The Effects of Meteorological Factors on Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica Beauv.) under Different Water Supply Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Site
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Experiment Design and Field Management
2.4. Measurements and Calculations
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
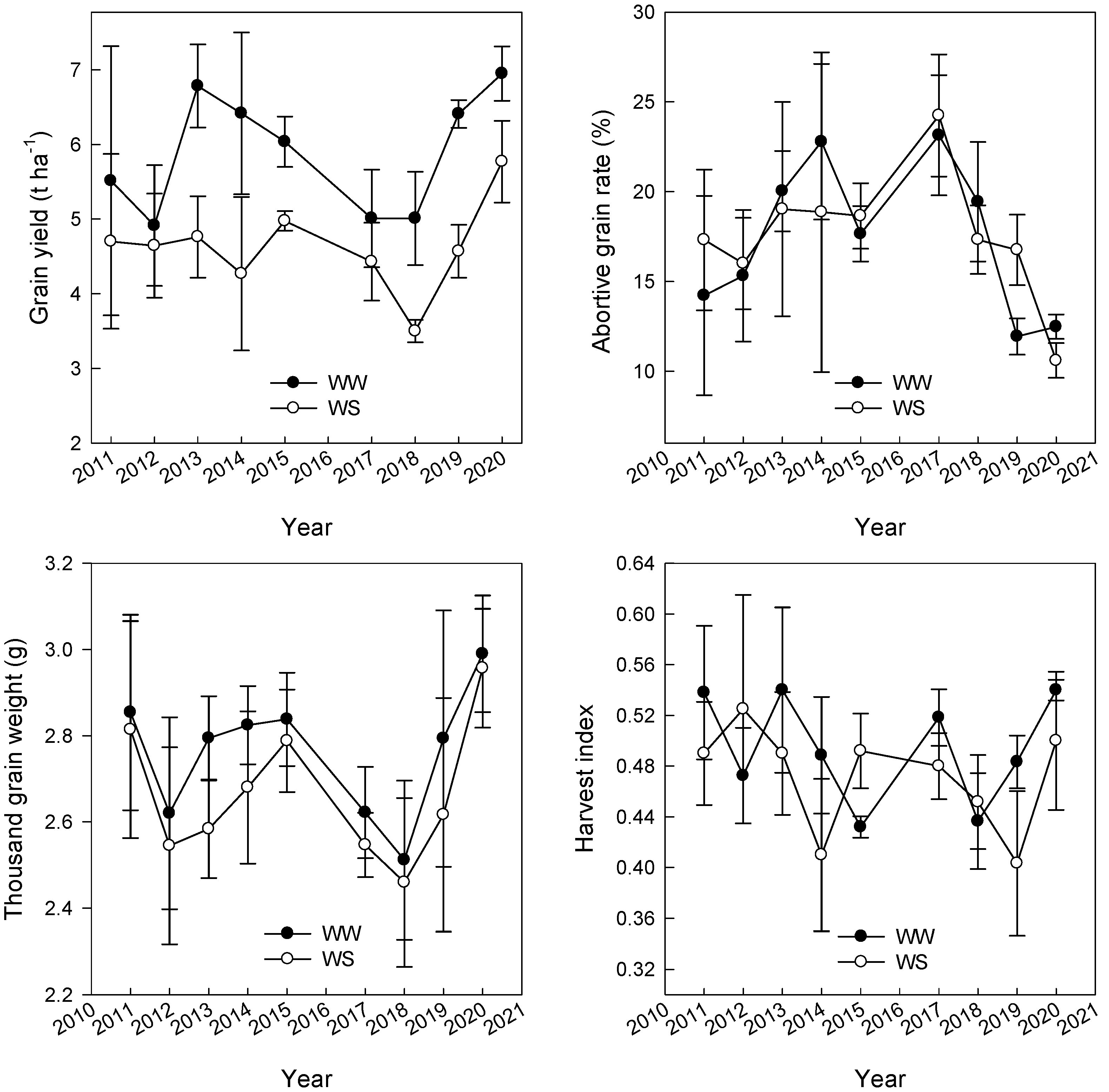
3.1. The Variation of Grain Yield and Related Traits
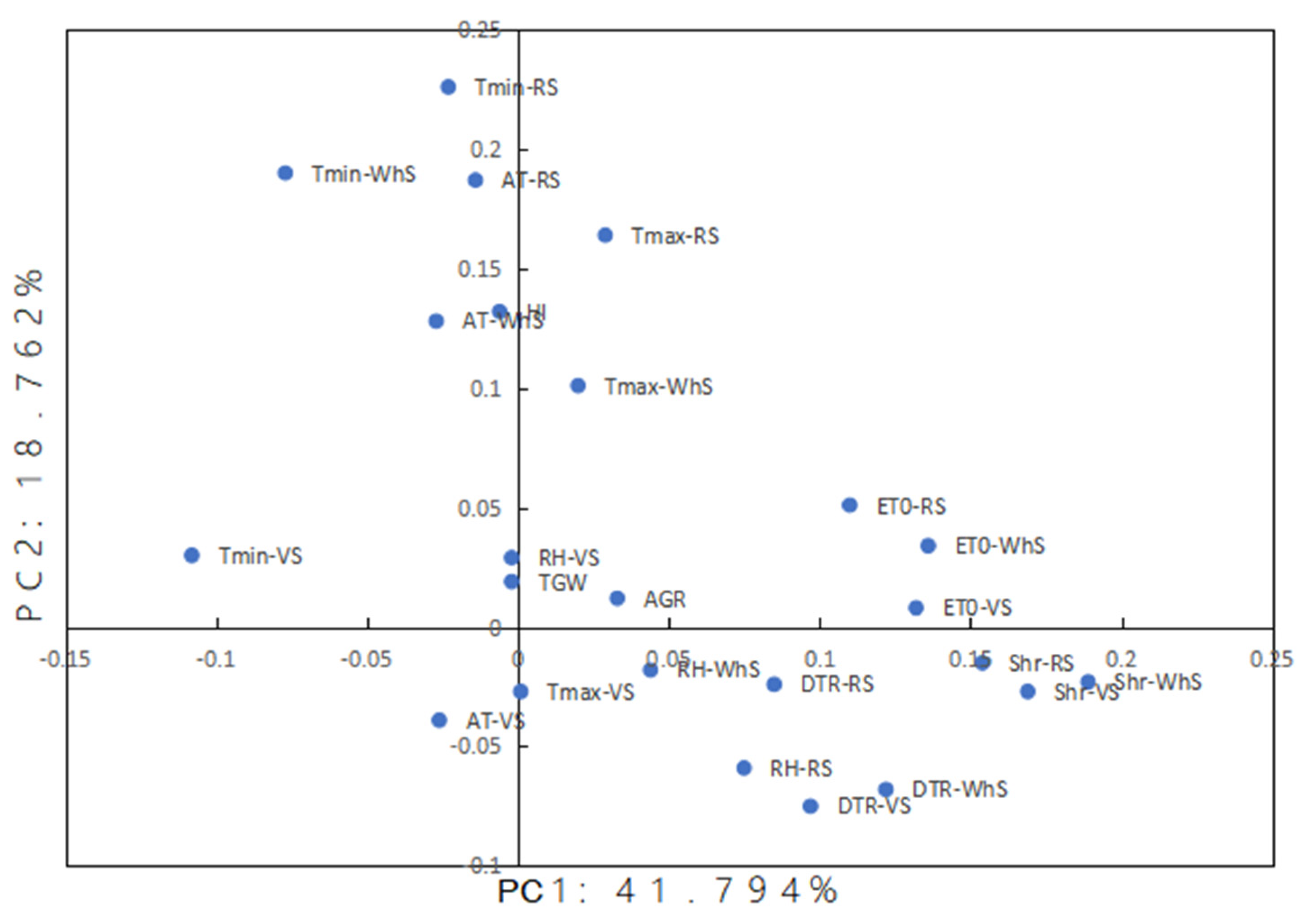
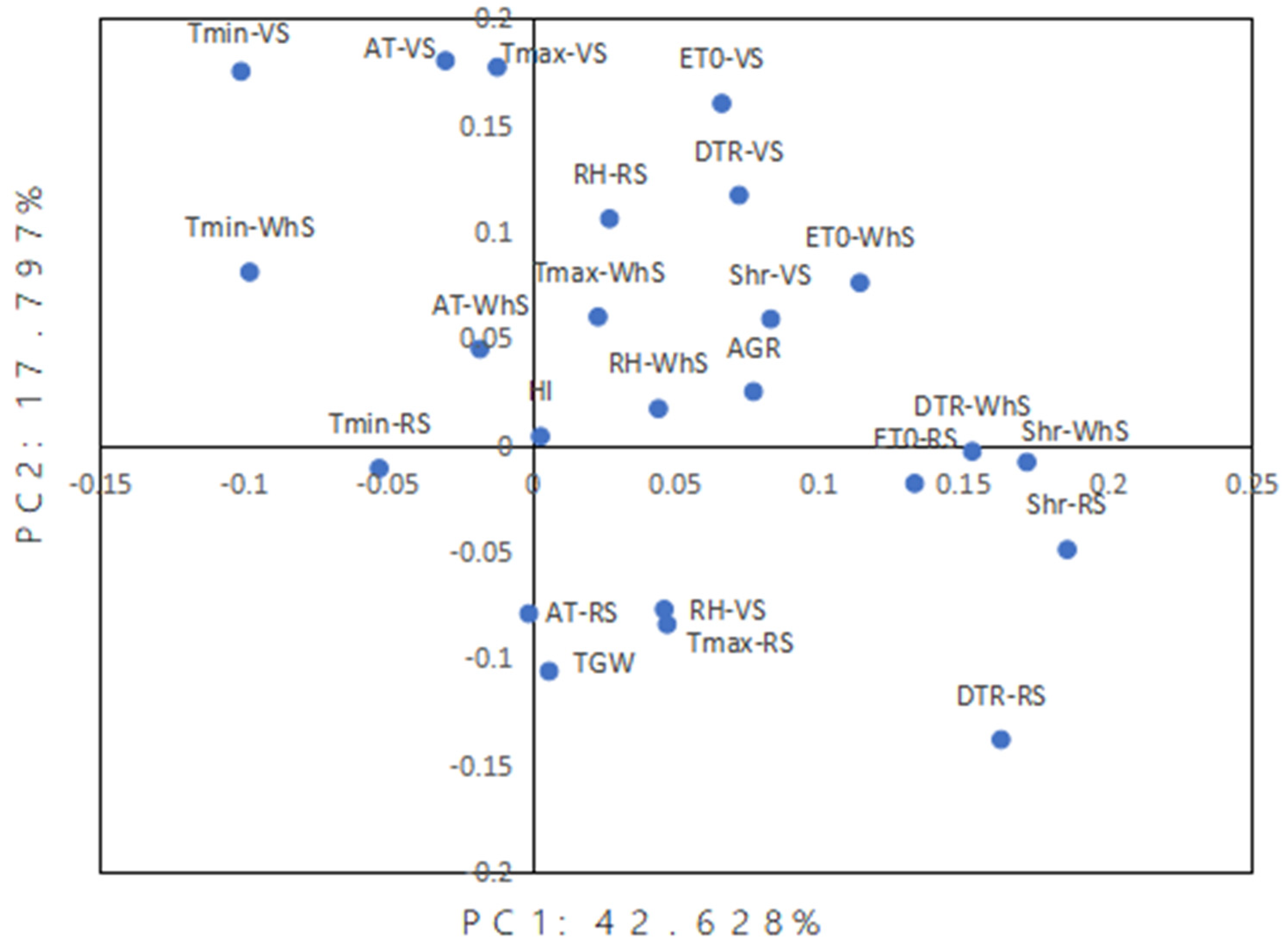
3.2. The Effect of Meteorological Factors on Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in Grain Yield
4.2. Meteorological Factors Play an Important Role in Grain Yield
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oelke, E.A.; Oplinger, E.S.; Putnam, D.H.; Durgan, B.R.; Doll, J.D.; Undersander, D.J. Millets. In Alternative Field Crops Manual; University of Wisconsin-Extension: Madison, WI, USA; University of Minnesota Centre for Alternative Plant and Animal Products and University of Minnesota Extension: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, A.S.M.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Shen, Q. Millet grains: Nutritional quality, processing, and potential health benefits. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, R. Phenolic and carotenoid profiles and antiproliferative activity of foxtail millet. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Shen, H.; Gao, J.; Hou, S.; Zhang, B.; Mayes, S.; Bennet, M.; Ma, J.; et al. A mini foxtail millet with an Arabidopsis-like life cycle as a C4 model system. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Zhang, B. Foxtail millet: A new model for C4 plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantz, H.L.; Piemeisel, L.N. The water requirement of plants at Akron, Colo. J. Agric. Res. 1927, 34, 1093–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Prasada Rao, K.E.; de Wet, J.M.J.; Brink, D.E.; Mengesha, M.H. Infraspecific variation and systematics of cultivated Setaria italica, foxtail millet (Poaceae). Econ. Bot. 1987, 41, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Yang, G.; Ma, Y. Chemical characteristics and fatty acid profile of foxtail millet bran oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2010, 87, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X. Production and genetic improvement of minor cereals in China. Crop J. 2017, 5, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Chen, L. Analysis of meteorological factors effecting on yield of Camellia oleifera and construction of yield forecasting model in Hu’nan province. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 32, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Shao, L.; Sun, H. Selecting traits to increase winter wheat yield under climate change in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2017, 207, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liang, H.; Wei, S.Q.; Jiang, L.G.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Zhao, Q. Effects of meteorological factors on the yield and quality of special rice in different periods after anthesis. Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 451–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Pang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Mei, X. Performance of new released winter wheat cultivars in yield: A case study in the North China plain. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Different sowing dates affected cotton yield and yield components. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2016, 10, 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bussel, L.G.J.; Stehfest, E.; Siebert, S.; Müller, C.; Ewert, F. Simulation of the phenological development of wheat and maize at the global scale. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, L.; Luo, Q.; Eamus, D.; Xu, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, E.; Liu, J.; Nielsen, C.D. Year patterns of climate impact on wheat yields. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 4, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.J.; Hubbard, K.G.; Wilhite, D.A. The relationship of climatic indices and variables to corn (maize) yields: A principal components analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1991, 55, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chang, L.; Wang, N.; Kong, W.; Wang, C. Effects of Meteorological Factors on Apple Yield Based on Multilinear Regression Analysis: A Case Study of Yantai Area, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lapuimakuni, S.; Khumaida, N.; Ardie, S.W. Evaluation of drought tolerance indices for genotype selection of foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Int. J. Trop. Drylands 2018, 2, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghatoleslami, M.J.; Kafi, M.; Majidi, E. Effect of deficit irrigation on yield, WUE and some morphological and phonological traits of three millet species. Pak. J. Bot. 2008, 40, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Lu, G.; Ge, Y.; Bai, C. Trait Selection for Yield Improvement in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica Beauv.) under Climate Change in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Boote, K.J.; Kadiyala, M.D.M.; Nedumaran, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Srinivas, K.; Bantilan, M.C.S. An assessment of yield gains under climate change due to genetic modifification of pearl millet. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, B.; Zhu, J.; Tao, H.; Xu, L.; Guo, B.; Wang, P. Effects of meteorological factors at different growth stages on yield traits of maize (Zea mays L.) in Heilonggang basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2013, 39, 919–927, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachimuthu, V.V.; Robin, S.; Sudhakar, D.; Raveendran, M.; Rajeswari, S.; Manonmani, S. Evaluation of rice genetic diversity and variability in a population panel by Principal Component Analysis. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiantzas, J.D. Temperature-and humidity-based simplified Penman’s ET0 formulae. Comparisons with temperature-based Hargreaves-Samani and other methodologies. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Irrigation before Sowing | Irrigation in Jointing Stage | Irrigation in Grain-Filling Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 14 June | 24 July | 22 August |
| 2012 | 15 June | 26 July | 24 August |
| 2013 | 17 June | 26 July | 23 August |
| 2014 | 14 June | 18 July | 23 August |
| 2015 | 16 June | 28 July | 25 August |
| 2017 | 13 June | 21 July | 19 August |
| 2018 | 12 June | 13 July | 11 August |
| 2019 | 10 June | 27 July | 23 August |
| 2020 | 16 June | 18 July | 22 August |
| Treatment | Year | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WW | 2011 | 7.51 | 3.43 | 5.51 | 32.70 |
| 2012 | 5.73 | 3.83 | 4.92 | 16.44 | |
| 2013 | 7.72 | 6.33 | 6.78 | 8.18 | |
| 2014 | 8.07 | 4.86 | 6.42 | 16.89 | |
| 2015 | 6.32 | 5.46 | 6.04 | 5.58 | |
| 2017 | 5.64 | 3.89 | 5.01 | 13.06 | |
| 2018 | 5.56 | 4.00 | 5.01 | 12.49 | |
| 2019 | 6.60 | 6.22 | 6.41 | 2.89 | |
| 2020 | 7.36 | 6.37 | 6.95 | 5.23 | |
| WS | 2011 | 6.10 | 3.23 | 4.70 | 24.89 |
| 2012 | 5.49 | 3.82 | 4.65 | 15.00 | |
| 2013 | 5.59 | 4.16 | 4.76 | 11.45 | |
| 2014 | 6.07 | 3.16 | 4.27 | 24.10 | |
| 2015 | 5.14 | 4.80 | 4.98 | 2.61 | |
| 2017 | 5.23 | 4.04 | 4.43 | 11.78 | |
| 2018 | 3.67 | 3.30 | 3.50 | 4.26 | |
| 2019 | 4.86 | 4.11 | 4.57 | 7.75 | |
| 2020 | 6.19 | 4.76 | 5.77 | 9.50 |
| Treatments | Principal Components | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WW | Eigen values | 10.031 | 4.503 | 3.929 | 2.899 | 1.544 |
| % of Variance | 41.794 | 18.762 | 16.369 | 12.080 | 6.435 | |
| Cumulative % | 41.794 | 60.556 | 76.925 | 89.005 | 95.440 | |
| WS | Eigen values | 10.231 | 4.271 | 3.934 | 2.711 | 1.808 |
| % of Variance | 42.628 | 17.797 | 16.393 | 11.294 | 7.533 | |
| Cumulative % | 42.628 | 60.425 | 76.818 | 88.111 | 95.644 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Lu, G.; Bai, C.; Ge, Y. The Effects of Meteorological Factors on Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica Beauv.) under Different Water Supply Conditions. Crops 2023, 3, 53-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops3010006
Zhang W, Wang B, Liu B, Chen Z, Lu G, Bai C, Ge Y. The Effects of Meteorological Factors on Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica Beauv.) under Different Water Supply Conditions. Crops. 2023; 3(1):53-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops3010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenying, Bianyin Wang, Binhui Liu, Zhaoyang Chen, Guanli Lu, Caihong Bai, and Yaoxiang Ge. 2023. "The Effects of Meteorological Factors on Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica Beauv.) under Different Water Supply Conditions" Crops 3, no. 1: 53-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops3010006
APA StyleZhang, W., Wang, B., Liu, B., Chen, Z., Lu, G., Bai, C., & Ge, Y. (2023). The Effects of Meteorological Factors on Grain Yield of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica Beauv.) under Different Water Supply Conditions. Crops, 3(1), 53-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops3010006





