A Multiscale Approach to Examine the Adsorption of Fatty Acid Surfactants in Bacterial Membranes
Abstract
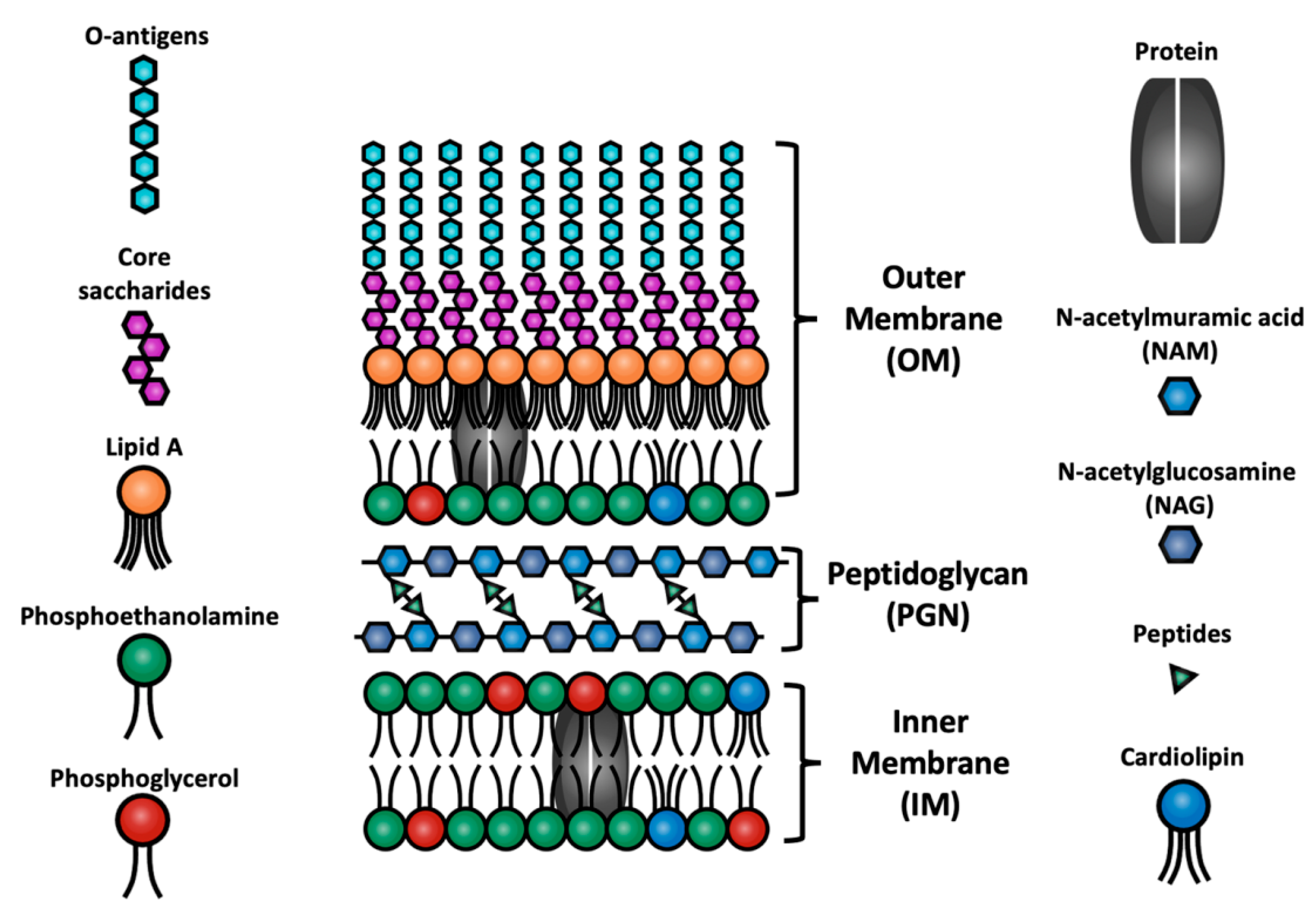
1. Introduction
2. Model and Method
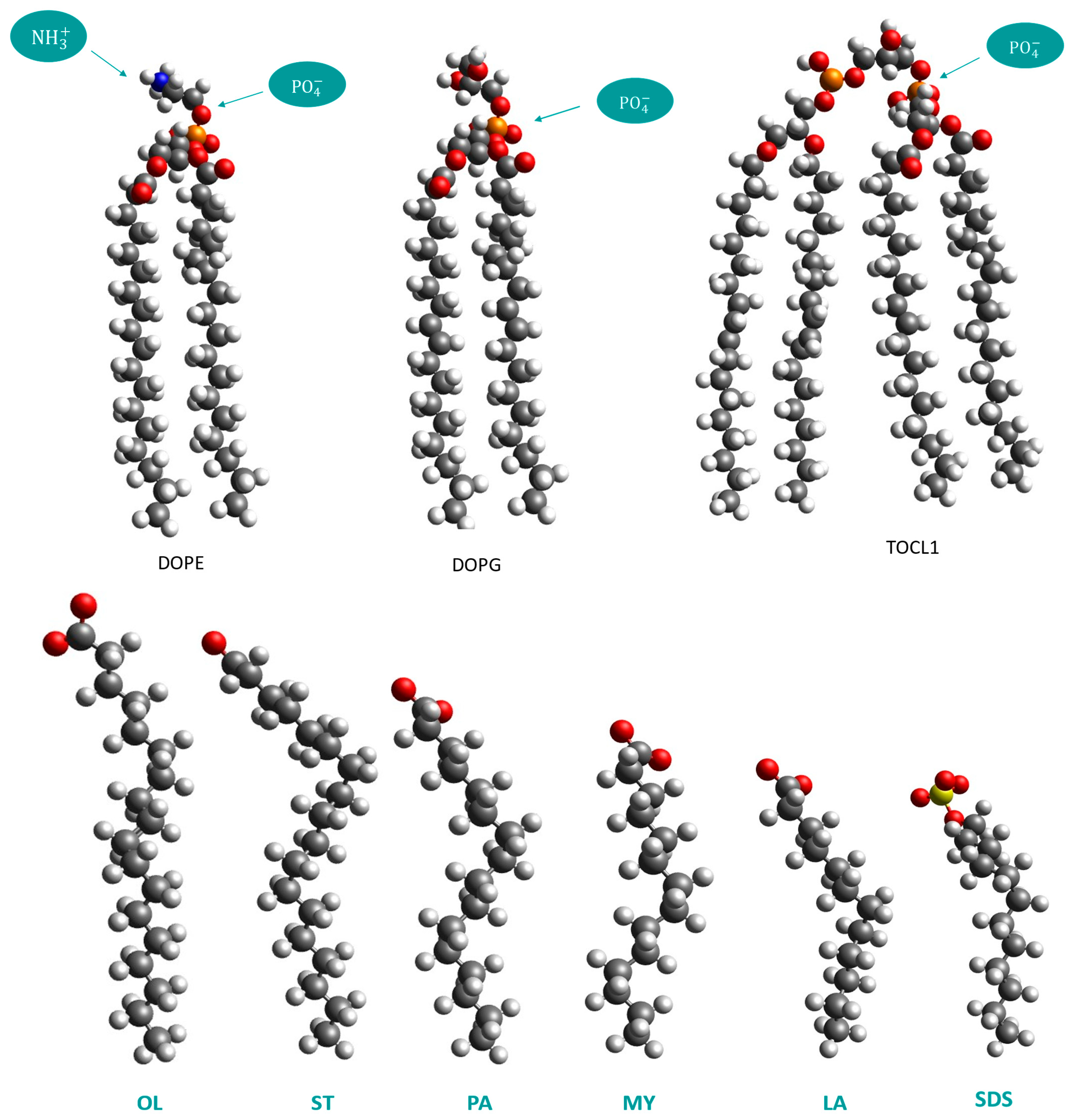
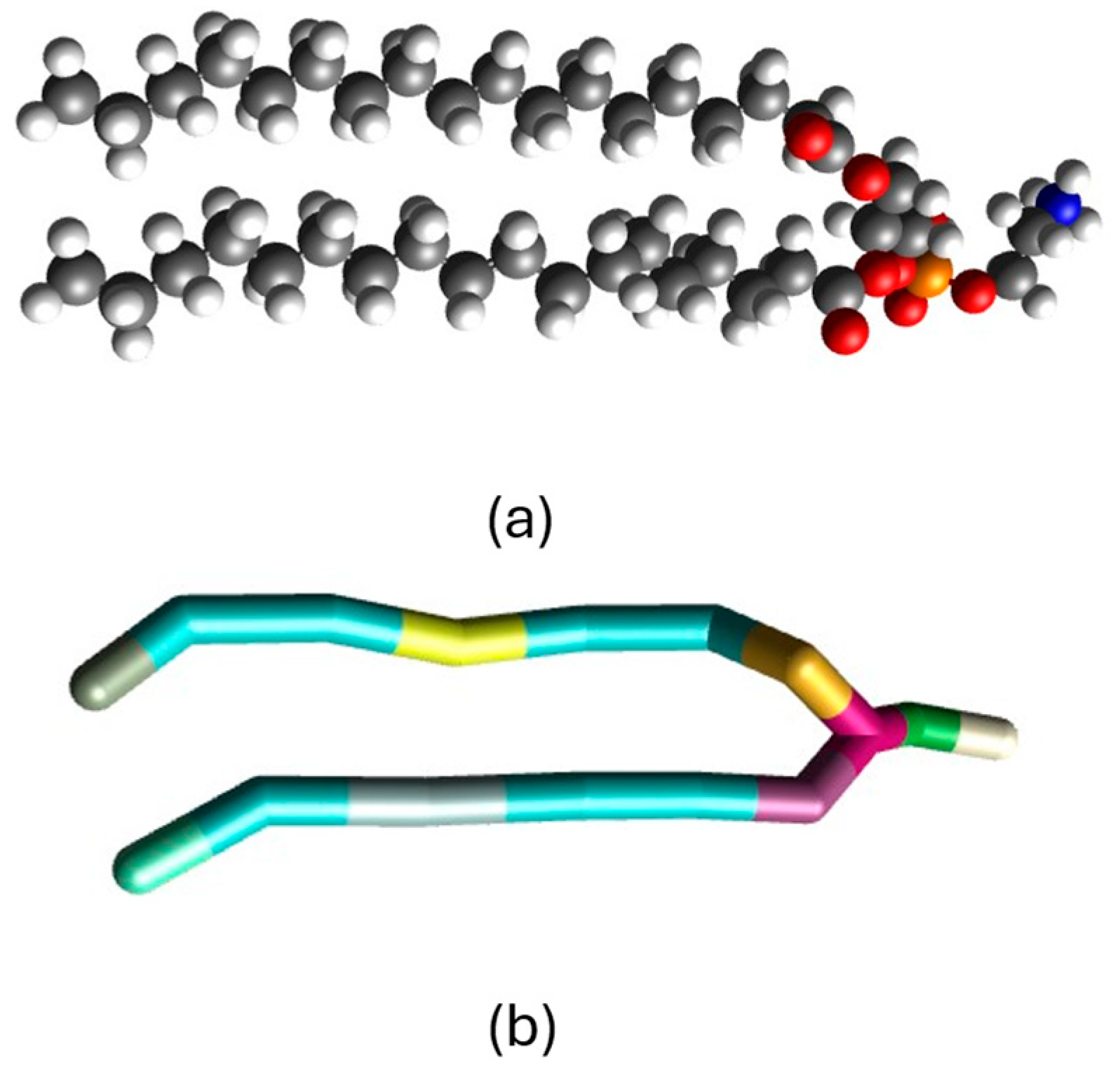
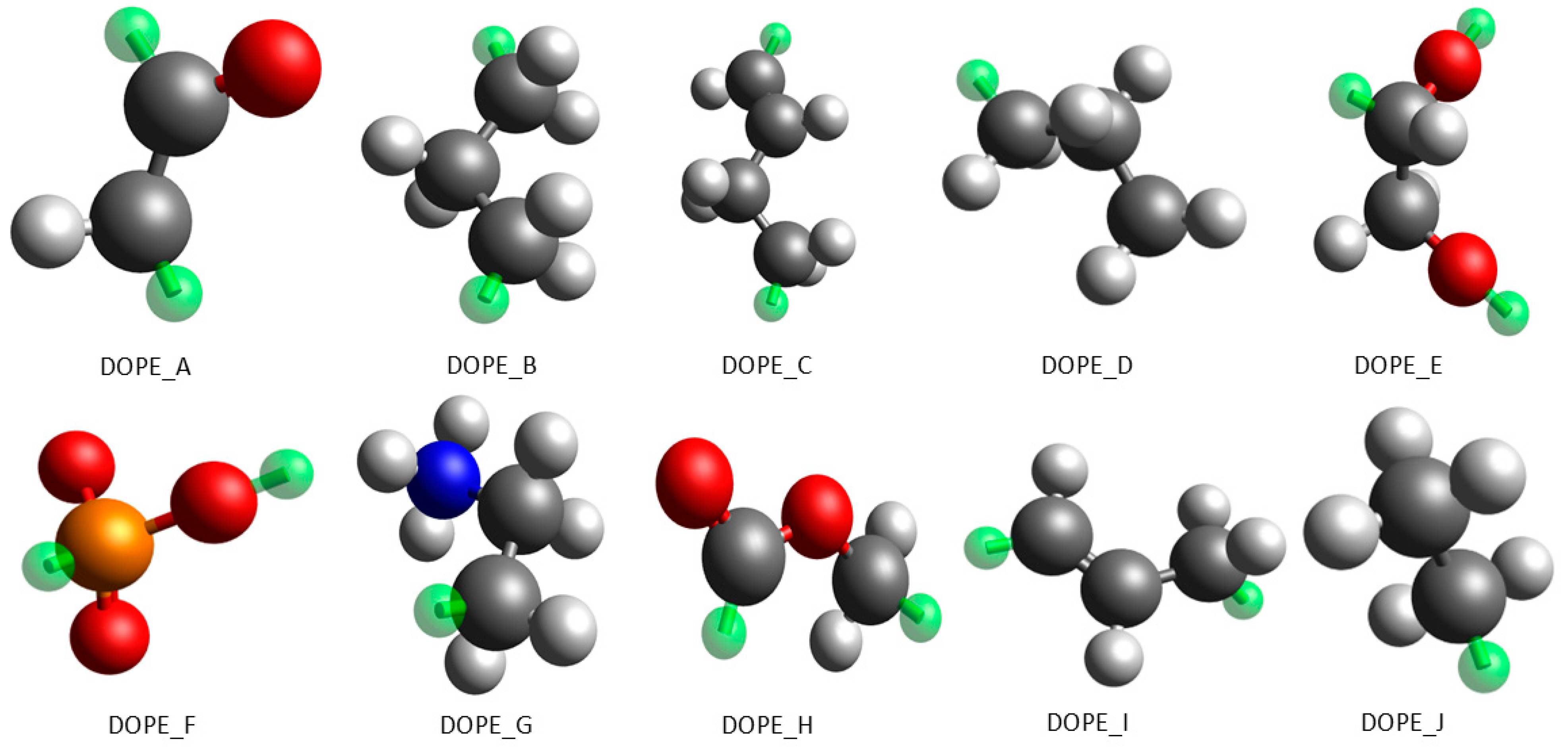
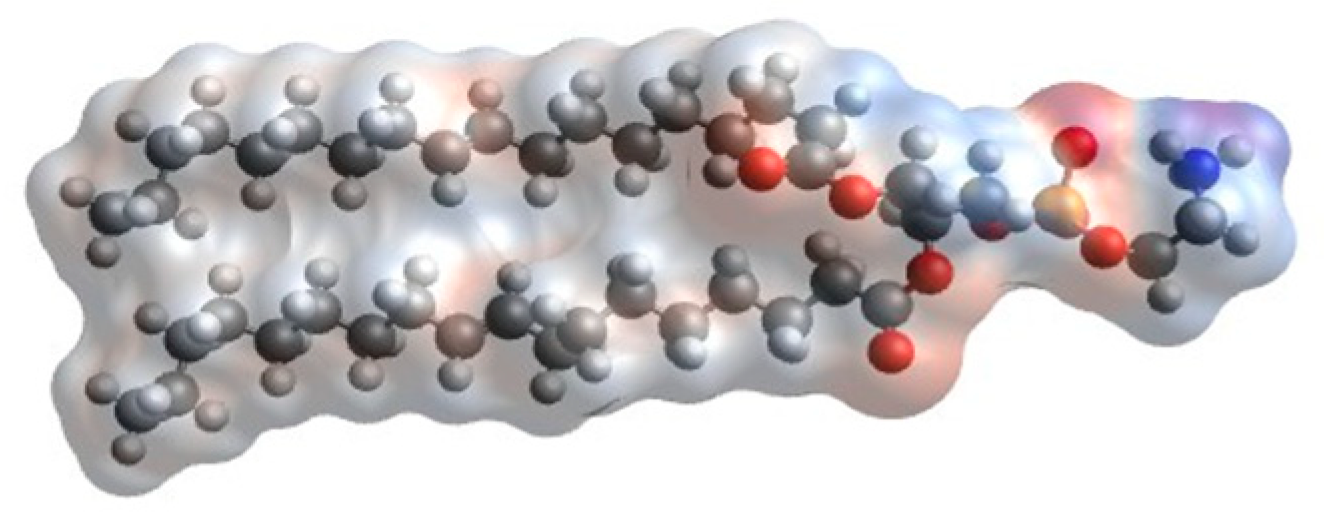
2.1. Mapping the Atomistic Structures to Coarse-Grained Models
2.2. Parameterization of the Coarse-Grained Interactions
2.2.1. Intramolecular Interaction Parameters
2.2.2. Intermolecular Interaction Parameters
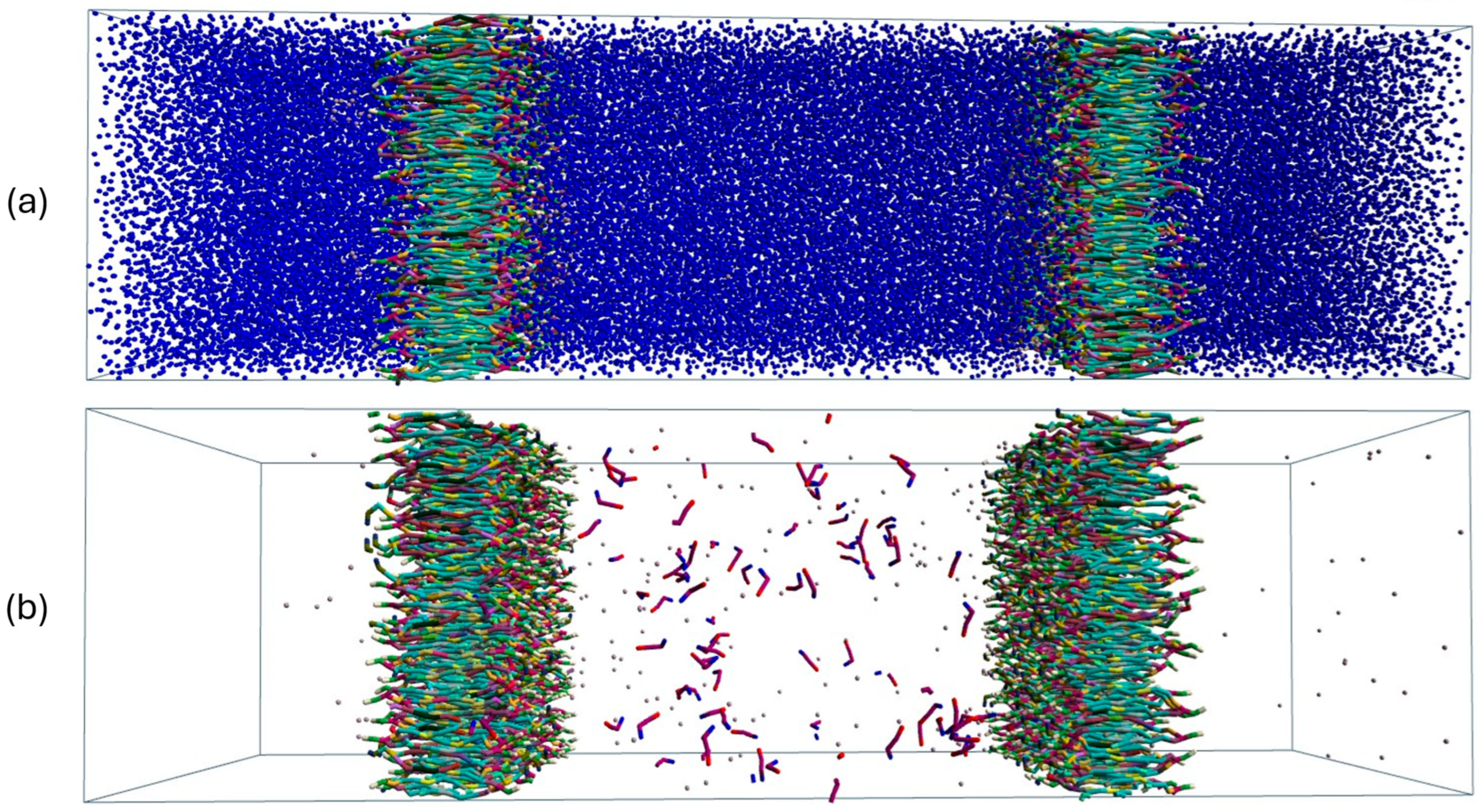
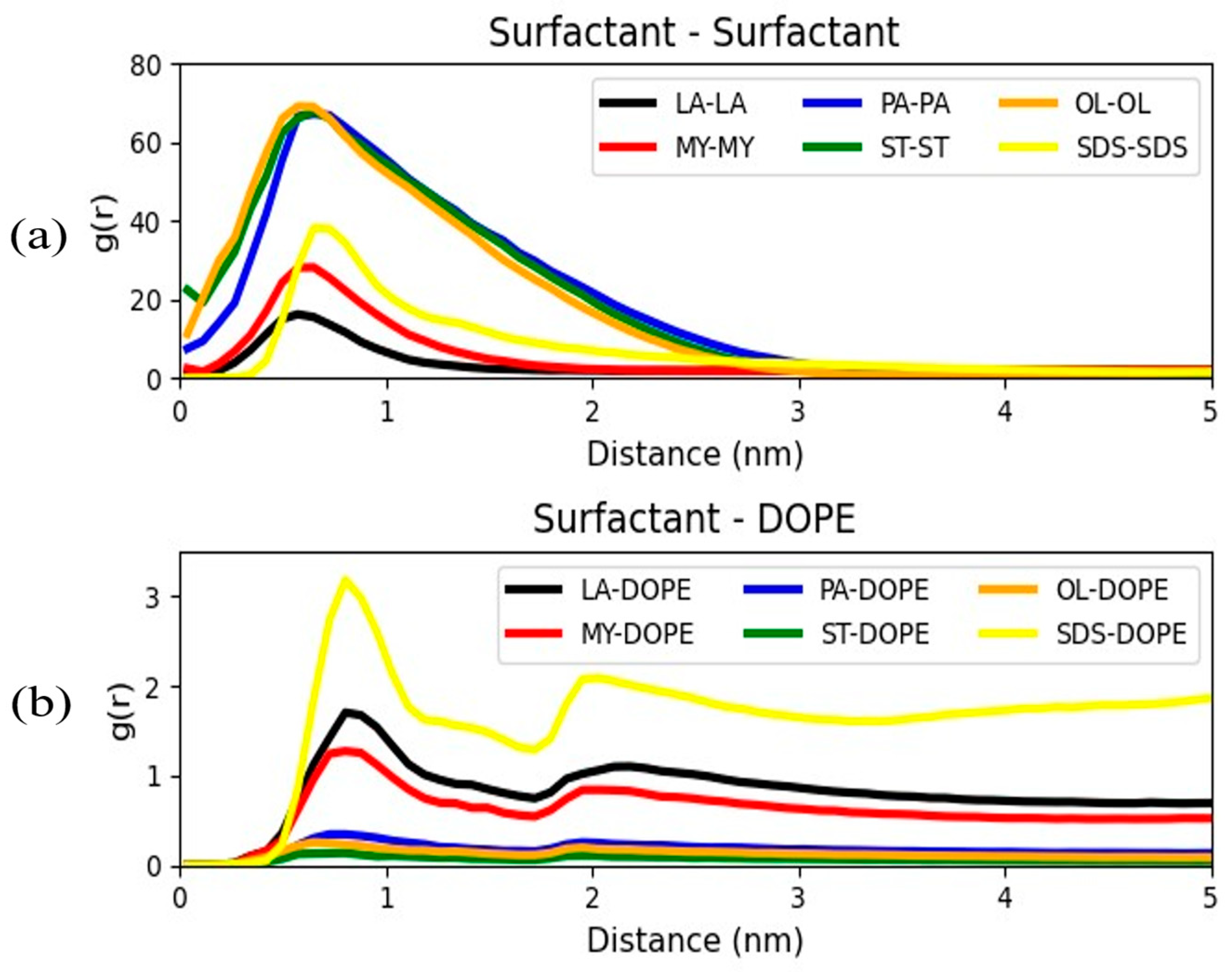
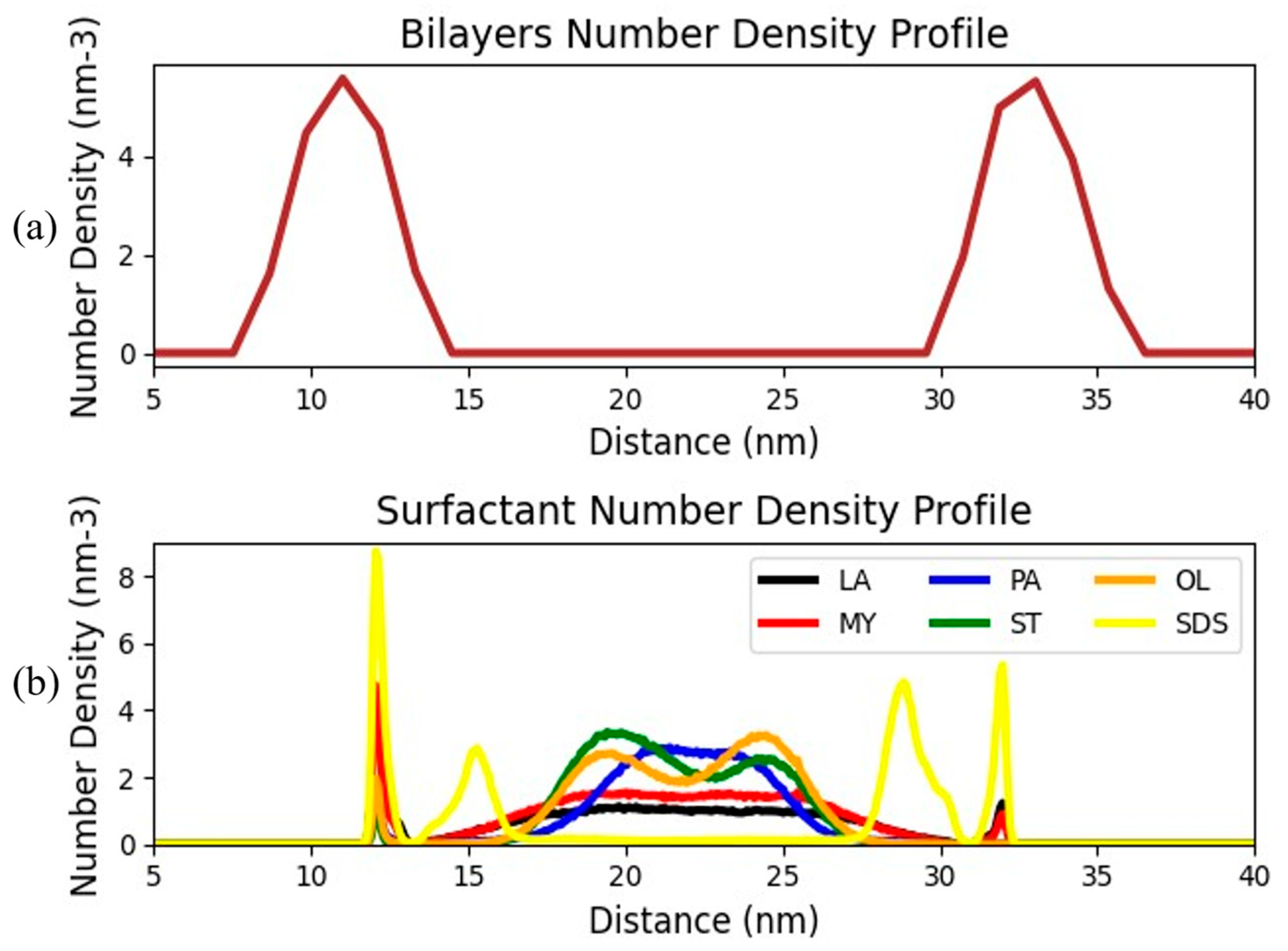
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falk, N. A Surfactants as Antimicrobials: A Brief Overview of Microbial Interfacial Chemistry and Surfactant Antimicrobial Activity. J. Surf. Deter. 2019, 22, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerklotz, H. Interactions of surfactants with lipid membranes. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 41, 205–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.B.; Yao, J.; Frank, M.W.; Jackson, P.; Rock, C.O. Membrane disruption by antimicrobial fatty acids releases low-molecular-weight proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 5294–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.K.F.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Santos, V.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactants: Multifunctional Biomolecules of the 21st Century. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhova, E.S.; Murzina, S.A. Mechanisms of the Antimicrobial Action of Fatty Acids: A Review. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2024, 60, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, E.K.; East, J.M.; Jones, O.T.; McWhirter, J.; Simmonds, A.C.; Lee, A.G. Interaction of fatty acids with lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1983, 728, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitta, F.; Motta, P.; Barbiroli, A.; Signorelli, M.; La Rosa, C.; Janaszewska, A.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B.; Fessas, D. Influence of Free Fatty Acids on Lipid Membrane–Nisin Interaction. Langmuir 2020, 36, 13535–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Shelley, J.C.; Klein, M.L. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Effect of Surfactant on a Biomembrane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 5979–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Vaiwala, R.; Gopinath, A.K.; Chockalingam, R.; Ayappa, K.G. Structure of the Bacterial Cell Envelope and Interactions with Antimicrobials: Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Langmuir 2024, 40, 7791–7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenaillon, O.; Skurnik, D.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. The population genetics of commensal Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, W.; Khalid, S. Molecular Simulations of Gram-Negative Bacterial Membranes Come of Age. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2020, 71, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Vaiwala, R.; Parthasarathi, S.; Patil, N.; Verma, A.; Waskar, M.; Raut, J.S.; Basu, J.K.; Ayappa, K.G. Interactions of Surfactants with the Bacterial Cell Wall and Inner Membrane: Revealing the Link between Aggregation and Antimicrobial Activity. Langmuir 2022, 38, 15714–15728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laatiris, A.; El Achouri, M.; Rosa Infante, M.; Bensouda, Y. Antibacterial activity, structure and CMC relationships of alkanediyl α,ω-bis(dimethylammonium bromide) surfactants. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, T.J. Methods for screening and evaluation of antimicrobial activity: A review of protocols, advantages, and limitations. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2024, 14, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, R.W.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. Development of the CHARMM Force Field for Lipids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauda, J.B.; Venable, R.M.; Freites, J.A.; O’Connor, J.W.; Tobias, D.J.; Mondragon-Ramirez, C.; Vorobyov, I.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Pastor, R.W. Update of the CHARMM All-Atom Additive Force Field for Lipids: Validation on Six Lipid Types. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7830–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjevik, Å.A.; Madej, B.D.; Dickson, C.J.; Lin, C.; Teigen, K.; Walker, R.C.; Gould, I.R. Simulation of lipid bilayer self-assembly using all-atom lipid force fields. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 10573–10584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeon, T.-J. The binding and insertion of imidazolium-based ionic surfactants into lipid bilayers: The effects of the surfactant size and salt concentration. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 5725–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, T.S.; Parkin, J.; Khalid, S. The Free Energy of Small Solute Permeation through the Escherichia coli Outer Membrane Has a Distinctly Asymmetric Profile. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 3446–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzyn, K.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. Structural Properties of the Water/Membrane Interface of a Bilayer Built of the E. coli Lipid A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 5846–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, W.; DeVane, R.; Klein, M.L. Coarse-grained molecular modeling of non-ionic surfactant self-assembly. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 2454–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Warren, D.B.; Pouton, C.W.; Chalmers, D.K. Using Molecular Dynamics to Study Liquid Phase Behavior: Simulations of the Ternary Sodium Laurate/Sodium Oleate/Water System. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11381–11393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, G.; Klein, M.L. Coarse-grain molecular dynamics simulations of diblock copolymer surfactants interacting with a lipid bilayer. Mol. Phys. 2004, 102, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.C.T.; Alessandri, R.; Barnoud, J.; Thallmair, S.; Faustino, I.; Grünewald, F.; Patmanidis, I.; Abdizadeh, H.; Bruininks, B.M.H.; Wassenaar, T.A.; et al. Martini 3: A general purpose force field for coarse-grained molecular dynamics. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiwala, R.; Ayappa, K.G. Martini-3 Coarse-Grained Models for the Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Outer Membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2024, 20, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, R.D.; Warren, P.B. Dissipative particle dynamics: Bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 4423–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; Rabone, K.L. Mesoscopic Simulation of Cell Membrane Damage, Morphology Change and Rupture by Nonionic Surfactants. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gao, L.; Fang, W. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulations for Phospholipid Membranes Based on a Four-To-One Coarse-Grained Mapping Scheme. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ji, Y.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Asymmetric Lipid Membranes under Shear Flows: A Dissipative Particle Dynamics Study. Membranes 2021, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevink, G.J.A.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. Efficient solvent-free dissipative particle dynamics for lipid bilayers. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 5129–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraaije, J.G.E.M.; van Male, J.; Becherer, P.; Serral Gracià, R. Coarse-Grained Models for Automated Fragmentation and Parametrization of Molecular Databases. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 2361–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcenter Culgi, version 2211. Software for Multiscale Computational Chemistry Simulations. Siemens Digital Industries Software B.V.: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2022.
- Parchekani, J.; Allahverdi, A.; Taghdir, M.; Naderi-Manesh, H. Design and simulation of the liposomal model by using a coarse-grained molecular dynamics approach towards drug delivery goals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.; Lyubartsev, A.P. Development of a bottom-up coarse-grained model for interactions of lipids with TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Comput. Chem. 2024, 45, 1364–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogerbrugge, P.J.; Koelman, J.M.V.A. Simulating Microscopic Hydrodynamic Phenomena with Dissipative Particle Dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 1992, 19, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, M.; Bylaska, E.J.; Govind, N.; Kowalski, K.; Straatsma, T.P.; Van Dam, H.J.J.; Wang, D.; Nieplocha, J.; Apra, E.; Windus, T.L.; et al. NWChem: A comprehensive and scalable open-source solution for large scale molecular simulations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2010, 181, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A.; Schüürmann, G. COSMO: A new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1993, 2, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A.; Eckert, F.; Reinisch, J.; Wichmann, K. Prediction of cyclohexane-water distribution coefficients with COSMO-RS on the SAMPL5 data set. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loschwitz, J.; Olubiyi, O.O.; Hub, J.S.; Strodel, B.; Poojari, C.S. Chapter Seven-Computer simulations of protein–membrane systems. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translatioal Science; Strodel, B., Barz, B., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 170, pp. 273–403. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, H.C. Molecular dynamics simulations at constant pressure and/or temperature. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraaije, J.G.E.M.; van Male, J.; Becherer, P.; Serral Gracià, R. Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients through Coarse-Grained Simulations Using the Automated-Fragmentation-Parametrization Method and the Recovery of Wilke–Chang Statistical Correlation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, P.P.; Steim, J.M. Physical properties of fatty acyl-CoA. Critical micelle concentrations and micellar size and shape. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 7573–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, W.U.; Jain, A.K. Electrometric determination of critical micelle concentration of soap solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interf. Electrochem. 1967, 14, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanis, I. A Multiscale Approach to Examine the Adsorption of Fatty Acid Surfactants in Bacterial Membranes. Physchem 2025, 5, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040050
Tanis I. A Multiscale Approach to Examine the Adsorption of Fatty Acid Surfactants in Bacterial Membranes. Physchem. 2025; 5(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanis, Ioannis. 2025. "A Multiscale Approach to Examine the Adsorption of Fatty Acid Surfactants in Bacterial Membranes" Physchem 5, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040050
APA StyleTanis, I. (2025). A Multiscale Approach to Examine the Adsorption of Fatty Acid Surfactants in Bacterial Membranes. Physchem, 5(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5040050





