Geomorphological Mapping Global Trends and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
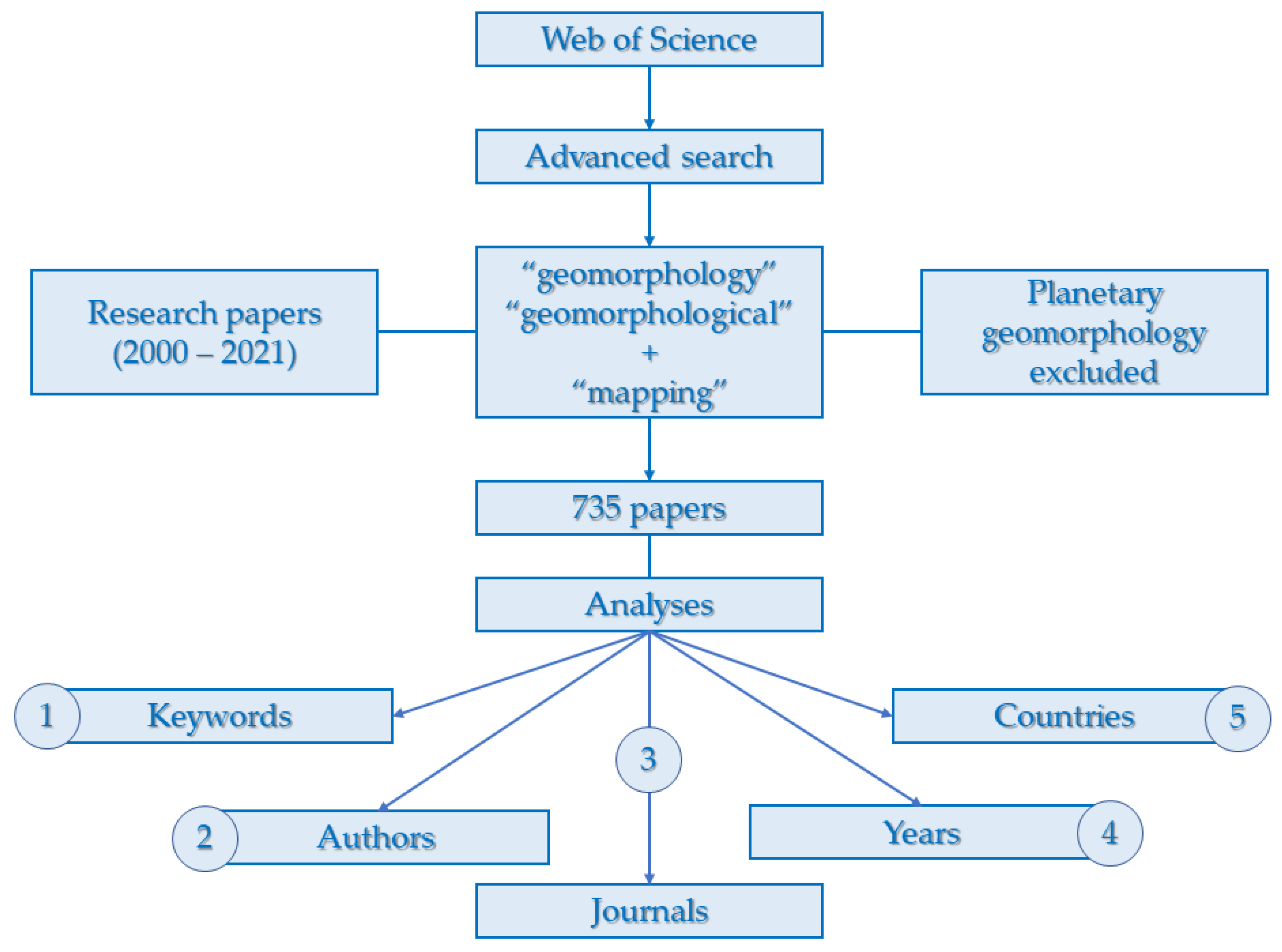
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Keywords
3.2. Authors
3.3. Journals
3.4. Country (Publication and Affiliation)
3.5. Years
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magliulo, P.; Valente, A. GIS-Based geomorphological map of the Calore River floodplain near Benevento (Southern Italy) overflooded by the 15th October 2015 event. Water 2020, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodroffe, C.D. Coasts: Geomorphology and Environment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, N.; Quesada-Román, A.; Granados-Bolaños, S. Mapping Mountain Landforms and Its Dynamics: Study Cases in Tropical Environments. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaymaker, O.; Spencer, T.; Embleton-Hamann, C. Recasting geomorphology as a landscape science. Geomorphology 2021, 384, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Borga, M.; Dalla Fontana, G. Geomorphological mapping: A review of approaches and applications in Italy. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2014, 37, 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd, R.J.; Williams, R.D.; Hoey, T.B.; Barrett, B.; Prasojo, O.A. Applications of Google Earth Engine in fluvial geomorphology for detecting river channel change. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2021, 8, e21496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, E.; Oriani, F.; Tonini, M.; Lambiel, C.; Mariéthoz, G. Using data-driven algorithms for semi-automated geomorphological mapping. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2115–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramis, F.; Guida, D.; Cestari, A. Nature and Aims of Geomorphological Mapping. In Developments in Earth Surface Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, T.P.; Goudie, A.S.; Viles, H.A. (Eds.) The History of the Study of Landforms or the Development of Geomorphology: Volume 5: Geomorphology in the Second Half of the Twentieth Century; Geological Society of London Memoirs: London, UK, 2022; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Goudie, A.S.; Burt, T.P.; Viles, H.A. The global transformation of geomorphology. Geol. Soc. Lond. Mem. 2022, 58, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroder, J.F. Treatise on Geomorphology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhan, F.B.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, F.; Chen, X.; Guo, J. Global Research Trends in Landslides during 1991–2014: A Bibliometric Analysis. Landslides 2015, 12, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-Mero, P.; Montalván-Burbano, N.; Paz-Salas, N.; Morante-Carballo, F. Volcanic Geomorphology: A Review of Worldwide Research. Geosciences 2020, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivero, S.; Bodin, X.; Farías-Barahona, D.; MacDonell, S.; Schaffer, N.; Robson, B.A.; Lambiel, C. Combination of aerial, satellite, and UAV photogrammetry for quantifying rock glacier kinematics in the Dry Andes of Chile (30 S) since the 1950s. Front. Remote Sens. 2021, 2, 784015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Román, A. Landslides and Floods Zonation Using Geomorphological Analyses in a Dynamic Catchment of Costa Rica. Rev. Cartogr. 2021, 102, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.M. Geomorphological mapping. Geol. Soc. Lond. Eng. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2001, 18, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Román, A.; Quirós-Arias, L.; Zamora-Pereira, J.C. Interactions between Geomorphology and Production Chain of High-Quality Coffee in Costa Rica. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.J.; Pain, C.F. Geomorphological mapping. In The SAGE Handbook of Geomorphology; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2011; pp. 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, M.P.; James, L.A.; Shroder, J.F., Jr.; Walsh, S.J. Geospatial technologies and digital geomorphological mapping: Concepts, issues and research. Geomorphology 2012, 137, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, I.C.; Gilvear, D.J.; Thoms, M.C.; Death, R.G. Framing Resilience for River Geomorphology: Reinventing the Wheel? River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Cao, W.; Sofia, G.; Evans, D.; Ellis, E.C. From Features to Fingerprints: A General Diagnostic Framework for Anthropogenic Geomorphology. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2019, 43, 95–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, W. A Review of Remote Sensing Applications in Geomorphology. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 1531–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, F.; Chen, X.; Guo, J. Quantitative Analysis of Tectonic Geomorphology Research Based on Web of Science from 1981 to 2021. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Mudd, S.M. Remote Sensing of Geomorphology, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada-Román, A.; Vargas-Sanabria, D. A geomorphometric model to determine topographic parameters controlling wildfires occurrence in tropical dry forests. J. Arid. Environ. 2022, 198, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocco, G.; Mendoza, M.; Velázquez, A. Remote sensing and GIS-based regional geomorphological mapping—A tool for land use planning in developing countries. Geomorphology 2001, 39, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, S.J. Geomorphology and Earth System Science. Geol. Soc. Lond. Mem. 2022, 58, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viles, H. Biogeomorphology: Past, Present and Future. Geomorphology 2020, 366, 106809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. The Research on the Development of Geomorphology in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada-Román, A. Disaster Risk Assessment of Informal Settlements in the Global South. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Román, A. Geomorphology of the Guacimal River Catchment, Costa Rica. J. Geogr. Cartogr. 2022, 5, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Román, A. Review of the Geomorphological Effects of the 1991 Limón Earthquake. Rev. Geol. Am. Cent. 2022, 65, 370–395. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Patel, P.P.; Sengupta, S. Evaluation of different digital elevation models for analyzing drainage morphometric parameters in a mountainous terrain: A case study of the Supin–Upper Tons Basin, Indian Himalayas. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Roman, A.; Campos, N.; Granados-Bolanos, S. Tropical Glacier Reconstructions during the Last Glacial Maximum in Costa Rica. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2021, 38, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelli, V.; Ghinoi, A.; Marchetti, M.; Soldati, M. Discovery and dating of Pre-LGM deposits in a high catchment of the Dolomites (Italy): New insights on climate-related geomorphological processes during the Late Pleistocene. Geomorphology 2019, 332, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Oguchi, T. Geomorphological Debates in Japan Related to Surface Processes, Tectonics, Climate, Research Principles, and International Geomorphology. Geomorphology 2020, 366, 106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piégay, H.; Kondolf, G.M.; Minear, J.T.; Vaudor, L. Trends in Publications in Fluvial Geomorphology over Two Decades: A Truly New Era in the Discipline Owing to Recent Technological Revolution? Geomorphology 2015, 248, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstappen, H.T. Old and New Trends in Geomorphological and Landform Mapping. Dev. Earth Surf. Process. 2011, 15, 13–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.X.; Dinneen, J.D.; Luczak-Roesch, M. A Novel Method for Resolving and Completing Authors’ Country Affiliation Data in Bibliographic Records. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2020, 5, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlRyalat, S.A.S.; Malkawi, L.W.; Momani, S.M. Comparing Bibliometric Analysis Using PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science Databases. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 152, e58494. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, A.; Kargina, M. A User-Friendly Method to Merge Scopus and Web of Science Data during Bibliometric Analysis. J. Mark. Anal. 2022, 10, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Rank | Keyword | NP |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geomorphology | 141 |
| 2 | Geomorphological mapping | 82 |
| 3 | Glacial geomorphology | 52 |
| 4 | Remote sensing | 48 |
| 5 | GIS | 39 |
| 6 | DEM | 33 |
| 7 | Lidar | 28 |
| 8 | Landslides | 25 |
| 9 | Fluvial geomorphology | 20 |
| 10 | Mapping | 20 |
| 11 | Holocene | 15 |
| 12 | Karst | 15 |
| 13 | Landslide | 15 |
| 14 | Coastal geomorphology | 14 |
| 15 | Quaternary | 13 |
| 16 | Tectonic Geomorphology | 13 |
| 17 | Palaeohydrology | 12 |
| 18 | Geomorphometry | 11 |
| 19 | Landscape evolution | 11 |
| Rank | Authors | AT | AF | CO | HI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Evans, D.J.A. | 16 | Durham University | UK | 57 |
| 2 | Gutierrez, F. | 13 | Zaragoza University | Spain | 52 |
| 3 | Miccadei, E. | 12 | Università degli Studi “G. d’Annunzio” di Chieti Pescara | Italy | 28 |
| 4 | Xu, S.Y. | 11 | Beijing Geosciences University | China | ND |
| 5 | Lovell, H. | 10 | Portsmouth University | UK | 18 |
| 6 | Lehmkuhl, F. | 9 | RWTH Aachen University | Germany | 54 |
| 7 | Piacentini, T. | 9 | Università degli Studi “G. d’Annunzio” di Chieti Pescara | Italy | 22 |
| 8 | Soldati, M. | 9 | Università di Modena e Reggio Emilia | Italy | 33 |
| 9 | Stroeven, A.P. | 9 | Stockholm University | Sweden | 42 |
| 10 | Glasser, N.F. | 8 | Aberystwyth University | England | 64 |
| 11 | Jansson, K.N. | 8 | Stockholm University | Sweden | 54 |
| 12 | Quesada-Román, A. | 8 | Universidad de Costa Rica | Costa Rica | 26 |
| 13 | Stokes, C.R. | 8 | Durham University | UK | 58 |
| 14 | Boston, C.M. | 7 | Portsmouth University | UK | 15 |
| 15 | Cofaigh, C.O. | 7 | Durham University | UK | 59 |
| Rank | Journal | NP |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geomorphology | 231 |
| 2 | Journal of Maps | 126 |
| 3 | Quaternary Science Reviews | 17 |
| 4 | Earth Surface Processes and Landforms | 15 |
| 5 | Geografia Fisica e Dinamica Quaternaria | 13 |
| 6 | Journal of Coastal Research | 9 |
| 7 | Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie | 8 |
| 8 | Geosciences | 7 |
| 9 | Marine Geology | 7 |
| 10 | Catena | 6 |
| 11 | Journal of South American Earth Sciences | 6 |
| 12 | Natural Hazards | 6 |
| 13 | Quaterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology | 6 |
| 14 | Remote Sensing | 6 |
| 15 | Arabian Journal of Geosciences | 5 |
| 16 | Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America | 5 |
| 17 | Geografiska Annaler Series A- Physical Geography | 5 |
| 18 | Landslides | 5 |
| 19 | Natural Harzards and Earth System Sciences | 5 |
| 20 | Water | 5 |
| Altitude Range (m a.s.l.) | NP | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 to 1000 | 431 | 69.4 |
| 1000 to 2000 | 102 | 16.4 |
| 2000 to 3000 | 54 | 8.7 |
| 3000 to 4000 | 15 | 2.4 |
| 4000 to 8833 | 19 | 3 |
| Total = 621 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quesada-Román, A.; Peralta-Reyes, M. Geomorphological Mapping Global Trends and Applications. Geographies 2023, 3, 610-621. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3030032
Quesada-Román A, Peralta-Reyes M. Geomorphological Mapping Global Trends and Applications. Geographies. 2023; 3(3):610-621. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuesada-Román, Adolfo, and Manuel Peralta-Reyes. 2023. "Geomorphological Mapping Global Trends and Applications" Geographies 3, no. 3: 610-621. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3030032
APA StyleQuesada-Román, A., & Peralta-Reyes, M. (2023). Geomorphological Mapping Global Trends and Applications. Geographies, 3(3), 610-621. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3030032







