Physiology, Genetics, and Breeding Strategies for Improving Anaerobic Germinability Under Flooding Stress in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Mechanisms of Rice Response to Anaerobic Germination
2.1. Phenotypic Adaptation
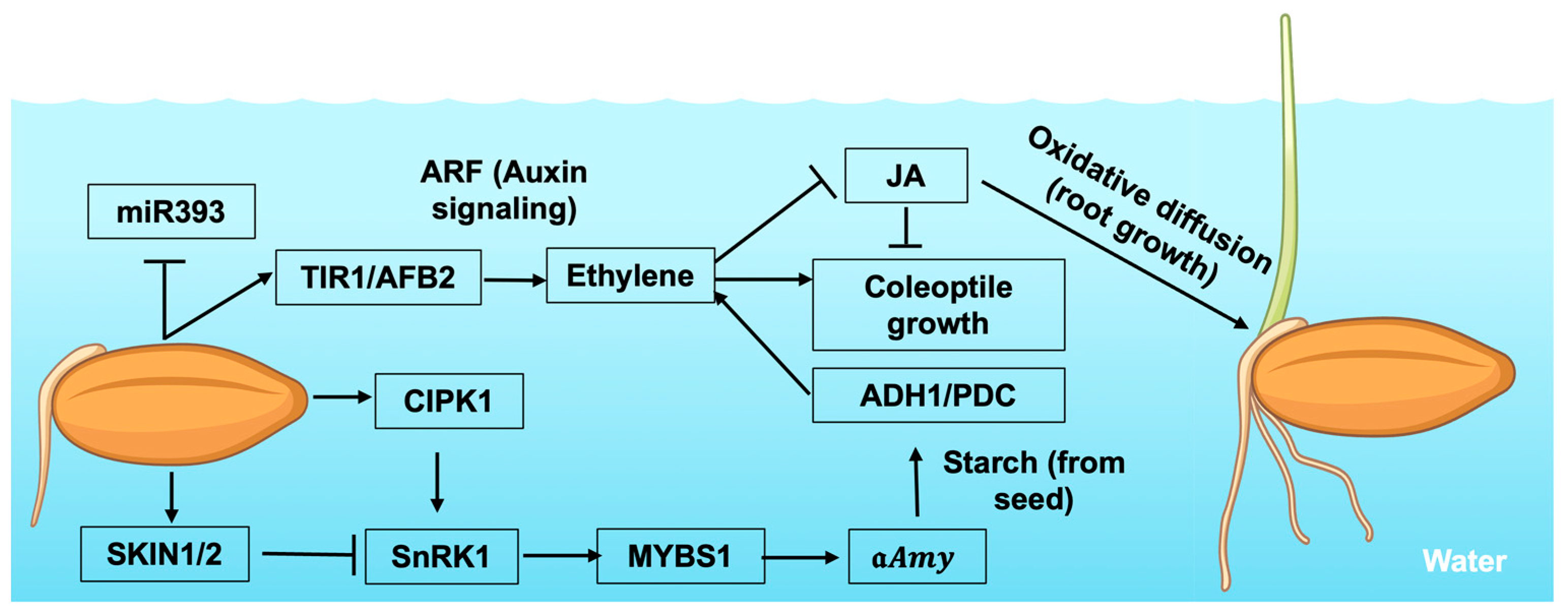
2.2. Hormonal Regulation
2.3. Changes in Carbohydrate Metabolism
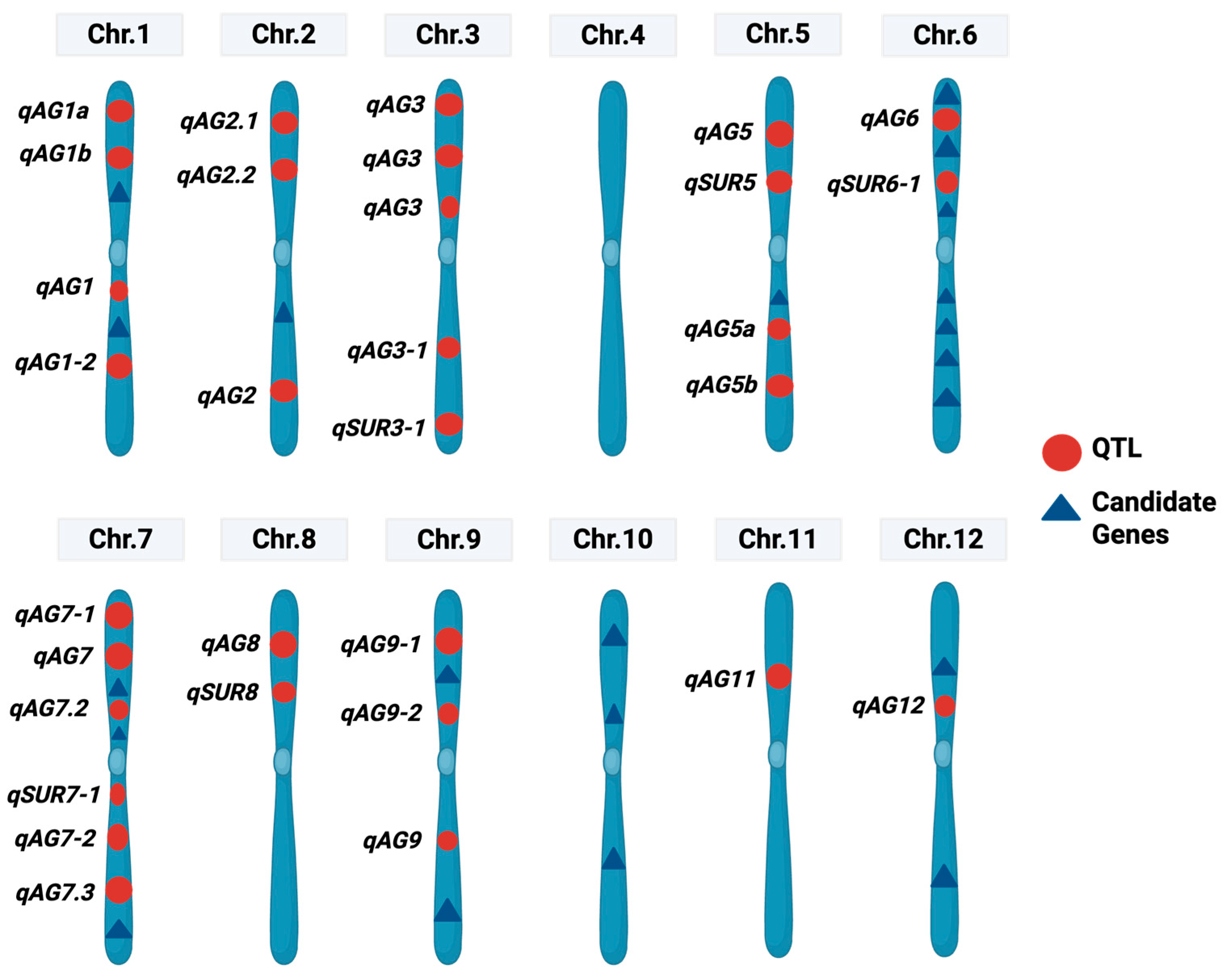
3. Genetic Mapping for AG Tolerance
3.1. Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping
| QTL Name | Marker | Chromosome | Position (cM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qAG-1 | XR2635–R1485 | 1 | 78 | [38] |
| qAG-2 | R418–C560 | 2 | 110 | |
| qAG-5a | G260–X105 | 5 | 80 | |
| qAG-5b | X105–C43 | 5 | 97 | |
| qAG-7 | X379–C213 | 7 | 108 | |
| qAG3 | id3002377–id3004190 | 3 | 29.8–37.9 | [41] |
| qAG7.1 | id7000519–id7002260 | 7 | 24.8–53.4 | |
| qAG7.2 | id7002427–id7003359 | 7 | 61.6–90.3 | |
| qAG7.3 | id7003853–id7004429 | 7 | 96–97.1 | |
| qAG-1-1 | RM582–RM10713 | 1 | 49–60.9 | [7] |
| qAG-1-2 | RM11125–RM104 | 1 | 83.7–159 | |
| qAG-2-1 | RM327–RM6318 | 2 | 78.8–97.5 | |
| qAG-3-1 | RM7097–RM520 | 3 | 115.6–138.7 | |
| qAG-7-1 | RID12i–RM5606 | 7 | 43.8–60.8 | |
| qAG-7-2 | RM21868–RM172 | 7 | 82.6–118.6 | |
| qAG-8-1 | RM210–RM149 | 8 | 86.7–100.6 | |
| qAG-9-1 | RM8303–RM5526 | 9 | 0.8–15.3 | |
| qAG-9-2 | RM3769–RM105 | 9 | 36–40.7 | |
| qAG2.1 | id2001831–id2003094 | 2 | 13.8–39.5 | [40] |
| qAG2.2 | id2006621–id2007526 | 2 | 75–83.2 | |
| qAG3 | id3007932–id3010875 | 3 | 97.7–115.8 | |
| qAG7 | id7000465–id7002784 | 7 | 29.4–153.5 | |
| qAG11 | id11009201–id11010245 | 11 | 109.8–122.1 | |
| qAG1a | 43,902–48,214 | 1 | 10 | [42] |
| qAG1b | id1006871–id327392 | 1 | 78 | |
| qAG8 | id8001299–id8107849 | 8 | 37 | |
| qAG11 | id11003544–id11194923 | 11 | 58 | |
| qAG2 | RM263–RM5378 | 2 | 145.4–154.8 | [39] |
| qAG5 | RM5361 | 5 | 0–16.2 | |
| qAG6 | RM204–RM402 | 6 | 0–29 | |
| qAG7.1 | RM3583–RM21427 | 7 | 73.5–79.9 | |
| qAG7.2 | RM7338–RM346 | 7 | 86.1–114.2 | |
| qAG7.3 | RM21803–RM234 | 7 | 121.5–143.4 | |
| qAG9 | RM553–RM3808 | 9 | 95.4–109.3 | |
| qAG12 | RM313–RM28766 | 12 | 67.6–133.1 |
3.2. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) for AG Tolerance in Rice
3.3. Omics Studies for AG Tolerance in Rice
| Gene ID | Description | Chromosome | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os06g03520 | DUF domain-containing protein | 6 | [49] |
| LOC_Os01g53090 | Putative infection-related protein | 1 | [48] |
| LOC_Os01g53930 | Glucose sensor | 1 | |
| LOC_Os05g51390 | Cytokinin-activating enzyme | 5 | |
| LOC_Os05g48990 | Related to cytokinin pathway | 5 | |
| LOC_Os06g35140 | Acts as MYB transcription factor | 6 | |
| LOC_Os06g35160 | Related to CBL-interacting protein kinase | 6 | |
| LOC_Os10g18480 | Encodes for an indole-4-acetate β ghucosyltransferase | 10 | |
| LOC_Os10g18530 | Encodes for cytoplasm O-glucosyltransferase | 10 | |
| LOC_Os06g04510 | Involved in substrate level phosphorylation to build ATP | 6 | [47] |
| LOC_Os02g0271900 | MYB family transcription factor | 2 | |
| LOC_Os06g0109600 | Adenylate kinase, putative, expressed | 6 | |
| LOC_Os06g0110000 | Cytochrome P450, putative, expressed | 6 | |
| LOC_Os06g0110200 | Late embryogenesis abundant group 1, putative, expressed | 6 | |
| LOC_Os07g0638300 | Peroxiredoxin, putative, expressed | 7 | |
| LOC_Os07g0638400 | Peroxiredoxin, putative, expressed | 7 | |
| LOC_Os07g0639400 | Peroxidase precursor, putative, expressed | 7 | |
| LOC_Os09g0531701 | Glycosyl transferase family 8 protein, expressed | 9 | |
| LOC_Os09g0532900 | MYB family transcription factor, putative, expressed | 9 | |
| LOC_Os10g0566800 | Peroxidase precursor, putative, expressed | 10 | |
| LOC_Os12g0539751 | Expressed protein | 12 | |
| LOC_Os12g0626500 | Late embryogenesis abundant protein D-34, putative, expressed | 12 | |
| LOC_Os10g0390500 | Alanine aminotransferase | 10 | [56] |
4. Breeding for AG Tolerance in Rice
4.1. Phenotypic Screening Method for AG Tolerance
4.2. AG-Tolerant Rice Germplasms
4.3. Marker-Assisted Breeding
5. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ACC | 1-aminocyclopropane 1-carboxylic acid |
| ADF 4 | Actin depolymerizing factor 4 |
| ADH | Alcohol dehydrogenase |
| AFB2 | AUXIN SIGNALING F-BOX 2 |
| AG | Anaerobic germination |
| ALDH | Aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| ARF | AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| CRISPR | Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats |
| DAS | Days after sowing |
| DSR | Direct-seeded rice |
| DUF | Domain of unknown function |
| eQTL | Expression quantitative trait locus |
| FCL | Flooded coleoptile length |
| FTI | Flood tolerance index |
| GA | Gibberellic acid |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association studies |
| HXK | Hexokinase |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulfide |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| KHO | Khao Hlan On |
| MAS | Marker-assisted selection |
| mETC | Mitochondrial electron transport chain |
| MYBS1 | MYB SUCROSE 1 |
| MYBS2 | MYB SUCROSE 2 |
| NCL | Normal coleoptile length |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| PDC | Pyruvate decarboxylase enzyme |
| RIL | Recombinant inbreed line |
| RFLP | Restriction fragment length polymorphism |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| SnRK1A | SUCROSE NONFERMENTING 1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE 1A |
| TF | Transcription factor |
| TIR1 | TRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE 1 |
| TUBA 1 | Tubulin a-1 chain |
| T6P | Trehalose 6 phosphates |
| QTL | Quantitative trait locus |
References
- Bailey-Serres, J.; Fukao, T.; Ronald, P.; Ismail, A.; Heuer, S.; Mackill, D. Submergence tolerant rice: SUB1’s journey from landrace to modern cultivar. Rice 2010, 3, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Tabassum, R.; Afzal, I. Enhancing the performance of direct seeded fine rice by seed priming. Plant Prod. Sci. 2006, 9, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Barsa, S.M.; Wahid, A. Priming of field-sown rice seed enhances germination, seedling establishment, allometry and yield. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 49, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M. Flooding and submergence tolerance. In Genomics and Breeding for Climate-Resilient Crops: Vol. 2 Target Traits; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 269–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.M.; Ella, E.S.; Vergara, G.V.; Mackill, D.J. Mechanisms associated with tolerance to flooding during germination and early seedling growth in rice (Oryza sativa). Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, M.; Aguilar, A.M.; Vaughan, D.A.; Seshu, D.V. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm suitable for direct sowing under flooded soil surface. Euphytica 1993, 67, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angaji, S.A.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Mackill, D.J.; Ismail, A.M. QTLs associated with tolerance of flooding during germination in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 2010, 172, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, B.; Ismail, A.M. Tolerance of anaerobic conditions caused by flooding during germination and early growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miro, B.; Longkumer, T.; Entila, F.D.; Kohli, A.; Ismail, A.M. Rice seed germination underwater: Morpho-physiological responses and the bases of differential expression of alcoholic fermentation enzymes. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Z.; Peng, L.; Huang, C.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z. UDP-glucosyltransferase OsUGT75A promotes submergence tolerance during rice seed germination. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Tabien, R.E.; Thomson, M.J.; Septiningsih, E.M. Genetic factors underlying anaerobic germination in rice: Genome-wide association study and transcriptomic analysis. Plant Genome 2024, 17, e20261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, G.; Greenway, H.; Atwell, B.J.; Ismail, A.M. Adaptation of rice to flooded soils. In Progress in Botany; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 75, pp. 215–253. [Google Scholar]
- Atwell, B.; Waters, I.; Greenway, H. The effect of oxygen and turbulence on elongation of coleoptiles of submergence-tolerant and-intolerant rice cultivars. J. Exp. Bot. 1982, 33, 1030–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magneschi, L.; Kudahettige, R.L.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Expansin gene expression and anoxic coleoptile elongation in rice cultivars. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, M.; Uchimiya, H. Coleoptile senescence in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ann. Bot. 2000, 86, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si-Ammour, A.; Windels, D.; Arn-Bouldoires, E.; Kutter, C.; Ailhas, J.; Meins, F., Jr.; Vazquez, F. miR393 and secondary siRNAs regulate expression of the TIR1/AFB2 auxin receptor clade and auxin-related development of Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Han, N.; Xie, Y.; Fang, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Bian, H. The miR393a/target module regulates seed germination and seedling establishment under submergence in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2288–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanthi-Kudahettige, R.; Magneschi, L.; Loreti, E.; Gonzali, S.; Licausi, F.; Novi, G.; Beretta, O.; Vitulli, F.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Transcript profiling of the anoxic rice coleoptile. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Straeten, D.; Zhou, Z.; Prinsen, E.; Van Onckelen, H.A.; Van Montagu, M.C. A comparative molecular-physiological study of submergence response in lowland and deepwater rice. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Engler, J.d.A.; Rouan, D.; Michiels, F.; Van Montagu, M.; Van Der Straeten, D. Tissue localization of a submergence-induced 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase in rice. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jackson, M.B. Ethylene-promoted elongation: An adaptation to submergence stress. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey-Serres, J.; Chang, R. Sensing and signalling in response to oxygen deprivation in plants and other organisms. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.M.; Hall, K.C.; Jackson, M.B. The effects of oxygen, carbon dioxide and ethylene on ethylene biosynthesis in relation to shoot extension in seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa) and barnyard grass (Echinochloa oryzoides). Ann. Bot. 1992, 69, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.M.; Jackson, M.B. Comparison of growth responses of barnyard grass (Echinochloa oryzoides) and rice (Oryza sativa) to submergence, ethylene, carbon dioxide and oxygen shortage. Ann. Bot. 1991, 68, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Yeh, T.-H.; Yang, C.-Y. Ethylene signaling involves in seeds germination upon submergence and antioxidant response elicited confers submergence tolerance to rice seedlings. Rice 2019, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.M.; Johnson, D.E.; Ella, E.S.; Vergara, G.V.; Baltazar, A.M. Adaptation to flooding during emergence and seedling growth in rice and weeds, and implications for crop establishment. AoB Plants 2012, 2012, pls019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, B.; Herath, V.; Wijaya, E.; Yeo, H.C.; Reyes, B.G.d.L.; Lee, D.-Y. Patterns of cis-element enrichment reveal potential regulatory modules involved in the transcriptional regulation of anoxia response of japonica rice. Gene 2012, 511, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, H.; Setter, T. Is there anaerobic metabolism in submerged rice plants? A view point. In Physiology of Stress Tolerance in Rice, Proceedings of the International Conference on Stress Physiology of Rice, Lucknow, India, 28 February–5 March 1994; Int. Rice Res. Inst.: Laguna, Philippines, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.-A.; Ho, T.-H.D.; Ho, S.-L.; Yu, S.-M. Three novel MYB proteins with one DNA binding repeat mediate sugar and hormone regulation of α-amylase gene expression. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1963–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-A.; Lim, E.-K.; Yu, S.-M. Sugar response sequence in the promoter of a rice α-amylase gene serves as a transcriptional enhancer. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 10120–10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-A.; Lin, C.-C.; Lee, K.-W.; Chen, J.-L.; Huang, L.-F.; Ho, S.-L.; Liu, H.-J.; Hsing, Y.-I.; Yu, S.-M. The SnRK1A protein kinase plays a key role in sugar signaling during germination and seedling growth of rice. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2484–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-W.; Chen, P.-W.; Lu, C.-A.; Chen, S.; Ho, T.-H.D.; Yu, S.-M. Coordinated responses to oxygen and sugar deficiency allow rice seedlings to tolerate flooding. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-R.; Lee, K.-W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hong, Y.-F.; Chen, J.-L.; Lu, C.-A.; Chen, K.-T.; Ho, T.-H.D.; Yu, S.-M. SnRK1A-interacting negative regulators modulate the nutrient starvation signaling sensor SnRK1 in source-sink communication in cereal seedlings under abiotic stress. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 808–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Ho, T.-H.D.; Liu, L.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Lin, S.-Y.; Lu, C.-A.; Yu, S.-M. Sugar starvation-regulated MYBS2 and 14-3-3 protein interactions enhance plant growth, stress tolerance, and grain weight in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21925–21935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazono, M.; Tsuji, H.; Li, Y.; Saisho, D.; Arimura, S.-I.; Tsutsumi, N.; Hirai, A. Expression of a gene encoding mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase in rice increases under submerged conditions. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Saika, H.; Matsumura, H.; Nagamura, Y.; Tsutsumi, N.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakazono, M. Cell division and cell elongation in the coleoptile of rice alcohol dehydrogenase 1-deficient mutant are reduced under complete submergence. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, I.; Fanucchi, F.; Paparelli, E.; Alpi, E.; Bachi, A.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Proteomic identification of differentially expressed proteins in the anoxic rice coleoptile. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hou, M.; Wang, C.; Wan, J. Quantitative trait loci and epistatic analysis of seed anoxia germinability in rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Sci. 2004, 11, 238–244. [Google Scholar]
- Septiningsih, E.M.; Ignacio, J.C.I.; Sendon, P.M.D.; Sanchez, D.L.; Ismail, A.M.; Mackill, D.J. QTL mapping and confirmation for tolerance of anaerobic conditions during germination derived from the rice landrace Ma-Zhan Red. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltazar, M.D.; Ignacio, J.C.I.; Thomson, M.J.; Ismail, A.M.; Mendioro, M.S.; Septiningsih, E.M. QTL mapping for tolerance of anaerobic germination from IR64 and the aus landrace Nanhi using SNP genotyping. Euphytica 2014, 197, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar, M.D.; Ignacio, J.C.I.; Thomson, M.J.; Ismail, A.M.; Mendioro, M.S.; Septiningsih, E.M. QTL mapping for tolerance to anaerobic germination in rice from IR64 and the aus landrace Kharsu 80A. Breed. Sci. 2019, 69, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Reinke, R.F. Identification of QTLs for tolerance to hypoxia during germination in rice. Euphytica 2018, 214, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Casal, C.; Quilloy, F.A.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Mendioro, M.S.; Dixit, S. Deciphering genetics underlying stable anaerobic germination in rice: Phenotyping, QTL identification, and interaction analysis. Rice 2019, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, N.-J.; Paek, N.-C. Photoblastism and ecophysiology of seed germination in weedy rice. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.M.; Cho, Y.-C.; Jeong, J.-U.; Mo, Y.-J.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, W.-J.; Baek, M.-K.; Kim, S.-M. QTL mapping and effect confirmation for anaerobic germination tolerance derived from the japonica weedy rice landrace PBR. Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Sasaki, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Yamagishi, J.; Kato, Y. Detection and characterization of quantitative trait loci for coleoptile elongation under anaerobic conditions in rice. Plant Prod. Sci. 2020, 23, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, K.; Li, D.; Luo, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M.; Yang, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. Identification of stable QTLs and candidate genes involved in anaerobic germination tolerance in rice via high-density genetic mapping and RNA-Seq. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-K.; Tung, C.-W. Genetic mapping of anaerobic germination-associated QTLs controlling coleoptile elongation in rice. Rice 2015, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Lu, Q.; Wu, W.; Niu, X.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, S.; Yuan, X.; Yu, H.; et al. Association mapping reveals novel genetic loci contributing to flooding tolerance during germination in indica rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Peng, Z.; Xia, A.; Yang, M.; Luo, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Dynamic genome-wide association analysis and identification of candidate genes involved in anaerobic germination tolerance in rice. Rice 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, T.; Pelayo, M.A.F.; Trijatmiko, K.R.; Gabunada, L.F.M.; Alam, R.; Jimenez, R.; Mendioro, M.S.; Slamet-Loedin, I.H.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Bailey-Serres, J.; et al. A trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase enhances anaerobic germination tolerance in rice. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghi, K.N.; Tondelli, A.; Valè, G.; Tagliani, A.; Marè, C.; Perata, P.; Pucciariello, C. Dissection of coleoptile elongation in japonica rice under submergence through integrated genome-wide association mapping and transcriptional analyses. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1832–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, M.; Mohanty, B.; Lim, S.-H.; Ha, S.-H.; Lee, D.-Y. Metabolic and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms underlying the anoxic adaptation of rice coleoptile. AoB Plants 2014, 6, plu026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-K.; Tung, C.-W. RNA-Seq analysis of diverse rice genotypes to identify the genes controlling coleoptile growth during submerged germination. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, J.; Senapati, S.; Ray, S.; Chakraborty, K.; Molla, K.A.; Basak, N.; Pradhan, B.; Yeasmin, L.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Sarkar, R.K. Transcriptomic and physiological studies identify cues for germination stage oxygen deficiency tolerance in rice. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 147, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, K.; Zhao, C.; Liang, S.; Yang, J.; Peng, Z.; Xia, A.; Yang, M.; Luo, L.; Huang, C.; et al. GWAS combined with WGCNA of transcriptome and metabolome to excavate key candidate genes for rice anaerobic germination. Rice 2023, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partheeban, C.; Srividhya, S.; Raveendran, M.; Vijayalakshmi, D. Designing new screening methods and physiological dissection of anaerobic stress tolerance in Rice. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rauf, M.; Choi, Y.-M.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.-C.; Oh, S.; Hyun, D.Y. Evaluation of anaerobic germinability in various rice subpopulations: Identifying genotypes suitable for direct-seeded rice cultivation. Euphytica 2019, 215, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibosh Bordoloi, D.B.; Sarma, D.S.D. Aerobic versus anaerobic germination performance of selected rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes with or without submergence tolerance. J. Exp. Biol. Agric. Sci. 2018, 6, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeraja, R.P.; Kota, S. Screening of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for anaerobic germination. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2018, 6, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Rahman, A.R.; Zhang, J. Preferential geographic distribution pattern of abiotic stress tolerant rice. Rice 2018, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ella, E.S.; Setter, T.L. Importance of seed carbohydrates in rice seedling establishment under anoxia. In Proceedings of the VI Symposium on Stand Establishment and ISHS Seed Symposium 504, Brasilia, Brazil, 1–5 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.M.; Kim, C.-S.; Jeong, J.-U.; Reinke, R.F.; Jeong, J.-M. Marker-assisted breeding for improvement of anaerobic germination in japonica rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, B.C.; Cruz, C.M.V.; McNally, K.L.; Virk, P.S.; Mackill, D.J. Rice molecular breeding laboratories in the genomics era: Current status and future considerations. Int. J. Plant Genom. 2008, 2008, 524847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartaj, A.; Udawela, K.; Herath, H. Marker assisted backcross breeding of Bg 358 (Oryza sativa L.) for the anaerobic germination tolerant QTL AG1. Trop. Agric. Res. 2016, 27, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mondal, S.; Khan, M.I.R.; Entila, F.; Dixit, S.; Cruz, P.C.S.; Ali, M.P.; Pittendrigh, B.; Septiningsih, E.M.; Ismail, A.M. Responses of AG1 and AG2 QTL introgression lines and seed pre-treatment on growth and physiological processes during anaerobic germination of rice under flooding. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xiong, W.; Yin, C.; Xie, X.; Jin, Y.-J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, B.; Ye, G.; Chen, S.; Luan, W.-J. Overexpression of OsARD1 improves submergence, drought, and salt tolerances of seedling through the enhancement of ethylene synthesis in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
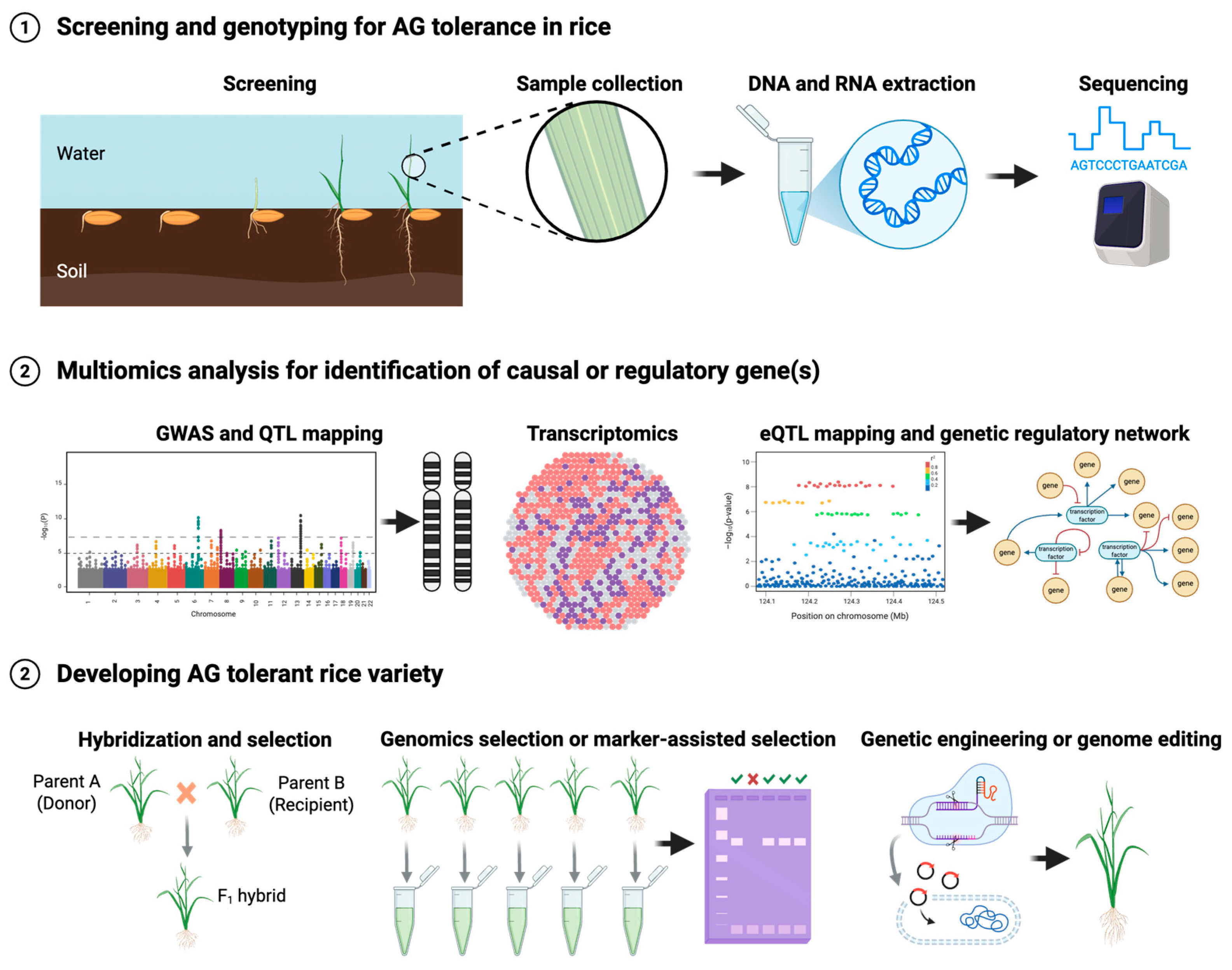
| Medium | Depth (cm) | Temp. (°C) | Period | Measured Traits | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 10 | 26–31 | 21 | Survival rate (21st DAS *) | [40,41] |
| Soil | 10 | 21 | Seedling survival (21st DAS) | [42] | |
| soil | 10 | 28 | 10 | Germination rate, coleoptile length (10th DAS) | [58] |
| Soil | 8 | 21 | Germination percentage, seedling height (14th and 21st DAS) | [43] | |
| Soil | 10 | 26 | 21 | Survival rate, shoot and root length (21st DAS) | [5] |
| Soil | 10 | - | 7 | % germination, shoot length, root length, seedling length (7th DAS) | [59] |
| Soil | 40 | - | 15 | Germination rate, seedling length, vigor index (15th DAS) | [60] |
| Soil | 10 | 26.2–30.9 | 7 | - | [55] |
| Soil | 10 | 30 | 21 | Germination rate (7th DAS), survival (21st DAS) | [39] |
| Soil | 10 | 30.1 | 21 | Germination rate and survival (21st DAS) | [7] |
| Water | 10 | 30 | 10 | Coleoptile length | [49] |
| Water | 5 | 25 | 7 | Coleoptile length | [54] |
| Water | 3.2 | 30 | 8 | Coleoptile length, shoot length (4th and 8th DAS) length, and weight of intact hulled seed | [52] |
| Water | 10 | 30 | 6 | Coleoptile length, coleoptile surface area, coleoptile volume, and coleoptile diameter (6th DAS) | [47] |
| Tolerant Cultivar | Population | Origin | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR 13A | Parental line | - | [62] |
| AC41620 | Parental line | - | [55] |
| F291, F274-2a | RIL | - | [54] |
| 8391 | Parental line | Laos | [53] |
| 8753 | Parental line | Indonesia | |
| Khao Hlan On | BC2F2 | Myanmar | [7] |
| Dholamon 64-3 | Parental line | Bangladesh | |
| Liu-Tiao-Nuo | Parental line | China | |
| Sossoka | Parental line | Guinea | |
| Kaolack | Parental line | Guinea | |
| Khao Hlan On | BC2F2, BC3F2 | Myanmar | [63] |
| Kinmaze | RIL | - | [38] |
| Ma-Zhan Red | F2:3 | China | [39] |
| Tai Nguyen | F2:3 | India | [42] |
| Kalarata | BC1F2:3 | India | [43] |
| Nanhi | F2 | - | [40] |
| Kharsu 80A | F2:3 | Pakistan | [41] |
| PBR | RIL | Republic of Korea | [45] |
| Khaiyan | Parental line | Bangladesh | [5] |
| Kalonchi | Parental line | Bangladesh | |
| Cody | Parental line | USA | |
| Lamone, Arborio | Parental line | - | [14] |
| Anaikomban, Muthuvellai, Rajamannar | Landraces | - | [57] |
| CR1009 | Parental line | - | |
| 498-2A BR8, Barkhe tauli, Improved blue rose, Para nellu, Jangli boro, Subo, Hwanggeumnodeul | Parental line | - | [58] |
| E775, E1810, E596, E1786, E 753, E773, E1846, E1195, E1049, E1772, E1723, E1701 and E1777 | Parental line | - | [60] |
| Solpuna | Parental line | India | [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakraborty, P.; Chakrabarty, S. Physiology, Genetics, and Breeding Strategies for Improving Anaerobic Germinability Under Flooding Stress in Rice. Stresses 2025, 5, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030049
Chakraborty P, Chakrabarty S. Physiology, Genetics, and Breeding Strategies for Improving Anaerobic Germinability Under Flooding Stress in Rice. Stresses. 2025; 5(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakraborty, Panchali, and Swapan Chakrabarty. 2025. "Physiology, Genetics, and Breeding Strategies for Improving Anaerobic Germinability Under Flooding Stress in Rice" Stresses 5, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030049
APA StyleChakraborty, P., & Chakrabarty, S. (2025). Physiology, Genetics, and Breeding Strategies for Improving Anaerobic Germinability Under Flooding Stress in Rice. Stresses, 5(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses5030049






