Port Efficiency Based on the Super-Efficiency EBM-DEA-SDM Model: Empirical Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Port Efficiency
2.2. Regression Methodology
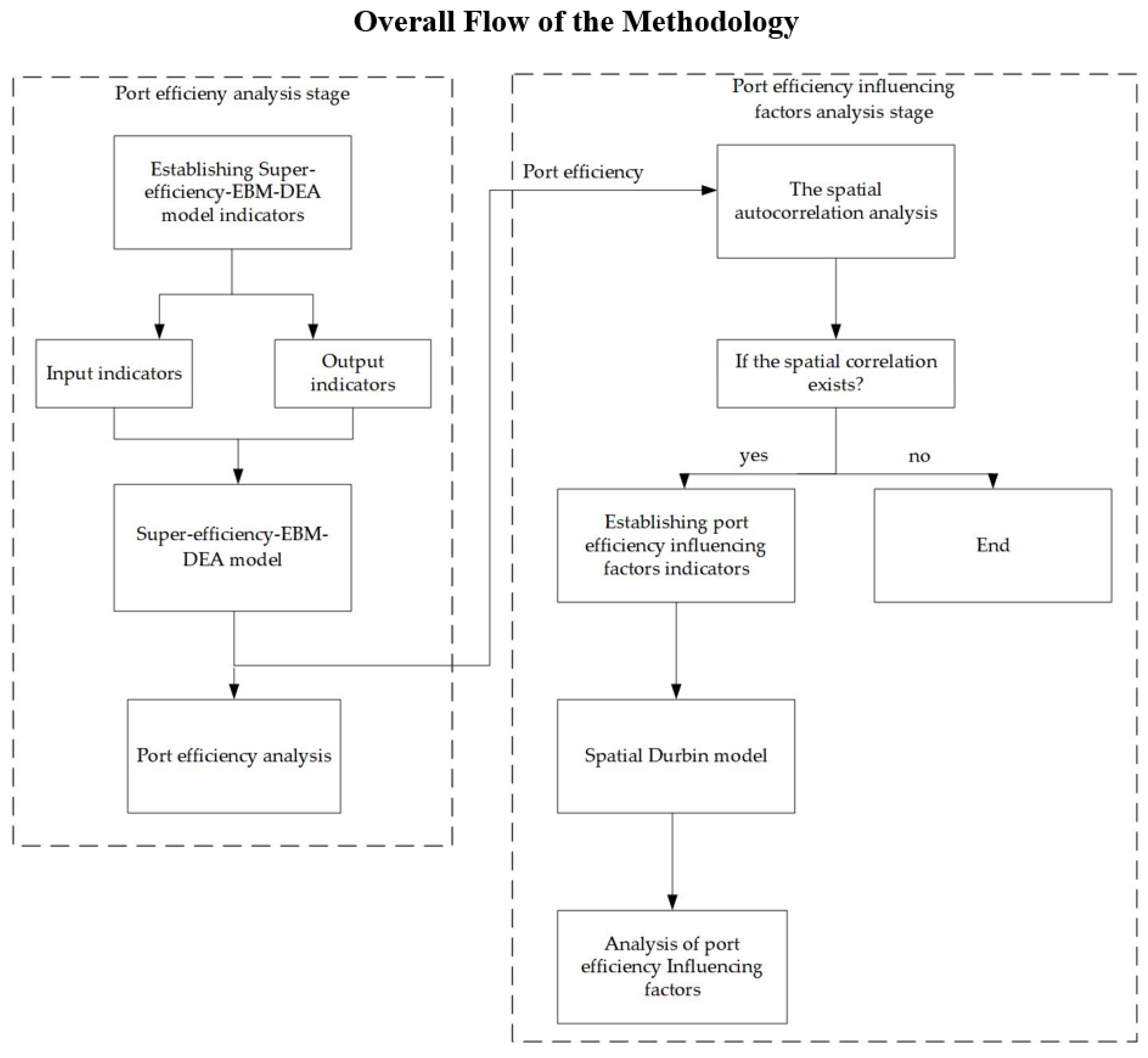
3. Methodology
3.1. The Super-Efficiency EBM-DEA Model with Undesirable Outputs
3.1.1. Non-Oriented EBM-DEA Model
3.1.2. EBM-DEA Model with Undesirable Outputs
3.1.3. The Super-Efficiency EBM-DEA Model
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
3.3. Spatial Durbin Model
3.4. Research Area and Indicator Selection
4. Analysis of the Characteristics of Port Efficiency
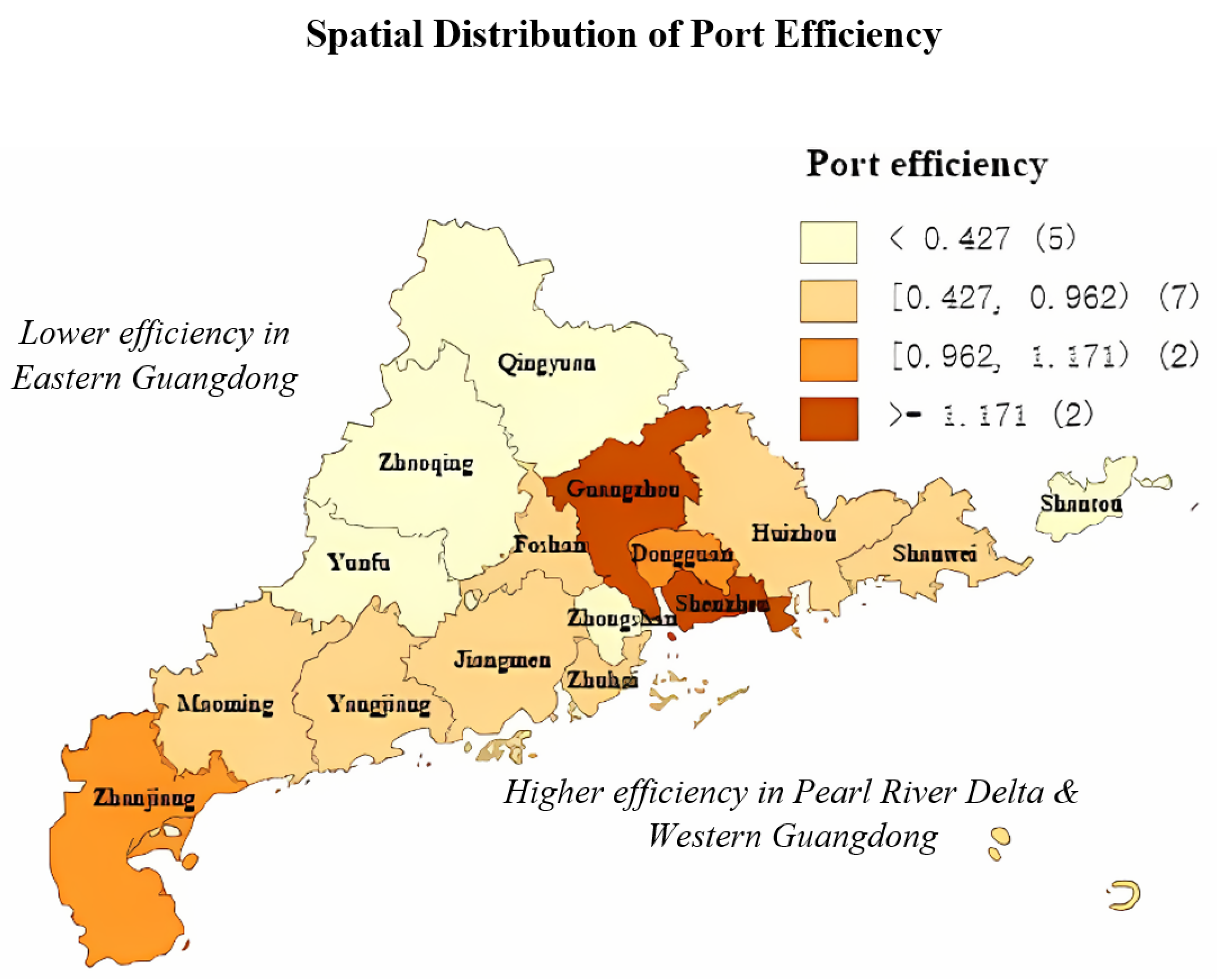
4.1. Port Efficiency Characteristics in Guangdong Province
4.2. Port Efficiency Time Series Change
4.3. Port Efficiency Characteristics in Different Port Clusters
5. The Spatial Autocorrelation of Port Efficiency
5.1. Spatial Characteristics of Port Efficiency
5.2. The global Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
6. Factors Influencing Port Efficiency
7. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Y.-T.; Jo, A.; Choi, K.-S.; Lee, S. Port efficiency and international trade in China. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2021, 17, 801–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottasso, A.; Conti, M.; de Sa Porto, P.C.; Ferrari, C.; Tei, A. Port infrastructures and trade: Empirical evidence from Brazil. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 107, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Bai, X. Impact of local port disruption on global container trade: An example of stressing testing Chinese ports using a D-vine copula-based quantile regression. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 228, 106295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meng, Z.-H.; Shang, Y.; Lv, Z.-F.; Jin, X.-X.; Fu, M.-L.; He, K.-B. Shipping emission forecasts and cost-benefit analysis of China ports and key regions’ control. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, J. Port efficiency and its influencing factors in the context of Pilot Free Trade Zones. Transp. Policy 2021, 105, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, L.; Tong, F.; Zhang, H. Optimal Management and Allocation of Superior Resources in Port Industries. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 94, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J. Green efficiency evaluation and improvement of Chinese ports: A cross-efficiency model. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 88, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fu, F.; Lv, J.; Wu, L.; Mao, H. Efficiency of DECA on ship emission and urban air quality: A case study of China port. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M. Research on Port Infrastructure, Port Efficiency and Urban Trade Development. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 115, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M. Measurement and Comparison of Economic Efficiency of Major Coastal Ports in China. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 115, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-L.; Seo, Y.-J.; Ha, M.-H. The efficiency of major container terminals in China: Super-efficiency data envelopment analysis approach. Marit. Bus. Rev. 2021, 6, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.S.; Khan, R.U.; Mustafa, T. Technical efficiency comparison of container ports in Asian and Middle East region using DEA. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2021, 37, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, Y.; Hayuth, Y. Port performance comparison applying data envelopment analysis (DEA). Marit. Policy Manag. 1993, 20, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Budría, E.; Díaz-Armas, R.; Navarro-Ibañez, M.; Ravelo-Mesa, T. A study of the efficiency of spanish port authorities using data envelopment analysis. Int. J. Transp. Econ. 1999, 26, 237–253. [Google Scholar]
- Tongzon, J. Efficiency measurement of selected Australian and other international ports using data envelopment analysis. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2001, 35, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, V.; Tovar, B. Metafrontier analysis on productivity for West Coast of South Pacific terminals. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 103, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.-H.; Choi, A.-Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, D. Environmental efficiency analysis of Chinese container ports with CO2 emissions: An inseparable input-output SBM model. J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 65, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, A.; Khalil, N.S. Evaluate and Analysis Efficiency of Safaga Port Using DEA-CCR, BCC and SBM Models–Comparison with DP World Sokhna. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 245, 042033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, H.O.; Lovell, C.A.K.; Schmidt, S.S.; Yaisawarng, S. Accounting for Environmental Effects and Statistical Noise in Data Envelopment Analysis. J. Prod. Anal. 2002, 17, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, X.; Luo, J.X.; Chen, J. Evaluation of port efficiency in shanghai port and busan port based on three-stage dea model with environmental concerns. Transport 2020, 35, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Sun, Q. Operation Efficiency Evaluation of Listed Port Companies in China. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 111, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.-Y.; Jo, G.-S.; Wang, Y.; Yeo, G.-T. The Relative Efficiency of Container Terminals in Small and Medium-Sized Ports in China. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2015, 31, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.P.; Felício, J.A.; Fernandes, R.L. Productivity analysis of Brazilian seaports. Marit. Policy Manag. 2012, 39, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estache, A.; de la Fé, B.T.; Trujillo, L. Sources of efficiency gains in port reform: A DEA decomposition of a Malmquist TFP index for Mexico. Util. Policy 2004, 12, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.; Petersen, N.C. A Procedure for Ranking Efficient Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1993, 39, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Qi, G.; Jin, M.; Yuen, K.F.; Chen, Z.; Li, K.X. Efficiency of Port State Control inspection regimes: A comparative study. Transp. Policy 2021, 106, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.J.; Goh, M. Container port efficiency in emerging and more advanced markets. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2010, 46, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-N.; Day, J.-D.; Lien, N.T.K.; Chien, L.Q. Integrating the Additive Seasonal Model and Super-SBM Model to Compute the Efficiency of Port Logistics Companies in Vietnam. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Goto, M. DEA environmental assessment of coal fired power plants: Methodological comparison between radial and non-radial models. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. An epsilon-based measure of efficiency in DEA—A third pole of technical efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zeng, L.; Li, P.; Lu, H.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Zheng, M.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, D.; et al. China’s transportation sector carbon dioxide emissions efficiency and its influencing factors based on the EBM DEA model with undesirable outputs and spatial Durbin model. Energy 2022, 238, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J. Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1958, 26, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Yang, D.; Wan, Y.; Han, T. Analysis on the features of Chinese dry ports: Ownership, customs service, rail service and regional competition. Transp. Policy 2019, 82, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, G.F.; Cariou, P. The impact of competition on container port (in)efficiency. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2015, 78, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.C.-L.; Zhang, A.; Cheung, W. Foreign participation and competition: A way to improve the container port efficiency in China? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2013, 49, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Ouyang, S. The influencing factors and spatial spillover effects of CO2 emissions from transportation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, K.-L.; Geng, J.-C. China’s regional ecological energy efficiency and energy saving and pollution abatement potentials: An empirical analysis using epsilon-based measure model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, B. Containerization, inter-port competition, and port selection. Marit. Policy Manag. 1985, 12, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalla, R.J. Canadian container ports: How have they fared? How will they do? Marit. Policy Manag. 1994, 21, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongzon, J.L. Determinants of port performance and efficiency. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 1995, 29, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-C.; Chiang, C.-H. Cooperation and Competitiveness of Intra-Regional Container Ports. J. East. Asia Soc. Transp. Stud. 2010, 8, 2283–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Vallega, A. Fonctions portuaires et polarisations littorales dans la nouvelle régionalisation de la Méditerranée, quelques réflexions. Villes Et Ports Développement Portuaire Croissance Spat. Des Villes Environ. Littoral 1979, 355–367. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, W.Y.; Loh, H.S. Next generation mega container ports: Implications of traffic composition on sea space demand. Marit. Policy Manag. 2019, 46, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Seo, Y.-J.; Ha, M.-H. The role of maritime, land, and air transportation in economic growth: Panel evidence from OECD and non-OECD countries. Res. Transp. Econ. 2019, 78, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Seo, Y.-J. The impact of seaports on the regional economies in South Korea: Panel evidence from the augmented Solow model. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2016, 85, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-J.; Park, J.S. The role of seaports in regional employment: Evidence from South Korea. Reg. Stud. 2017, 52, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Y. Is uncertainty always bad for the performance of transportation systems? Commun. Transp. Res. 2021, 1, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Province | Cargo Throughput (‘000 Tons) | Province | Container Throughput (‘000 TEUs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 1,757,880 | Guangdong | 60,440 |
| Shandong | 1,688,810 | Shanghai | 43,500 |
| Zhejiang | 1,414,470 | Zhejiang | 32,190 |
| Hebei | 1,204,460 | Shandong | 31,910 |
| Liaoning | 820,040 | Tianjin | 18,350 |
| Author(s) | Methodology | Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Roll and Hayuth [14] | DEA | Inputs: berth length, berth area, number of bridge cranes, number of yard cranes, number of straddle carriers; Outputs: container throughput. |
| MartÍNez-BudrÍA et al. [15] | DEA-BCC | Inputs: berth length, container berth length; Outputs: container throughput, cargo throughput. |
| Tongzon [16] | DEA-CCR | Inputs: number of cranes, berths and tugs, terminal area, delay time and labor;Outputs: container throughput, ship working rate. |
| Estache et al. [26] | DEA-Malmquist | Inputs: length of docks, number of workers; Outputs: the volume of merchandise handled (loading and unloading). |
| Wu and Goh [29] | Super-efficiency DEA | Inputs: terminal area, total quay length, number of pieces of equipment; Outputs: container throughput. |
| Ding et al. [24] | DEA-Malmquist | Inputs: terminal length, handling equipment quantity, staff quantity; Outputs: container throughput. |
| Chang and Tovar [18] | SBM-DEA | Inputs: number of workers, a capital variable approximated by the stock of net fixed assets, obtained from each terminal; Outputs: container throughput, gerolling freight and bulk cargo. |
| Elsayed and Shabaan Khalil [20] | SBM-DEA | Inputs: number of berth, berth length, land area, fixed cranes, yard cranes, water area, storage, terminal, depth of berth, passenger station, labor; Outputs: cargo throughput. |
| Na et al. [19] | SBM-DEA | Inputs: berth lengths, port area, number of quay cranes, and number of yard cranes; Outputs: container throughput and emission. |
| Wang et al. [30] | Super-SBM | Inputs: total assets, owner’s equity; Outputs: net revenue, gross profit. |
| Huang et al. [22] | Three-stage DEA | Inputs: the number of production berths, the length of production quay and the number of container cranes; Outputs: cargo throughput, container throughput. |
| Xiao et al. [28] | Super-SBM | Inputs: number of inspections; Outputs: inspections with deficiencies (DEF), inspections with detentions (DET) |
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dongguan Port | 0.801 | 0.886 | 0.926 | 0.914 | 0.936 | 0.874 | 0.830 | 0.807 | 0.865 | 0.962 |
| Foshan Port | 0.202 | 0.207 | 0.234 | 0.224 | 0.259 | 0.227 | 0.240 | 0.170 | 0.378 | 0.427 |
| Guangzhou Port | 1.115 | 1.197 | 1.268 | 1.103 | 1.175 | 1.090 | 1.177 | 1.225 | 1.193 | 1.171 |
| Huizhou Port | 0.637 | 0.557 | 0.605 | 0.610 | 0.563 | 0.664 | 0.413 | 0.463 | 0.614 | 0.684 |
| Jiangmen Port | 0.279 | 0.298 | 0.310 | 0.290 | 0.311 | 0.252 | 0.258 | 0.198 | 0.261 | 0.446 |
| Maoming Port | 0.582 | 0.533 | 0.503 | 0.535 | 0.514 | 0.502 | 0.338 | 0.346 | 0.423 | 0.514 |
| Qingyuan Port | 0.189 | 0.201 | 0.210 | 0.307 | 0.352 | 0.363 | 0.375 | 0.326 | 0.272 | 0.229 |
| Shantou Port | 0.423 | 0.462 | 0.480 | 0.440 | 0.455 | 0.368 | 0.315 | 0.229 | 0.205 | 0.308 |
| Shanwei Port | 0.401 | 0.455 | 0.548 | 0.308 | 0.394 | 0.357 | 0.344 | 0.491 | 0.382 | 0.436 |
| Shenzhen Port | 1.062 | 1.085 | 1.106 | 1.018 | 1.132 | 1.076 | 1.187 | 1.277 | 1.215 | 1.210 |
| Yangjiang Port | 0.575 | 0.603 | 0.551 | 0.624 | 0.613 | 0.644 | 0.687 | 0.699 | 0.664 | 0.566 |
| Yunfu Port | 0.154 | 0.156 | 0.173 | 0.151 | 0.149 | 0.168 | 0.180 | 0.162 | 0.195 | 0.220 |
| Zhanjiang Port | 1.010 | 1.048 | 1.049 | 1.031 | 1.063 | 1.050 | 1.158 | 1.163 | 1.077 | 1.026 |
| Zhaoqing Port | 0.177 | 0.202 | 0.227 | 0.243 | 0.344 | 0.383 | 0.325 | 0.394 | 0.309 | 0.282 |
| Zhongshan Port | 0.647 | 0.635 | 0.772 | 0.804 | 0.739 | 0.486 | 0.520 | 0.525 | 0.194 | 0.205 |
| Zhuhai Port | 0.303 | 0.537 | 0.530 | 0.489 | 0.540 | 0.442 | 0.426 | 0.348 | 0.506 | 0.538 |
| Factors | Indicators/Calculations | Prediction of Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Development Level | GDP | Positive |
| Opening Level | Total import and export foreign trade | Positive |
| Port-city relationship | RCI | Positive |
| Transportation structure | The proportion of the total water freight volume to total freight volume | Unknown |
| Coefficient | Std.Err. | Z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnx1 | 0.314 | 0.091 | 3.45 | 0.001 |
| lnx2 | −0.061 | 0.055 | −1.12 | 0.263 |
| x3 | 0.176 | 0.045 | 3.89 | 0.000 |
| x4 | 0.426 | 0.228 | 1.87 | 0.062 |
| w1x_lnx1 | 0.050 | 0.010 | 4.91 | 0.000 |
| w1x_lnx2 | −0.041 | 0.016 | −2.49 | 0.013 |
| w1x_x3 | −0.048 | 0.036 | −1.34 | 0.182 |
| w1x_x4 | −0.153 | 0.158 | −0.97 | 0.333 |
| −0.019 | 0.113 | −0.17 | 0.068 | |
| Sigma | 0.101 | 0.018 | 5.65 | 0.000 |
| cons | −2.053 | 0.515 | −3.99 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Y.; Liu, W.; Loh, H.S. Port Efficiency Based on the Super-Efficiency EBM-DEA-SDM Model: Empirical Evidence from China. Future Transp. 2023, 3, 23-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3010002
Gu Y, Liu W, Loh HS. Port Efficiency Based on the Super-Efficiency EBM-DEA-SDM Model: Empirical Evidence from China. Future Transportation. 2023; 3(1):23-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Yimiao, Wanwan Liu, and Hui Shan Loh. 2023. "Port Efficiency Based on the Super-Efficiency EBM-DEA-SDM Model: Empirical Evidence from China" Future Transportation 3, no. 1: 23-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3010002
APA StyleGu, Y., Liu, W., & Loh, H. S. (2023). Port Efficiency Based on the Super-Efficiency EBM-DEA-SDM Model: Empirical Evidence from China. Future Transportation, 3(1), 23-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp3010002





