Investigation of the Self-Cleaning Property of Photocatalytic Coatings at a Laboratory Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates
2.2. Photocatalytic Products
2.3. Photocatalytic Dispersion Application
2.4. X-ray Diffraction
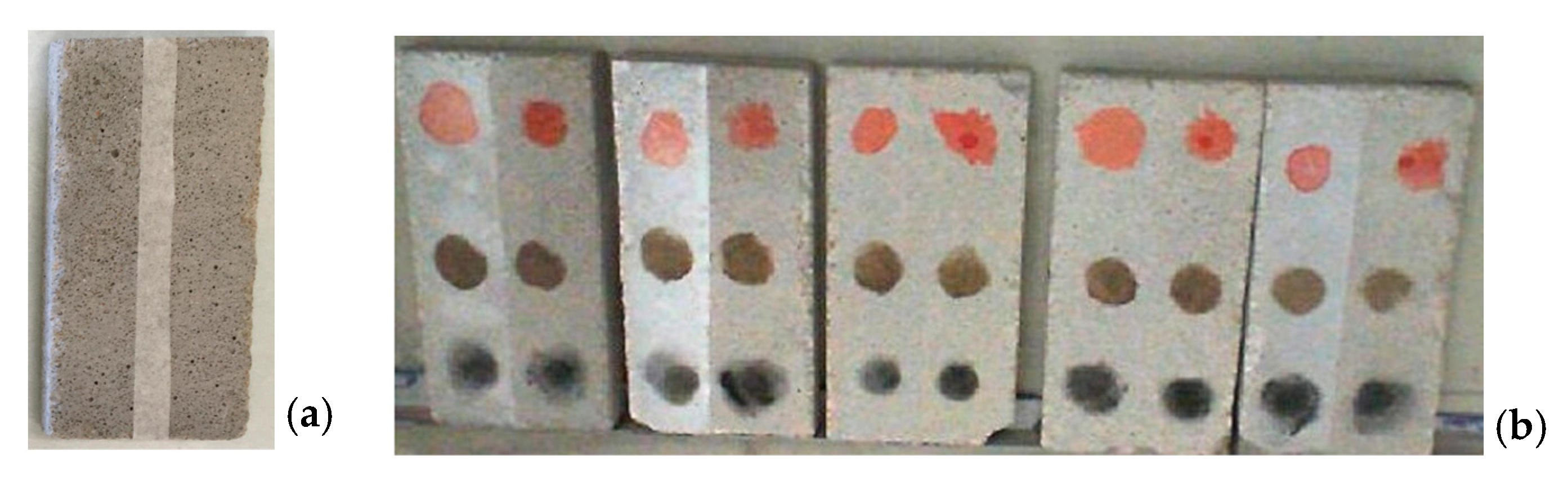
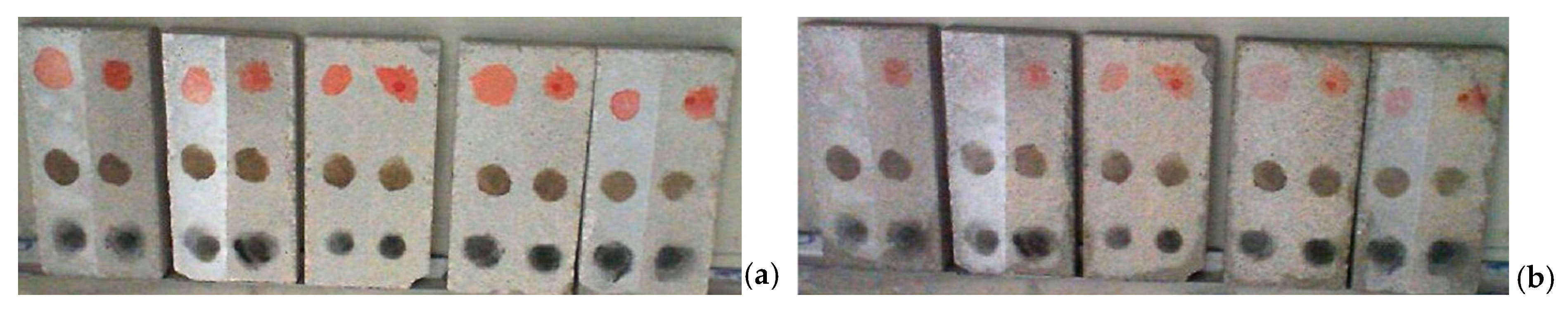
2.5. Surface Contamination
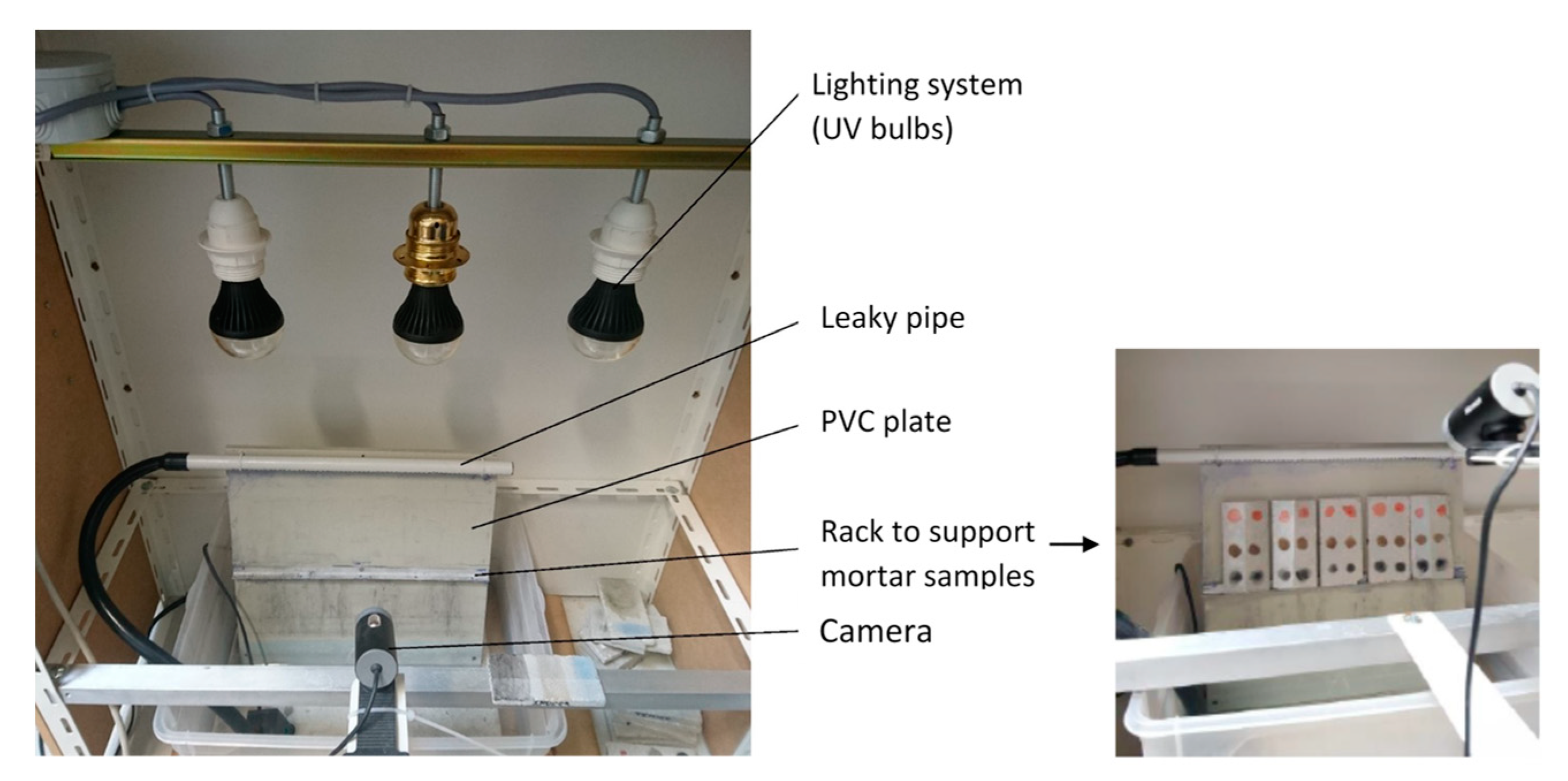
2.6. Self-Cleaning Experiments
2.7. Spectrophotometry
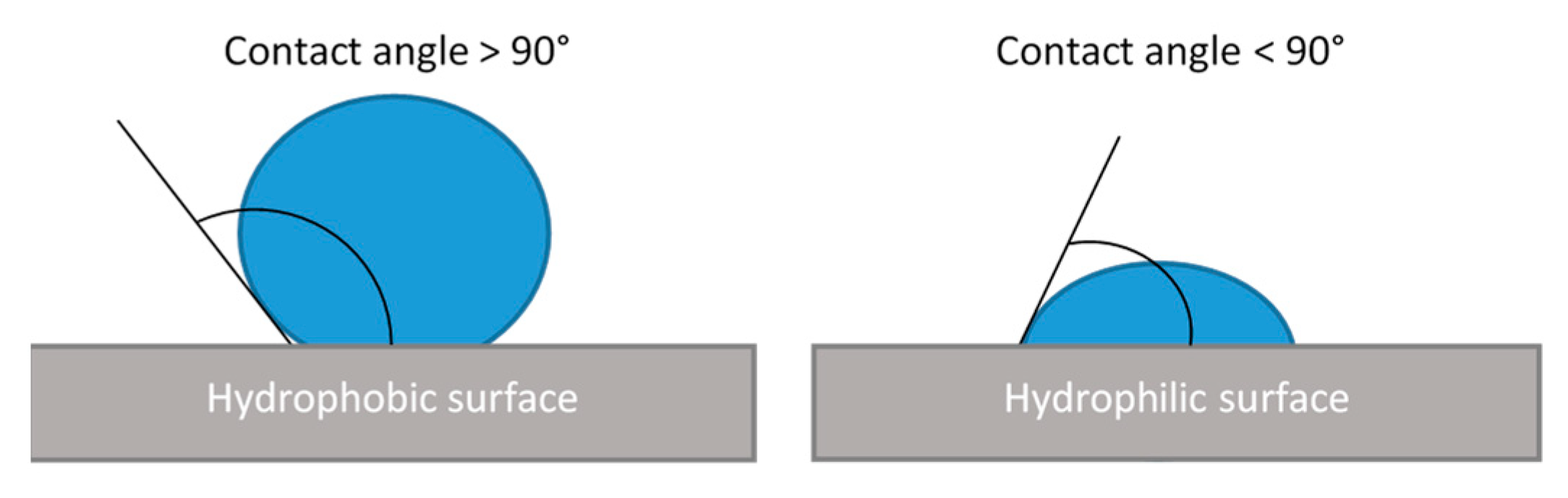
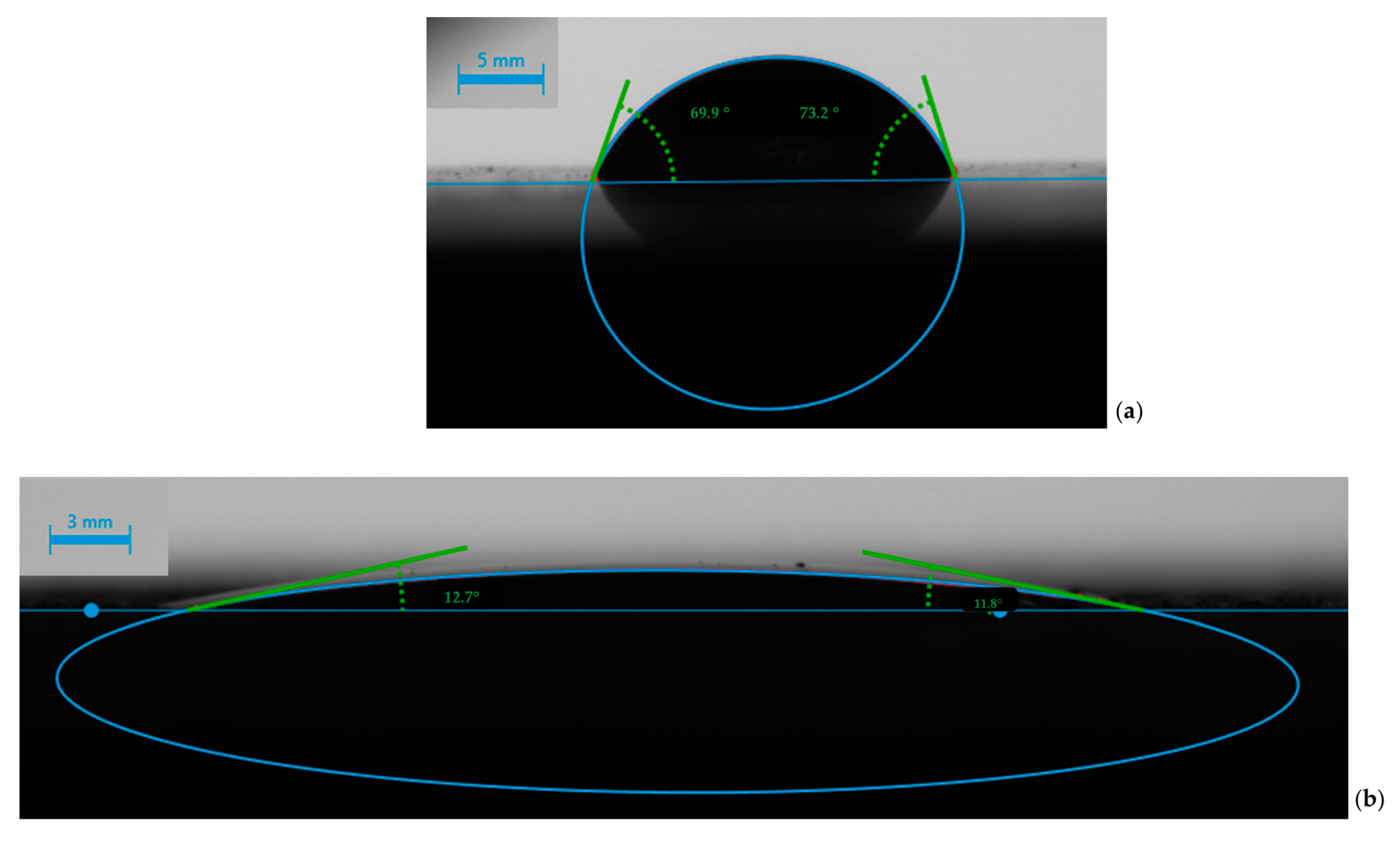
2.8. Water Contact Angle Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
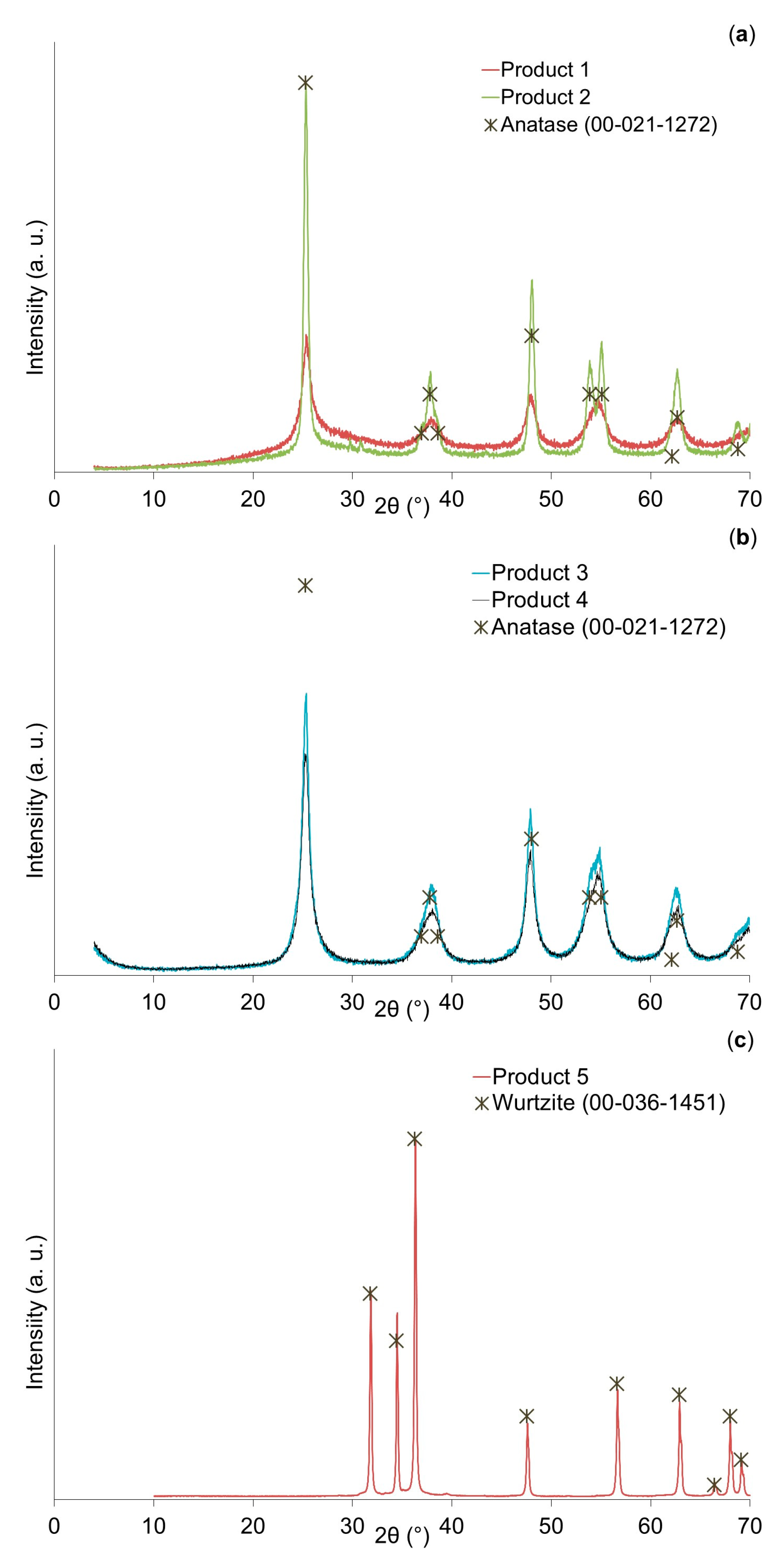
3.1. XRD Analyses
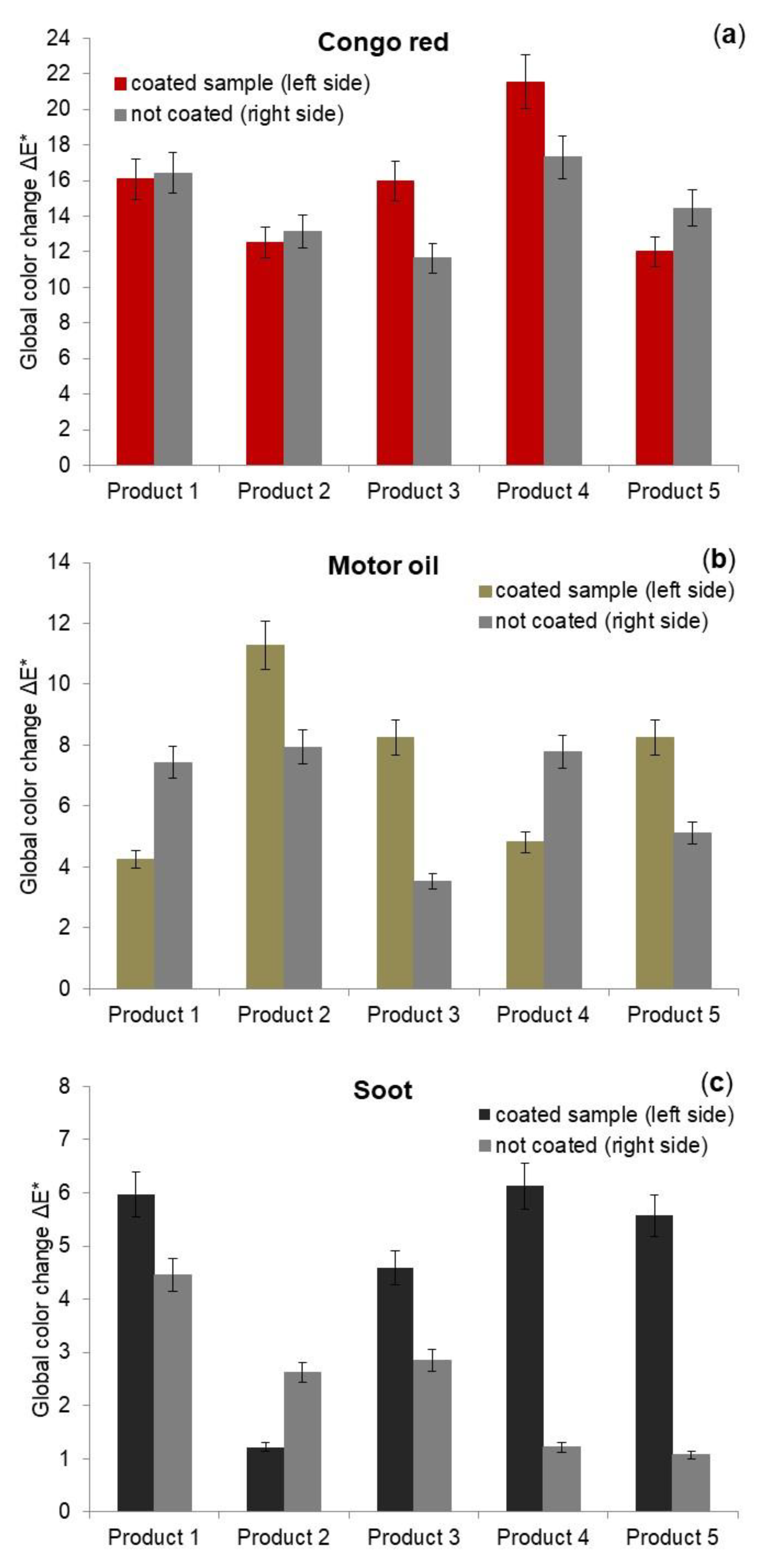
3.2. Stain Degradation Quantification
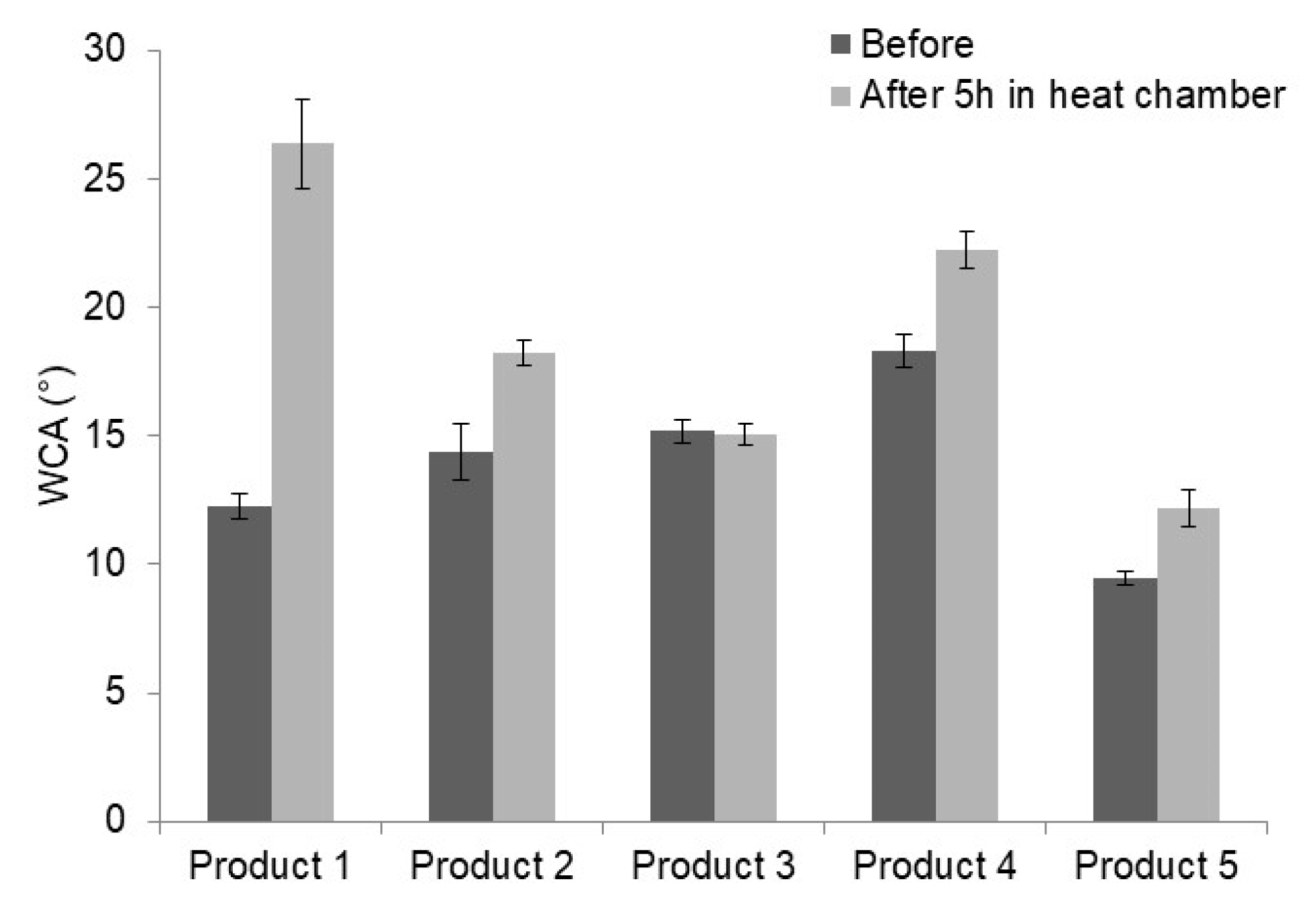
3.3. Wettability of the Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamilton, R.; Crabbe, H. Environment, Pollution and Effects. In The Effects of Air Pollution on Cultural Heritage; Hamilton, R., Kucera, V., Tidblad, J., Watt, J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–27. ISBN 978-0-387-84893-8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wen, C.-Y.; Yang, A.-S.; Juan, Y.-H. The Effects of Lateral Entrainment on Pollutant Dispersion inside a Street Canyon and the Corresponding Optimal Urban Design Strategies. Build. Environ. 2021, 195, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Biswas, B.; Willett, I.R.; Cribb, J.; Kumar Singh, B.; Paul Nathanail, C.; Coulon, F.; Semple, K.T.; Jones, K.C.; Barclay, A.; et al. Chemical Pollution: A Growing Peril and Potential Catastrophic Risk to Humanity. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, F.; Vicente, R.; Mendes Silva, J. Review of Environmental and Air Pollution Impacts on Built Heritage: 10 Questions on Corrosion and Soiling Effects for Urban Intervention. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 37, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the Sacred Lotus, or Escape from Contamination in Biological Surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Ensikat, H.-J. The Hydrophobic Coatings of Plant Surfaces: Epicuticular Wax Crystals and Their Morphologies, Crystallinity and Molecular Self-Assembly. Micron 2008, 39, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Sasic, S.; Liu, K.; Salameh, S.; Ras, R.H.A.; van Ommen, J.R. Nature–Inspired Self–Cleaning Surfaces: Mechanisms, Modelling, and Manufacturing. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 155, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Amirfazli, A. Microtextured Superhydrophobic Surfaces: A Thermodynamic Analysis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 132, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otitoju, T.A.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. Superhydrophilic (Superwetting) Surfaces: A Review on Fabrication and Application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, N.T.; John, H. Titanium Dioxide Based Self-Cleaning Smart Surfaces: A Short Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, Q.; Meng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C. Recent advances in photocatalytic self-cleaning performances of TiO2-based building materials. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 20584–20597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X.; Tryk, D.A. TiO2 Photocatalysis and Related Surface Phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 515–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.; Vormoor, M. Photo-Induced Hydrophilicity and Self-Cleaning: Models and Reality. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7491–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K. Relationship between Photocatalytic Activity, Hydrophilicity and Self-Cleaning Effect of TiO2/SiO2 Films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 191, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Yao, W.; She, A. Enhanced Self-Cleaning Capacity of RBP@TiO2 Based Building Coating: Synergetic Effect of Photocatalysis and Photo-Induced Superhydrophilicity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 388, 131699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, F.; Yang, S. A Review of Self-Cleaning Photocatalytic Surface: Effect of Surface Characteristics on Photocatalytic Activity for NO. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, Z.; Jalilisadrabad, S.; Amrollahi, R. Investigating the Impact of Using Modified Cool Materials by Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)-Based Photocatalytic Self-Cleaning Nanoparticles in Urban Facades on Urban Microclimate Parameters. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. Self-Cleaning Applications of TiO2 by Photo-Induced Hydrophilicity and Photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176–177, 396–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.-Z.; Maury-Ramirez, A.; Poon, C.S. Self-Cleaning Ability of Titanium Dioxide Clear Paint Coated Architectural Mortar and Its Potential in Field Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3583–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X. Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysis: Present Situation and Future Approaches. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2006, 9, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.J.; Jameel, Z.N.; Al-Hussaini, I.H.M. Review on: Titanium Dioxide Applications. Energy Procedia 2019, 157, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Meng, F.; Ma, C.; Yan, Y.; Meng, M. Nitrogen-doped hydrogenated TiO2 modified with CdS nanorods with enhanced optical absorption, charge separation and photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Z.; Sun, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, W.; Ding, H. Construction of R-TiO2/n-TiO2 heterophase photocatalysts for efficient degradation of organic pollutants. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, L. Photocatalysis of Cementitious Materials: Clean Buildings and Clean Air. MRS Bull. 2004, 29, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Jalali, S. Nanotechnology: Advantages and Drawbacks in the Field of Construction and Building Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folli, A.; Campbell, S.B.; Anderson, J.A.; Macphee, D.E. Role of TiO2 Surface Hydration on NO Oxidation Photo-Activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2011, 220, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Relinque, E.; Rodriguez-Garcia, J.R.; Castillo, A.; Castellote, M. Characteristics and Efficiency of Photocatalytic Cementitious Materials: Type of Binder, Roughness and Microstructure. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 71, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.; Chan, C.; Tytgat, T.; Craeye, B.; Costarramone, N.; Lacombe, S.; Lenaerts, S. Photocatalytic Degradation of Soot Deposition: Self-Cleaning Effect on Titanium Dioxide Coated Cementitious Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedillo-González, E.I.; Riccò, R.; Montorsi, M.; Montorsi, M.; Falcaro, P.; Siligardi, C. Self-Cleaning Glass Prepared from a Commercial TiO2 Nano-Dispersion and Its Photocatalytic Performance under Common Anthropogenic and Atmospheric Factors. Build. Environ. 2014, 71, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andaloro, A.; Mazzucchelli, E.S.; Lucchini, A.; Pedeferri, M.P. Photocatalytic Self-Cleaning Coatings for Building Facade Maintenance. Performance Analysis through A Case-Study Application. J. Facade Des. Eng. 2016, 4, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.L.; Dondi, M.; Raimondo, M.; Hotza, D. Photocatalytic Ceramic Tiles: Challenges and Technological Solutions. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Segundo, I.; Ferreira, C.; Freitas, E.F.; Carneiro, J.O.; Fernandes, F.; Júnior, S.L.; Costa, M.F. Assessment of Photocatalytic, Superhydrophobic and Self-Cleaning Properties on Hot Mix Asphalts Coated with TiO2 and/or ZnO Aqueous Solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliarini, E.; Bondioli, F.; Goffredo, G.B.; Cordoni, C.; Munafò, P. Self-Cleaning and de-Polluting Stone Surfaces: TiO2 Nanoparticles for Limestone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliarini, E.; Bondioli, F.; Goffredo, G.B.; Licciulli, A.; Munafò, P. Self-Cleaning Materials on Architectural Heritage: Compatibility of Photo-Induced Hydrophilicity of TiO2 Coatings on Stone Surfaces. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, L.; Quagliarini, E.; Bondioli, F.; D’Orazio, M. Durability of Self-Cleaning TiO2 Coatings on Fired Clay Brick Façades: Effects of UV Exposure and Wet & Dry Cycles. Build. Environ. 2014, 71, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, P.; Goffredo, G.B.; Quagliarini, E. TiO2-Based Nanocoatings for Preserving Architectural Stone Surfaces: An Overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 84, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, Z.; Colombeau, L.; Yesmurzayeva, N.; Baros, F.; Vanderesse, R.; Hamieh, T.; Toufaily, J.; Frochot, C.; Roques-Carmes, T.; Acherar, S. Dye-Sensitized Nanoparticles for Heterogeneous Photocatalysis: Cases Studies with TiO2, ZnO, Fullerene and Graphene for Water Purification. Dyes Pigments 2018, 159, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetchakun, K.; Wetchakun, N.; Sakulsermsuk, S. An Overview of Solar/Visible Light-Driven Heterogeneous Photocatalysis for Water Purification: TiO2- and ZnO-Based Photocatalysts Used in Suspension Photoreactors. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 71, 19–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.E. X-ray Diffraction; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1990; ISBN 978-0-486-66317-3. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, H.; Alemu, H.; Macheli, L.; Sekota, M.; Thakurdesai, M.; Gundu Rao, T.K. Role of Particle Size in Visible Light Photocatalysis of Congo Red Using TiO2·[ZnFe2O4]x Nanocomposites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Sarukawa, K.; Tokieda, K.; Matsumura, M. Morphology of a TiO2 Photocatalyst (Degussa, P-25) Consisting of Anatase and Rutile Crystalline Phases. J. Catal. 2001, 203, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, C.M.; Mohamed, A.R. Roles of Titanium Dioxide and Ion-Doped Titanium Dioxide on Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants (Phenolic Compounds and Dyes) in Aqueous Solutions: A Review. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 1648–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttrell, T.; Halpegamage, S.; Tao, J.; Kramer, A.; Sutter, E.; Batzill, M. Why Is Anatase a Better Photocatalyst than Rutile—Model Studies on Epitaxial TiO2 Films. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, J.; Yu, J. New Understanding of the Difference of Photocatalytic Activity among Anatase, Rutile and Brookite TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20382–20386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, A.; Hamandi, M.; Simonet, F.; Jouguet, B.; Dappozze, F.; Guillard, C. Impact of Rutile and Anatase Phase on the Photocatalytic Decomposition of Lactic Acid. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 253, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katal, R.; Masudy-Panah, S.; Tanhaei, M.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Jiangyong, H. A Review on the Synthesis of the Various Types of Anatase TiO2 Facets and Their Applications for Photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Zhang, D.; Mo, Y.; Song, L.; Brewer, E.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Photocatalytic Activity of Polymer-Modified ZnO under Visible Light Irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A Review of ZnO Nanoparticles as Solar Photocatalysts: Synthesis, Mechanisms and Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fori, M.; Dobretsov, S.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Dutta, J. Antifouling Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanorod Coatings. Biofouling 2014, 30, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, L.; Iglesias, A.; Faraldos, M.; Bahamonde, A.; Rosal, R. Antimicrobial Surfaces with Self-Cleaning Properties Functionalized by Photocatalytic ZnO Electrosprayed Coatings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlyuk, L.; Babich, O.; Ivanova, S.; Vasilchenco, N.; Atuchin, V.; Korolkov, I.; Russakov, D.; Prosekov, A. Antimicrobial Potential of ZnO, TiO2 and SiO2 Nanoparticles in Protecting Building Materials from Biodegradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 146, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, M.; Balasubramanian, K. Enhanced UV Photodetection Behavior of Cr Doped Wurtzite ZnO Crystalline Nanorods. Opt. Mater. 2020, 110, 110492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.L.; Gatto, S.; Pirola, C.; Naldoni, A.; Di Michele, A.; Cerrato, G.; Crocellà, V.; Capucci, V. Photocatalytic Degradation of Acetone, Acetaldehyde and Toluene in Gas-Phase: Comparison between Nano and Micro-Sized TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 146, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.S.; Mahdjoub, N.; Vishnyakov, V.; Kelly, P.J.; Kriek, R.J. The Effect of Crystalline Phase (Anatase, Brookite and Rutile) and Size on the Photocatalytic Activity of Calcined Polymorphic Titanium Dioxide (TiO2). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachheb, H.; Puzenat, E.; Houas, A.; Ksibi, M.; Elaloui, E.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.-M. Photocatalytic Degradation of Various Types of Dyes (Alizarin S, Crocein Orange G, Methyl Red, Congo Red, Methylene Blue) in Water by UV-Irradiated Titania. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 39, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahi, R.K.; Yu, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Mejia, M.L.; Falkner, J.C.; Nolte, W.; Colvin, V.L. Photodegradation of Congo Red Catalyzed by Nanosized TiO2. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2005, 242, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.R.; Kasiri, M.B. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes in the Presence of Nanostructured Titanium Dioxide: Influence of the Chemical Structure of Dyes. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2010, 328, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle, A.P.; de Souza, M.L.; Loh, K.; Ando, R.; John, V.M. The Performance of a Self-Cleaning Cool Cementitious Surface. Energy Build. 2016, 114, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.M.; Deshmukh, S.P.; More, K.V.; Shevale, V.B.; Mullani, S.B.; Dhodamani, A.G.; Delekar, S.D. Sulfated TiO2/WO3 Nanocomposite: An Efficient Photocatalyst for Degradation of Congo Red and Methyl Red Dyes under Visible Light Irradiation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 225, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansiviero, M.T.C.; dos Santos, D.S.; Job, A.E.; Aroca, R.F. Layer by Layer TiO2 Thin Films and Photodegradation of Congo Red. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2011, 220, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmi Khairol, N.; Sapawe, N.; Danish, M. Photocatalytic Study of ZnO-CuO/ES on Degradation of Congo Red. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibhadon, A.O.; Fitzpatrick, P. Heterogeneous Photocatalysis: Recent Advances and Applications. Catalysts 2013, 3, 189–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochkind, M.; Pasternak, S.; Paz, Y. Using Dyes for Evaluating Photocatalytic Properties: A Critical Review. Molecules 2015, 20, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.; Huygh, D.; Craeye, B.; Lenaerts, S. Effect of Process Parameters on the Photocatalytic Soot Degradation on Self-Cleaning Cementitious Materials. Catal. Today 2014, 230, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.; Wang, J.; Crow, M. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Soot by P25 TiO2 Films. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Dionísio, A. Self-Cleaning Property of Mortars with TiO2 Addition Using Real Diesel Exhaust Soot. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangiuli, D.; Lettieri, M.; Masieri, M.; Calia, A. Field Study in an Urban Environment of Simultaneous Self-Cleaning and Hydrophobic Nanosized TiO2-Based Coatings on Stone for the Protection of Building Surface. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettieri, M.; Colangiuli, D.; Masieri, M.; Calia, A. Field Performances of Nanosized TiO2 Coated Limestone for a Self-Cleaning Building Surface in an Urban Environment. Build. Environ. 2019, 147, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, M.V.; Paolini, R.; Rossini, M.; Aslan, A.B.; Zinzi, M.; Poli, T.; Pedeferri, M.P. Long Term Self-Cleaning and Photocatalytic Performance of Anatase Added Mortars Exposed to the Urban Environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hal, M.; Lenaerts, S.; Verbruggen, S.W. Photocatalytic soot degradation under UV and visible light. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22262–22272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, S.; Tomoishi, S.; Kameshima, Y.; Fujii, E.; Miyake, M. Self-Cleaning Efficiency of Titanium Dioxide Surface under Simultaneous UV Irradiation of Various Intensities and Water Flow. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 122, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobaldi, D.M.; Graziani, L.; Seabra, M.P.; Hennetier, L.; Ferreira, P.; Quagliarini, E.; Labrincha, J.A. Functionalised Exposed Building Materials: Self-Cleaning, Photocatalytic and Biofouling Abilities. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 10316–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Irie, H.; Fujishima, A. TiO2 Photocatalysis: A Historical Overview and Future Prospects. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Product | Description | Crystal Form | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product 1 | Ultrafine TiO2 powder | Anatase at 85 wt% | 350 |
| Product 2 | Ultrafine TiO2 powder | Anatase at 95 wt% | 90 |
| Product 3 | Aqueous dispersion of ultrafine TiO2 particles (pH = 11) | Anatase at 18 wt% | 330 |
| Product 4 | Aqueous dispersion of ultrafine TiO2 particles (pH = 8.5) | Anatase at 10 wt% | 300 |
| Product 5 | ZnO—Nanopowder < 100 nm | Wurtzite | 15–25 |
| Weather Conditions Simulated at Lab Scale | Duration (min) |
|---|---|
| Resting period 1 (no light, no water flow) | 36 |
| UV light | 60 |
| Resting period 2 (no light, no water flow) | 35 |
| Water flow | 2 |
| Product | Position of the Peak with the Highest Intensity in Degrees) | Full Width at Half-Maximum (FWHM) | Crystallite Mean Size in nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product 1 | 25.398 | 0.629 | 12.7 |
| Product 2 | 25.315 | 0.118 | 67.6 |
| Product 3 | 25.363 | 0.197 | 40.6 |
| Product 4 | 25.224 | 0.354 | 22.5 |
| Product 5 | 36.228 | 0.163 | 65.7 |
| Surface Treatment | Reference Cement Paste | Product 1 | Product 2 | Product 3 | Product 4 | Product 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WCA (°) | 69.16 ± 1.4 | 12.26 ± 0.94 | 14.38 ± 2.24 | 15.17 ± 0.92 | 18.32 ± 1.29 | 9.46 ± 0.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hot, J.; Castelló Lux, K.; Ringot, E. Investigation of the Self-Cleaning Property of Photocatalytic Coatings at a Laboratory Scale. Photochem 2023, 3, 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem3040028
Hot J, Castelló Lux K, Ringot E. Investigation of the Self-Cleaning Property of Photocatalytic Coatings at a Laboratory Scale. Photochem. 2023; 3(4):461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem3040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleHot, Julie, Kevin Castelló Lux, and Erick Ringot. 2023. "Investigation of the Self-Cleaning Property of Photocatalytic Coatings at a Laboratory Scale" Photochem 3, no. 4: 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem3040028
APA StyleHot, J., Castelló Lux, K., & Ringot, E. (2023). Investigation of the Self-Cleaning Property of Photocatalytic Coatings at a Laboratory Scale. Photochem, 3(4), 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/photochem3040028









