A Framework for the Dynamic Mapping of Precipitations Using Open-Source 3D WebGIS Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
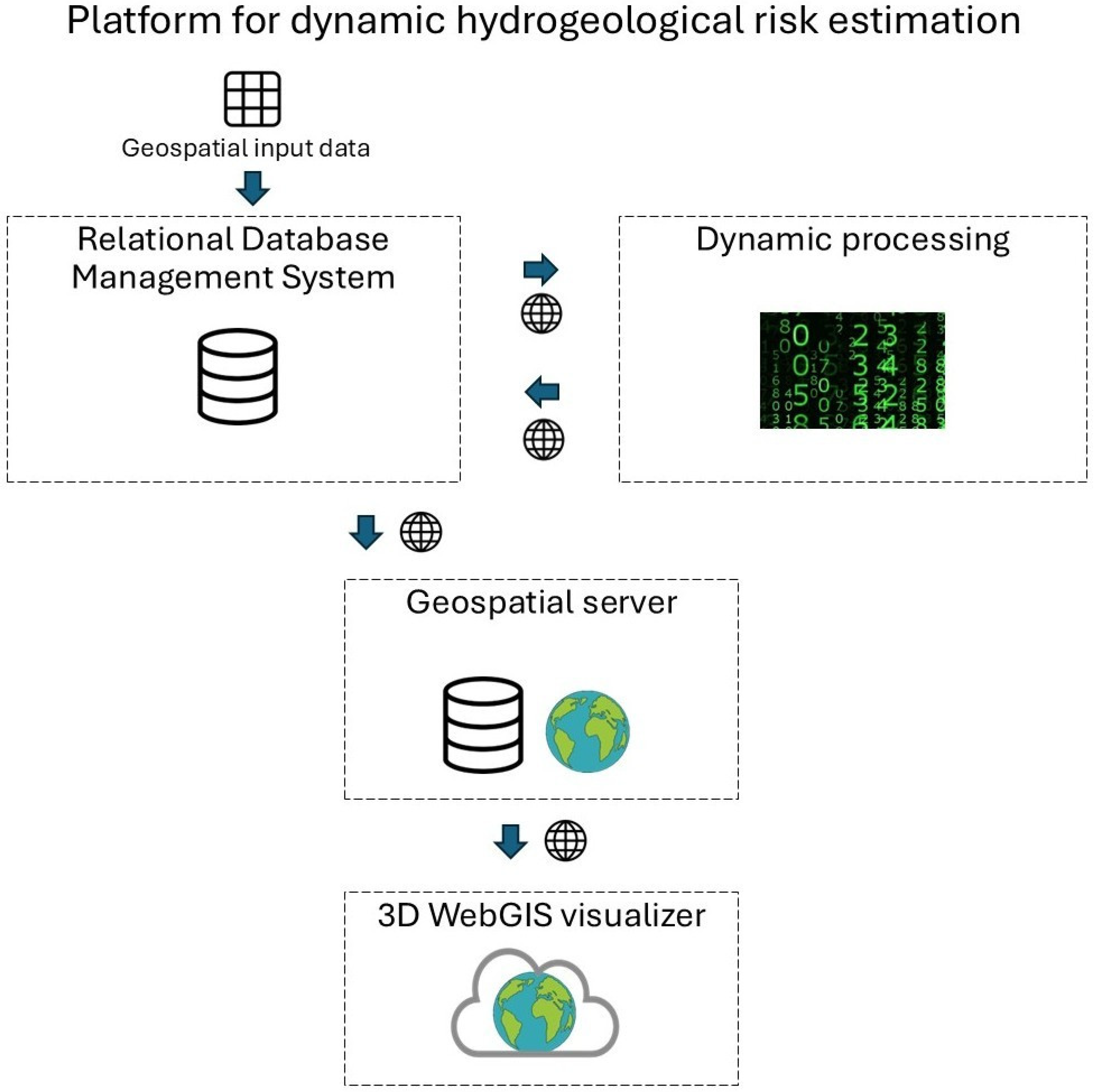
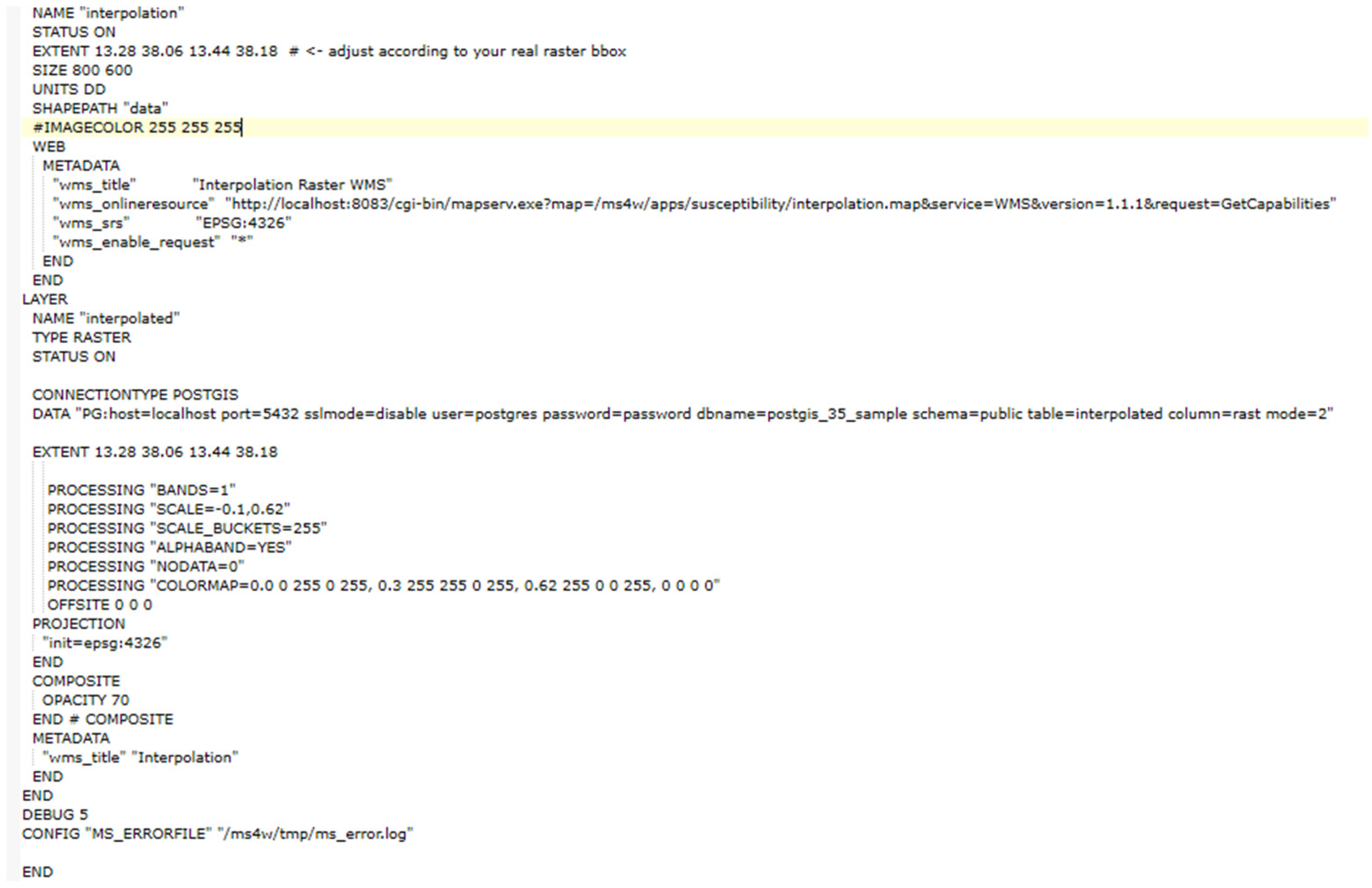
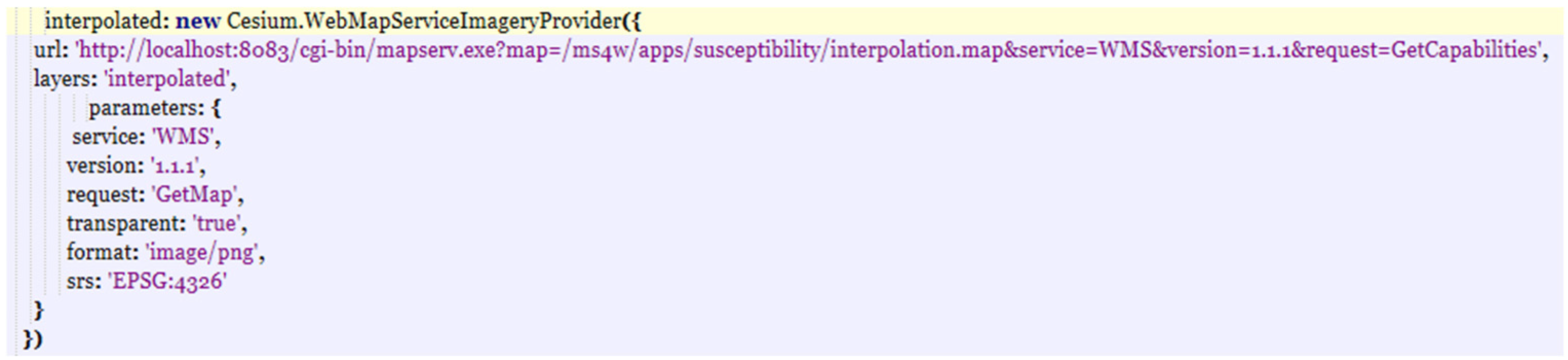
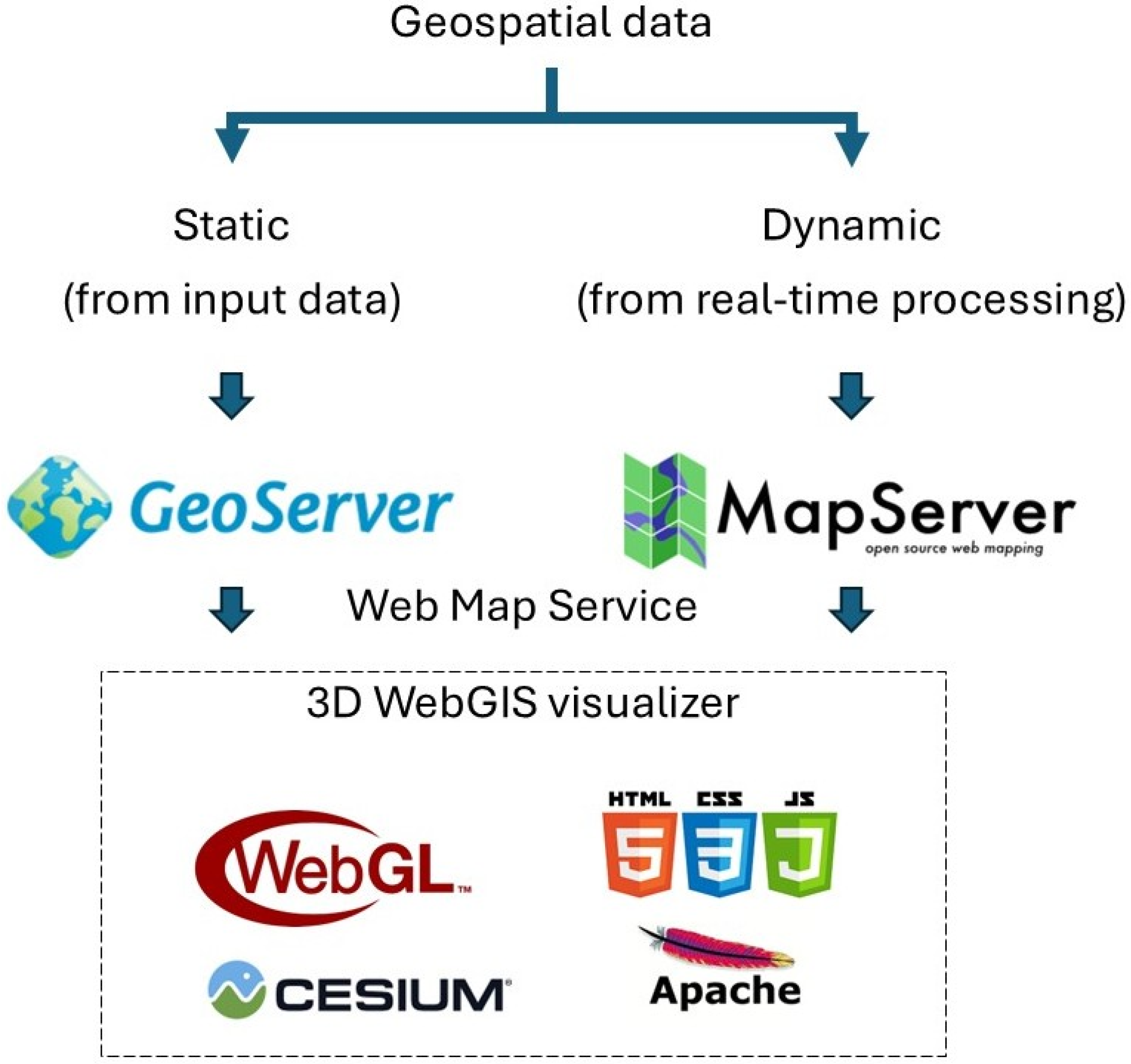
2. Materials and Methods
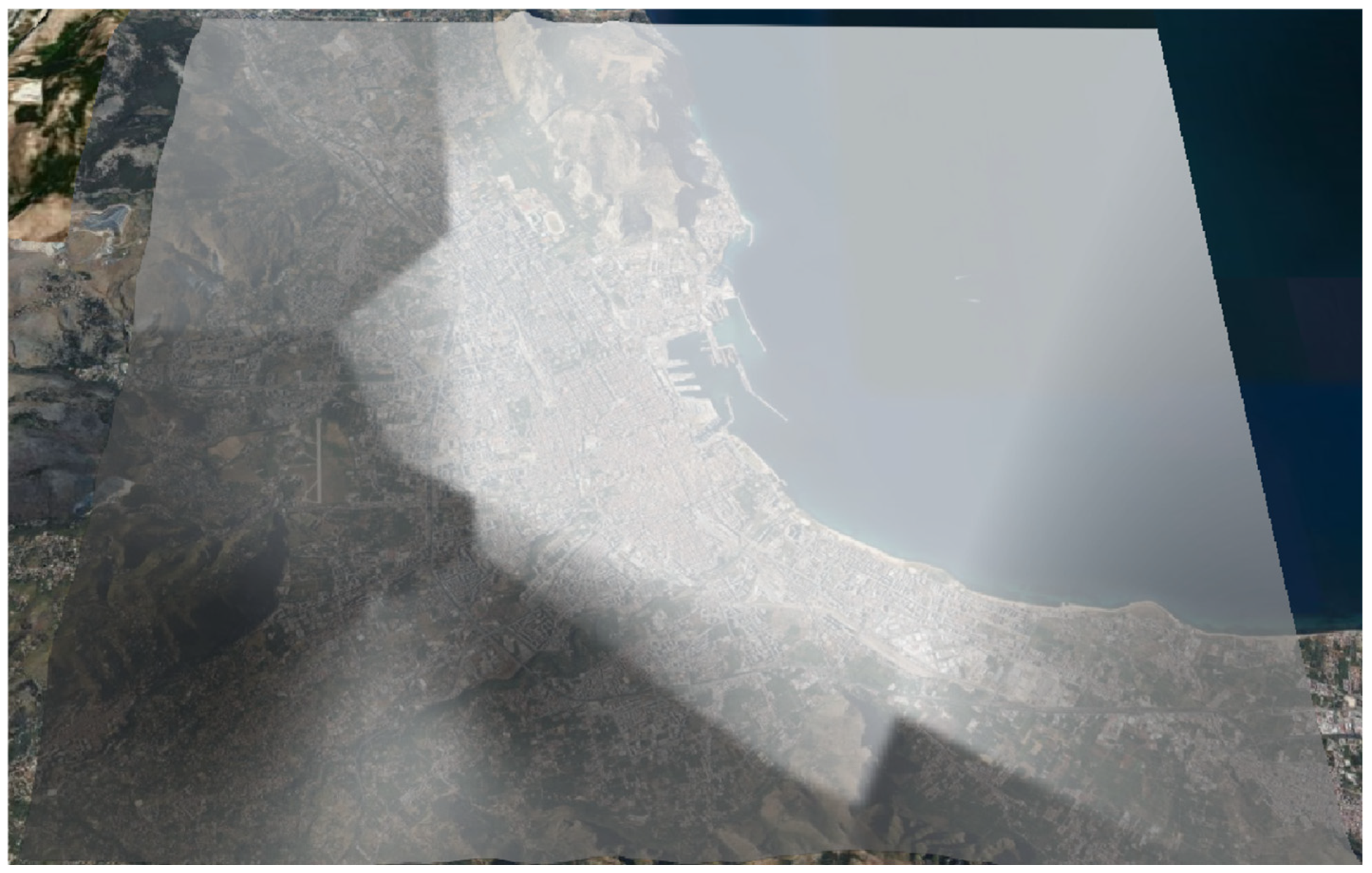
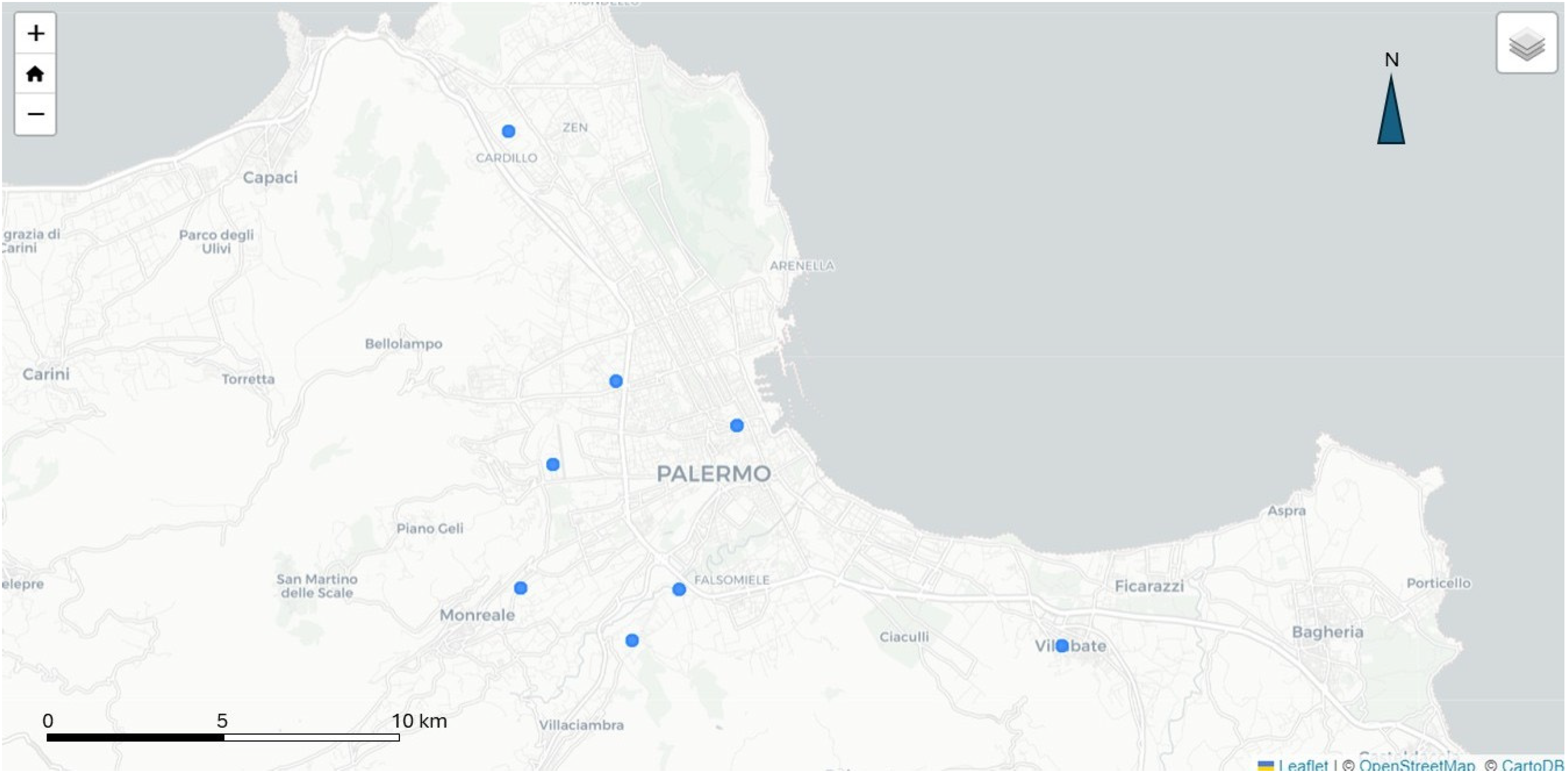
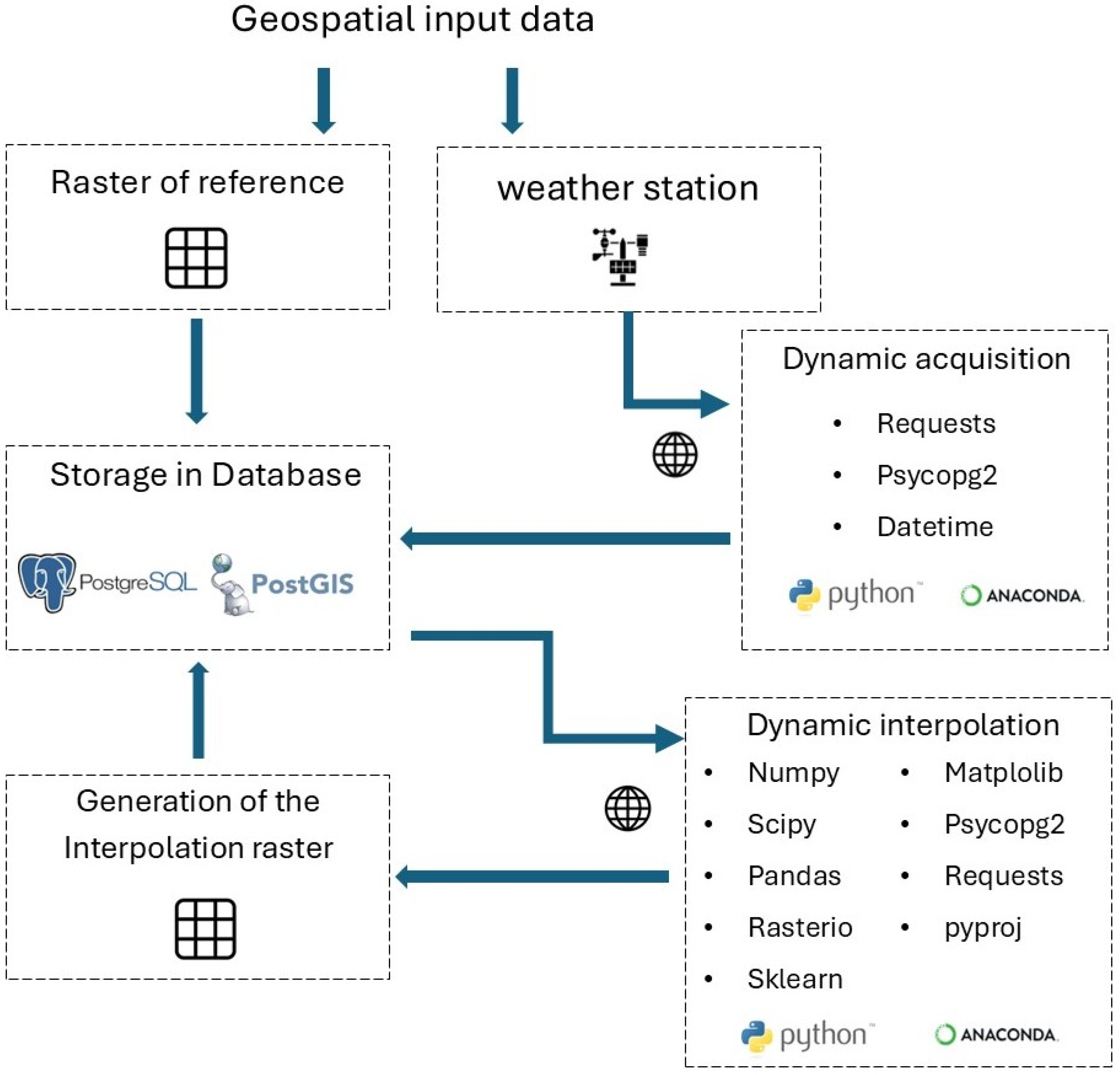
3. Dynamic Mapping of Precipitations: The Case Study of Palermo (Italy)
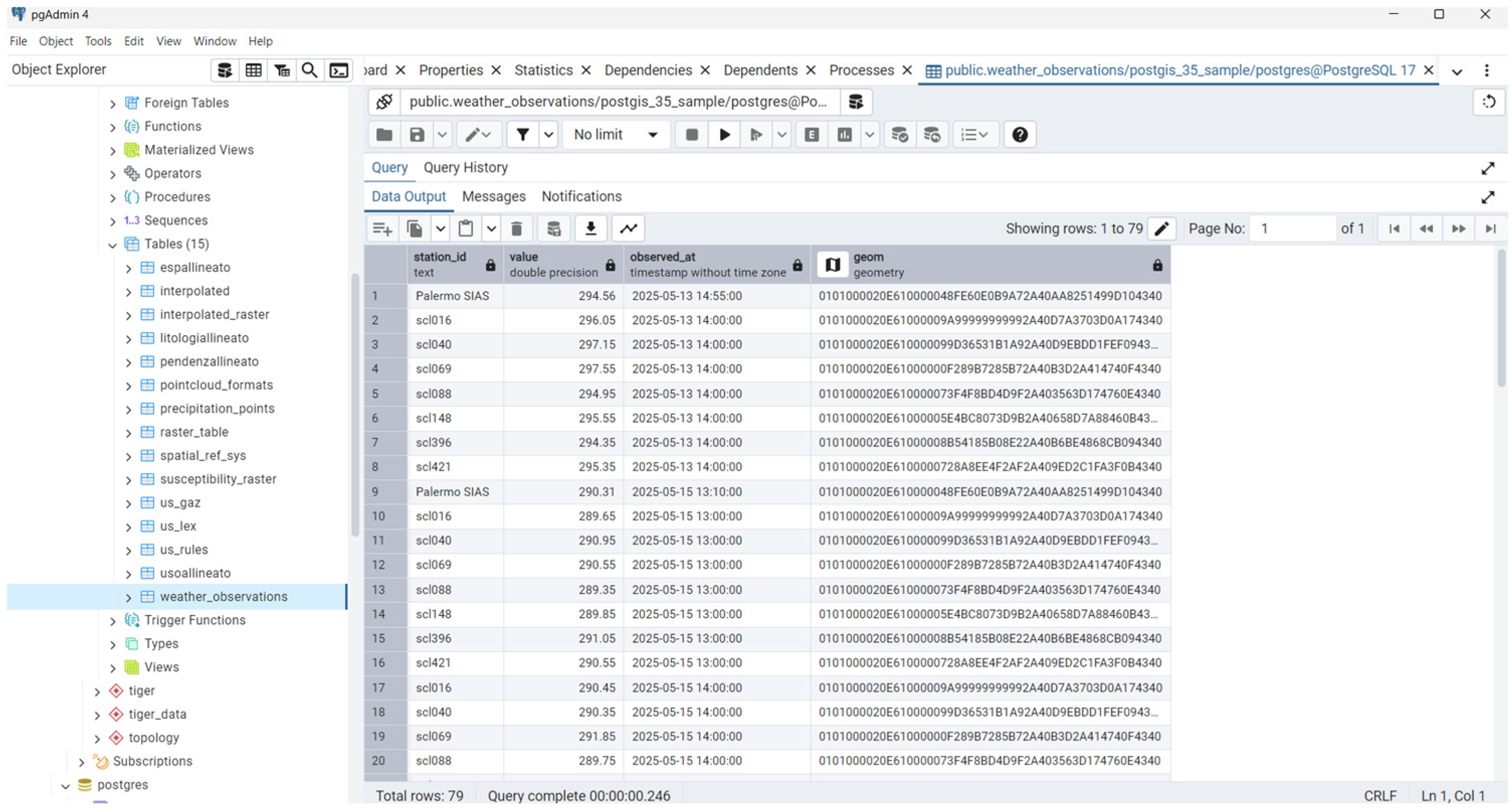
- Station id, a column that defines each weather station uniquely.
- Observed_at, a column that defines the time of acquisition.
- Value, a column that defines the double precision number indicating the single acquisition (mm) of A water column.
- Numpy and Scipy, open-source Python libraries for matrix operations, multidimentional arrays, and math functions.
- Pandas, an open-source Python library for the management of tables and data frameworks.
- Rasterio, an open-source Python library for accessing geospatial raster data in GIS environment.
- Sklearn, an open-source Python library for classification, regression, clustering, and machines for vectorial support.
- Matplotlib 3.10, an open-source Python library for creating static, animated, and interactive images from Python operations.
- psycopg2, an open-source Python library for communication between Python scripts and the PostgreSQL database.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broome, J. The ethics of climate change. Sci. Am. 2008, 298, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; An, B.; Gao, T.; Yao, T. Ice thickness and morphological analysis reveal the future glacial lake distribution and formation probability in the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Glob. Planet. Change 2022, 216, 103923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.I.; Rathburn, S.L.; Capps, D.M. Landslide response to climate change in permafrost regions. Geomorphology 2019, 340, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, M.; Huggel, C. Effects of climate change on mass movements in mountain environments. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 36, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Barrand, N.E.; Bracegirdle, T.J.; Convey, P.; Hodgson, D.A.; Jarvis, M.; Jenkins, A.; Marshall, G.; Meredith, M.P.; Roscoe, H. Antarctic climate change and the environment: An update. Polar Rec. 2014, 50, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escanilla-Minchel, R.; Alcayaga, H.; Soto-Alvarez, M.; Kinnard, C.; Urrutia, R. Evaluation of the Impact of Climate Change on Runoff Generation in an Andean Glacier Watershed. Water 2020, 12, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Nõges, T.; Nõges, P.; Attayde, J.L.; Zohary, T.; Coppens, J.; et al. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to change in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Takasaki, Y. Natural disaster poverty and development: An Introduction. World Dev. 2017, 94, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Nohrstedt, D.; Mård, J.; Burchardt, S.; Albin, C.; Bondesson, S.; Breinl, K.; Deegan, F.M.; Fuentes, D.; Lopez, M.G.; et al. An Integrative Research Framework to Unravel the Interplay of Natural Hazards and Vulnerabilities. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, B.; Winsemius, H.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Ward, P.J. Declining vulnerability to river floods and the global benefits of adaptation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2271–E2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mård, J.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Mazzoleni, M. Nighttime light data reveal how flood protection shapes human proximity to rivers. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, H.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Vorogushyn, S.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Apel, H.; Aronica, G.T.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Bouwer, L.M.; Bubeck, P.; Caloiero, T.; et al. Adaptation to flood risk: Results of international paired flood event studies. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondino, E.; Scolobig, A.; Borga, M.; Albrecht, F.; Mård, J.; Weyrich, P.; Di Baldassarre, G. Exploring changes in hydrogeological risk awareness and preparedness over time: A case study in northeastern Italy. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernello, G.; Mondino, E.; Bortolini, L. People’s Perception of Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Mitigation: The Case of Veneto Region (Italy). Sustainability 2022, 14, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponziani, F.; Pandolfo, C.; Stelluti, M.; Berni, N.; Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T. Assessment of rainfall thresholds and soil moisture modeling for operational hydrogeological risk prevention in the Umbria region (central Italy). Landslides 2012, 9, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mo, P. A unified landslide classification system for loess slopes: A critical review. Geomorphology 2019, 340, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrile, V.; Genovese, E.; Cotroneo, F. Geomatics, soft computing, and innovative simulator: Prediction of susceptibility to landslide risk. AIMS Geosci. 2024, 10, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiameli, M.; Cappello, A.; Mussumeci, G. Spatial data and GIS for the assessment of the environmental impact at Mount Etna. Ann. Geophys. 2025, 68, V112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, G.; Barchiesi, F.; Catallo, F.; Dramis, F.; Fubelli, G.; Lucifora, S.; Puglisi, C. GIS Methodology to Assess Landslide Susceptibility: Application to a River Catchment of Central Italy. J. Maps 2009, 5, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Mondini, A.; Peruccacci, S. Optimal landslide susceptibility zonation based on multiple forecasts. Geomorphology 2010, 114, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaoqiang, M.; Zhenming, S.; Gang, L.; Ming, P.; Liu, L.; Hongchao, Z.; Changshi, Z. A novel deep learning framework for landslide susceptibility assessment using improved deep belief networks with the intelligent optimization algorithm. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 167, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazali, A.; Leila, H.B.; Tamer, E.; Gary, T. Optimizing landslide susceptibility mapping using machine learning and geospatial techniques. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102583. [Google Scholar]
- Haoyuan, H. Landslide susceptibility assessment using locally weighted learning integrated with machine learning algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121678. [Google Scholar]
- Aricò, M.; La Guardia, M.; Lo Brutto, M. 3D Data Integration for Web Fruition of Underground Archaeological Sites: A Web Navigation System for the Hypogeum of Crispia salvia (Marsala, Italy). Heritage 2023, 6, 5899–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Guardia, M.; Koeva, M.; D’Ippolito, F.; Karam, S. 3D data integration for web based open source webgl interactive visualisation. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci 2022, XLVIII-4/W4-2022, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, F.; Barbieri, F.; Fascia, R.; Ioli, F.; Pinto, L. An Open-Source Web Platform for 3D Documentation and Storytelling of Hidden Cultural Heritage. Heritage 2024, 7, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birr, S.; Mönch, J.; Sommerfeld, D.; Preim, U.; Preim, B. The LiverAnatomyExplorer: A WebGL-based surgical teaching tool. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2013, 33, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; He, Q.; Yan, Y.; Ma, B.; Yue, C.; Xie, Y. Implementation of interactive three-dimensional visualization of air pollutants using WebGL. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 114, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, F.; Ioli, F.; Barbieri, F.; Rivieri, C.; Dondi, M.; Pinto, L. Rediscovering cultural heritage sites by interactive 3D exploration: A practical review of open-source WebGL tools. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, B.; Wohlfahrt, R.; Wosniok, C. Web-Based 4D visualization of marine geo-data using WebGL. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 41, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Li, Z. A research for 3D WebGIS based on WebGL. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology, Harbin, China, 24–26 December 2011; Volume 1, pp. 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, S. PolarGlobe: A web-wide virtual globe system for visualizing multidimensional, time-varying, big climate data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1562–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pispidikis, I.; Dimopoulou, E. Development of a 3D WebGIS System for Retrieving and Visualizing CityGML Data Based on Their Geometric and Semantic Characteristics by Using Free and Open Source Technology. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2016, IV-2/W1, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, J.; Pan, M.; Huang, J. Application of 3D WebGIS and real-time technique in earthquake information publishing and visualization. Earthq. Sci. 2015, 28, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasoy, K.; Kocaman, S. Development of a Geo-Analytics Platform for Post-Disaster Ground Assessment. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2021, XLIII-B3-2021, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, H.; Bian, H.; Mei, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xue, P. Multi-Scalar Oblique Photogrammetry-Supported 3D webGIS Approach to Preventive Mining-Induced Deformation Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanbaev, I.; Champion, E.; McMeekin, D.A. A Web GIS-Based Integration of 3D Digital Models with Linked Open Data for Cultural Heritage Exploration. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, A.; Monterisi, C.; Saponieri, A.; Addona, F.; Damiani, L.; Archetti, R.; Tarantino, E. An Interactive WebGIS Framework for Coastal Erosion Risk Management. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derong, L.; Liang, H.; Gao, K. Design of Soil Pollution Prevention and Control Evaluation and Analysis Platform based on WebGIS. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Symposium on Computer Technology and Information Science (ISCTIS), Xi’an, China, 12–14 July 2024; pp. 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, H.; Qin, Y.; Fu, P.; Guo, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, X. Web GIS for Sustainable Education: Towards Natural Disaster Education for High School Students. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguelva, N.M.; Mustapha, H.; Hubert, F. Towards A 3d Web Tool For Visualization And Simulation Of Urban Flooding: The Case Of Metropolitan Cities In Cameroon. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Rev. (IJASER) 2023, 4, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, R.; Ju, N.; Xu, Q.; He, C. 3D WebGIS-based platform for debris flow early warning: A case study. Eng. Geol. 2015, 197, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilsedar, C.E.; Fissore, F.; Pirotti, F.; Brovelli, M.A. Extraction and visualization of 3D building models in urban areas for flood simulation. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W11, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Beccali, G.; Cellura, M.; Culotta, S.; Lo Brano, V.; Marvuglia, A. A Web-Based Autonomous Weather Monitoring System of the Town of Palermo and Its Utilization for Temperature Nowcasting. In Computational Science and Its Applications–ICCSA 2008; Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Laganà, A., Taniar, D., Mun, Y., Gavrilova, M.L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5072, pp. 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellura, M.; Culotta, S.; Lo Brano, V.; Marvuglia, A. Nonlinear Black-Box Models for Short-Term Forecasting of Air Temperature in the Town of Palermo. In Geocomputation, Sustainability and Environmental Planning; Murgante, B., Borruso, G., Lapucci, A., Eds.; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 348, pp. 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- About PostGIS. Available online: https://postgis.net/docs/ (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Anaconda Documentation. Available online: https://www.anaconda.com/docs/main (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- GeoServer Overview. Available online: https://docs.geoserver.org/main/en/user/introduction/overview.html (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- An Introduction to MapServer. Available online: https://mapserver.org/introduction.html (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- CesiumJS. Available online: https://cesium.com/learn/cesiumjs-learn/ (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Italia Meteo. Meteohub. Available online: https://meteohub.mistralportal.it/app/maps/observations (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- European Commission. INSPIRE Data Specification on Environmental Monitoring Facilities—Technical Guidelines; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2024; Available online: https://knowledge-base.inspire.ec.europa.eu/publications/inspire-data-specification-environmental-monitoring-facilities-technical-guidelines_en (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Daud, M.; Ugliotti, F.M.; Osello, A. Comprehensive Analysis of the Use of Web-GIS for Natural Hazard Management: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, M.; Quaroni, D. Development of a 3D WebGIS Application for the Visualization of Seismic Risk on Infrastructural Work. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues da Silva, A.; Estima, J.; Marques, J.; Gamito, I.; Serra, A.; Moura, L.; Ricardo, A.M.; Mendes, L.; Ferreira, R.M.L. A Web GIS Platform to Modeling, Simulate and Analyze Flood Events: The RiverCure Portal. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, M.; Quaroni, D. A System for Analysis and Simulating Hydraulic and Hydrogeological Risks Through WebGIS 3D Digital Platforms. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschieri, D.L.D.; Sobrino, N.; Macii, E. Web-GIS Application for Hydrogeological Risk Prevention: The Case Study of Cervo Valley. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Guardia, M.; Koeva, M.; Díaz-Vilariño, L.; Nourian, P. Open-Source Solutions for Real-Time 3D Geospatial Web Integration. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2024, XLVIII-4-2024, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Guardia, M.; Angrisano, A.; Mussumeci, G. A Framework for the Dynamic Mapping of Precipitations Using Open-Source 3D WebGIS Technology. Geographies 2025, 5, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5030040
La Guardia M, Angrisano A, Mussumeci G. A Framework for the Dynamic Mapping of Precipitations Using Open-Source 3D WebGIS Technology. Geographies. 2025; 5(3):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5030040
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Guardia, Marcello, Antonio Angrisano, and Giuseppe Mussumeci. 2025. "A Framework for the Dynamic Mapping of Precipitations Using Open-Source 3D WebGIS Technology" Geographies 5, no. 3: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5030040
APA StyleLa Guardia, M., Angrisano, A., & Mussumeci, G. (2025). A Framework for the Dynamic Mapping of Precipitations Using Open-Source 3D WebGIS Technology. Geographies, 5(3), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5030040






