Quantitative-Genetic Evaluation of Resistances to Five Fungal Diseases in A Large Triticale Diversity Panel (×Triticosecale)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Field Design
2.2. Inoculations
2.3. Trait Recording
2.4. Phenotypic Data Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Triticale as A Man-Made Crop
4.2. Genetic Variation for Disease Resistances
4.3. Correction of FHB Data
4.4. Breeding Multi-Resistant Triticale
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oettler, G. The fortune of a botanical curiosity—triticale: Past, present and future. J. Agric. Sci. 2005, 143, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Data. Production. Crops and Livestock Products. Triticale. 2022. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Linde-Laursen, I.B. Reaction of triticale wheat and rye to the powdery mildew fungi, Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici and E. graminis f. sp. secalis. Z. Pflanzenzücht. 1977, 79, 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Klocke, B.; Flath, K.; Miedaner, T. Virulence phenotypes in powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis) populations and resistance genes in triticale (× Triticosecale). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 137, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidig, F.; Feike, T.; Hadasch, S.; Rentel, D.; Klocke, B.; Miedaner, T.; Piepho, H.P. Breeding progress of disease resistance and impact of disease severity under natural infections in winter wheat variety trials. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audenaert, K.; Troch, V.; Landschoot, S.; Haesaert, G. Biotic stresses in the anthropogenic hybrid triticale (×Triticosecale Wittmack): Current knowledge and breeding challenges. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 140, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menardo, F.; Praz, C.R.; Wyder, S.; Ben-David, R.; Bourras, S.; Matsumae, H.; McNally, K.E.; Parlange, F.; Riba, A.; Roffler, S.; et al. Hybridization of powdery mildew strains gives rise to pathogens on novel agricultural crop species. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troch, V.; Audenaert, K.; Bekaert, B.; Höfte, M.; Haesaert, G. Phylogeography and virulence structure of the powdery mildew population on its ’new’ host triticale. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troch, V.; Audenaert, K.; Vanheule, A.; Bekaert, B.; Höfte, M.; Haesaert, G. Evaluation of resistance to powdery mildew in triticale seedlings and adult plants. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolmer, J.A. Genetics of resistance to wheat leaf rust. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996, 34, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseniuk, E. Triticale Diseases—A Review. In Triticale: Today and Tomorrow. Developments in Plant Breeding; Guedes-Pinto, H., Darvey, N., Carnide, V.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 499–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodkiewicz, W.; Strzembicka, A.; Apolinarska, B. Chromosomal location in triticale of leaf rust resistance genes introduced from Triticum monococcum. Plant Breed. 2008, 127, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, B.; Herselman, L.; Bender, C.M.; Pretorius, Z.A. Microsatellite analysis of selected Puccinia triticina races in South Africa. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2012, 41, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Epidemiology and control of stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) on wheat. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 27, 314–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellings, C.R. Global status of stripe rust: A review of historical and current threats. Euphytica 2011, 179, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Weinert, J.; Wolf, G.A. Infection of triticale cultivars by Puccinia striiformis: First report on disease severity and yield loss. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2004, 111, 461–464. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/43216280 (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Hovmøller, M.S.; Walter, S.; Bayles, R.A.; Hubbard, A.; Flath, K.; Sommerfeldt, N.; Leconte, M.; Czembor, P.; Rodriguez-Algaba, J.; Thach, T.; et al. Replacement of the European wheat yellow rust population by new races from the centre of diversity in the near-Himalayan region. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovmøller, M.S.; Patpour, M.; Rodriguez-Algaba, J.; Thach, T.; Fejer Justesen, A.; Grønbech Hansen, J. GRRC Report of Yellow and Stem Rust Genotyping and Race Analyses 2020; Aarhus University: Aarhus, Denmark, 2021; Available online: https://agro.au.dk/fileadmin/www.grcc.au.dk/International_Services/Pathotype_YR_results/GRRC_annual_report_2020.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Losert, D.; Maurer, H.P.; Leiser, W.L.; Würschum, T. Defeating the warrior: Genetic architecture of triticale resistance against a novel aggressive yellow rust race. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedaner, T.; Juroszek, P. Climate change will influence disease resistance breeding in wheat in Northwestern Europe. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.A.; Luig, N.H.; Milne, D.L.; Cusick, J. Vulnerability of triticales to wheat stem rust. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1983, 5, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Saari, E.E. Biotic Stress in Triticale. In Proceedings of the International Triticale Symposium, Passo Fundo, Brazil, 1–5 October 1990; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, K.N.; McIntosh, R.A. Inheritance of wheat stem rust resistance in triticale. Plant Breed. 1998, 117, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakulinski, W.; Nowicki, B.; Zamorski, C. Podatnosc form ozimych ×Triticosecale Wittmack na porazenie przez Puccinia graminis Pers. Progr. Plant Prot. 2006, 46, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, C.M. Stem Rust Resistance in South African Wheat and Triticale. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera Firpo, P.D.; Newcomb, M.; Flath, K.; Sommerfeldt-Impe, N.; Szabo, L.J.; Carter, M.; Luster, D.G.; Jin, Y. Characterization of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici isolates derived from an unusual wheat stem rust outbreak in Germany in 2013. Plant Pathol. 2017, 66, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.A. The Role of Specific Genes in Breeding for Durable Stem Rust Resistance in Wheat and Triticale. In Breeding Strategies for Resistance to the Rusts of Wheat; Simmonds, N.W., Rajaram, S., Eds.; CIMMYT: Texcoco, México, 1988; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.J.; McIntosh, R.A. Allelism of two genes for stem rust resistance in triticale. Euphytica 1988, 38, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wellings, C.R.; McIntosh, R.A.; Park, R.F. Seedling resistances to rust diseases in international triticale germplasm. Crop Pasture Sci. 2010, 61, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flor, H.H. Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1971, 9, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.A.; Wellings, C.R.; Park, R.F. The Genes for Resistance to Stem Rust in Wheat and Triticale. In Wheat Rusts: An Atlas of Resistance Genes; McIntosh, R.A., Wellings, C.R., Park, R.F., Eds.; CSIRO Publications: East Melbourne, Australia, 1995; pp. 87–152. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, R.A.; Yamazaki, Y.; Dubcovsky, J.; Rogers, J.; Morris, C.; Appels, R.; Xia, X.C. Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. In Proceedings of the 12th International Wheat Genetics Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 8–13 September 2013; Available online: https://shigen.nig.ac.jp/wheat/komugi/genes/macgene/2013/GeneCatalogueIntroduction.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- McIntosh, R.A.; Dubcovsky, J.; Rogers, W.J.; Xia, X.C.; Raupp, W.J. Catalogue of Gene Symbols for Wheat: 2020 Supplement. Available online: https://shigen.nig.ac.jp/wheat/komugi/genes/symbolClassList.jsp (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Serfling, A.; Kopahnke, D.; Habekuss, A.; Novakazi, F.; Ordon, F. Wheat Diseases: An Overview. In Achieving sustainable Cultivation of Wheat. Breeding Quality Traits, Pests and Diseases; Langridge, P., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 263–294. [Google Scholar]
- Oettler, G.; Schmid, T. Genotypic variation for resistance to Septoria nodorum in triticale. Plant Breed. 2000, 119, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseniuk, E.; Góral, T. Triticale Biotic Stresses-Known and Novel Foes. In Triticale; Eudes, F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikpa, D.S.; Lieberherr, B.; Maurer, H.P.; Longin, C.F.H.; Miedaner, T. Comparison of rye, triticale, durum, and bread wheat genotypes for Fusarium head blight resistance and deoxynivalenol contamination. Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, R.; Miedaner, T.; Wirsel, S.G.R. Biology, Diversity, and Management of FHB-Causing Fusarium Species in Small-Grain Cereals. In Agricultural Applications. The Mycota XI., 2nd ed.; Kempken, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 199–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venske, E.; Dos Santos, R.S.; Farias, D.D.R.; Rother, V.; Da Maia, L.C.; Pegoraro, C.; Costa de Oliveira, A. Meta-analysis of the QTLome of Fusarium head blight resistance in bread wheat: Refining the current puzzle. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buerstmayr, M.; Steiner, B.; Buerstmayr, H. Breeding for Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat—Progress and challenges. Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedaner, T.; Schneider, B.; Oettler, G. Means and variances for Fusarium head blight resistance of F2–derived lines from winter triticale and winter wheat crosses. Euphytica 2006, 152, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettler, G.; Heinrich, N.; Miedaner, T. Estimates of additive and dominance effects for Fusarium head blight resistance of winter triticale. Plant Breed. 2004, 123, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalih, R.; Maurer, H.P.; Miedaner, T. Genetic architecture of Fusarium head blight resistance in four winter triticale populations. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miedaner, T.; Akel, W.; Flath, K.; Jacobi, A.; Taylor, M.; Longin, F.; Würschum, T. Molecular tracking of multiple disease resistance in a winter wheat diversity panel. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beukert, U.; Liu, G.; Thorwarth, P.; Boeven, P.H.; Longin, C.F.H.; Zhao, Y.; Ganal, M.; Serfling, A.; Ordon, F.; Reif, J.C. The potential of hybrid breeding to enhance leaf rust and stripe rust resistance in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miedaner, T.; Schmid, J.E.; Flath, K.; Koch, S.; Jacobi, A.; Ebmeyer, E.; Taylor, M. A multiple disease test for field-based phenotyping of resistances to Fusarium head blight, yellow rust and stem rust in wheat. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 151, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, U. Growth Stages of Mono- and Dicotyledonous Plants. BBCH Monograph. 2001. Available online: https://www.julius-kuehn.de/media/Veroeffentlichungen/bbch%20epaper%20en/page.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Snijders, C.H.A.; Perkowski, J. Effects of head blight caused by Fusarium culmorum on toxin content and weight of wheat kernels. Phytopathology 1990, 80, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedaner, T.; Gang, G.; Geiger, H.H. Quantitative-genetic basis of aggressiveness of 42 isolates of Fusarium culmorum for winter rye head blight. Plant Dis. 1996, 80, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepho, H.P.; Möhring, J. Computing heritability and selection response from unbalanced plant breeding trials. Genetics 2007, 177, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehr, W.R. Principles of Cultivar Development. Vol. 1. Theory and Technique; MacMillan Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Emrich, K.; Wilde, F.; Miedaner, T.; Piepho, H.P. REML approach for adjusting the Fusarium head blight rating to a phenological date in inoculated selection experiments of wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, M.; Lein, V.; Lacoudre, F.; Lafferty, J.; Müller, E.; Vida, G.; Bozhanova, V.; Ibraliu, A.; Thorwarth, P.; Piepho, H.P.; et al. Simultaneous improvement of grain yield and protein content in durum wheat by different phenotypic indices and genomic selection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.G.; Cullis, B.R.; Gilmour, A.R.; Gogel, B.J. ASReml-Rreference Manual. Release 3.0. Technical Report; Queensland Government, Department of Primary Industries: Queensland, Australia, 2009. Available online: https://asreml.kb.vsni.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/ASReml-R-3-Reference-Manual.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/old/3.4.4/ (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Snedecor, G.W.; Cochran, W.G. Statistical Methods, 8th ed.; Iowa State university Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, E.; Flath, K.; Tessenow, I. Bewertung der Resistenz von Getreidesortimenten Planung und Auswertung der Versuche mit Hilfe der SAS-Anwendung RESI 2. Berichte aus dem Julius Kühn-Institut 154, 2010. Available online: https://docplayer.org/127959023-Berichte-aus-dem-julius-kuehn-institut.html (accessed on 17 May 2022). (in German).
- Losert, D.; Maurer, H.P.; Marulanda, J.J.; Würschum, T. Phenotypic and genotypic analyses of diversity and breeding progress in European triticale (× Triticosecale Wittmack). Plant Breed. 2017, 136, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H.P.; (University of Hohenheim, State Plant Breeding Institute, Stuttgart, Germany). Personal communication, 2022.
- Falconer, D.S.; Mackay, F.C. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 4th ed.; Longman: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, R.; Korzun, V. Genes, Markers and Linkage Data of Rye (Secale cereale L.), 11th Updated Inventory, V. 01.21, 2021. Available online: http://www.rye-gene-map.de (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Randhawa, H.; Puchalski, B.J.; Frick, M.; Goyal, A.; Despins, T.; Graf, R.J.; Laroche, A.; Gaudet, D.A. Stripe rust resistance among western Canadian spring wheat and triticale varieties. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivera, P.D.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Badebo, A.; Jin, Y. Identification of resistance to races of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici with broad virulence in triticale (× Triticosecale). Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galiano-Carneiro, A.L.; Boeven, P.H.; Maurer, H.P.; Würschum, T.; Miedaner, T. Genome-wide association study for an efficient selection of Fusarium head blight resistance in winter triticale. Euphytica 2019, 215, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbarz, M.; Tyrka, M.; Woźniak-Strzembicka, A.; Czajowski, G.; Wardyńska, A.; Tyrka, D.; Pojmaj, M.; Wędzony, M. Quantitative trait loci mapping of adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in triticale. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2020, 177, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyda, M.M.; Tyrka, M.; Gołębiowska, G.; Rapacz, M.; Wędzony, M. Genetic mapping of adult-plant resistance genes to powdery mildew in triticale. J. Appl. Genet. 2022, 63, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Amores, J.; Michel, S.; Miedaner, T.; Longin, C.F.H.; Buerstmayr, H. Genomic predictions for Fusarium head blight resistance in a diverse durum wheat panel: An effective incorporation of plant height and heading date as covariates. Euphytica 2020, 216, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.J.; McIntosh, R.A. Linkage and expression of genes for resistance to leaf rust and stem rust in triticale. Genome 1990, 33, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikpa, D.S.; Koch, S.; Fromme, F.J.; Siekmann, D.; Würschum, T.; Miedaner, T. Genome-wide association mapping and genomic prediction of Fusarium head blight resistance, heading stage and plant height in winter rye (Secale cereale). Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merrick, L.F.; Burke, A.B.; Chen, X.; Carter, A.H. Breeding with major and minor genes: Genomic selection for quantitative disease resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 713667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.; Hickey, L.T.; Christopher, J.; Rutkoski, J.; Poland, J.; Hayes, B.J. Multivariate genomic selection and potential of rapid indirect selection with speed breeding in spring wheat. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 1945–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
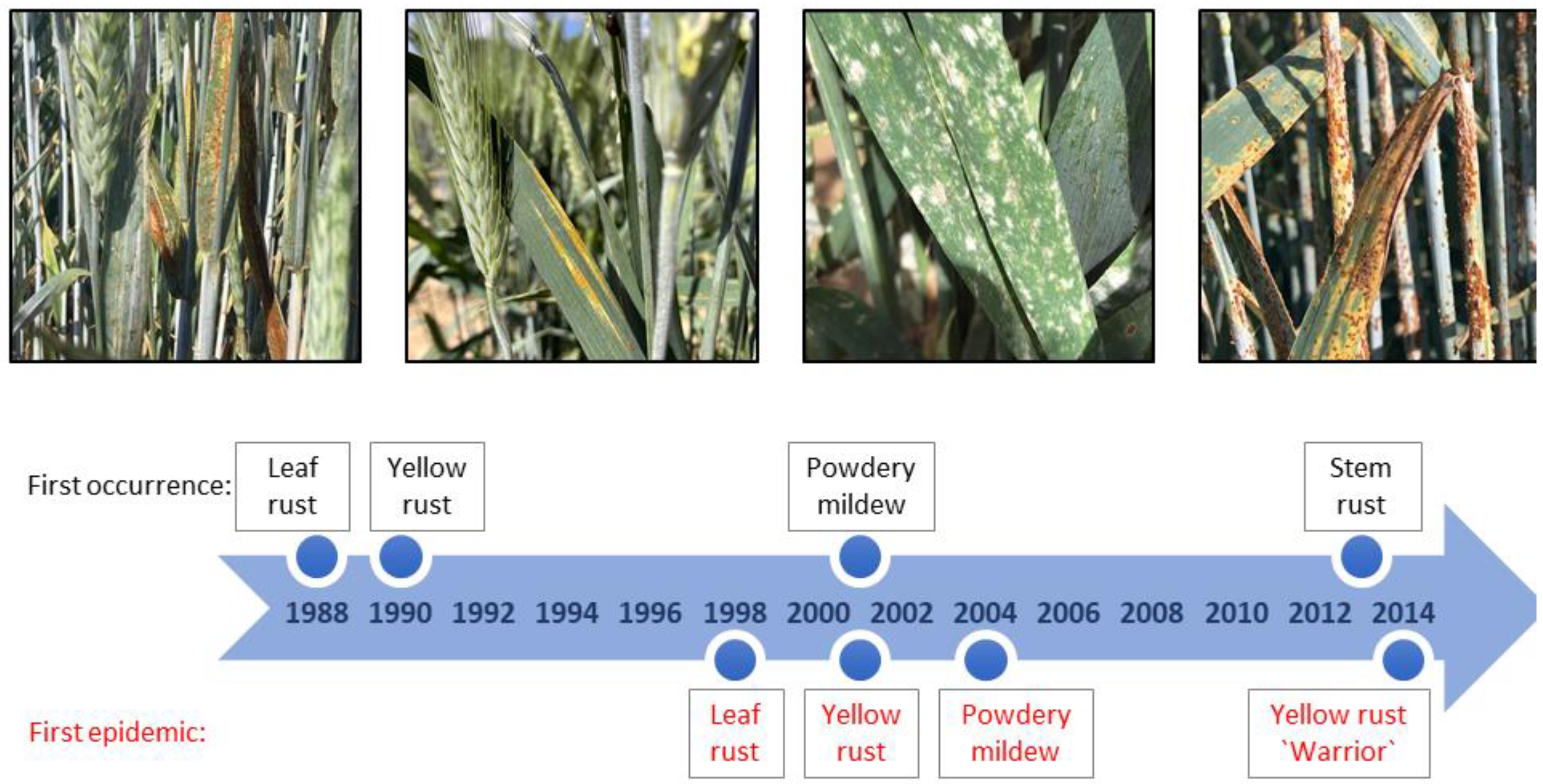
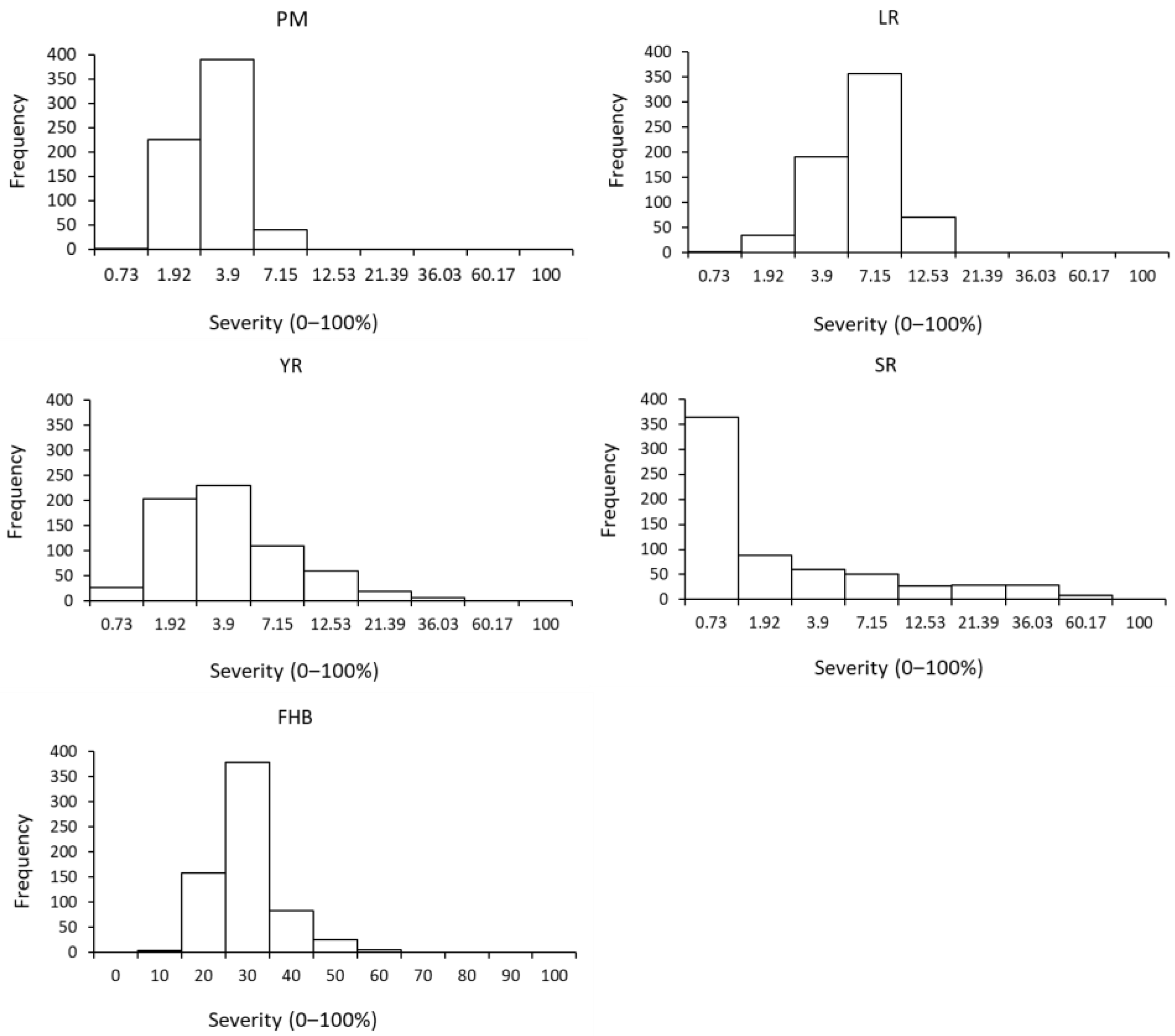
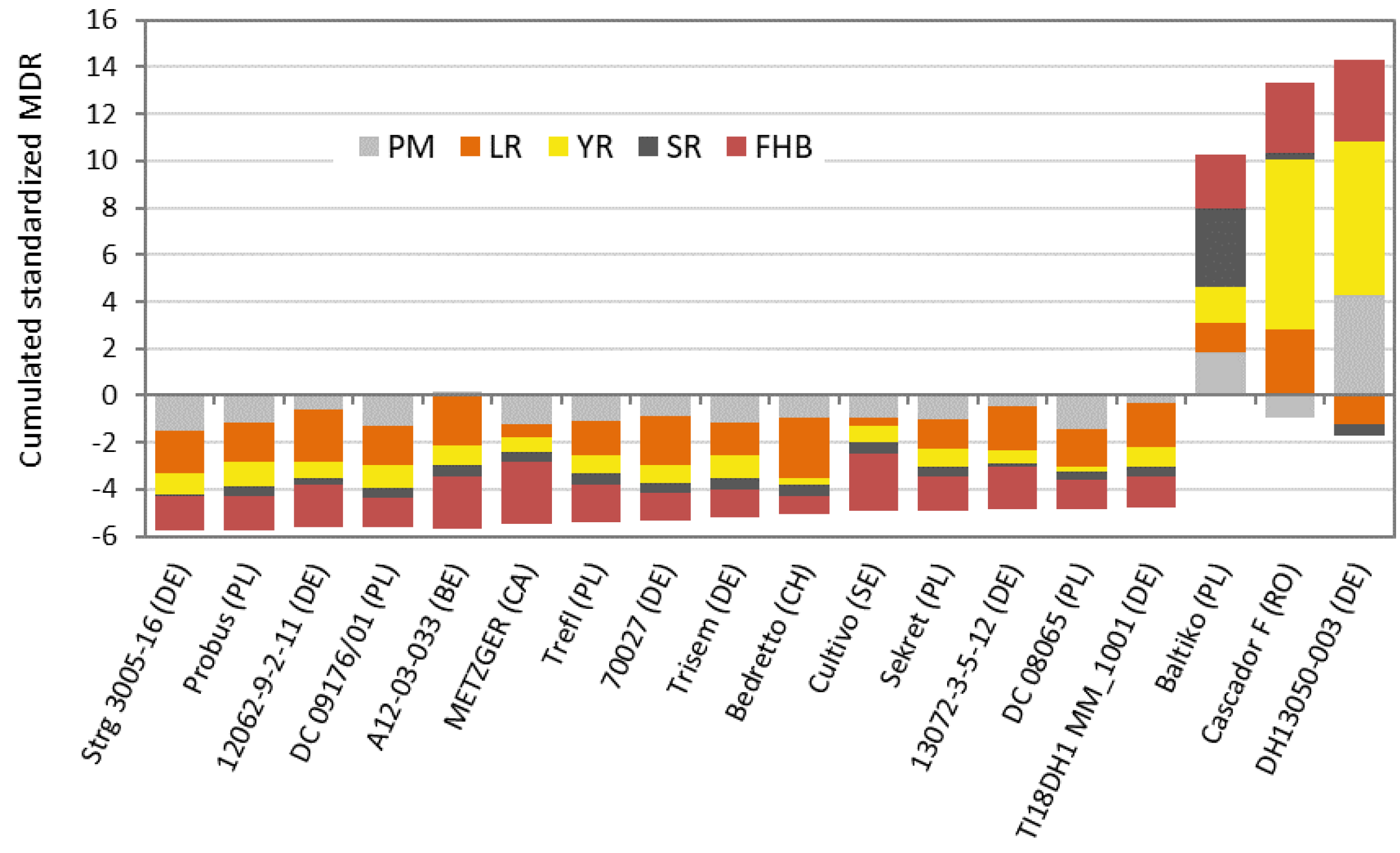
| Trait, Abbreviation | Environments (Total Number) | Artificial Infection | Rating Scale a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powdery mildew (PM) | BOH19, HOH19, OLI19, PZO19, HOH20, OLI20 (6) | No | 1–9 |
| Leaf rust (LR) | HOH19, BOH20 (2) | No | 1–9 |
| Yellow rust (YR) | HOH18, BOH19, HOH20, BOH20, PZO20 (5) | HOH20 only | % |
| Stem rust (SR) | HOH18, HOH19, BOH19, PZO19, HOH20, PZO20 (6) | Yes | % |
| Fusarium head blight (FHB) | HOH18, OLI18, HOH19, OLI19, BOH19, HOH20, OLI20, BOH20 (8) | Yes | % |
| Plant height (PH) | HOH18, OLI18, HOH19, OLI19, BOH19, PZO19, HOH20, OLI20, BOH20 (9) | − | cm |
| Heading stage (HS) | HOH18, OLI18, HOH19, OLI19, BOH19, HOH20, OLI20, BOH20 (8) | − | BBCH |
| Trait | BLUEs | Variance components | H2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Min | Max | LSD5% | ||||||
| PM (1–9) | 2.4 | 0.5 | 6.0 | 1.03 | 27.3 | 0.43 *** | 0.29 *** | 0.87 | 0.78 |
| LR (1–9) | 4.4 | 2.8 | 6.5 | 2.35 | 22.7 | 1.0 *** | 2.6 *** | 1.6 | 0.42 |
| YR (%) | 3.8 | 0.0 | 33.4 | 6.20 | 32.2 | 1.5 *** | − a | 0.1 | 0.79 |
| SR (%) | 4.0 | 0.0 | 56.8 | 8.45 | (224.7) b | 80.8 *** b | 24.9 *** | 4.9 | 0.91 b |
| FHB (%) | 24.6 | 6.8 | 54.4 | 7.87 | 32.6 | 64.17*** | 45.61 *** | 43.07 | 0.85 |
| PH (cm) | 115.05 | 74.3 | 170.7 | 4.60 | 13.3 | 232.61 *** | 9.81 *** | 15.55 | 0.99 |
| HS (BBCH) | 55.45 | 44.8 | 61.5 | 1.36 | 4.7 | 6.91 *** | 0.59 *** | 1.65 | 0.96 |
| Trait | PH | PM | LR | YR | SR | FHB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uni-Variate | Co-Variate | Multi-Variate | ||||||
| HS | −0.33 *** | 0.13 ** | −0.02 | 0.06 | −0.01 | 0.35 *** | 0.29 *** | 0.01 |
| PH | −0.05 | −0.10 ** | −0.07 | 0.09 * | −0.19 *** | −0.06 | 0.04 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miedaner, T.; Flath, K.; Starck, N.; Weißmann, S.; Maurer, H.P. Quantitative-Genetic Evaluation of Resistances to Five Fungal Diseases in A Large Triticale Diversity Panel (×Triticosecale). Crops 2022, 2, 218-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops2030016
Miedaner T, Flath K, Starck N, Weißmann S, Maurer HP. Quantitative-Genetic Evaluation of Resistances to Five Fungal Diseases in A Large Triticale Diversity Panel (×Triticosecale). Crops. 2022; 2(3):218-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops2030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiedaner, Thomas, Kerstin Flath, Norbert Starck, Sigrid Weißmann, and Hans Peter Maurer. 2022. "Quantitative-Genetic Evaluation of Resistances to Five Fungal Diseases in A Large Triticale Diversity Panel (×Triticosecale)" Crops 2, no. 3: 218-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops2030016
APA StyleMiedaner, T., Flath, K., Starck, N., Weißmann, S., & Maurer, H. P. (2022). Quantitative-Genetic Evaluation of Resistances to Five Fungal Diseases in A Large Triticale Diversity Panel (×Triticosecale). Crops, 2(3), 218-232. https://doi.org/10.3390/crops2030016






