Density and Viscosity of Orange Oil, Turpentine, and Their Hydrogenated Derivatives as Biofuel Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Densimeter
2.2.2. Viscometer
3. Results and Discussion
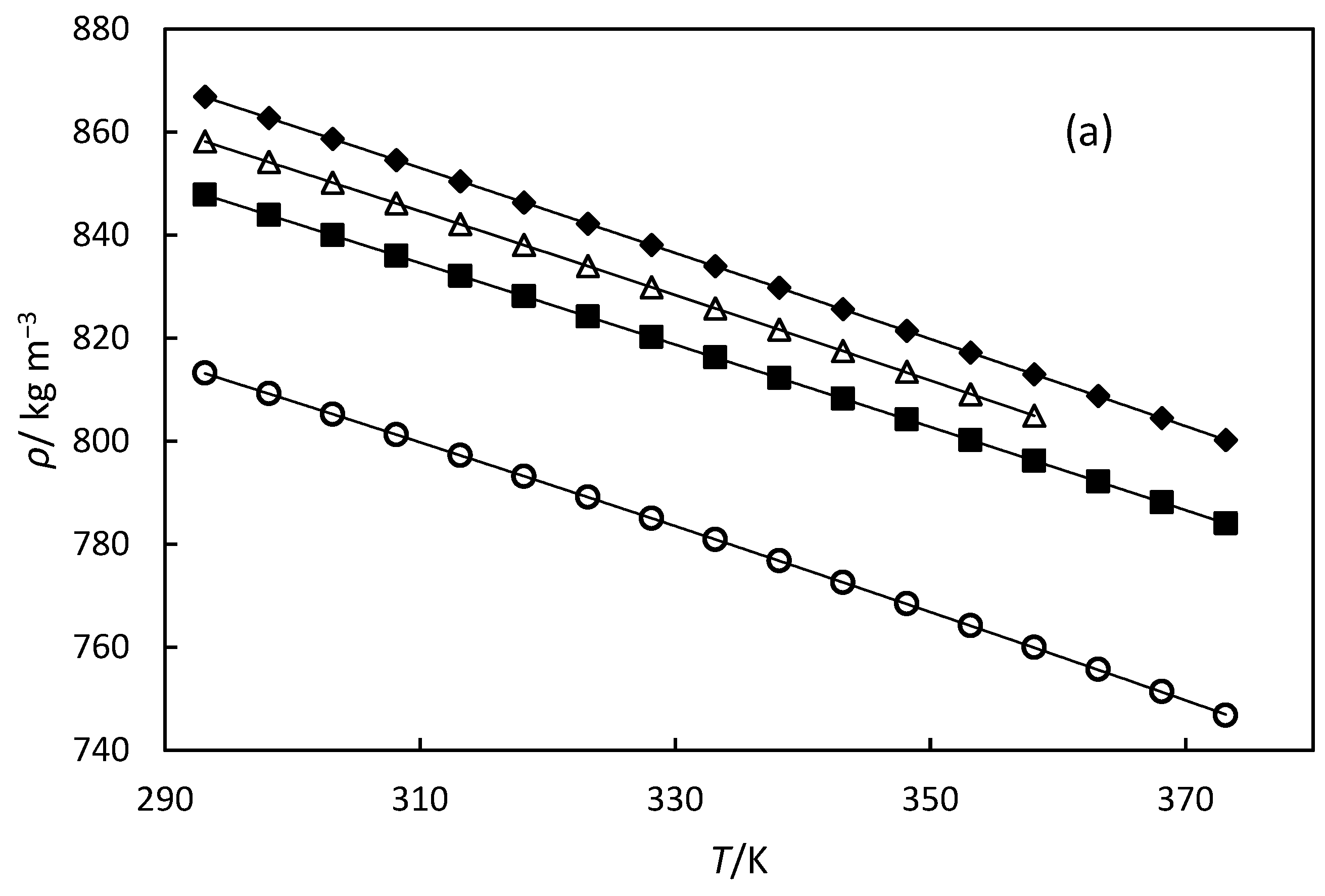
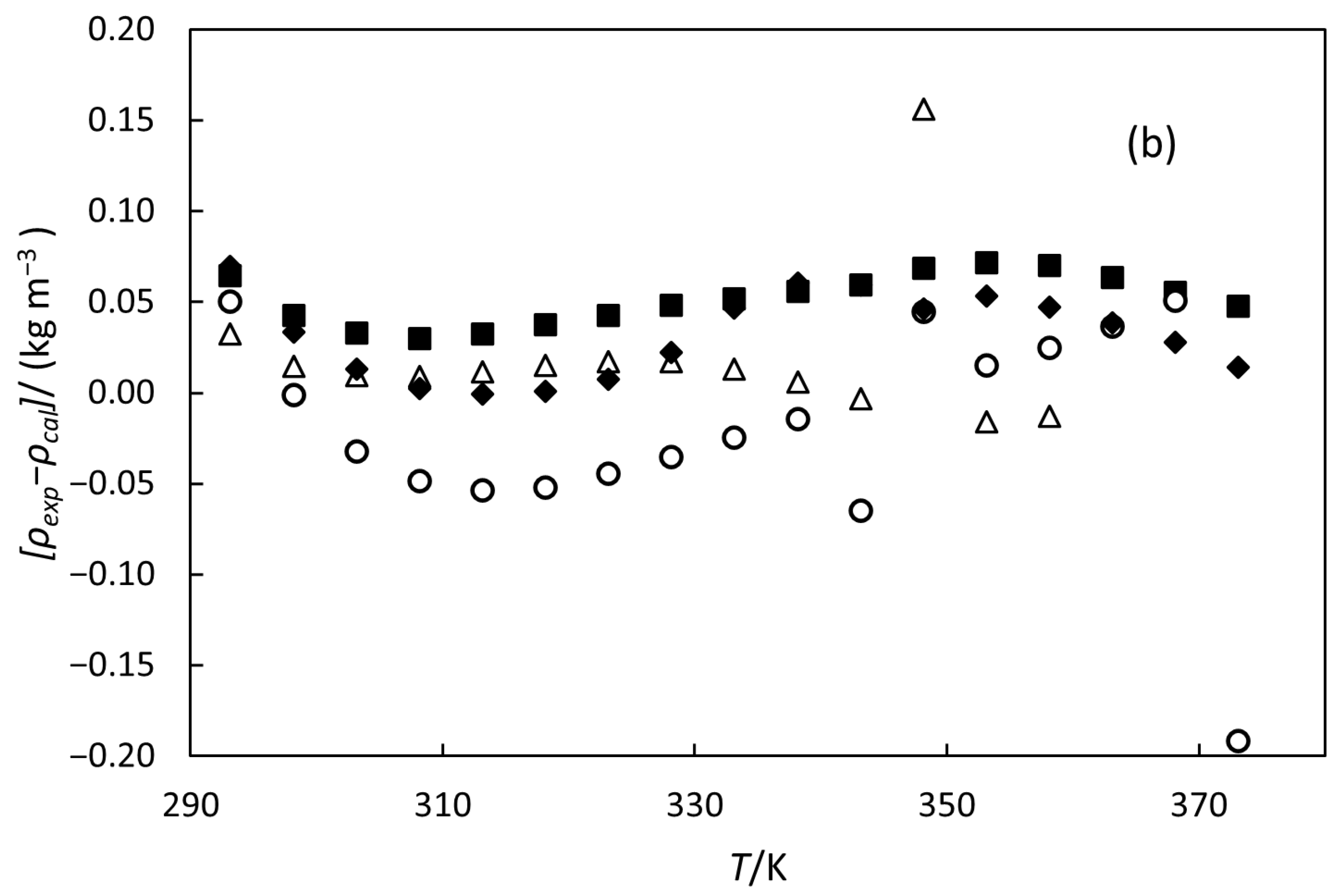
3.1. Density
3.2. Viscosity
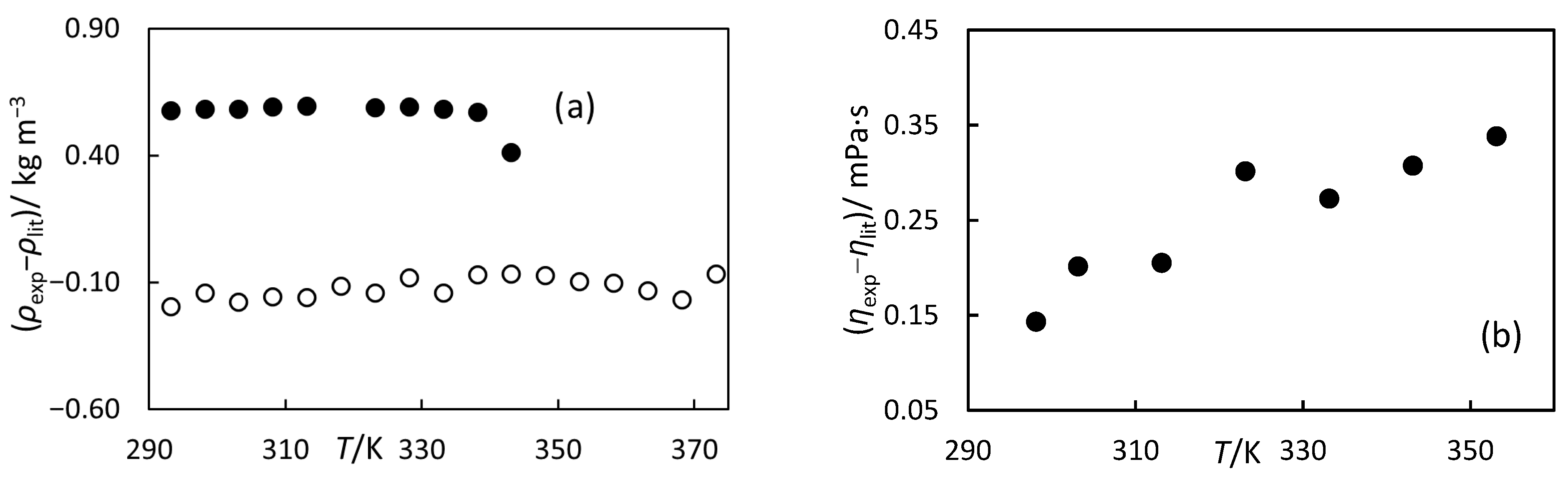
3.3. Comparison with Standards
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. Global Energy Review 2025, IEA, Paris. Licence: CC BY 4.0. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2025 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Demirbas, A. Progress and recent trends in biofuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudul, H.M.; Hagos, F.Y.; Mamat, R.; Adam, A.A.; Ishak, W.F.W.; Alenezi, R. Production, characterization and performance of biodiesel as an alternative fuel in diesel engines—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, K.; Vellaiyan, S.; Venkatesan, E.P.; Khan, S.A.; Mahmoud, Z.; Saleel, C.A. Challenges and Opportunities of Low Viscous Biofuel—A Prospective Review. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 16545–16560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, D.; Bustamante, F.; Alarcón, E.; Donate, J.M.; Canoira, L.; Lapuerta, M. Improvements of Thermal and Thermochemical Properties of Rosin by Chemical Transformation for Its Use as Biofuel. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6383–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A. By-product recovery and valorisation in the kraft industry: A review of current trends in the recovery and use of turpentine and tall oil derivatives. Biomass 1982, 2, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, V.; Mancini, G.; Ruggeri, B.; Fino, D. Citrus waste as feedstock for bio-based products recovery: Review on limonene case study and energy valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, R.; García, D.; Bustamante, F.; Alarcón, E.; Lapuerta, M. Oxyfunctionalized turpentine: Evaluation of properties as automotive fuel. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 2210–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivu, R.M.; Martins, J.; Popescu, F.; Ion, I.V.; Krisztina, U.; Fratita, M. The use of turpentine as additive for diesel oil. A review. J. Therm. Eng. 2025, 11, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, K.; Nagarajan, G. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a compression ignition engine operating on neat orange oil. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, K.; Nagarajan, G. Experimental investigation on a C.I. engine using orange oil and orange oil with DEE. Fuel 2009, 88, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.A.; Van, T.C.; Hossain, F.M.; Jafari, M.; Dowell, A.; Islam, M.A.; Nabi, M.N.; Marchese, A.J.; Tryner, J.; Rainey, T.; et al. Fuel properties and emission characteristics of essential oil blends in a compression ignition engine. Fuel 2019, 238, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso, D.; García, D.; Ballesteros, R.; Lapuerta, M.; Canoira, L. Hydrogenated or oxyfunctionalized turpentine: Options for automotive fuel components. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18342–18350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoso, D.; Ballesteros, R.; Bolonio, D.; García-Martínez, M.-J.; Lapuerta, M.; Canoira, L. Hydrogenated Turpentine: A Biobased Component for Jet Fuel. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso, D.; Bolonio, D.; Ballesteros, R.; Lapuerta, M.; Canoira, L. Hydrogenated orange oil: A waste derived drop-in biojet fuel. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals 2E; McGraw Hill LLC: Columbus, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, R.K.; Rehman, A.; Sarviya, R.M. Impact of alternative fuel properties on fuel spray behavior and atomization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1762–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Dong, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, G.; Zheng, Z.; Yao, M. Experimental investigation of the effects of diesel fuel properties on combustion and emissions on a multi-cylinder heavy-duty diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 171, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R. Introduction to Internal Combustion Engines; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- CEN. EN 14214:2012+A2:2019 - Fatty Acid Methyl Esters (FAME) for Use in Diesel Engines and Heating Applications—Requirements and Test Methods. 2012. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/0a2c5899-c226-479c-b277-5322cc71395d/en-14214-2012a2-2019 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Standard Specification for Biodiesel Fuel (B100) Blend Stock for Distillate Fuels. 2002. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/astm/2c940cfb-8fce-4ba2-a929-2ad8232f3d0c/astm-d6751-02 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Tesfa, B.; Mishra, R.; Gu, F.; Powles, N. Prediction models for density and viscosity of biodiesel and their effects on fuel supply system in CI engines. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunatti-Montoya, M.; Hegel, P.E.; Pereda, S. Density and viscosity of orange peel oil saturated with pressurized CO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2024, 214, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares Sousa, A.; Nieto de Castro, C.A. Density of α-pinene, Β-pinene, limonene, and essence of turpentine. Int. J. Thermophys. 1992, 13, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton Paar. Density Meters. Available online: https://www.anton-paar.com/uk-en/products/group/density-meter/ (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Wikipedia Contributors. Oscillating U-tube. Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Oscillating_U-tube&oldid=979631440 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Gonzalez, M.A.; Tenorio, M.J.; Bismilla, A.Z.; D’Oliveira, E.J.; Costa Pereira, S.-C.; Sanchez-Vicente, Y. Molecular dynamics simulations and experimental measurements of density and viscosity of phase change material based on stearic acid with graphene nanoplatelets. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2025, 593, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCGM 100:2008; Evaluation of Measurement Data—Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement. Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology: Paris, France, 2008.
- Schroeder, J.A.; Penoncello, S.G.; Schroeder, J.S. A Fundamental Equation of State for Ethanol. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2014, 43, 043102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, E.W.; Bell, I.H.; Huber, M.L.; McLinden, M.O. NIST Standard Reference Database 23: Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties-REFPROP, Version 10.0; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17034:2016; General Requirements for the Competence of Reference Material Producers. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/29357.html (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- ISO/IEC 17025 for Laboratory Testing/Calibration. Available online: https://www.ukas.com/resources/resources/soas-17025/ (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Clará, R.A.; Marigliano, A.C.G.; Sólimo, H.N. Density, Viscosity, and Refractive Index in the Range (283.15 to 353.15) K and Vapor Pressure of α-Pinene, d-Limonene, (±)-Linalool, and Citral Over the Pressure Range 1.0 kPa Atmospheric Pressure. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozdanić, N.; Simić, Z.; Kijevčanin, M.; Radović, I. High Pressure Densities and Derived Thermodynamic Properties of Pure (1R)-(+)-α-Pinene, (1S)-(−)-β-Pinene, and Linalool: Experiment and Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2024, 69, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Fang, W. Density and Viscosity of the Ternary System Pinane + n-Dodecane + Methyl Laurate and Corresponding Binary Systems at T = 293.15–333.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 2706–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.N.D.C. The Viscosity of Liquids. Nature 1930, 125, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, R.; Comelli, F.; Castellari, C. Excess molar enthalpies of binary mixtures containing phenetole+α-pinene or β-pinene in the range (288.15–313.15) K, and at atmospheric pressure: Application of the extended cell model of Prigogine. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 363, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratas, M.J.; Freitas, S.V.D.; Oliveira, M.B.; Monteiro, S.C.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Biodiesel Density: Experimental Measurements and Prediction Models. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.V.D.; Pratas, M.J.; Ceriani, R.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Evaluation of Predictive Models for the Viscosity of Biodiesel. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
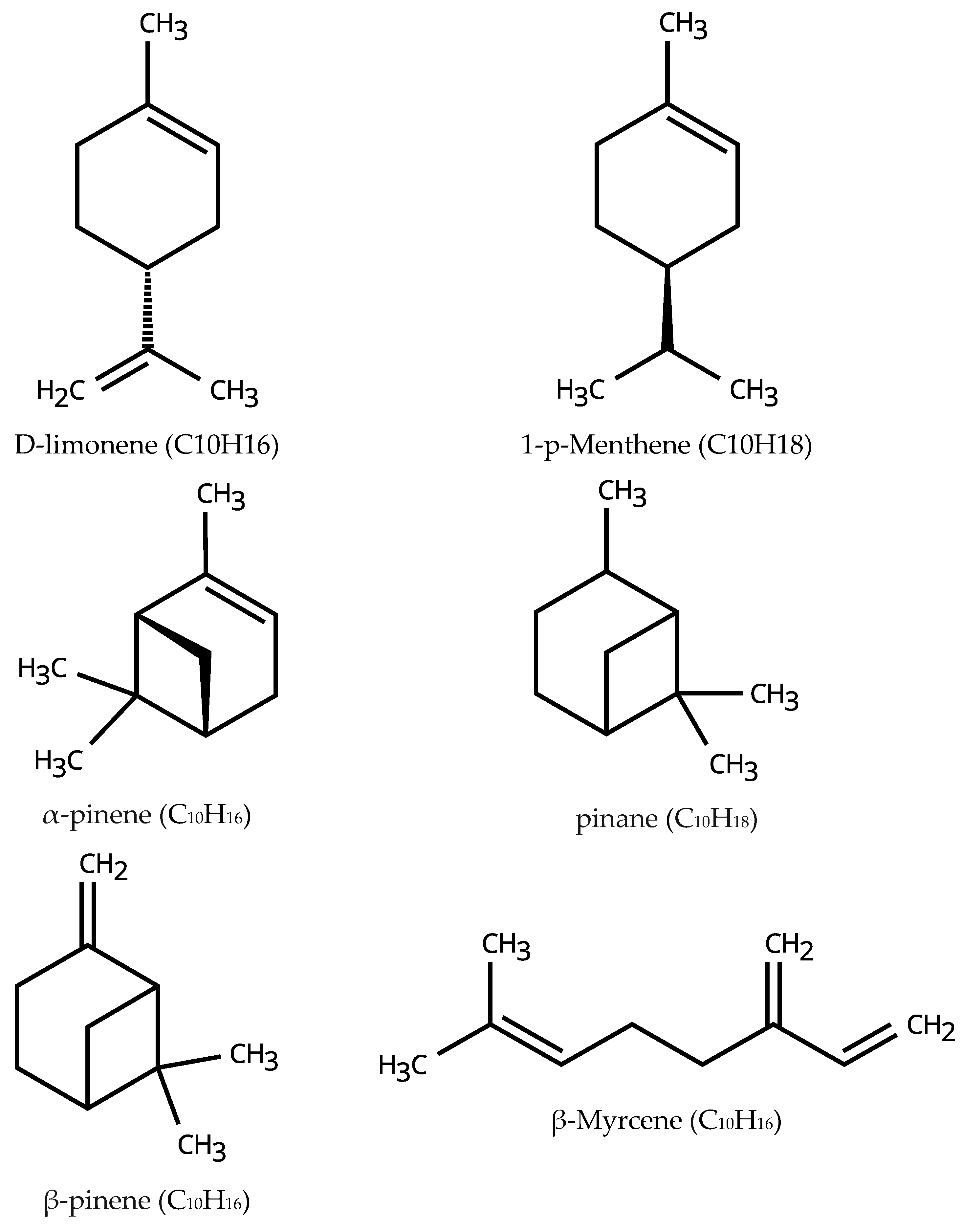

| Compound | Orange Oil | 51% Hydrogenated Orange Oil | Compound | Turpentine | 59% Hydrogenated Turpentine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-limonene | 94.0 | 5.5 | α-pinene | 67.3 | 39.6 |
| β-Myrcene | 2.4 | 0 | β-pinene | 21.5 | 0 |
| 1-p-Menthene | 0 | 83.1 | pinane | 0 | 54.2 |
| Total | 96.4 | 88.6 | Total | 88.8 | 93.8 |
| Substance | N2500 Standard Oil | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| T/K | ρexp/kg m−3 | ρlit/kg m−3 | 100 (ρexp − ρlit) ρexp−1 |
| 293.15 | 821.11 | 821.30 | −0.02 |
| 298.15 | 817.66 | 817.80 | −0.02 |
| 303.15 | 814.22 | 814.40 | −0.02 |
| 308.15 | 810.78 | 810.94 | −0.02 |
| 313.15 | 807.34 | 807.50 | −0.02 |
| 318.15 | 803.90 | 804.02 | −0.01 |
| 323.15 | 800.46 | 800.60 | −0.02 |
| 328.15 | 797.01 | 797.09 | −0.01 |
| 333.15 | 793.56 | 793.70 | −0.02 |
| 338.15 | 790.10 | 790.17 | −0.01 |
| 343.15 | 786.64 | 786.71 | −0.01 |
| 348.15 | 783.18 | 783.25 | −0.01 |
| 353.15 | 779.70 | 779.80 | −0.01 |
| 358.15 | 776.22 | 776.33 | −0.01 |
| 363.15 | 772.73 | 772.87 | −0.02 |
| 368.15 | 769.24 | 769.41 | −0.02 |
| 373.15 | 765.73 | 765.80 | −0.01 |
| Substance | Ethanol | ||
| T/K | ρexp/kg m−3 | ρcal/kg m−3 | 100 (ρexp − ρcal) ρexp−1 |
| 293.15 | 790.00 | 789.42 | 0.07 |
| 298.15 | 785.71 | 785.13 | 0.07 |
| 303.15 | 781.40 | 780.82 | 0.07 |
| 308.15 | 777.06 | 776.47 | 0.08 |
| 313.15 | 772.68 | 772.09 | 0.08 |
| 318.15 | 768.26 | 767.66 | 0.08 |
| 323.15 | 763.78 | 763.19 | 0.08 |
| 328.15 | 759.24 | 758.65 | 0.08 |
| 333.15 | 754.63 | 754.05 | 0.08 |
| 338.15 | 749.95 | 749.38 | 0.08 |
| 343.15 | 745.04 | 744.63 | 0.06 |
| N2500 Standard Oil | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| T/K | ηexp/mPa∙s | ηlit/mPa∙s | (ηexp − ηlit)/mPa∙s |
| 298.2 | 3.43 | 3.283 | 0.14 |
| 303.2 | 3.21 | 3.013 | 0.20 |
| 313.2 | 2.54 | 2.336 | 0.20 |
| 323.2 | 2.22 | 1.919 | 0.30 |
| 333.2 | 1.88 | 1.607 | 0.27 |
| 343.2 | 1.76 | 1.449 | 0.31 |
| 353.2 | 1.52 | 1.178 | 0.34 |
| Substance | Orange Oil | |
|---|---|---|
| T/K | ρ/kg m−3 | u (ρ)/kg m−3 |
| 293.15 | 847.82 | 0.02 |
| 298.15 | 843.89 | 0.02 |
| 303.15 | 839.96 | 0.02 |
| 308.15 | 836.02 | 0.03 |
| 313.15 | 832.08 | 0.03 |
| 318.15 | 828.13 | 0.03 |
| 323.15 | 824.18 | 0.03 |
| 328.15 | 820.21 | 0.03 |
| 333.15 | 816.24 | 0.03 |
| 338.15 | 812.25 | 0.04 |
| 343.15 | 808.25 | 0.03 |
| 348.15 | 804.25 | 0.04 |
| 353.15 | 800.24 | 0.04 |
| 358.15 | 796.20 | 0.05 |
| 363.15 | 792.16 | 0.05 |
| 368.15 | 788.10 | 0.05 |
| 373.15 | 784.04 | 0.01 |
| Substance | 79% Hydrogenated Orange Oil | |
| T/K | ρ/kg m−3 | u (ρ)/kg m−3 |
| 293.15 | 813.20 | 0.02 |
| 298.15 | 809.22 | 0.02 |
| 303.15 | 805.23 | 0.02 |
| 308.15 | 801.23 | 0.03 |
| 313.15 | 797.21 | 0.03 |
| 318.15 | 793.17 | 0.03 |
| 323.15 | 789.11 | 0.03 |
| 328.15 | 785.03 | 0.03 |
| 333.15 | 780.91 | 0.03 |
| 338.15 | 776.78 | 0.04 |
| 343.15 | 772.55 | 0.03 |
| 348.15 | 768.46 | 0.03 |
| 353.15 | 764.20 | 0.03 |
| 358.15 | 759.95 | 0.03 |
| 363.15 | 755.67 | 0.03 |
| 368.15 | 751.38 | 0.03 |
| 373.15 | 746.79 | 0.03 |
| Substance | Turpentine | |
| T/K | ρ/kg m−3 | u (ρ)/kg m−3 |
| 293.15 | 866.84 | 0.01 |
| 298.15 | 862.74 | 0.01 |
| 303.15 | 858.64 | 0.01 |
| 308.15 | 854.53 | 0.01 |
| 313.15 | 850.43 | 0.02 |
| 318.15 | 846.31 | 0.02 |
| 323.15 | 842.19 | 0.02 |
| 328.15 | 838.06 | 0.02 |
| 333.15 | 833.93 | 0.02 |
| 338.15 | 829.78 | 0.02 |
| 343.15 | 825.60 | 0.02 |
| 348.15 | 821.39 | 0.02 |
| 353.15 | 817.19 | 0.02 |
| 358.15 | 812.97 | 0.02 |
| 363.15 | 808.73 | 0.01 |
| 368.15 | 804.48 | 0.01 |
| 373.15 | 800.21 | 0.01 |
| Substance | 98% Hydrogenated Turpentine | |
| T/K | ρ/kg m−3 | u (ρ)/kg m−3 |
| 293.15 | 858.18 | 0.12 |
| 298.15 | 854.17 | 0.12 |
| 303.15 | 850.16 | 0.12 |
| 308.15 | 846.14 | 0.12 |
| 313.15 | 842.10 | 0.12 |
| 318.15 | 838.05 | 0.13 |
| 323.15 | 833.98 | 0.12 |
| 328.15 | 829.88 | 0.13 |
| 333.15 | 825.76 | 0.13 |
| 338.15 | 821.63 | 0.13 |
| 343.15 | 817.47 | 0.14 |
| 348.15 | 813.46 | 0.14 |
| 353.15 | 809.10 | 0.15 |
| 358.15 | 804.90 | 0.15 |
| Orange Oil | 79% Hydrogenated Orange Oil | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficients and 95% Confidence Bounds | ||||||
| Value | Lower | Upper | Value | Lower | Upper | |
| A/kg m−3 | 1060.2 | 1058.9 | 1061.5 | 996.10 | 989.26 | 1002.93 |
| B/kg m−3 K−1 | −0.66788 | −0.67573 | −0.66002 | −0.46459 | −0.50577 | −0.42342 |
| C∙104/kg m−3 K−2 | −1.9354 | −2.0532 | −1.8176 | −5.4418 | −6.0594 | −4.8242 |
| AAD/kg m−3 | 0.05 | 0.05 | ||||
| 100∙AARD | 0.006 | 0.006 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9999997 | 0.9999919 | ||||
| RMSE/kg m−3 | 0.012 | 0.06 | ||||
| Turpentine | 98% Hydrogenated Turpentine | |||||
| Coefficients and 95% Confidence Bounds | ||||||
| Value | Lower | Upper | Value | Lower | Upper | |
| A/kg m−3 | 1083.1 | 1080.6 | 1085.7 | 1059.9 | 1052.1 | 1067.6 |
| B/kg m−3K−1 | −0.66424 | −0.67980 | −0.64868 | −0.58119 | −0.62885 | −0.53353 |
| C∙104/kg m−3 K−2 | −2.5172 | −2.7505 | −2.2838 | −3.6482 | −4.3797 | −2.9167 |
| AAD/kg m−3 | 0.03 | 0.024 | ||||
| 100∙AARD | 0.004 | 0.0023 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9999987 | 0.9999942 | ||||
| RMSE/kg m−3 | 0.024 | 0.04 | ||||
| Substance | Main Component/ | T/ | ρ/ | Apparatus | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mass%) | K | kg m−3 | ||||
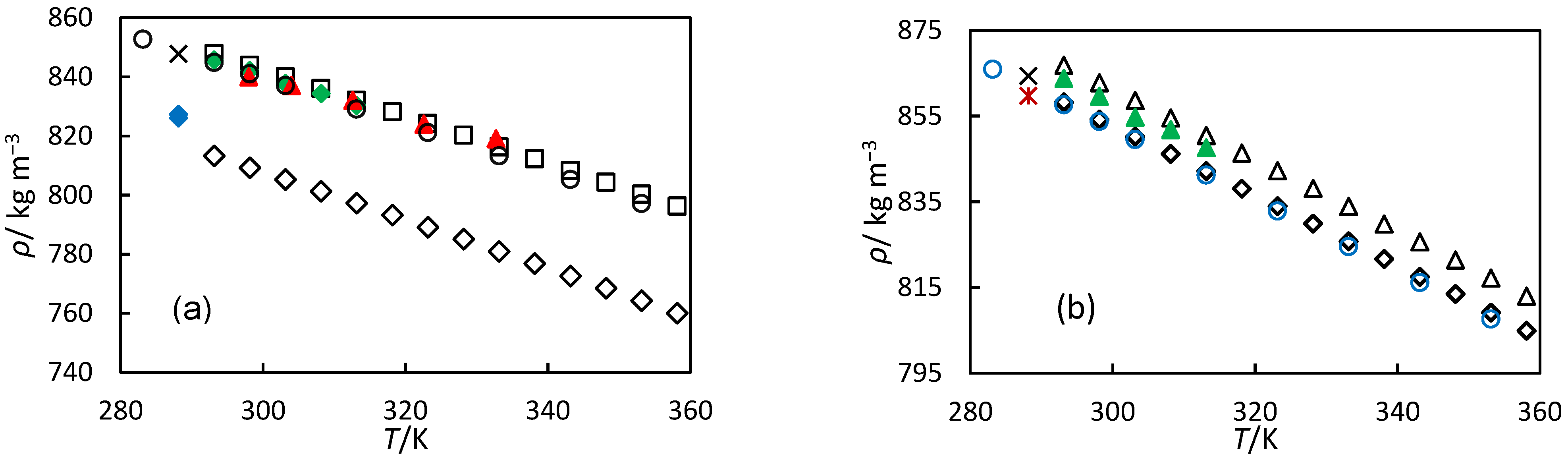
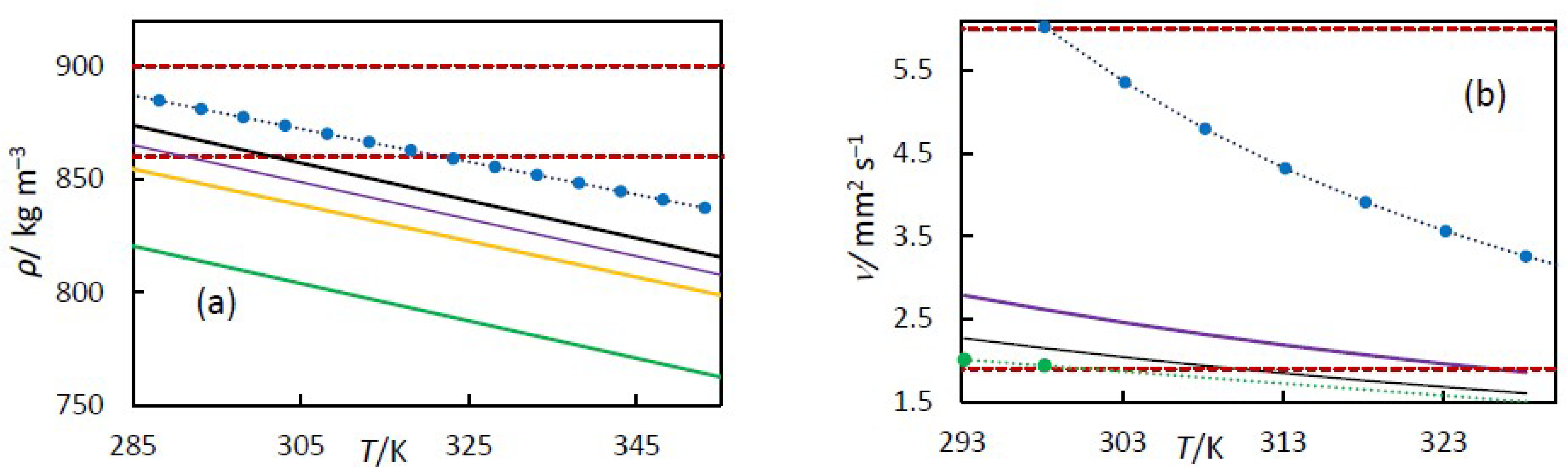
| Orange oil | d-Limonene | 94.0 | 288.15 | 847.80 | Pycnometer | [15] |
| Orange oil | Limonene | 99.0 | 298.00 | 840.00 | Pycnometer | [23] |
| 304.00 | 837.00 | |||||
| 312.60 | 832.00 | |||||
| 322.60 | 824.00 | |||||
| 332.70 | 819.00 | |||||
| Orange oil | Limonene | 96.6 | 293.15 | 845.70 | Anto PaarVTD | [24] |
| 298.15 | 842.16 | |||||
| 303.15 | 837.68 | |||||
| 308.15 | 834.33 | |||||
| 313.15 | 830.30 | |||||
| Limonene | d-Limonene | 97.5 | 283.15 | 852.70 | VTD | [33] |
| 293.15 | 844.80 | |||||
| 298.15 | 841.00 | |||||
| 303.15 | 837.00 | |||||
| 313.15 | 829.00 | |||||
| 323.15 | 821.10 | |||||
| 333.15 | 813.20 | |||||
| 343.15 | 805.20 | |||||
| 353.15 | 797.10 | |||||
| 51% hydrogenated orange oil | 1-p-Menthene | 83.1 | 288.15 | 826 | Pycnometer | [15] |
| 47% hydrogenated D-limonene | 1-p-Menthene | 93.5 | 288.15 | 827.3 | Pycnometer | [15] |
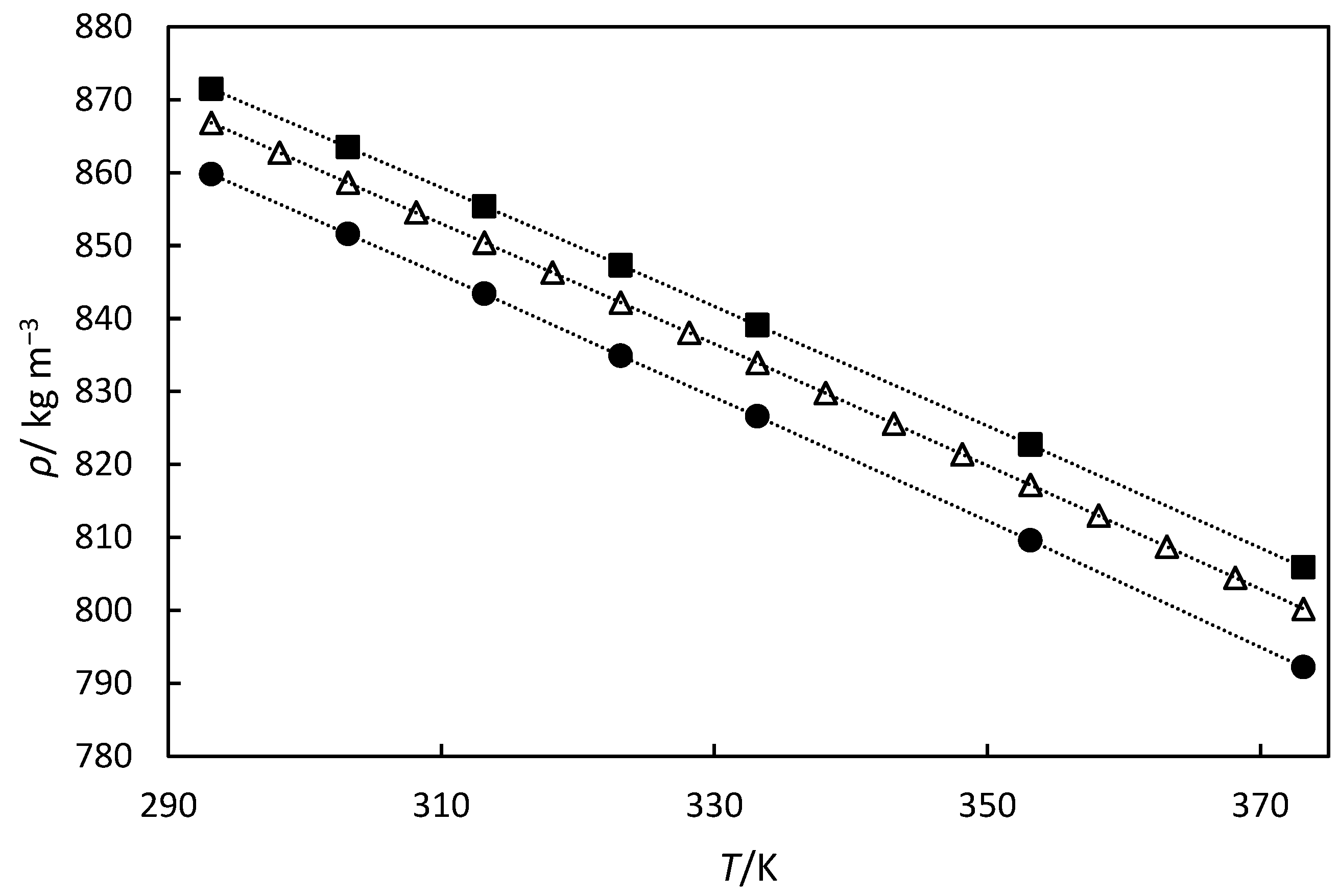
| Turpentine | α-pinene | 67.3 | 288.15 | 864.3 | Pycnometer | [14] |
| Turpentine | α-pinene | 69.8 | 293.15 | 863.75 | Anto Paar VTD | [24] |
| 298.15 | 859.59 | |||||
| 303.15 | 854.71 | |||||
| 308.15 | 851.79 | |||||
| 313.15 | 847.6 | |||||
| α-pinene | α-pinene | 98 | 293.15 | 859.8 | Anto Paar VTD | [34] |
| 303.15 | 851.6 | |||||
| 313.15 | 843.4 | |||||
| 323.15 | 834.9 | |||||
| 333.15 | 826.6 | |||||
| 353.15 | 809.6 | |||||
| 373.15 | 792.2 | |||||
| β-pinene | β-pinene | 98 | 293.15 | 871.5 | Anto Paar VTD | [34] |
| 303.15 | 863.5 | |||||
| 313.15 | 855.4 | |||||
| 323.15 | 847.3 | |||||
| 333.15 | 839.1 | |||||
| 353.15 | 822.7 | |||||
| 373.15 | 805.9 | |||||
| 59% hydrogenated turpentine | pinane | 54.2 | 288.15 | 859.7 | Pycnometer | [14] |
| pinane | pinane | 98.5 | 293.15 | 857.62 | Anto Paar VTD | [35] |
| 298.15 | 853.72 | |||||
| 303.15 | 849.79 | |||||
| 308.15 | 845.86 | |||||
| 313.15 | 841.93 | |||||
| 318.15 | 837.98 | |||||
| 323.15 | 834.04 | |||||
| 328.15 | 830.08 | |||||
| 333.15 | 826.12 | |||||
| Substance | Turpentine | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| T/K | η/mPa∙s | ρ/kg m−3 | ν/mm2 s−1 |
| 293.2 | 1.96 | 866.84 | 2.26 |
| 298.2 | 1.87 | 862.74 | 2.17 |
| 303.2 | 1.74 | 858.64 | 2.02 |
| 308.2 | 1.66 | 854.53 | 1.94 |
| 313.2 | 1.57 | 850.43 | 1.84 |
| Substance | 98% Hydrogenated Turpentine | ||
| T/K | η/mPa∙s | ρ/kg m−3 | ν/mm2 s−1 |
| 293.2 | 2.39 | 858.18 | 2.79 |
| 298.2 | 2.22 | 854.17 | 2.60 |
| 303.2 | 2.09 | 850.16 | 2.46 |
| 308.2 | 1.97 | 846.14 | 2.33 |
| 313.2 | 1.84 | 842.10 | 2.18 |
| 318.2 | 1.73 | 838.05 | 2.06 |
| 323.2 | 1.61 | 833.98 | 1.93 |
| 328.2 | 1.56 | 829.88 | 1.88 |
| Substance | 79% Hydrogenated Orange Oil | ||
| T/K | η/mPa∙s | ρ/kg m−3 | ν/mm2 s−1 |
| 293.2 | 1.63 | 813.20 | 2.01 |
| 298.2 | 1.57 | 809.22 | 1.94 |
| Turpentine | 98% Hydrogenated Turpentine | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Viscosity | ||||||
| Coefficients and 95% Confidence Bounds | ||||||
| Value | Lower | Upper | Value | Lower | Upper | |
| A/mPa·s | 0.0569 | 0.0286 | 0.0851 | 0.0391 | 0.0325 | 0.0456 |
| b/K | 1038.5 | 888.7 | 1188.3 | 1206.0 | 1154.6 | 1257.3 |
| AAD/mPa∙s | 0.010 | 0.012 | ||||
| 100AARD | 0.5 | 0.7 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9939 | 0.9982 | ||||
| RMSE/mPa·s | 0.0142 | 0.0136 | ||||
| Kinematic Viscosity | ||||||
| Coefficients and 95% Confidence Bounds | ||||||
| Value | Lower | Upper | Value | Lower | Upper | |
| A/mm2 s−1 | 0.0883 | 0.0449 | 0.1318 | 0.0621 | 0.0516 | 0.0727 |
| b/K | 951.25 | 802.67 | 1099.80 | 1114.80 | 1062.80 | 1166.70 |
| AAD/mm2 s−1 | 0.011 | 0.011 | ||||
| 100AARD | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9929 | 0.9978 | ||||
| RMSE/mm2 s−1 | 0.0164 | 0.0163 | ||||
| Substance | Main Component/ | T/ | η/ | ν/ | Method | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mass%) | K | mPa∙s | mm2 s−1 | ||||
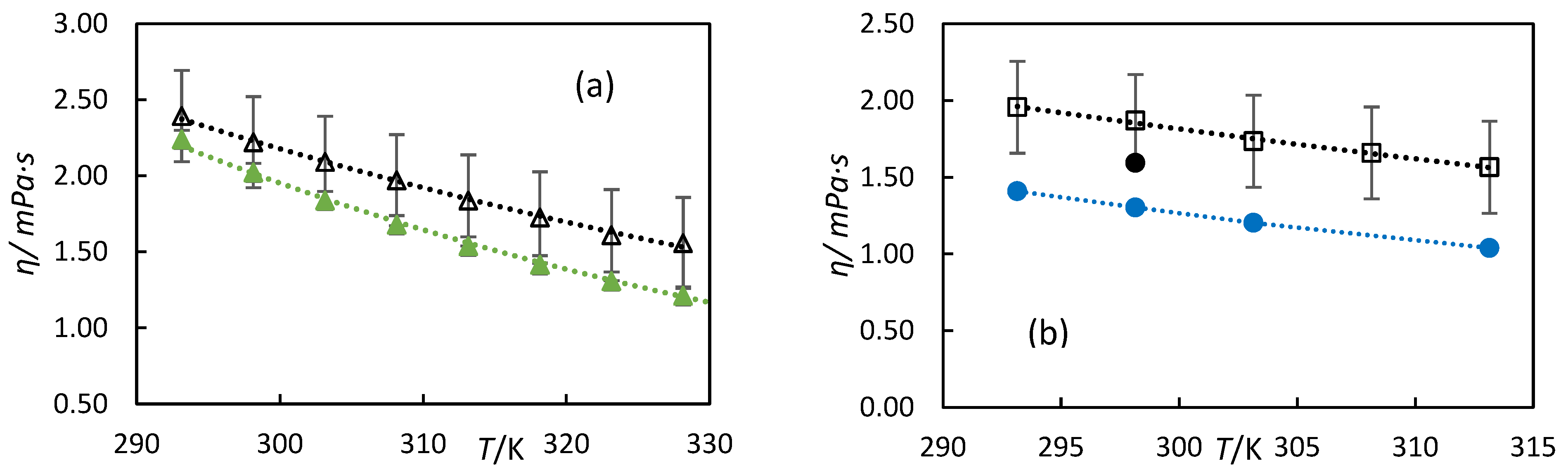
| Orange oil | Limonene | 94.0 | 313 | 0.99 | CANNON-FENSKE capillary viscometer | [15] | |
| Orange oil | Limonene | 99.0 | 293.15 | 1.1 | Falling weight viscometer | [23] | |
| 303.15 | 0.96 | ||||||
| 313.15 | 0.78 | ||||||
| 323.15 | 0.65 | ||||||
| 333.15 | 0.64 | ||||||
| Limonene | Limonene | 97.5 | 283.15 | 1.08 | Anton Paar Stabinger viscometer | [33] | |
| 293.15 | 0.93 | ||||||
| 298.15 | 0.90 | ||||||
| 303.15 | 0.82 | ||||||
| 313.15 | 0.72 | ||||||
| 323.15 | 0.65 | ||||||
| 333.15 | 0.58 | ||||||
| 343.15 | 0.52 | ||||||
| 353.15 | 0.48 | ||||||
| 51% hydrogenated orange oil | 1-p-Menthene | 83.1 | 313.00 | 1.14 | CANNON-FENSKE capillary viscometer | [15] | |
| 47% hydrogenated D-limonene | 1-p-Menthene | 93.5 | 313.00 | 0.98 | |||
| Turpentine | α-pinene | 67.3 | 313 | 1.35 | CANNON-FENSKE capillary viscometer | [14] | |
| α-pinene | α-pinene | 313 | 1.29 | ||||
| α-pinene | α-pinene | 98.8 | 283.15 | 1.676 | Ubbelohde capillary viscometers | [33] | |
| 293.15 | 1.409 | ||||||
| 298.15 | 1.303 | ||||||
| 303.15 | 1.203 | ||||||
| 313.15 | 1.039 | ||||||
| 323.15 | 0.908 | ||||||
| 333.15 | 0.804 | ||||||
| 343.15 | 0.71 | ||||||
| 353.15 | 0.635 | ||||||
| β-pinene | β-pinene | 99 | 298.15 | 1.594 | Ubbelhode capillary viscometers | [37] | |
| β-pinene | β-pinene | 313 | 1.42 | CANNON-FENSKE capillary viscometer | [14] | ||
| 59% hydrogenated turpentine | pinane | 54.2 | 313 | 1.70 | CANNON-FENSKE capillary viscometer | [14] | |
| Pinane | pinane | 98.5 | 293.15 | 2.24 | Falling ball viscometer (Anton Paar, AMVn) | [35] | |
| 298.15 | 2.023 | ||||||
| 303.15 | 1.838 | ||||||
| 308.15 | 1.679 | ||||||
| 313.15 | 1.538 | ||||||
| 318.15 | 1.415 | ||||||
| 323.15 | 1.308 | ||||||
| 328.15 | 1.211 | ||||||
| 333.15 | 1.126 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mellows, B.; Sanchez-Vicente, Y. Density and Viscosity of Orange Oil, Turpentine, and Their Hydrogenated Derivatives as Biofuel Components. Thermo 2025, 5, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040059
Mellows B, Sanchez-Vicente Y. Density and Viscosity of Orange Oil, Turpentine, and Their Hydrogenated Derivatives as Biofuel Components. Thermo. 2025; 5(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleMellows, Brent, and Yolanda Sanchez-Vicente. 2025. "Density and Viscosity of Orange Oil, Turpentine, and Their Hydrogenated Derivatives as Biofuel Components" Thermo 5, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040059
APA StyleMellows, B., & Sanchez-Vicente, Y. (2025). Density and Viscosity of Orange Oil, Turpentine, and Their Hydrogenated Derivatives as Biofuel Components. Thermo, 5(4), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/thermo5040059







