Machine Learning Prediction of Henry’s Law Constant for CO2 in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Molecular Descriptors
2.3. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.4. Model Validation
2.5. SHAP-Based Leverage
3. Results and Discussion
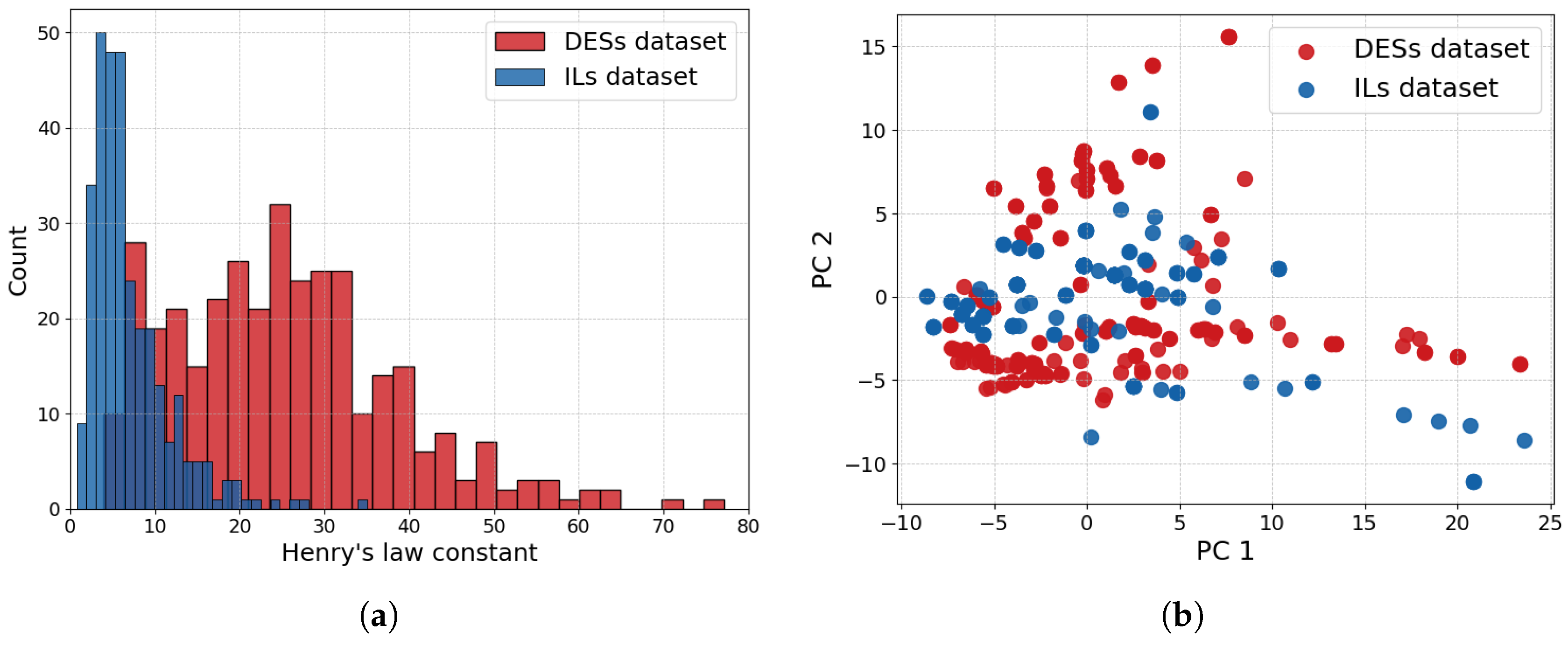
3.1. Dataset Analysis
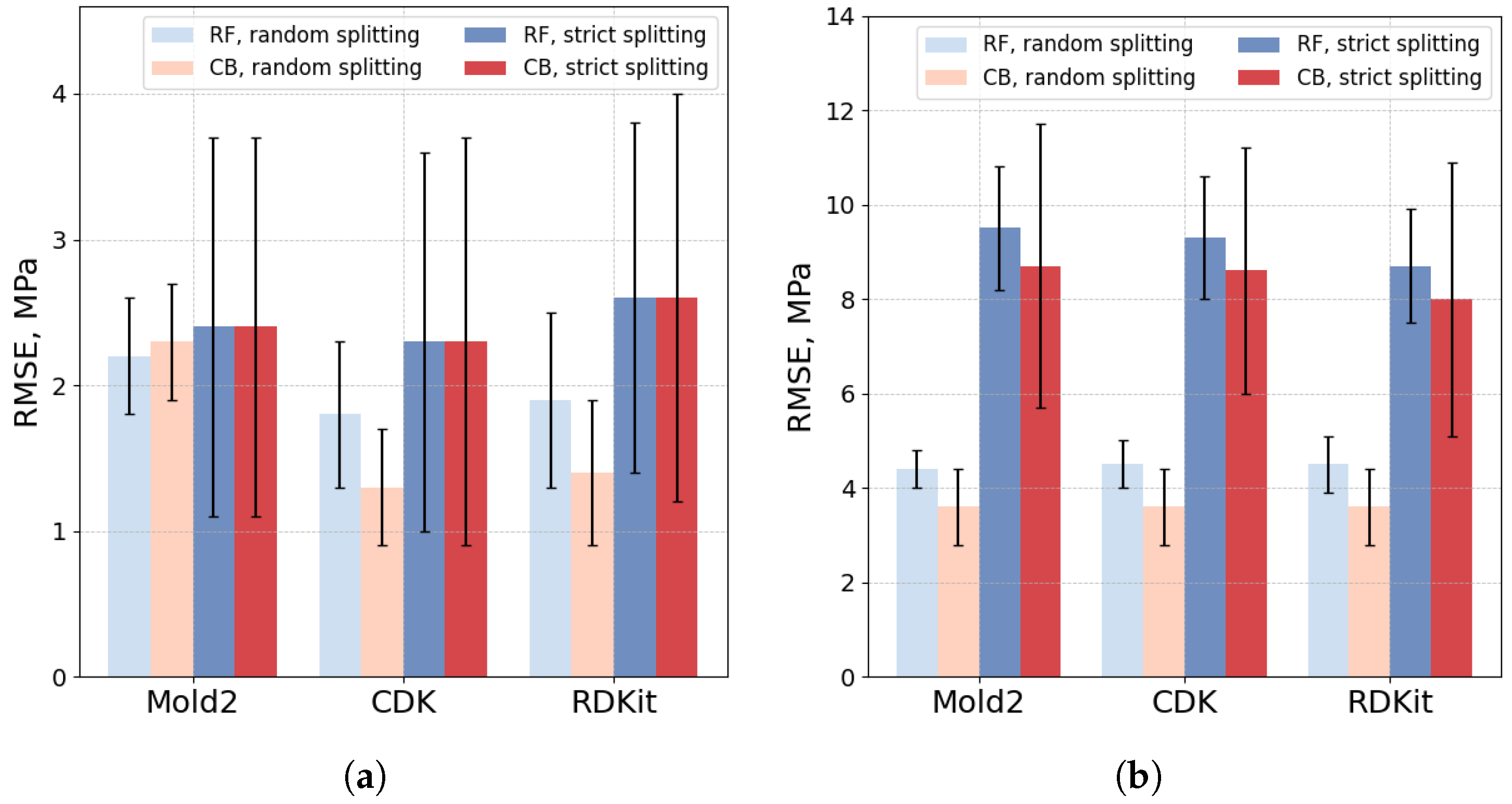
3.2. Models for Individual Datasets
3.3. Models for Combined Datasets
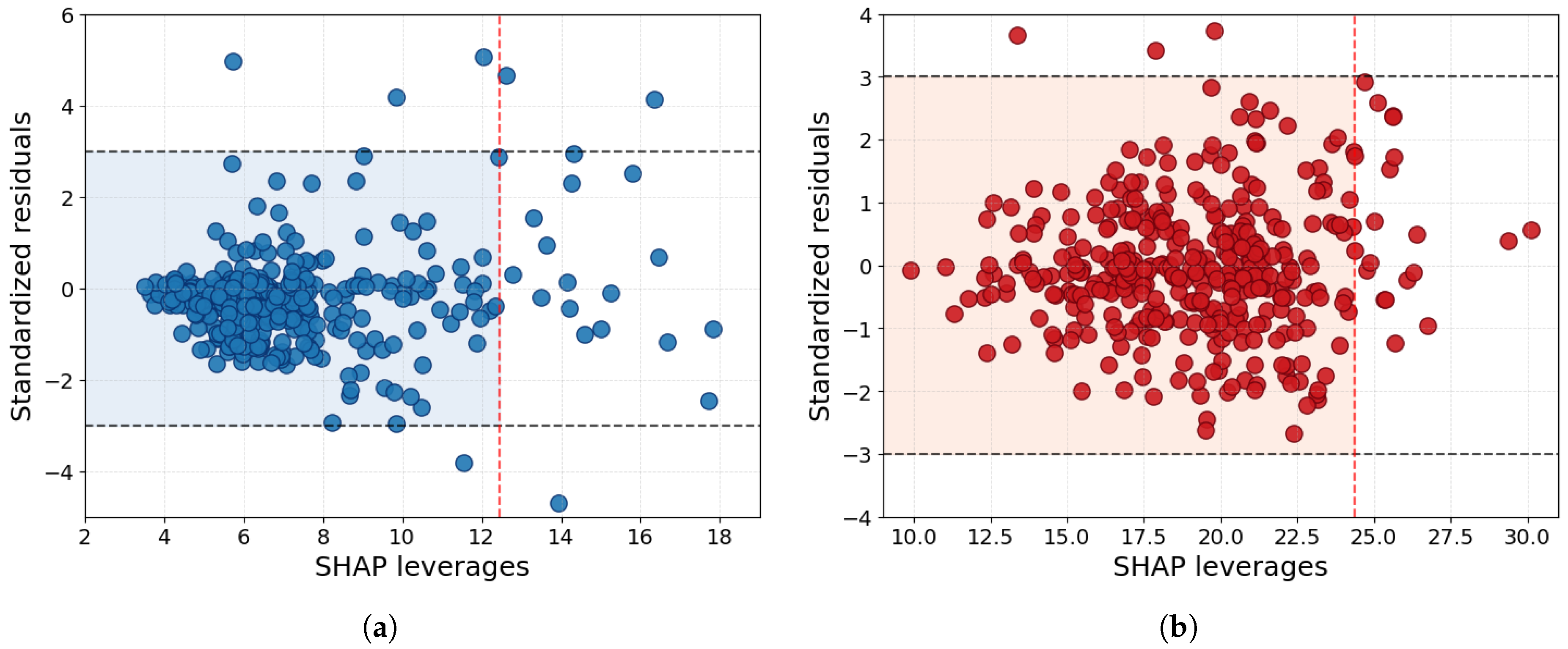
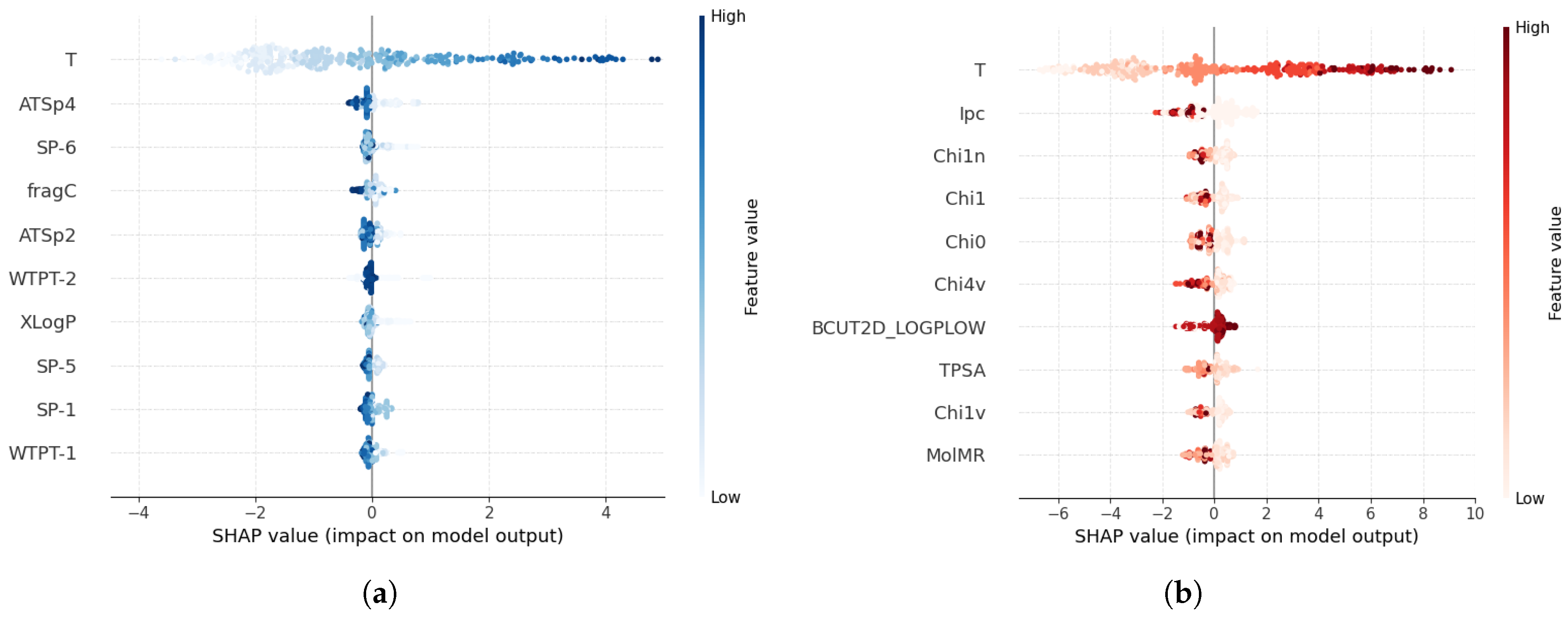
3.4. Applicability Domain and Feature Importance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X. Technical perspective of carbon capture, utilization, and storage. Engineering 2022, 14, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liang, S.; Wang, R.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Xie, B.; Toe, C.Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Industrial carbon dioxide capture and utilization: State of the art and future challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8584–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeClerc, H.O.; Erythropel, H.C.; Backhaus, A.; Lee, D.S.; Judd, D.R.; Paulsen, M.M.; Ishii, M.; Long, A.; Ratjen, L.; Gonsalves Bertho, G.; et al. The CO2 Tree: The Potential for Carbon Dioxide Utilization Pathways. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 13, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snæbjörnsdóttir, S.Ó.; Sigfússon, B.; Marieni, C.; Goldberg, D.; Gislason, S.R.; Oelkers, E.H. Carbon dioxide storage through mineral carbonation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.Y.W.; Ngu, L.H.; How, B.S. Review of carbon capture absorbents for CO2 utilization. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 394–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q. Research progress of carbon capture technology based on alcohol amine solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, D.; Ge, C.; Fan, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; et al. Tuning ionic liquid-based functional deep eutectic solvents and other functional mixtures for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Jia, C.; Li, Z.; Du, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, Z.; Yao, J. Recent advances and future perspectives in carbon capture, transportation, utilization, and storage (CCTUS) technologies: A comprehensive review. Fuel 2023, 351, 128913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.y.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Sun, Z. Chemical accuracy prediction of molecular solvation and partition in ionic liquids with educated estimators. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 123202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, L.A.; Hancu, D.; Beckman, E.J.; Brennecke, J.F. Green processing using ionic liquids and CO2. Nature 1999, 399, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaie, M.; Rezaei, N.; Zendehboudi, S. A systematic review on CO2 capture with ionic liquids: Current status and future prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 96, 502–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godény, M.; Schröder, C. Reactive Molecular Dynamics in Ionic Liquids: A Review of Simulation Techniques and Applications. Liquids 2025, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Zhu, X.; Cui, G.; Jiang, D.E.; Deng, D.; Li, H.; Dai, S. The strategies for improving carbon dioxide chemisorption by functionalized ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15518–15527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmobarak, W.F.; Almomani, F.; Tawalbeh, M.; Al-Othman, A.; Martis, R.; Rasool, K. Current status of CO2 capture with ionic liquids: Development and progress. Fuel 2023, 344, 128102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Efficient Absorption of CO2 by Protic-Ionic-Liquid Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem.-Asian J. 2024, 19, e202400234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Mumford, K.; Stevens, G.W.; Fei, W.; Wang, Y. Recent advances in carbon dioxide capture and utilization with amines and ionic liquids. Green Chem. Eng. 2020, 1, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Peng, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Q.; Cai, R.; Deng, C.; Liu, B.; Sun, C.; Chen, G. Mixed solvent of alcohol and protic ionic liquids for CO capture: Solvent screening and experimental studies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 33173–33185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, N.; Xie, Y.; Ji, X. Hybrid solvents based on ionic liquids/deep eutectic solvents for CO2 separation. Sci. Talks 2023, 6, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhune, A.; Dey, R. Green and sustainable solvents of the future: Deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 379, 121676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Coutinho, J.A. Everything you wanted to know about deep eutectic solvents but were afraid to be told. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2023, 14, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Liu, C.; Zeng, S.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, J.; Zhao, Y. Prediction of Henry’s law constant of CO2 in ionic liquids based on SEP and Sσ-profile molecular descriptors. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 262, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaslani, D.; Gorji, Z.E.; Gorji, A.E.; Riahi, S. Descriptive and predictive models for Henry’s law constant of CO2 in ionic liquids: A QSPR study. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 120, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, W.L.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.Y. Prediction of Henry’s law constants of CO2 in imidazole ionic liquids using machine learning methods based on empirical descriptors. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ren, S.; Hou, Y.; Wu, W. Novel Strategy of Machine Learning for Predicting Henry’s Law Constants of CO2 in Ionic Liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6090–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Kodama, D.; Chowdhury, F.A.; Yamada, H.; Mori, H. Machine learning-boosted design of ionic liquids for CO2 absorption and experimental verification. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X. Screening deep eutectic solvents for CO2 capture with COSMO-RS. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.M.; Corbett, P.T.; Murray-Rust, P.; Glen, R.C. Chemical name to structure: OPSIN, an open source solution. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.M.; Fadeeva, Y.A.; Shmukler, L.E. Predictive modeling of physicochemical properties and ionicity of ionic liquids for virtual screening of novel electrolytes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 391, 123323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Xie, Q.; Ge, W.; Qian, F.; Fang, H.; Shi, L.; Su, Z.; Perkins, R.; Tong, W. Mold2, molecular descriptors from 2D structures for chemoinformatics and toxicoinformatics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willighagen, E.L.; Mayfield, J.W.; Alvarsson, J.; Berg, A.; Carlsson, L.; Jeliazkova, N.; Kuhn, S.; Pluskal, T.; Rojas-Chertó, M.; Spjuth, O.; et al. The Chemistry Development Kit (CDK) v2. 0: Atom typing, depiction, molecular formulas, and substructure searching. J. Cheminform. 2017, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, A.P.; Hersey, A.; Félix, E.; Landrum, G.; Gaulton, A.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; De Veij, M.; Leach, A.R. An open source chemical structure curation pipeline using RDKit. J. Cheminform. 2020, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.; Fadeeva, Y.A.; Safonova, E.; Shmukler, L. Predictive modeling of antibacterial activity of ionic liquids by machine learning methods. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2022, 101, 107775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, E.; Greenman, K.P.; Chung, Y.; Li, S.C.; Graff, D.E.; Vermeire, F.H.; Wu, H.; Green, W.H.; McGill, C.J. Chemprop: A machine learning package for chemical property prediction. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 64, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.M.; Fadeeva, Y.A.; Shmukler, L.E.; Tetko, I.V. Machine learning models for phase transition and decomposition temperature of ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 366, 120247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Unbiased boosting with categorical features. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 6639–6649. [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, D.M.; Kolker, A.M. Viscosity of deep eutectic solvents: Predictive modeling with experimental validation. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2025, 587, 114217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.M.; Lukanov, M.M.; Rusanov, A.I.; Mamardashvili, N.Z.; Ksenofontov, A.A. Machine learning approach for predicting the yield of pyrroles and dipyrromethanes condensation reactions with aldehydes. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 74, 102173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A next-generation hyperparameter optimization framework. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2623–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Oprisiu, I.; Novotarskyi, S.; Tetko, I.V. Modeling of non-additive mixture properties using the Online CHEmical database and Modeling environment (OCHEM). J. Cheminform. 2013, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.; Fadeeva, Y.A.; Shmukler, L.; Tetko, I. Beware of proper validation of models for ionic Liquids! J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P. Principles of QSAR models validation: Internal and external. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2007, 26, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.M.; Kalikin, N.N.; Budkov, Y.A.; Gurikov, P.; Kruchinin, S.E.; Jouyban, A.; Kiselev, M.G. Improved Solubility Predictions in scCO2 Using Thermodynamics-Informed Machine Learning Models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2025, 65, 4043–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.M.; Fadeeva, Y.A.; Golubev, V.A.; Kolker, A.M. Designing deep eutectic solvents for efficient CO2 capture: A data-driven screening approach. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 325, 124614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makarov, D.M.; Fadeeva, Y.A.; Kolker, A.M. Machine Learning Prediction of Henry’s Law Constant for CO2 in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Liquids 2025, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020016
Makarov DM, Fadeeva YA, Kolker AM. Machine Learning Prediction of Henry’s Law Constant for CO2 in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Liquids. 2025; 5(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakarov, Dmitriy M., Yuliya A. Fadeeva, and Arkadiy M. Kolker. 2025. "Machine Learning Prediction of Henry’s Law Constant for CO2 in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents" Liquids 5, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020016
APA StyleMakarov, D. M., Fadeeva, Y. A., & Kolker, A. M. (2025). Machine Learning Prediction of Henry’s Law Constant for CO2 in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. Liquids, 5(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids5020016






