The Detection of Propionate Utilization by Bacteria Isolated from a Plastic Recycling Site
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
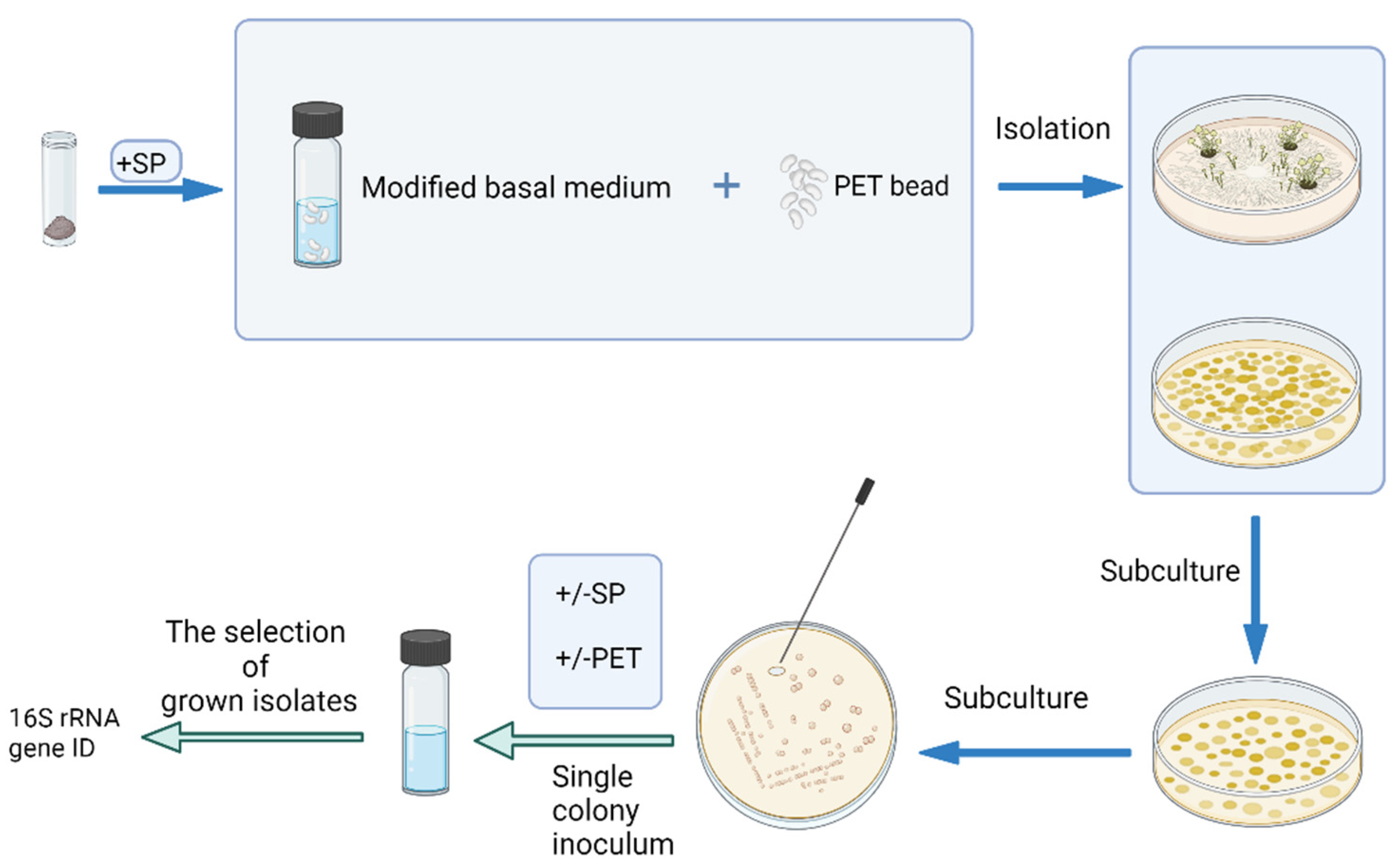
2.1. Environmental Sampling
2.2. Culture-Based Bacteria Isolation
2.3. Conserved Gene Amplification and Sequencing for Microbial Identification
2.4. Evaluation of Bacterial Growth at Different Levels of Sodium Propionate
2.5. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
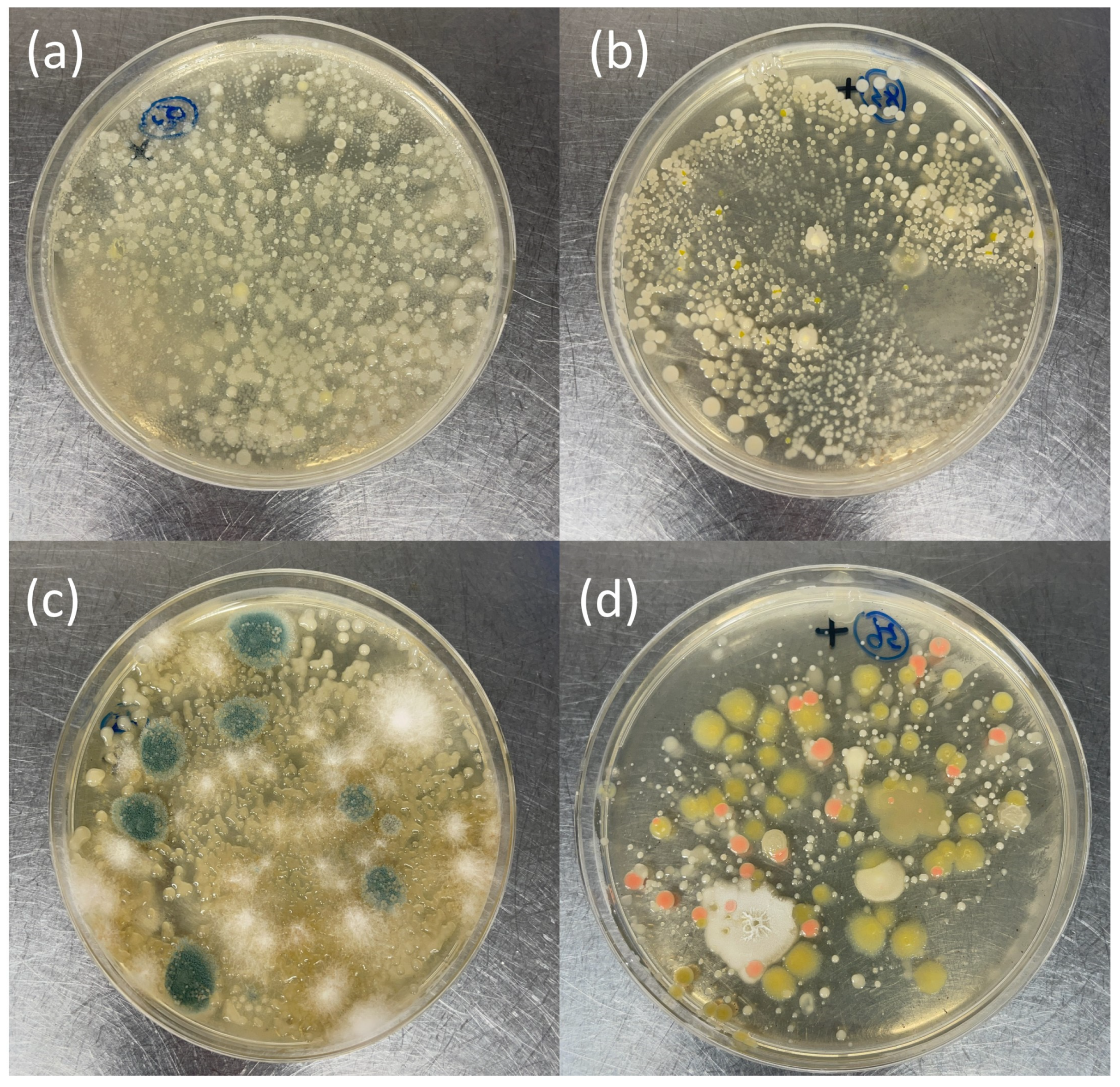
3.1. Bacterial Phenotypic Observations during Culture-Based Isolation
3.2. Molecular Identification Based on 16S Sequences
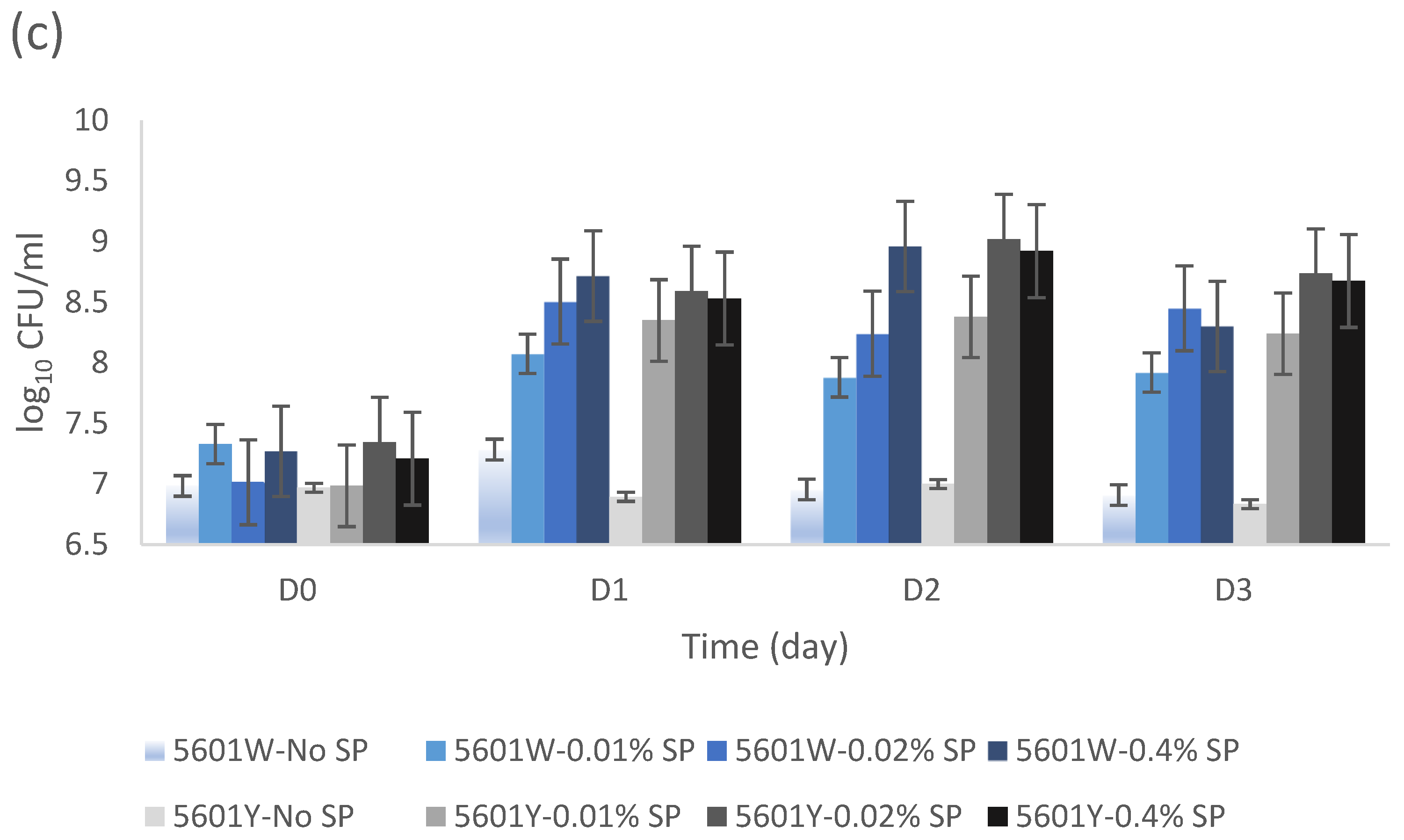
3.3. Bacterial Growth Dependency on Varied SP Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Isolates ID | Growth on 0.04% SP | Growth on PET |
|---|---|---|
| 0111 | + | - |
| 0211 | + | - |
| 0304 | + | - |
| 0311 | + | - |
| 0312 | + | - |
| 0321 | + | - |
| 0601 | + | - |
| 1302 | + | - |
| 1304 | + | - |
| 1903 | + | - |
| 0811 | + | - |
| 0821 | + | - |
| 0831 | + | - |
| 0832 | + | - |
| 1311 | + | - |
| 1421 | + | - |
| 1911 | + | - |
| 2303 | + | - |
| 2303 | + | - |
| 2511 | + | - |
| 2521 | + | - |
| 2801 | + | - |
| 2901 | + | - |
| 2902 | + | - |
| 3301 | + | - |
| 3303 | + | - |
| 3321 | + | - |
| 3521 | + | - |
| 3701 | + | - |
| 3703 | + | - |
| 4112 | + | - |
| 4121 | + | - |
| 4221 | + | - |
| 4401 | + | - |
| 4402 | + | - |
| 5001 | + | - |
| 5101 | + | - |
| 5501 | + | - |
| 5502 | + | - |
| 5601W | ++ | - |
| 5601Y | ++ | - |
| 6001 | + | - |
| 6002 | + | - |
| 6302 | + | - |
| 6303 | + | - |
| 6402 | + | - |
| 6412 | + | - |
| 6502 | + | - |
| 6712 | + | - |
| 6911 | + | - |
| 6931 | + | - |
| 7401 | + | - |
| 7402 | + | - |
| 7501 | + | - |
| 7502 | + | - |
| 7801 | ++ | - |
| 7802 | ++ | - |
| 8321 | + | - |
| 8322 | + | - |
| 8803 | + | - |
| 8821 | + | - |

References
- Mehnaz, S.; Javaid, A. Microbes and plastic waste management. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 3, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Y. Microbial Degradation and Valorization of Plastic Wastes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 507487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, A.R.; Hasan, H.A.; Muhamad, M.H.; Ismail, N.I.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Microbial degradation of microplastics by enzymatic processes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3057–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tender, C.; Devriese, L.I.; Haegeman, A.; Maes, S.; Vangeyte, J.; Cattrijsse, A.; Dawyndt, P.; Ruttink, T. Temporal Dynamics of Bacterial and Fungal Colonization on Plastic Debris in the North Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7350–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.a.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. Colonization Characteristics of Bacterial Communities on Plastic Debris Influenced by Environmental Factors and Polymer Types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10763–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Elsamahy, T.; Zhu, D.; Sun, J. Biodegradability of polyethylene by efficient bacteria from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms and investigation of its degradation mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, L.; Chevalier, L.; Gabba, E.; Ley, K.; Winters, K. Propionate-induced synthesis of odd-chain-length fatty acids by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1977, 131, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezina, N.; Yada, B. Improvement of the poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)(PHBV) production by dual feeding with levulinic acid and sodium propionate in Cupriavidus necator. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-H.; Brigham, C.J.; Budde, C.F.; Boccazzi, P.; Willis, L.B.; Hassan, M.A.; Yusof, Z.A.M.; Rha, C.; Sinskey, A.J. Optimization of growth media components for polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production from organic acids by Ralstonia eutropha. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-K.; Dulermo, T.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Nicaud, J.-M. Optimization of odd chain fatty acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Men, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, F.; Tian, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Biodegradation of Polyethylene by Enterobacter sp. D1 from the Guts of Wax Moth Galleria mellonella. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugg, T.D.H.; Ahmad, M.; Hardiman, E.M.; Singh, R. The emerging role for bacteria in lignin degradation and bio-product formation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, G.E.; Veenhoff, L.M. The natural variation in lifespans of single yeast cells is related to variation in cell size, ribosomal protein, and division time. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, U.; Rogall, T.; Blöcker, H.; Emde, M.; Böttger, E.C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 7843–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucero, M.E.; Unc, A.; Cooke, P.; Dowd, S.; Sun, S. Endophyte Microbiome Diversity in Micropropagated Atriplex canescens and Atriplex torreyi var. griffithsii. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Ki, C.-S.; Lee, N.Y. Identification of Clinical Mold Isolates by Sequence Analysis of the Internal Transcribed Spacer Region, Ribosomal Large-Subunit D1/D2, and β-Tubulin. Ann. Lab. Med. 2012, 32, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Madriz, M.F. Preservation of food. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Caballero, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 4766–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarek, K.; Lipińska, E.; Hać-Szymańczuk, E.; Kieliszek, M.; Ścibisz, I. Propionibacterium spp.—Source of propionic acid, vitamin B12, and other metabolites important for the industry. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 515–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julinová, M.; Kupec, J.; Alexy, P.; Hoffmann, J.; Sedlařík, V.; Vojtek, T.; Chromčáková, J.; Bugaj, P. Lignin and starch as potential inductors for biodegradation of films based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and protein hydrolysate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozali, M.; Triwulandari, E.; Haryono, A.; Yuanita, E. Effect of lignin on morphology, biodegradability, mechanical and thermal properties of low linear density polyethylene/lignin biocomposites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 223, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyoshi, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Nishida, T. Polyethylene degradation by lignin-degrading fungi and manganese peroxidase. J. Wood Sci. 1998, 44, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Pometto III, A.L.; Fratzke, A.; Bailey, T.B., Jr. Biodegradation of degradable plastic polyethylene by Phanerochaete and Streptomyces species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, N.; Jamal, A.; Ali, M.I. Lignin peroxidase isoenzyme: A novel approach to biodegrade the toxic synthetic polymer waste. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parija, S.C. Pseudomonas, Burkholderia and Acinetobacter. In Textbook of Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 553–561. [Google Scholar]
- Mahenthiralingam, E.; Baldwin, A.; Dowson, C.G. Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria: Opportunistic pathogens with important natural biology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussud, C.; Meistertzheim, A.; Conan, P.; Pujo-Pay, M.; George, M.; Fabre, P.; Coudane, J.; Higgs, P.; Elineau, A.; Pedrotti, M. Evidence of niche partitioning among bacteria living on plastics, organic particles and surrounding seawaters. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusa, M.; Lehto, J.; Aromaa, H.; Knuutinen, J.; Bomberg, M. Uptake of radioiodide by Paenibacillus sp., Pseudomonas sp., Burkholderia sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from a boreal nutrient-poor bog. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S.; Jain, K.; Madamwar, D. Metabolism of pyrene through phthalic acid pathway by enriched bacterial consortium composed of Pseudomonas, Burkholderia, and Rhodococcus (PBR). 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Sun, J.; Dong, W.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xin, F.; Jiang, M. Characterization of a novel esterase and construction of a Rhodococcus-Burkholderia consortium capable of catabolism bis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holder, J.W.; Ulrich, J.C.; DeBono, A.C.; Godfrey, P.A.; Desjardins, C.A.; Zucker, J.; Zeng, Q.; Leach, A.L.B.; Ghiviriga, I.; Dancel, C.; et al. Comparative and Functional Genomics of Rhodococcus opacus PD630 for Biofuels Development. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Gurav, R.; Choi, T.-R.; Jung, H.-R.; Yang, S.-Y.; Song, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-G.; Yoon, J.-J.; Yang, Y.-H. Effect of synthetic and food waste-derived volatile fatty acids on lipid accumulation in Rhodococcus sp. YHY01 and the properties of produced biodiesel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 192, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horswill, A.R.; Escalante-Semerena, J.C. Propionate catabolism in Salmonella typhimurium LT2: Two divergently transcribed units comprise the prp locus at 8.5 centisomes, prpR encodes a member of the sigma-54 family of activators, and the prpBCDE genes constitute an operon. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brämer, C.O.; Silva, L.F.; Gomez, J.G.C.; Priefert, H.; Steinbüchel, A. Identification of the 2-Methylcitrate Pathway Involved in the Catabolism of Propionate in the Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Producing Strain Burkholderia sacchari IPT101T and Analysis of a Mutant Accumulating a Copolyester with Higher 3-Hydroxyvalerate Content. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.M.; Silva-Queiroz, S.R.; Cabrera Gomez, J.G.; Silva, L.F. Disruption of the 2-methylcitric acid cycle and evaluation of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate biosynthesis suggest alternate catabolic pathways of propionate in Burkholderia sacchari. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Isolates ID | Sequencing Result: BLAST 0.7–1.0 kb E = 0 | Colony Feature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequenced from the PA End (Forward Sequencing) | Sequenced from the PH End (Reverse Sequencing) | ||
| 0111 | Pseudomonas nitritireducens | Pseudomonas knackmussi | Cream coloured colonies |
| 0211 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas monteilii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 0304 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Mucoid colonies |
| 0311 | Pseudomonas aestus | Pseudomonas aestus | Cream coloured colonies |
| 0312 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 0321 | Pseudomonas nitritireducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 0601 | Pseudomonas multiresinivorans | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Mucoid colonies |
| 1302 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Brown colonies |
| 1304 | Pseudomonas helmanticensis | Pseudomonas helmanticensis | Cream coloured colonies |
| 1903 | Achromobacter kerstersii | Achromobacter deleyi | Cream coloured colonies |
| 0811 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Mucoid colonies |
| 0821 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Cream coloured colonies |
| 0831 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Mucoid colonies |
| 0832 | Pseudomonas plecoglossicida | Pseudomonas plecoglossicida | Mucoid colonies |
| 1311 | Pseudomonas koreensis | Pseudomonas koreensis | Mucoid colonies |
| 1421 | Rhodococcus sp. | Rhodococcus sp. | Cream coloured colonies |
| 1911 | Pseudomonas nitritireducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 2303 | Pseudomonas putida | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 2303 | Pseudomonas putida | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 2511 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas monteilii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 2521 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Mucoid colonies |
| 2801 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Cream coloured colonies |
| 2901 | Pseudomonas plecoglossicida | Pseudomonas cremoricolorata | Cream coloured colonies |
| 2902 | Pseudomonas cremoricolorata | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Mucoid colonies |
| 3301 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 3303 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Mucoid colonies |
| 3321 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Cream coloured colonies |
| 3521 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas plecoglossicida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 3701 | Pseudomonas nitritireducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Mucoid colonies |
| 3703 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 4112 | Cupriavidus metallidurans | Cupriavidus metallidurans | Cream coloured colonies |
| 4121 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas monteilii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 4221 | Achromobacter insuavis | Achromobacter deleyi | Cream coloured colonies |
| 4401 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas citronellolis | Mucoid colonies |
| 4402 | Pseudomonas plecoglossicida | Pseudomonas cremoricolorata | Cream coloured colonies |
| 5001 | Pseudomonas protegens | Pseudomonas protegens | Cream coloured colonies |
| 5101 | Pseudomonas putida | Pseudomonas cremoricolorata | Cream coloured colonies |
| 5501 | Pseudomonas nitritireducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 5502 | Enterobacter ludwigii | Enterobacter ludwigii | Mucoid colonies |
| 5601W | Rhodococcus qingshengii | Rhodococcus qingshengii | Creamy white colonies |
| 5601Y | Burkholderia cenocepacia | Burkholderia diffusa | Yellow colonies |
| 6001 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Mucoid colonies |
| 6002 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Mucoid colonies |
| 6302 | Pseudomonas mediterranea | Pseudomonas corrugata | Cream coloured colonies |
| 6303 | Achromobacter kerstersii | Achromobacter deleyi | Cream coloured colonies |
| 6402 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Mucoid colonies |
| 6412 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Cream coloured colonies |
| 6502 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 6712 | Pseudomonas nitritireducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 6911 | Achromobacter deleyi | Achromobacter deleyi | Mucoid colonies |
| 6931 | Pseudomonas nitritireducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 7401 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas monteilii | Cream coloured colonies |
| 7402 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 7501 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Mucoid colonies |
| 7502 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Mucoid colonies |
| 7801 | Burkholderia ambifaria | Burkholderia ambifaria | Mucoid colonies |
| 7802 | Burkholderia pyrrocinia | Burkholderia metallica | Light yellow colonies |
| 8321 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 8322 | Pseudomonas monteilii | Pseudomonas putida | Cream coloured colonies |
| 8803 | Pseudomonas nitroreducens | Pseudomonas knackmussii | Mucoid colonies |
| 8821 | Pseudomonas knackmussi | Pseudomonas knackmussi | Cream coloured colonies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Subharat, P.; Palevich, F.; Mills, J.; Brightwell, G. The Detection of Propionate Utilization by Bacteria Isolated from a Plastic Recycling Site. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 4, 856-874. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020059
Wu S, Subharat P, Palevich F, Mills J, Brightwell G. The Detection of Propionate Utilization by Bacteria Isolated from a Plastic Recycling Site. Applied Microbiology. 2024; 4(2):856-874. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020059
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shuyan, Pornchanok Subharat, Faith Palevich, John Mills, and Gale Brightwell. 2024. "The Detection of Propionate Utilization by Bacteria Isolated from a Plastic Recycling Site" Applied Microbiology 4, no. 2: 856-874. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020059
APA StyleWu, S., Subharat, P., Palevich, F., Mills, J., & Brightwell, G. (2024). The Detection of Propionate Utilization by Bacteria Isolated from a Plastic Recycling Site. Applied Microbiology, 4(2), 856-874. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol4020059







