Characterization of Alginate from Drifted Pelagic Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans Along the Moroccan Atlantic Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Identification of the Sargassum Species
2.2. Alginate Extraction
2.3. Intrinsic Viscosity [η] and Molecular Weight (Mv)
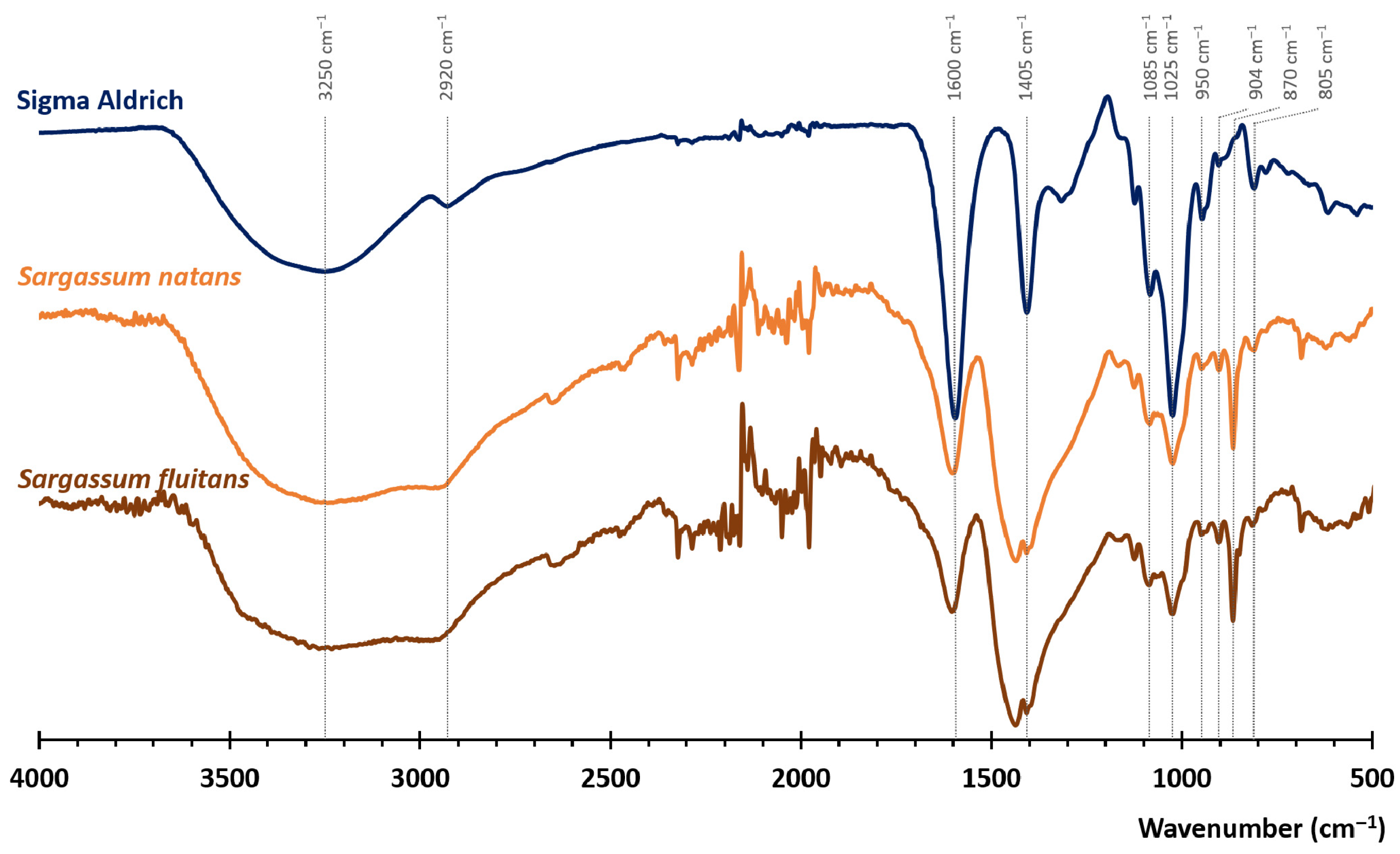
2.4. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
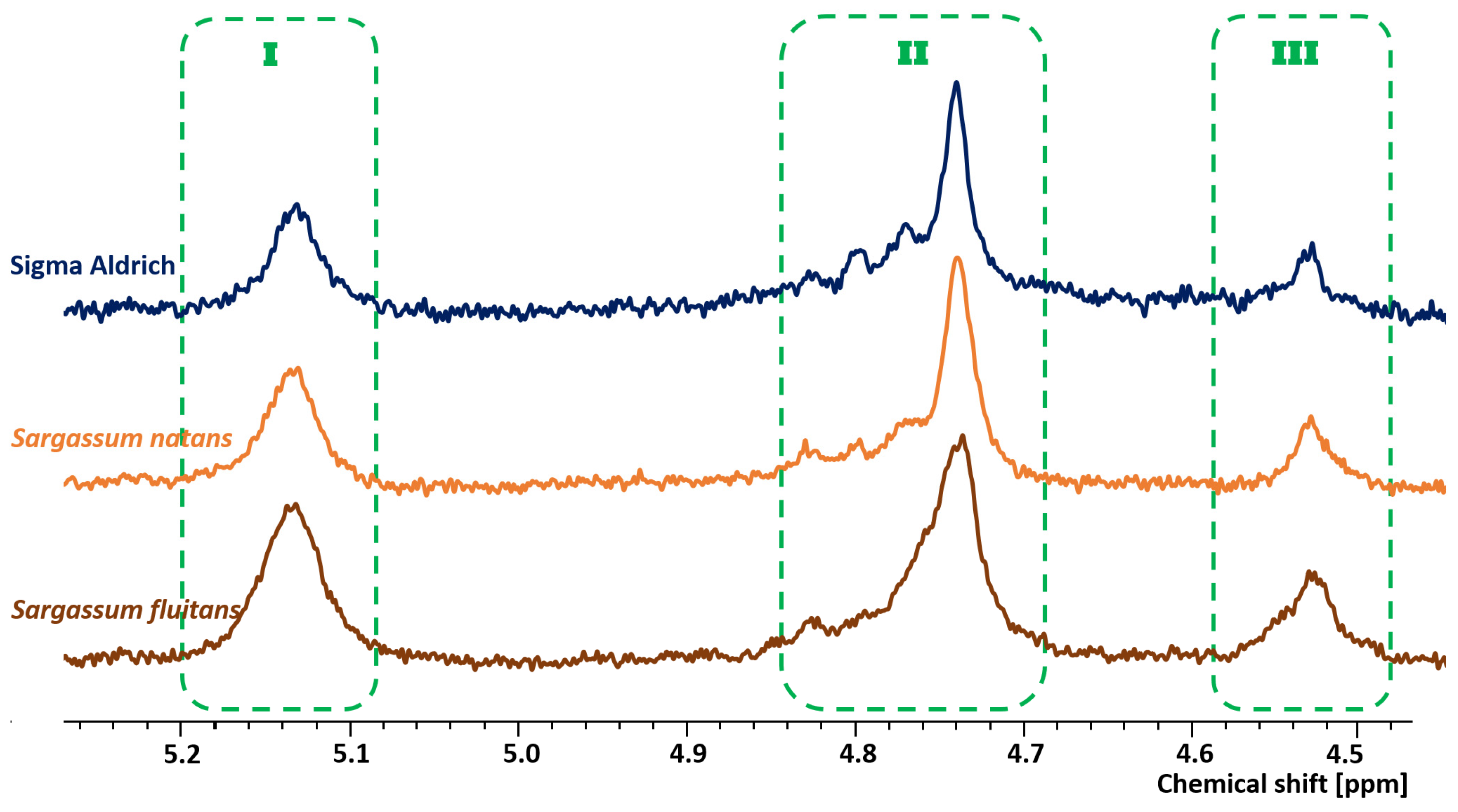
2.5. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H NMR)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Properties
3.1.1. Alginate Yields
3.1.2. Intrinsic Viscosity [η] and Molecular Weight (Mw)
3.2. Chemical Properties
3.2.1. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.2.2. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H NMR)
4. Challenges and Opportunities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Mattio, L.; De Ramon N’Yeurt, A.; Uwai, S.; Dominguez, H.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Connan, S.; Critchley, A.T. A concise review of the highly diverse genus Sargassum C. Agardh with wide industrial potential. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 1453–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, J.M.; Goodwin, D.S.; Siuda, A.N.S. Recent Sargassum inundation events in the Caribbean: Shipboard observations reveal dominance of a previously rare form. J. Oceanogr. 2015, 28, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Mitchum, G.; Lapointe, B.; Montoya, J.P. The great Atlantic Sargassum belt. Science 2019, 365, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleyne, K.S.T.; Johnson, D.; Neat, F.; Oxenford, H.A.; Vallѐs, H. Seasonal variation in morphotype composition of pelagic Sargassum influx events is linked to oceanic origin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botánica Marina de Canarias: BotMar ULL. Video Post Showing Pelagic Brown Algae (Sargassum) Ashore in the Canary Islands Following Currents from the Sargasso Sea. Facebook Video, 28 March 2024. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/watch/?v=832189685604811 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Gabriel, D.; Maridakis, C.; Fredericq, S. Gone with the wind: An unexpected Sargassum inundation in the mid-Atlantic Azores archipelago. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 204, 116522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineur, F.; Arenas, F.; Assis, J.; Davies, A.J.; Engelen, A.H.; Fernandes, F.; Malta, E.-J.; Thibaut, T.; Van Nguyen, T.; Vaz-Pinto, F.; et al. European seaweeds under pressure: Consequences for communities and ecosystem functioning. J. Sea Res. 2014, 98, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, E.; Slocum, A.H.; Ceballos, M.L.; Aponte, P.; Bisonó-León, A.G. Beyond the Bloom: Invasive seaweed Sargassum spp. as a catalyst for sustainable agriculture and blue economy—A multifaceted approach to biodegradable films, biostimulants, and carbon mitigation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abka-Khajouei, R.; Tounsi, L.; Shahabi, N.; Patel, A.K.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Structures, properties and applications of alginates. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedy, S.H.; El Hafez, M.S.M.A.; Dar, M.A.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L. Evaluation and characterization of alginate extracted from brown seaweed collected in the Red Sea. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Bourgougnon, N.; Deslandes, E. Carbohydrates from seaweeds. In Seaweed in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 223–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Ale, M.T.; Ajalloueian, F.; Meyer, A.S. Characterization of alginates from Ghanaian brown seaweeds: Sargassum spp. and Padina spp. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 71, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, I.I.; Zulkifli, N.; Selvakumaran, S.A.; Lazim, N.A.M. Bioactive algal-derived polysaccharides: Multi-functionalization, therapeutic potential and biomedical applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, A.E. Quantitative observations on the pelagic Sargassum vegetation of the western North Atlantic: With preliminary discussion of morphology and relationships. Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Coll. 1939, 6, 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Calumpong, H.P.; Maypa, A.P.; Magbanua, M. Population and alginate yield and quality assessment of four Sargassum species in Negros Island, central Philippines. Hydrobiologia 1999, 398, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.R.; Sousa, A.P.A.; Silva Filho, E.A.T.; Melo, D.F.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; de Paula, R.C.M.; Lima, M.G.S. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of Sargassum vulgare alginate from Brazil. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.A.; Ramirez, M.; Mucci, A.; Larsen, B. Extraction, isolation and cadmium binding of alginate from Sargassum spp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Bissoon, R.; Bajnath, E.; Mohammed, K.; Lee, T.; Bissram, M.; John, N.; Jalsa, N.K.; Lee, K.-Y.; Ward, K. Multistage extraction and purification of waste Sargassum natans to produce sodium alginate: An optimization approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Rivers, A.; Stuckey, D.C.; Ward, K. Alginate extraction from Sargassum seaweed in the Caribbean region: Optimization using response surface methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, C.N.S.; Premarathna, A.D.; Humayun, S.; Agyei-Tuffour, B.; Goosen, N.J.; Tuvikene, R. Physico- and biochemical properties of alginates extracted from Ecklonia maxima and Sargassum fluitans using a simple cascade process. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauta, J.; Calbrix, E.; Capblancq, S.; Cecutti, C.; Peydecastaing, J.; Delgado Raynaud, C.; Rouilly, A.; Simon, V.; Vaca-Medina, G.; Vandenbossche, V.; et al. Global chemical characterization of Sargassum spp. seaweeds from different locations on Caribbean Islands: A screening of organic compounds and heavy metals contents. Phycology 2024, 4, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcin, N.; Thesnor, V.; Duvauchelle, V.; Ponce-Mora, A.; Gimeno-Mallench, L.; Narayanin-Richenapin, S.; Brelle, L.; Bejarano, E.; Yacou, C.; Sylvestre, M.; et al. Characterization of alginates of Sargassum from the Archipelago of Guadeloupe. Separations 2024, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Simister, R.; Campbell, S.; Marston, M.; Bose, S.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; Gomez, L.D.; Gallimore, W.A.; Tonon, T. Biomass composition of the golden tide pelagic seaweeds Sargassum fluitans and S. natans (morphotypes I and VIII) to inform valorisation pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Llanes, F.; Volesky, B.; Mucci, A. Metal selectivity of Sargassum spp. and their alginates in relation to their α-L-guluronic acid content and conformation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertagnolli, C.; Espindola, A.P.D.M.; Kleinübing, S.J.; Tasic, L.; Da Silva, M.G.C. Sargassum filipendula alginate from Brazil: Seasonal influence and characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Llanes, F.; Volesky, B.; Diaz-Pulido, G.; McCook, L.; Mucci, A. H-NMR study of Na alginates extracted from Sargassum spp. in relation to metal biosorption. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2003, 110, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteiro, C. Alginate Production from Marine Macroalgae, with Emphasis on Kelp Farming. In Alginates and Their Biomedical Applications; Springer Series in Biomaterials Science and Engineering; Rehm, B., Moradali, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 11, pp. 27–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, C.; Mahabir, S.; Mohammed, K.; John, N.; Lee, K.Y.; Ward, K. Calcium alginate thin films derived from Sargassum natans for the selective adsorption of Cd2+, Cu2+, and Pb2+ ions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourest, E.; Volesky, B. Alginate Properties and Heavy Metal Biosorption by Marine Algae. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1997, 67, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, R.E.; Su, P.; Puri, M.; Raston, C.L.; Zhang, W. Release of encapsulated bioactives influenced by alginate viscosity under in-vitro gastrointestinal model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yao, L.; Nie, S.; Xu, Y. Low-viscosity sodium alginate combined with TiO2 nanoparticles for improving neuroblastoma treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.; Salem, D.M.S.A.; Sallam, M.A.E.; Mishrikey, M.M.; Beltagy, A.I. Characterization of the alginates from algae harvested at the Egyptian Red Sea coast. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Atouani, S.; Bentiss, F.; Reani, A.; Zrid, R.; Belattmania, Z.; Pereira, L.; Mortadi, A.; Cherkaoui, O.; Sabour, B. The invasive brown seaweed Sargassum muticum as new resource for alginate in Morocco: Spectroscopic and rheological characterization. Phycol. Res. 2016, 64, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathlouthi, M.; Koenig, J.L. Vibrational spectra of carbohydrates. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1986, 44, 7–89. [Google Scholar]
- Fenoradosoa, T.A.; Ali, G.; Delattre, C.; Laroche, C.; Petit, E.; Wadouachi, A.; Michaud, P. Extraction and characterization of an alginate from the brown seaweed Sargassum turbinarioides Grunow. J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidi, S.; Bentiss, F.; Jama, C.; Khaya, K.; Belattmania, Z.; Reani, A.; Sabour, B. Isolation and structural characterization of alginates from the kelp species Laminaria ochroleuca and Saccorhiza polyschides from the Atlantic coast of Morocco. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasdalen, H.; Larsen, B.; Smidsrød, O. Study of the composition and sequence of uronate residues in alginates. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 68, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, L.; Deng, L.; Li, H. Varying ratios of M/G in alginate to modulate macrophages polarization and its application for wound healing in diabetic. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belattmania, Z.; Kaidi, S.; El Atouani, S.; Katif, C.; Bentiss, F.; Jama, C.; Reani, A.; Sabour, B.; Vasconcelos, V. Isolation and FTIR-ATR and 1H NMR characterization of alginates from the main alginophyte species of the Atlantic coast of Morocco. Molecules 2020, 25, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Y.; Amin, F.; Usman, Y.; Sarfraz, M.F. Alginate-based hydrogels with inorganic nanomaterials: A promising approach for wound healing and bone tissue regeneration. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 212, 113057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shang, W.; Huang, Y.; Ge, J.; Ye, J.; Qu, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, C.; Hu, P.; Liu, Y. Sodium alginate/chitosan composite scaffold reinforced with biodegradable polyesters/gelatin nanofibers for cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 285, 138054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, D.; Vázquez-Delfín, E.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Vásquez-Elizondo, R.M.; Qui-Minet, Z.N.; Salazar-Garibay, A. Challenges and Opportunities in Relation to Sargassum Events Along the Caribbean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 699664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanno, J.; Berthet, S.; Muller-Karger, F.; Aumont, O.; Sheinbaum, J. An extreme North Atlantic Oscillation event drove the pelagic Sargassum tipping point. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Algal Species | Alginate Yields (% dw) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Sargassum fluitans | 21.1–22.8% | [17] |
| Sargassum oligocystum | 16.3–20.5% | |
| Sargassum natans | 23% | [12] |
| Sargassum vulgare | 17% | |
| Sargassum natans * | 7–19% | [18] |
| 28% | [19] | |
| Sargassum fluitans | 21.1% | [20] |
| Pelagic Sargassum * | 17.75–30.19% | [21] |
| Pelagic Sargassum | 2.62–9.11% | [22] |
| Sargassum natans I * | 11.13% | [23] |
| Sargassum natans VIII * | 12.18% | |
| Sargassum fluitans III * | 9.36% | |
| Sargassum oligocystum | 37% | [24] |
| Sargassum filipendula | 17% | [25] |
| Sargassum fluitans * | 45% | [26] |
| Sargassum fluitans * | 21.2 ± 0.57% | This study |
| Sargassum natans * | 18.1 ± 0.11% |
| Species | [η] (dL/g) | Mw × 10−5 (g/mol) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sargassum natans * | - | 3.14–3.2 | [19] |
| Sargassum fluitans | 6.3 | 3 | [29] |
| Sargassum fluitans * | 0.57–11.6 | - | [26] |
| Sargassum vulgare | 4.1–6.9 | 1.94–3.3 | [16] |
| Sargassum asperifolium | 15.2 | 7.34 | [32] |
| Sargassum latifolium | 8.7 | 4.16 | |
| Sargassum natans * | 1.39 | 0.65 | This study |
| Sargassum fluitans * | 0.80 | 0.37 | |
| Commercial alginate | 1.83 | 0.85 |
| Species | FG | FM | FGG | FGM | FMG | FMM | M/G | η | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sargassum natans 1 * | 0.35 | 0.65 | - | - | - | - | 1.87 | - | [23] |
| Sargassum natans VIII * | 0.34 | 0.66 | - | - | - | - | 1.97 | - | |
| Sargassum fluitans * | 0.35 | 0.65 | - | - | - | - | 1.94 | - | |
| Sargassum natans | 0.68 | 0.32 | 0.61 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.47 | 0.32 | [12] |
| Sargassum fluitans | 0.64 | 0.36 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.57 | 0.34 | [17] |
| 0.76 | 0.24 | 0.66 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 0.43 | [20] | |
| 0.45 | - | 0.28 | - | - | - | - | - | [29] | |
| Sargassum fluitans * | 0.84 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.19 | - | [26] |
| Sargassum natans * | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.49 | 0.40 | [19] |
| 0.66 | 0.34 | 0.62 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.32 | 0.51 | 0.18 | [18] | |
| Sargassum muticum | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 1.04 | 1.35 | [39] |
| Sargassum vulgare | 0.44 | 0.56 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 1.27 | 0.04 | [16] |
| 0.59 | 0.41 | 0.49 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 0.7 | 0.41 | [12] | |
| Sargassum thunbergii | 0.66 | 0.34 | 0.48 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.53 | 0.76 | [24] |
| Sargassum polycystum | 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.77 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.68 | |
| Sargassum filipendula | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.78 | 0.45 | [25] |
| Sargassum fluitans * | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 1.08 | 1.03 | This study |
| Sargassum natans * | 0.44 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 1.27 | 1.12 | |
| Commercial alginate | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.46 | 1.87 | 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamal, K.; Belattmania, Z.; Khaya, K.; Chaouti, A.; Bentiss, F.; Jama, C.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Sabour, B. Characterization of Alginate from Drifted Pelagic Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans Along the Moroccan Atlantic Coast. Physchem 2025, 5, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040051
Kamal K, Belattmania Z, Khaya K, Chaouti A, Bentiss F, Jama C, Stiger-Pouvreau V, Sabour B. Characterization of Alginate from Drifted Pelagic Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans Along the Moroccan Atlantic Coast. Physchem. 2025; 5(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamal, Khansae, Zahira Belattmania, Khaoula Khaya, Abdellatif Chaouti, Fouad Bentiss, Charafeddine Jama, Valérie Stiger-Pouvreau, and Brahim Sabour. 2025. "Characterization of Alginate from Drifted Pelagic Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans Along the Moroccan Atlantic Coast" Physchem 5, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040051
APA StyleKamal, K., Belattmania, Z., Khaya, K., Chaouti, A., Bentiss, F., Jama, C., Stiger-Pouvreau, V., & Sabour, B. (2025). Characterization of Alginate from Drifted Pelagic Sargassum natans and Sargassum fluitans Along the Moroccan Atlantic Coast. Physchem, 5(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040051








