Abstract
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have emerged as novel alternatives to common solvents and VOCs. Their employment as electrolytes in batteries has been an area of intense research. In this context, understanding changes in the physicochemical properties of DESs in the presence of Li salts becomes of utmost importance. Solvatochromic probes have the potential to gauge such changes. It is reported herein that one such UV–vis molecular absorbance probe, Reichardt’s betaine dye 33, effectively manifests changes taking place in a DES Glyceline composed of H-bond accepting salt choline chloride and H-bond donor glycerol in a 1:2 molar ratio, as salt LiCl is added. The lowest energy intramolecular charge–transfer absorbance band of this dye exhibits a 17 nm hypsochromic shift as up to 3.0 molal LiCl is added to Glyceline. The estimated parameter shows a linear increase with the LiCl mole fraction. Spectroscopic responses of betaine dye 33, N,N-diethyl-4-nitroaniline and 4-nitroaniline are used to assess empirical Kamlet–Taft parameters of dipolarity/polarizability (), H-bond-donating acidity (α) and H-bond-accepting basicity () as a function of LiCl concentration in Glyceline. LiCl addition to Glyceline results in an increase in α and no change in and . It is proposed that the added lithium interacts with the oxygen of the –OH functionalities on the glycerol rendering of the solvent with increased H-bond-donating acidity. It is observed that pyrene, a popular fluorescence probe of solvent polarity, does respond to the addition of LiCl to Glyceline, however, the change in pyrene response starts to become noticeable only at higher LiCl concentrations ( ≥ 1.5 m). Reichardt’s betaine dye is found to be highly sensitive and versatile in gauging the physicochemical properties of DESs in the presence of LiCl.
1. Introduction
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have emerged as viable alternatives not only to toxic organic solvents but also to ionic liquids [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. While many commonly used organic solvents are hazardous to the immediate environment and belong to the class of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), recent toxicity reports are not favorable as far as common ionic liquids are concerned [7,8]. Escalating costs associated with the manufacture of many organic solvents combined with the complexity of synthesis and purification of most ionic liquids further restrict the use of these solvent media in science and technology today [7,8]. A DES, in this context, affords a solubilizing media that is mostly non-toxic and inexpensive. DESs can be prepared by simple mixing of two judiciously selected constituents. There have been many discoveries in the types of DESs depending upon the constituents but the most important are type III DESs. They consist of an H-bond donor (HBD) and an H-bond acceptor (HBA), that are inexpensive, non-toxic, and easily acquired. After mixing the two constituents, the melting point of the resulting mixture is usually much lower than the melting points of each of the constituents resulting in a liquid state of matter under ambient conditions. Among several classes of DESs proposed in the recent literature, the ones prepared by mixing a common ammonium salt, such as HBA with a suitable HBD, are perhaps the most investigated so far [3,5,9]. Specifically, the DESs constituted of choline chloride as the HBA and one of the HBDs, namely urea, glycerol, ethylene glycol, and malonic acid, are the initial DESs in this class that were reported around two decades ago [3,5,9]. Applications of these DESs in various strata of science and technology have been growing ever since [2,3].
One of the major areas of application of DESs is in electrochemistry, where DESs have shown potential as worthy electrolytes for batteries [10,11]. As a consequence, salt-added DESs have become a solvent system subject to rigorous investigation of late. In this context, investigations of potential uses for DESs in Li-ion batteries have naturally emerged. Changes in the physicochemical properties of the DESs due to the presence of Li salt have subsequently become an active area of research. Understanding of the solvation and dynamics of Li salts within DESs is being pursued by researchers worldwide.
Solvatochromic probe behavior within a Li salt-added DES system can reveal changes in the physicochemical properties of the milieu due to the addition of the Li salt; it also reveals information on solute solvation and dynamics in the process [12,13,14]. Information gained from the responses of spectroscopic probes can be useful in understanding reactivity, separation, extraction, and electrochemistry involving solutes with similar functionalities. We have found that Reichardt’s betaine dye 33 (structure provided in Figure 1), which is known to manifest dipolarity/polarizability along with the H-bond donating (HBD) acidity of the solubilizing medium, is effectively able to gauge the consequences of adding LiCl to the DES constituted of choline chloride (ChCl) and glycerol (Gly) in a 1:2 molar ratio named Glyceline. The use of betaine dyes to obtain physicochemical changes and solute solvation affords a simple and effective way to obtain insights to such complex systems.
Figure 1.
Structure of Reichardt’s betaine dye 33.
2. Materials and Methods
Glycerol (≥99.5%), choline chloride (≥99.0%) and LiCl with >99% (by mass) purity were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and stored in an Auto Secador desiccator cabinet. 2,6-Dichloro-4-(2,4,6-triphenylpyridinium-1-yl)phenolate (betaine dye 33) was purchased in the highest available purity from Fluka (≥99%, HPLC grade). 4-Nitroaniline (NA) and N,N-diethyl-4-nitroaniline (DENA) were purchased in the highest purity from Spectrochem Co., Ltd. (Mumbai, India). and Frinton Laboratories, respectively. Pyrene [≥99.0% (GC), puriss for fluorescence] was obtained in highest purity from Sigma-Aldrich Co.
The calculated amount of glycerol and choline chloride was transferred to a glass vial and weighed using an analytical balance with a precision of ±0.1 mg. The components were mixed thoroughly to obtain a homogeneous solution and subjected to vacuum for approximately 6 h. As per the requirement, a pre-calculated amount of LiCl was added to this solution and mixed over a magnetic stirrer at 60 °C until all of the LiCl was dissolved, and a homogeneous solution was obtained. Stock solution of all of the probes was prepared by dissolving the required amount in ethanol in a pre-cleaned amber glass vial and stored at 4 ± 1 °C to retard any photochemical reaction. An appropriate amount of the probe solution from the stock was transferred to the 1 cm path length quartz cuvette. Ethanol was evaporated using a gentle stream of high purity nitrogen gas to achieve the desired final concentration of the probe. A pre-calculated amount of LiCl was added—Glyceline DES was directly added to the cuvette and the solution was thoroughly mixed. The final concentrations of DENA, NA, betaine dye 33 and pyrene were ~20, 20, 50 and 10 µM, respectively. A Perkin-Elmer Lambda 35 double-beam spectrophotometer with variable bandwidth was used for the acquisition of the UV−vis molecular absorbance spectra of DENA, NA and betaine dye 33. Steady-state fluorescence spectra of pyrene ( = 337 nm) were acquired on an Edinburgh Instruments Ltd. (Livingston, UK) spectrofluorimeter (FLS1000-SS-S) with STGM325-X grating excitation and STGM325-M grating emission monochromators with a 450 W Xe arc lamp as the excitation source, a single cell TEC holder and a Red PMT as the detector. All spectra were duly corrected by subtracting the spectral responses from suitable blanks prior to data analysis. Data analysis was performed using SigmaPlot v14.5 software.
3. Results and Discussion
UV–vis molecular absorbance spectra of Reichardt’s betaine dye 33 dissolved in LiCl-added Glyceline under ambient conditions are presented in Figure 2A (the maximum molal concentration of LiCl in the system was = 3.0 mol·kg−1, which corresponds to mole fraction = 0.24). A careful examination of the spectra reveals that the lowest energy absorbance band of the dye shows systematic monotonic hypsochromic shift as LiCl is added to Glyceline. It is well-established that 2,6-diphenyl-4-(2,4,6-triphenylpyridinium-1-yl)phenolate (Reichardt’s betaine dye 30) exhibits an unusually high solvatochromic band shift; the lowest energy intramolecular charge-transfer absorption band of betaine dye 30 is hypsochromically-shifted by ca. 357 nm in going from relatively nonpolar diphenyl ether (~810 nm) to water (~453 nm) [15,16,17]. It is established that the negative solvatochromism of betaine dye 30 originates from the differential solvation of its highly polar equilibrium ground-state and the less polar first Franck–Condon excited-state with increasing solvent polarity [15,16,17]. There is a considerable charge transfer from the phenolate to the pyridinium part of the zwitterionic molecule. Because of its zwitterionic nature the solvatochromic probe behavior of betaine dye 30 is strongly affected by the HBD acidity of the solvent; HB-donating solvents stabilize the ground-state more than the excited-state. The empirical scale of solvent ‘polarity’, for betaine dye 30, is defined as the molar transition energy of the dye traditionally in kcal·mol−1 at room temperature and normal pressure according to the expression = 28591.5/ in nm [15,16,17]. However, in the present work a derivative of betaine dye 30, 2,6-dichloro-4-(2,4,6-triphenylpyridinium-1-yl)phenolate (betaine dye 33), is used to investigate LiCl-added Glyceline system due to it having certain advantages over betaine dye 30. The low solubility of betaine dye 30 in many H-bonded solvent systems renders it unsuitable for our investigations. Betaine dye 33, on the other hand, has no such problems due to inherent structural differences with betaine dye 30. For historical reasons, it has been related to number 33, and the lowest energy absorbance transition of this dye [i.e., (33)] is calculated the same way is calculated [17].
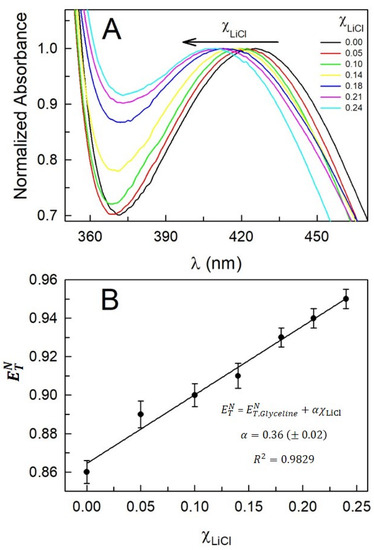
Figure 2.
Absorbance spectra of Reichardt’s betaine dye 33 [50 µM] in Glyceline and LiCl-added Glyceline under ambient conditions (panel A) and variation in with a mole fraction of LiCl () (panel B). The solid straight line is the best fit obtained from the linear regression analysis. Error in is ≤±0.007.
Thus, from the absorbance spectra of betaine dye 33 presented in Figure 2A, the corresponding (33) are estimated and converted into using Equations (1) and (3):
R = 0.9926, standard error of estimate = 0.8320, n = 20
(30) was obtained from (33) (i.e., Equation (1)) by acquiring the lowest energy UV–vis absorbance band for both the dyes in 20 different solvents, and performing linear regression analysis between the two.
Here, TMS stands for tetramethylsilane. From (30)WATER = 63.1 kcal·mol−1 and (30)TMS = 30.7 kcal·mol−1, we obtain
is easier to conceive as it is dimensionless and varies between 0 for TMS (extreme non-polar) and 1 for water (extreme polar) [17]. Table 1 lists the lowest energy absorbance maxima of betaine dye 33 along with the estimated for the LiCl-added Glyceline system. A hyposchromic shift of 17 nm is observed in going from no LiCl to 3.0 m of LiCl in Glyceline which transforms to an increase in from 0.86 to 0.95. It is convenient to note that a plot of versus exhibits good linear behavior (R2 > 0.98) with a slope of 0.36 (±0.02) (Figure 2B). Thus, it is concluded that as LiCl is added to Glyceline, the dipolarity/polarizabilty and/or HBD acidity of the system increases; and the increase is effectively manifested in the spectral response of the Reichardt’s betaine dye 33 in a linear manner with the mole fraction of LiCl.

Table 1.
Absorbance maxima for Reichardt’s betaine dye 33 , DENA and NA and corresponding estimated Kamlet–Taft empirical solvent parameters, at different mole fractions of LiCl in Glyceline under ambient conditions. Error in are ≤±0.5 nm. Error in is ≤±0.007 and errors in α, and are ≤±0.005.
Whether the increase in upon addition of LiCl to the DES Glyceline is due to the increase in the dipolarity/polarizabilty or the HBD acidity or both is explored by assessing empirical Kamlet–Taft solvatochromic indicators of solvent dipolarity/polarizability , HBD acidity (α), and HBA basicity (β) [18,19,20,21,22]. The is estimated from the absorption maximum (, in kK) of DENA, a non-hydrogen bond donor solute, using [18,19]:
and then α was estimated from (30) and values [18,20].
The δ parameter in Equation (5) is a “polarizability correction term” equal to 0.0 for nonchlorinated aliphatic solvents, 0.5 for polychlorinated aliphatics, and 1.0 for aromatic solvents [21]. Finally, β values are determined from the enhanced solvatochromic shift of NA relative to its homomorph DENA, –Δν(DENA–NA)/kK [18,22]:
Interestingly, the UV–vis absorbance spectra of both DENA and NA, respectively, do not show any statistically meaningful variation upon addition of up to 3.0 m LiCl to the DES Glyceline (Figure 3A). Based on Equations (4) and (6), this subsequently reflects in no change in the β and the parameters as LiCl is added to Glyceline (Table 1). The parameter α, which depends on the parameter along with (Equation (5)), does increase with an increasing concentration of LiCl in Glyceline (Figure 3B).
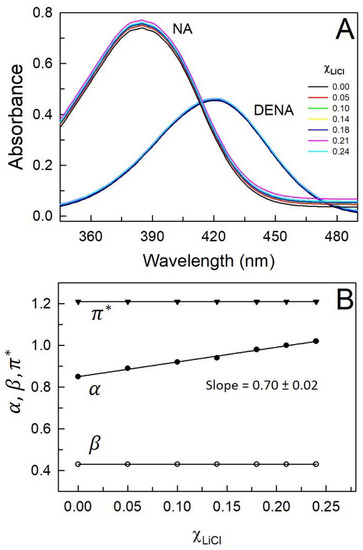
Figure 3.
UV–visible absorbance spectra of N,N-diethyl-4-nitroaniline (DENA, 20 µM) and 4-nitroaniline (NA, 20 µM) (panel A) and variation in with mole fraction of LiCl () within Glyceline (panel B) under ambient conditions. Errors in are ≤±0.005.
The Kamlet–Taft empirical parameters for solvent polarity (, α, and β) clearly indicate the surprising outcome that, as LiCl is added to DES Glyceline, dipolarity/polarizability of the medium does not change, nor does the H-bond accepting basicity—the medium acquires more H-bond donating acidity [parameter α increases linearly with increasing within the system with a slope = 0.70 (±0.02)]. Within Glyceline, it is reported that the of ChCl are involved in H-bonding with the –OH functionalities of glycerol that in turn contribute to DES formation [23]. We believe that added preferentially combines with the oxygen of the –OH functionalities of glycerol thus rendering the HBD acidity of the medium to increase [24]. The diminished HBA basicity due to this is compensated by the presence of additional of the LiCl. Since both added and are involved in various H-bonding within the system, diminishing their charges, no effective increase in dipolarity/polarizability is observed.
Since fluorescence polarity probes are known for their higher sensitivity, we employed pyrene as one of such probes to assess the effect of LiCl addition on DES Glyceline. Fluorescence emission spectra of pyrene is constituted of five vibronic bands with band 1-to-band 3 intensity ratio (Py I1/I3) increases monotonically with increasing dipolarity of the pyrene cybotactic region [25,26,27,28,29]. Emission spectra of pyrene in LiCl-added Glyceline is acquired at five different temperatures in the range 298.15 to 358.15 K (representative spectra are shown in Figure 4A).
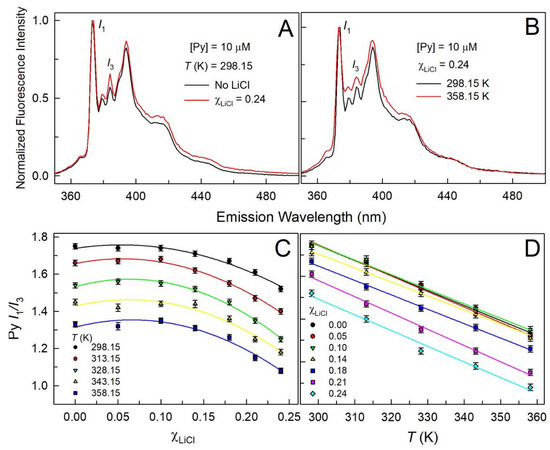
Figure 4.
Fluorescence emission spectra of pyrene within Glyceline in the absence and presence of LiCl ( = 0.24) at 298.15 K (panel A) and at 298.15 K and 358.15 K at = 0.24 (panel B). Band 1 to 3 emission intensity ratio of pyrene (Py I1/I3) within LiCl-added Glyceline for temperatures ranging between 298.15 and 358.15 K (panel C) and for different LiCl mole fractions at all investigated temperatures (panel D). Error in Py I1/I3 is ≤±0.02.
The estimated Py I1/I3 at different are plotted in Figure 4C. A careful examination of the data reveals that statistically meaningful changes in Py I1/I3 start to appear only above 1.5 m LiCl—for < 1.5 m, the pyrene probe is not able to manifest polarity changes in the system as LiCl is added to Glyceline. Betaine dye 33 response, however, could effectively reflect the changes in the medium at very low LiCl concentrations as well. It is interesting to note that at higher LiCl concentrations, the Py I1/I3 decreases suggesting a decrease in the dipolarity of the pyrene cybotactic region in the presence of LiCl. We again invoke the explanation given above that both and tie up with the charged species present in the solution thus lowering the dipolarity of the medium—this lowering in dipolarity may be overshadowed by the increased HBD acidity that becomes reflected in the response of the betaine dye 33. Further support for this is afforded by the variation in Py I1/I3 of the LiCl-added Glyceline as the temperature is increased (Figure 4B shows pyrene emission spectra at two different temperatures). Figure 4D depicts the clear decrease in Py I1/I3 as the temperature of LiCl-added Glyceline system is increased—the decrease is observed to be linear. This observation is akin to the decrease in static dielectric constants (ε) of several liquids, including several DESs and ionic liquids, as the temperature is increased. Also, similar observations were reported for the LiCl-added ChCl:Urea and glycerol, respectively, as well as LiTf2N-added 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ([C2C1im][Tf2N]) at similar temperatures [30,31,32].
4. Conclusions
Reichardt’s betaine dye 33 is able to effectively manifest the changes taking place in DES Glyceline as LiCl salt is added. The response of the betaine dye 33 in concert with responses from DENA and NA (to obtain empirical Kamlet–Taft parameters) affords a scenario where it is clear that as LiCl is added to Glyceline, the HBD acidity of the medium increases with little or no change in the dipolarity/polarizability and HBA basicity. The interaction of Li species with the oxygens of the –OH functionalities of glycerol imparts increased HBD acidity to the medium with other interactions compensating for each other in such a manner that there is little or no increase in dipolarity/polarizability and HBA basicity. The fluorescence probe pyrene is able to reflect the decrease in the dipolarity but only at higher LiCl concentrations ( ≥ 1.5 m). A decrease in dipolarity with increasing temperature, however, is amply manifested through the pyrene response. The sensitivity and versatility of Reichardt’s betaine dye in effective gauging changes in the physicochemical properties of the liquid medium is amply demonstrated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, visualization, writing—original draft, M.K.; data collection, A.K.; writing—review and editing, supervision, resources, project administration, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was generously supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, EMR-II (CSIR-EMR-II), Government of India, through a grant to Siddharth Pandey [grant number 01(3043)/21/EMR-II].
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Manish Kumar would like to acknowledge the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) of the Government of India for his Senior Research Fellowship (SRF).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Deep eutectic solvents: Sustainable media for nanoscale and functional materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRocca, M.M.; Baker, G.A.; Heitz, M.P. Assessing rotation and solvation dynamics in ethaline deep eutectic solvent and its solutions with methanol. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 155, 034505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Banu, S.; Sahu, A.K.; Kumar, B.P.; Mishra, A.K. Molecular-level insights into inherent heterogeneity of maline deep eutectic system. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 350, 118478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; De la Guardia, M.; Andruch, V.; Vilková, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents vs. Ionic Liquids: Similarities and Differences. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. Ionic liquids toxicity-benefits and threats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, H.; Jordão, N.; Branco, L.C. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as Low-Cost and Green Electrolytes for Electrochromic Devices. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Fan, L.; Kong, X.; Lu, Y. Progress in Electrolytes for Rechargeable Li-Based Batteries and Beyond. Green Energy Environ. 2016, 1, 18–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acree, W.E., Jr.; Wilkins, D.C.; Tucker, S.A.; Griffin, J.M.; Powell, J.R. Spectrochemical Investigations of Preferential Solvation. 2. Compatibility of Thermodynamic Models versus Spectrofluorometric Probe Methods for Tautomeric Solutes Dissolved in Binary Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Pandey, S. Solvatochromic probe response within ionic liquids and their equimolar mixtures with tetraethylene glycol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 11259–11270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, R.; Nunes, N.; Elvas-Leitão, R.; Martins, F. Using Solvatochromic Probes to Investigate Intermolecular Interactions in 1,4-Dioxane/Methanol/Acetonitrile Solvent Mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, J.; de Paz, J.L.G.; Reichardt, C. On the Molecular Structure and UV/vis Spectroscopic Properties of the Solvatochromic and Thermochromic Pyridinium-N-Phenolate Betaine Dye B30. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 6226–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Polarity of Ionic Liquids Determined Empirically by Means of Solvatochromic Pyridinium N-phenolate Betaine Dyes. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Solvatochromic Dyes as Solvent Polarity Indicators. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2319–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.L.M.; Abraham, M.H.; Taft, R.W. Linear Solvation Energy Relationships. 23. A Comprehensive Collection of the Solvatochromic Parameters, Pi*, Alpha, and Beta, and Some Methods for Simplifying the Generalized Solvatochromic Equation. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.L.; Taft, R.W. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. 6. The π* Scale of Solvent Polarities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 6027–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, R.W.; Kamlet, M.J. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. 2. The α-Scale of Solvent Hydrogen-Bond Donor (HBD) Acidities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, R.W.; Abboud, J.L.M.; Kamlet, M.J. Solvatochromic comparison method. 20. Linear solvation energy relationships. 12. The d.delta. term in the solvatochromic equations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Taft, R.W. The Solvatochromic Comparison Method. I. The ß-Scale of Solvent Hydrogen-Bond Acceptor (HBA) Basicities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, D.P.; Lalas, S. Glycerol and Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Mixtures as Emerging Green Solvents for Polyphenol Extraction: The Evidence so Far. Molecules 2020, 25, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Troya, D.; Korovich, A.G.; Bostwick, J.E.; Colby, R.H.; Madsen, L.A. Uncorrelated Lithium-Ion Hopping in a Dynamic Solvent–Anion Network. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.C.; Winnik, M.A. The Py scale of solvent polarities. Can. J. Chem. 1984, 62, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Baker, S.N.; Pandey, S.; Baker, G.A. Fluorescent Probe Studies of Polarity and Solvation within Room Temperature Ionic Liquids: A Review. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 1313–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, K.W., Jr.; Acree, W.E., Jr. Experimental Artifacts and Determination of Accurate Py Values. Analyst 1986, 111, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Street, K.W., Jr.; Acree, W.E., Jr.; Fetzer, J.C.; Shetty, P.H.; Poole, C.F. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Solute Probes. Part V: Fluorescence Spectra of Pyrene, Ovalene, Coronene, and Benzo[ghi]perylene Dissolved in Liquid Alkylammonium Thiocyanate Organic Salts. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, S.A.; Cretella, L.E.; Waris, R.; Street, K.W., Jr.; Acree, W.E., Jr.; Fetzer, J.C. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Solute Probes. Part VI: Effect of Dissolved Oxygen and Halogenated Solvents on the Emission Spectra of Select Probe Molecules. Appl. Spectrosc. 1990, 44, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, D.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, S. Pyrene Fluorescence To Probe a Lithium Chloride-Added (Choline Chloride + Urea) Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Anjali; Dhingra, D.; Yadav, A.; Pandey, S. Effect of lithium salt on fluorescence quenching in glycerol: A comparison with ionic liquid/deep eutectic solvent. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadyan, A.; Pandey, S. Florescence Quenching within Lithium Salt-Added Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 5106–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).