Turning Waste into Resources: Bibliometric Study on Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures in Geotechnical Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
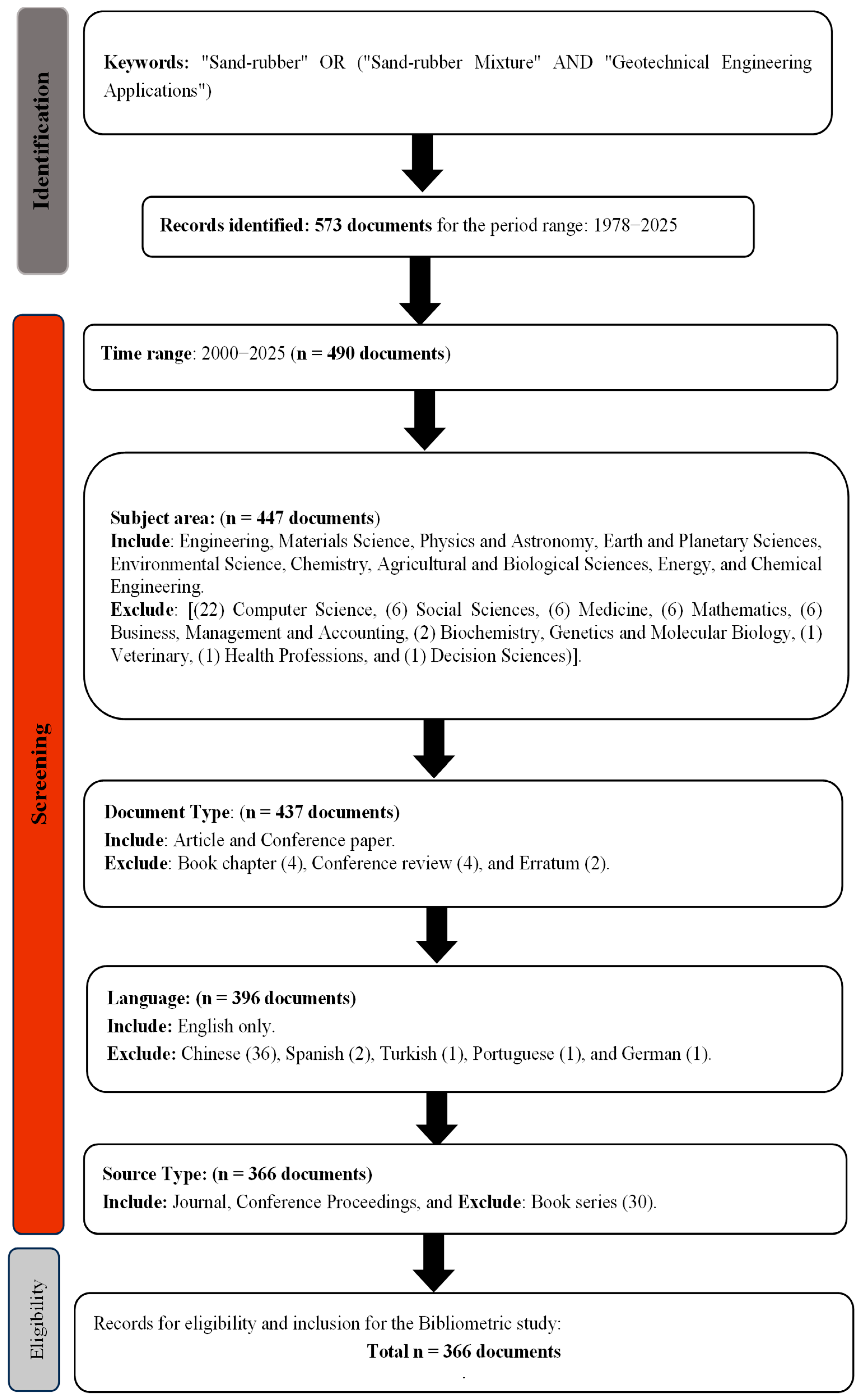
2.1. Source and Search Strategy of Data
2.2. Screening
2.3. Selection of Data for Bibliometric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Publication Trends
3.2. Document Type Distribution
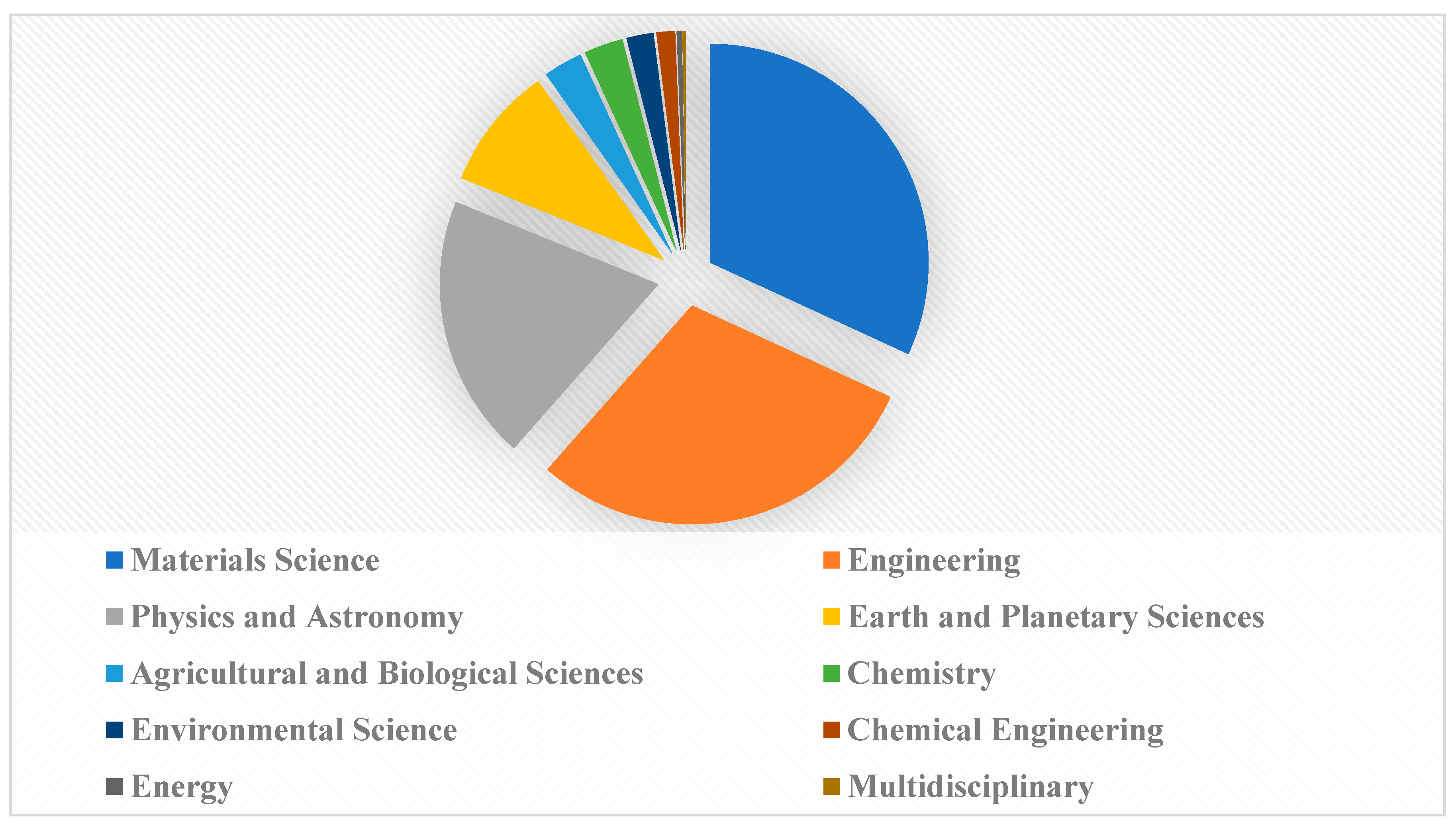
3.3. Subject Area Distribution
3.4. Journals Networking on Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures
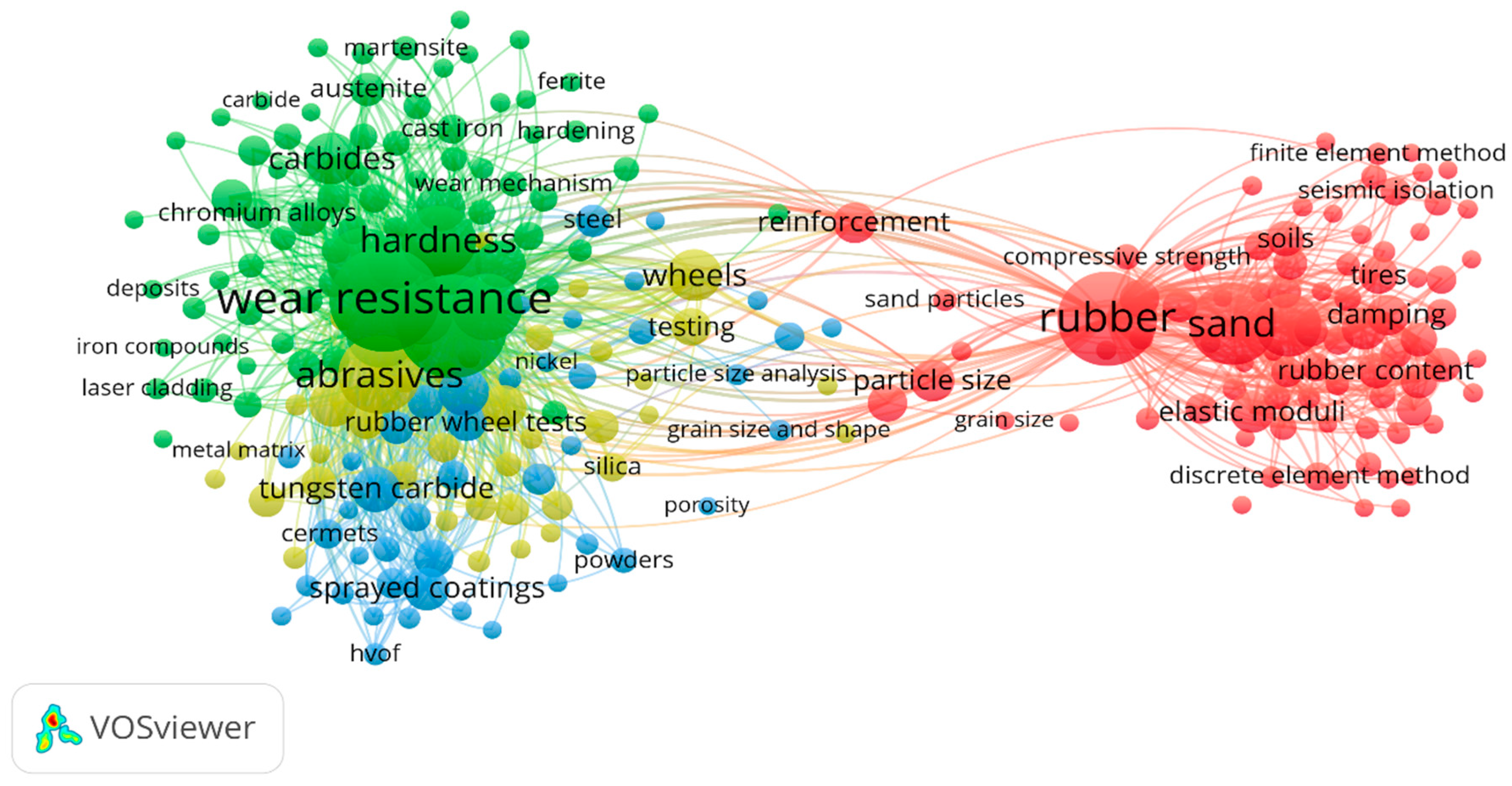
3.5. Research Areas of the Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures
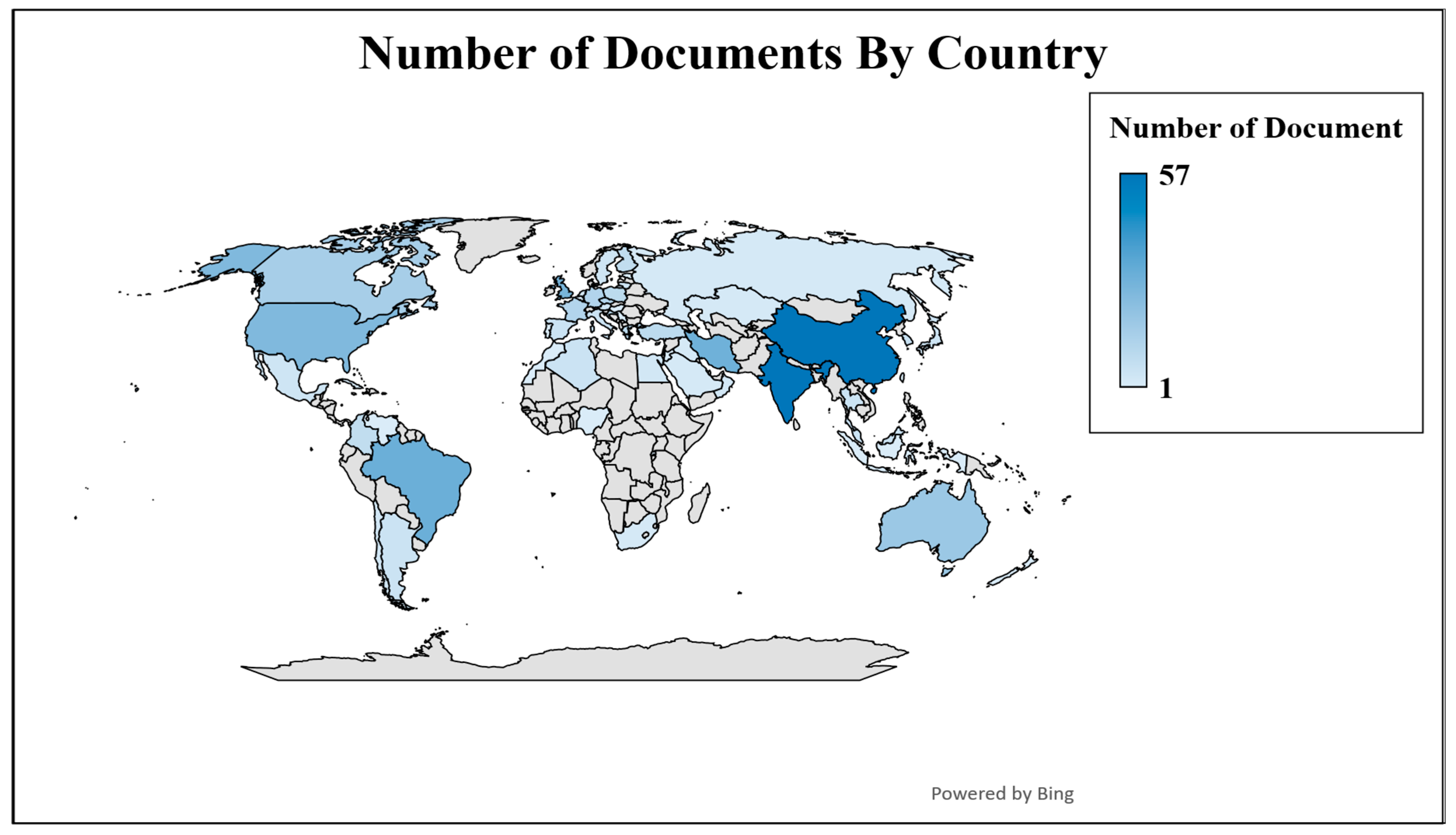
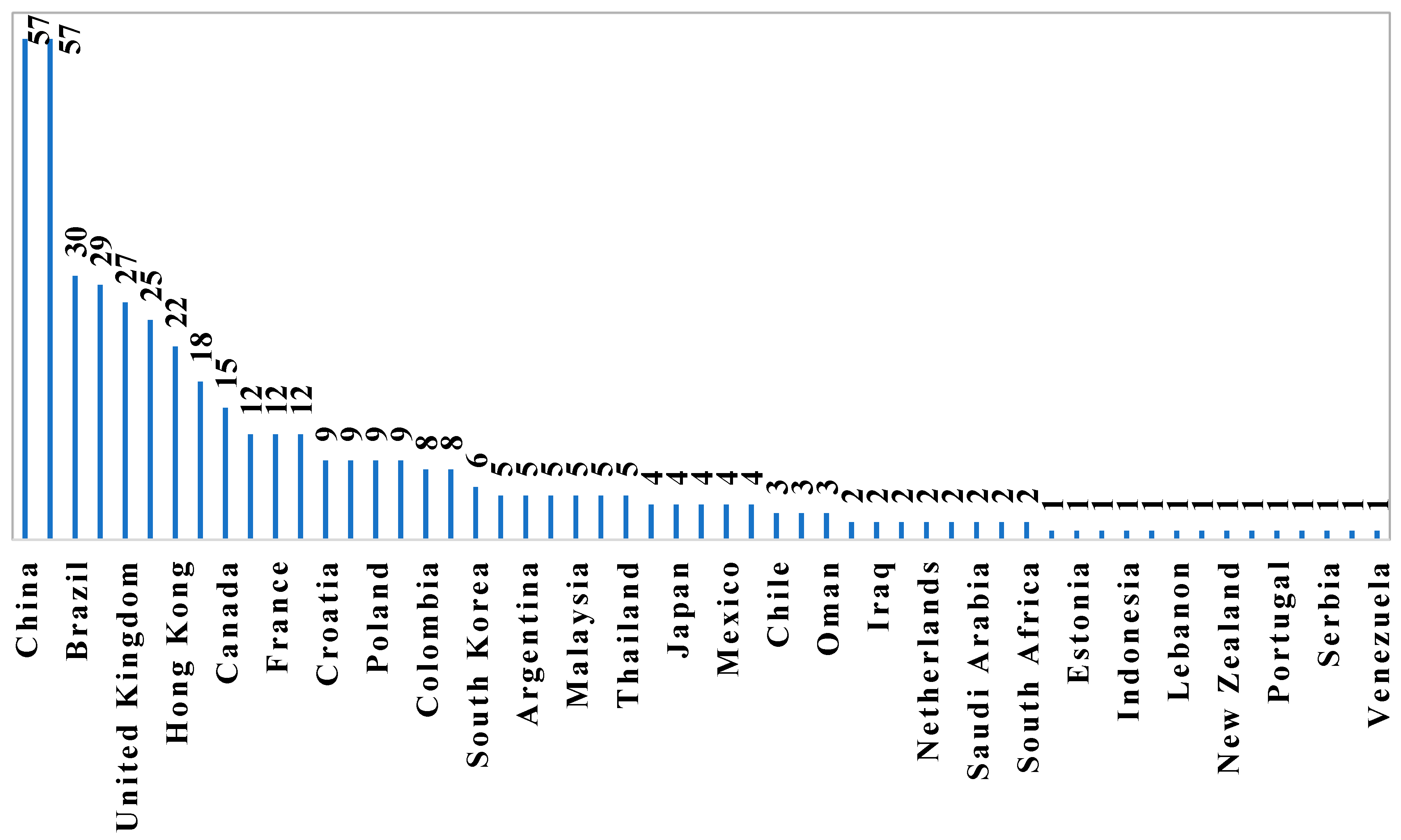
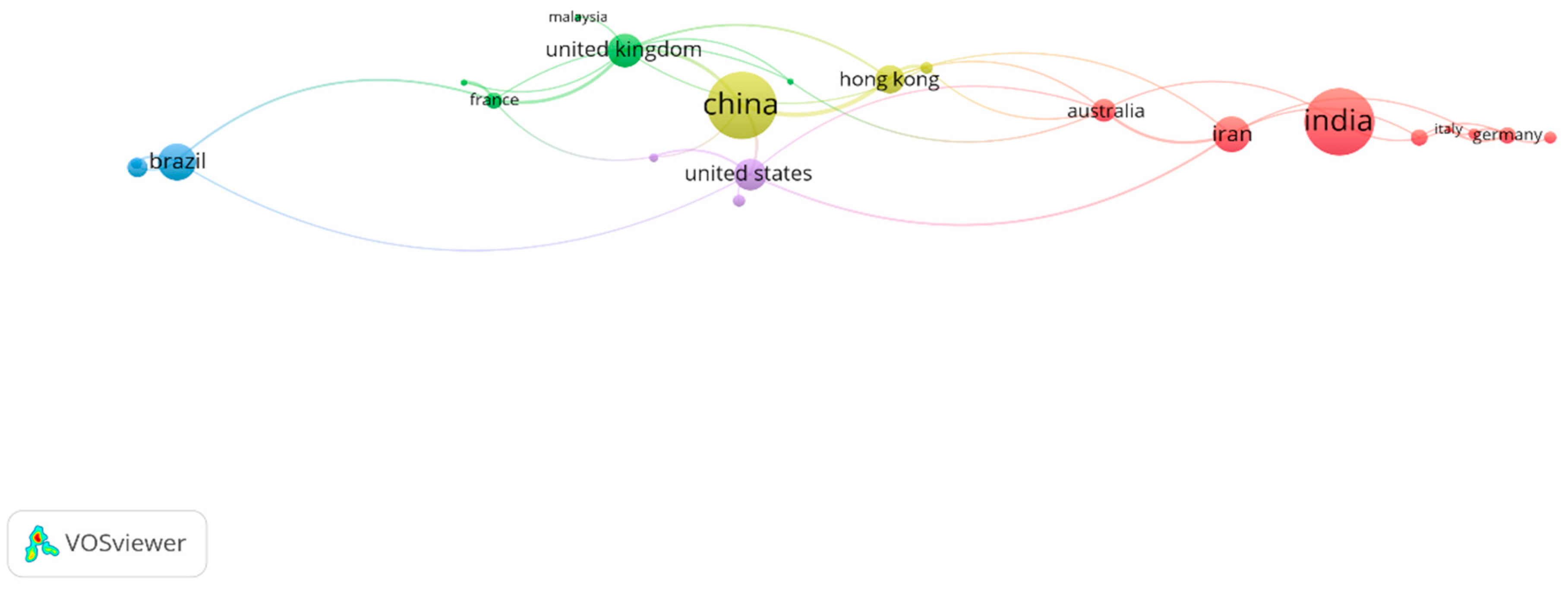
3.6. Countries Leading the Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures
4. Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures for Geotechnical Engineering Applications
5. Limitations and Future Works
5.1. Limitations
5.2. Future Works
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moasas, A.M.; Amin, M.N.; Khan, K.; Ahmad, W.; Al-Hashem, M.N.A.; Deifalla, A.F.; Ahmad, A. A worldwide development in the accumulation of waste tires and its utilization in concrete as a sustainable construction material: A review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, Q.B.; Chong, R.O.; Nguyen, P.T.T.; Le, D.K.; Le, P.K.; Phan-Thien, N.; Duong, H.M. Recycling of waste tire fibers into advanced aerogels for thermal insulation and sound absorption applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Dou, H.; Yang, L.; Cao, Z. Numerical Study on the Mechanical Behavior of Sand–Rubber Mixtures under True Triaxial Tests. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B.r., M.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Engineering properties of sand–rubber tire shred mixtures. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 15, 1061–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, B.R.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Cyclic Simple Shear Response of Sand–Rubber Tire Chip Mixtures. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04020136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, B.R.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Comparison of Cyclic Triaxial Test Results on Sand-Rubber Tire Shred Mixtures with Dynamic Simple Shear Test Results. In Proceedings of the Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics V, Austin, TX, USA, 10–13 June 2018; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; pp. 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Moran, K.D.; Miller, E.L.; Brander, S.M.; Harper, S.; Garcia-Jaramillo, M.; Carrasco-Navarro, V.; Ho, K.T.; Burgess, R.M.; Thornton Hampton, L.M.; et al. Where the rubber meets the road: Emerging environmental impacts of tire wear particles and their chemical cocktails. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fondjo, A.A.; Vuwane, B.; Theron, E. Improvement of Geotechnical Properties of Heaving Soils Using Alternative Methods: A Review. In Theory and Applications of Engineering Research Vol. 1; B P International: Hugli-Chinsurah, India, 2023; pp. 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnadish, A.M.; Bangalore Ramu, M.; Kasim, N.; Alawag, A.M.; Baarimah, A.O. A Bibliometric Analysis and Review on Applications of Industrial By-Products in Asphalt Mixtures for Sustainable Road Construction. Buildings 2024, 14, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, B.R.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Effect of Specimen Size on the Dynamic Properties of River Sand and Rubber Tire Shreds from Cyclic Triaxial and Cyclic Simple Shear Tests. In Geotechnical Characterization and Modelling; Latha Gali, M., PPallepati, R.R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gücek, S.; Gürer, C.; Žlender, B.; Taciroğlu, M.V.; Korkmaz, B.E.; Gürkan, K.; Bračko, T.; Macuh, B.; Varga, R.; Jelušič, P. Use of Lignin, Waste Tire Rubber, and Waste Glass for Soil Stabilization. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, B.R.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Static and Large-Strain Dynamic Properties of Sand–Rubber Tire Shred Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 4017165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, B.R.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Dynamic Pore Pressure Responses of Sand–Rubber Tire Shred Mixtures from Cyclic Simple Shear and Cyclic Triaxial Tests. In Soil Dynamics; Sitharam, T.G., Dinesh, S.V., Jakka, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, B.R.; Boominathan, A.; Banerjee, S. Factors Affecting Strength and Stiffness of Dry Sand-Rubber Tire Shred Mixtures. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 2763–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Bai, W.; Yi, S.; Huang, X.; Lu, Y.; Baghbani, A. Vertical Response of Stress Transmission Through Sand–Tire Mixture Under Impact. Buildings 2024, 14, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Xie, K.; Guo, Z.; Wang, P. Experimental investigation and multivariable prediction model of the compressibility of fine gravel-rubber mixtures considering particle size effect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 483, 141759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Liu, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Cui, X.; Su, X.; Yu, S.; Lian, J. Experimental investigation of the mechanical behaviour of sand-rubber-gravel mixtures. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2025, 84, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, F.A.; El Maaddawy, T.; Abu-Jdayil, B. Impact of crumb rubber on the performance of unsaturated polyester-dune sand mortar. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Ding, J.; Deng, H.; Mosallam, A.S. Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Structural Applications of Rubber Concrete: A State-of-the-Art-Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, A.; Rouhanifar, S.; Richard, P.; Cazacliu, B.; Ibraim, E. Sand–rubber mixtures undergoing isotropic loading: Derivation and experimental probing of a physical model. Granul. Matter 2018, 20, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Sengupta, A.; Reddy, G.R. Performance of sand and shredded rubber tire mixture as a natural base isolator for earthquake protection. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2015, 14, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, H.; Kalatehjari, R.; Hajihassani, M.; Kharghani, M.; Asteris, P.G. Sand–Tire Shred Mixture Performance in Controlling Surface Explosion Hazards That Affect Underground Structures. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badarayani, P.; Cazacliu, B.; Ibraim, E.; Artoni, R.; Richard, P. Sand Rubber Mixtures under Oedometric Loading: Sand-like vs. Rubber-like Behavior. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kwok, C.Y.; Sandeep, C.S.; Senetakis, K. Sand type effect on the behaviour of sand-granulated rubber mixtures: Integrated study from micro- to macro-scales. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Wang, X.; Yin, Z.-Y. DEM-based study on the mechanical behaviors of sand-rubber mixture in critical state. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boominathan, A.; Dhanya, J.S.; Silpa, P.J. Use of Sand-Rubber Mixture (SRM)-Filled Trenches for Pile Driving Induced Vibration Screening. In Challenges and Innovations in Geomechanics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, J.H. Application of Sand-Rubber Mixtures to Mitigate Vibration and Ground Shock. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, T.S.; Chakrabortty, P.; Hegde, A. Interaction between geogrid and sand-crumb rubber mixtures in laboratory pullout conditions. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2023, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.R.; Rodrigue, D. Application of Waste Tire in Construction: A Road towards Sustainability and Circular Economy. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yin, Z. Small Strain Stiffness of Sand-Rubber Mixtures With Particle Size Disparity Effect. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2025, 49, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Fan, Q.; Mi, P.; Li, M.; Mu, W.; Na, J. Review of aging mechanisms, mechanical properties, and prediction models of fiber-reinforced composites in natural environments. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 14448–14474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Su, J.; Liang, C. Evolution of topics in education research: A systematic review using bibliometric analysis. Educ. Rev. 2020, 72, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazel, M.A.; Mohammed, F.; Ahmad, M.; Baarimah, A.O.; Ibrahim, M.A. Blockchain-Based Healthcare: Trend Mapping through Bibliometric Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Emerging Smart Technologies and Applications (eSmarTA), Taiz, Yemen, 10–11 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, K.H.; Roslan, M.F.; Ishak, N.S.; Ilias, M.; Dani, R. Unearthing hidden research opportunities through bibliometric analysis: A review. Asian J. Res. Educ. Soc. Sci. 2023, 5, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mekhlafi, A.-B.A.; Kanwal, N.; Alhajj, M.N.; Isha, A.S.N.; Baarimah, A.O. Trends in Safety Culture Research: A Scopus Analysis. Safety 2025, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarimah, S.O.; Baarimah, A.O.; Alaloul, W.S.; Bazel, M.A.; Mohammed, F.; Bawahab, M. A Bibliometric Analysis on the Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Petroleum Engineering. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (ICDABI), Virtual, 25–26 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousafzai, A.K.; Sutanto, M.H.; Khan, M.I.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Baarimah, A.O.; Khan, N.; Memon, A.M.; Sani, A. Systematic Literature Review and Scientometric Analysis on the Advancements in Electrically Conductive Asphalt Technology for Smart and Sustainable Pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2025, 2679, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrah, A.; Al-Zghoul, T.; Baarimah, A.O.; Al-Karablieh, E. A bibliometric analysis of olive mill wastewater treatment methods from 1988 to 2023. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, L.D.A.; Susanti, H.; Admirasari, R.; Praharyawan, S.; Iwamoto, K. Bibliometric insights into microalgae cultivation in wastewater: Trends and future prospects for biolipid production and environmental sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleminski, R.; Kazienko, P.; Kajdanowicz, T. Analysis of direct citation, co-citation and bibliographic coupling in scientific topic identification. J. Inf. Sci. 2022, 48, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasria, N.A.; Alhatabat, Z.; Ershaid, D.; Almaqtari, F.A. Artificial intelligence and its applications in financial process and finance: A bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2025, 8, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Bin Mokaizh, A.A.; Baarimah, A.O.; Al-Zghoul, T. From agro-waste to bioactive wealth: Analyzing nutraceutical extraction and applications. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 11, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarimah, A.O.; Bin Mokaizh, A.A.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Al-Zghoul, T. Visualization and networking analysis of processing seafood towards future trends: A bibliometric analysis from 2010 to 2024. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Z.; Huang, L.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Sandanayake, M.; Liu, E.; Ahn, Y.H.; et al. Conversion of waste into sustainable construction materials: A review of recent developments and prospects. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 27, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y. Experimental investigation on static and dynamic characteristics of granulated rubber-sand mixtures as a new railway subgrade filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, C. Geosynthetics 101. engrxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Ruffing, D.; Elton, D. Fundamentals of Ground Improvement Engineering; CRC Press: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuvat, A.; Sadoglu, E.; Zardari, S. Experimental Investigation of Sand–Rubber–Bitumen Mixtures as a Geotechnical Seismic Isolation Material. Int. J. Geomech. 2024, 24, 04023293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyasree, S.L.; Jithin, K.M.; Varghese, R.M. Geotechnical Seismic Base Isolation Using Rubber Sand Mixtures—Review. In Proceedings of the 17th Symposium on Earthquake Engineering (Vol. 4); Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjelloun, M.; Bouferra, R.; Ibouh, H.; Jamin, F.; Benessalah, I.; Arab, A. Mechanical Behavior of Sand Mixed with Rubber Aggregates. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasalloti, A.; Chiaro, G.; Murali, A.; Banasiak, L. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Granulated Rubber Mixed with Granular Soils—A Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittella, H.; Yoon, L.W.; Ramarad, S.; Lai, Z.-W. Rubber waste management: A review on methods, mechanism, and prospects. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 194, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhanifar, S.; Afrazi, M.; Fakhimi, A.; Yazdani, M. Strength and deformation behaviour of sand-rubber mixture. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 15, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J. Experimental Investigations on the State-Dependent Thermal Conductivity of Sand-Rubber Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04021492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinçliler, A.; Baykal, G.; Dengili, K. Determination of static and dynamic behavior of recycled materials for highways. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2004, 42, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, S.; Kowalska, M.; Viana da Fonseca, A. Cyclic and Dynamic Behavior of Sand–Rubber and Clay–Rubber Mixtures. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 3449–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubeša, I.N.; Barišić, I.; Ducman, V.; Korat, L. Draining capability of single-sized pervious concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, H.; Kuribayashi, K.; Kuroda, S.; Hu, Y. Performance evaluation of waste tires in protecting embankment against earthquake loading. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 21, 4019–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, H. Seismic isolation by rubber–soil mixtures for developing countries. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2008, 37, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Sridhar Babu, B.; Chakravarthy, C.N.; Muthalagu, R. Mechanical characterization and thermal behaviors of tungsten carbide reinforced thermoplastic composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Islam, M.M.; Li, J.; Roychand, R.; Saberian, M.; Chen, F. A comprehensive review on the application of renewable waste tire rubbers and fibers in sustainable concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; He, H.; Senetakis, K.; Yin, Z. DEM analysis of the load transfer mechanism of sand-rubber mixtures subjected to constrained compression. Powder Technol. 2024, 446, 120133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, P.; Prodanovic, N.; Hurtig, K.; Steinerová, V.; Fojt, J.; Janata, M.; Brožek, V. Corrosion Properties and Bond Strength in Normal Strength Concrete of Al2O3 Plasma-Sprayed Plain Bars with ZrCC/Organofunctional Silane Coating. Buildings 2024, 14, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Amoosoltani, E. The effect of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement and crumb rubber on mechanical properties of Roller Compacted Concrete Pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiyuan, W.; Yurui, L.; Ali, N. Sustainability in Geotechnical Engineering: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2024, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammelis, P.; Margaritis, N.; Dallas, P.; Rakopoulos, D.; Mavrias, G. A Review on Management of End of Life Tires (ELTs) and Alternative Uses of Textile Fibers. Energies 2021, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Singh, S. Sustainable Municipal Solid Waste Management in India: A Policy Agenda. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerani, A.; Kurmus, H.; Conti, D.; Cash, L.; Semcesen, A.; Abdurahman, M.; Rahman, M.T. Environmental impacts and leachate analysis of waste rubber incorporated in construction and road materials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinot, V.; Sivapriya, S.V. Use of Recycled Materials in Geotechnical Engineering Practice. J. Solid Waste Technol. Manag. 2025, 51, 34–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprakash, B.G.; Dinesh, S.V. Dynamic Properties of Sand–Fines Mixtures. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 2327–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Su, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y. The Impact of High-Speed Rail Opening on City Economics along the Silk Road Economic Belt. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, J.; Sheikh, N.; Mastello, D.; Indraratna, B.; Mashiri, M. The direct shear strength of sand-tyre shred mixtures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geotechnical Engineering (ICGEColombo2015), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 10–11 August 2015; pp. 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Cabalar, A.F. Direct Shear Tests on Waste Tires–Sand Mixtures. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2011, 29, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Roy Bahadur, L.; Kumar, S. Performance of geocell reinforced rubber sand mixtures under undrained triaxial test. Soils Rocks 2024, 47, e2024001024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldin, K.M.; Radwan, A.M.; Rashed, A.S.; Mahmoud, M.A. Effect of Tire-Rubber Inclusion on The Physical and Mechanical Be-havior of Granular Soils. Eng. Res. J. 2024, 183, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rkaby, A.H.J. Strength and Deformation of Sand-Tire Rubber Mixtures (STRM): An Experimental Study. Stud. Geotech. Mech. 2019, 41, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, A.; Eidgahee, D.R. An Investigation on the Shear Strength Parameters of Sand-Rubber Mixtures Under the Applied Stress Paths. In Proceedings of the GeoShanghai 2018 International Conference: Fundamentals of Soil Behaviours, Shanghai, China, 27–30 May 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balunaini, U.; Prezzi, M. Interaction of Ribbed-Metal-Strip Reinforcement with Tire Shred–Sand Mixtures. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2010, 28, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi, M. Shear strength characteristics of sand-mixed with granular rubber. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2004, 22, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, D.V.; Umu, S.U. Dynamic Properties of Clean Sand Modified with Granulated Rubber. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5209494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.A.; Hong, L.S. Utilization of Shredded Rubber Tires for Cement-Stabilized Soft Clays. In Proceedings of the Ground Improvement and Geosynthetics, Shanghai, China, 3–5 June 2010; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

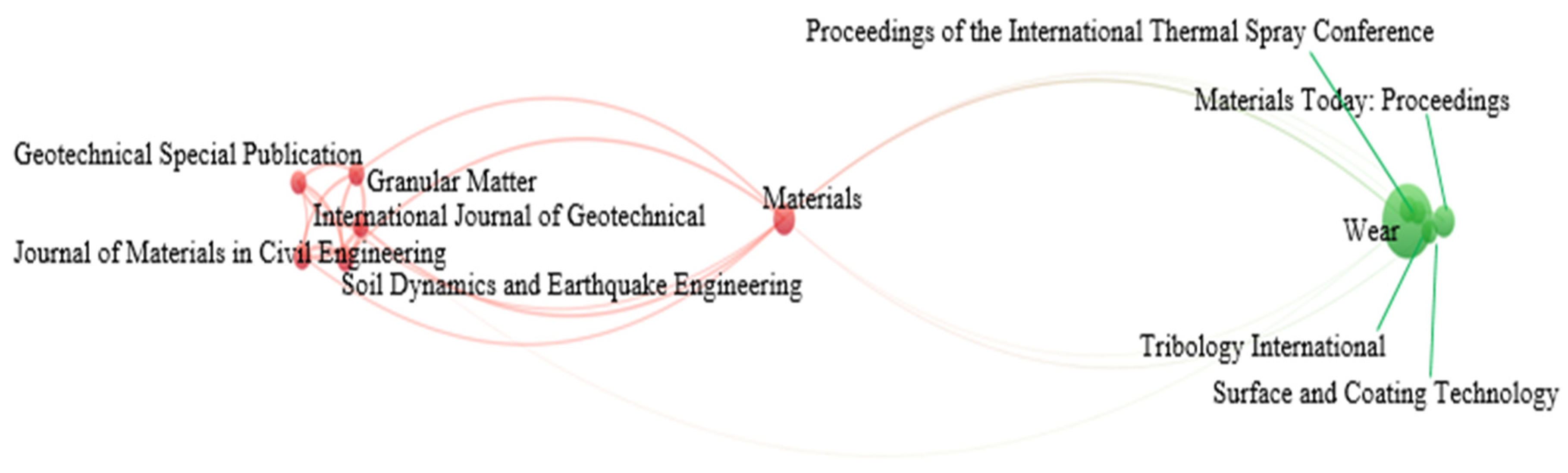
| Journal | Cluster | Links | TLS | Documents | Citations | Avg. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wear | 2 | 8 | 229 | 61 | 3081 | 50.5082 |
| Surface and Coatings Technology | 2 | 6 | 54 | 11 | 969 | 88.0909 |
| Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering | 1 | 7 | 930 | 7 | 593 | 84.7143 |
| Tribology International | 2 | 6 | 101 | 6 | 428 | 71.3333 |
| Geotechnical and Geological Engineering | 1 | 7 | 685 | 5 | 353 | 70.6 |
| Materials and Design | 2 | 6 | 25 | 5 | 309 | 61.8 |
| Materials Science and Engineering: A | 2 | 6 | 23 | 5 | 292 | 58.4 |
| Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering | 1 | 7 | 648 | 7 | 152 | 21.7143 |
| Granular Matter | 1 | 7 | 614 | 6 | 120 | 20 |
| Construction and Building Materials | 1 | 8 | 462 | 5 | 112 | 22.4 |
| Materials | 1 | 13 | 323 | 11 | 103 | 9.3636 |
| Materials Today: Proceedings | 2 | 7 | 30 | 6 | 85 | 14.1667 |
| International Journal of Geomechanics | 1 | 8 | 949 | 6 | 67 | 11.1667 |
| Geotechnical Special Publication | 1 | 7 | 426 | 6 | 44 | 7.3333 |
| Proceedings of the International Thermal Spray Conference | 2 | 5 | 23 | 7 | 36 | 5.1429 |
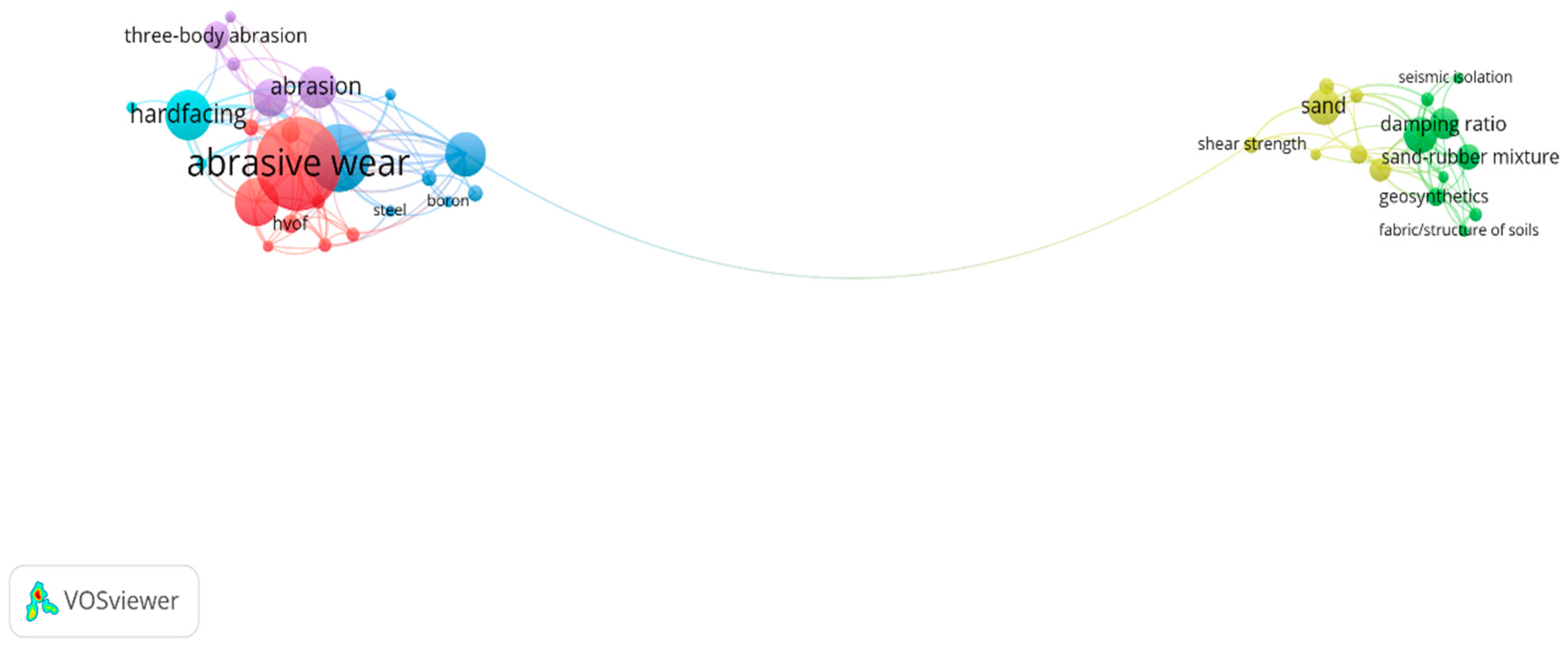
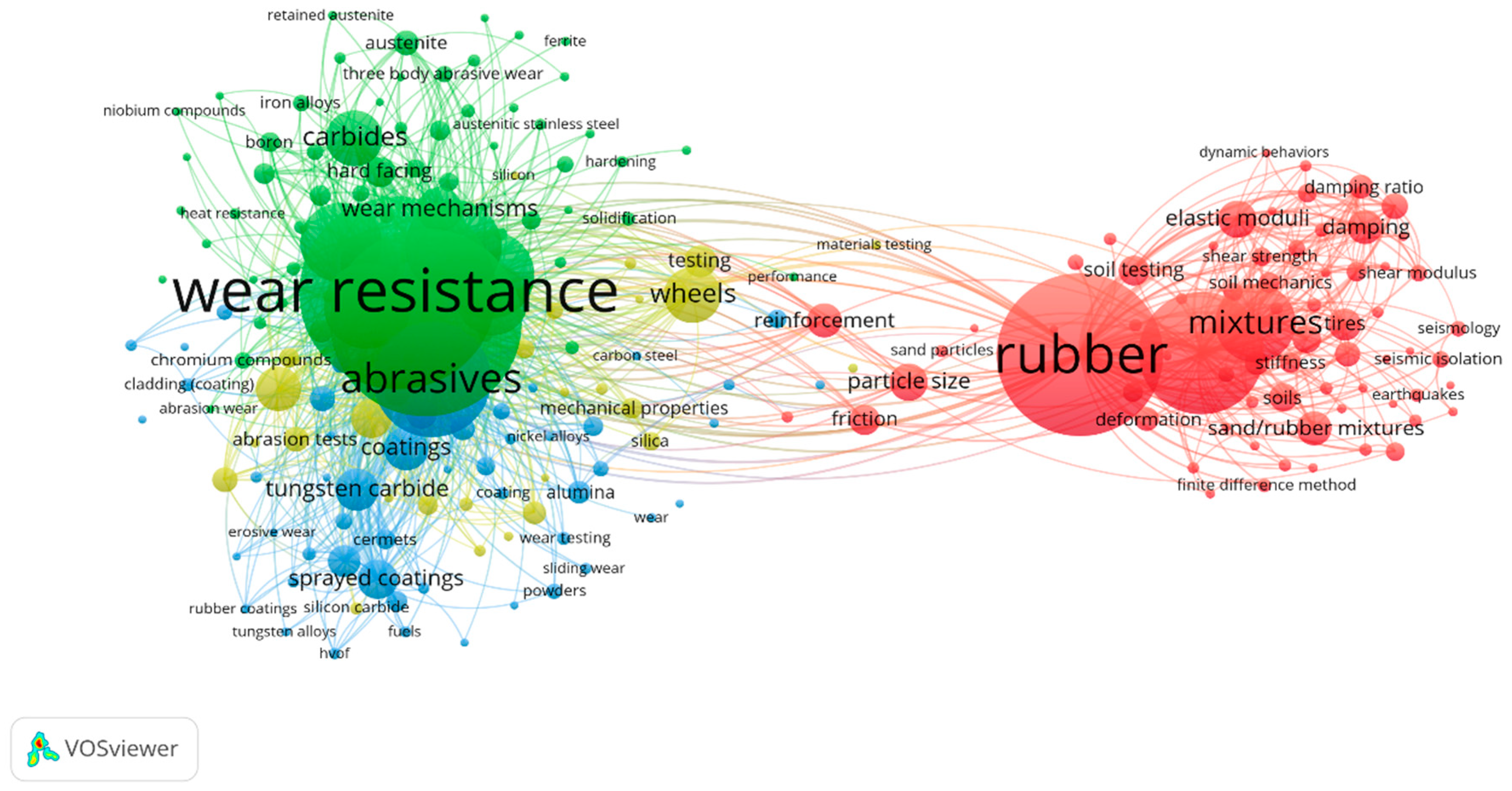
| Keywords | TLS | Cluster | Occurrences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wear | 34 | 3 | 32 |
| Shear Modulus | 31 | 2 | 16 |
| Microstructure | 29 | 3 | 20 |
| Abrasive Wear | 28 | 1 | 46 |
| Hardness | 27 | 5 | 17 |
| Hardfacing | 26 | 6 | 23 |
| Abrasion | 23 | 5 | 19 |
| Damping Ratio | 23 | 2 | 14 |
| Wear Resistance | 19 | 1 | 22 |
| Geosynthetics | 16 | 2 | 8 |
| Coating | 15 | 1 | 6 |
| Sand | 15 | 4 | 16 |
| HVOF | 14 | 1 | 8 |
| Heat Treatment | 12 | 3 | 7 |
| Sand–Rubber Mixtures | 12 | 2 | 10 |
| Particle-Scale Behavior | 11 | 2 | 6 |
| Three-Body Abrasion | 11 | 5 | 12 |
| Fabric/Structure of Soils | 10 | 2 | 5 |
| Granulated Rubber | 10 | 2 | 6 |
| WC-CO | 10 | 1 | 6 |
| Wear Testing | 10 | 5 | 6 |
| Discrete Element Method | 9 | 4 | 8 |
| Sand–Rubber Mixture | 9 | 4 | 11 |
| Sand–Rubber Mixtures | 9 | 4 | 5 |
| Tungsten Carbide | 9 | 1 | 5 |
| ASTM G65 | 8 | 1 | 7 |
| Carbide | 8 | 6 | 5 |
| Damping | 8 | 4 | 6 |
| Mechanical Properties | 8 | 1 | 6 |
| Wear Mechanism | 8 | 1 | 9 |
| Rubber | 7 | 4 | 7 |
| Steel | 7 | 3 | 5 |
| Boron | 6 | 3 | 5 |
| Coatings | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| Shear Strength | 5 | 4 | 7 |
| Sliding Wear | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Abrasion Resistance | 4 | 3 | 7 |
| Seismic Isolation | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| Abrasive Wear Resistance | 1 | 6 | 5 |
| Country | Cluster | Links | TLS | Documents | Citations | Avg. Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hong Kong | 2 | 19 | 9453 | 22 | 897 | 40.7727 |
| India | 1 | 24 | 7332 | 57 | 1338 | 23.4737 |
| Iran | 2 | 22 | 6972 | 29 | 554 | 19.1034 |
| China | 2 | 24 | 6794 | 57 | 1316 | 23.0877 |
| United Kingdom | 2 | 23 | 4677 | 27 | 895 | 33.1481 |
| Australia | 2 | 23 | 3815 | 18 | 450 | 25 |
| Greece | 2 | 22 | 3372 | 9 | 820 | 91.1111 |
| United States | 2 | 21 | 2847 | 25 | 645 | 25.8 |
| France | 2 | 23 | 2041 | 12 | 370 | 30.8333 |
| Germany | 1 | 22 | 1818 | 12 | 503 | 41.9167 |
| Turkey | 1 | 20 | 1413 | 9 | 250 | 27.7778 |
| Poland | 3 | 21 | 1338 | 9 | 155 | 17.2222 |
| Algeria | 2 | 18 | 1255 | 5 | 74 | 14.8 |
| South Korea | 2 | 18 | 898 | 6 | 545 | 90.8333 |
| Spain | 2 | 22 | 814 | 5 | 131 | 26.2 |
| Canada | 1 | 22 | 771 | 15 | 389 | 25.9333 |
| Brazil | 1 | 24 | 708 | 30 | 434 | 14.4667 |
| Italy | 1 | 14 | 502 | 5 | 480 | 96 |
| Finland | 1 | 19 | 494 | 8 | 405 | 50.625 |
| Czech Republic | 1 | 22 | 340 | 12 | 238 | 19.8333 |
| Colombia | 1 | 20 | 270 | 8 | 492 | 61.5 |
| Malaysia | 1 | 19 | 158 | 5 | 88 | 17.6 |
| Thailand | 1 | 10 | 72 | 5 | 32 | 6.4 |
| Croatia | 1 | 12 | 35 | 8 | 8 | 1 |
| Argentina | 1 | 10 | 33 | 5 | 210 | 42 |
| Title | Type of Sand and Rubber Used | Mixing Ratio | Geotechnical Application | Main Findings | Advantages | Limitations | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance of Geocell-Reinforced Rubber–Sand Mixtures | Sand and rubber (425 μm to 12 mm) | 10–40% rubber by volume | Load-bearing capacity in geotechnical structures | Improved shear strength with increasing rubber size and confining pressure | High energy absorption for seismic loads | Limited efficiency at low rubber content | 2024 | [75] |
| Effect of Tire-Rubber Inclusion on The Physical and Mechanical Behavior of Granular Soils | Fine granular soil and tire shreds | Various rubber-to-sand ratios | Soil stabilization and compaction | Optimal rubber geometry enhances shear strength and void ratio | Improved compaction efficiency | High anisotropy affects mechanical properties | 2024 | [76] |
| Sand–Rubber Mixtures under Oedometric Loading | Sand and rubber chips of various sizes | Various ratios based on density and void saturation | Embankment stabilization, retaining wall backfill | High deformability of rubber-rich mixtures, rubber-like or sand-like behavior classification | Enhanced compressibility control | Void saturation leads to loss of sand-like behavior | 2023 | [23] |
| Sand–Tire Shred Mixture Performance in Controlling Surface Explosion Hazards | Sand and tire shreds | 10%, 20%, 30% rubber by weight | Blast energy dissipation for underground structures | Effective energy dissipation, but depends on mixture thickness | Increased structural protection | Ineffective in thin layers | 2021 | [22] |
| Engineering Properties of Sand–Rubber Tire Shred Mixtures | River sand and fine rubber tire shreds | Various controlled proportions | Shear behavior, compressibility, and drainage characteristics | Increase in rubber content reduces shear strength and increases compressibility | Ductility enhancement and energy absorption | Reduction in shear strength and permeability | 2021 | [4] |
| Strength and Deformation of Sand–Tire Rubber Mixtures (STRM) | Sand and granulated rubber | 0–50% rubber by weight | Highway embankments, retaining wall backfill | Optimal shear strength at 10–20% rubber content, decreasing beyond 30% | Enhances ductility and stress–strain behavior | High rubber content leads to lower stress ratio | 2019 | [77] |
| An Investigation on the Shear Strength Parameters of Sand–Rubber Mixtures | Sand and granulated rubber/rubber chips | 30% rubber by weight | Road embankments and backfills | Higher friction angle with chip rubber than with sand alone | Improved load distribution | High rubber content reduces stiffness | 2018 | [78] |
| The Direct Shear Strength of Sand–Tire Shred Mixtures | Sand and tire shreds | Various proportions | Lightweight structural fill | Increased shear strength with optimal tire shred content | Cost-effective fill material | High variability in behavior | 2015 | [73] |
| Direct Shear Tests on Waste Tires–Sand Mixtures | Fine angular sand, coarse rotund sand, and shredded waste rubber | 5%, 10%, 20%, and 50% by dry weight | Shear strength and internal friction analysis | Increase in rubber decreases shear strength and internal friction angle | Lightweight fill material | Decrease in shear strength at high rubber content | 2011 | [74] |
| Interaction of Ribbed-Metal-Strip Reinforcement with Tire Shred–Sand Mixtures | Tire shreds of different sizes and sand | 0%, 12%, 25%, 100% by weight | MSE wall backfill material | Higher pullout capacity in mixtures than in pure tire shreds | Improved reinforcement properties | Variability in tire shred sizes affects consistency | 2010 | [79] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bangalore Ramu, M.; Baarimah, A.O.; Mokaizh, A.A.B.; Mushtaha, A.W.; Al-Mekhlafi, A.-B.A.; Alawag, A.M.; Alzubi, K.M. Turning Waste into Resources: Bibliometric Study on Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures in Geotechnical Engineering. Geotechnics 2025, 5, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5040071
Bangalore Ramu M, Baarimah AO, Mokaizh AAB, Mushtaha AW, Al-Mekhlafi A-BA, Alawag AM, Alzubi KM. Turning Waste into Resources: Bibliometric Study on Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures in Geotechnical Engineering. Geotechnics. 2025; 5(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleBangalore Ramu, Madhusudhan, Abdullah O. Baarimah, Aiman A. Bin Mokaizh, Ahmed Wajeh Mushtaha, Al-Baraa Abdulrahman Al-Mekhlafi, Aawag Mohsen Alawag, and Khalid Mhmoud Alzubi. 2025. "Turning Waste into Resources: Bibliometric Study on Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures in Geotechnical Engineering" Geotechnics 5, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5040071
APA StyleBangalore Ramu, M., Baarimah, A. O., Mokaizh, A. A. B., Mushtaha, A. W., Al-Mekhlafi, A.-B. A., Alawag, A. M., & Alzubi, K. M. (2025). Turning Waste into Resources: Bibliometric Study on Sand–Rubber Tire Mixtures in Geotechnical Engineering. Geotechnics, 5(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics5040071









