Abstract
Solid solutions of the metallocenes ferrocene (Cp2Fe), nickelocene (Cp2Ni), and cobaltocene (Cp2Co) have been prepared by manually grinding the components together, or by co-crystallizing them from solution. In the solid solutions Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni and Cp2Co/Cp2Ni, the cyclopentadienyl (Cp) protons relax via dipolar electron–proton interactions, which represent the dominant relaxation mechanism. The 1H T1 relaxation times of the molecules Cp2Ni and Cp2Co, dissolved in CDCl3, and in the solid solutions, show that the relaxation takes place intramolecularly. The relaxation of the protons is propagated exclusively via the unpaired electrons of the metal centers to which their Cp rings are coordinated, due to the large intermolecular distances that are greater than 3.91 Å. In contrast, the intramolecular distances between the electrons of the metal atoms and the protons of their coordinated Cp rings are merely 2.70 Å. Using these intramolecular distances and the 1H T1 relaxation times, the electron relaxation times T1e have been determined as 17 × 10−13 s in CDCl3 solutions and 45 × 10−13 s in the solid state for Cp2Ni. The corresponding T1e times for Cp2Co are calculated as ca. 5 × 10−13 s and 20 × 10−13 s. Grinding Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni together leads to two different 1H T1 relaxation times for the protons of Cp2Fe. The longer T1 relaxation time indicates domains that consist mostly of Cp2Fe molecules. The short T1 times show a close contact of Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni molecules. An analysis of the short 1H T1 times reveals the presence of at least two to three short distances of 3.91 Å between Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni molecules. These results support the hypothesis that dry grinding of the metallocenes Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni in ratios that were changed in 10% increments from 90%/10% to 30%/70% leads to domains that mostly consist of Cp2Fe molecules, and additionally to domains that contain a mixture of the components on the molecular level.
1. Introduction
The study of paramagnetic molecular systems in solution and in the solid state is an important field of NMR spectroscopy, directed at elucidating their structural and electronic properties [1,2]. Among various paramagnetic complexes, the classic 3d metallocenes, such as chromocene (Cp2Cr), vanadocene (Cp2V), cobaltocene (Cp2Co), and nickelocene (Cp2Ni), containing unpaired electrons at the metal centers, are of great interest [3,4,5,6]. Besides the phenomenological interest in their dynamics [7,8,9], surface-adsorbed metallocenes are especially important as precursors for single-atom catalysts [8] and the Union Carbide catalyst [10]. Recently, our group has investigated solid solutions [11] of Cp2Fe, Cp2Co, and Cp2Ni that were obtained by co-crystallization from solutions [12,13,14], and by grinding the components together in the absence of a solvent [15,16]. While EPR spectroscopy proved to be less useful for probing the distribution of the components in the crystal lattice [16], the NMR chemical shifts, linewidths, and Chemical Shift Anisotropy (CSA) [17,18,19,20,21] could successfully be applied as criteria to study the surface-adsorbed, dissolved, and neat metallocenes, as well as their solid solutions.
The nature of the paramagnetic shifts in these metallocenes is well studied experimentally and theoretically and described in numerous publications that have been summarized in a recent review [1]. However, studies of the NMR relaxation properties of the metallocenes have been very limited, besides the common observation of the paramagnetic relaxation rate enhancement. One of the possible reasons for the limited studies and knowledge base might be the fact that most of the 3d metallocenes, like Cp2Co and Cp2Ni, are highly reactive and air-sensitive [15]. This feature complicates the preparation of clean samples in solutions and in the solid state, which is particularly important for collecting reliable proton NMR relaxation data with highly reproducible 1H T1 time measurements.
Recently, the 1H T1 criterion has been applied as a tool for studying solid solutions with the components Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni [15], as well as Cp2Fe/Cp2Co and Cp2Co/Cp2Ni [16]. These solid solutions have been prepared by manually grinding the components together with a mortar and pestle in the absence of any solvent or, alternatively, by co-crystallizing the mixed metallocenes from a solution [12,13,14]. The collected data, particularly the measured 1H T1 relaxation times and their changes when varying the ratios of the components, were considered mainly phenomenologically. In the presented work, these data [15,16], in combination with the results of additional 1H NMR experiments, are discussed in a comprehensive manner. Hereby, the focus lies on the mechanisms of the proton relaxation in paramagnetic metallocenes, and the quantitative interpretation of the 1H T1 data. In general, this study is directed at a better understanding of the level of mixing of the components after grinding them together. Deeper insights about solid–solid mixtures will also be beneficial for other fields like heterogeneous catalysis [22,23] and mechanochemistry [24].
2. Results and Discussion
Among the various proton relaxation mechanisms effective in paramagnetic solids, generally the following relaxation pathways are discussed: (a) Proton spin diffusion, (b) Fermi-contact electron-nucleus coupling, (c) relaxation via dipolar proton-electron interactions, and (d) Curie relaxation [1,2]. Due to the high magnetic field strength and ‘high’ temperature commonly used in the NMR experiments, relaxation pathway (d), the Curie contribution, is recognized to be insignificant [1]. The relaxation pathways (a), (b), and (c) are analyzed in the following.
2.1. Proton Spin Diffusion
The spin diffusion relaxation mechanism, which is, in principle, possible for protons in the presence of paramagnetic centers, can be ruled out due to the following reasons: 1. This mechanism is ineffective for mobile solids [2]. The Cp rings in metallocenes undergo extremely fast rotation even in the solid state [3,20,25]. This rotation leads to very rapid reorientation of the intermolecular proton-proton dipolar vectors. 2. Spin diffusion generally leads to an exponential relaxation, especially at the fast spin diffusion limit [2] in contrast to the non-exponential relaxation observed in our study (see below). 3. In the presence of spin diffusion, the 1H T1 relaxation times in the mixtures of Cp2Co and Cp2Ni should be equal, or at least very close for both components. As follows from our measurements, presented below, these relaxation times are very different. 4. Spin diffusion is dependent on the spinning rates [26]. However, the T1 relaxation times of the Cp2Fe protons in a solid solution of Cp2Fe and Cp2Co (50%/50%), prepared by co-crystallization of equal amounts of the dissolved components, were determined as 9.6 ms and 8.4 ms at spinning rates of 10 kHz and 11 kHz, respectively. Since the frictional heating effect is negligible when increasing the rotational speed from 10 to 11 kHz [27], this indicates that the T1 relaxation times are practically independent of the spinning rates. All these results speak against option (a), the spin diffusion mechanism, and leave (b) and (c) as possible relaxation pathways.
Regarding (c), in the absence of spin diffusion, unpaired electrons located at a metal center can facilitate the proton relaxation via dipolar interactions between the proton (H) and electron spins (S), as described in Equation (1) [28,29].
1/T1(H)dip = (2/5) × (μ0/4π)2γH2 × γS2 × ħ2 × S(S + 1) × r(H−S)−6 × c × (T1e/(1+ ωH2 × T1e2))
Furthermore, the proton relaxation can be propagated through pathway (b), Fermi-contact electron-nucleus coupling as described in Equation (2) [30].
1/T1(H)CON = (1/3) × (μ0/4π)2 × S(S + 1) × (A/ħ)2 × T1e{1 + (ωH − ωS)2 × T1e2}−1
In these equations, T1e is the electron spin-lattice relaxation time, r(H-S) indicates the proton-electron distance, A represents the Fermi-contact coupling constant, and S equals 1 and ½ for the electrons at the Ni and Co centers, respectively.
2.2. Fermi-Contact Electron-Nucleus Coupling
It is well known that in cases where the Fermi-contact coupling is the primary mechanism of relaxation, the 1H T2 relaxation times are dramatically shorter than the 1H T1 times. For example, in paramagnetic metal complexes, the T2 relaxation times even of 13C nuclei, which have a smaller gyromagnetic ratio than protons, can be shorter than 5 × 10−4 s [30].
For solid paramagnetic species, the T2 times can be obtained from the signal halfwidths Δν via the equation T2 = 1/Δν. We estimated the 1H T2 times in solid solutions with different ratios of Cp2Co and Cp2Ni using a Gaussian line shape fit for the signals (Table 1). The 1H T2 times for Cp2Co were in the range of 0.71 ms to 0.72 ms, and those for Cp2Ni were between 0.37 ms and 0.40 ms (Table 1). These T2 relaxation times are not significantly shorter than the corresponding 1H T1 times in the ranges of 2.3–2.8 ms for Cp2Co and 0.38–0.46 ms for Cp2Ni (Table 1). Therefore, the 1H T1 and T2 relaxation time data show that the Fermi-contact mechanism is not dominant.

Table 1.
Halfwidths Δν of the isotropic lines (kHz) and 1H T1 times (ms) determined at a spinning rate of 10 kHz for Cp2Co and Cp2Ni solid solutions prepared by grinding the components together [16], and 1H T2 times (ms) calculated from the linewidths for Gaussian line shapes.
It should also be noted that a similar scenario is observed for CDCl3 solutions of Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni mixtures (see below), where the halfwidth Δν of the nickelocene resonance is ca. 530 Hz, corresponding to a 1H T2 time of 0.6 ms. Again, this T2 relaxation time is not significantly shorter than the measured 1H T1 time of about 0.94 ms.
An additional factor that is important for the interpretation of the proton relaxation times in solid paramagnetic metallocenes is the observation of MAS effects on their 1H NMR spectra. Figure 1 shows, as an example, the 1H MAS and static NMR spectra recorded for a 50%/50% mixture of Cp2Co and Cp2Ni prepared by grinding the components together.
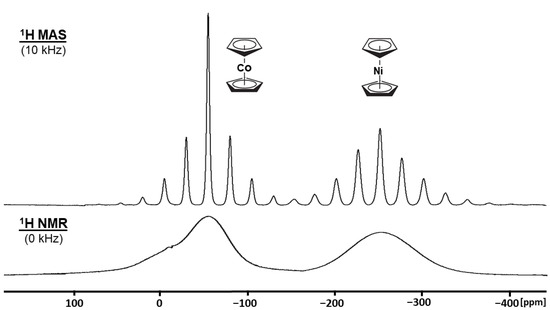
Figure 1.
1H NMR spectra of a 50/50 mixture of Cp2Co and Cp2Ni prepared by grinding the components together. 1H wideline NMR spectrum of the static sample (bottom) and MAS spectrum recorded with a sample spinning rate of 10 kHz (top).
The wideline NMR spectrum of this mixture exhibits two extremely broad resonances with estimated halfwidths of 6.8 and 9.4 kHz centered at about −58 and −250 ppm, corresponding to the paramagnetic components Cp2Co and Cp2Ni, respectively (Figure 1, bottom). The significant upfield shift in the resonances, compared to the diamagnetic analog Cp2Fe, is due to the one and two unpaired electrons at the Co and Ni centers. The overall signal shapes are symmetric, with the number of rotational sidebands being larger for the Cp2Ni signal. The changes in the spinning sideband intensities with different amounts of the components in solid solutions have been reported earlier [15,16]. The substantial line-broadening of the signals is also caused by the unpaired electrons, again via dipolar electron-nucleus interactions and/or Fermi-contact coupling [1,2]. In contrast, under MAS conditions, the 1H NMR signals show extended sideband patterns with relatively narrow isotropic lines with Δν of 1.39 kHz for Cp2Co and 2.45 kHz for Cp2Ni (Figure 1, top). Since the Fermi-contact interactions cannot be reduced substantially by mechanical sample rotation, the relaxation mechanism (b) cannot be dominant.
Finally, it should be mentioned that the bulk magnetic susceptibility (BMS), which also contributes to the signal shape in the spectra of static samples and to the sideband intensities and their halfwidths in the MAS spectra, does not significantly influence the T1 relaxation times [1,2]. Therefore, the proton relaxation data reported earlier for paramagnetic metallocenes [15,16] can be discussed in this contribution in terms of pathway (c) as the dominant relaxation mechanism. This result is in complete agreement with the literature [1,31].
2.3. Dipolar Proton-Electron Interactions
The dipolar interactions between proton spins (H) and electron spins (S) are outlined in Equation (1) above. The relaxation data of the metallocenes Cp2Fe, Cp2Co, and Cp2Ni, which are most important in the context of the presented study, are summarized in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
1H T1 relaxation times (ms) of the Cp resonances in solid solutions of Cp2Ni and Cp2Co, prepared by grinding the components together with the indicated molar ratios. The T1 times were obtained by fitting procedures with a stretched exponential f(t) = exp(−τ/T1)β for the Cp signals.

Table 3.
1H T1 relaxation times (10% accuracy) of Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni [15] and Cp2Fe/Cp2Co [16] mixtures dissolved in CDCl3 with the indicated molar ratios. M stands for Ni or Co.
The data in Table 2 show that the proton relaxation in solid mixtures of Cp2Co and Cp2Ni is non-exponential, following a stretched exponential function f(t) = exp(−τ/T1)β. This behavior can be explained by the presence of a T1 time distribution that is often observed in solids [2]. In contrast, in CDCl3 solutions, the diamagnetic and paramagnetic components relax exponentially due to the isotropic molecular motions. In solution, the T1 time of the Cp2Co protons is 9.58 ms, whereas that for Cp2Ni amounts to 0.96 ms [15,16].
To improve our understanding of the proton relaxation in solid Cp2Ni/Cp2Co mixtures, it is useful to consider the common crystal structure of these metallocenes [32,33], displayed in Figure 2. According to the X-ray data, the shortest average intramolecular and intermolecular metal (electron)—proton distances are 2.70 Å and 3.91 Å, respectively. In terms of the dipolar electron-nucleus relaxation corresponding to Equation (1), the difference in these distances leads to a ratio T1(H…S)/T1(H-S) of (3.91/2.7)6, which equals 9.22. In other words, the T1(H…S) time due to intermolecular dipolar proton-electron interaction will be about nine times longer than the T1(H-S) relaxation time caused by intramolecular H-S interactions.
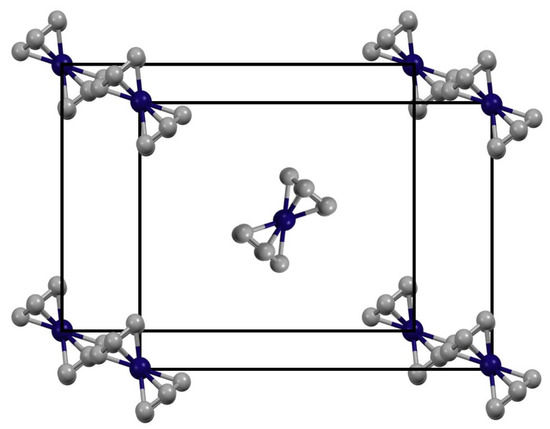
Figure 2.
The single crystal unit cell of the metallocenes Cp2Fe, Cp2Co, and Cp2Ni. The schematic presentation was created using data from the literature [32,33]. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity.
Since the number of nearest neighbors surrounding one metallocene molecule in the crystal lattice is eight (Figure 2), the total relaxation time observed can be expressed via Equation (3).
1/T1(obs) = 1/T1(H-S) + 8 · 1/T1(H…S)
The relaxation time 1H T1(obs) of 0.27 ms has been measured for the Cp2Ni signal in the 10%/90% Cp2Co/Cp2Ni mixture (Table 2). This solid solution contains a large excess of nickelocene. Therefore, it can be assumed that the eight nearest Cp2Ni neighbors are present and that the intermolecular distances for nickelocene are preserved. Based on Equation (3) and the fact that T1(H…S)/T1(H-S) is about 9, the relaxation time 1H T1(obs) corresponds to the T1(H-S)Ni value of 0.51 ms for the intramolecular relaxation, and a T1(H…S)Ni relaxation time of 0.57 ms for the total intermolecular interactions.
The same calculation, performed for the 90%/10% Cp2Co/Cp2Ni solid solution with the measured relaxation time 1H T1(obs) of 2 ms (Table 2), gives a T1(H-S)Co value of 3.8 ms for the intramolecular relaxation, and the T1(H…S)Co time of 4.2 ms corresponding to the total intermolecular interactions. In other words, these estimates for Cp2Co and Cp2Ni show that practically one-half of the observed relaxation rate can be provided by intermolecular interactions with the surrounding molecules.
Considering the data summarized in Table 2, it is obvious that the measured 1H T1 relaxation times of both components in the solid solutions Cp2Ni/Cp2Co do not change significantly even when the ratios are varied over a large range. The 1H T1 relaxation times show the average values of 2.5 ms for Cp2Co and 0.38 ms for Cp2Ni. Importantly, the 1H T1 times listed in Table 2 do not follow the component ratios, and their small variations can be attributed to 20–30% errors in the 1H T1 determinations due to the samples being highly air-sensitive. In other words, in the mixtures that were prepared by grinding Cp2Ni and Cp2Co together, the Cp protons of the components relax independently via the unpaired electrons of their own metal centers. This result reveals the absence of substantial intermolecular relaxation contributions. This effect is most likely caused by increased intermolecular distances because of the destruction of the crystal structures. In fact, when the intermolecular distances in a crystal of Cp2Ni grow, for example, by a factor of 1.5, the T1(H…S)Ni time of 0.57 ms, corresponding to the total intermolecular interactions, will be increased by a factor of 11. In addition, the 1H T1 relaxation time in polycrystalline nickelocene has been measured as 0.23 ms, which is shorter than the times summarized in Table 2. Thus, the 1H T1 relaxation times of 2.5 ms and 0.38 ms mentioned above can be attributed to T1(H-S)Co and T1(H-S)Ni relaxation times that characterize the intramolecular relaxation contributions.
The conclusions drawn for solid Cp2Co and Cp2Ni mixtures on the basis of the relaxation data in Table 2 agree with the 1H T1 relaxation measurements carried out for paramagnetic metallocenes in the mixtures with diamagnetic ferrocene dissolved in CDCl3 (Table 3). The 1H T1 relaxation times of Cp2Co and Cp2Ni have been determined as 9.6 ms and about 1 ms, respectively. They are independent of the fractions of Cp2Fe that change over a large range from 0% to 90%. The Cp2Fe rather plays the role of a diluting agent, like the solvent. Therefore, the 1H T1 relaxation times for Cp2Co and Cp2Ni in solution again represent the intramolecular electron-proton dipolar relaxation contributions.
The 1H T1 relaxation time of pure Cp2Fe in the CDCl3 solution (Table 3) is much shorter (4.9 s, Table 3) than that in the solid state (14–15 s) [16]. Such a shortening is expected due to the rapid isotropic reorientations of the Cp2Fe molecules in solutions. In contrast, the 1H T1 relaxation times of both paramagnetic compounds grow significantly when going from the solid state (Table 2) to the CDCl3 solution (Table 3). Based on the relaxation mechanism (c) via the dipolar electron–proton interactions, this observation can be explained by the electron relaxation time, T1e, that can change with increasingly rigid environments [34].
Equation (1) can be used to calculate the T1e relaxation time for Cp2Ni in solution. The 1H T1 relaxation time of Cp2Ni, determined for the CDCl3 solution as ca. 1 ms for all Cp2Ni/Cp2Fe ratios (Table 3), and the intramolecular Ni(electron)—proton distance of 2.70 Å, derived from the X-ray structure, result in the T1e relaxation time of 17 × 10−13 s. Analogously, the longer T1e relaxation time of 45 × 10−13 s can be obtained for solid Cp2Ni from the 1H T1 time of 0.38 ms (Table 2). In the same way, the T1e relaxation time for Cp2Co can be calculated as ca. 5 × 10−13 s and 20 × 10−13 s, characterizing the relaxation of the unpaired electrons of the Co centers in solution and in the solid state, respectively. It should be noted that the T1e relaxation time of 17 × 10−13 s obtained here for Cp2Ni in CDCl3 is longer than that reported as 3 × 10−13 s for Cp2Ni dissolved in toluene [31]. The latter value, however, has been estimated from the NMR linewidths and not based on the relaxation time.
Co-crystallization of dissolved metallocenes leads to solid solutions with a homogeneous distribution of the different molecules on a molecular level in the crystal lattice. This homogeneous distribution of different metallocenes has been proven by single-crystal X-ray analysis previously [15]. Hence, only one T1 relaxation time is found for each metallocene. In a different approach, the migration of one metallocene into an existing crystal lattice of another in the absence of a solvent has been demonstrated by the 1H T1 relaxation experiments for mixtures of Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni prepared by grinding the components together with varied molar ratios [15]. While grinding is a complex process regarding the obtainable particle sizes [35], we could demonstrate earlier that even in the absence of a solvent and without grinding, the volatile Cp2Ni migrates into single crystals of Cp2Fe [15]. The main feature of the 1H T1 relaxation behavior of Cp2Fe after grinding with Cp2Ni was its bi-exponential character [15]. Two different 1H T1 times were obtained for Cp2Fe molecules in domains composed mostly of ferrocene, and for Cp2Fe molecules at the edges of these domains, and therewith close to Cp2Ni molecules. Hereby, the long 1H T1 time of 14–18 s was determined for Cp2Fe molecules residing far away from paramagnetic Cp2Ni molecules [15]. However, it remained unclear how close the Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni molecules are located in the fast-relaxing domains when the mixtures are prepared by grinding the components together in the absence of a solvent. Here, we analyze these domains on the basis of the short 1H T1 times obtained for the fast-relaxing T1 components with errors around 20–25% for the Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni mixtures that are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
The 1H T1 times (ms) of fast-relaxing Cp2Fe molecules obtained with bi-exponential function treatments of the inversion-recovery experiments performed for the Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni mixtures prepared by dry grinding of the components [15].
The data in Table 4 show that the fraction of the fast-relaxing T1 component grows with the Cp2Ni content and reaches a maximum of 0.40–0.42. This value can be caused by a limitation in the mixing technique. As shown above, the 1H T1(H…S)Ni relaxation time in Cp2Ni is 0.57 ms. This represents also the total intermolecular dipolar electron—proton relaxation that will contribute to the relaxation of the diamagnetic Cp2Fe when it is surrounded by 8 Cp2Ni molecules at a distance of 3.91 Å in a Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni crystal. Consequently, the short 1H T1 relaxation time of 2–3 ms, obtained experimentally for the fast-relaxing Cp2Fe, will correspond to 2–3 short contacts (3.91 Å) between the Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni molecules. In other words, each Cp2Fe molecule is surrounded by 2 to 3 neighboring Cp2Ni molecules. This shows that the components are mixed in the solid solution Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni on a molecular level in the fast-relaxing domain. It is also possible that the number of short contacts is larger, but at increased intermolecular distances.
It is remarkable that for mixed crystals of Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni grown from 50/50 solutions, the 1H T1 relaxation time of the Cp2Fe does not exhibit a slow-relaxing component. This indicates that large domains composed of only Cp2Fe are absent, and a more homogeneous distribution of the Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni molecules in the crystal lattice prevails throughout the bulk of the material. The 1H T1 relaxation time of Cp2Fe has been measured as 4 ms [15], which is close to the values of 2–3 ms reported in Table 4.
3. Conclusions
The proton T1 relaxation times in solid solutions of Cp2Co/Cp2Ni and Cp2Fe/Cp2Ni, prepared by co-crystallization and by grinding the components together, have been analyzed. The results show that the dipolar electron—proton interactions are the dominant relaxation mechanism. It has been concluded that Cp2Ni and Cp2Co protons in CDCl3 solutions, as well as in the mixtures prepared by grinding the components, relax independently via their own unpaired electrons. Intermolecular relaxation contributions are negligible due to the increased intermolecular distances that are much larger than 3.91 Å. Using these 1H T1 relaxation times and the intramolecular Ni(electron)—proton distances of 2.70 Å that were obtained from the single crystal X-ray structure, the electron relaxation times T1e are determined as 17 × 10−13 s in CDCl3 and 45 × 10−13 s in the solid state. The corresponding T1e relaxation times for Cp2Co are calculated as ca. 5 × 10−13 s in solution and 20 × 10−13 s in the solid.
The fast-relaxing T1 components in mixtures of Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni, prepared by grinding the components together, have been analyzed with the Cp2Ni content increasing from 10% to 70%. At least 2–3 short contacts with distances of 3.91 Å between Cp2Fe and Cp2Ni molecules are present. It is possible that the number of contacts is larger, but at increased intermolecular distances. Overall, the proton T1 time analysis illustrates that the components in solid solutions, which were obtained by co-crystallization from solutions, mix on the molecular level throughout the crystal lattice. In case the solid solutions are prepared by manual grinding, domains mostly populated by one species remain, and the homogeneous mixing only takes place at the interfaces. In summary, the presented study provides new insights into relaxation mechanisms of metallocenes, and it demonstrates that paramagnetic solution- and solid-state NMR spectroscopy is a valuable method for monitoring mechanochemical processes [24,35] and for probing multi-component materials [36] on the molecular level.
4. Experimental Section
Materials and sample preparation. Cp2Fe, Cp2Ni, and Cp2Co were purchased from Fisher Scientific and sublimed under an inert gas atmosphere prior to use. All metallocenes and solid solutions were stored in a glove box operated with purified nitrogen.
The solid solutions of metallocenes were obtained by co-crystallizing them from DCM solutions after weighing in the desired amounts of the components. The crystals contained the metallocenes in the same ratios as the initially prepared solution, as determined by filtering the crystals off from the mother liquor, dissolving them in a deuterated solvent, and measuring the integrals of the metallocene signals. The integrals confirmed that the compositions corresponded to the initial ratios of the metallocenes in the prepared solutions. Alternatively, the solid solutions have been generated by manually grinding the desired amounts of the solid metallocenes together for 30 min with an agate mortar and pestle that did not absorb the metallocenes. All materials were densely packed into 4 mm ZrO2 rotors. Cobaltocene and nickelocene are air-sensitive and, therefore, nitrogen was used as the bearing and drive gas for MAS measurements.
Solid-state NMR measurements. The solid-state NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance-Neo 400 spectrometer (Bruker Biospin, Karlsruhe, Germany). The 4 mm MAS probehead was equipped with a broadband and a 1H NMR channel. The 1H NMR spectra were acquired using a single pulse program. Eight scans were sufficient for spectra with good S/N ratios. The spectra were processed without line broadening; however, the 1H background signal was subtracted. TMS functioned as the external 1H chemical shift standard. For the static regime, the temperature control unit of the spectrometer was calibrated by the standard procedure that is based on liquid methanol in a MAS rotor. When spinning, temperature corrections have been applied following the protocol for 4 mm rotors [27]. At a spinning speed of 10 kHz, 295 K of the drive and bearing gas corresponds to 298.3 K within the rotor based on the correction [27]. The frictional heating effect is negligible when going from 10 to 11 kHz according to this well-known protocol [27].
The proton T1 relaxation times were determined at spinning rates of 10 and 11 kHz using standard inversion–recovery pulse programs (180°−τ−90°). The RF pulses were calibrated prior to the measurements (2.5 μs at 105.3 W power). The acquisition time was varied from 0.005 to 0.001 s. The τ delays increased incrementally from 0.00005 to 50 s for ferrocene/cobaltocene mixtures and from 0.000015 to 5.0 s for nickelocene/cobaltocene systems. After each pulse cycle, complete relaxation was achieved by sufficiently long recycle delays, which amounted to 50 s for mixtures of ferrocene and cobaltocene and 5 s for the solid solutions of nickelocene and cobaltocene. No linebroadening was necessary after accumulating 8 scans. Processing the relaxation time data was performed by subjecting the experimentally obtained inversion−recovery curves, featuring the signal intensities versus τ times, to a conventional nonlinear fitting computer program based on the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm. Since the 1H resonances of the metallocenes measured in this contribution have different chemical shifts, the T1 times for their mixtures were determined using two carrier frequencies centered at the positions of the two resonances. The error margin of the T1 time measurements is estimated to be about 10–15%.
The line shape analyses of the wideline signals were performed with the programs and software package of the Bruker spectrometer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.I.B. and J.B.; Methodology, G.E.H.-W., D.W.E., N.B., V.I.B. and J.B.; Software, G.E.H.-W., D.W.E., N.B. and V.I.B.; Validation, N.B. and V.I.B.; Formal analysis, G.E.H.-W., D.W.E., N.B., V.I.B. and J.B.; Investigation, G.E.H.-W., V.I.B. and J.B.; Resources, J.B.; Data curation, G.E.H.-W., D.W.E. and V.I.B.; Writing—original draft, V.I.B. and J.B.; Writing—review and editing, G.E.H.-W., D.W.E. and N.B.; Visualization, G.E.H.-W. and J.B.; Supervision, J.B.; Project administration, J.B.; Funding acquisition, J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (CHE-1900100).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Pell, A.J.; Pintacuda, G.; Grey, C.P. Paramagnetic NMR in solution and the solid state. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2019, 111, 1–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmutov, V.I. Strategies for solid-state NMR studies of materials: From diamagnetic to paramagnetic porous solids. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 530–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümel, J.; Hiller, W.; Herker, M.; Köhler, F.H. Solid-State Paramagnetic NMR Spectroscopy of Chromocenes. Organometallics 1996, 15, 3474–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümel, J.; Hofmann, P.; Köhler, F.H. NMR Spectroscopy of Paramagnetic Complexes. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1993, 31, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, H.; Köhler, F.H.; Xie, X. Solid-state NMR spectroscopy of paramagnetic metallocenes. J. Magn. Reson. 2001, 150, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, F.H.; Xie, X. Vanadocene as a Temperature Standard for 13C and 1H MAS NMR and for Solution-State NMR Spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1997, 35, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluff, K.J.; Schnellbach, M.; Hilliard, C.R.; Blümel, J. The adsorption of chromocene and ferrocene on silica: A solid-state NMR study. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 744, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluff, K.J.; Blümel, J. Adsorption of Metallocenes on Silica. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 16562–16575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, J.W.; Harmon-Welch, G.E.; Hoefler, J.C.; Bakhmutov, V.I.; Blümel, J. Molecular Dynamics and Surface Interactions of Nickelocene Adsorbed on Silica: A Paramagnetic Solid-State NMR Study. Langmuir 2022, 38, 7422–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnellbach, M.; Blümel, J.; Köhler, F.H. The Union Carbide catalyst (Cp2Cr + SiO2), studied by solid-state NMR. J. Organomet. Chem. 1996, 520, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D., Jr. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-471-35446-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Horst, J.H.; Deij, M.A.; Cains, P.W. Discovering New Co-Crystal. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilborg, A.; Norberg, B.; Wouters, J. Pharmaceutical salts and cocrystals involving amino acids: A brief structural overview of the state-of-art. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagden, N.; Berry, D.J.; Parkin, A.; Javed, H.; Ibrahim, A.; Gavan, P.T.; De Matos, L.L.; Seaton, C.C. Current directions in co-crystal growth. New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon-Welch, G.E.; Hoefler, J.C.; Trujillo, M.R.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Bakhmutov, V.I.; Blümel, J. Creating Solid Solutions of Metallocenes: Migration of Nickelocene into the Ferrocene Crystal Lattice in the Absence of a Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon-Welch, G.E.; Bakhmutov, V.I.; Blümel, J. Paramagnetic Solid-State NMR Study of Solid Solutions of Cobaltocene with Ferrocene and Nickelocene. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderovich, I.G.; Limbach, H.-H. Solid State NMR for Nonexperts: An Overview of Simple but General Practical Methods. Solids 2021, 2, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Spiess, H.W. Multidimensional Solid-State NMR and Polymers; Academic Press: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, T.M. A Compilation of Chemical Shift Anisotropies; Farragut Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe, C.A. Solid-State NMR for Chemists; C.F.C. Press: Guelph, ON, Canada, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Stejskal, E.O.; Memory, J.D. High-Resolution NMR in the Solid State; Oxord University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, F.R. Supported Metal Complexes; D. Reidel Publishing Co.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- DeVos, D.E.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Jacobs, P.A. (Eds.) Chiral Catalyst Immobilization and Recycling; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Reynes, J.F.; Leon, F.; Garcia, F. Mechanochemistry for Organic and Inorganic Synthesis. ACS Org. Inorg. Au 2024, 4, 432–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Takamizawa, S. Deformation twinning of ferrocene crystals assisted by the rotational mobility of cyclopentadienyl rings. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 5688–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S. Effects of magic-angle spinning on spin-lattice relaxations in talc. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 1994, 3, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Stark, R.E. A general protocol for temperature calibration of MAS NMR probes at arbitrary spinning speeds. Solid State NMR 2010, 38, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloembergen, N.; Purcell, E.M.; Pound, R.V. Relaxation effects in nuclear magnetic resonance absorption. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 679–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloembergen, N. Proton relaxation times in paramagnetic solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1957, 27, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, S.K.K. Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Paramagnetic Metal-Organic and -Inorganic Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Le Mans University, Le Mans, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rettig, M.F.; Drago, R.S. Electron delocalization in paramagnetic metallocences. I. Nuclear magnetic resonance contact shifts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1969, 91, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, D.; Grepioni, F. Crystal construction and molecular interplay in solid ferrocene, nickelocene, and ruthenocene. Organometallics 1992, 11, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antipin, M.Y.; Boese, R.; Auga, N.; Schmid, G. Redetermination of the cobaltocene crystal structure at 100 K and 297 K: Comparison with ferrocene and nickelocene. Struct. Chem. 1993, 4, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirvelu, V.; Eaton, G.R.; Eaton, S.S. Impact of chlorine substitution on spin–lattice relaxation of triarylmethyl and 1,4-benzosemiquinone radicals in glass-forming solvents between 25 and 295 K. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2010, 37, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elbendari, A.M.; Ibrahim, S.S. Optimizing key parameters for grinding energy efficiency and modeling of particle size distribution in a stirred ball mill. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herndon, R.M.; Abdelrahman, M.; Woelk, K. Assessing Asphalt Binder Aging with 1H Spin-lattice NMR Relaxometry: A Comparative Study of Temperature and UV Radiation Effects. J. Mod. Ind. Manuf. 2024, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).