Phototoxicity of Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones: A Mechanistic Review About Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
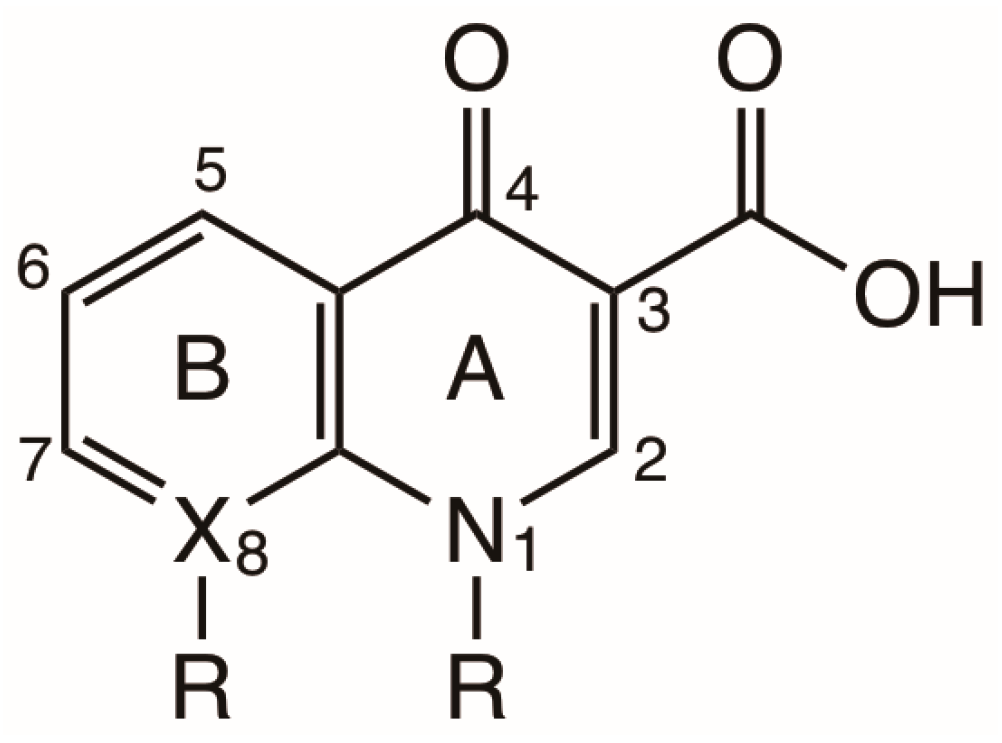
2. Structure and Properties
2.1. Photophysical and Photochemical Processes in Qs and FQs
2.2. Structure and Photochemistry of Qs and FQs
2.2.1. Decarboxylation
2.2.2. Side Chain Oxidation and C-N Cleavage in FQs
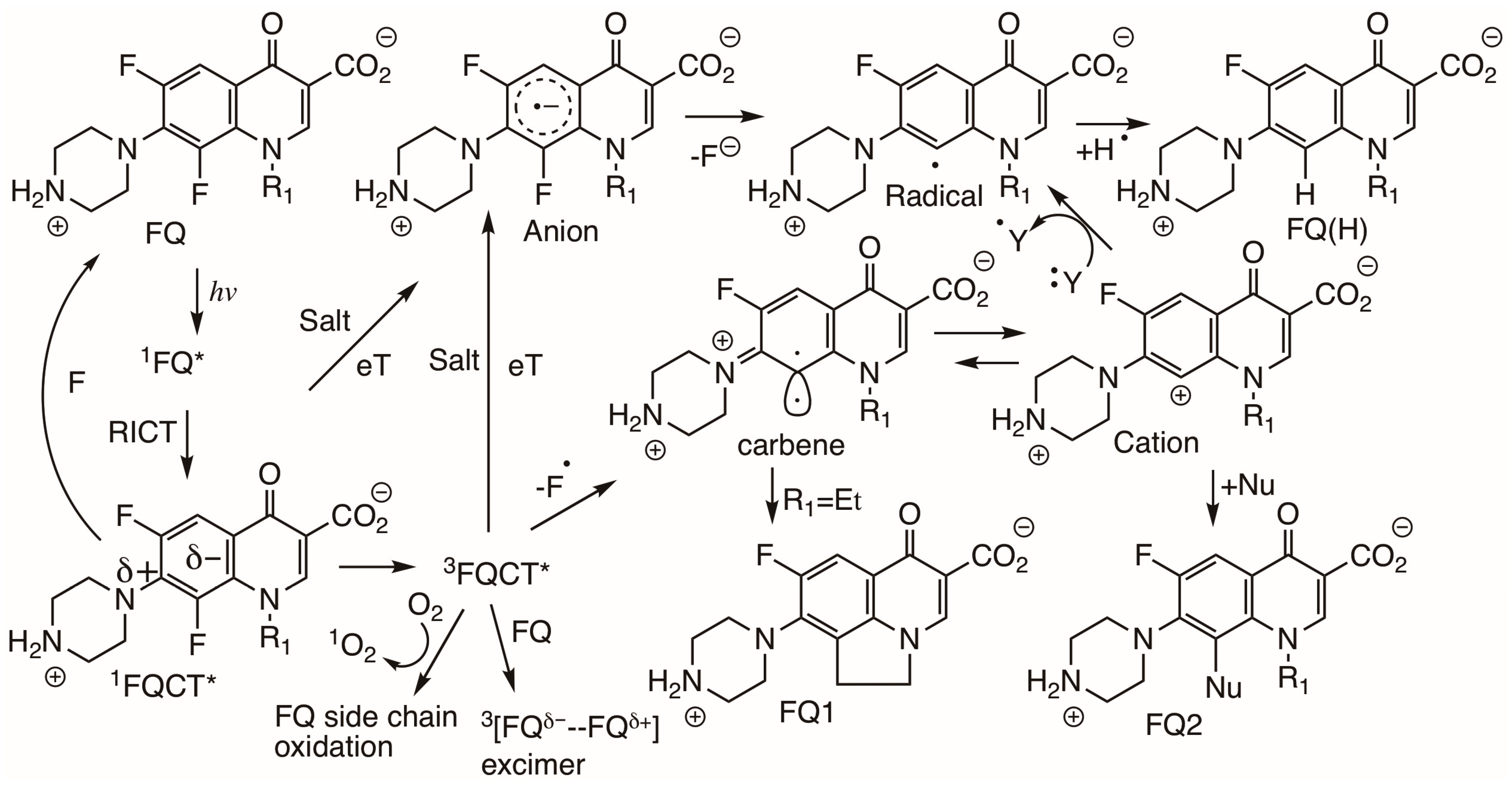
2.2.3. C6-F Cleavage in FQs and Phototoxicity
2.2.4. C8-F Cleavage in FQs and Phototoxicity
2.2.5. C5 Substitution in FQs and Phototoxicity
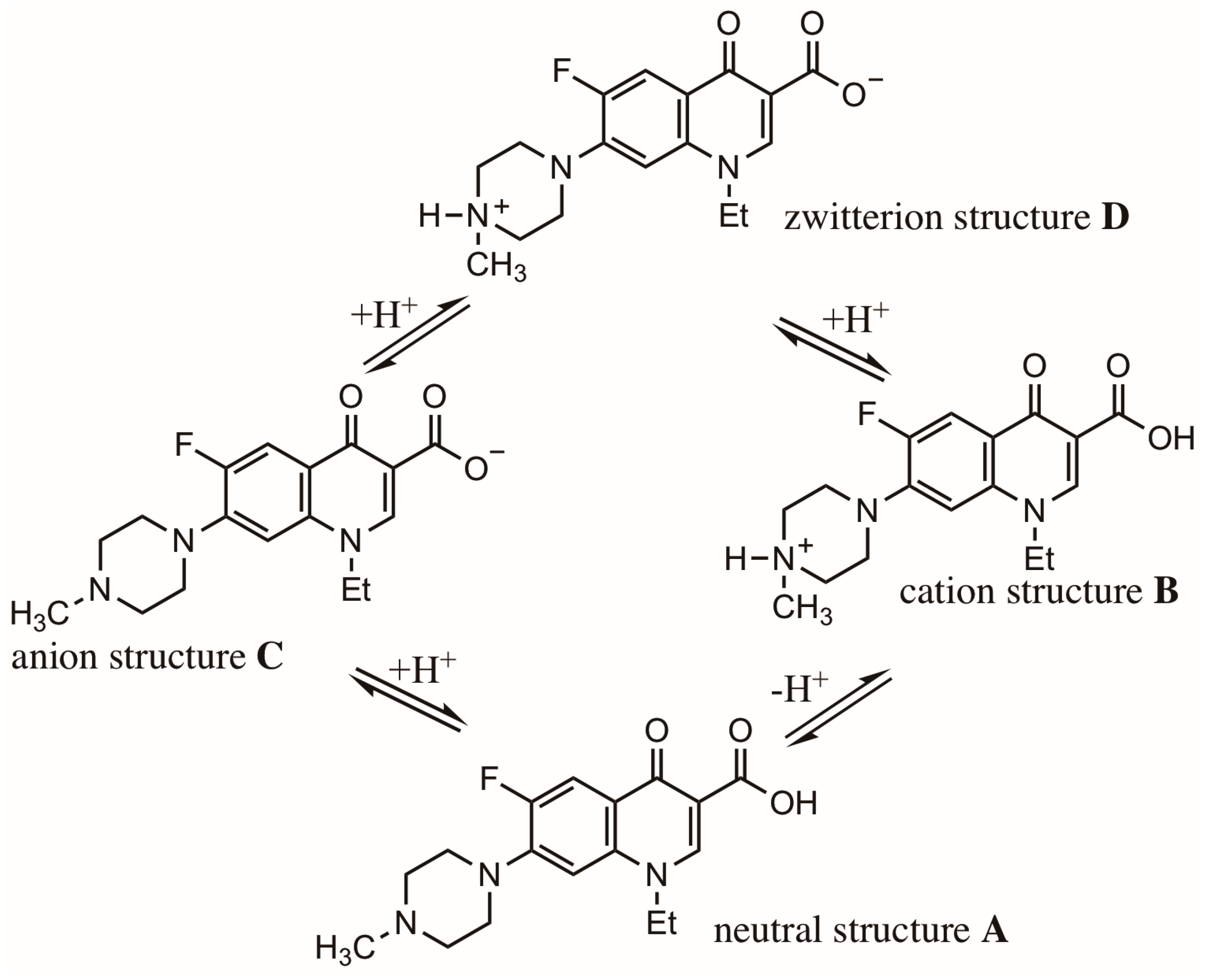
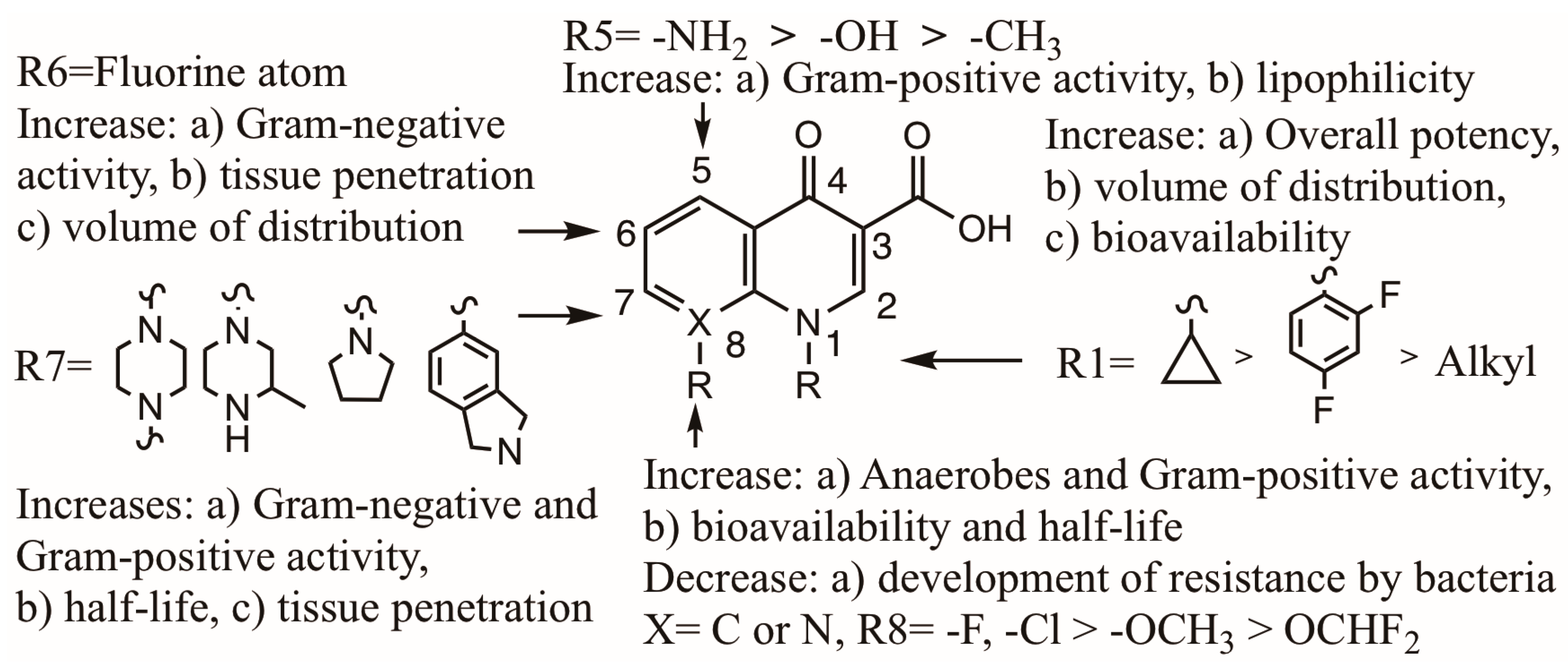
2.3. Structure and Biological Properties of Qs and FQs
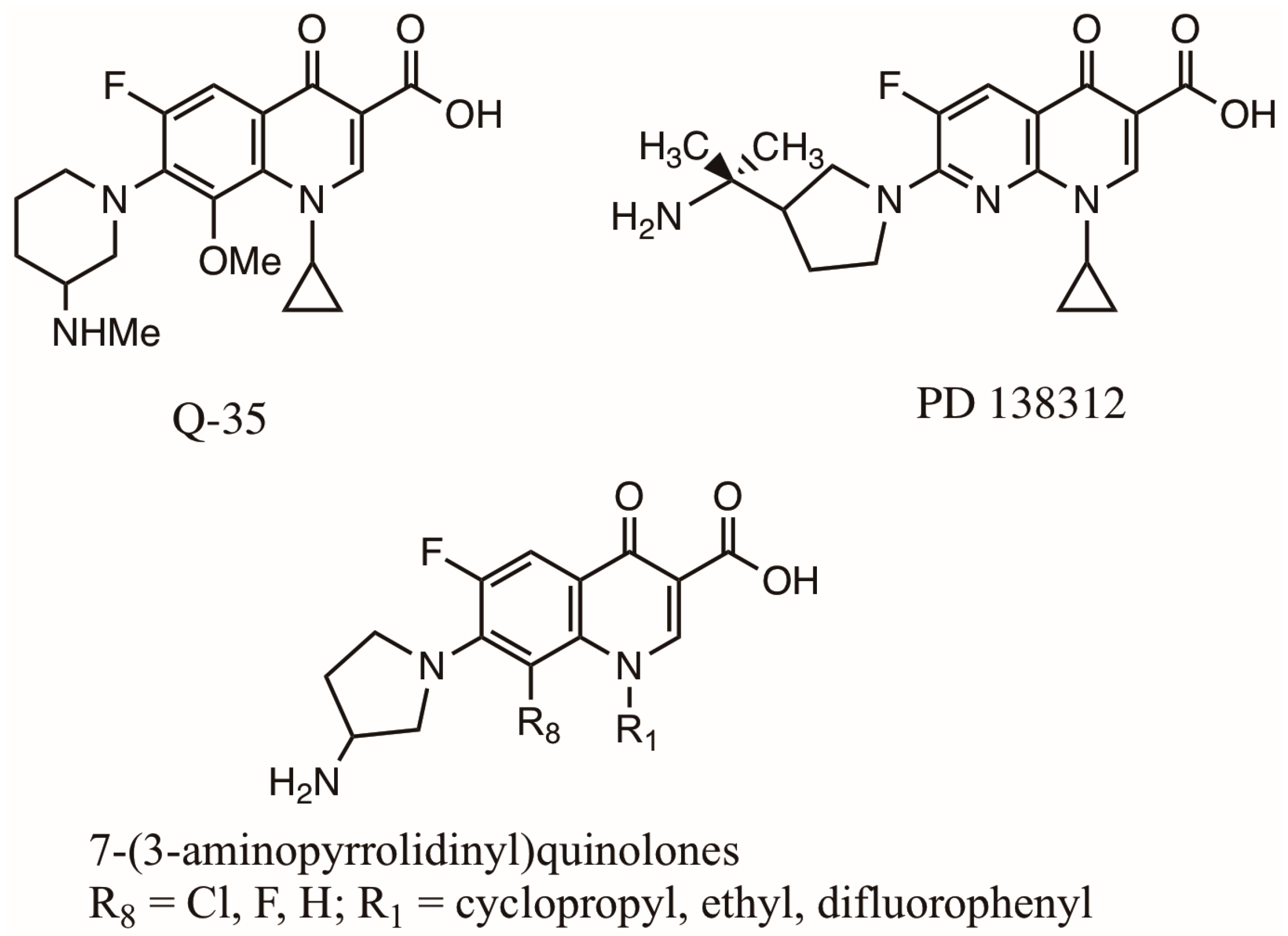
2.4. Qs and FQs Developed in Recent Decades
- (1).
- They have a broader spectrum of activity, and they are active against resistant bacteria.
- (2).
- Delafloxacin and finafloxacin are very active in an acidic pH.
- (3).
- Due to a high binding capacity to phosphatidylserine, lascufloxacin has a high tissue penetration.
- (4).
- With the exception of nemonoxacin, they contain a F in C6, which increases the biological activity against Gram-negative bacteria and the degree of penetration into bacterial cells.
- (5).
- They have an alkyl, aryl or cyclopropyl substituent on N1. This increases the bacterial activity, volume of distribution and bioavailability.
- (6).
- They contain a cyclic amine in C7, different to the piperazine present in earlier FQs.
- (7).
- They do not contain a F atom on C8, which is known to cause severe adverse effects, such as phototoxicity. Some of them contain a methoxy on C8, which is known to reduce phototoxicity.
- (8).
- They all present mild adverse effects, including phototoxicity.
3. Relationship Between Photophysics, Photochemistry and Phototoxicity of FQs
3.1. Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways Involved with Monohalogenated FQs
3.2. Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways Involved with Dihalogenated FQs
3.3. Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways for Nonhalogenated Qs Like Nalidixic Acid
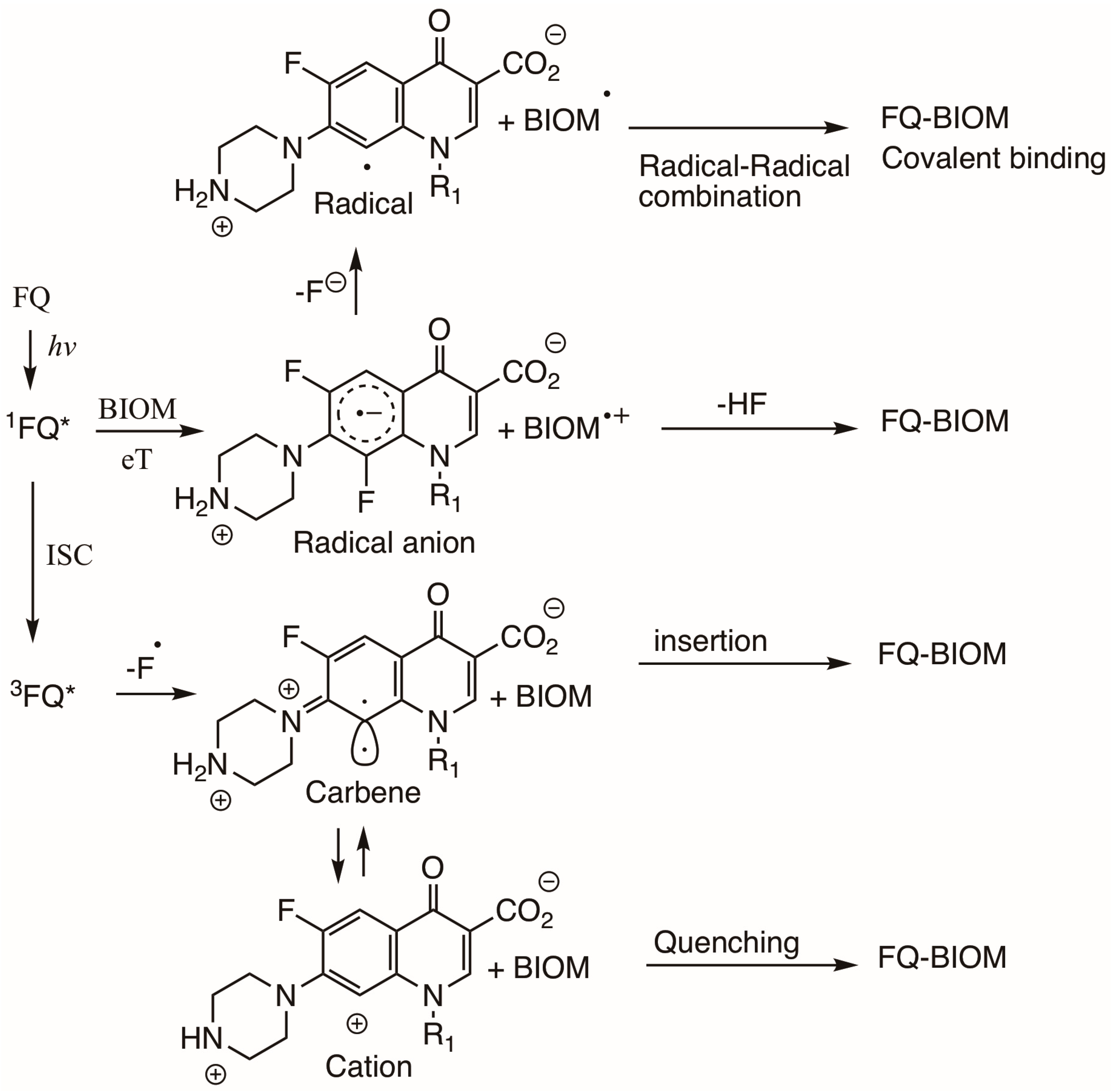
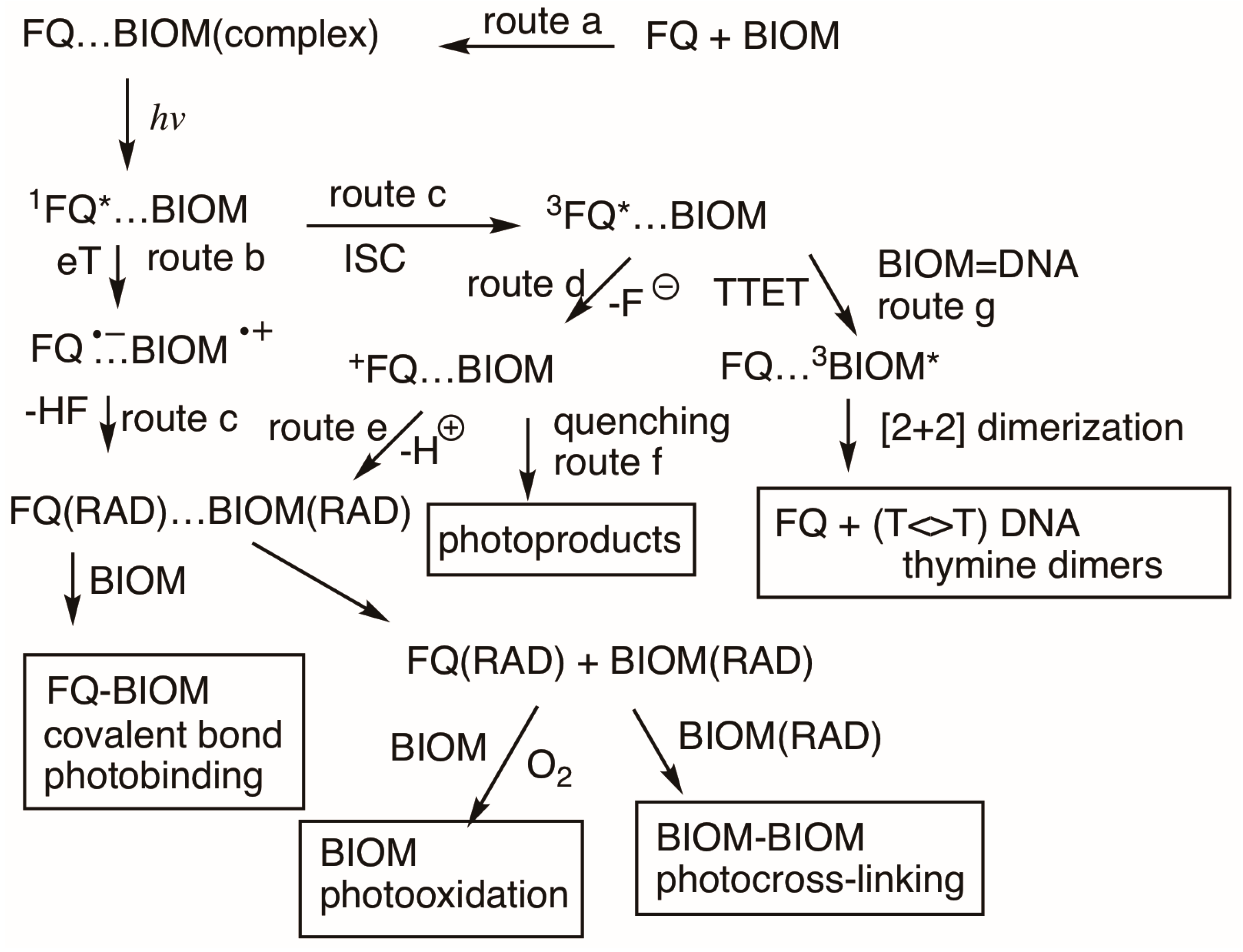
3.4. Photosensitized Biological Damage by Qs and FQs
3.5. Photochemical Reactions Between Q Intermediates and Monomers of Biomolecules
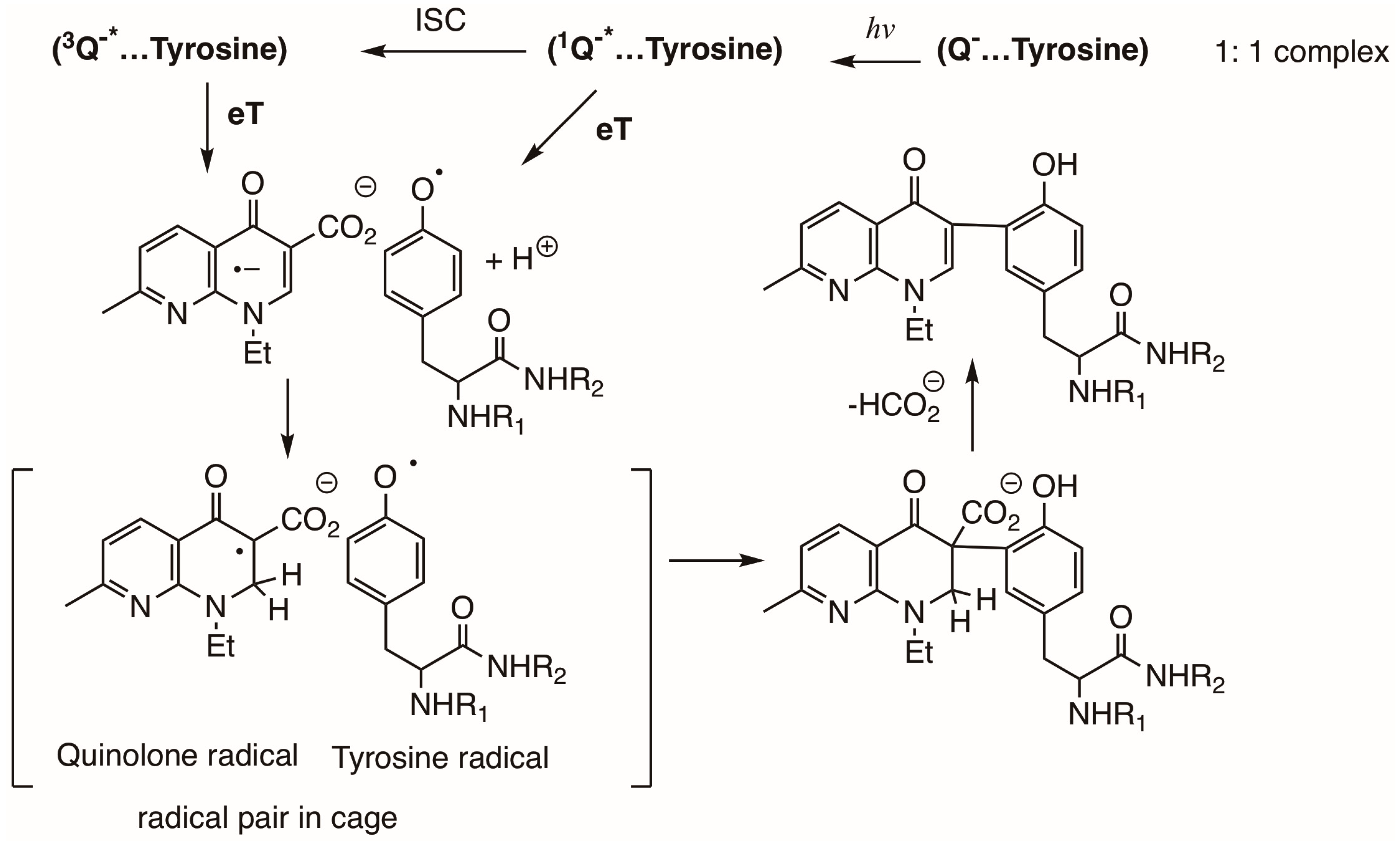
3.6. Photosensitized Reactions with Proteins by Qs and FQs
3.7. Photosensitized Reactions in DNA by Qs and FQs
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitscher, L.A. Bacterial Topoisomerase Inhibitors: Quinolone and Pyridone Antibacterial Agents. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 559–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfred, K.J.; Kerns, R.J.; Osheroff, N. Mechanim of Quinolone Action and Resistance. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, V.E.; Osheroff, N. Type II Topoisomerases as targets for Quinolone Antibacterials: Turning Dr. Jeryll into Mr Hyde. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2001, 7, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhi, N.; Bahraminejad, M.; Saeedi, M.; Mirfazli, S.S. A review: DFA-approved fluorine-containing small molecules from 2015 to 2022. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 260, 115758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanel, G.G.; Ennis, K.; Vercaigne, L.; Walkty, A.; Gin, A.S.; Embil, J.; Smith, H.; Hoban, D.J. A Critical Review of the Fluoroquinolones. Focus on Respiratory Tract Infections. Drugs 2002, 62, 13–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, A.; Monti, A. Photophysics and photochemistry of fluoroquinolonas. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisacchi, G.S. Origins of the Quinolone Class of Antibacterials: An Expanded Discovery Story. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4874–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, A.; Badshah, S.L.; Muska, M.; Ahmad, N.; Khan, K. The Current Case of Quinolones: Synthetic Approaches and antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2016, 21, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Saxena, N.; Mehrotra, A.; Srivastava, N. Review: Studies on the Synthesis of Quinolone Derivatives with their Antibacterial Activity (Part 1). Curr. Org. Chem. 2020, 24, 817–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Shankhdhar, S.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, N. Part 2. Studies on the Synthesis of Quinolone Derivatives with Their Biological Activity. Curr. Org. Chem. 2024, 28, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, S.; Leyva, E. Thermochemical reaction of 7-azide-1-ethyl-6,8-difluoroquinolone-3-carboxylate with heterocyclic amines. An expeditious synthesis of novel fluoroquinolone derivatives. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, E.; de Loera, D.; Leyva, S. Photochemistry of 7-azide-1-ethyl-3-carboxylate-6,8-difluoroquinolone: A novel reagent for photoaffinity labeling. Tett. Lett. 2008, 49, 6759–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.I.; Lu, L.; Plaisance, C.J.; Daniel, C.P.; Flanagan, C.J.; Wenger, D.M.; McGregor, D.; Varrassi, G.; Kaye, A.M.; Ahmadzadeh, S.; et al. Fluoroquinolones: Neurobiological Complications and Side Effets in Clinical Practice. Cureus 2024, 16, e54565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, R.C.; Ambrose, P.G. Antimicrobial Safety: Focus on Fluoroquinolones. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, S144–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon, C. Comparison of Side Effects of Levofloxacin versus Other Fluoroquinolones. Chemotheraphy 2001, 47, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, N.G.; Diez-Santos, I.; Abbot, L.R.; Maxwell, A. Quinolones: Mechanism, Lethality and Their Contributions to Antibiotic Resistance. Molecules 2020, 25, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, X.; Feng, L.S. 4-Quinolone derivatives and their activities against Gram positive Pathogens. Eur. J. Chem. 2017, 143, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takács-Novák, K.; Noszál, B.; Hermecz, I.; Keresztúri, G.; Podányi, B.; Szász, G. Protonation Equilibria of Quinolone Antibacterials. J. Pharm. Sci. 1990, 79, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.; Tóth, G.; Azocs, L.; Kökósi, J.; Kraszni, M.; Gyéresi, A.; Noszál, B. Triprotic site-specific acid-base equilibria and related properties of fluoroquinolone antibacterials. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 66, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresta, M.; Guccione, S.; Beccari, A.R.; Furneri, P.M.; Puglisi, G. Combining molecular modeling with experimental methodologies: Mechanism of membrane permeation and accumulation of ofloxacin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 10, 3871–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barret, R. Importance and Evaluation of Liphophilicity. In Therapeutical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuprys, A.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.K.; Drogui, P.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R. Y: Fluoroquinolones metal complexation and its environmental impacts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 376, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Ohta, Y.K.I.; Kitaoka, H. Photochemical behavior of Sitafloxacin, Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic, in an Aqueous Solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, R.; Anwar, Z.; Mustn, N.; Ahmad, I. Photochemistry of Fluoroquinolones: A Review. Baqai J. Health Sci. 2017, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sortino, S.; De Guidi, G.; Giuffrida, S.; Monti, S.; Velardita, A. pH Effects on the Spectroscopic and photochemical Behavior of Enoxacin: A Steady-State and Time-Resolved Study. Photochem. Photobiol. 1998, 67, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratnam, S.; Claridge, J. Primary Photophysical Properties of Ofloxacin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, 72, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sortino, S.; Marconi, G.; Giuffrida, S.; De Guidi, G.; Monti, S. Photophysical Properties of Rubofloxacin in Neutral Aqueous Solution. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 70, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belvedere, A.; Boscá, F.; Cuquerella, M.C.; De Guidi, G.; Miranda, M.A. Photoinduced N-Demethylation of Rufloxacin and its Methyl Ester Under Aerobic Conditions. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, S.; Sortino, S.; Fasani, E.; Albini, A. Multifaceted Photoreactivity of 6-Fluoro-7-aminoquinolones from the Lowest Excited States in Aqueous Media: A Study of Nanosecond and Picosecond Spectroscopic Techniques. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazin, M.; Bosca, F.; Marin, M.L.; Miranda, M.A.; Patterson, L.K.; Santus, R.; Laser, A. Flash Study and Pulse Radiolysis Study of Primary Photochemical Processes of Flumequine. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, 72, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeersch, G.; Ronfard-Haret, J.C.; Bazin, M.; Carillet, V.; Morliere, P.; Santus, R. Type I and Type II Photosensitization by the Antibacterial Drug Nalidixic Acid. A laser Flash Photolysis Study. Photochem. Photobiol. 1991, 54, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mella, M.; Fasani, E.; Albini, A. Photochemistry of 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid(=Ciprofloxacin) in Aqueous Solutions. Helv. Chim. Acta 2001, 84, 2508–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasani, E.; Barberis Negra, F.F.; Mella, M.; Monti, S.; Albani, A. Photoinduced C-F Cleavage in Some Fluorinated 7-Amino-4-quinolone-3-carboxylic Acids. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 5388–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, L.J.; Sik, R.H.; Chignell, C.F. Fluoroquinolone Antimicrobials: Singlet Oxygen, Superoxide and Phototoxicity. Photochem. Photobiol. 1998, 67, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheife, R.T.; Cramer, W.R.; Decker, E.L. Photosensitizing potential of ofloxacin. Int. J. Dermatol. 1993, 32, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokura, Y.; Nishijima, T.; Yagi, H.; Furukawa, F.; Takigawa, M. Photohaptenic Properties of Fluoroquinolones. Photochem. Photobiol. 1996, 64, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasani, E.; Profumo, A.; Albini, A. Structure and Medium-Dependent Photodecomposition of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics. Photochem. Photobiol. 1998, 68, 666–674. [Google Scholar]
- Condorelli, G.; De Guidi, G.; Giuffrida, S.; Sortino, S.; Chillemi, R.; Sciuto, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Photosensitization Induced by Drugs XII. Photochemistry and Photosensitization of Rufloxacin. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999, 70, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belvedere, A.; Boscá, F.; Catalfo, A.; Cuquerella, M.C.; de Guidi, G.; Miranda, M.A. Type II Guanine Oxidation Photoinduced by the Antibacterial Fluoroquinolone Rufloxacin in Isolated DNA and in 2′Deoxyguanosine. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 5, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosa, G.; Scaiano, J.C. Laser Techniques in the Study of Drug Photochemistry. Photochem. Photobiol. 2004, 80, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, D.J.; Chakraborty, M.; Abdelaziz, N.; Duley, A.; Gudmundsdottir, A.D. Review of laser flash photolysis of organic molecules (2015–2018). Photochemistry 2020, 47, 70–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W. Photochemical properties of Gemifloxacin: A laser flash photolysis study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2015, 143, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Tang, R.; Tang, Z.; Xing, Z.; Yao, S.; Fu, H.; Wang, W. Photophysical properties of gatifloxacin in aquous solution by laser photolysis and pulse radiolysis. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuquerella, M.C.; Miranda, M.A.; Boscá, F. Role of Singlet Intramolecular Charge Transfer in the photophysical Properties of Norfloxacin and Its Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuquerella, M.C.; Boscá, F.; Miranda, M.A. Photonucleic Aromatic Substitution of 6-fluoroquinolones in Basic Media: Triplet Quenching of Hydroxide Anion. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 7256–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasani, E.; Mella, M.; Albani, A. Photochemistry of the Phototoxic Drug Lomefloxacin: Paths Observed in the presence of Amines or NaOH and from the Methyl Ester. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 5075–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Chen, J.; Song, B.; Ma, H.; Fu, Z.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M. Time-gated luminescence imaging of singlet oxygen photoinduced by fluoroquinolones and functionalized graphenes in Daphnia magna. Aquatic Toxicol. 2017, 191, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosca, F.; Lhiaubet-Vallet, V.; Cuquerella, M.C.; Castell, J.V.; Miranda, M.A. The Triplet Energy of Thymine in DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6318–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, G.; Facciolo, L.; Canton, M.; Vedaldi, D.; Dall’Acqua, F.; Aloisi, G.G.; Amelia, M.; Barbafina, A.; Elisei, F.; Latterini, L. Photophysical and phototoxic properties of the antibacterial fluoroquinolones levofloxacin and moxifloxacin. Chem. Biodivers. 2004, 1, 782–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovdahl, M.J.; Priebe, S.R. Characterization of clinafloxacin photodegradation products by LC-MS/MS and NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasani, E.; Monti, S.; Manet, I.; Tilocca, F.; Petali, L. Inter- and Intramolecular Photochemical Reactions of Fleroxacin. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, F.; Navaratnam, S.; Edge, R.; Allen, N.S. Primary Photophysical Properties of Moxifloxacin. A Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, S.; Sortino, S. Laser flash photolysis study for Photoionization in fluoroquinolones. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002, 1, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, S.; Bosca, F. Photoreactivity of Fluoroquinolones: Nature of Aryl cations Generated in Water. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3940–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, S.; Cuquerella, M.C.; Lhiaubert-Vallet, V.; Edge, R.; Bosca, F. Seeking the mechanism responsible for fluoroquinolone photomutagenicity: A pulse radiolysis, steady-state, and laser flash photolysis study. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 67, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, F.; Navaratnam, S.; Allen, N.S. Formation of Secondary Triplet Species after Excitation of Fluoroquinolones in the Presence of Relative Strong Bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12238–12239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-Gonzalez, C.; Soldevilla, S.; Garcia-Lainez, G.; Bosca, F. Chemical tuning for potential antitumor fluoroquinolonas. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2019, 141, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, S.; Bosca, F. Assessing physical properties of amphoteric fluoroquinolones using phosphorescence spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 227, 117569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuquerella, M.C.; Andreu, I.; Soldevilla, S.; Bosca, F. Triplet Excimers of Fluoroquinolones in Aquous Media. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 5030–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; HaiXia, L.; SiDe, Y.; WenFeng, W. Effects of pH and polarity on the excited states of norfloxacin and its 4′-N-acetyk derivative: A steady-state and time-resolved study. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iesce, M.R.; Cermola, F.; Termussi, F. Photooxygenation of Heterocycles. Curr. Org. Chem. 2005, 9, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miolo, G.; Viola, G.; Vedaldi, D.; Dall’Acqua, F.; Fravolini, A.; Tabarrini, O. In vitro phototoxic properties of new 6-des-fluoro and 6-fluoro-8-methylquinolones. Toxicol. Vitr. 2002, 16, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Baker, C.A. Fluoroquinolone Toxicity Profiles: A Review Focusing on Newer Agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wammer, K.H.; Korte, A.R.; Lundeen, R.A.; Sundberg, J.E.; McNeill, K.; Arold, W.A. Direct photochemistry of three fluoroquinolone antibacterial: Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin. Water Res. 2013, 47, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, G.; Hidalgo, M.E.; Vivanco, J.M.; Escobar, J. Induces and Photoinduced DNA Damage by Quinolones: Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin and Nalidixic Acid Determined by Comet Assay. Photochem. Photobiol. 2005, 81, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagala, J.M.; Hagen, S.E.; Joannides, T.; Kiely, J.S.; Laborde, E.; Schroeder, M.C.; Sesnie, J.A.; Shapiro, M.A.; Suto, M.J.; Vanderroest, S. Quinolone antibacterials containing the new 7-[3-(1-aminoethyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl] side chain: The effects of the 1-aminoethyl moiety and its stereochemical configurations on potency and in vivo efficacy. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagala, J.M.; Bridges, A.J.; Culbertson, T.P.; Gambino, L.; Hagen, S.E.; Karrick, G.; Porter, K.; Sanchez, J.P.; Sesnie, J.A.; Spense, F.G.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Activity of 5-Amino and 5-Hydroxyquinolones, and the Overwhelming Influence of the Remote N1-Substituent in Determining the Structure-Activity Relationship. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 34, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, J.H.; Reeves, D.S. Clinical features and Management of Adverse Effects of Quinolone Antibacterials. Drug Saf. 1991, 6, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagala, J.M. Structure-activity and structure-side-effect relationships for the quinolone antibacterial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1994, 33, 685–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabe, K.; Goto, K.; Jindo, T.; Sekiguchi, M.; Furuhama, K. Structure-phototoxicity relationship in Balb/c mice treated with fluoroquinolone derivatives, followed by ultraviolet-A irradiation. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 157, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, L.; Tillotson, G. Safety of Fluoroquinolones: An Update. Can. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 131, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasani, E.; Rampi, M.; Albini, A. Photochemistry of some fluoroquinolones: Effect of pH and chloride ion. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1999, 9, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasani, E.; Mella, M.; Caccia, D.; Tassi, S.; Fagnoni, M.; Albini, A. The photochemistry of Lomefloxacin. An aromatic carbene as the key intermediate in photodecomposition. Chem. Commun. 1997, 14, 1329–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.J.; Li, G.; Chignell, C.F. Photogeneration of Fluoride by the Fluoroquinolone Antimicrobial Agents Lomefloxacion and Fleroxacin. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 65, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimura, T.; Ohno, T.; Matsukura, H.; Nobuhara, Y. Photodegradation Kinetics of the New Antibacterial Fluoroquinolone Derivative, Orbifloxacin, in Aqueous Solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 43, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimura, T.; Nobuhara, Y.; Matsukura, H. Photodegradation Products of a New Antibacterial Fluoroquinolone Derivative, Orbifloxacin, in Aqueous Solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimura, T.; Kohno, K.; Nobuhara, Y.; Matsukura, H. Photoreaction and Active Oxygen Generation by Photosensitization of a New Fluoroquinolone Derivative, Orbifloxacin, in the Presence of Chloride Ion. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, M.; Ruesing, G.; Soergel, F.; Holzgrabe, U. Defluorinated Sparfloxacin as a New Product Identified by Liquid Chromathography Coupled with UV Detection and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Antimicrob. Agent. Chemother. 1998, 42, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroz, H.B.; Kempt, T.J.; Przybytniak, G.K. Substituent effects on the production and electronic spectra of intermediates in the photodecomposition of ArN2+. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1992, 68, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, G.; Richard, C.; Köhler, G. Formation and reactivity of 4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dienylidene in the photolysis of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solution at ambient temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 11470–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichiarante, V.; Pretali, L.; Fasani, E.; Albani, A. Photochemistry of some nonzwitterionic fluoroquinolones. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 265, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasani, E.; Mella, M.; Monti, S.; Albani, A.A. Unexpected Photoreactions of Some 7-Amino-6-fluoroquinolones in Phosphate Buffer. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 2001, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K. Comparative grepafloxacin photoxicity in mouse skin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1998, 42, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, A.; Mujtaba, S.F.; Kushwawa, H.N.; Ali, D.; Yadav, N.; Singh, S.K.; Ray, R.S. Photosensitizing mechanism and identification of of levofloxacin photoproducts at ambient UV radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Guo, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ji, T.; Lin, Z.; Wang, W. Effect of C-5 position on the photochemical properties and phototoxicity of antofloxacin and levofloxacin: A stable and transient stydy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. Biol. 2016, 155, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.E.; Kennelley, G.E.; Amaye-Obu, T.; Jowdy, P.F.; Ghadersohi, S.; Nasir-Moin, M.; Paragh, G.; Berman, A.A.; Huss, W.J. The phenomenon of phototoxicity and long-term risks of commonly prescribed and structurally diverse drugs. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2024, 19, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marutani, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Otabe, Y.; Nagamuta, M.; Tanaka, K.; Miyoshi, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Nagano, H.; Matsubara, S.; Kamide, R.; et al. Reduced Phototoxicity of a Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Agent with a Methoxy Group at the 8 Position in Mice Irradiated with Long-Wavelenght UV Light. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, S.E.; Domagala, J.M.; Gracheck, S.J.; Sesnie, J.A.; Stier, M.A.; Suto, M.J. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of New Quinolones Containing a 7-[3-(1-amino-1-methylethyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl] Moiety. Gram-Positive Agents with Excellent Oral Activity and Low Side Effect Potential. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Nakata, Y.; Yazaki, A. New Finding on the Structure-phototoxicity Relationship and Photostability of Fluoroquinolones with Various Substituents at Position 1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, N.J.; Barratt, M.D.; Lovell, W.W.; Ferguson, J.; Gibbs, N.K. Comparison of an In Vitro Cellular Photoxicity Model Against Controlled Clinical Trials of Fluoroquinolone Skin Phototoxicity. Toxicol. Vitr. 2000, 14, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, Y.; Inoue, R.; Ochi, M.; Gandy, G.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Combined Use of In Vitro Phototoxic Assessments and cassete Dosing Pharmacokinetics Study for Photoxicity Caracterizacion of Fluoroquinolones. AAPS J. 2011, 30, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J. Phototoxicity Due to Fluoroquinolones. In Quinolone Antimicrobial Agents; Hooper, D.C., Rubinstein, E., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-119-73865-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, P.C.; Hunter, P.A. The fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Past, present and future perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 16, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, L.R. Quinolone Molecular Structure-Activity Relationships: What We Have Learned about Improving antimicrobial Activity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, S180–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighty, K.E.; Gootz, T.D. The chemistry and biological profile of trovafloxacin. J. Antimicrob. Agent Chemother. 1997, 39 (Suppl. B), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.N.; Lamb, H.M. Gemifloxacin. Drugs 2000, 59, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhao, X.; Domagala, J.; Drlica, K. Fluoroquinolone Action against Mycobacteria: Effect of C-8 Substituents on Growth, Survival, and Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, A.; Hoshino, K.; Kimura, Y.; Hayakawa, I.; Sato, K. Contribution of the C-8 Substituent of DU-6859, A new Potent Fluoroquinolone, to Its Activity against DNA Gyrase Mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Nishino, T. Improved Bactericidal Activity of Q-35 against Quinolone-Resistant Staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 1522–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kocsis, B.; Gulyás, D.; Szabó, D. Delafloxacin, Finafloxacin, and Zabofloxacin: Novel Fluoroquinolones un the Antibiotic Pipeline. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.; Lungu, I.-A.; Moldovan, O.L.; Tanase, C.; Hancu, G. Structural characterization of the Millenian Fluoroquinolones-Shaping the Fifth Generation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, B.; Domokos, J.; Szabo, D. Chemical structure and pharmacokinetics of novel quinolone agents represented by avarofloxacion, delafloxacin, finafloxacin, zabofloxacin and nemonoxacin. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, B.J.; He, W.; Amsler, K.M.; Foleno, B.D.; Macielag, M.J.; Lynch, A.S.; Bush, K. In Vitro Antibacterial Activities of JNJ-Q2, a New Broad-Spectrum Fluoroquinolone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candel, F.J.; Peñuelas, M. Delafloxacin: Design, development and potential place in therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 20, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.C.J.; Mercuro, N.N.J.; Davis, S.L.; Rybak, M.J. Delafloxacin,: Place in Therapy and Review of Microbiologic, Clinical and Pharmacologic Properties. Infec. Dis. Ther. 2018, 7, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, A.S.; Mody, P.; Brewer, D.J.; Humphries, R.M. The Fluoroquinolones: An Update for the Clinical Microbiologist. Clin. Mic. News. 2021, 43, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coba-Males, M.A.; Lavecchia, M.J.; Alcívar-León, C.D.; Santamaría-Aguirre, J. Novel Fluoroquinolones with Possible Antibacterial Activity in Gram-Negative Resistant Pathogens: In Silico Drug Discovery. Molecules 2023, 28, 6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Huang, H. Review of nemonoxacin with special focus on clinical development. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.M.; Ziora, Z.M.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. Quinolone Antibiotics. Med. Chem. Commun. 2019, 10, 1719–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turban, A.; Guérin, F.; Dinh, A.; Cattoir, V. Updated Review on Clinically-Relevant Properties of Delafloxacin. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosca, F. A Photochemical Aproach to Fluoroquinolones Toxicity. In Advances in Molecular Toxicology; Elsevier: Alpharetta, GA, USA, 2016; Volume 9, pp. 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- de Guidi, G.; Bracchitta, G.; Catalfo, A. Photosensitization reactions of fluoroquinolones and their biological consequences. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 1214–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.; Munteanu, A.-C.; Arbvanasi, E.-M.; Uivarosi, V. Overview of Side-Effects on Antibacterial Fluoroquinolones. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 15, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, A.M. Safety of Fleroxacin in Clinical Trials. Am. J. Med. 1993, 94, 201S–203S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.R.; Fakouhi, T.D.; Harrison, G.I.; Roniker, B.; Swabb, E.A.; Hawk, J.L.M. The UVR wavelength dependence for lomefloxacin photosensitization of human skin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 1996, 32, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Door, M.B.; Magner, D.J.; Talbot, G.H. Safety profile of sparfloxacin, a new fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Clin. Ther. 1999, 21, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Ray, R.S.; Farooq, M.; Pant, A.B.; Hans, R.K. Photosensitizing potential of ciprofloxacin at ambient level of UV radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reus, A.A.; Usta, M.; Kenny, J.D.; Clements, P.J.; Priumboom-Bress, I.; Aylott, M.; Lunch, A.M.; Krul, C.A.M. The in vivo rat skin photomicronucleous assay: Phototoxicity and photogenotoxicity evaluation of six fluoroquinolones. Mutagenesis 2012, 27, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuquerella, M.C.; Lhiuaubet-Vallet, V.; Bosca, F.; Miranda, M.A. Photosensitised pyrimidine dimerization in DNA. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrot, L.; Agapakis-Causse, C. Differences in the photogenotoxicity potential of two fluoroquinolones as shown in diploid yeast strain (Saccharomyces cerevisae) and supercoiled plasmid DNA. Mutat. Res. 2000, 468, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-R.; Lee, H.-C.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, J.-K.; Yang, K.; Bark, K.M. Spectroscopic Properties of Fuoroquinolone Antibiotics and Nanosecond Solvation Dynamics in Aerosol-OT Reverse Micelles. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, 71, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosca, F. Seeking to Shed Some Light on the Binding of Fluoroquinolones to Albumins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freccero, M.; Fasani, E.; Mella, M.; Manet, I.; Monti, S.; Albani, A. Modeling the Photochemistry of the Reference Phototoxic Drug Lomefloxacin by Steady-State and Time Resolved Experiments, and DFT and Post H-F Calculations. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuquerella, M.C.; Miranda, M.A.; Boscá, F. Generation of Detectable Singlet Aryl Cations by Photodehalogenation of Fluoroquinolonas. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 6441–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasani, E.; Manet, I.; Capobianco, M.L.; Monti, S.; Preti, L.; Albani, A. Fluoroquinolones as potential photochemotherapeutic agents: Covalent addition to guanosine monophosphate. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3621–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polischuck, A.V.; Emelina, T.B.; Cramariuc, O.; Chukharev, V.I.; Karaseva, T.E.; Karasev, V.E. Photolysis and Quantum Chemical calculations of the Nalidixic Acid Radical States. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2012, 82, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, S.; Manet, I.; Manoli, F.; Capobianco, M.L.; Marconi, G. Gaining and Insight Into the Photoreactivity of a Drug in a Protein Environment: A Case Study of Nalidixic Acid and Serum Albumin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 5742–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Chignell, C.F.; Rammal, M.; Smith, F.; Hmilton, M.G.; Andley, U.P.; Roberts, J.E. Detection and Prevention of Ocular Phototoxicity of Ciprofloxacin and Other Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics. Photochem. Photobiol. 2010, 86, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, S.; Cuquerella, M.C.; Bosca, F. Understanding of the Photoallergic Properties of Fluoroquinolones: Photoreactivity of Lomefloxacin with Aminoacids and Albumin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvaigo, S.; Douki, T.; Odin, F.; Caillat, S.; Ravanat, J.-L.; Cadet, J. Analysis of Fluoroquinolone-mediated Photosensitization of 2′-Deoxiguanosine, Calf Thymus and Cellular DNA: Determination of Type I, Type II and Triplet-Triplet Energy Transfer Mechanism Contribution. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 73, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhiaubet-Vallet, V.; Bosca, F.; Miranda, M.A. Photosensitized DNA Damage: The case of Fluoroquinolones. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuquerella, M.C.; Boscá, F.; Miranda, M.A.; Belvedere, A.; Catalfo, A.; de Guido, G. Photochemical Properties of Ofloxacin involved in Oxidative DNA Damage: A comparison with Rufloxacin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhiaubet-Vallet, V.; Cuquerella, M.C.; Castell, J.V.; Bosca, F.; Miranda, M.A. Triplet excited fluoroquinolonas as mediators for thymine cyclobutane dimer formation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 7409–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Acqua, F.; Viola, G.; Vedaldi, D.; Aloisi, G.G.; Elsei, F.; Latterini, L.; Passeri, R. Photoinduced modifications of fluoroquinolone drugs in bovine serum albumin (BSA) and ribonuclease a (RNAse) as model proteins. ARKIVOC 2007, 8, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sortino, S.; Condorelli, G. Complexes between fluoroquinolones and calf thymus DNA: Binding mode and photochemical reactivity. New J. Chem. 2002, 26, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, G.S.; Yeo, J.A.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.K.; Holmén, A.; Akerman, B.; Nordén, B. Binding mode of norfloxacin to calf thymus DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6451–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douki, T.; Reynaud-Angelin, A.; Cadet, J.; Sage, E. Bipyridine photoproducts rather than oxidative lesions are the main type of DNA damage involved in the genotoxic effect of solar UVA radiation. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 9221–9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanat, J.L.; Saint-Pierre, C.; DiMascio, P.; Martinez, G.R.; Medeiros, M.H.G.; Cadet, J. Damage to isolated DNA mediated by singlet oxygen. Helv. Chim. Acta 2001, 84, 3702–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouret, S.; Philippe, C.; Gracia-Chantegrel, J.; Banyasz, A.; Karpati, S. UVA-induced cyclobutale pyrimidibe dimers in DNA: A direct photochemical mechanism? Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.; Courdavault, S.; Ravanat, J.L.; Douki, T. UVB and UVA radiation mediated damage to isolated and cellular DMA. Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, 77, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysan, A.; Viari, A.; Vigny, P.; Voituriez, L.; Cadet, J.; Moustacchi, E.; Sage, E. Formation of cyclobutene thymine dimers photosensitized by pyridopsoralens: Quantitative and qualitative distribution within DNA. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 7080–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Sanjuán, D.; Olaso-González, G.; González-Ramírez, I.; Serrano-Andrés, L.; Merchant, M. Molecular Basis of DNA photodimerization: Intrinsic production of cyclobutane cytosine dimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10768–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, T.; González-Luque, R.; Merchán, M.; Serrano-Adrés, L. On the intrinsic population of the lowest triplet state of uracil. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 441, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etinski, M.; Fleig, T.; Marian, C.M. Intersystem crossing and characterization of dark states in the pyrimidine nucleobases uracil, thymine, and 1-methylthymine. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 11809–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dine, I.; Mulugeta, E.; Melaku, Y.; Belete, M. Recent advances in the synthesis of pharmaceutically active 4-quinolone and its analogues: A review. RSV Adv. 2023, 13, 8657–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Lv, Z.; Liu, M. 4-Quinolone hybrids and their antibacterial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; An, Z.; Loh, K.Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X. Recent Advances in the catalytic synthesis of 4-Quinolones. Chem 2019, 5, 1059–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, P.; Arora, N.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Monga, V. Recent advances in the synthetic and medicinal perspective of quinolones: A review. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryhoriv, H.; Kovalenko, S.M.; Georgiyants, M.; Sidorenko, L.; Georgiyants, V. Comprehensive review on chemical synthesis and chemotherapeutic potential of 3-heteroaryl fluoroquinolone hybrids. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.H.H.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.A.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Abdelhafez, E.M.N. Current Trends and Future Directions of Fluoroquinolones. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 3132–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Compound | Medium | T–T Absorption λmax nm | Quantum Yield Triplet Formation ΦT | εmaxTΦT | Triplet Lifetime τT/μs | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norfloxacin | NaHCO3 0.001 M | 620 | ≥0.5 | 3400 | 1.3 | [29] |
| Enoxacin | NaHCO3 0.001 M | 520 | ≥0.5 | 3500 | 0.85 | [29] |
| PB 0.01 M | 520 | 3500 | 0.09 | [25] | ||
| Rufloxacin | PB 0.01 M | 640 | ≥0.4 | 2800 | 10 | [27,29] |
| 640 | 0.36 | 2100 | 7 | [28] | ||
| Ofloxacin | PB 0.01 M | 620 | ≥0.3 | 2300 | 1.8 | [29] |
| 610 | 0.33 | 3600 | 40 | [26] | ||
| Lomefloxacin | NaHCO3 0.001 M | 500 | ≤0.2 | 900 | 0.1 | [29] |
| Flumequine | PB 0.02 M pH 8 | 575 | 0.9 | 12,600 | 10 | [30] |
| Nalidixic acid | Buffer H2O pH 9.2 | 620 | ≥ 0.6 | 5400 | 100 | [31] |
| Ciprofloxacin | NaHCO3 0.001 M | 610 | 1.5 | [32] |
| Compound | Φ∆ a | kq/106 M−1 s−1 | Rate of Generation of DMPO/•OOH a.u./min b | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norfloxacin | 0.081 | 1.8 (0.1) | 0.25 | [34] |
| Pefloxacin | 0.045 | 12 (1) | [34] | |
| Enoxacin | 0.061 | 1.4 (0.2) | 1.7 | [34] |
| Rufloxacin | 0.32 | [27] | ||
| Ofloxacin | 0.076 | 5.6 (0.6) | 0.06 c | [34] |
| 0.13 | [26] | |||
| Lomefloxacin | 0.072 | 18 (3) | 0.17 | [34] |
| Fleroxacin | 0.029 | 6.9 (0.7) | 0.36 | [34] |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.092 | 5.2 (0.2) | 0.20 | [34] |
| Nalidixic acid | 0.15 | 250 | 10.1 | [34] |
| Flumequine | 0.34 | 3.4 (0.4) | [34] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leyva, E.; Loredo-Carrillo, S.E.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, I.R.; de Loera, D.; Navarro-Tovar, G.; López, L.I. Phototoxicity of Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones: A Mechanistic Review About Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways. Photochem 2025, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem5030017
Leyva E, Loredo-Carrillo SE, Rodríguez-Gutiérrez IR, de Loera D, Navarro-Tovar G, López LI. Phototoxicity of Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones: A Mechanistic Review About Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways. Photochem. 2025; 5(3):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem5030017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeyva, Elisa, Silvia E. Loredo-Carrillo, Irving R. Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, Denisse de Loera, Gabriela Navarro-Tovar, and Lluvia I. López. 2025. "Phototoxicity of Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones: A Mechanistic Review About Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways" Photochem 5, no. 3: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem5030017
APA StyleLeyva, E., Loredo-Carrillo, S. E., Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, I. R., de Loera, D., Navarro-Tovar, G., & López, L. I. (2025). Phototoxicity of Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones: A Mechanistic Review About Photophysical and Photochemical Pathways. Photochem, 5(3), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem5030017









