EvoFuzzy: Evolutionary Fuzzy Approach for Ensembling Reconstructed Genetic Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- i.
- A new network aggregation method that employs a fuzzy trigonometric differential evolution, which offers a more robust and flexible solution than traditional methods currently used to build consensus networks.
- ii.
- A novel fuzzy gene expression predictor, in which the confidence levels of networks are interpreted as regulatory relationship strengths and are used to predict gene expression levels.
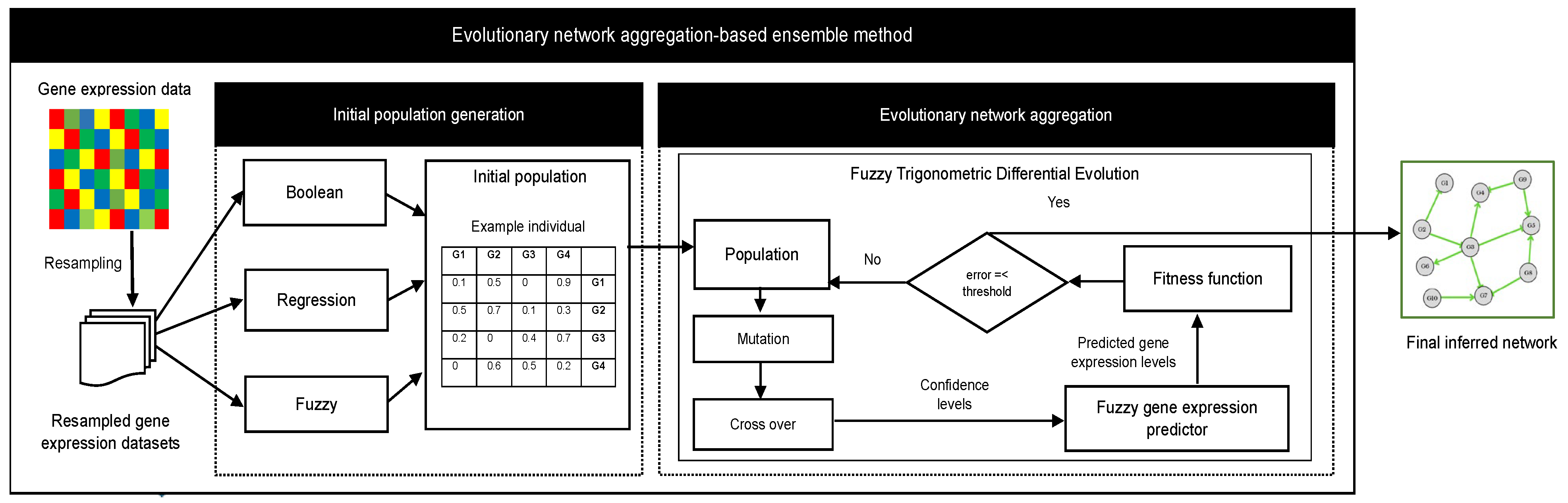
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Evolutionary Network Aggregation-Based Ensemble Method
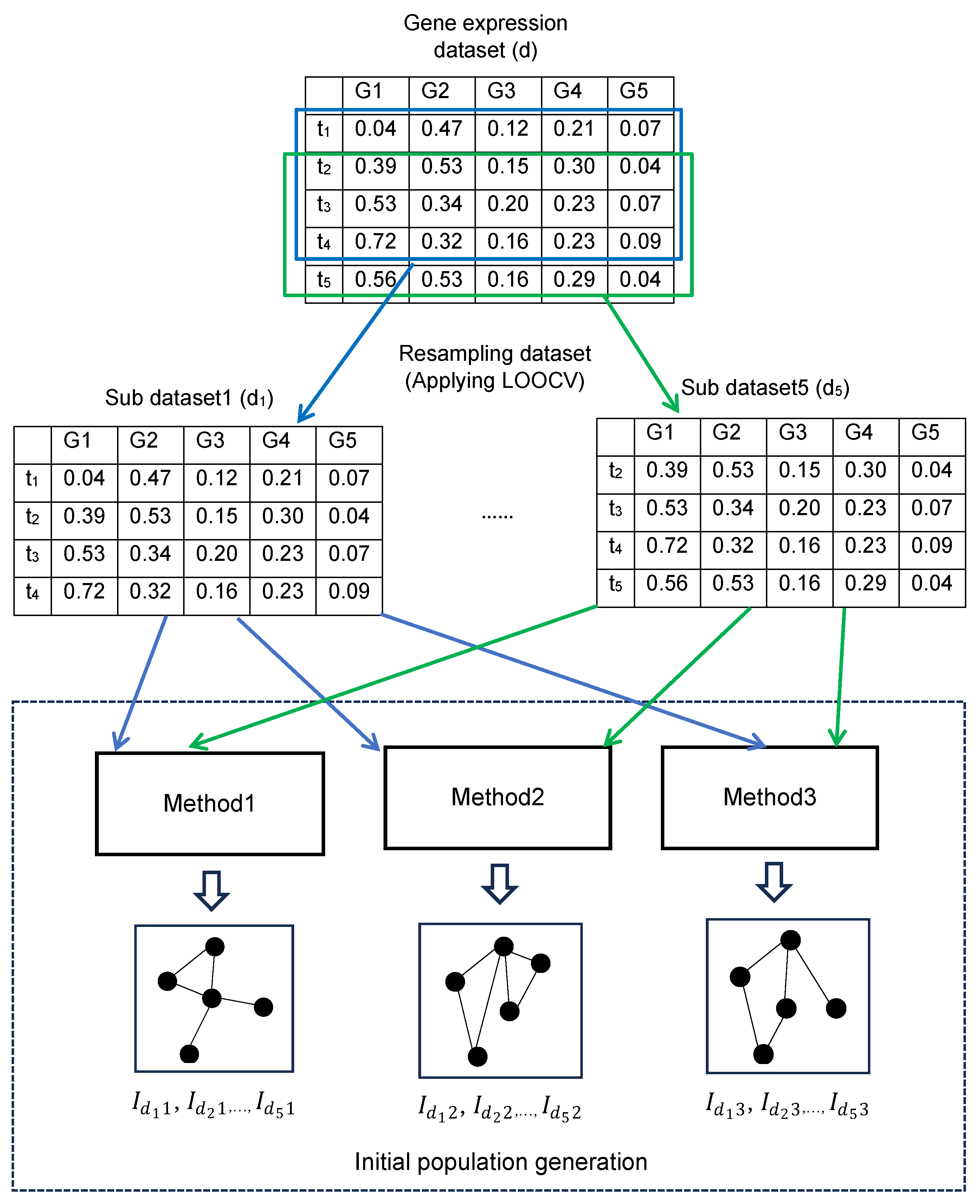
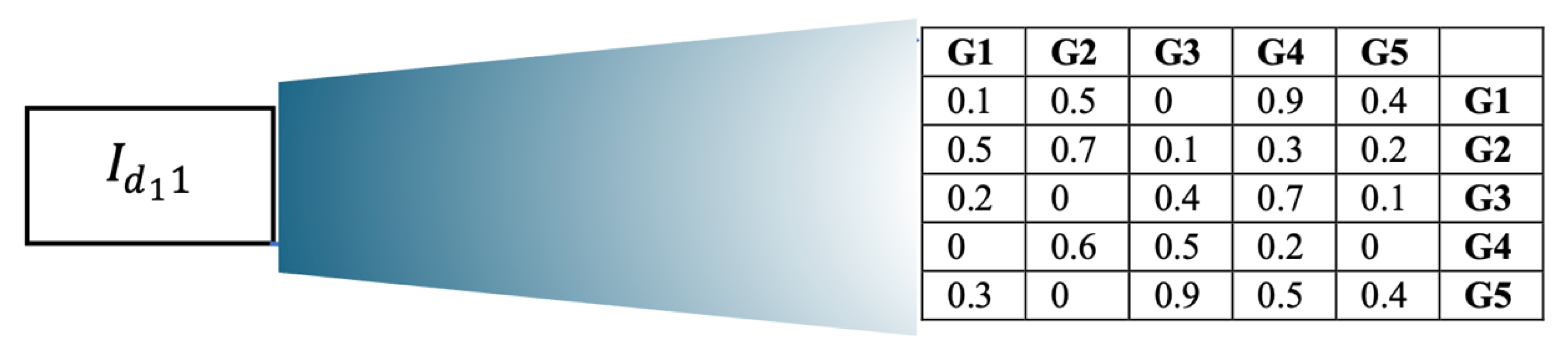
2.1.1. Generation of the Initial Population
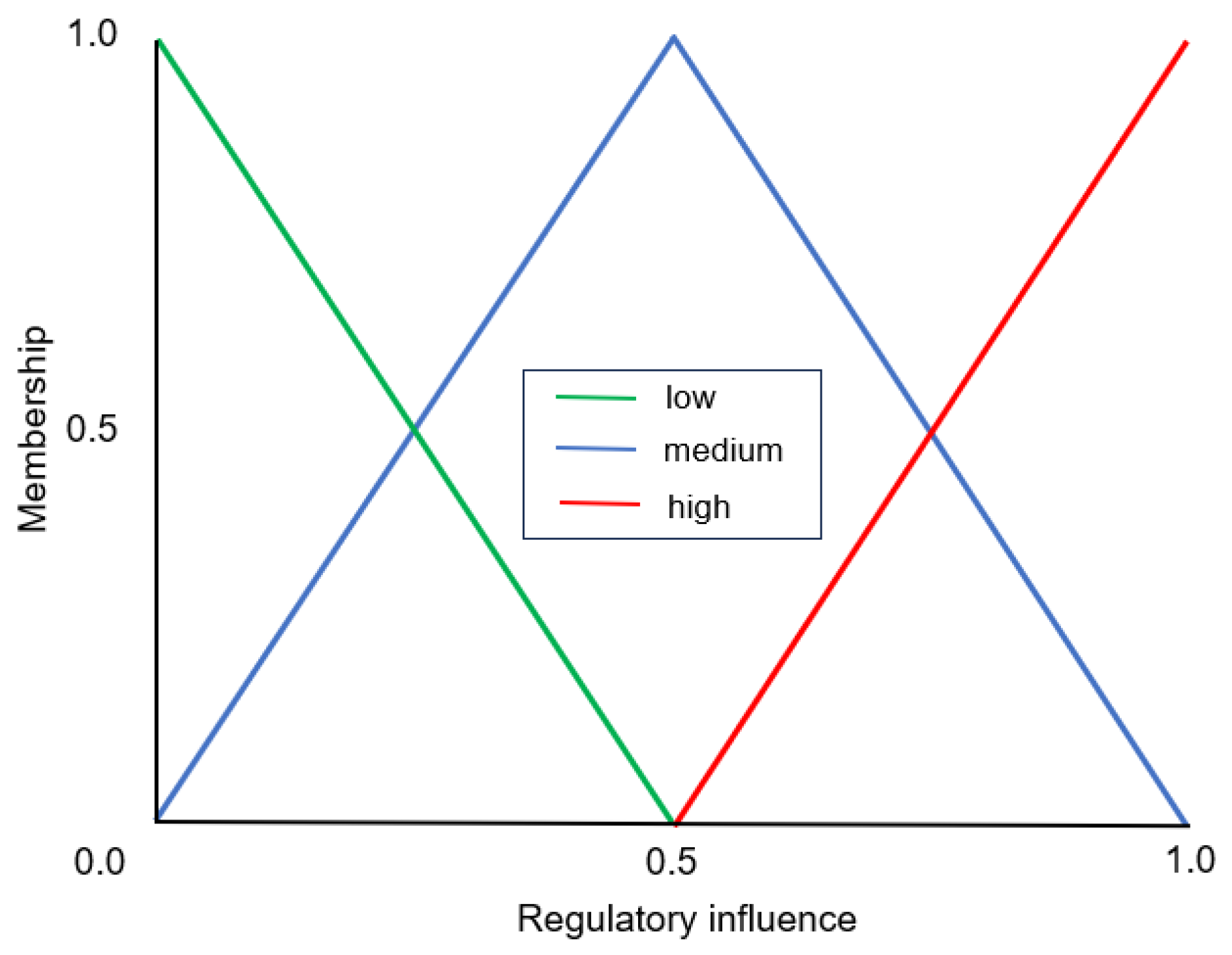
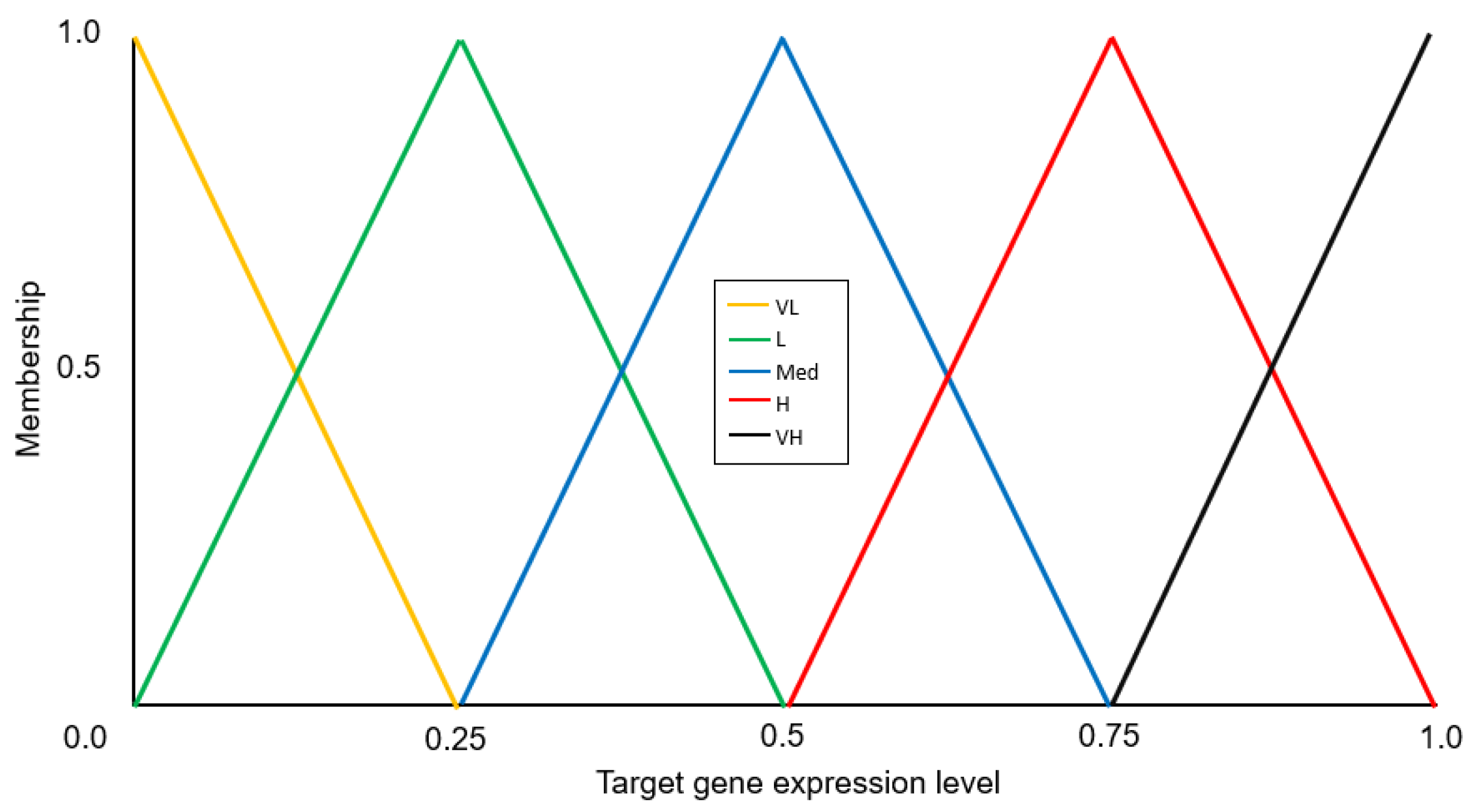
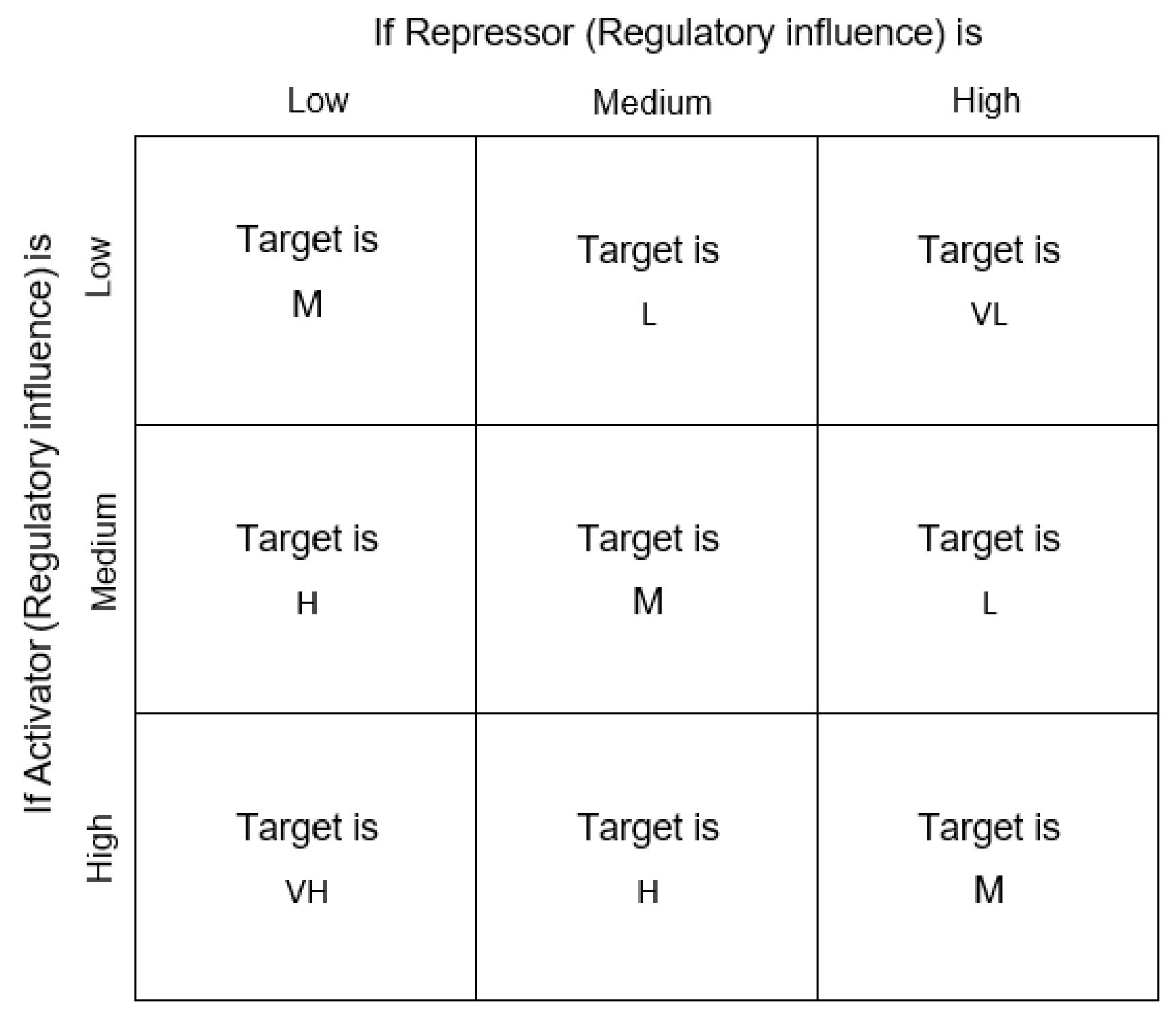
2.1.2. Evolutionary Network Aggregation
“If the regulatory influence of an activator is Low AND the regulatory influence of the repressor is High, then the expression level of the target gene will be Very Low”.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experiments on Simulated Datasets
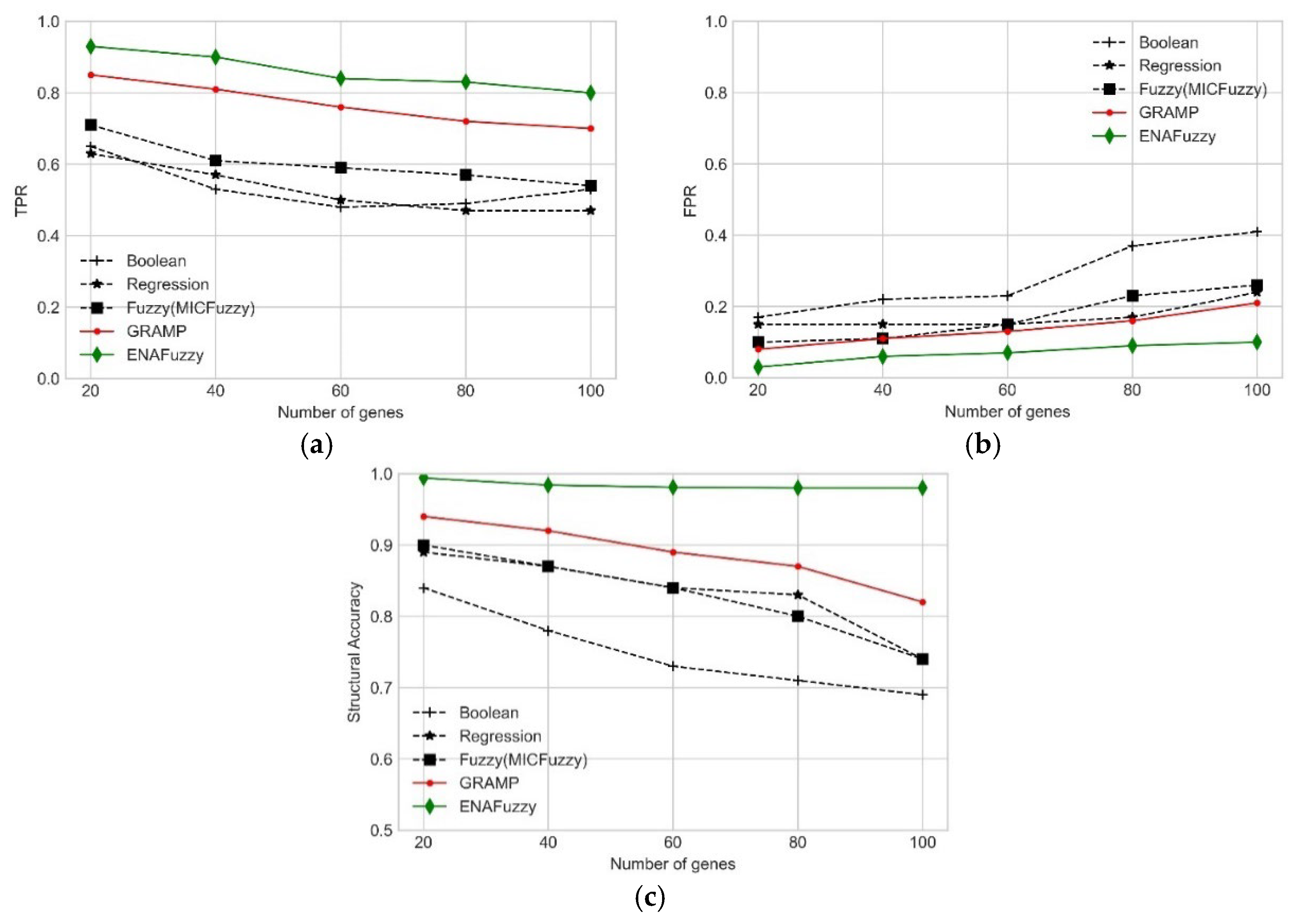
Comparison of Performance with Other State-of-the-Art Methods
3.2. Experiments on Real Gene Expression Datasets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peter, I.S. The function of architecture and logic in developmental gene regulatory networks. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2020, 139, 267–295. [Google Scholar]
- Marku, M.; Pancaldi, V. From time-series transcriptomics to gene regulatory networks: A review on inference methods. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1011254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Cai, Z.; He, X.; Zheng, W.; Liu, J. An approach of gene regulatory network construction using mixed entropy optimizing context-related likelihood mutual information. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, H.N.; Chetty, M.; Shatte, A.; Hallinan, J. An Efficient Boolean Modelling Approach for Genetic Network Inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Melbourne, Australia, 13–15 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, H.N.; Chetty, M.; Shatte, A.; Hallinan, J. Filter feature selection based Boolean Modelling for Genetic Network Inference. Biosystems 2022, 221, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, H.N.; Chetty, M.; Lim, S.; Hallinan, J. MICFuzzy: A maximal information content based fuzzy approach for reconstructing genetic networks. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbach, D.; Prill, R.J.; Schaffter, T.; Mattiussi, C.; Floreano, D.; Stolovitzky, G. Revealing strengths and weaknesses of methods for gene network inference. Biophys. Comput. Biol. 2010, 107, 6286–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbach, D.; Costello, J.C.; Küffner, R.; Vega, N.M.; Prill, R.J.; Camacho, D.M.; Allison, K.R.; Kellis, M.; Collins, J.J.; Stolovitzky, G. Wisdom of crowds for robust gene network inference. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, T.; Ghosh, S.; Yamanaka, R.; Kitano, H. Harnessing Diversity towards the Reconstructing of Large Scale Gene Regulatory Networks. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Coruzzi, G.; Shasha, D. EnsInfer: A simple ensemble approach to network inference outperforms any single method. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawad, D.M.; Katebi, A.; Kabir, M.W.U.; Hoque, M.T. AGRN: Accurate gene regulatory network inference using ensemble machine learning methods. Bioinform. Adv. 2023, 3, vbad032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Ortiz, A.; García-Nieto, J.; Aldana-Montes, J.F.; Navas-Delgado, I. GENECI: A novel evolutionary machine learning consensus-based approach for the inference of gene regulatory networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 155, 106653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, H.N.; Chetty, M.; Lim, S.; Hallinan, J. GRAMP: A gene ranking and model prioritisation framework for building consensus genetic networks. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 302, 112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, H.N.; Chetty, M.; Shatte, A.; Hallinan, J. Ensemble Regression Modelling for Genetic Network Inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 15–17 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, H.N.; Chetty, M.; Lim, S.; Hallinan, J.; Nguyen, H. A Robust Ensemble Regression Model for Reconstructing Genetic Networks. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Gold Coast, Australia, 18–23 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh-Thu, V.A.; Irrthum, A.; Wehenkel, L.; Geurts, P. Inferring Regulatory Networks from Expression Data Using Tree-Based Methods. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-Thu, V.A.; Geurts, P. dynGENIE3: Dynamical GENIE3 for the inference of gene networks from time series expression data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, W.; Han, S.W.; Jeon, M.; Jang, H.J.; Jang, I.-S.; Kang, J. BTNET: Boosted tree based gene regulatory network inference algorithm using time-course measurement data. BMC Syst. Biol. 2018, 12, 20–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluru, M.; Shrivastava, H.; Chockalingam, S.P.; Shivakumar, S.; Aluru, S. EnGRaiN: A supervised ensemble learning method for recovery of large-scale gene regulatory networks. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkesson, J.; Lubovac-Pilav, Z.; Magnusson, R.; Gustafsson, M. ComHub: Community predictions of hubs in gene regulatory networks. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peignier, S.; Sorin, B.; Calevro, F. Ensemble Learning Based Gene Regulatory Network Inference. In Proceedings of the in 2021 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Washington, DC, USA, 1–3 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, C.; Kuwahara, H.; Yu, G.; Guo, L.; Gao, X. Learning gene regulatory networks from gene expression data using weighted consensus. Neurocomputing 2017, 220, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyssinck, J.; Huynh-Thu, V.A.; Geurts, P.; Dhaene, T.; Demeester, P.; Saeys, Y. NIMEFI: Gene Regulatory Network Inference using Multiple Ensemble Feature Importance Algorithms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chi, Y.; Zhu, C. A Dynamic Multiagent Genetic Algorithm for Gene Regulatory Network Reconstruction Based on Fuzzy Cognitive Maps. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 24, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachedes, L.N.S.; Silva, J.E.H.D.; Bernardino, H.S.; Oliveira, I.L.D. High-performance cartesian genetic programming on GPU for the inference of gene regulatory networks using scRNA-seq time-series data. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, Boston, MA, USA, 9–13 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, P. An Improved PSO Algorithm Based on Mutation Operator and Simulated Annealing. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2015, 10, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefelov, A.; Lytvynenko, V.; Voronenko, M.; Babichev, S.; Osypenko, V. Reconstruction of the Gene Regulatory Network by Hybrid Algorithm of Clonal Selection and Trigonometric Differential Evolution. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 38th International Conference on Electronics and Nanotechnology (ELNANO), Kyiv, Ukraine, 24–26 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, J.; Chetty, M.; Shatte, A.; Hallinan, J. Combining kinetic orders for efficient S-System modelling of gene regulatory network. Biosystems 2022, 220, 104736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.-Y.; Lampinen, J. A Trigonometric Mutation Operation to Differential Evolution. J. Glob. Optim. 2003, 27, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, N.; O’SHaughnessy, A.; Hendrich, B. Transcriptional repressors: Multifaceted regulators of gene expression. Development 2013, 140, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, K. Fuzzy logic based approaches for gene regulatory network inference. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 97, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffter, T.; Marbach, D.; Floreano, D. GeneNetWeaver: In silico benchmark generation and performance profiling of network inference methods. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, M.; Rosenberg, R.; Shraiman, B.I.; Alon, U. Assigning numbers to the arrows: Parameterizing a gene regulation network by using accurate expression kinetics. Biol. Sci. 2002, 99, 10555–10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, I.; Barnett, J.; Hannett, N.; Harbison, C.T.; Rinaldi, N.J.; Volkert, T.L.; Wyrick, J.; Zeitlinger, D.K.; Gifford, T.S. Jaakkola and R. A. Young, “Serial regulation of transcriptional regulators in the yeast cell cycle. Cell 2001, 106, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, P.T.; Sherlock, G.; Zhang, M.Q.; Iyer, V.R.; Anders, K.; Eisen, M.B.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D.; Futcher, B. Comprehensive Identification of Cell Cycle–regulated Genes of the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Microarray Hybridization. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiolo, M.; Milone, D.H.; Stegmayer, G. Extreme learning machines for reverse engineering of gene regulatory networks from expression time series. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, S.; Kwon, Y.-K. A neuro-evolution approach to infer a Boolean network from time-series gene expressions. Bioinformatics 2020, 36 (Suppl. S2), i762–i769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
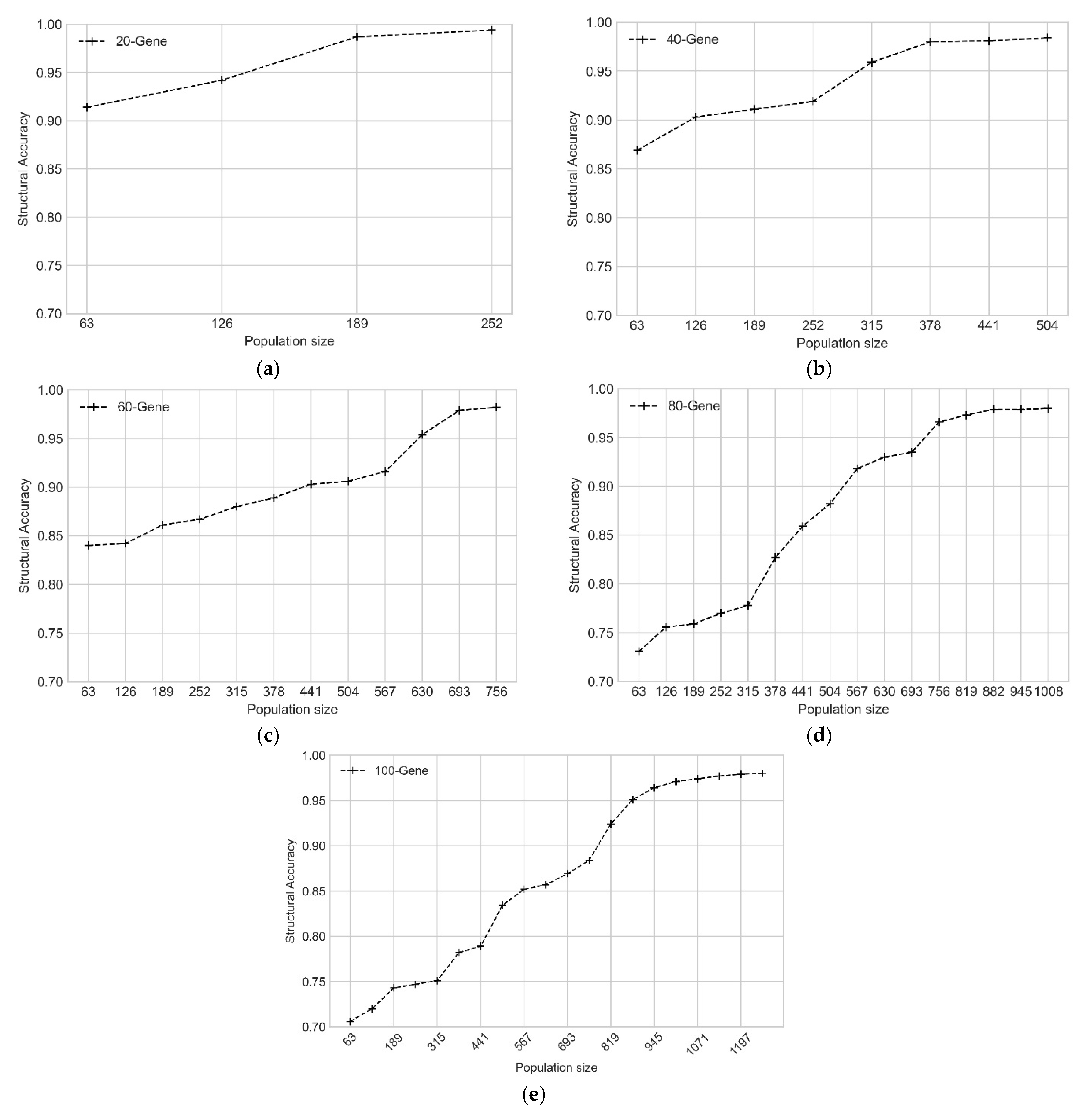

| Number of Genes | Population Size | Number of Generations |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 252 | 308 |
| 40 | 504 | 761 |
| 60 | 756 | 1194 |
| 80 | 1008 | 2831 |
| 100 | 1260 | 6115 |
| Network | Population Size | Number of Generations |
|---|---|---|
| CDC-15 (9-gene) | 96 | 581 |
| CDC-28 (9-gene) | 69 | 266 |
| S. cerevisiae (11-gene) | 72 | 470 |
| Method | CDC-15 (9-Gene) | CDC-28 (9-Gene) | S. cerevisiae (11-Gene) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GENIE3 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.67 |
| dynGENIE3 | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.67 |
| BTNET | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.69 |
| Boolean | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.69 |
| Regression | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.74 |
| Fuzzy (MICFuzzy) | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.76 |
| GRAMP | 0.81 | 0.94 | 0.90 |
| EvoFuzzy | 0.84 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| Regulation | Boolean | Regression | Fuzzy (MICFuzzy) | GRAMP | EvoFuzzy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lexA → uvrD | y | y | y | y | |
| lexA → lexA | y | y | y | y | |
| lexA→ umuD | y | y | y | y | |
| lexA → recA | y | y | y | y | |
| lexA → uvrA | y | y | y | y | y |
| lexA → uvrY | y | y | y | y | |
| lexA → ruvA | |||||
| lexA → polB | y | y | y | y | |
| recA → lexA | y | y | y |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakulugamuwa Gamage, H.; Gill, J.; Chetty, M.; Lim, S.; Hallinan, J. EvoFuzzy: Evolutionary Fuzzy Approach for Ensembling Reconstructed Genetic Networks. BioMedInformatics 2025, 5, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5040059
Nakulugamuwa Gamage H, Gill J, Chetty M, Lim S, Hallinan J. EvoFuzzy: Evolutionary Fuzzy Approach for Ensembling Reconstructed Genetic Networks. BioMedInformatics. 2025; 5(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakulugamuwa Gamage, Hasini, Jaskaran Gill, Madhu Chetty, Suryani Lim, and Jennifer Hallinan. 2025. "EvoFuzzy: Evolutionary Fuzzy Approach for Ensembling Reconstructed Genetic Networks" BioMedInformatics 5, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5040059
APA StyleNakulugamuwa Gamage, H., Gill, J., Chetty, M., Lim, S., & Hallinan, J. (2025). EvoFuzzy: Evolutionary Fuzzy Approach for Ensembling Reconstructed Genetic Networks. BioMedInformatics, 5(4), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5040059






