Hearables: In-Ear Multimodal Data Fusion for Robust Heart Rate Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Data Fusion Methods
2.1.1. Rankawat and Dubey’s [18] Method
2.1.2. Li et al. [17] Method
2.2. Validation of Methods on In-Ear Measurements
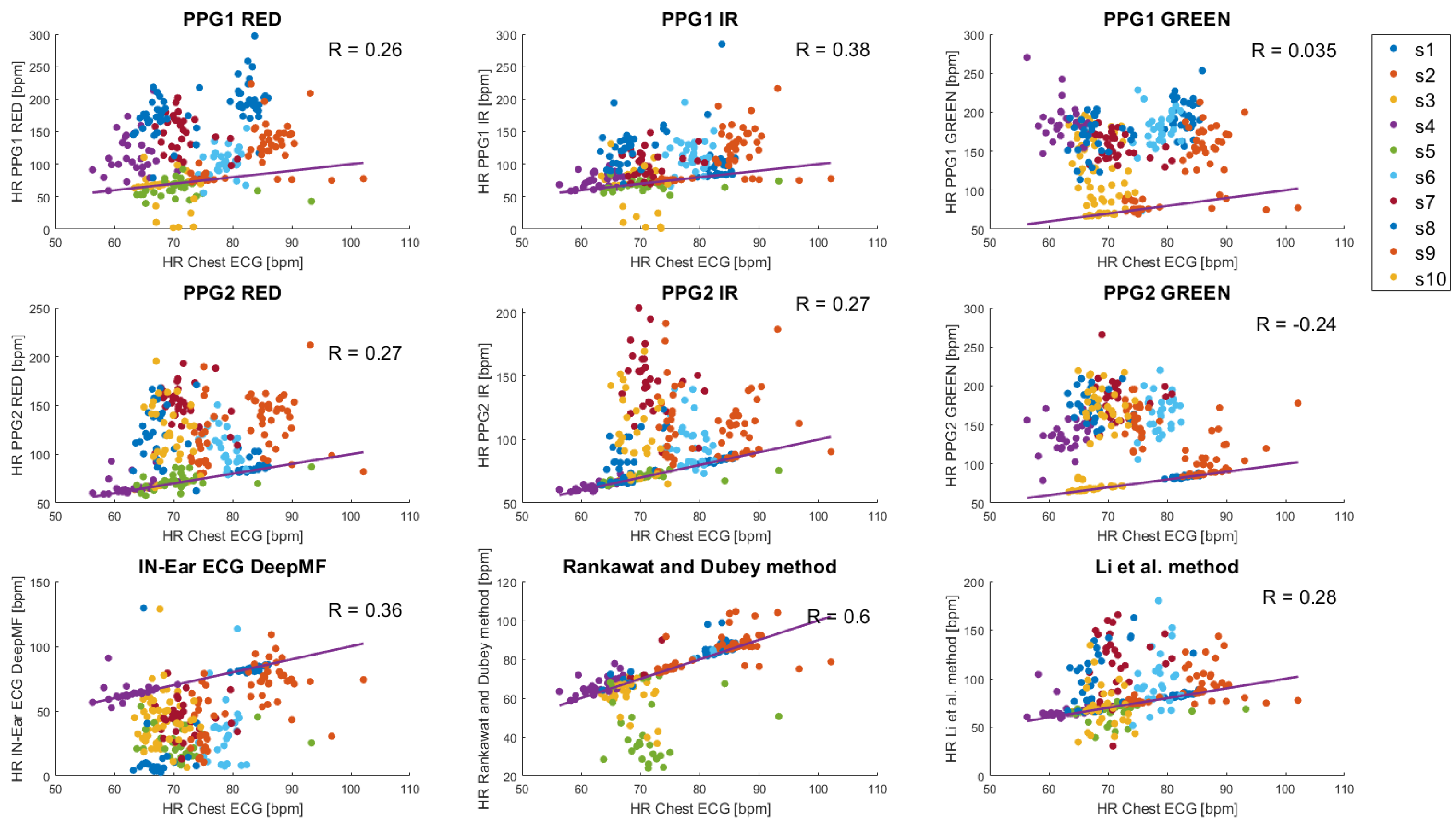
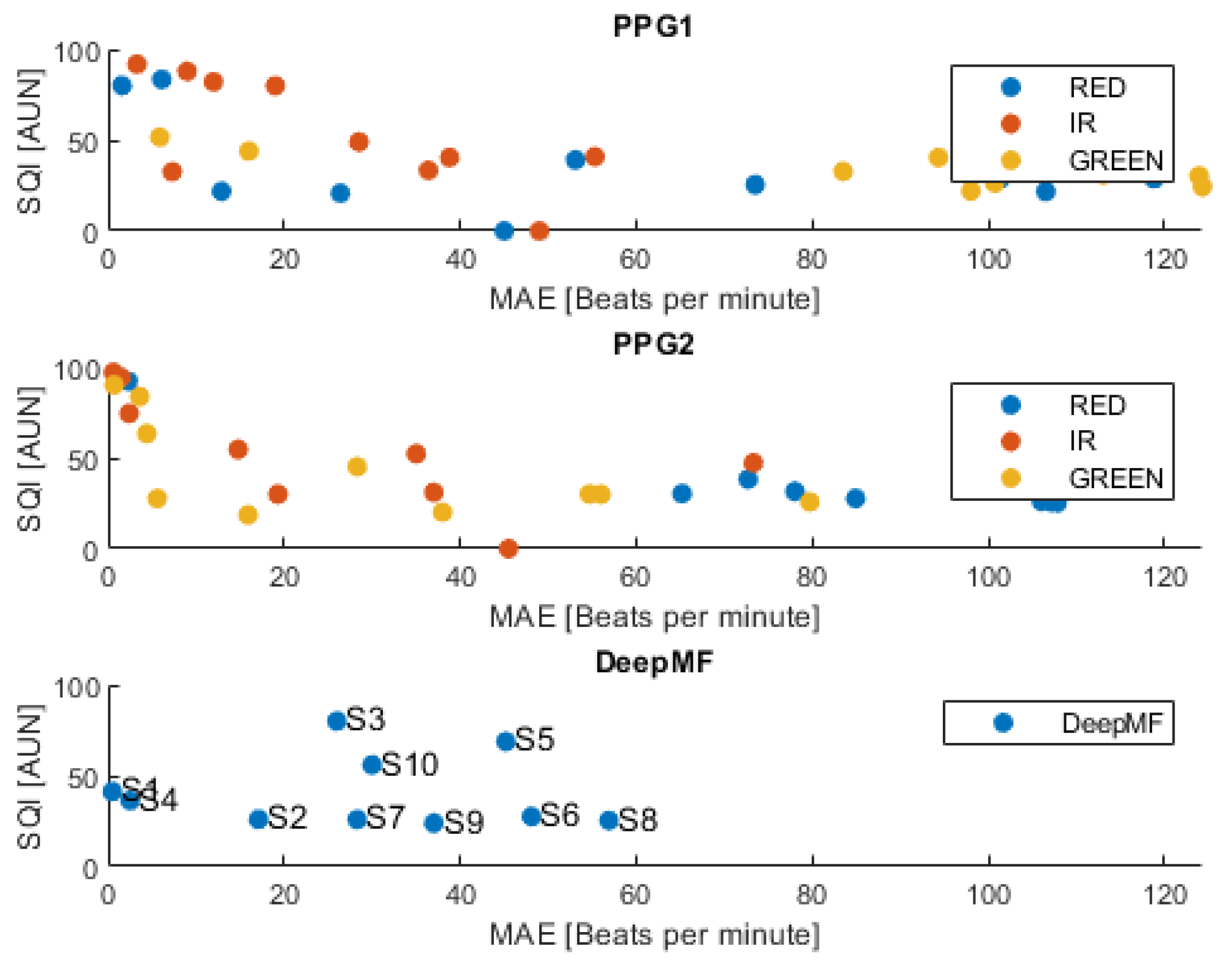
3. Results
4. Discussion
- The enhancement of data fusion methods by refining the assessment of weights.
- The development of a PPG beat detector optimized for low-amplitude in-ear PPG signals.
- The improvement of SQI estimation methods towards more reliable HR estimation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HR | heart rate |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| PPG | photoplethysmographm |
| SQI | signal quality index |
References
- Ruiz-Alias, S.A.; García-Pinillos, F.; Soto-Hermoso, V.M.; Ruiz-Malagón, E.J. Heart rate monitoring of the endurance runner during high intensity interval training: Influence of device used on training functions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Sport. Eng. Technol. 2021, 237, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Garatachea, N.; Almeida, R.; Casajus, J.A.; Bailón, R. Validation of heart rate monitor Polar RS800 for heart rate variability analysis during exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fariha, M.; Ikeura, R.; Hayakawa, S.; Tsutsumi, S. Analysis of Pan-Tompkins algorithm performance with noisy ECG signals. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 1532, p. 012022. [Google Scholar]
- Smital, L.; Haider, C.R.; Vitek, M.; Leinveber, P.; Jurak, P.; Nemcova, A.; Smisek, R.; Marsanova, L.; Provaznik, I.; Felton, C.L.; et al. Real-time quality assessment of long-term ECG signals recorded by wearables in free-living conditions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 2721–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamis, H.; Weiss, R.; Xie, Y.; Chang, C.W.; Lovell, N.H.; Redmond, S.J. QRS detection algorithm for telehealth electrocardiogram recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, S. Performance analysis of ten common QRS detectors on different ECG application cases. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9050812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, K.; Larentzakis, A.V.; Khamis, N.N.; Alsuhaibani, G.I.; Alaska, Y.A.; Giallafos, E.J. Can wearable devices accurately measure heart rate variability? A systematic review. Folia Medica 2018, 60, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Rosenberg, W.; Chanwimalueang, T.; Goverdovsky, V.; Peters, N.S.; Papavassiliou, C.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Feasibility of recording cardiac rhythms from head and in-ear locations. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 171214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarici, M.; Von Rosenberg, W.; Hammour, G.; Davies, H.; Amadori, P.; Ling, N.; Demiris, Y.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Feasibility of recording cardiac rhythms from single in-ear locations. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11, 221620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goverdovsky, V.; Von Rosenberg, W.; Nakamura, T.; Looney, D.; Sharp, D.J.; Papavassiliou, C.; Morrell, M.J.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Multimodal physiological in-ear sensing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Occhipinti, E.; Nassibi, A.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Heart Rate Variability from Ear Electrocardiogram and Ear Photoplethysmogram (Ear-ECG and Ear-PPG). In Proceedings of the 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Sydney, Australia, 24–27 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Occhipinti, E.; Davies, H.J.; Hammour, G.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Artefact removal in Ear-EEG for continuous 24/7 monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Padua, Italy, 18–23 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hammour, G.; Yarici, M.; von Rosenberg, W.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Feasibility and validation of in-ear electrocardiogram. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 5777–5780. [Google Scholar]
- Passler, S.; Müller, N.; Senner, V. In-ear pulse rate measurement: A valid alternative to heart rate derived from electrocardiography? Sensors 2019, 19, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlini, A.; Montanari, A.; Min, C.; Li, H.; Sassi, U.; Kawsar, F. In-ear PPG for vital signs. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2021, 21, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkow, K.J.; Dang, T.; Ferlini, A.; Ma, D.; Mascolo, C. hEARt: Motion-resilient Heart Rate Monitoring with In-ear Microphones. In Proceedings of the the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Atlanta, GA, USA, 13–17 March 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Mark, R.G.; Clifford, G.D. Robust heart rate estimation from multiple asynchronous noisy sources using signal quality indices and a Kalman filter. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 29, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankawat, S.A.; Dubey, R. Robust heart rate estimation from multimodal physiological signals using beat signal quality index based majority voting fusion method. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 33, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankawat, S.A.; Rankawat, M.; Dubey, R. ECG artifacts detection in noncardiovascular signals using Slope Sum Function and Teager Kaiser Energy. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on BioSignal Analysis, Processing and Systems (ICBAPS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–28 May 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, G.F. Kalman filter. In Computer Vision: A Reference Guide; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Vest, A.N.; Da Poian, G.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Nemati, S.; Shah, A.J.; Clifford, G.D. An open source benchmarked toolbox for cardiovascular waveform and interval analysis. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.J.; Hammour, G.; Zylinski, M.; Nassibi, A.; Stanković, L.; Mandic, D.P. The Deep-Match Framework: R-Peak Detection in Ear-ECG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Clifford, G.D. Signal quality and data fusion for false alarm reduction in the intensive care unit. J. Electrocardiol. 2012, 45, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Jonkman, M.; De Boer, F. Frequency Bands Effects on QRS Detection. Biosignals 2010, 2003, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.; Karmakar, C.; Natgunanathan, I.; Yearwood, J.; Palaniswami, M. Robustness of electrocardiogram signal quality indices. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, Z.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C. A novel attentional deep neural network-based assessment method for ECG quality. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhong, G.; He, J.; Yang, C. Multi-task cascaded assessment of signal quality for long-term single-lead ECG monitoring. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 83, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, D.T.; Villajuan, S.O.; Edkins, L.; Cleary, S.; Saleem, J.J. Wearable heart rate monitor technology accuracy in research: A comparative study between PPG and ECG technology. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–14 October 2022; SAGE Publications Sage CA: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 61, pp. 1292–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, P.H.; Kotzen, K.; Mejía-Mejía, E.; Aston, P.J.; Budidha, K.; Mant, J.; Pettit, C.; Behar, J.A.; Kyriacou, P.A. Detecting beats in the photoplethysmogram: Benchmarking open-source algorithms. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.M.; Ercole, A. Multi-scale peak and trough detection optimised for periodic and quasi-periodic neuroscience data. In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, A.; Frigo, G.; Narduzzi, C.; Giorgi, G. Robust estimation and tracking of heart rate by PPG signal analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Turin, Italy, 22–25 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sjoding, M.W.; Dickson, R.P.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Gay, S.E.; Valley, T.S. Racial bias in pulse oximetry measurement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2477–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermond, M.; Davies, H.J.; Occhipinti, E.; Nassibi, A.; Mandic, D.P. Reducing racial bias in SpO2 estimation: The effects of skin pigmentation. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Sydney, Australia, 24–27 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, V.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Qiu, Q.; Hughes, S.; Zheng, D. Quantitative comparison of photoplethysmographic waveform characteristics: Effect of measurement site. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Source Type | SQI ≥ 0.9 | 0.9 > SQI ≥ 0.8 | 0.8 > SQI ≥ 0.7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular signals | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| Non-cardiovascular signals | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| PPG1 | PPG2 | In-Ear ECG | Data Fusion | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject | RED | IR | GREEN | RED | IR | GREEN | DeepMF | Rankawat and Dubey [18] | Li et al. [17] |
| 1 | 119.8 | 19.0 | 113.0 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 2.2 |
| 2 | 106.5 | 38.8 | 124.3 | 15.9 | 45.5 | 65.2 | 17.1 | 13.6 | 35 |
| 3 | 1.6 | 9.0 | 94.3 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 26.0 | 3.5 | 1.3 |
| 4 | 53.1 | 12.0 | 123.9 | 4.4 | 1.5 | 72.7 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 4.4 |
| 5 | 12.9 | 7.3 | - | 5.6 | 2.4 | - | 45.2 | 26.7 | 7.6 |
| 6 | 26.4 | 36.4 | 98.0 | 28.3 | 19.3 | 84.9 | 48.1 | 1.6 | 25.3 |
| 7 | 73.5 | 28.5 | 83.5 | 79.7 | 73.3 | 107.8 | 28.3 | 6.6 | 43.8 |
| 8 | 101.3 | 55.3 | 100.7 | 54.7 | 14.8 | 107.2 | 56.9 | 2.7 | 31.6 |
| 9 | 6.1 | 3.3 | 5.9 | 37.6 | 35.2 | 78.3 | 37.0 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| 10 | 44.6 | 49.5 | 16.1 | 56.0 | 36.5 | 106.3 | 29.8 | 15.5 | 17.3 |
| Mean | 54.5 | 25.9 | 84.4 | 28.6 | 23.0 | 69.5 | 29.1 | 8.0 | 17.2 |
| std | 39.6 | 19.5 | 50.3 | 27.6 | 24.5 | 41.7 | 16.7 | 8.4 | 15.7 |
| PPG1 | PPG2 | In-Ear ECG | Data Fusion | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject | RED | IR | GREEN | RED | IR | GREEN | DeepMF | Rankawat and Dubey [18] | Li et al. [17] |
| 1 | 49.7 | 50.8 | 73.4 | 30.3 | 4.6 | 2.8 | 31.9 | 2.2 | 5.8 |
| 2 | 71.2 | 63.3 | 81.6 | 70.6 | 71.0 | 8.8 | 30.6 | 14.2 | 12.1 |
| 3 | 18.0 | 27.7 | 101.4 | 64.8 | 28.7 | 11.9 | 58.4 | 31.1 | 14.7 |
| 4 | 56.4 | 50.7 | 76.1 | 55.6 | 21.9 | 9.5 | 12.7 | 4.1 | 14.3 |
| 5 | 42.5 | 36.0 | - | 27.8 | 23.5 | - | 77.0 | 15.8 | 34.1 |
| 6 | 33.6 | 33.0 | 44.5 | 50.8 | 52.8 | 44.5 | 70.7 | 28.1 | 23.0 |
| 7 | 20.4 | 18.0 | 31.4 | 15.0 | 12.9 | 25.0 | 71.6 | 23.6 | 18.2 |
| 8 | 20.2 | 22.5 | 40.9 | 55.4 | 60.3 | 50.7 | 78.6 | 3.6 | 33.8 |
| 9 | 21.8 | 16.5 | 20.6 | 18.5 | 22.4 | 35.3 | 62.5 | 11.2 | 13.7 |
| 10 | 19.7 | 15.7 | 12.7 | 12.4 | 31.8 | 15.2 | 25.6 | 15.4 | 13.6 |
| Mean | 35.4 | 33.4 | 53.6 | 40.1 | 32.9 | 22.6 | 52.0 | 14.9 | 18.3 |
| std | 18.8 | 16.6 | 33.4 | 21.7 | 21.5 | 17.7 | 24.3 | 10.2 | 9.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Żyliński, M.; Nassibi, A.; Occhipinti, E.; Malik, A.; Bermond, M.; Davies, H.J.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: In-Ear Multimodal Data Fusion for Robust Heart Rate Estimation. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 911-920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020051
Żyliński M, Nassibi A, Occhipinti E, Malik A, Bermond M, Davies HJ, Mandic DP. Hearables: In-Ear Multimodal Data Fusion for Robust Heart Rate Estimation. BioMedInformatics. 2024; 4(2):911-920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleŻyliński, Marek, Amir Nassibi, Edoardo Occhipinti, Adil Malik, Matteo Bermond, Harry J. Davies, and Danilo P. Mandic. 2024. "Hearables: In-Ear Multimodal Data Fusion for Robust Heart Rate Estimation" BioMedInformatics 4, no. 2: 911-920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020051
APA StyleŻyliński, M., Nassibi, A., Occhipinti, E., Malik, A., Bermond, M., Davies, H. J., & Mandic, D. P. (2024). Hearables: In-Ear Multimodal Data Fusion for Robust Heart Rate Estimation. BioMedInformatics, 4(2), 911-920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020051







