Abstract
The brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[BPH], is a damaging pest of rice in Asia. Insecticides and rice varietal resistance are widely implemented BPH management practices. However, outbreaks of BPH have been linked to excessive insecticide use—challenging the compatibility of these two management practices. IR62 is a variety with resistance against BPH, the whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera Horváth [WBPH], and the green leafhopper, Nephotettix virescens (Distant)[GLH]. We compared BPH responses to IR62 and to the susceptible variety IR64 treated with buprofezin, carbofuran, cartap hydrochloride, cypermethrin, deltamethrin, fipronil, or thiamethoxam + chlorantraniliprole. In greenhouse bioassays, cypermethrin, fipronil and thiamethoxam + chlorantraniliprole reduced egg laying on both varieties, and, together with buprofezin, reduced nymph survival to zero. Buprofezin, carbofuran, and cartap hydrochloride stimulated egg laying, and carbofuran increased nymph biomass, but these effects were reduced on IR62. Planthopper populations were ten times higher on deltamethrin-treated rice than untreated rice in a screenhouse experiment. Host resistance failed to buffer against this insecticide-induced resurgence in BPH and WBPH. However, IR62 reduced the effect in GLH. Rice treated with cypermethrin and fipronil had reduced yields compared to untreated controls, suggesting possible phytotoxic effects. We found little evidence of synergies between the two management practices; but host resistance did buffer against the undesirable effects of some insecticides.
1. Introduction
The brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[BPH], is among the most damaging pests of rice in Asia [1]. BPH occurs throughout the year in tropical Asia where farmers can produce between one and three rice crops per year. At optimal temperatures, the planthopper completes about three generations per crop, thereby, rapidly building up populations in regions of intensive rice production [1,2]. Furthermore, BPH populations respond to high levels of nitrogenous fertilizers by increasing feeding efficiency, growth rates, development rates, and reproductive output—thereby further enhancing population growth [3,4]. During the northern hemisphere spring, planthoppers migrate from tropical Asia to Korea, Japan, and Northeastern China where large numbers of planthoppers can sometimes overwhelm natural enemies, thereby causing extensive damage to early-season rice crops in these regions [5,6,7].
The management of BPH has relied heavily on two principal methods: firstly, public research has focused on developing rice varieties with resistance (i.e., host plant resistance [HPR]) to the planthopper based on conventional crosses between naturally resistant traditional landraces and high-yielding rice varieties [8]. Resistant varieties have been deployed to farmers’ fields since the 1970s; however, BPH populations can often rapidly adapt to this resistance—a phenomenon known as ‘virulence adaptation’ [9,10,11]. Currently, there are several resistance genes available from rice landraces and wild rice species, such that virulence adaptation, can now be better managed [12]. The second most prominent BPH management method is the use of chemical insecticides [2,13,14]. The development of insecticides is mainly conducted through private companies. Beginning in the early 2000s, large increases in the trade and use of insecticides have been reported throughout Asia [2]. Furthermore, trends suggest that farmers increasingly apply insecticides prophylactically and these applications are not in response to observed high pest densities as recommended by Integrated Pest Management (IPM) principals [2,15,16]. Several detailed studies have shown that some commonly-used insecticides actually enhance the growth rates of BPH populations and, in many cases, will ultimately lead to localized outbreaks of BPH in farmers’ fields [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. The deployment of resistant rice and the prophylactic application of insecticides might therefore be antagonistic to achieving successful BPH management. Furthermore, where farmers conduct prophylactic insecticide applications, HPR cannot achieve one of its principal objectives, that of reducing pesticide inputs and maintaining a healthy rice environment [12]. Indeed, in such cases, resistance can become simply an ‘insurance’ against insecticide-induced BPH outbreaks and may inadvertently contribute to an overuse of insecticides.
The mechanisms by which insecticides lead to BPH resurgence have received considerable research attention. Recently, Wu et al. (2020) [27], reviewed much of the available information. Resurgence has been noted across a wide range of insecticide products that have two main effects in the rice ecosystem. Firstly, certain insecticides enhance the feeding rates, growth rates, development, reproductive output, and migration potential of BPH either through direct effects on planthopper physiology, known as hormesis, or indirectly, by inducing susceptibility in the host plant (i.e., by lowering phenol concentrations and enhancing sugar mobilization) [18,28]. Secondly, many insecticides will have a greater effect in reducing natural enemy populations than in reducing BPH populations, thereby depleting the pest regulation capacity of the rice ecosystem [29,30,31,32,33,34]. The higher susceptibility of natural enemies to insecticides compared to BPH and other pests has been attributed to a greater mobility of natural enemies and, thereby, higher probabilities of exposure to the insecticides; furthermore, many predatory and parasitic arthropods have slower population growth rates than BPH [35], which reduces the potential for natural enemies to develop insecticide resistance.
Horgan (2018) [12] reviewed studies where insecticides were applied to both resistant and susceptible rice varieties to compare effects. In many cases, insecticides reduced the effectiveness of resistance; however, relative resistance was often maintained across test varieties—albeit with some minor exceptions [28,36,37]. However, only ten published studies have examined the combined effects of host resistance and insecticides on BPH population development [18,20,31,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]; a further three studies examined effects on the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera Horváth [WBPH], an increasingly common pest of rice in Asia [28,36,44]. Only seven of these studies have been published since 2000, and, to our knowledge, there have been no published studies since 2018 that compare the actions of insecticides on BPH-susceptible and resistant rice (based on records retrieved using Google Scholar). As a consequence, information on interactions between currently-effective BPH resistance genes, and commonly used insecticides, is largely unavailable. Based on the materials (rice varieties and insecticides) used in previous studies, there is clearly a need to further examine the possible synergistic and/or antagonistic effects of combining host resistance and insecticides for BPH management.
In the present study, we examine the effects of seven widely available insecticides on the integrity of resistance in rice against BPH. We selected a rice variety, IR62, with relatively strong resistance against BPH populations from across Asia [11,45]. This variety possesses the Bph3 and Bph32 resistance genes derived from the Indian landrace PTB33. Because of its relatively high effectiveness, IR62 and doner varieties with the Bph3 locus containing either the Bph3 or Bph32 resistance genes have been extensively studied in recent years [46,47,48]. We also selected insecticides that are currently used to manage insect herbivores in rice in Asia. Many of the products are not specifically recommended for use against BPH; however, resurgence is often the result of applications against other insect pests (i.e., BPH is a secondary pest), and particularly against rice leaffolders [49]. We examined the indirect, plant-mediated effects of insecticides on BPH because our focus was on possible insecticide-plant interactions, as well as on direct insecticide effects on BPH. Therefore, we conducted our experiments in greenhouses and in a screenhouse that were largely free of natural enemies. Furthermore, because of possible phytotoxic effects of insecticides on rice plants [50,51], and the potential role of such phytotoxicity in determining BPH-rice interactions [49], we also assessed insecticide effects on plant growth and yields in the screenhouse. We discuss our results in terms of applying HPR and insecticide treatments according to IPM principles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Herbivore Species
BPH were obtained from colonies reared at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) in the Philippines. Planthoppers were initially collected in 2009 from rice fields in Laguna Province. The founder population (ca 500 individuals) was placed in wire mesh cages of 120 × 60 × 60 cm (H × W × L) under greenhouse conditions (temperatures [T] 25–37 °C; 70–90% relative humidity [RH], 12h:12h day:night [D:N]) and was continuously reared on ≥30 days after sowing [DAS] rice plants (variety = TN1). Feeding plants were replaced every two weeks. The colony received periodic (each year) introgressions of wild-caught individuals from the same collection sites. BPH from the Laguna Province have been screened for virulence and are largely adapted to feed on rice varieties with the Bph1, bph2, bph5, bph7, Bph18, Bph25, and Bph26 genes [11,45]. The colonies were also tested for levels of resistance to insecticides and have moderate resistance to imidacloprid and high resistance to BPMC [52].
2.2. Plant Materials
We used two varieties in our experiments. IR62 was selected as a variety with high resistance to BPH populations throughout South and Southeast Asia [53]. Resistance in IR62 was derived from PTB33 and is attributed to the Bph3/Bph32 resistance genes [48,53]. BPH has reduced feeding, lower weight gain, slower development, and reduced egg-laying on IR62 compared to susceptible varieties [4]. The variety also has moderate resistance to WBPH and to the green leafhopper, Nephotettix virescens (Distant) [GLH] [45,54]. Furthermore, resistance derived from PTB33 and associated with the Bph3 locus appears to be highly durable, since BPH populations with virulence against PTB33-derived varieties, including IR62, are still rare despite over 30 years of deployment in regions of Mindanao (Philippines) and in Cambodia [55]. The variety IR64 was selected as a susceptible variety. IR64 has the Bph1 gene for resistance, but BPH populations throughout Asia have adapted to this gene [11,53]. Nevertheless, IR64 has additional quantitative resistance that contributes to tolerance (i.e., a relatively high capacity to withstand damage) of BPH in the variety [56]. IR64 was released by IRRI in 1985 and is considered a mega-variety in Asia [57]. Because of its popularity, the variety has been enhanced using marker-assisted breeding to incorporate traits such as flood tolerance (i.e., IR64-Sub1, released in 2009) [57]. For our experiments, seeds of both varieties were acquired from the IRRI-germplasm bank.
2.3. Insecticides
We used seven insecticides in our experiments. The insecticides were selected based on their availability at IRRI. Buprofezin (2-tert-butylimini-3-isopropyl-5-phenyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazin-5-one) (25SC; 200 mL ha−1) contains the growth regulator thiadezine and is used against planthoppers and leafhoppers in rice. It is the recommended insecticide to combat high densities of planthoppers in rice because it has relatively low toxicity to natural enemies [58]. We used two synthetic pyrethroids, cypermethrin (cyan-(3-pheboxyphenyl)-methyl-(3-CS,2-dichloroethenyl)-2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane carboxylate) (10EC; 800 mL ha−1), and deltamethrin ((S)-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1R,3R)-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethyl-cyclopropane-carboxylate) (25EC; 500 mL ha−1); cypermethrin has been commonly used in rice production to combat rice tungro virus that is transmitted by rice leafhoppers [59]. Deltamethrin is a broad-spectrum insecticide that is also sometimes used to manage leafhoppers. Both pyrethroids were previously noted to cause BPH resurgence [39,60,61] and are currently not recommended for use in rice [62]. Nevertheless, cypermethrin and deltamethrin are still commonly used on rice in some countries, including Indonesia and Bangladesh [13,14,61]. For this reason, we included both products in our experiments. We used the carbamate insecticide carbofuran (2,2-Dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-7-flmethyl-carbamate) (3G; 3 kg ha−1) as a systemic insecticide that is sometimes recommended for control of rice pests including planthoppers [63,64]. Carbofuran has been banned in the European Union, the USA, and Canada, but is still used in much of Asia [65]. We used thiamethoxam 20% + chlorantraniliprole 20% (3-[(2-chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)methyl]-5-methyl-1,3,5-oxadiazinan-4-ylidene nitramide + 5-bromo-N-[4-chloro-2-methyl-6-(methylcarbamoyl)phenyl]-2-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)pyrazole-3-carboxamide) (40 WG; 75 g ha−1), i.e., a combined neonicotinoid and diamide product, as a further systemic insecticide. The product is absorbed through the plant to give broad-spectrum control of rice pests [66]. Finally, we used fipronil (5-Amino-1-[2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-(trifluoromethanesulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonitrile) (50SC; 500 mL ha−1) and cartap hydrochloride (S-[3-carbamoylsulfanyl-2-(dimethylamino)propyl] carbamothioate-hydrochloride) (a nereistoxin analogue) (50SP; 400 g ha−1) as two broad-spectrum insecticides commonly used to control leaffolders in Asian rice [67,68,69,70]. All insecticides were applied at recommended rates with quantities estimated based on the surface soil area of each experimental unit. Insecticides were applied by trained pesticide applicators using standard protective equipment, in a well-ventilated environment (an insect screenhouse). Any evaluations of treated rice plants were conducted at a minimum of 3 days post-application.
2.4. Effects of HPR and Insecticides on BPH Preferences
We assessed the effects of the insecticides on oviposition by BPH in a multichoice and in binary choice bioassays. For both tests, seedlings of IR62 and IR64 were planted individually in #0 pots (5 × 5 cm: H × Diameter) in a greenhouse (T = 25–37 °C; RH = 70–90% D:N = 12 h:12 h). At 27 days after sowing (DAS), the seedlings were treated with one of each of the seven insecticides as described above, or were sprayed with water (i.e., untreated control). We used water as a control because some of the products were diluted with water. Plants were returned to the greenhouse at 30 DAS. For each variety in the multichoice bioassay, eight plants at 30 DAS—one for each treatment—were placed together in a wire mesh cage of 120 × 60 × 60 cm (H × W × L). The plants were arranged in a circular configuration, each separated by 10 cm such that adjacent plants did not touch each other or the cage walls. The cages were replicated five times for each rice variety, with plants positioned randomly during each replication. Twenty gravid female N. lugens were placed at the center of each cage and allowed to lay eggs for 3 days, after which all adults were manually removed from the cages. Eggs were allowed to develop in the plants for a further 4 days, after which the plants were collected, wrapped in moistened tissue paper and stored in a refrigerator. Within 5 days, all plants were dissected under a stereo microscope (Nikon SMZ-2B, Tokyo, Japan) to count the egg clusters. Egg clusters were removed from the plant tissues and the numbers of eggs per cluster were recorded. The total number of eggs was estimated as the sum of eggs per plant from all clusters.
For the binary choice tests, one plant (either IR62 or IR64) for each insecticide treatment was placed together with a control (untreated) plant of the same variety, in an acetate cage of 30 × 25 × 50 cm (H × W × L) (i.e., two plants per cage). This produced 14 treatment × variety combinations (7 insecticides × 2 varieties). Each combination of plant pairs was replicated three times with cages positioned randomly on greenhouse benches and replicates of each combination pair placed in separate greenhouse compartments. Five gravid females were placed between the two pots in each cage and allowed to move within the cage and lay eggs. After 3 days, all adults were manually removed from the cages. The plants were collected 4 days after removal of the adults to allow the eggs to develop. Plants were placed in moist tissue paper and stored in a refrigerator until clusters and eggs were counted under a stereomicroscope (as described above). For both bioassays, the replicates were each placed in separate greenhouse compartments (i.e., 5 or 3 blocks).
2.5. Effects of HPR and Insecticides on BPH Fitness
We conducted two BPH antibiosis tests in the greenhouse. We examined egg laying by gravid females on each variety and for each insecticide treatment using an oviposition test. At 30 DAS, treated and control plants were individually caged by placing an acetate tube 45 × 5 cm (H × Diameter) with a mesh top over each pot. A recently mated, gravid BPH was placed inside each cage through a slit in the acetate and was allowed to feed and oviposit. After 3 days, the females were manually removed from the cages. Plants were left for 4 days to allow eggs to develop. The plants were then collected and dissected under a stereo microscope to count the clusters and eggs (as described above).
We examined the effects of host resistance and insecticide treatments on BPH nymphs in a survival test. At 30 DAS, treated and control plants were individually caged as described above. Recently emerged nymphs (≤2 instar) were collected from the colony using a suction-pooter and placed inside the cages at a density of ten per cage through a slit in the acetate. The nymphs were allowed to feed and develop for 15 days, after which the number of survivors and their developmental stages were recorded. For both bioassays, plants were dried in a forced draft oven at 60 °C for 7 days and were weighed. For the survival bioassay, the nymphs were also dried and weighed to estimate dry biomass and thereby control for varying consumption of plant liquids. Both bioassays were replicated five times (i.e., 8 treatments × 2 varieties × 5 replicates = 80 pots per bioassay), with each replicate placed in a separate greenhouse compartment (i.e., 5 blocks).
2.6. Effects of HPR and Insecticides in a Screenhouse Environment
The combined effects of insecticide treatments and HPR were investigated using rice plants grown in an insect-proof screenhouse. The screenhouse consisted of six concrete bays (dimensions 26.6 × 2.5 m (L × W)) filled with flooded paddy soil. Temperatures in the screenhouse varied between 21 and 34 °C, and RH varied between 70 and 90%. Rainwater could pass through the screenhouse roof: during the experiment, 160 mm of precipitation was recorded, representing the Philippines dry season. The screenhouse had no artificial lighting (i.e., D:N = 12 h:12 h).
In one of the bays, translucent plastic barriers were erected to delimitate five experimental blocks of 1.50 × 3.00 m. Each block was further divided into eight cubicles of 0.75 m2 using the same plastic materials. The barriers were supported by bamboo stakes and reached a height of 1.50 m and a depth into the paddy soil of approx. 0.30 m. After the barriers were installed, two 23 DAS seedlings each of IR62 and IR64 were randomly transplanted to each cubicle at 25 × 25 cm spacing. We used a standard fertilizer regime to simulate farmers’ fields. The seedlings were treated with ammonium sulphate at 100 kg ha−1 split equally into three applications (i.e., one basal and two top dressings). Solophos and muriate of potash was also applied at 20 kg ha−1 as a basal application. Plants were continuously watered and the cubicles were manually weeded until rice plants were harvested. Cubicles in each of the five blocks received one of the eight treatments (seven insecticides and a control). Treatments were randomly assigned to cubicles within blocks. The insecticide applications were made at 30 and 60 DAS, to simulate farmer practices under intensive rice production systems where farmers apply insecticides ≥ two times [14]; however, in our experiment, we did not mix insecticides.
Rice herbivores, including BPH, WBPH, and GLH, occurred at low densities in the screenhouse. Therefore, at the opposite end of the screenhouse (separated by a distance of 20 m), a bay with >50 DAS TN1 rice plants was infested with high densities of BPH (approx. 200 BPH plant−1). This acted as a potential source of planthoppers to attack the treated IR62 and IR64 plants in our experiment. Natural enemies were largely absent from the screenhouse because of the insect-proof cladding (1 mm × 1 mm mesh bore). Microparasitoids (Oligosita spp. and Anagrus spp.) that could pass through the screen occasionally attacked planthopper eggs in the screenhouse (estimated 5–10% of eggs parasitized, unpublished data).
The IR62 and IR64 plants were continuously monitored to assess grain maturation. When about 85% of the rice grain was mature, any arthropods on the plants were collected using a vacuum sampler and stored in plastic vials. The plants were then destructively harvested by carefully pulling the plant from the soil to maintain intact roots. The plant roots were washed under running water and each plant was placed inside a paper bag. The plants and arthropods were then dried in a forced draft oven at 60 °C for 7 days and weighed. Arthropods were separated by species and counted. The plants were separated into roots, shoots, and panicles, and the numbers of reproductive and vegetative tillers were recorded. Rice grain was removed from the panicles and separated as filled and non-filled grain. The dried grain was counted and weighed.
2.7. Data Analyses
The numbers of egg clusters and eggs laid in rice plants during the multichoice test were analyzed using univariate general linear models (GLM) on ranked (within replicate) data. Separate analyses were conducted for IR62 and IR64 plants. Data from the binary choice bioassays were analyzed using paired t-tests. The numbers of egg clusters and eggs laid in treated and non-treated plants during the oviposition bioassay were compared using univariate GLM with plant biomass initially included as a covariate, but later removed because it had no significant effect. Cluster and egg numbers were ranked within blocks before analyses. Average cluster size was estimated by dividing the number of eggs in each plant by the number of clusters. Cluster size was analyzed using univariate GLM, removing the block effect. Similarly, the proportions of surviving nymphs and nymph biomass from the survival bioassay were analyzed using univariate GLMs, initially including plant biomass as a covariate. Data from the survival bioassay were ranked before analyses. Too few nymphs survived under some treatments to examine development rates or the sex of surviving adults. We estimated the combined effects of HPR and each insecticide ‘x’ as -((fitness on untreated IR64 − fitness on x-treated IR62)/fitness on untreated IR64). To estimate the effect of the insecticide alone, we removed the effect on HPR which we estimated as fitness on untreated IR62 − fitness on untreated IR64. Fitness was assessed from the oviposition bioassay as the numbers of eggs laid, and from the survival bioassay as nymph biomass. Where nymph mortality on insecticide-treated IR64 plants approached 100%, HPR effects were regarded as insignificant.
We also examined combined and insecticide effects from the screenhouse data based on densities of BPH and WBPH (see below). Effects were calculated using insecticide and HPR combinations for each replicated block (N = 5). Estimated effects were compared across treatments using univariate GLMs. Because three herbivores (BPH, WBPH, and GLH) occurred in our screenhouse plots, we used a split-plot multivariate GLM to analyze herbivore densities. Total planthopper and leafhopper biomass and density, and plant growth parameters (tiller number, biomass, yield, grain number, proportion of grain unfilled, and grain size) were analyzed using split-plot univariate GLMs. The covariate plant biomass was initially included in analyses of the effects on herbivores, but had no effect and was subsequently removed. Similarly, the covariate herbivore biomass was initially included in analyses of plant growth parameters, but had no effect and was subsequently removed. The combined effects of insecticide and HPR and the separate effects of each insecticide (calculated as indicated above) on BPH and WBPH were also analyzed using univariate GLM.
Post-hoc Tukey tests were applied to all significant treatment factors. Residuals were plotted following all parametric analyses and were found to be normal and homogenous.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of HPR and Insecticides on BPH Preferences
Treatments affected the number of clusters and eggs that were laid in IR62 plants (ranked clusters and eggs: F7,32 = 4.738, p < 0.001), and in IR64 plants (clusters: F7,32 = 6.229, p < 0.001; eggs: F7,32 = 7.757, p < 0.001) (Figure 1A,B). Fewer eggs were laid on IR64 plants treated with the pyrethroids (cypermethrin and deltamethrin), fipronil, and thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole compared to plants treated with buprofezin, carbofuran, and cartap hydrochloride (Figure 1B). Cypermethrin-treated IR62 plants also had fewer eggs than buprofezin-treated IR62 plants (Figure 1A). Although BPH females tended to lay fewer eggs in many of the insecticide-treated rice plants in the binary choice experiments, there were no statistically significant differences between the numbers of eggs laid in treated-IR62 (t ranges from −0.746 to 3.186, p > 0.05) or treated-IR64 (t ranges from −0.108 to 2.789, p > 0.05) compared to corresponding non-treated plants (Figure 1C,D).
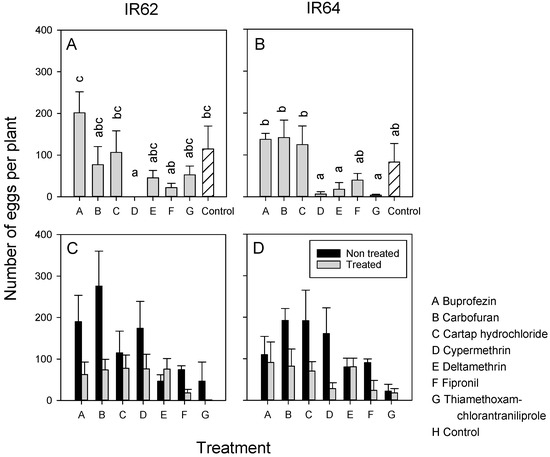
Figure 1.
Results from multichoice (A,B) and binary choice (C,D) bioassays conducted in the greenhouse. Bioassays were conducted separately for IR62 (A,C) and IR64 (B,D). Plants were treated with one of seven insecticides (A to G) as identified in the legend. Control plants were sprayed with water. Error bars are presented (N = 5 for (A,B), N = 3 for (C,D)). Lowercase letters (a–c) indicate homogenous treatment groups (Tukey p < 0.05).
3.2. Effects of HPR and Insecticides on BPH Fitness
More eggs were laid on IR64 plants than on IR62 plants, but BPH produced similar numbers of egg clusters on both plants. The lower numbers of eggs in IR62 were due to smaller clusters on the variety (Table 1). The numbers of eggs and clusters were affected by insecticide treatment with fewer eggs and clusters on cypermethrin-treated, fipronil-treated, and thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole-treated plants than on plants under the remaining treatments (Table 1). The treatment-effects were not affected by host variety (i.e., interactions were non-significant Table 1). Insecticide treatments had no effect on cluster size in the bioassay (Table 1). There was no significant effect of combined insecticide and HPR (F6,28 = 0.449, p = 0.840) on observed changes in egg laying during the bioassay, but the estimated insecticide effect was greater for thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole, fipronil, and cypermethrin than for buprofezin, cartap hydrochloride, and carbofuran (F6,28 = 3.140, p = 0.018: Figure 2A).

Table 1.
Results from greenhouse oviposition and survival tests with IR62 (resistant) and IR64 (susceptible), each treated with one of seven insecticides. Numbers are means ± SEM (N = 5).
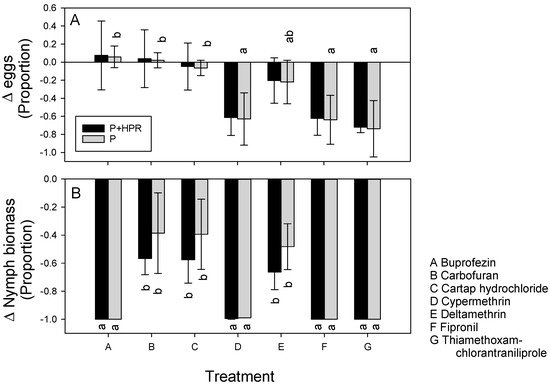
Figure 2.
Estimated combined effects of HPR and insecticide (P + HPR: black bars) and estimated pesticide effect alone (P: grey bars) on (A) egg laying, and (B) nymph biomass in greenhouse bioassays. Effects are indicated as proportional changes in fitness parameters compared to untreated IR64. Negative numbers indicate reduced fitness. Standard errors are indicated (N = 5). Lowercase letters (a,b) indicated homogenous treatment groups based on Tukey pairwise comparisons (p < 0.05) (see also Table 1).
Nymph survival and biomass were not affected by rice variety (Table 1). Buprofezin, fipronil, thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole, and cypermethrin reduced survival to 0% in the bioassay, and all insecticides except carbofuran resulted in lower survival and biomass than on untreated plants (Table 1). There were significant interactions because of higher nymph mortality and a resulting lower biomass on carbofuran-treated IR62 compared to untreated IR62 but lower mortality and a higher biomass of nymphs on carbofuran-treated IR64 than on untreated IR64 (Table 1). There was no significant effect of insecticide treatment (F6,28 = 0.946, p = 0.479) on observed changes in nymph biomass during the bioassay, but the estimated combined effects of pesticide and HPR was greater for thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole, fipronil, cypermethrin, and buprofezin than for cartap hydrochloride and carbofuran (F6,28 = 5.699, p = 0.001) (Figure 2B).
3.3. Effects of HPR and Insecticides on Planthoppers and Leafhoppers
Plants in the screenhouse were colonized by BPH, WBPH, and GLH. Densities for each species were similar on IR62 and IR64 (Wilk’s λ = 0.994, p = 0.952). There was a significant treatment effect on all three species (Wilk’s λ = 0.586, p = 0.049) because of high densities on deltamethrin-treated plants (Table 2). The numbers and biomass of all three species combined were also greater on deltamethrin-treated plants than on the remaining treatments (Table 2). Host resistance reduced GLH densities under the deltamethrin treatment, but had no apparent effect on densities under the other treatments (Table 2). There were significant combined effects of HPR and insecticide on the numbers of BPH (F6,24 = 2.686, p = 0.039) and WBPH (F6,24 = 2.482, p = 0.052); this was almost exclusively due to the resurgence effect of deltamethrin on the planthoppers (BPH: F6,24 = 2.686, p = 0.039; WBPH: F6,24 = 2.482, p = 0.052) (Figure 3).

Table 2.
Densities and biomass of planthoppers and leafhoppers on IR62 (resistant) and IR64 (susceptible) rice plants under seven insecticide treatments and on control, untreated plants. Numbers are means ± SEM (N = 5).
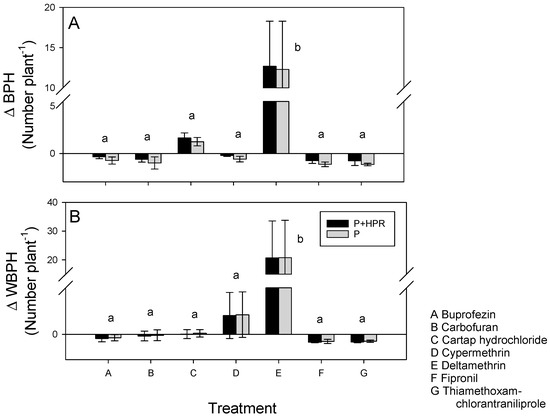
Figure 3.
Estimated combined effects of HPR and insecticide (P + HPR: black bars) and estimated pesticide effect alone (P: grey bars) on (A) BPH densities, and (B) WBPH densities on IR62 in the screenhouse. Effects are indicated as proportional changes in planthopper densities compared to untreated IR64. Negative numbers indicate reduced densities, positive numbers are increased densities. Standard errors are indicated (N = 5). Lowercase letters (a,b) indicate homogenous treatment groups based on Tukey pairwise comparisons (p < 0.05) (see also Table 2).
3.4. Direct and Indirect Effects of Insecticides on Rice Development
IR62 plants had more tillers and attained a greater biomass than IR64 plants in the screenhouse (Table 3). IR62 grain matured faster and plants were harvested earlier than the IR64 plants (Table 3). IR62 plants also produced more grain (number of grain), and had higher yields than IR64, but had smaller grain and more unfilled grain than IR64 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Rice growth parameters for IR62 (resistant) and IR64 (susceptible) under seven insecticide treatments and for control, non-treated plants in a screenhouse environment. Numbers are means ± SEM.
Insecticides affected plant growth directly and indirectly (through increased planthopper densities). Plants treated with cypermethrin and deltamethrin had fewer tillers, had a lower biomass, and under cypermethrin had lower yields than untreated plants (Table 3). Plants treated with fipronil also had reduced yields, due to lower grain numbers compared to untreated plants (Table 3). Although yields were not affected, treatment with cartap hydrochloride increased the proportion of unfilled grain compared to untreated plants of both varieties. Cartap hydrochloride and cypermethrin also caused a delay in grain maturation on IR62 and IR64, respectively, relative to thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole treated plants (Table 3).
There were several significant interactions: tiller numbers on both plants were similar under buprofezin, fipronil, and thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole treatments, but were otherwise higher on IR62 (Table 3); biomass was lower on IR64 under carbofuran and cypermethrin treatments but was otherwise similar on both plants (Table 3); buprofezin delayed grain maturation on IR62, but maturation was otherwise faster on IR62 compared to IR64 (Table 3); yields under buprofezin, fipronil, and thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole were similar for IR62 and IR64, but otherwise yields were higher on IR62 (Table 3); grain numbers were higher on IR62 than IR64 except under fipronil treatments (Table 3); the proportions of grain unfilled were higher on IR62, but were similar between varieties under the fipronil treatment (Table 3); 1000-grain weight was higher in IR64, but similar on both varieties when treated with cartap hydrochloride (Table 3).
4. Discussion
Our results, using a highly resistant rice variety and some commonly used insecticides, indicate a range of possible effects on planthoppers and rice plants by combining these two management practices.
4.1. Synergies
The most predictable effect of combining HPR and insecticides is a synergy in reducing BPH numbers. This is suggested because planthoppers are weakened by the host’s resistance and should, therefore, be more susceptible to the toxic effects of insecticides [40]. Using spray towers over potted plants, Heinrichs et al. (1984) [40] examined the combined effects of a range of insecticides (that included carbofuran) with resistance by comparing BPH mortality on six resistant and two susceptible rice varieties. Their results indicated that mortality was greatest when insecticides were applied to BPH on resistant varieties. The effects were similar when the study was repeated with WBPH for three insecticides (including carbofuran) on the resistant variety N22 (Wbph1 gene) [40]. In our study, host resistance reduced egg laying and nymph biomass on non-treated IR62 compared to non-treated IR64. Egg laying was also reduced on plants treated with cypermethrin, fipronil, or thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole (Table 1). Based on the results of our choice and no-choice oviposition bioassays, cypermethrin acted mainly as a deterrent of gravid females, whereas fipronil and thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole directly reduced egg laying. Despite similar BPH responses to both the insecticides and resistant host, there were no apparent synergies between any of these insecticides and resistance in reducing egg numbers in the oviposition bioassay. In contrast to these three insecticides, our bioassays indicated that buprofezin, carbofuran, and cartap hydrochloride can lead to higher numbers of eggs on treated plants compared to untreated plants (Table 1). These effects were not statistically significant and may be exaggerated because bioassays were conducted over relatively short time scales. For example, planthoppers will sometimes respond to stresses, such as high temperatures, by increasing oviposition rates [71,72]. Furthermore, the stimulation of egg-laying by these chemicals was not apparent in our screenhouse experiment (Table 2). Nevertheless, our results do indicate that host resistance reduced the magnitude of any stimulatory effect on oviposition: egg numbers on buprofezin-treated, carbofuran-treated, and cartap hydrochloride-treated IR64 in the no-choice bioassay were twice as high as on the corresponding IR62 plants. In cases such as these, the resistance of IR62 functions as a buffer, or ‘insurance’, against possible undesired pesticide effects [12,38].
Although buprofezin appeared to stimulate oviposition, the growth hormone had a strong impact on nymph development, leading to zero survival of exposed nymphs in our greenhouse bioassay. Cypermethrin, fipronil, and thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole also reduced nymph survival to zero in the greenhouse bioassay (Table 1). Where insecticides have such high efficiencies, any fitness losses to BPH due to host resistance then become redundant. Unlike buprofezin, carbofuran also stimulated nymph biomass on IR64 in the survival bioassay (Table 1); however, nymph biomass was lower on carbofuran-treated IR62 than on non-treated IR62, indicating that the host’s resistance buffered against undesired stimulatory effects on BPH, and may have functioned synergistically to augment mortality and slow BPH growth. Such buffering allows insecticides to be used against other pests without inducing secondary outbreaks of non-target pests. In our screenhouse experiment, herbivore densities were generally low on both IR62 and IR64 for most treatments (except deltamethrin) and were below threshold densities for insecticide applications—which are normally about 25–50 planthoppers per hill [13,73]. Under such low densities, it was not possible to observe the impact of host resistance on planthopper population build-up. There was some indication of higher densities on cartap hydrochloride-treated IR62 in the screenhouse, which may be related to the stimulatory effects of the product on egg laying, and the low mortality of nymphs on cartap hydrochloride-treated plants as observed in the greenhouse bioassays (Table 1). Field studies from the Philippines have indicated that IR62 effectively reduces BPH densities during wet and dry seasons [4]. However, farmers are rarely aware of which anti-herbivore resistance their rice varieties possess, and frequently apply pesticides regardless of resistance, thereby reducing their farm profits [38,41]. For example, Joshi et al. (1992) [41] reported widespread outbreaks of BPH on IR62 in Mindanao, Philippines, after applications of decamethrin (a pyrethroid) to the resistant variety. Where such resurgence-causing insecticides are applied, resistance seems to be often incapable of reducing the stimulatory effects of the insecticide and it loses its capacity to buffer against outbreaks.
4.2. Antagonisms
Several insecticides are associated with increasing densities of planthoppers, and with resurgence outbreaks in farmers’ fields [27,29,30,41,49,61,74]. Indeed, patches of ‘hopperburn’ (i.e., dead rice plants resulting from planthopper damage) are often an indicator of high insecticide use in tropical Asia [2,14]. In many cases, these resurgence-causing insecticides were once effective in reducing planthopper densities, but over time, populations developed resistance against the products. The resulting low toxicity can then have a stimulatory effect on planthopper feeding and development [21,23,24,27,43]. This may be through hormesis, which is a direct response by the planthopper to low-level exposure to the toxic chemical, or it may result from physiological changes to the rice plants that ultimately benefit the planthopper [18,49]. In our screenhouse study, we induced a resurgence outbreak of BPH, WBPH, and, to a lesser extent, GLH on deltamethrin-treated rice plants (Table 2). The combined densities of all three herbivores increased almost 10 times on the treated plants. Furthermore, herbivore biomass increased by between four and six times. Although the resurgence effects of deltamethrin have been documented in previous studies [20,29,30,31,39,75], we could not predict from our greenhouse studies that any such outbreak would occur. Egg laying was unaffected by deltamethrin in our choice and no-choice experiments and nymph survival and development both declined on deltamethrin-treated rice in the survival bioassay (Table 1). The massive increases in planthopper densities on deltamethrin-treated plants in our study seem to result from a heightened attraction of adult BPH and WBPH to the plants [49], particularly since numbers were so low on all other plants, including both treated and non-treated plants. However, once on the plants, planthoppers also apparently had enhanced fitness. Cuong et al. (1997) [31] observed higher population densities of BPH on deltamethrin-treated rice in Vietnam, albeit with lower-level increases on resistant varieties. Furthermore, in a greenhouse study, Azzam et al. (2009) [20] found that deltamethrin reduced pre-oviposition times, increased the duration of oviposition, and increased egg hatchability and female longevity. Nanthakumar et al. (2012) [43] further showed that deltamethrin increased BPH feeding efficiency on resistant and susceptible rice plants, as determined through honeydew production and population size. In studies with WBPH, Salim and Heinrichs (1987) [36] showed deltamethrin to increase settling (antixenosis), feeding, and population growth; and Suri and Singh (2011) [28] showed deltamethrin to increase WBPH reproductive rates and nymph survival. In our study, the observed resurgence of planthoppers was similar on both varieties, indicating, as was previously noted by Joshi et al. (1992) [41], that resurgence-causing pyrethroids are antagonistic to resistance in IR62.
Though not statistically significant, cartap hydrochloride also increased BPH numbers on IR62, but not on IR64, in our screenhouse study. This indicates that the product may also be antagonistic to the host’s resistance mechanisms. The stronger effect on IR62 may be related to the differences between IR62 biomass, growth rates, and anatomy (i.e., a larger plant with higher tillering), compared to IR64 (Table 3). Once resistance is no longer effective because of chemically-enhanced BPH fitness, these plant characteristics, which have been related to observed preferences in BPH and other sap-sucking insects [3,49], could further accelerate the build-up of BPH populations on cartap hydrochloride-treated plants. To further test this idea, experiments could be conducted using near-isogenic rice lines that differ mainly in the presence or absence of tagged resistance genes [76]. Such tests would avoid confounding differences in plant anatomy between test varieties. IR62 resistance to BPH has been well studied [4]. The variety is also resistant to WBPH at older plant stages [54]. Therefore, in our study, deltamethrin was also antagonistic to this WBPH-resistance (Table 2). However, BPH feeding also facilitates WBPH population growth [54,77] and there may have been added indirect, plant-mediated effects [77] that augmented WBPH populations on both varieties in our experiment. IR62 is also resistant to GLH [45]. In our experiments, GLH densities also increased on deltamethrin-treated plants, but the effect was only apparent on IR64. Therefore, GLH-resistance in IR62 apparently buffered against deltamethrin-associated increases in GLH on the variety, as was also noted from field studies in Vietnam [31]. Deltamethrin is currently not recommended for use in rice [20,28,78]; however, the product continues to be marketed in rice-dominated regions throughout Asia [13,14,79]. Although cypermethrin has been associated with BPH outbreaks and was consequently removed for use on rice in Thailand and Vietnam [62], we did not observe cypermethrin-induced resurgence in our screenhouse experiment. Nevertheless, cypermethrin has been associated with resurgence of BPH in South Asia [61], and we have noted stimulatory effects of cypermethrin on other rice herbivores in the Philippines (Horgan, unpublished data).
4.3. Phytotoxicity
Phytotoxicity is relatively common following applications of insecticides [18,28,50]. Phytotoxic effects may change a plant’s physiology, without consequences for crop yields. However, such changes to plant physiology could have indirect effects on herbivores. For example, deltamethrin, methyl parathion, and quinalphos produce increases in total sugars and reducing sugars, as well as increasing the protein contents of the rice leaf sheath and leaf blade [28]. Several insecticides also reduce plant phenols in rice—which increases the rice plant’s susceptibility to BPH and other insects [27]. In our screenhouse experiment, we noted several changes to rice anatomy and yields. Importantly, we noted that cypermethrin and fipronil both reduced rice yields (Table 3). This was not due to indirect herbivore effects, because planthopper and leafhopper densities were consistently low on rice treated with these insecticides. The effects therefore probably resulted from direct phytotoxic effects on the plants. Furthermore, these effects were most pronounced on treated IR62 plants. Other minor effects on grain production included increased proportions of unfilled grain in cartap hydrochloride-treated plants, and delays in grain maturation on cartap hydrochloride-treated and cypermethrin-treated plants (Table 3). Despite the high densities of BPH and WBPH on deltamethrin-treated plants, yields were not significantly lower than in control, non-treated plants. Both IR62 and IR64 have been noted for their high tolerance to BPH damage, particularly under high nitrogenous fertilizer applications [3,4,56] as used in our screenhouse experiment. Therefore, where plants have high tolerance to damage, applying insecticides could also result in profitability losses on rice farms, and in the case of insecticide-induced pest population increases, tolerance might buffer against subsequent yield losses. There are few reports of the phytotoxicity of insecticides to rice: carbofuran is toxic to rice at high concentrations, but may also enhance the growth of rice plants through interactions with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the rhizosphere [80]. Future studies could more carefully assess field-grown plants for possible phytotoxic effects, particularly if insecticides have the potential to directly reduce yields.
4.4. Management implications
Global trends suggest that resistance in rice has failed to reduce insecticide applications [2]. This may be due to aggressive marketing by agrochemical companies and strategies to increase pesticide sales, such as promoting prophylactic applications [16]. Because we selected our test insecticides (except the pyrethroids) without any a priori criteria, our results suggest that many currently used insecticides probably have some negative effects on yield, either directly through phytotoxic effects, or indirectly by inducing pest resurgence. Furthermore, our results indicate that even where pests reach high densities, as on deltamethrin-treated plants in the screenhouse, these densities do not necessarily lead to significant yield reductions.
Among the products we used, buprofezin, although it had little effect on oviposition, was effective in reducing nymph survival. Furthermore, there were only minor apparent phytotoxic effects on the rice plants. Buprofezin has a low toxicity to natural enemies in rice fields [58] and is therefore the most compatible of the insecticides with strategies to increase rice field biodiversity and restore ecosystem services [32,33,34,81,82]. Thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole was also effective in reducing both oviposition and nymph survival and had no apparent toxic effects on rice plants. However, thiamethoxam-chlorantraniliprole and other neonicotinoids, although moderately toxic, can have severe effects on beneficial hymenopteran parasitoids [83], although they have apparently low toxicity to predatory mirid bugs [84]. The remaining insecticides either directly reduced yields, or were associated with higher BPH biomass or densities in our experiments.
We noted few synergies with HPR, although nymph biomass and/or survival was lower in cartap hydrochloride and carbofuran-treated IR62 plants compared to corresponding IR64 plants. Meanwhile, cartap hydrochloride and deltamethrin were antagonistic to resistance in IR62 in the screenhouse experiment. Among the strongest effects of HPR was to act as a buffer against GLH population build-up on deltamethrin-treated IR62, and against carbofuran-induced increases in BPH nymph biomass in the survival bioassay. Therefore, HPR may play a role in reducing the possibilities of secondary outbreaks of BPH and other insects. The combined use of HPR and targeted insecticides against BPH creates redundancy in the rice field and counters measures to manage insecticide resistance and virulence by unnecessarily exposing plant protection products to evolving pest populations. HPR (and host plant tolerance) can be effective against target pests as revealed in previous studies [4] and could be incorporated into other pest management practices, particularly agroecological practices such as ecological engineering, with which it is highly compatible [81,85,86].
5. Conclusions
Based on our results and the results of previous studies, HPR and the application of chemical insecticides against BPH rarely produce synergistic effects. Antagonistic effects, where chemicals caused increases in BPH fitness or populations on resistant rice, were more apparent in our study. In particular, deltamethrin caused an outbreak of BPH in our screenhouse study. Nevertheless, HPR can buffer against the insecticide-induced enhancement of herbivore fitness (hormesis) and potentially reduce possibilities of secondary outbreaks, as was suggested from results with cartap hydrochloride in our study. Based on our results, we suggest that carbofuran, cartap hydrochloride, cypermethrin, deltamethrin, and fipronil should be avoided in rice, particularly in the Philippines (where this research was conducted), due to their resurgence-causing potential or because of direct reductions to rice yields.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.G.H.; methodology, F.G.H., A.P.-C. and M.L.P.A.; formal analysis, F.G.H. and A.P.-C.; investigation, F.G.H., A.P.-C. and M.L.P.A.; data curation, F.G.H., A.P.-C. and M.L.P.A.; writing—original draft preparation, F.G.H. and A.P.-C.; writing—review and editing, F.G.H., A.P.-C. and M.L.P.A.; visualization, F.G.H.; supervision, F.G.H. and M.L.P.A.; project administration, F.G.H.; funding acquisition, F.G.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia [CSISA]: OPP52303) and the Global Rice Science Platform (GRiSP) under the directorship of Achim Dobermann. A.P.-C. was partially funded by The Spanish Government through Becas Faro International.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Fame Ramal, Carmencita Bernal, Alberto Naredo, Reyeul Quintana, Vincent Virtudes, Marol Recide, Jenyrose Geronda, and Ellen Genil for assistance during this study. The contributions of Rodante Abas (sadly deceased) during three decades of entomological research at IRRI are gratefully acknowledged. Rice lines were supplied through the Genebank of IRRI.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bottrell, D.G.; Schoenly, K.G. Resurrecting the ghost of green revolutions past: The brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G. Integrated pest management for sustainable rice cultivation: A holistic approach. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Rice: Cultivation, Pest and Disease Management; Sasaki, T., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Scientific: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 309–342. [Google Scholar]
- Horgan, F.G.; de Freitas, T.F.S.; Crisol-Martínez, E.; Mundaca, E.A.; Bernal, C.C. Nitrogenous fertilizer reduces resistance but enhances tolerance to the brown planthopper in fast-growing, moderately resistant rice. Insects 2021, 12, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, F.G.; Peñalver Cruz, A.; Bernal, C.C.; Ramal, A.F.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Wilby, A. Resistance and tolerance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), in rice infested at different growth stages across a gradient of nitrogen applications. Field Crops Res. 2018, 217, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereward, J.P.; Cai, X.; Matias, A.M.A.; Walter, G.H.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. Migration dynamics of an important rice pest: The brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) across Asia—Insights from population genomics. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 2449–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Guo, J.; Fu, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, K. Seasonal migration pattern of Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) over the Bohai Sea in northern China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Lu, M.-H.; Wan, G.-J.; Chen, F.-J.; Liu, W.-C.; Zhai, B.-P.; Hu, G. Brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens was concentrated at the rear of the typhoon Soudelor in eastern China in August 2015. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, D.; Kohli, A.; Horgan, F.G. Rice resistance to planthoppers and leafhoppers. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2013, 32, 162–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Yoshida, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Myint, K.K.M.; Yasui, H.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Matsumura, M. Long-term virulence monitoring of differential cultivars in Japan’s immigrant populations of Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in 2001–2009. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2021, 56, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, K.K.M.; Yasui, H.; Takagi, M.; Matsumura, M. Virulence of long-term laboratory populations of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stal), and whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Homoptera: Delphacidae), on rice differential varieties. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2009, 44, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Ramal, A.F.; Bentur, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Bhanu, K.V.; Sarao, P.S.; Iswanto, E.H.; Van Chien, H.; Phyu, M.H.; Bernal, C.C.; et al. Virulence of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) populations from South and South East Asia against resistant rice varieties. Crop Prot. 2015, 78, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G. Integrating gene deployment and crop management for improved rice resistance to Asian planthoppers. Crop Prot. 2018, 110, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.B.M.A.; Islam, K.S.; Jahan, M.; Ara, A.; Afrin, S. Farmer’s perception about resurgence of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata Lugens (Stål) in Bangladesh. Bangladesh Rice J. 2020, 23, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triwidodo, H. Brown planthoppers infestations and insecticides use pattern in Java, Indonesia. AGRIVITA J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 42, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres, A.; Wyckhuys, K.A.; Kiss, J.; Tóth, F.; Burgio, G.; Pons, X.; Avilla, C.; Vidal, S.; Razinger, J.; Bazok, R.; et al. An update of the Worldwide Integrated Assessment (WIA) on systemic pesticides. Part 4: Alternatives in major cropping systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29867–29899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, L.; van der Werf, W.; Tittonell, P.; Wyckhuys, K.A.; Bianchi, F.J. Neonicotinoids in global agriculture: Evidence for a new pesticide treadmill? Ecol. Soc. 2020, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-C.; Xu, J.-X.; Yuan, S.-Z.; Liu, J.-L.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Xu, J.-F. Pesticide-induced susceptibility of rice to brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 100, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-C.; Qiu, H.-M.; Yang, G.-Q.; Liu, J.-L.; Liu, G.-J.; Wilkens, R.M. Effective duration of pesticide-induced susceptibility of rice to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål, Homoptera: Delphacidae), and physiological and biochemical changes in rice plants following pesticide application. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2004, 50, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.-H.; Wu, J.-C.; Yu, Y.-S.; Liu, J.-L.; Yue, J.-F.; Wang, M.Y. Selective insecticide-induced stimulation on fecundity and biochemical changes in Tryporyza incertulas (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, S.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.-C.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.-P.; Yang, G.-Q.; Guo, Y.-R. Comparisons of stimulatory effects of a series of concentrations of four insecticides on reproduction in the rice brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Int. J. Pest Manag. 2009, 55, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.-Q.; Hu, J.-H.; Wu, J.-C.; Yang, G.-Q.; Gu, H. Insecticide-induced changes in protein, RNA, and DNA contents in ovary and fat body of female Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, R. Effect of fipronil on the reproduction, feeding, and relative fitness of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2009, 44, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.-Q.; Wang, L.-P.; Zhao, K.-F.; Wu, J.-C.; Huang, L.-J. Mating pair combinations of insecticide-treated male and female Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) planthoppers influence protein content in the male accessory glands (MAGs) and vitellin content in both fat bodies and ovaries of adult females. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.-Q.; Wu, J.-C.; Zhao, K.-F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.-Q. Induction of Nlvg and suppression of Nljhe gene expression in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) adult females and males exposed to two insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-H.; Wu, J.-C.; Yin, J.-L.; Gu, H.-N. Physiology of insecticide-induced stimulation of reproduction in the rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)): Dynamics of protein in fat body and ovary. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2010, 56, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-P.; Shen, J.; Ge, L.-Q.; Wu, J.-C.; Yang, G.-Q.; Jahn, G.C. Insecticide-induced increase in the protein content of male accessory glands and its effect on the fecundity of females in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ge, L.; Liu, F.; Song, Q.; Stanley, D. Pesticide-induced planthopper population resurgence in rice cropping systems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, K.S.; Singh, G. Insecticide-induced resurgence of the whitebacked planthopper Sogatella furcifera (Horvath) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) on rice varieties with different levels of resistance. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabellar, L.T.; Heinrichs, E.A. Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice brown planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabellar, L.T.; Heinrichs, E.A. Relative toxicity of insecticides to rice planthoppers and leafhoppers and their predators. Crop Prot. 1986, 5, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, N.L.; Ben, P.T.; Phuong, L.T.; Chau, L.M.; Cohen, M.B. Effect of host plant resistance and insecticide on brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) and predator population development in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Crop Prot. 1997, 16, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preetha, G.; Stanley, J.; Suresh, S.; Samiyappan, R. Risk assessment of insecticides used in rice on mirid bug, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter, the important predator of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stal.). Chemosphere 2010, 80, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Endo, S.; Kazano, H. Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice planthoppers: Spiders, the mirid bug and the dryinid wasp. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2000, 35, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Lu, W.; Liu, F. Sublethal effects of four synthetic insecticides on the generalist predator Cyrtorhinus lividipennis. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settle, W.H.; Ariawan, H.; Astuti, E.T.; Cahyana, W.; Hakim, A.L.; Hindayana, D.; Lestari, A.S. Managing tropical rice pests through conservation of generalist natural enemies and alternative prey. Ecology 1996, 77, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, M.; Heinrichs, E.A. Insecticide-induced changes in the levels of resistance of rice cultivars to the whitebacked planthopper Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Crop Prot. 1987, 6, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.-L.; Xu, H.-W.; Wu, J.-C.; Hu, J.-H.; Yang, G.-Q. Cultivar and insecticide applications affect the physiological development of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Environ. Entomol. 2014, 37, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheng, C.; Chang, W. Studies on varietal resistance to the brown planthopper in Taiwan. In Brown Planthopper: Threat to Rice Production in Asia; International Rice Research Institute, Ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 1979; pp. 251–271. [Google Scholar]
- Reissig, W.H.; Heinrichs, E.A.; Valencia, S.L. Insecticide-induced resurgence of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, on rice varieties with different levels of resistance. Environ. Entomol. 1982, 11, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs, E.A.; Fabellar, L.T.; Basilio, R.P.; Wen, T.-C.; Medrano, F. Susceptibility of rice planthoppers Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae) to insecticides as influenced by level of resistance in the host plant. Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Shepard, B.; Kenmore, P.; Lydia, R. Insecticide-induced resurgence of brown planthopper (BPH) on IR62. Int. Rice Res. Newsl. 1992, 17, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.-R.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, M.-X.; Zhang, X.-X. Complex influence of rice variety, fertilization timing, and insecticide on population dynamics of Sogatella furcifera (Horvath), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae) and their natural enemies in rice in Hangzhou, China. J. Pest Sci. 2004, 77, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthakumar, M.; Jhansi Lakshmi, V.; Shashi Bhushan, V.; Balachandran, S.M.; Mohan, M. Decrease of rice plant resistance and induction of hormesis and carboxylesterase titre in brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) by xenobiotics. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 102, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.-W.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Ye, G.-Y.; Cheng, J.-A. Studies on cultivar-induced changes in insecticide susceptibility and its related enzyme activities of the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Horvath)(Homopter: Delphacidae). Insect Sci. 2002, 9, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Horgan, F.G.; Srinivasan, T.S.; Bentur, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Bhanu, K.V.; Sarao, P.S.; Van Chien, H.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Bernal, C.C.; Ramal, A.F.; et al. Geographic and research center origins of rice resistance to Asian planthoppers and leafhoppers: Implications for rice breeding and gene deployment. Agronomy 2017, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairin, J.; Phengrat, K.; Teangdeerith, S.; Vanavichit, A.; Toojinda, T. Mapping of a broad-spectrum brown planthopper resistance gene, Bph3, on rice chromosome 6. Mol. Breed. 2007, 19, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Gao, F.; Wu, X.; Lu, X.; Zeng, L.; Lv, J.; Su, X.; Luo, H.; Ren, G. Bph32, a novel gene encoding an unknown SCR domain-containing protein, confers resistance against the brown planthopper in rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.D.; Zheng, S.-H.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Matsumura, M.; Yasui, H.; Fujita, D. Substitution mapping and characterization of brown planthopper resistance genes from indica rice variety, ‘PTB33′ (Oryza sativa L.). Breed. Sci. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, S.; Heinrichs, E.A. Factors affecting insecticide-induced resurgence of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens on Rice. Environ. Entomol. 1980, 9, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.T.; Kröger, R. Effect of three insecticides and two herbicides on rice (Oryza sativa) seedling germination and growth. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, I.; Han, M.; Jang, B. Effect of insecticide and fungicide on phytotoxicity of herbicide in rice. Korean J. Weed Sci. 1986, 6, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Horgan, F.G.; Garcia, C.P.F.; Haverkort, F.; de Jong, P.W.; Ferrater, J.B. Changes in insecticide resistance and host range performance of planthoppers artificially selected to feed on resistant rice. Crop Prot. 2020, 127, 104963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khush, G.S.; Virk, P.S. IR Varieties and Their Impact; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, T.S.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Bernal, C.C.; Ramal, A.F.; Subbarayalu, M.K.; Horgan, F.G. Interactions between nymphs of Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) on resistant and susceptible rice varieties. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2016, 51, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver Cruz, A.; Arida, A.; Heong, K.L.; Horgan, F.G. Aspects of brown planthopper adaptation to resistant rice varieties with the Bph3 gene. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2011, 141, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.N.; Cohen, M.B. Detection and analysis of QTLs for resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, in a doubled-haploid rice population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackill, D.J.; Khush, G.S. IR64: A high-quality and high-yielding mega variety. Rice 2018, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrichs, E.A.; Basilio, R.P.; Valencia, S.L. Buprofezin, a selective insecticide for the management of rice planthoppers (Homoptera: Delphacidae) and leafhoppers (Homoptera: Cicadellidae). Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, M.K.; Anjaneyulu, A. Use of cypermethrin, a synthetic pyrethroid, in the control of rice tungro virus disease and its vector. Trop. Pest Manag. 1984, 30, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorley, W. Spider mortality implicated in insecticide-induced resurgence of whitebacked planthopper (WBPH) and brown planthopper (BPH) in Kedah, Malaysia. Int. Rice Res. Newsl. 1987, 10, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, A.; Islam, K.S.; Jahan, M.; Ara, A.; Khan, M.A.I. Factor influencing the resurgence of brown planthopper in Bangladesh. SAARC J. Agric. 2020, 18, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalada, M.M.; Luecha, M.; Heong, K.L. Social impacts of planthopper outbreaks: Case study from Thailand. In Rice Planthoppers: Ecology, Management, Socio Economics and Policy; Heong, K.L., Cheng, J., Escalada, M.M., Eds.; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2015; pp. 209–226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.P.; He, H.M.; Yu, J.Z.; Hu, X.Q.; Zhu, Y.H.; Wang, Q. Residues of carbosulfan and its metabolites carbofuran and 3-hydroxy carbofuran in rice field ecosystem in China. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2016, 51, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, S.; Barman, M.; Samanta, N.R.A. Bio-efficacy trials of carbofuran 3% CG against insect pests of rice. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Donley, N. The USA lags behind other agricultural nations in banning harmful pesticides. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, A.; Gore, J.; Musser, F.; Cook, D.; Catchot, A.; Walker, T.; Dobbins, C. Efficacy of selected insecticides applied to hybrid rice seed. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 109, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, B. Persistence and metabolism of Fipronil in rice (Oryza sativa Linnaeus) Field. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 90, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, S.; Prajapati, C.; Singh, D.; Singh, R. Field evaluation of insecticides and bio-pesticides against rice leaf folder, Cnaphalocrocis Medinalis (Guenee). Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2011, 19, 324–326. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Satoh, M.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Otuka, A.; Watanabe, T.; Van Thanh, D. Species-specific insecticide resistance to imidacloprid and fipronil in the rice planthoppers Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera in East and South-east Asia. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, J.; Shao, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z. Fipronil resistance in the whitebacked planthopper (Sogatella furcifera): Possible resistance mechanisms and cross-resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Arida, A.; Ardestani, G.; Almazan, M.L.P. Temperature-dependent oviposition and nymph performance reveal distinct thermal niches of coexisting planthoppers with similar thresholds for development. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, F.G.; Arida, A.; Ardestani, G.; Almazan, M.L.P. Intraspecific competition counters the effects of elevated and optimal temperature on phloem-feeding insects in tropical and temperate rice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogawa, K.; Cheng, C. Economic thresholds, nature of damage, and losses caused by the brown planthopper. In Brown Planthopper: Threat to Rice Production in Asia; International Rice Research Institute, Ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 1979; pp. 125–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Atlihan, R.; Chi, H.; Chu, D. Demographic analysis of progeny fitness and timing of resurgence of Laodelphax striatellus after insecticides exposure. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.-F.; Shi, Z.-P.; Wu, J.-C. Insecticide-induced enhancement of flight capacity of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.D.; Verdeprado, H.; Zita, D.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Matsumura, M.; Virk, P.S.; Brar, D.S.; Horgan, F.G.; Yasui, H.; Fujita, D. The development and characterization of near-isogenic and pyramided lines carrying resistance genes to brown planthopper with the genetic background of japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2019, 8, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Arida, A.; Ardestani, G.; Almazan, M.L.P. Positive and negative interspecific interactions between coexisting rice planthoppers neutralise the effects of elevated temperatures. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Long, G.-Y.; Jin, D.-C. Effects of sublethal concentrations of deltamethrin on fitness of white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Horváth). Int. J. Pest Manag. 2019, 65, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Kudavidanage, E.P. Use and avoidance of pesticides as responses by farmers to change impacts in rice ecosystems of southern Sri Lanka. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, P.K.; Adhya, T.K.; Rajaranamohan Rao, V. Influence of repeated applications of carbofuran on nitrogenase activity and nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with rhizosphere of tropical rice. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Crisol Martínez, E.; Stuart, A.M.; Bernal, C.C.; de Cima Martín, E.; Almazan, M.L.P.; Ramal, A.F. Effects of vegetation strips, fertilizer levels and varietal resistance on the integrated management of arthropod biodiversity in a tropical rice ecosystem. Insects 2019, 10, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widiarta, I.N.; Matsumura, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakasuji, F. Effects of sublethal doses of imidacloprid on the fecundity of green leafhoppers, Nephotettix spp. (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and their natural enemies. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2001, 36, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Preetha, G.; Stanley, J.; Suresh, S.; Kuttalam, S.; Samiyappan, R. Toxicity of selected insecticides to Trichogramma chilonis: Assessing their safety in the rice ecosystem. Phytoparasitica 2009, 37, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.J.; Krishnaiah, N.; Pasalu, I.; Lingaiah, T.; Krishnaiah, K. Safety of thiamethoxam to Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter (Hemiptera: Miridae), a predator of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stal) in rice. J. Biol. Control 2001, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Horgan, F.G.; Ramal, A.F.; Villegas, J.M.; Jamoralin, A.; Bernal, C.C.; Perez, M.O.; Pasang, J.M.; Naredo, A.I.; Almazan, M.L.P. Effects of bund crops and insecticide treatments on arthropod diversity and herbivore regulation in tropical rice fields. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, L.L.; Heinrichs, E.A.; Machado, V.; Andreis, T.F.; Pandolfo, M.; de Salles, S.M.; de Oliviera, J.V.; Fiuza, L.M. Impact of lambdacyhalothrin on arthropod natural enemy populations in irrigated rice fields in southern Brazil. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2013, 33, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).