Abstract
Nuclear technology, while offering significant benefits across various sectors, poses potential health risks due to uranium (U) contamination, particularly through its internalization and subsequent interactions with biological systems. This study investigates the binding of uranyl (UO22+) and zinc (Zn2+) ions to Human Serum Albumin (HSA) that is already bound to fatty acids (FAs), using all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The analysis focuses on the structural and dynamic alterations in the protein’s multi-metal binding site (MBS-A) caused by FA binding. Results reveal that FA binding induces a conformational change in HSA, disrupting the pre-formed MBS-A binding site, while still allowing uranyl and zinc ions to interact with residue D249 through strong Coulombic interactions. Secondary binding sites, associated with calcium and zinc binding, remain largely unaffected by FAs, providing alternative coordination for metal ions. This study also explores the binding and unbinding pathways of the metal ions using well-tempered meta-dynamics (WT-MtD), showing that while FA binding disrupts the primary metal binding site, it does not completely inhibit the binding of both uranyl and zinc ions. These findings offer new insights into the nature of uranium’s interactions with blood serum proteins and the role of fatty acids in modulating these interactions, which may help in designing future strategies for managing uranium contamination in biological systems.
1. Introduction
Nuclear technology plays an important role in shaping up modern societies by offering a wide range of benefits. It not only generates electricity but also makes major footprints in agriculture, medicine, desalination, space technology, etc. Uranium (U) is used as a predominant fuel source in both commercial nuclear power plants and research nuclear reactors. U is handled in different processes of nuclear fuel cycle i.e., from fabrication of fuel pins or pellets to the reprocessing of spent fuel to recover valuable radioisotopes such as unspent uranium, Pu, and important fission products like 137Cs, 106Rh, etc. [1]. In spite of engineered safety features, there is a likelihood of internal contamination from U in these facilities. Once inside the body, U is transported to various organs, e.g., liver, bone, and kidney, by binding with the components of blood serum [2,3]. Being divalent, uranyl ion (UO22+) is assumed to mimic the chemistry of calcium in the body [4], although it does not play any vital role in any known biological functions. The interaction of U with biological ligands and its subsequent deposition in target organs might have some health impact due to interference with the natural functions of bio-essential elements and radio-toxicity. Understanding the mechanisms by which U interacts with body fluids and accumulates in target organs is essential. A detailed comprehension of these interactions is necessary to design effective decorporation strategies.
Human Serum Albumin (HSA) is found to be the most abundant (~55%) blood plasma protein [5]. The interactions of various transition metal ions e.g., Zn2+, Ca2+, Cd2+, Co2+, and Ni2+, with HSA are well established [6,7,8,9,10,11]. Transition metal ions are generally bound to the N-terminal binding site or the multi-metal binding site (MBS-A/B) [9]. It is also known that fatty acids (FAs) are predominantly carried by HSA in blood plasma [12]. FAs not only provide vital source of metabolic energy but also play indispensable role in the body for synthesis of hormone and membrane lipids. On the other hand, the complexation behavior of HSA with actinides like U is poorly explored. Few experimental attempts are made to understand the interactions of U with HAS [13,14,15,16]. However, these spectroscopic based studied are unable to provide a clear picture on the structure, binding site, or mechanism of interaction.
It is understood that the interaction of a specific ligand can influence binding of another ligand to HSA. In blood, HSA transports both metal ions such as Zn2+ and FAs. Isothermal titration calorimetric based competitive binding studies have revealed that Zn2+ binding with HSA are moderated by physiologically relevant amounts of FAs. It is also known that metal binding to HSA at the MBS-A and FA binding at high-affinity site 2 of HSA are inter-reliant. If a FA binds to the site 2 of HSA, it induces significant conformational fluctuations in the protein that deter the binding of metal at the MBS-A site [17,18,19]. The interactions between the Zn2+ ion and FAs with albumin is reviewed by Barnett et al. [20] Recently, attempts are made to understand the binding aspects of uranyl and zinc ions by employing all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations [21,22]. It is observed that uranyl ion can bind with HSA at the Zn2+ binding MBS-A site. The binding is predominantly facilitated by Coulombic interaction between D249 residue of the MBS-A site and metal ions [21]. Attempts are also made to understand the influence of fatty acids (FAs) on the already metal ion-bound HAS [22]. Results depict that FAs improve the binding of UO22+ ion while weakening the binding of Zn2+ binding HSA. However, the potential effects of uranyl binding with HSA, already docked with FAs, are yet to be explored.
In the present study, all-atom MD simulations are employed to understand the structure of the metal ion binding site, binding/unbinding pathways of metal ions at MBS-A site of HSA already bound to FAs.
2. Theoretical Methodology
The crystal structure of the FA-bound HSA (PDB ID: 1E7I) [23] is taken from the RCSB protein data bank. It is known that Zn2+ ion binds to HSA at MBS-A involving H67, H247, and D249 residues. The PDB2PQR server is used to protonate the desired residues at physiological pH (7.4) and all the simulations are performed at that pH [24]. A Zn2+ or uranyl ion is added to the MBS-A of HSA which already contains seven stearic acid (FA) molecules. The three systems (see Figure 1) are then solvated in a triclinic box of dimension 10.7 nm × 7.0 nm × 10.6 nm comprising 23,000 to 24,000 TIP3P water molecules. The water molecules are modelled by using TIP3P topology. NaCl salt is added not only to neutralize the system but also to mimic physiological concentration of ions (0.015 M).
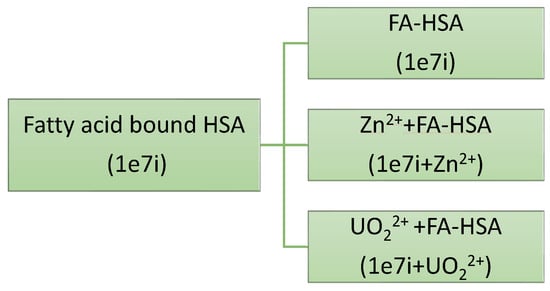
Figure 1.
Schematic to study the complexation of metal ions with fatty acid bound HSA.
The GROMACS [25] engine is used to run all the MD simulations by employing CHARMM31 force field parameters and it is specifically designed for lipid simulations. Uranyl ion force field parameters are taken from literature [26]. After energy minimization, Nose-Hoover thermostat [27,28] is used to maintain the temperature of 310 K for all the three systems. At first, the NPT ensemble is used to equilibrate all the three systems for 10 ns. Isotropic pressure coupling is employed to maintain the pressure of 1 atm during the simulations. After that, the NVT ensemble is invoked for equilibrium simulations for 100 ns. All bonds involving hydrogen atoms are constrained by using the LINCS [29] algorithm. Periodic boundary conditions in all three dimensions, with the minimum image conventions are employed. Long-range electrostatic interactions are modelled by using Particle-mesh Ewald sum formalism [30].The equilibration is checked by analyzing energy, the radius of gyration and the root mean square deviation (< 0.05 nm).
It is widely understood that conventional MD fails to capture the protein–ligand binding/unbinding processes within realistically possible time frames due to its intrinsic slow nature. To overcome the bottleneck, well-tempered meta dynamics (WT-MtD) [31] is used to investigate the uranyl and Zn2+ ion binding to the FA-bound HSA. In the standard MtD simulation, a suitable descriptor of the system, i.e., the collective variable (CV) is formulated. After that, the history-dependent Gaussian shaped biasing potential is added to the system along the chosen CV, . In MtD simulation using the physical potential energy is enhanced by a time-dependent biasing term, which at time t reads as,
where and are, respectively, the height and width of the Gaussian bias that are added with a frequency, . The enhanced bias accelerates the rare events and reconstructs the potential of mean force (PMF), in the region , explored by the CV, in time t. The details of the WT-MtD and its advantage over other enhanced sampling methods are provided in Supplementary Information. All The WT-MtD simulations are performed using the PLUMED [32] plugin seamlessly integrated into the GROMACS.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The HSA Binding Site and Its Interactions with UO22+ and Zn2+ Ions
The multi-metal binding site MBS-A of HSA comprises His67, His247 and Asp249 residues. UO22+ and Zn2+ interacts with the His67(or H67), His247(or H247) and Asp249(or D249) in HAS [21]. In the present study, metal ions are docked at MBS-A of fatty acid-bound HSA(FA-HSA). The equilibrated Zn2+ docked MBS-A snapshot is depicted in Figure 2. The separation between the ions and centre-of-mass (COM) of the HSA binding pocket are computed along the equilibrium trajectory and presented in Figure 3 for both Zn2+ and UO22+ ions.
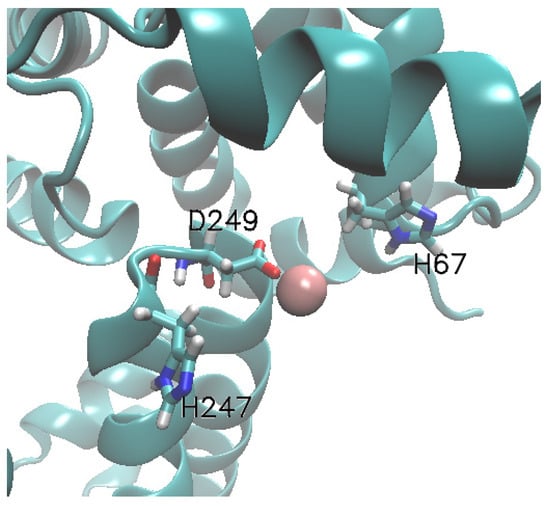
Figure 2.
Structure of the albumin MBS-A binding site with Zn2+. The whole protein is represented by new-cartoon and binding site protein residues are represented in licorices. The ions are shown in van der Waal representation.
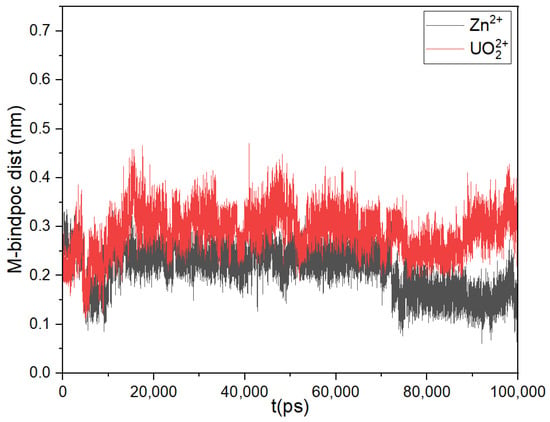
Figure 3.
Separation between HSA binding pocket and Zn2+ and UO22+.
Figure 3 depicts that the variation in COM separation between the MBS-A binding site and metal ions is within ± 0.15 nm. But when the separation between individual binding residues and metal ions has been determined, presented in histogram (Figure 4), it shows that in the case of both systems, H67 and H247 moves away from binding pocket and only D249 continues to interact with Zn2+ and UO22+. This was anticipated considering that the protein bound to FA undergoes a conformational change causing the disruption of the pre-formed binding site MBS-A [18,19].
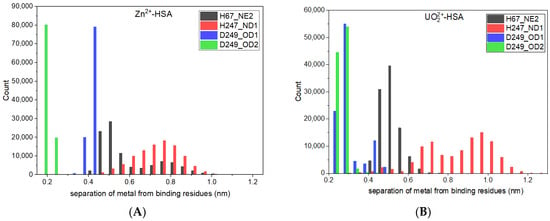
Figure 4.
Histogram of separation between ion and HSA binding residues for (A) Zn2+, and (B) UO22+.
Short-range Coulomb and Lennard-Jones interactions are calculated from the equilibrium trajectory (Table 1). It is clear from Table 1 that Zn2+ and UO22+ interact with only D249 via electrostatic forces, whereas, short-range Lennard-Jones interactions are very weak in comparison to the Coulomb interactions. The binding of UO22+ and Zn2+ is facilitated by strong short-range Coulomb interactions.

Table 1.
Short-range (SR) Coulomb and Lennard-Jones interaction values of the ions with the amino acid residues of the MBS-A binding site residues. Single word abbreviations of amino acids are used.
For additional information on the metal ions and FA-HSA binding, hydrogen bond (HB) dynamics are analyzed for all the systems, which is described in detail in next section.
3.2. Hydrogen Bonding Dynamics
Hydrogen bonding (HB) is an important factor in overall structure of protein [33,34,35]. The hydrogen bonds present within the binding pocket will be altered by metal ions binding to HSA. The HB bonds formations are investigated on the basis of geometric criteria [36,37]. A HB is considered to be formed when the distance between the hydrogen bond donor (D) atom and acceptor (A) atom is less than 3.0 Å, and the H-D-A angle is lower than 35°. The HB lifetime correlation function, is measured from the trajectory of the equilibrium MD simulations to realize the microscopic aspects of hydration dynamics. The details of formula and calculations are provided in Supplementary Information. The fitting parameters of the correlation functions, their amplitude and average lifetime of HB bonds for all HSA systems are provided in Table 2. The plots of the functions are shown in Figure 5.

Table 2.
Exponential fitting parameters (time constants and amplitude) of hydrogen bond time correlation functions and average hydrogen bonds lifetime (ps) at the MBS-A binding pocket for various systems from equilibrium simulations. “--” in the table shows no HB formation.
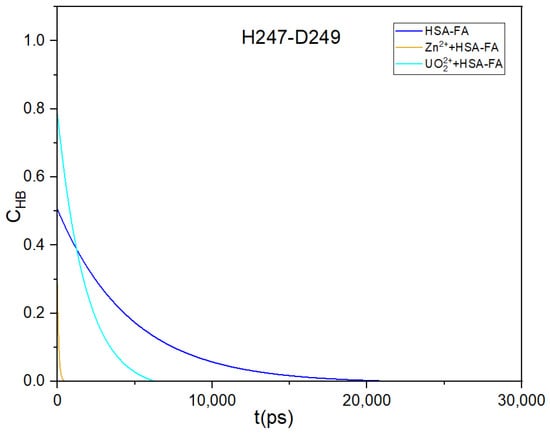
Figure 5.
Time dependent HB lifetime correlation function, CHB(t) are shown for H247-D249 pair.
From Table 2 and Figure 5, it is clear that in all the systems, H247-D249 HB is prominent compared to that of H67-D249 HB. In our previous study [22], we observed that D249 residues form strong HB with both H67 and H247 in ligand-free form, which is crucial for the overall HSA structure. Fatty acid binding induces alterations in HSA protein structure similar to N(neutral) to B(basic) transformation [12]. The transition leads to loosening of HSA structure localized to domain I with some contribution from domain II. In the present study, the interdomain hydrogen bonding between H67 and D249 is already diminished because of FAs binding to HSA. The remaining HB between H247 and D249 is further reduced on introduction of metal ions indicating interaction between metal and binding residues. Further, to understand binding and unbinding process, well-tempered meta-dynamics has been employed and the results have been discussed in next section.
3.3. Potential of Mean Force
The binding and un-binding process from the protein can encompass a substantial number of local minima (basins) and barriers. Within the biological system, the process of transitioning from one basin to another across a barrier during binding or unbinding can lead to extended periods of entrapment in a basin, transforming the process into a collection of rare infrequent occurrences. In numerous instances, various factors such as protein flexibility or solvent effects introduce additional intricacies to the interactions between ligands and proteins. Therefore, in the present study, WT version of the MtD method is used to investigate the binding and un-binding of UO22+ and Zn2+ with the HSA-FA system. The COM separation between the ion-binding pocket of HSA and the ion is taken as collective variable (CV) for the WT-MtD simulations. The potential of mean force (PMF) profiles are derived from the converged WT-MtD simulations for all the systems. The PMF plots of zinc and uranyl ion with HSA-FAs are given in Figure 6.
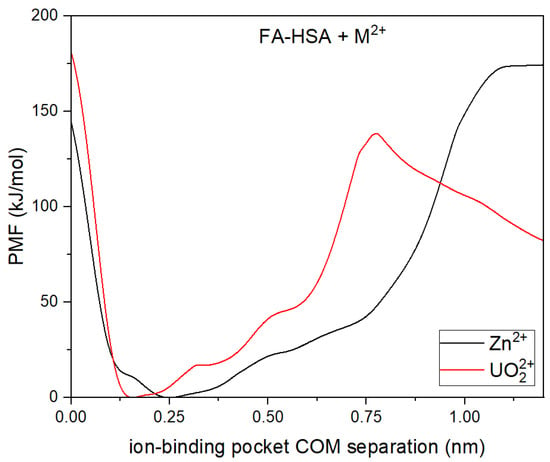
Figure 6.
The PMF profiles of metal binding with FA-HSA systems by employing COM between the ion and the binding pocket as the collective variable.
When introducing metal ions to HSA that is already bound to fatty acids, initial observations might suggest that the metals are strongly binding to MBS-A. From Figure 6, it appears that both zinc and uranyl ions binding with HSA is favorable which is usually the case as observed in our previous work [21]. The measured energy barriers provide valuable insight into the physiological relevance of metal ion binding and release processes in physiological conditions. Barriers within a biologically accessible range suggest that dynamic exchange between primary and secondary binding sites on HSA is feasible. However, the unbinding of metal ions from HSA requires overcoming a substantial energy barrier, making spontaneous release unlikely. Notably, the enhanced binding of uranyl ions in the presence of fatty acids suggests a potential risk for increased metal retention, with implications for toxicity and clearance mechanisms in the body. Overall, these results underscore the dynamical nature of metal ion binding and its sensitivity towards physiological conditions such as concentration of fatty acids.
However, it is important to note that the binding of fatty acids to HSA leads to disruption of the pre-formed MBS-A. In order to gain insight into this, snapshots of the different local energy minima that the system goes through are captured and analyzed (available in Supplementary Information, Figure S1). Interestingly, even though the original binding site is no longer intact, the metal now exhibits greater accessibility to D249. This interaction with D249 is coupled with the metal forming bonds with nearby anionic residues implicated in the calcium and secondary zinc binding sites [9,38]. It is worthwhile to mention that while FA disrupts the primary zinc binding site MBS-A causing its subsequent release [19,20], the secondary binding sites on HSA remained unaffected in the presence of FA [18].When fatty acids are pre-bound to HSA, causing the structure to become more open, the introduction of zinc leads to interactions with nearby anionic residues. These anionic residues are associated with secondary zinc-binding sites [9]. These observations are consistent with the results obtained by Kassar [18] and colleagues in their isothermal calorimetric investigations. The secondary binding sites on HSA remained unaffected in the presence of FAs. The analysis led to the conclusion that as the availability of MBS-A decreased due to the interaction with fatty acids, a portion of the Zn2+ ions were released from binding, some found binding to the secondary site(s) on albumin, and others were observed to bind to HRG (Histidine-rich glycoprotein) [18]. On the contrary, behaviour of uranyl binding to HSA resembles the binding pattern observed for calcium. Earlier studies often described calcium binding to be nonspecific to albumin, involving various carboxylate side chains on the surface of albumin. However, recent investigations indicate distinct binding sites on various albumin types like BSA, ESA, RSA, etc. [11,38]. Majorek et al. identified three binding sites for calcium in BSA, with the key site involving ASP248 (corresponding to ASP249 in HSA). Notably, two residues, Asp13 and Asp254 (corresponding to ASP255 in HSA), which participate in Ca2+ binding, are also part of secondary zinc binding sites. This suggests the potential for cross-talk between Zn2+ and Ca2+ binding at multiple sites within HSA. Interestingly, when FAs are introduced to the system, uranyl binding is not disrupted as observed with zinc; instead, it becomes stronger in the presence of FAs. Prior reports have indicated that long-chain FAs enhance calcium binding to HAS [39].
Further, short-range Coulomb and Lennard-Jones interactions are also evaluated at each minimum for all the systems (see Table 3). From the table it is evident that both metal ions interact with D249 strongly through Columbic forces. The interaction with other participant residues from MBS-A, i.e., H67 and H247 remains negligible. Apart from this both ions interacts with neighboring anionic residues E252 and E100 which are associated with secondary zinc and calcium binding sites. These observations provide a comprehensive explanation for the PMF plots that were observed and further enhance the validity of the results.

Table 3.
Short-range (SR) Coulomb and Lennard-Jones interaction values of the ions with the amino acid residues of the MBS-A binding site and other neighbouring residues at minimum of PMF profiles. Single word abbreviations of amino acids are used.
4. Conclusions
This study provides a detailed MD simulation-based investigation into the interactions of uranyl (UO22+) and zinc (Zn2+) ions with Human Serum Albumin (HSA) that is already bound to fatty acids (FAs). The interaction of UO22+ and Zn2+ ions with HSA was investigated at the multi-metal binding site (MBS-A), consisting of residues H67, H247, and D249. However, when FA binds to HSA, it induces a conformational change in the protein, disrupting the pre-formed MBS-A binding site. Despite this, D249 continues to interact with both metal ions, suggesting that FA binding leads to a reorganization of the protein structure, opening up new opportunities for metal ion binding at secondary sites. The analysis of the center-of-mass separation and the electrostatic (Coulombic) interactions reveals that the binding of both metal ions to HSA is mainly governed by electrostatic forces with D249. While the short-range Lennard-Jones interactions are weak, the Coulombic interactions are significant, driving the binding process. This study also emphasizes the role of hydrogen bonding, particularly between H247 and D249, although these interactions are weakened when FA is bound to HSA. The presence of fatty acids results in a noticeable disruption of the original metal binding site (MBS-A), with the binding of both uranyl and zinc ions being less stable. Nonetheless, the ions show increased accessibility to D249 and interactions with neighboring residues associated with secondary metal binding sites, such as E252 and E100. These findings suggest that while FA binding alters the primary metal binding site, secondary binding sites remain largely unaffected and can accommodate the metal ions. Using well-tempered meta-dynamics (WT-MtD) simulations, the binding and unbinding processes of the metal ions were examined. This study revealed that both UO22+ and Zn2+ ions can bind to HSA even in the presence of fatty acids, though the overall stability of the metal-protein complex is affected by the conformational changes induced by FA binding.
In summary, the binding behavior of zinc and uranyl ions to HSA is significantly influenced by the presence of fatty acids. If fatty acids are pre-bound to HSA, causing the structure to become more open, the introduction of zinc leads to interactions with nearby secondary zinc-binding comprising of anionic residues [9,18]. While FAs disrupt the primary zinc-binding site MBS-A, leading to redistribution of Zn2+ ions to secondary binding sites or HRG, the uranyl ion exhibits enhanced binding in the presence of FAs, mirroring calcium’s binding behavior [18]. This differential behaviour is attributed to changes in protein conformation, particularly the increased accessibility of residues like D249 and neighboring anionic sites. The observed interactions, corroborated by energy minima analysis and interaction energy data, reveal the complex interplay between metal ions, fatty acids, and albumin, underscoring the relevance of secondary binding sites in metal transport and regulation.
Overall, this study sheds light on the complex interactions between HSA, fatty acids, and metal ions such as UO22+ and Zn2+. The results suggest that fatty acid binding plays a critical role in altering the binding properties of HSA, providing valuable insights into the potential effects of UO22+ binding in human body fluids. The present work not only helps to gain an in-depth understanding of actinides’ fate in the biological systems, but also assists in refining the assessment of possible health hazards and their prevention. Present findings may help in designing future strategies for decorporation therapies for uranium exposure and offer tangible applications in addressing metal exposure and related health challenges.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/liquids5020014/s1, Figure S1: Snapshots of the binding milestones are shown for FA-bound HSA protein with both Zn2+ and UO22+ ions at (A) minima for Zn2+, and (B) minima for UO22+. Figure S2: A simple schematic diagram which illustrate the computational methodology used in the present work. Table S1: Secondary structure analysis of different HSA systems using VADAR [40].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.P.; methodology, A.K.P.; formal analysis, V.M.; data curation, V.M.; writing—original draft, A.K.P. and V.M.; writing—review and editing, V.M., P.D.S. and A.K.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by DAE under project RBA4013.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article and included in the associated Supplementary Information.
Acknowledgments
The authors express gratitude to the late T. Bandyopadhyay for many helpful discussions. A.C. Bhasikuttan, N. Choudhury, C. Majumder and R.B. Oza are also acknowledged for their encouraging support throughout this project. The authors express their gratitude for the ANUPAM computational facility offered by the BARC computer centre.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors affirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Manohar, S.; Sugilal, G.; Bajpai, R.K.; Kaushik, C.P.; Raj, K. Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Tomar, B.S., Rao, P.R.V., Roy, S.B., Panakkal, J.P., Raj, K., Nandakumar, A.N., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dose Coefficients for Intakes of Radionuclides by Workers; ICRP Publication: London, UK, 1995; Volume 68.
- Individual Monitoring for Internal Exposure of Workers; Ann. ICRP 27; ICRP Publication: London, UK, 1997; Volume 78.
- Occupational Intakes of Radionuclides: Part 1; ICRP Publication: London, UK, 2015; Volume 130.
- Rabbani, G.; Ahn, S.N. Structure, enzymatic activities, glycation and therapeutic potential of human serum albumin: A natural cargo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, W.; Sokołowska, M.; Kurowska, E.; Faller, P. Binding of transition metal ions to albumin: Sites, affinities and rates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, P.J.; Viles, J.H. 1H and 113Cd NMR Investigations of Cd2+ and Zn2+ Binding Sites on Serum Albumin: Competition with Ca2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendzik, M.; Pushie, M.J.; Stefaniak, E.; Haas, K.L. Structure and Affinity of Cu(I) Bound to Human Serum Albumin. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handing, K.B.; Shabalin, I.G.; Kassaar, O.; Khazaipoul, S.; Blindauer, C.A.; Stewart, A.J.; Chruszcz, M.; Minor, W. Circulatory zinc transport is controlled by distinct interdomain sites on mammalian albumins. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokołowska, M.; Wszelaka-Rylik, M.; Poznański, J.; Bal, W. Spectroscopic and thermodynamic determination of three distinct binding sites for Co(II) ions in human serum albumin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majorek, K.A.; Porebski, P.J.; Dayal, A.; Zimmerman, M.D.; Jablonska, K.; Stewart, A.J.; Chruszcz, M.; Minor, W. Structural and immunologic characterization of bovine, horse, and rabbit serum albumins. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 52, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vusse, G.J. Albumin as fatty acid transporter. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 24, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, M.R., Jr.; Kumar, C.V. Site-selective photocleavage of proteins by uranyl ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 45, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, J.; Frelon, S.; Garnier, C.; Coppin, F. Determinations of uranium(VI) binding properties with some metalloproteins (transferrin, albumin, metallothionein and ferritin) by fluorescence quenching. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 20, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montavon, G.; Apostolidis, C.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Repinc, U.; Morgenstern, A. Spectroscopic study of the interaction of U(VI) with transferrin and albumin for speciation of U(VI) under blood serum conditions. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Pandey, B.N. The interaction of human serum albumin with selected lanthanide and actinide ions: Binding affinities, protein unfolding and conformational changes. Biochimie 2016, 123, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coverdale, J.P.C.; Katundu, K.G.H.; Sobczak, A.I.S.; Arya, S.; Blindauer, C.A.; Stewart, A.J. Ischemia-modified albumin: Crosstalk between fatty acid and cobalt binding. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 135, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassaar, O.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Blindauer, C.A.; Stewart, A.J. Plasma free fatty acid levels influence Zn2+-dependent histidine-rich glycoprotein-heparin interactions via an allosteric switch on serum albumin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Stewart, A.J.; Sleep, D.; Sadler, P.J.; Pinheiro, T.J.; Blindauer, C.A. A molecular mechanism for modulating plasma Zn speciation by fatty acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.P.; Blindauer, C.A.; Kassaar, O.; Khazaipoul, S.; Martin, E.M.; Sadler, P.J.; Stewart, A.J. Allosteric modulation of zinc speciation by fatty acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, V.; Pathak, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Binding of human serum albumin with uranyl ion at various pH: An all atom molecular dynamics study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Pathak, A.K.; Sawant, P.D.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Fatty acid influence on zinc and uranyl ion binding to human serum albumin: An all atoms molecular dynamics investigation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.A.; Grüne, T.; Curry, S. Crystallographic analysis reveals common modes of binding of medium and long-chain fatty acids to human serum albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 303, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinsky, T.J.; Czodrowski, P.; Li, H.; Nielsen, J.E.; Jensen, J.H.; Klebe, G.; Baker, N.A. PDB2PQR: Expanding and upgrading automated preparation of biomolecular structures for molecular simulations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W522–W525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for Highly Efficient, Load-Balanced, and Scalable Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, N.; Tiwari, S.P.; Maginn, E.J. Force field development for actinyl ions via quantum mechanical calculations: An approach to account for many body solvation effects. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 10885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S. A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A Gen. Phys. 1985, 31, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.; Fraaije, J. LINCS: A Linear Constraint Solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L. A Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald Method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barducci, A.; Bussi, G.; Parrinello, M. Well-Tempered Metadynamics: A Smoothly Converging and Tunable Free-Energy Method. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 020603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, M.; Branduardi, D.; Bussi, G.; Camilloni, C.; Provasi, D.; Raiteri, P.; Donadio, D.; Marinelli, F.; Pietrucci, F.; Broglia, R.A.; et al. PLUMED: A Portable Plugin for Free-Energy Calculations with Molecular Dynamics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2009, 180, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Water isotope effect on the thermostability of a polio viral RNA hairpin: A metadynamics study. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 146, 165104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Unbinding of fluorinated oxime drug from the AChE gorge in polarizable water: A well-tempered metadynamics study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Protein-Drug Interactions with Effective Polarization in Polarizable Water: Oxime Unbinding from AChE Gorge. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 14460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzar, A.; Chandler, D. Effect of Environment on Hydrogen Bond Dynamics in Liquid Water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzar, A.; Chandler, D. Structure and hydrogen bond dynamics of water–dimethyl sulfoxide mixtures by computer simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Haag, S.L.; Patel, J.S.; Ytreberg, F.M.; Bernards, M.T. Paired Simulations and Experimental Investigations into the Calcium-Dependent Conformation of Albumin. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguanno, J.J.; Ladenson, J.H. Influence of fatty acids on the binding of calcium to human albumin. Correlation of binding and conformation studies and evidence for distinct differences between unsaturated fatty acids and saturated fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, L.; Ranjan, A.; Zhang, H.; Monzavi, H.; Boyko, R.F.; Sykes, B.D.; Wishart, D.S. VADAR: A web server for quantitative evaluation of protein structure quality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).