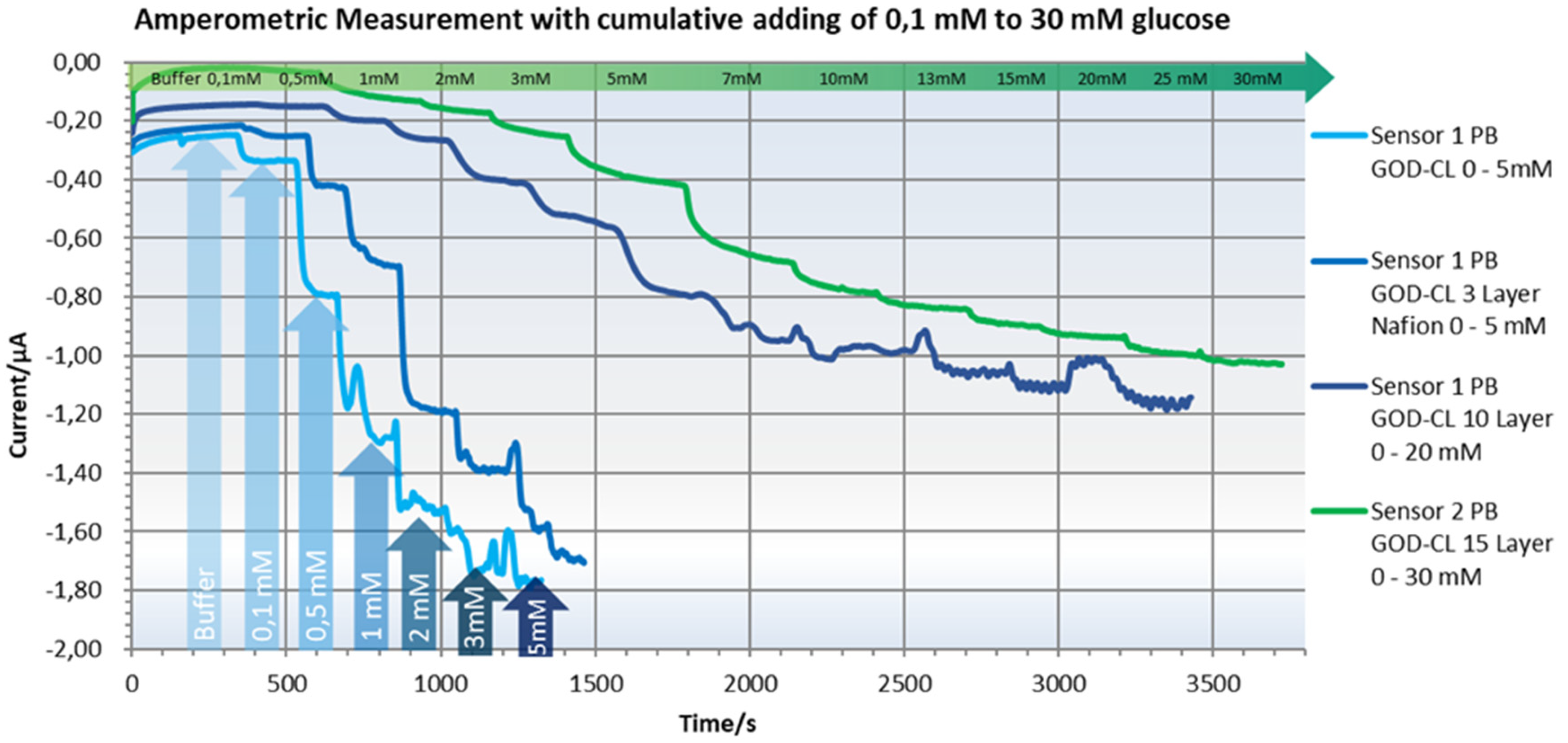
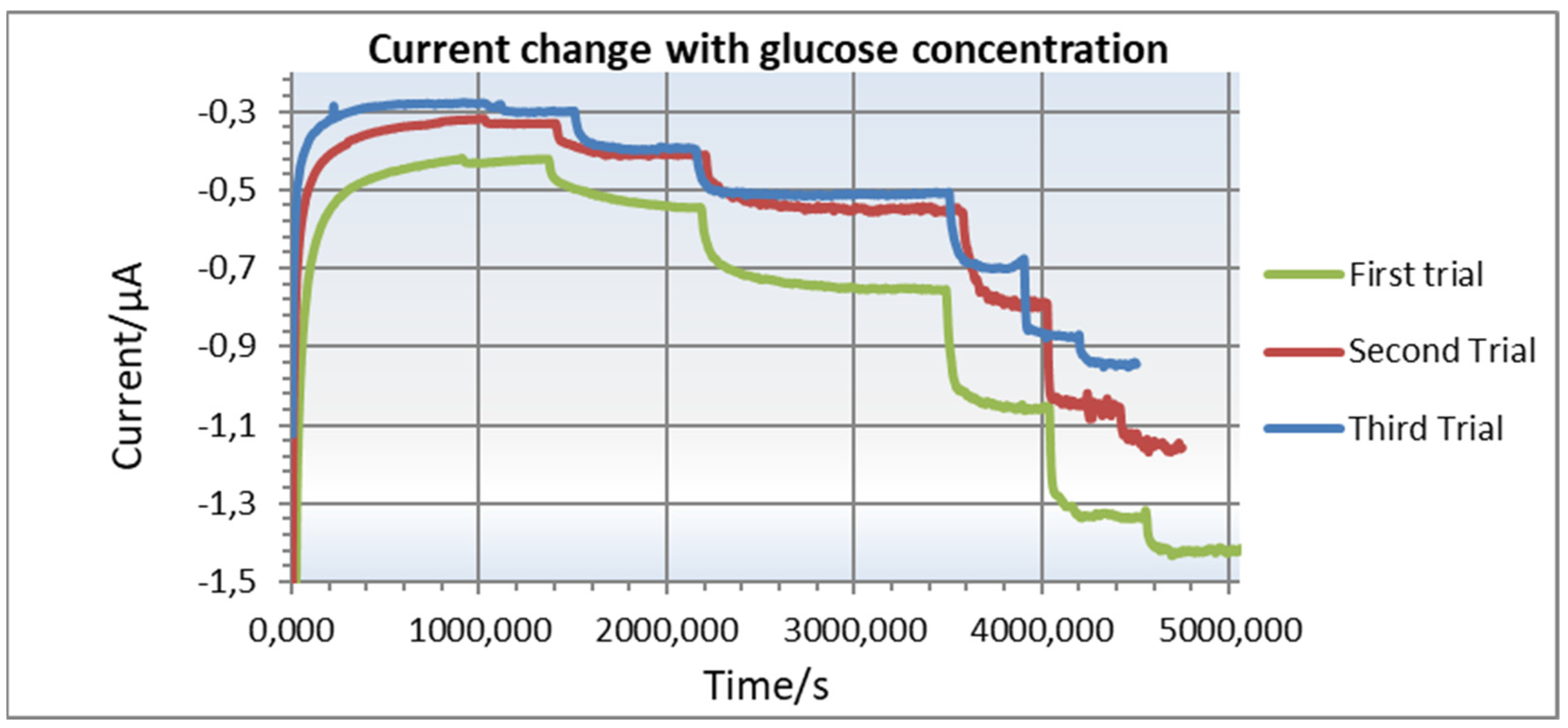
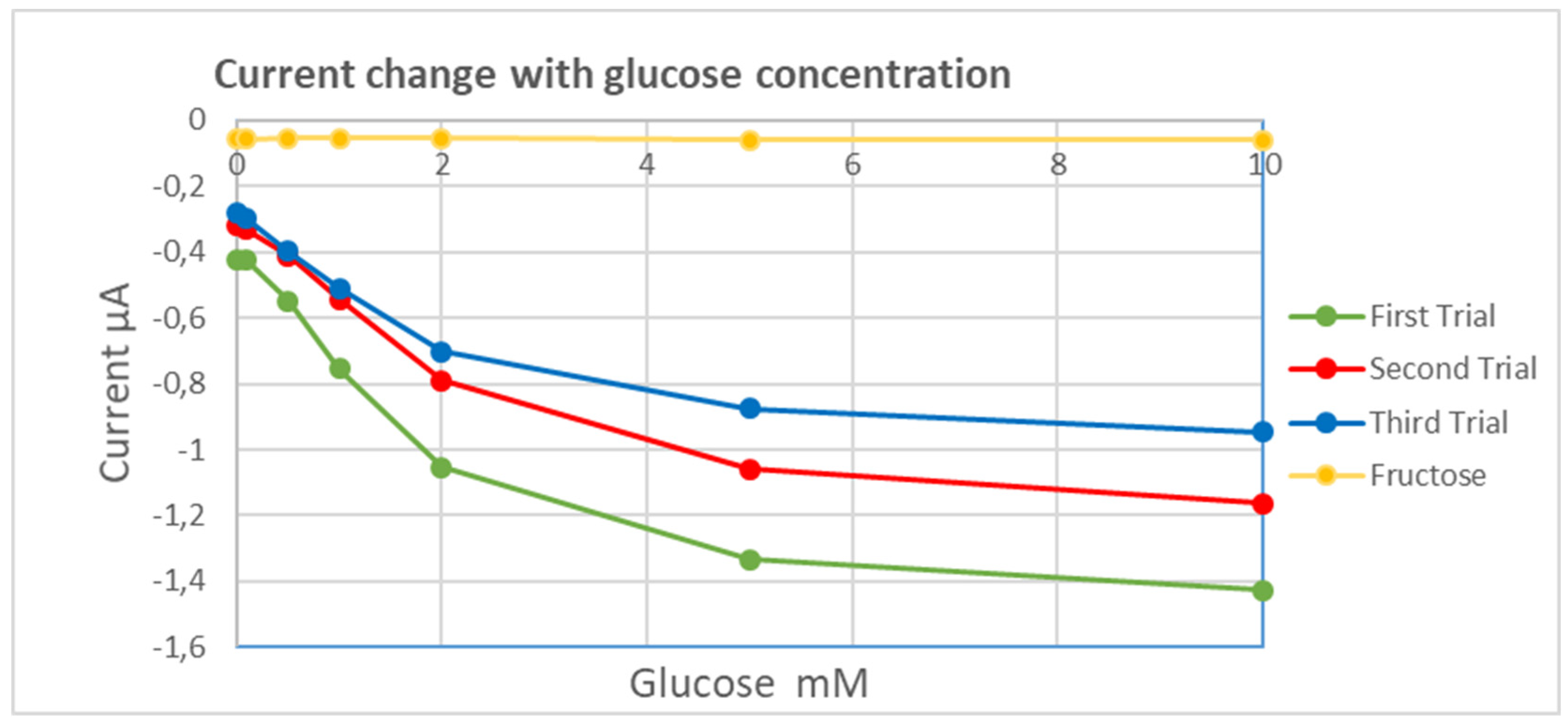
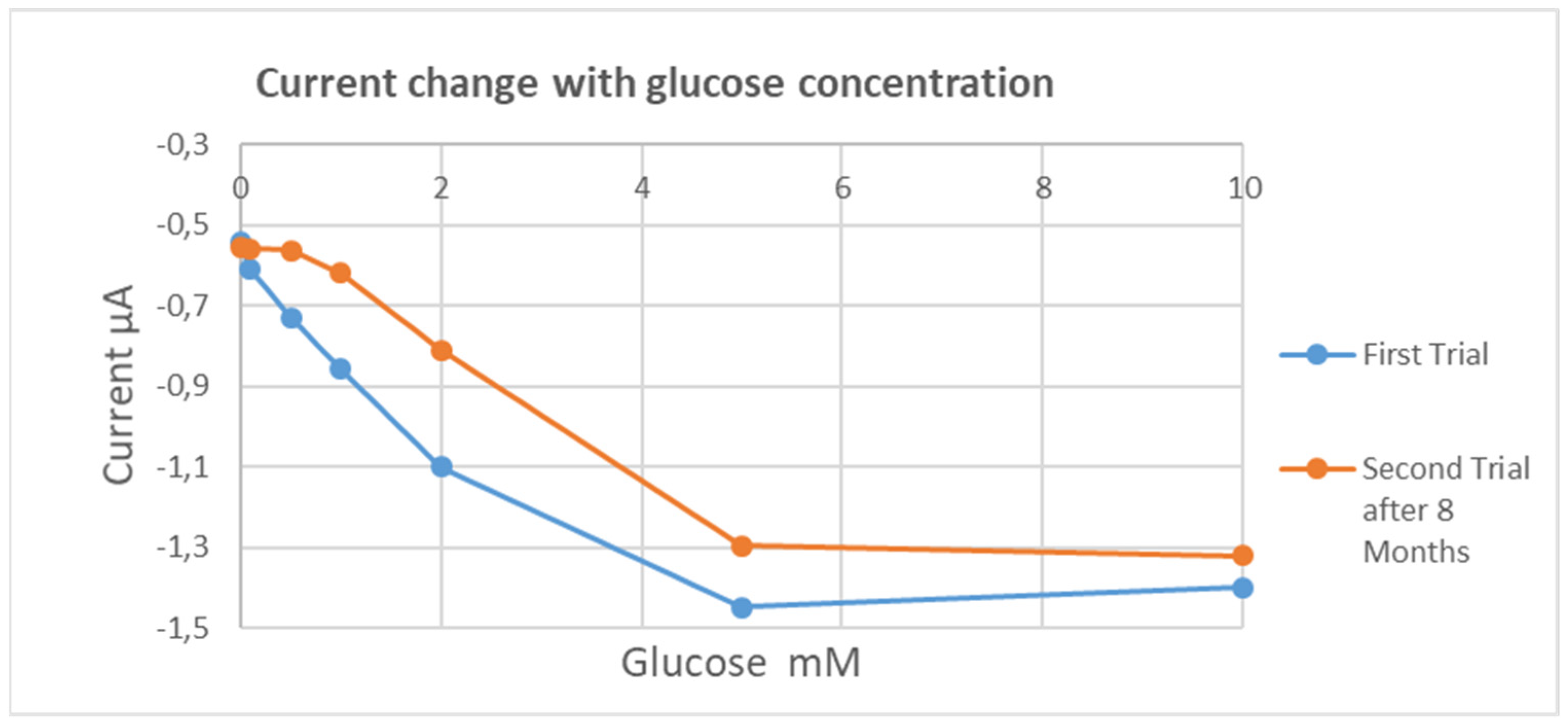
8. Experimental Results
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.R.; Hambleton, I.; Beagley, J.; Linnenkamp, U.; Shaw, J.E. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, T.; Brinks, R.; Hoyer, A.; Kuss, O.S.; Rathmann, W. The Prevalence and Incidence of Diabetes in Germany. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2016, 113, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Martínez, M.; González-González, M.; Martagón, A.J.; Hlavinka, V.; Willson, R.C.; Rito-Palomares, M. Recent Developments in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Screening of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2022, 22, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitanda, I.; Fujimura, Y.; Nohara, S.; Hoshi, Y.; Itagaki, M.; Tsujimura, S.J. Paper-Based Disk-Type Self-Powered Glucose Biosensor Based on Screen-Printed Biofuel Cell Array. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B1063–B1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.labce.com/spg506346_clinical_significance_of_glucose_in_the_urine.aspx (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Ngo, H.-D.; Bäuscher, M.; Schiffer, M.; Medinaa, D.M.; Jorcano, J.L.; Acedo, P.; Atta, R.M.H. Development, Simulation and Characterization of a novel Incontinence Sensor System using 2D-Printing Technology with Conductive Polymer PEDOT:PSS. In Printed and Flexible Sensor Technology: Fabrication and Applications; Hg. von Institute of Physics IOP: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bäuscher, M.; Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Mackowiak, P.; Merchau, N.; Ehrmann, O.; Schneider-Ramelow, M.; Lang, K.D.; Ngo, H.D. Simulation And Electrical Characterization of A Novel 2D-Printed Incontinence Sensor With Conductive Polymer PEDOT:PSS For Medical Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC), Singapore, 4–7 December 2018; pp. 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, H.D.; Hoang, T.H.; Baeuscher, M.; Wang, B.; Mackowiak, P.; Grabbert, N.; Weiland, T.; Ehrmann, O.; Lang, K.D.; Schneider-Ramelow, M.; et al. A Novel Low Cost Wireless Incontinence Sensor System (Screen-Printed Flexible Sensor System) for Wireless Urine Detection in Incontinence Materials. Proceedings 2018, 2, 716. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Xie, X.; Tan, Q.; Kang, H.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Feng, G. Blood glucose sensors and recent advances: A review. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2022, 15, 2230003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villena Gonzales, W.; Mobashsher, A.T.; Abbosh, A. The Progress of Glucose Monitoring—A Review of Invasive to Minimally and Non-Invasive Techniques, Devices and Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Carbon-nanotube based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Voeroes, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical biosensors-sensor principles and architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Barfidokht, A.; Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: An updated review (2010–2020). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7671–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Shao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jin, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase assembled on graphene and application to glucose detection. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 8606–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, X.; Heinig, N.F.; Thomas, J.P.; Zhang, L.; Leung, K.T. Nonenzymatic Saliva-Range Glucose Sensing Using Electrodeposited Cuprous Oxide Nanocubes on a Graphene Strip. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4790–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.T.; Ashfaq, S.; Bokov, D.O.; Alanazi, A.M.; Hachem, K.; Suksatan, W.; Sillanpää, M. High-Sensitivity Biosensor Based on Glass Resonance PhC Cavities for Detection of Blood Component and Glucose Concentration in Human Urine. Coatings 2021, 11, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.S.; Agarwal, B.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, C.; Roy, K.; Chinnappan, A.; Narayan, R.J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ghosh, R. Recent Advancement in Biofluid-Based Glucose Sensors Using Invasive, Minimally Invasive, and Non-Invasive Technologies: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redon, P.; Shahzad, A.; Iqbal, T.; Wijns, W. Development of a New Detection Algorithm to Identify Acute Coronary Syndrome Using Electrochemical Biosensors for Real-World Long-Term Monitoring. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://diagnostics.roche.com/global/en/products/instruments/combur-chemstrip-ins-656.html (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Available online: http://main.diabetes.org/dforg/pdfs/archive/2012-07-anatomy-of-a-test-strip.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Kim, H.Y.; Jang, K.J.; Veerapandian, M.; Kim, H.C.; Seo, Y.T.; Lee, K.N.; Lee, M.-H. Reusable urine glucose sensor based on functionalized graphene oxide conjugated Au electrode with protective layers. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 3, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Lee, A.-R. Recent developments in blood glucose sensors. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 2, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abikshyeet, P.; Ramesh, V.; Oza, N. Glucose estimation in the salivary secretion of diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2009, 5, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Padmashree, S.; Jayalekshmi, R. Correlation of salivary glucose, blood glucose and oral candidal carriage in the saliva of type 2 diabetics: A case–control study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2014, 5, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.T.; Gupta, S.; Sunitha, J.; Dawar, G.; Sinha, N.; Rallan, N.S. Correlation of salivary glucose level with blood glucose level in diabetes mellitus. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2017, 21, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, C.; Mak, J.W. Salivary glucose in monitoring glycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2017, 16, 2251–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.; Kim, H.T.; Park, Y.J.; Park, S.R.; Lee, M.-H. Fabrication of Repeatedly Usable Pt-Electrode Chip Coated with Solidified Glucose Oxidase and Ascorbate Oxidase for the Quantification of Glucose in Urine. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2019, 3, 1500104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezhhan, H.; Akhond, M.; Shamsipur, M. A novel nanoplatform encapsulating glucose oxidase for spectrophotometric biosensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, A.; Gabriel, G.; Villa, R.; del Campo, F.J. Inkjet-printed electrochemical sensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.; Park, S. Review of urinary continence care products using sensor technology to improve effectiveness. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2019, 233, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Feng, W.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, L.; Nie, Y. A promising method for diabetes early diagnosis via sensitive detection of urine glucose by Fe Pd/rGO. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 164, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadifar, M.; Tahernia, M.; Choi, S. An Equipment-Free, Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Visual Monitoring of Glucose Levels in Urine. SLAS Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2019, 24, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekcin, M.; Sayar, E.; Yalcin, M.K.; Bahadir, S.K. Wearable and Flexible Humidity Sensor Integrated to Disposable Diapers for Wetness Monitoring and Urinary Incontinence. Electronics 2022, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.; Vyas, C.; Grieve, B.; Bartolo, P. Recent Advances in Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, G.V.; Nikolakov, D.P.; Ruskova, I.N.; Gieva, E.E.; Spasova, M.L. Healthcare Sensing and Monitoring. In Enhanced Living Environments; Lecture Notes in Computer, Science; Ganchev, I., Garcia, N., Dobre, C., Mavromoustakis, C., Goleva, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; p. 11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.D.; Timchalk, C.A. Nanotechnology-based electrochemical sensors for biomonitoring chemical exposures. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, R.S.; Bera, R.K.; Raj, C.R. Nanomaterial-based functional scaffolds for amperometric sensing of bioanalytes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3431–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putzbach, W.; Ronkainen, N.J. Immobilization Techniques in the Fabrication of Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors: A Review. Sensors 2013, 13, 4811–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, P.M.; Gong, P.; Levicky, R.; Shepard, K.L. Active CMOS sensor array for electrochemical biomolecular detection. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.; Harrison, D.; Baltes, H. A CMOS Potentiostat for Amperometric Chemical Sensors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1987, 22, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakerow, R.; Kappert, H.; Spiegel, E.; Manoli, Y. Low Power Single Chip CMOS Potentiostat. In Proceedings of the International Solid-State Sensors and Actuators Conference-TRANSDUCERS’95, Eurosensors IX, Stockholm, Sweden, 25–29 June 1995; Volume 1, pp. 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Mulliken, G.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Thakor, N. VLSI potentiostat array for distributed electrochemical neural recording. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS 2002, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 26–29 May 2002; Volume 2, pp. 740–743. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.; O’Hare, D.; Chao, I.J.; Wei, H.W.; Liang, Y.F.; Liu, B.D.; Lee, M.H.; Lin, H.Y. Integrated potentiostat for electrochemical sensing of urinary 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid with molecularly imprinted poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-T.; Yuan, R.-T. Design of a portable mini potentiostat for electrochemical biosensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 25–26 March 2017; pp. 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LMP91000 Sensor AFE System: Configurable AFE Potentiostat for Low-Power Chemical-Sensing Applications. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/lmp91000.pdf?ts=1674208714033&ref_url=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Precision Analog Microcontroller with Chemical Sensor Interface. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/aducm355.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- High Precision, Impedance, and Electrochemical Front End. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ad5940-5941.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Damiati, S.; Schuster, B. Electrochemical Biosensors Based on S-Layer Proteins. Sensors 2020, 20, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyare, R. Internet of things: Ubiquitous home control and monitoring system using android based smart phone. Int. J. Internet Things 2013, 2, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nia, A.M.; Mozaffari-Kermani, M.; Sur-Kolay, S.; Raghunathan, A.; Jha, N.K. Energy-efficient long-term continuous personal health monitoring. IEEE Trans. Multi-Scale Comput. Syst. 2015, 1, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemdar, H.; Ersoy, C. Wireless sensor networks for healthcare: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2688–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosenia, A.; Sur-Kolay, S.; Raghunathan, A.; Jha, N.K. Wearable Medical Sensor-Based System Design: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Multi-Scale Comput. Syst. 2017, 3, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Fatima, I.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.K. Daily life activity tracking application for smart homes using android smartphone. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Advances Communication Technology (ICACT), Pyeong Chang, Republic of Korea, 19–22 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Valiūnienė, A.; Rekertaitė, A.I.; Ramanavičienė, A.; Mikoliūnaitė, L.; Ramanavičius, A. Fast Fourier transformation electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for the investigation of inactivation of glucose biosensor based on graphite electrode modified by Prussian blue, polypyrrole and glucose oxidase. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 532, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Cusenza, R.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Paper-based synthesis of Prussian Blue Nanoparticles for the development of whole blood glucose electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2018, 187, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lai, Z.; Wang, R.; Guo, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Planar Amperometric Glucose Sensor Based on Glucose Oxidase Immobilized by Chitosan Film on Prussian Blue Layer. Sensors 2002, 2, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihar, E.; Wustoni, S.; Pappa, A.M.; Salama, K.N.; Baran, D.; Inal, S. A fully inkjet-printed disposable glucose sensor on paper. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2018, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick, J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hwang, B.J. Biosensors Incorporating Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2015, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, M.; Cho, H.R.; Kang, T.; Shin, K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hubl, M.; Atta, R.M.; Kaufhold, R.; Wang, B.; Ngo, H.D. Nano-Materials-Based Printed Glucose Sensor for Use in Incontinence Products for Health-Care Applications. Micro 2023, 3, 521-536. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020035
Hubl M, Atta RM, Kaufhold R, Wang B, Ngo HD. Nano-Materials-Based Printed Glucose Sensor for Use in Incontinence Products for Health-Care Applications. Micro. 2023; 3(2):521-536. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleHubl, Moritz, Raghied M. Atta, Robin Kaufhold, Bei Wang, and Ha Duong Ngo. 2023. "Nano-Materials-Based Printed Glucose Sensor for Use in Incontinence Products for Health-Care Applications" Micro 3, no. 2: 521-536. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020035
APA StyleHubl, M., Atta, R. M., Kaufhold, R., Wang, B., & Ngo, H. D. (2023). Nano-Materials-Based Printed Glucose Sensor for Use in Incontinence Products for Health-Care Applications. Micro, 3(2), 521-536. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3020035






