Abstract
Assessment of the environmental impact of organic chemicals has become an important subject in chemical science. Efficient quantitative descriptors of their impact are their partition coefficients logPow, logKoa and logKaw. We present a group-additivity method that has proven its versatility for the reliable prediction of many other molecular descriptors for the calculation of the first two partition coefficients and indirectly of the third with high dependability. Based on the experimental logPow data of 3332 molecules and the experimental logKoa data of 1900 molecules at 298.15 K, the respective partition coefficients have been calculated with a cross-validated standard deviation S of only 0.42 and 0.48 log units and a goodness of fit Q2 of 0.9599 and 0.9717, respectively, in a range of ca. 17 log units for both descriptors. The third partition coefficient logKaw has been derived from the calculated values of the former two descriptors and compared with the experimentally determined logKaw value of 1937 molecules, yielding a standard deviation σ of 0.67 log units and a correlation coefficient R2 of 0.9467. This approach enabled the quick calculation of 29,462 logPow, 27,069 logKoa and 26,220 logKaw values for the more than 37,100 molecules of ChemBrain’s database available to the public.
1. Introduction
Environmental considerations of organic molecules as potential contaminants have become an important subject in recent years. Several descriptors have been applied to quantify their impact on the natural environment, among them the octanol/water partition coefficient logPow (more recently named logKow), a standard model for the description of the lipophilicity of drugs in medicinal and agricultural chemistry, whereby octanol is the substitute for the natural organic matter, and the octanol/air partition coefficient Koa and the air/water partition coefficient logKaw both indicate the role of the chemicals for air-breathing organisms [1,2,3]. In view of the time consumption and costs of their experimental determination, fast mathematical methods for the prediction of their value attributed to a molecule have been developed. An excellent comprehensive overview of the various methods for the prediction of the logKow—among many other descriptors—is given by Nieto-Draghi et al. [4]. Cappelli et al. [5] analysed a series of free programs based on atom/fragment contributions, hydrophobicity contributions of atoms, the number of carbon atoms and heteroatoms as well as Monte Carlo methods to calculate logPow and found correlation coefficients R2 of between 0.7 and 0.8 and root mean square errors (RMSE) from 0.8 to 1.5. A number of authors [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13] have successfully carried out logPow calculations for a large variability of compounds based on various group-additivity methods. Plante and Werner [14] presented a logPow prediction method based on the combination of the calculated data of the four different open-source group-additivity calculation methods AlogP, XlogP2, SlogP and XlogP3 into a single model, providing a best RMSE of 0.63. Ulrich et al. [15] used deep neural networks (DNNs) for the logPow calculations, based on ca. 14,000 different SMILES representations of molecules including potential tautomers, whereby, however, a substantial number of compounds might have been presented as duplicates and triplicates to the DNNs. Their best prediction performance yielded an RMSE of 0.47. Recently, an entirely different path was followed by Sun et al. [16]: since logPow is proportional to the Gibbs free energy of the transfer from one solvent to another, it can be calculated using the free solvation energy in these solvents. Sun used the molecular mechanics–Poisson Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) method for the determination of the free energies of solvation. Their best RMSE for the 707 compounds test set was 0.91.
Many publications [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28] dealing with the prediction of the coefficient Koa, based on various QSPR methods, are limited to specific chemical families, thus lacking general applicability. Li et al. [29] used a group-additivity method based on five fragment constants and one structural correction factor for the evaluation of logKoa, limited to halogenated aromatic pollutants. Recently, Ebert et al. [30] suggested a general-purpose fragment model for the calculation of the air/water partition coefficient logKaw resembling the atom group-additivity method presented in one of our earlier papers [13] for the calculation of—among several further descriptors—the octanol/water partition coefficient logPow.
The goal of the present paper was to suggest the extension of a simple tool, which has already served well for the prediction of the octanol/water coefficient logPow described in [13], to enable it to calculate all three mentioned partition coefficients at once by means of a uniform computer algorithm based on the atom group-additivity method detailed in [13]. Since under common standard conditions, any third partition coefficient can be directly calculated from the other two if we neglect the effect of the contamination of water in octanol (and vice versa) influencing the determination of the logPow values, which will be addressed later on, it made sense to select the two coefficients for which any group parameters could be founded on the most reliable as well as the largest number of experimental data. It turned out that the experimental data for the partition coefficients logPow and logKoa provided excellent basis sets for the evaluation of their respective tables of atom and special group parameters. Accordingly, from the subsequently calculated values of a molecule’s logPow and logKoa, its air/water partition coefficient logKaw should easily be evaluable following the equation logKaw ≈ logPow − logKoa.
2. Method
The calculation method is based on a regularly updated object-oriented database of more than 37,100 compounds stored in their geometry-optimised 3D structure, encompassing pharmaceuticals, herbicides, pesticides, fungicides, textile and other dyes, ionic liquids, liquid crystals, metal–organics, lab intermediates and many more, collecting—among further molecular experimental and calculated descriptors—a large set of experimental logPow, logKoa and logKaw data, outlined in the respective sections below. It should be stressed that for the calculation of the partition coefficients, the 3D geometry-optimised form of the compounds is not required—except for the algorithm-based determination of intramolecular hydrogen bridges, the impact of which will be discussed further down. In order to avoid structural ambiguities in the presentation of the chemical structures to the computer algorithm defining the molecules´ atom groups, a special algorithm ensured at the time of the input of a new compound that any six-membered aromatic ring system is defined by six aromatic bonds instead of alternating single–double-bonds.
2.1. Definition of the Atom and Special Groups
The details of the atom group-additivity model applied in the present study have been outlined in [13]. Accordingly, the definition of the atom types and their immediate atomic neighbourhood and meaning are retained as described in Table 1 of [13] and are also valid for both the logPow and logKoa descriptors. However, since these atom groups are not able to cover certain additional structural effects such as intramolecular hydrogen-bridge bonds and the influence of saturated cyclic compared to saturated noncyclic systems, a number of additional special groups had to be introduced. In a paper applying a different group-additivity method for the calculation of logPow, Klopman et al. [8] discovered that the inclusion of a correction value per carbon atom in pure saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons improved compliance with the experiment. This has indeed been confirmed in the present study.
In order to take account of these and further potential structure-related peculiarities, the list of atom groups has been extended by “special groups” for which the column-title terms “atom type” and “neighbours” in the subsequent tables should not be taken literally, but which the computer algorithm treats in the same way as ordinary atom groups. In Table 1, the respective special groups, their nomenclature and meaning are detailed. In order to enable a future comparison of the contributions of the special group parameter sets within this study, the same special groups have been applied for the calculation of both descriptors logPow and logKoa.

Table 1.
Special groups and their meaning.
At present, the list of elements is limited to H, B, C, N, O, P, S, Si and halogen, but an extension is always possible, provided that corresponding molecules with experimental descriptor data are available.
2.2. Calculation of the Atom and Special Group Contributions
Since the algorithm for the evaluation of the parameter values of the atom groups has been outlined in detail in [13], its four steps may just be summarised as follows: the first step encompasses the selection of all the compounds from a database of, at present, more than 37,100 compounds for which the experimental descriptor data in question are known and their storage is in a temporary compounds list. In the second step, the molecules in the temporary list are broken down into their constituting atom groups, whereby their central atoms, called “backbone atoms”, are characterised in that they are bound to at least two covalently bound neighbour atoms. The atom groups’ atom types and neighbour terms are generated according to the rules described in [13] and their occurrence is registered. Any molecule carrying an atom group that is not found in the pre-defined group parameters table is discarded from the temporary compound list. The third step generates an M × (N + 1) matrix, wherein M is the number of molecules, N + 1 is the number of pre-defined atom groups plus the container for the molecule´s descriptor value, and the matrix element (i,j) contains the number of registered occurrences of the jth atom group in the ith molecule. Atom groups and their related jth column, which are not present in any molecule of the temporary molecules list, are removed from the M × (N + 1) matrix. In the final step, this adjusted matrix is normalised into an Ax = B matrix, followed by its balancing by means of fast Gauss–Seidel calculus [31] to receive the atom and special group parameters x. These parameters are then added to their related atom and special group in the corresponding parameter table assigned to the specific descriptor.
The group parameter calculation is then immediately followed by the computation of each molecule’s descriptor value in question, on the basis of these group parameters according to Equation (1) outlined in the next section, and compared with its experimental value to receive the related statistics data, which are finally added at the bottom of the parameter table. Following the above-mentioned procedure resulted in the two parameter sets in Table 2 and Table 3, designed for the calculation of the molecules’ logPow and logKoa values, respectively.

Table 2.
Atom and special groups and their contribution in logPow calculations.

Table 3.
Atom and special groups and their contribution in logKoa calculations.
2.3. Calculation of Descriptors logPow and logKoa
Based on the aforementioned respective atom-group-parameter tables, the descriptors logPow and logKoa of a molecule can now easily be calculated by simply summing up the contribution of each atom and special group occurring in the molecule, following Equation (1), wherein i and j are the number of atom groups Ai and special groups Bj, respectively, ai is the contribution of atom group Ai, bj is the contribution of special group Bj and c is the constant listed at the top of the respective parameter tables.
Descriptor calc = ∑aiAi + ∑bjBj + c
In Table 4, a typical example is presented with endosulfan sulphate (Figure 1), demonstrating the ease of the calculation of logKoa for which the experimental value was 9.68 [30]. Note that the term “endocyclic bonds” only concerns C-C single bonds.

Table 4.
Example calculation of the logKoa of endosulfan sulphate.
Figure 1.
Endosulfan sulphate (graphics by ChemBrain IXL).
Evidently, the group-additivity method is limited to the calculation of a molecule’s logPow or logKoa for which a parameter value in the respective Table 2 or Table 3 is known for each atom group that is found in the molecule. Beyond this, since the reliability of these parameter values increases with the number of independent molecules upon which their calculation is based, the lowest reliability limit for these parameters was set to three molecules, which, as a consequence, excluded any atom group based on less than three molecules from further calculations. Accordingly, only atom groups for which the number of molecules is three or more, shown in the rightmost columns of Table 2 and Table 3, have been accepted as “valid” for descriptor calculations. This explains the lower number of molecules for which the logPow and logKoa have been calculated (lines B, C and D in Table 2 and Table 3) than the number upon which the evaluation of the complete set of parameters is based (line A).
2.4. Cross-Validation Calculations
The plausibility of the group-parameter calculations was immediately checked by applying a 10-fold cross-validation algorithm, which comprises 10 recalculations of the complete set of group parameters, whereby, before each recalculation, every other 10th compound of the total compounds’ list is temporarily removed from the calculation and separated into a test list, thus ensuring that each molecule has played the role of a test sample once. The combined test data were then statistically worked up and their results added to Table 2 and Table 3 at the bottom in lines E, F, G and H. It may be noticed that the total number of test compounds shown in the right-most column of the statistics lines is lower than that in the training set in lines B, C and D; this is a consequence of the requirement that only “valid” atom groups are to be used for descriptor calculations, and due to the 10% lower number of training samples in each recalculation, the number of “valid” atom groups (as defined in the prior section) tends to decrease to an unpredictable degree. Atom groups, which are represented by less than three molecules, as shown in the right-most column, and are thus not “valid” for descriptor calculations, are therefore remnants of the parameter calculation based on the complete compound set (line A in Table 2 and Table 3). Nevertheless, they have deliberately been left in Table 2 and Table 3 for use in future calculations with additional molecules potentially carrying under-represented atom groups in this ongoing project.
3. Sources
3.1. Sources of logPow Values
The majority of the experimental logPow data originates from the comprehensive collection of Klopman et al. [8], supplemented by works of Sangster [32] and Lipinski et al. [33], already cited in [13]. Additional data have been provided for unsubstituted and substituted, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, alcohols and esters in the works of Tewari et al. [34]; for heterocycles, hetarenes and carboxylic acids by Ghose et al. [6,7]; complemented for amines, amides and nitro derivatives by Leo [10]. Further data for the aforementioned compound classes have been found in papers by Abraham et al. [35], for certain drugs by Hou and Xu [12] and Wang et al. [11], for organophosphorus derivatives by Czerwinski et al. [36], for the specific energetic compound 2,4-dinitroanisole by Boddu et al. [37], for a number of fluorobenzenes, -anilines and -phenols by Li et al. [38] and finally for a number of pesticides and oil constituents in a paper by Saranjampour et al. [39].
3.2. Sources of logKoa Values
Recently, Ebert et al. [40] published a comprehensive collection of more than 2000 experimental logKoa values upon which the present study is essentially based. This set of data has been complemented with data for 75 chloronaphthalene derivatives by Puzyn et al. [41], for 14 PAHs by Odabasi et al. [42], for some methylsiloxanes and dimethylsilanol by Xu and Kropscott [43] and for ethyl nitrate by Easterbrook et al. [44].
3.3. Sources of logKaw Values
Ebert’s paper [30], cited in the introductory section, presented in their supplementary information a large collection of experimental logKaw data, which served as reference values for the calculated data. Sander [45] provided an extensive library of Henry’s law constants for more than 2600 compounds, which, after translation into logKaw values at 298.15 K, complemented Ebert’s data set.
4. Results
4.1. Partition Coefficient logPow
As shown at the bottom of Table 2, the number of molecules upon which the present group parameter set is based is 3332, substantially larger than the 2780 samples in our earlier paper [13]. Beyond this, the significantly better statistical results in Table 2 (lines B to H) with, e.g., a cross-validated (cv) standard deviation S of 0.42 (line H) vs. the earlier value of 0.51 is the result of the removal of molecules from the parameter computation for which the experimental value deviates by more than three times the value of S. The 122 molecules thus removed (3.5% of the total set) have been collected in an outlier list, available in the Supplementary Materials. The larger number of compounds for the group parameter computation not only significantly improved the statistical results but also enlarged the list of “valid” atom groups from 195 to 214, enabling the calculation of the logPow value of at present 29,462 molecules (79.4% of the total dataset). The correlation coefficients R2 of 0.9648, the (cross-validated) Q2 of 0.9599 and the cv standard error S of 0.42, based on 3246 and 3164 molecules, respectively, are significantly better than in our earlier paper [13] and compare very well not only with Klopman’s [8] results, which are based on a group-additivity method comparable to ours and have R2 and Q2 values of 0.93 and 0.926, respectively, but also with the statistical results of more elaborate calculation methods published recently [4,5,14,15,16]. As shown in the correlation diagram of Figure 2 and the histogram for Figure 3, the experimental logPow values range from −4.6 to +12.53 with a fairly even Gaussian error distribution.
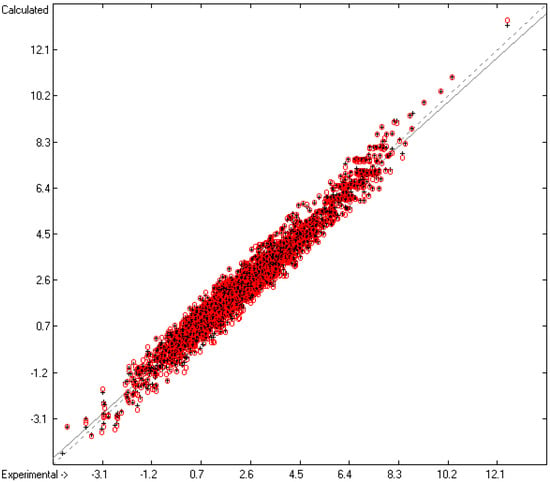
Figure 2.
Correlation diagram of the logPow data. Cross-validation data are superpositioned as red circles (10-fold cross-valid.: N = 3246; Q2 = 0.9599; regression line: intercept = 0.1052; slope = 0.9636).
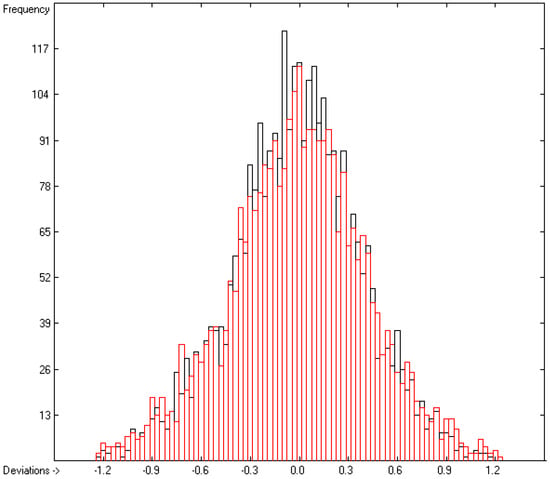
Figure 3.
Histogram of the logPow data. Cross-validation data are superpositioned as red bars. (σ = 0.39; S = 0.42; experimental values range from −4.6 to +12.53).
It is worth mentioning that the observation discussed in our earlier paper (see Table 9 in [13]) concerning the two forms of amino acids (nonionic or zwitterionic) is not only confirmed by the new and extended group parameter set of Table 2 but also that the logPow differences in nearly all cases even more clearly distinguish the two forms. On the other hand, the ambiguous results concerning the keto/enol forms of the compounds listed in Table 10 in [13] could not be lifted by the new parameter set, which is not surprising in view of the sometimes strong solvent dependence of the equilibrium, as exemplified with acetylacetone [46]. In view of the discussion of certain particularities concerning the subsequent calculation of the third partition coefficient logKaw in Section 4.3, it should be stressed at this point that the calculated logPow values for the hydrocarbons do not show any abnormal or systematic deviations from experimental values.
4.2. Partition Coefficient logKoa
The calculation of the group parameter set of Table 3 used for the prediction of the logKoa values is essentially based on the curated data set provided in Ebert’s paper [40], whereby compounds with just one “backbone atom” such as halomethanes or hydrocyanide had to be omitted as they are obviously not calculable using the present method. After the removal of another 129 compounds as outliers (6.36% of the total), following the same exclusion criterion as in the previous section, 1900 samples with their experimental data (line A in Table 3) remained for the computation of the group parameter values. Again, the outliers have been collected in a separate list available in the Supplementary Materials for readers who might want to re-evaluate their logKoa values.
The subsequent calculation of the logKoa values of 1829 training and 1765 test molecules based on 167 “valid” atom and special groups (line A) revealed excellent statistical results with a correlation coefficient R2 of 0.9765, a standard deviation s of 0.44 (lines B and D) and a cross-validated Q2 of 0.9717 with a corresponding S of 0.48 (lines F and H), visualised in the correlation diagram on Figure 4 and the histogram on Figure 5. These statistical data even outperform those given in Ebert’s paper and thus also the competing methods mentioned therein such as COSMOtherm [47] and EPI-Suite KOAWIN [48], not only confirming the versatility but also the reliability of the present group-additivity approach, which allowed the calculation of the logKoa value for 27,044 molecules (72.9% of the entire database). Again, it should be kept in mind that just like in Section 4.1, any particularly large or systematic deviations between the experimental and calculated logKoa values for the hydrocarbons could not be observed.
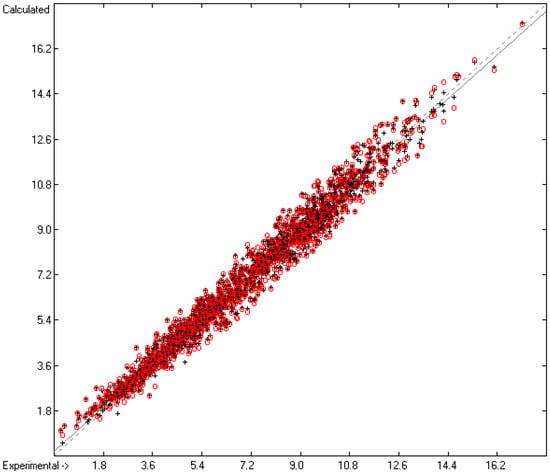
Figure 4.
Correlation diagram of the logKoa data. Cross-validation data are superpositioned as red circles (10-fold cross-valid.: N = 1829; Q2 = 0.9717; regression line: intercept = 0.1997; slope = 0.9729; MAPD = 6.39%).
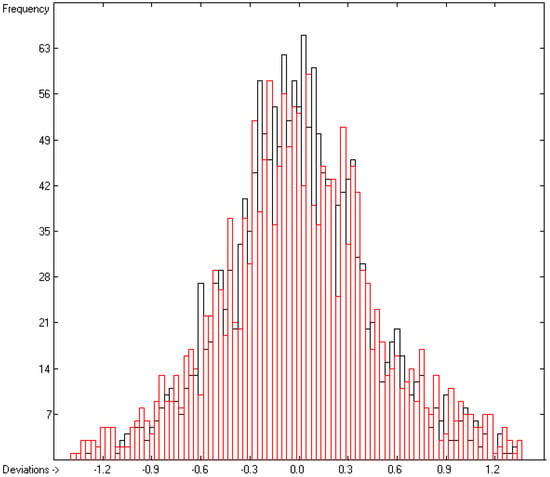
Figure 5.
Histogram of the logKoa data. Cross-validation data are superpositioned as red bars (σ = 0.44; S = 0.48; experimental values range from 0.28 to 17.15).
4.3. Partition Coefficient logKaw
Once the partition coefficients logPow and logKoa were calculated by means of the group-additivity method based on Table 2 and Table 3, respectively, it was easy to determine the logKaw values, applying Equation (2) on each molecule in the database for which both descriptors had been calculated, adding up to 26,220 molecules. In order to assess the quality of the logKaw values, it is important to recognise the flaws of this approach: while the logPow values were experimentally measured in a mixture of water-saturated octanol and octanol-saturated water, the logKoa measurements occurred in dry octanol, an aspect that has been discussed in detail by Ebert et al. [40]. Hence, Equation (2) serves only as an approximation. In addition, since both descriptors on the right side of the equation appear with their own standard error, the error-propagation rule stipulates a standard error of logKaw that is clearly larger than either of the two constituting descriptors. Entering the standard errors S for the test molecules of 0.42 (for logPow) and 0.48 (for logKoa) into an error-propagation calculation, the expected standard error S for logKaw is 0.638.
logKaw (calc) = logPow (calc) − logKoa (calc)
In order to test the reliability of the thus-calculated logKaw values, a representative number of experimentally determined logKaw data, extracted from the comprehensive databases of Ebert et al. [30] and Sander [45], were added to the database. In the latter case, the Henry’s law solubility constants Hscp were translated into the corresponding logKaw values at 298.15 K. The comparison of the calculated with the experimental logKaw values is visualised in the correlation diagram of Figure 6 and the histogram in Figure 7.
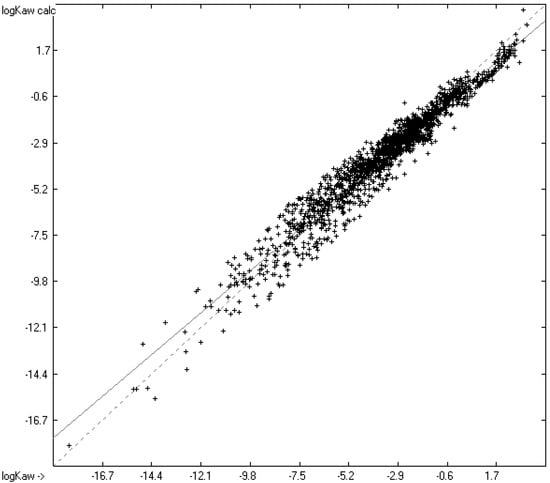
Figure 6.
Correlation diagram of the logKaw data (N = 1937; Q2 = 0.9467; regression line: intercept = −0.4196; slope = 0.9044).
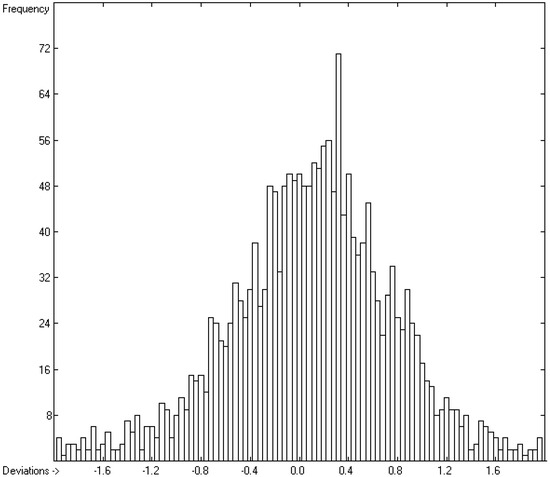
Figure 7.
Histogram of the logKaw data (S = 0.67; experimental values range from −17.99 to +3.71).
The complete set of experimental data was separated from the outliers, applying the same exclusion conditions as for the logPow and logKoa values, and the outliers were collected in a corresponding list, available in the Supplementary Materials. Comparison of the remaining dataset with the calculated values yielded a standard error of 0.67, slightly higher than that predicted by the error-propagation calculation. A detailed analysis of the experimental data revealed two potential explanations for the inordinate scatter: (1) Within a series of substitution isomers, e.g., the tetra- or hexachlorobiphenyls, the tri- or pentachlorodiphenyl ethers or the dichloroanisoles, the experimental logKaw values varied in a range of up to and over 1 unit, which was hard to assign to the specific positioning of the substituents. At any rate, the group-additivity-based calculation of the logPow and logKoa values was not able to distinguish between these substitution isomers. (2) Sander’s comprehensive database of Henry’s law constants [45], listing the experimental Hscp values for a compound originating from various authors, showed for many compounds large differences between their Hscp values, in some cases exceeding one unit after translation into logKaw, e.g., for undecane, acetylacetone or anthraquinone.
A thorough analysis of the correlation diagram in Figure 6 and the histogram in Figure 7 revealed an interesting peculiarity, visible as an indentation at the upper end of the correlation diagram and as a weak hump on the right side of the histogram: except for some siloxanes with experimental logKaw values above 1.6 and normal scatter about calculated values, the predicted logKaw for the remaining compounds with experimental logKaw values above −1.0 were nearly systematically too low by ca. 0.5–1 units. It turned out that they were all pure hydrocarbons, in particular alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. The correlation diagram of the logKaw data in Figure 8, focussing on these hydrocarbons, confirms this observation.
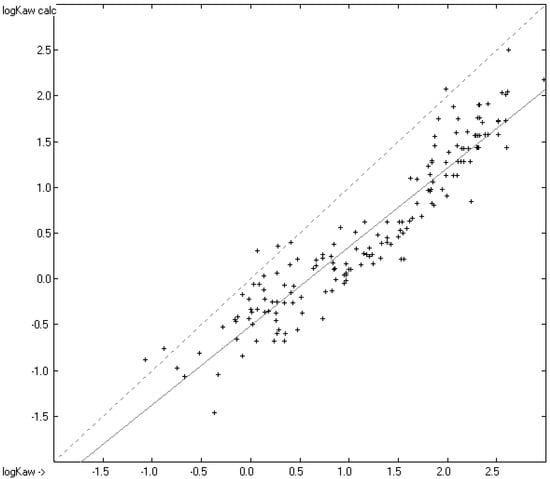
Figure 8.
Correlation diagram of the logKaw data for alkanes, alkenes and alkynes (N = 170).
Since, as mentioned in Section 4.1 and Section 4.2, no particularly large or systematic deviations between the experimental and calculated logPow and logKoa data for the hydrocarbons could be detected, a potential explanation for this peculiarity might be based on the experimental conditions for the determination of the logPow values as mentioned by Ebert et al. [40]: since water-saturated octanol is a more polar solvent than pure octanol, while octanol-saturated water is less polar than pure water, the experimental logPow values, measured in an octanol/water mixture, tend to be shifted to smaller absolute values than theory would predict. While this is true for all measured solutes, it is possibly most effective for the least polar solutes such as the mentioned hydrocarbons, thus leading to experimental logPow values that are particularly low for the hydrocarbons. As a consequence, their calculation based on the group-additivity method predicts equally low logPow values, which again lead to low logKaw data when Equation (2) is applied and when compared with experimental logKaw values that are determined under pure air/water conditions.
4.4. Interpretation of the Special Groups’ Contributions to logPow and logKoa, and Ultimately for logKaw
While the atom group parameters are descriptor-specific and their comparison between descriptors does not make sense, special groups serve as differentiators of molecules that carry these groups from those that do not. Therefore, their meanings have overlapping descriptors; their values, however, must be viewed in the context of the value range of the descriptors. In the present case, the value ranges of logPow and logKoa are similar (ca. 17 log units) and in the same area, and thus, a direct comparison of the special group contributions in Table 2 and Table 3 is permissible and leads to a few interesting observations: While the groups “(COH)n”, “Alkane”, “Unsaturated HC” and “Endocyclic bonds” in both tables only contribute to a minor degree (but nevertheless improve the statistical results) and consequently show only minor differences between the two tables, a significant difference was found for the groups “H/H Acceptor” and “(COOH)n”. The former special group, taking account of intramolecular hydrogen bridges, indicates a small but clearly higher chance of being a compound carrying an intramolecular H-bridge towards the octanol side in an octanol/water mixture, thus raising the logPow value. In contrast, the same H-bridge-carrying molecule has its inclination significantly shifted to the air side in an octanol/air environment compared to that without H-bridges, expressed in its lower logKoa value. The reason may be found in the lower solvent–solute interaction caused by the H-bridge being bound intramolecularly, leading in both cases to a preference for the less polar of the respective two media. A typical example is the compound couple 2- and 3-nitroaniline, sampled in Table 5, where the former molecule carries a H-bridge between an amino-H and an oxygen of the nitro group.

Table 5.
Experimental (calculated) logPow and logKoa values of 2- and 3-nitroaniline.
An inverse effect can be found with molecules carrying two or more carboxylic acid functions: While the additional contribution of a second or third COOH function shows little effect in an octanol/water environment with a slightly increased shift towards water, leading to a lower logPow value, in an octanol/air environment, each additional COOH group drastically tilts the equilibrium towards the octanol side, thus strongly raising the logKoa value. This may be demonstrated by the couple of hexanoic/1,6-hexanedioic acid, where both have the same carbon-chain length but where the second molecule carries two carboxylic acid functions, which tilts the octanol/air equilibrium by a factor of more than 10,000 towards the octanol side as shown in Table 6. Now, it is well known that monocarboxylic acids usually exist as dimeric associates in all three aggregate states. This association effect on the solubility is inherently taken into account in the atom group parameter evaluation of the COOH function. On the other hand, dicarboxylic acids do not only form dimers but also cyclical and linear oligomeric associates, with drastic consequences on their solubility in the various solvents. It is these additional associations that are considered by the special group “(COOH)n”.

Table 6.
Experimental (calculated) logPow and logKoa of hexanoic and 1,6-hexanedioic acid.
As a consequence, solutes with a low tendency to interact with solvents, either inherent or induced by intramolecular hydrogen bridges, show a trend to higher logKaw values; the additional intermolecular association of di- and tricarboxylic acids, on the other hand, results in a significantly lower logKaw value, as exemplified in Table 7, where the respective calculated data in Table 5 and Table 6 have been applied in Equation (2). The experimental logKaw values have been extracted from Ebert et al. [30].

Table 7.
Experimental and calculated logKaw of some examples.
5. Conclusions
The present study, which is part of an ongoing project, put to use a tool for the simple and reliable calculation of the two partition coefficients logPow and logKoa that has proven its unmatched versatility in the equally reliable prediction of now up to 19 physical, thermodynamic, solubility-, optics-, charge- and environment-related molecular descriptors [13,49,50,51,52,53,54,55], based on a common group-additivity method. The large database of more than 3300 and 1900 experimental data, respectively, upon which the group parameters for the logPow and logKoa calculations are founded enabled their prediction for nearly 29,500 and more than 27,000 molecules, respectively, of the presently more than 37,100 compounds in ChemBrain’s database. In addition, these results also allowed the trustworthy calculation of the third partition coefficient logKaw for more than 26,000 compounds. The big advantage of the present approach is its ease of use by simply adding, by means of paper and pencil, the parameters of the atoms and groups found in a particular molecule, which are listed in the respective Table 2 and Table 3.
The mentioned project’s software is called ChemBrain IXL, available from Neuronix Software, version ChemBrain IXL 5.9.70.1 (www.neuronix.ch (accessed on 27 November 2023), Rudolf Naef, Lupsingen, Switzerland).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/liquids4010011/s1: The lists of compounds used in the present work, collected in their 3D structure together with their experimental data, are available as standard SDF files for use in external chemical software under the names of “S01. Compounds List for logPow-Parameters Calculations.sdf”, “S02. Compounds List for logKoa-Parameters Calculations.sdf” and “S03. Compounds List with exp logKaw Data”. The compounds used in the correlation diagrams and histograms are listed with their names and experimental and calculated data under the respective names of “S04. Compounds with Experimental vs. Calculated logPow Values.doc”, “S05. Compounds with Experimental vs. Calculated logKoa Values.doc”, “S06. Compounds with Experimental vs. Calculated logKaw Values.doc” and “S07. Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes with Exp. vs. Calc. logKaw Values.doc”. In addition, for each of the three partition coefficients, a list of their outliers has been added under the names of “S08. Outliers of logPow.doc”, “S09. Outliers of logKoa.doc” and “S10. Outliers of logKaw.doc”. Beyond this, the Supplementary Materials encompass all the figures and tables cited in the text as .tif and .doc files, respectively.
Author Contributions
R.N. developed the project ChemBrain and its software upon which this paper is based, and also fed the database, calculated and analysed the results and wrote the paper. W.E.A.J. suggested the extension of ChemBrain’s tool and contributed experimental data and the great majority of the literature references. Beyond this, R.N. is indebted to W.E.A.J. for the many valuable discussions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
R.N. is indebted to the library of the University of Basel for allowing him full and free access to the electronic literature database.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Simonich, S.L.; Hites, R.A. Organic Pollutant Accumulation in Vegetation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, M.S. Bioaccumulation of Hydrophobic Chemicals in Agricultural Food Chains. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, W.J.; Shunthirsasingham, C.; Dettenmaier, E.M.; Zaleski, R.T.; Fantke, P.; Arnot, J.A. A Review of Measured Bioaccumulation Data on Terrestrial Plants for Organic Chemicals:Metrics, Variability, and the Need for Standardized Measurement Protocols. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Draghi, C.; Fayet, G.; Creton, B.; Rozanska, X.; Rotureau, P.; de Hemptinne, J.-C.; Ungerer, P.; Rousseau, B.; Adamo, C. A General Guidebook for the Theoretical Prediction of Physicochemical Properties of Chemicals for Regulatory Purposes. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13093–13164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelli, C.I.; Benfenati, E.; Cester, J. Evaluation of QSAR models for predicting the partition coefficient (log P) of chemicals under the REACH regulation. Environ. Res. 2015, 43, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Crippen, G.M. Atomic physicochemical parameters for three-dimensional structure-directed quantitative structure-activity relationships I. Partition coefficients as a measure of hydrophobicity. J. Computer. Chem. 1986, 7, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Pritchett, A.; Crippen, G.M. Atomic physicochemical parameters for three dimensional structure directed quantitative structure-activity relationships III: Modeling hydrophobic interactions. J. Comput. Chem. 1988, 9, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopman, G.; Li, J.-Y.; Wang, S.; Dimayuga, M. Computer automated log P calculations based on an extended group contribution approach. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1994, 34, 752–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanadhan, V.N.; Ghose, A.K.; Revankar, G.R.; Robins, R.K. Atomic physicochemical parameters for three dimensional structure directed quantitative structure-activity relationships. 4. Additional parameters for hydrophobic and dispersive interactions and their application for an automated superposition of certain naturally occurring nucleoside antibiotics. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1989, 29, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, A.J. Calculating log Poct from structures. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1281–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fu, Y.; Lai, L. A new atom-additive method for calculating partition coefficients. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1997, 37, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.J.; Xu, X.J. ADME evaluation in drug discovery. 2. Prediction of partition coefficient by atom-additive approach based on atom-weighted solvent accessible surface areas. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naef, R. A Generally Applicable Computer Algorithm Based on the Group Additivity Method for the Calculation of Seven Molecular Descriptors: Heat of Combustion, LogPO/W, LogS, Refractivity, Polarizability, Toxicity and LogBB of Organic Compounds; Scope and Limits of Applicability. Molecules 2015, 20, 18279–18351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plante, J.; Werner, S. JPlogP: An improved logP predictor trained using predicted data. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, N.; Goss, K.-U.; Ebert, A. Exploring the octanol–water partition coefficient dataset using deep learning techniques and data augmentation. Com. Chem. 2021, 4, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, T.; He, X.; Man, V.H.; Wang, J. Development and test of highly accurate endpoint free energy methods. 2: Prediction of logarithm of n-octanol–water partition coefficient (logP) for druglike molecules using MM-PBSA method. J. Comput. Chem. 2023, 44, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Harner, T.; Schramm, K.W.; Quan, X.; Xue, X.; Wu, W.; Kettrup, A. Quantitative relationships between molecular structures, environmental temperatures and octanol/air partition coefficients of PCDD/Fs. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Harner, T.; Yang, P.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Schramm, K.W.; Kettrup, A. Quantitative predictive models for octanol/air partition coefficients of polybrominated diphenyl ethers at different temperatures. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Harner, T.; Schramm, K.W.; Quan, X.; Xue, X.; Kettrup, A. Quantitative relationships between molecular structures, environmental temperatures and octanol/air partition coefficients of polychlorinated biphenyls. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2003, 27, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Quan, X.; Qu, B.; Liang, X. Octanol/air partition coefficients of polybrominated biphenyls. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staikova, M.; Wania, F.; Donaldson, D. Molecular polarizability as a single parameter predictor of vapour pressures and octanoleair partitioning coefficients of non-polar compounds: A priori approach and results. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xue, X.; Liang, X. Prediction of octanol/air partition coefficients of semivolatile organic compounds based on molecular connectivity index. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Y. Qspr modeling of n-octanol/air partition coefficients and liquid vapor pressures of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Shi, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Improved 3D-QSPR analysis of the predictive octanol/air partition coefficients of hydroxylated and methoxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Li, H. QSPR study on the octanol/air partition coefficient of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by using molecular distance-edge vector index. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y. Prediction of octanol-air partition coefficients for polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) using 3D-SQAR models. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H. Comparison of prediction methods for octanol-air partition coefficients of diverse organic compounds. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, J. Development of polyparameter linear free energy relationship models for octanol/air partition coefficients of diverse chemicals. Environ. Sci. Process. Impact. 2017, 19, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, X.; Huang, L. The fragment constant method for predicting octanol/air partition coefficients of persistent organic pollutants at different temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2006, 35, 1365–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, R.-U.; Kühne, R.; Schüürmann, G. Henry’s Law Constant—A General-Purpose Fragment Model to Predict Log Kaw from Molecular Structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardtwig, E. Fehler—Und Ausgleichsrechnung; Bibliographisches Institut AG: Mannheim, Germany, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Sangster, J. Octanol-water partition coefficients of simple organic compounds. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1989, 18, 1111–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, Y.B.; Miller, M.M.; St. Wasik, P.; Martire, D.E. Aqueous Solubility and Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient of Organic Compounds at 25.0 °C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1982, 27, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.H.; Chadha, H.S.; Whiting, G.S.; Mitchell, R.C. Hydrogen Bonding. 32. An Analysis of Water-Octanol and Water-Alkane Partitioning and the Δlog P Parameter of Seiler. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St. Czerwinski, E.; Skvorak, J.P.; Maxwell, D.M.; Lenz, D.E.; St. Baskin, I. Organophosphorus Compounds on Biodistribution and Percutaneous Toxicity. J. Biochem. Mol. Tox. 2006, 20, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddu, V.M.; Abburi, K.; St. Maloney, W.; Damavarapu, R. Thermophysical Properties of an Insensitive Munitions Compound, 2,4-Dinitroanisole. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Shan, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.-Y. Determination of lgKow and QSPR Study on Some Fluorobenzene Derivatives. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2009, 28, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Saranjampour, P.; Vebrosky, E.N.; Armbrust, K.L. Salinity Impacts on Water Solubility and n-Octanol/Water Partition Coefficients of Selected Pesticides and Oil Constituents. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, R.-U.; Kühne, R.; Schüürmann, G. Octanol/Air Partition Coefficient. A General-Purpose Fragment Model to Predict Log Koa from Molecular Structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzyn, T.; Falandysz, J.; Rostkowski, P.; Piliszek, S.; Wilczynska, A. Computational estimation of logarithm of octanol/air partition coefficients and subcooled vapour pressures for each of 75 chloronaphtalene congeners. Phys.-Chem. Prop. Distr. Model. Organohal. Compds. 2004, 66, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabasi, M.; Cetin, E.; Sofuoglu, A. Determination of octanol–air partition coefficients and supercooled liquid vapor pressures of PAHs as a function of temperature: Application to gas–particle partitioning in an urban atmosphere. Atm. Environ. 2006, 40, 6615–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kropscott, B. Method for Simultaneous Determination of Partition Coefficients for Cyclic Volatile Methylsiloxanes and Dimethylsilanediol. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easterbrook, K.D.; Vona, M.A.; Osthoff, H.D. Measurement of Henry’s law constants of ethyl nitrate in deionized water, synthetic sea salt solutions, and n-octanol. Chemosphere 2024, 346, 140482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, R. Compilation of Henry’s law constants (version 5.0.0) for water as solvent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 10901–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.; Dwek, R.A. An n.m.r. study of keto-enol tautomerism in β-diketones. J. Chem. Soc. B 1966, 1966, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COSMOlogic GmbH Co. KG. A Dassault Systemes Company, Version 19.0.4, COSMOthermX. 2019. Available online: www.cosmologic.de (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- US EPA. Estimation Programs Interface Suite for Microsoft Windows; Version 4.11, Module KOAWIN v. 1.11; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Naef, R.; Acree, W.E., Jr. Calculation of Five Thermodynamic Molecular Descriptors by Means of a General Computer Algorithm Based on the Group-Additivity Method: Standard Enthalpies of Vaporization, Sublimation and Solvation, and Entropy of Fusion of Ordinary Organic Molecules and Total Phase-Change Entropy of Liquid Crystals. Molecules 2017, 22, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naef, R.; Acree, W.E. Application of a General Computer Algorithm Based on the Group-Additivity Method for the Calculation of Two Molecular Descriptors at Both Ends of Dilution: Liquid Viscosity and Activity Coefficient inWater at Infinite Dilution. Molecules 2018, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naef, R.; Acree, W.E., Jr. Calculation of the Surface Tension of Ordinary Organic and Ionic Liquids by Means of a Generally Applicable Computer Algorithm Based on the Group-Additivity Method. Molecules 2018, 23, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naef, R. Calculation of the Isobaric Heat Capacities of the Liquid and Solid Phase of Organic Compounds at 298.15K by Means of the Group-Additivity Method. Molecules 2020, 25, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naef, R.; Acree, W.E., Jr. Calculation of the Vapour Pressure of Organic Molecules by Means of a Group-Additivity Method and Their Resultant Gibbs Free Energy and Entropy of Vaporization at 298.15 K. Molecules 2021, 26, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naef, R.; Acree, W.E., Jr. Revision and Extension of a Generally Applicable Group-Additivity Method for the Calculation of the Standard Heat of Combustion and Formation of Organic Molecules. Molecules 2021, 26, 6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naef, R.; Acree, W.E., Jr. Revision and Extension of a Generally Applicable Group Additivity Method for the Calculation of the Refractivity and Polarizability of Organic Molecules at 298.15 K. Liquids 2022, 2, 327–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).