Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Koga Watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Spatial Data
Digital Elevation Model
Soil Data
Land Use/Cover Data
2.2.2. The Weather and Hydrological Data
Weather Data
Hydrological Data
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Image Processing and Classification
2.3.2. Image Classification Accuracy Assessment
2.3.3. Weather and Hydrological Data Analysis
Data Quality Tests
Sediment Data Analysis
2.4. SWAT Model Description
2.4.1. The Hydrological Components of SWAT
2.4.2. Sediment Component of SWAT
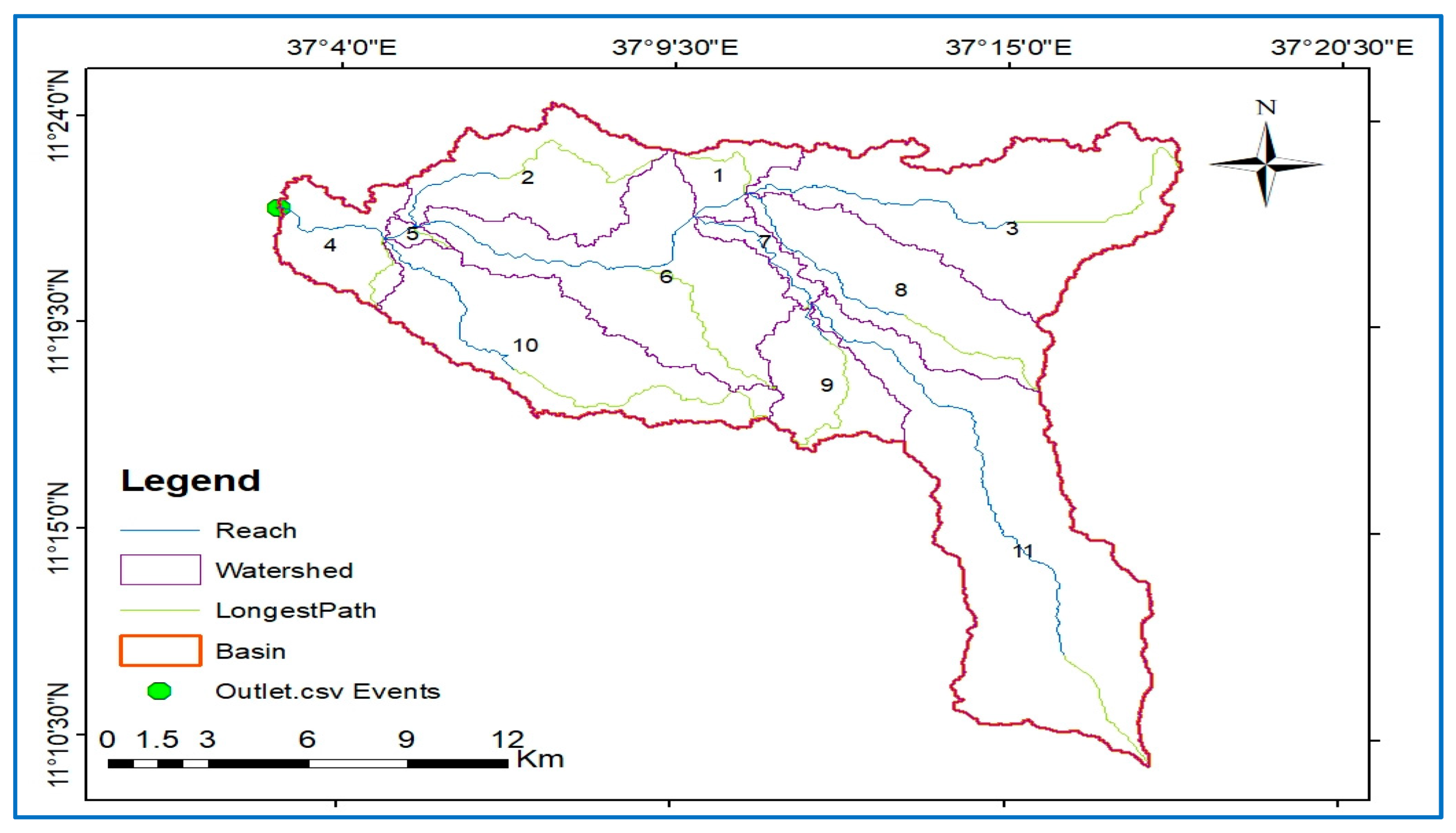
2.5. SWAT Model Setup and Watershed Delineation
2.6. Model Sensitivity Analysis, Calibration, and Validation
2.7. Model Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
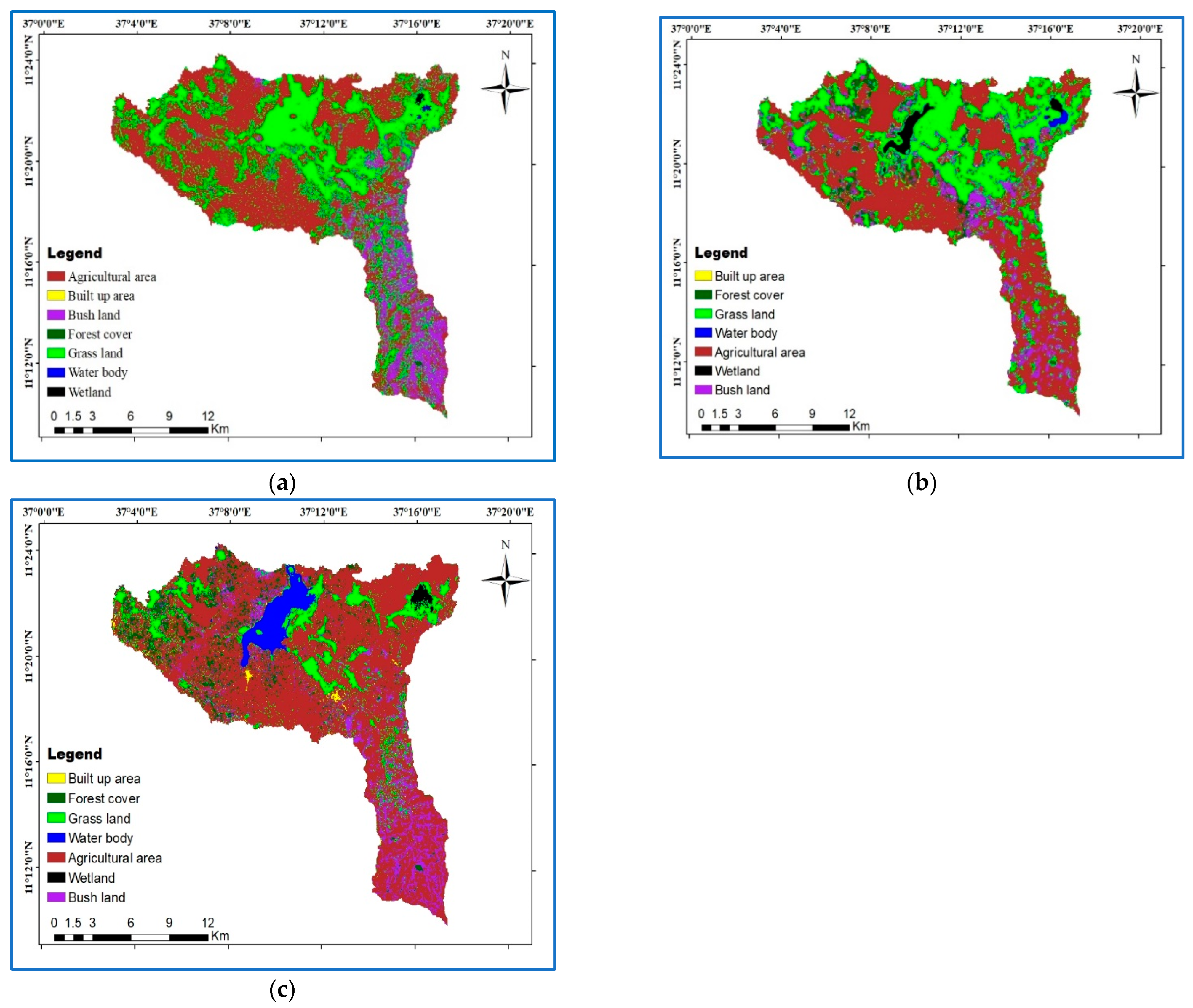
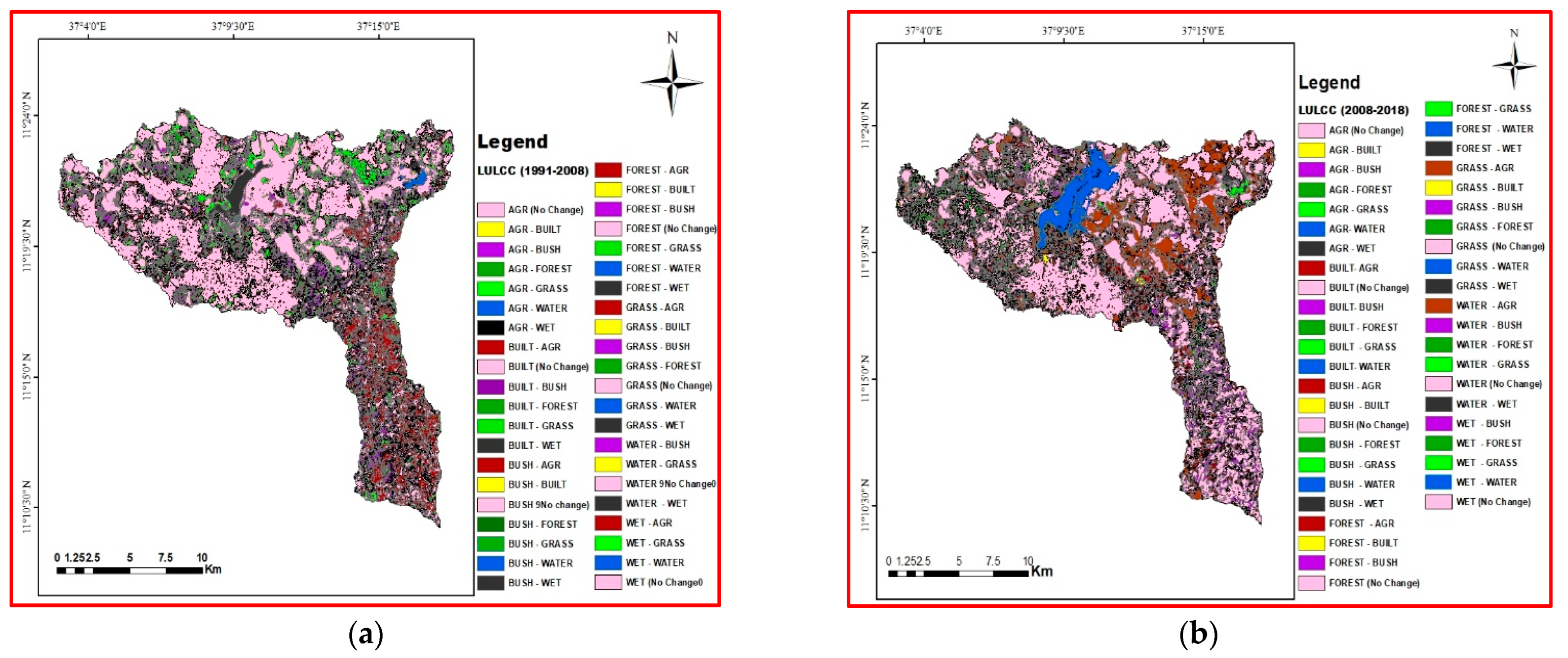
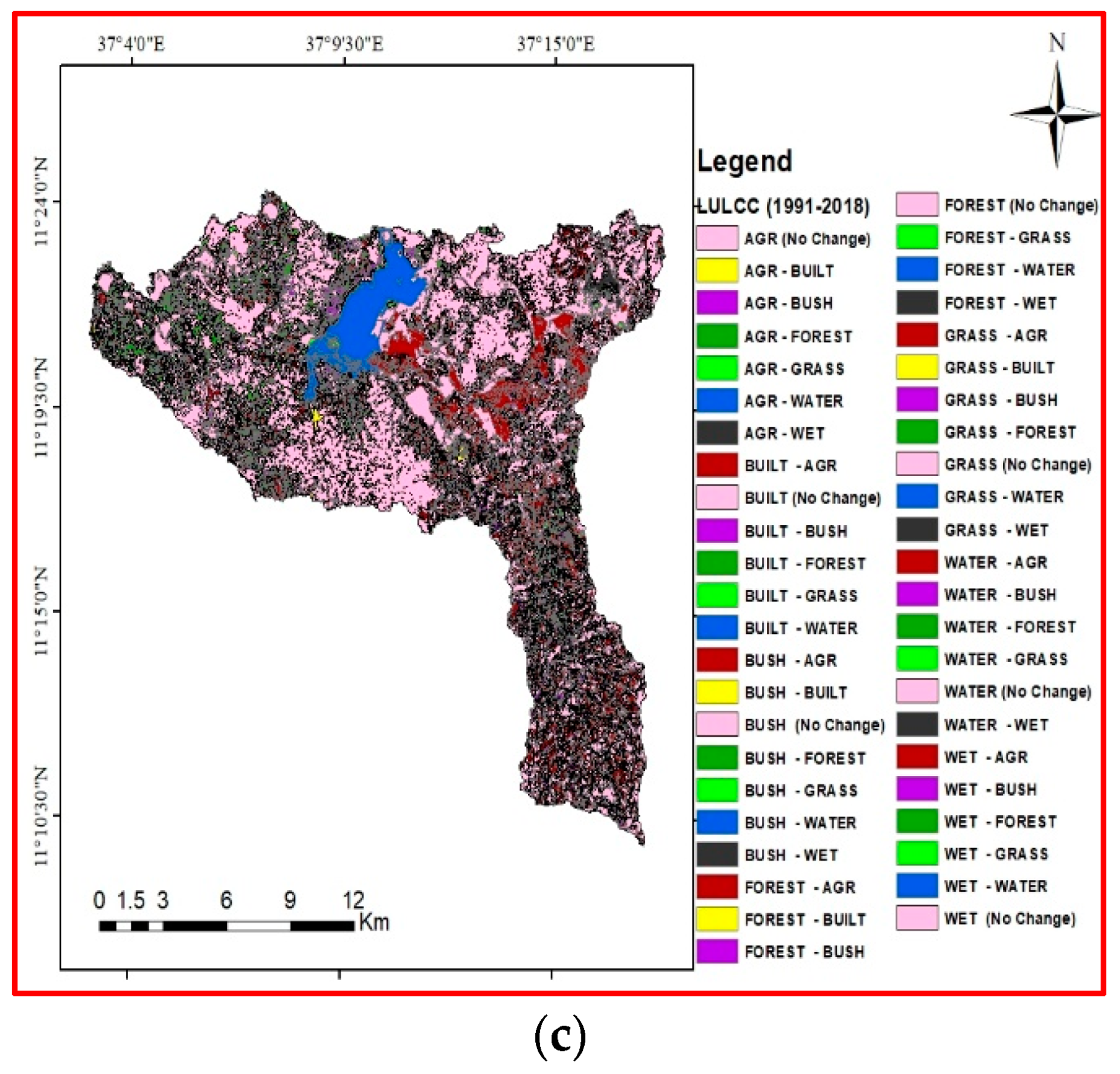
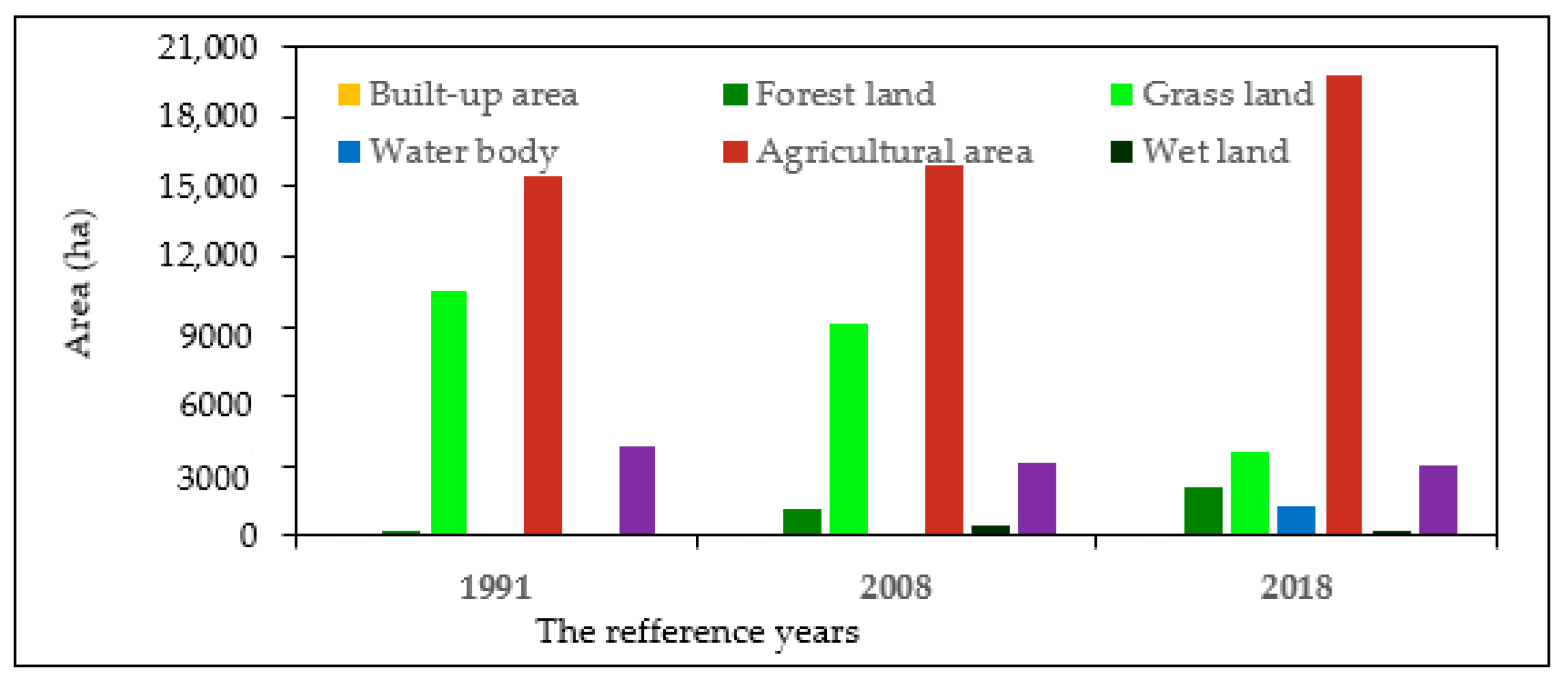
3.1. Land Use/Cover Change Detection
3.2. Landsat Image Classification Accuracy Assessment
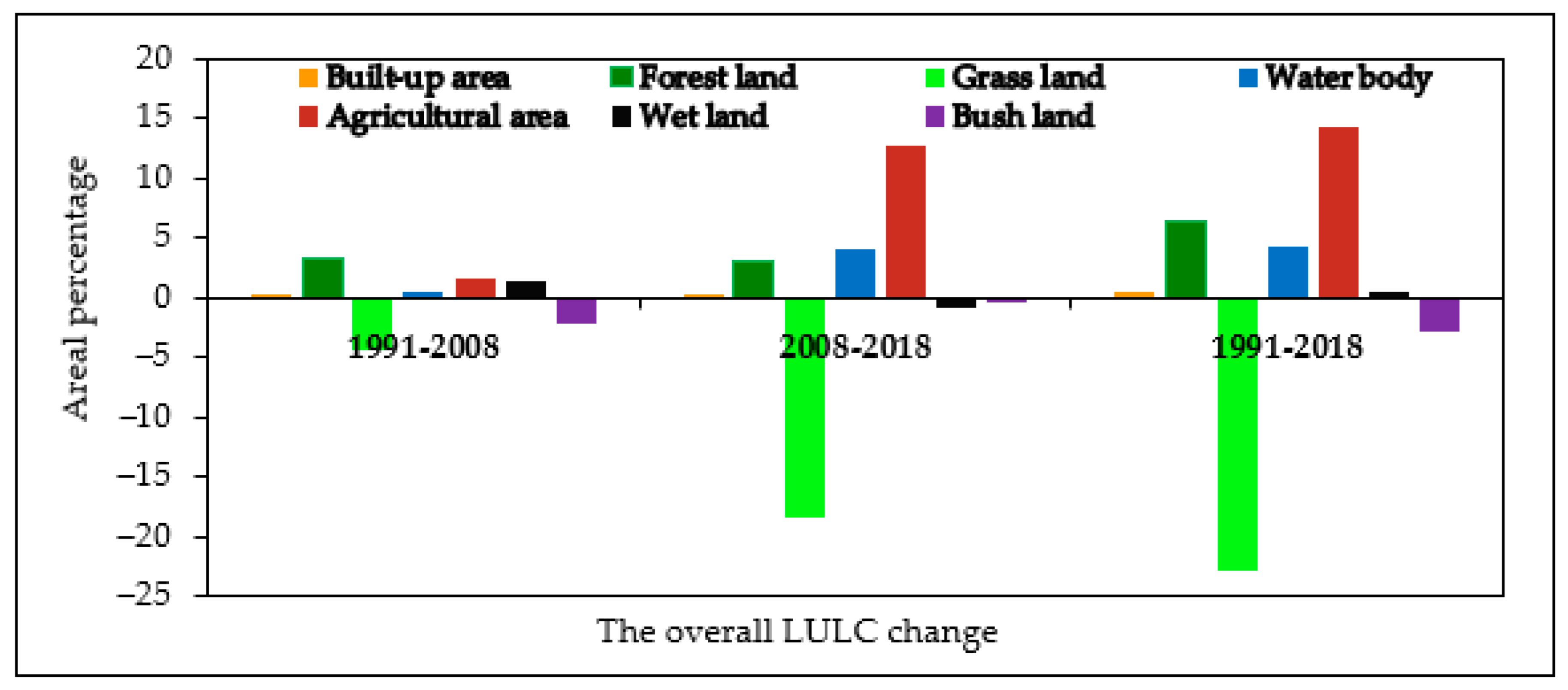
3.3. The Magnitude of Land Use/Cover Changes
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis of the Flow and Sediment Yield Parameters
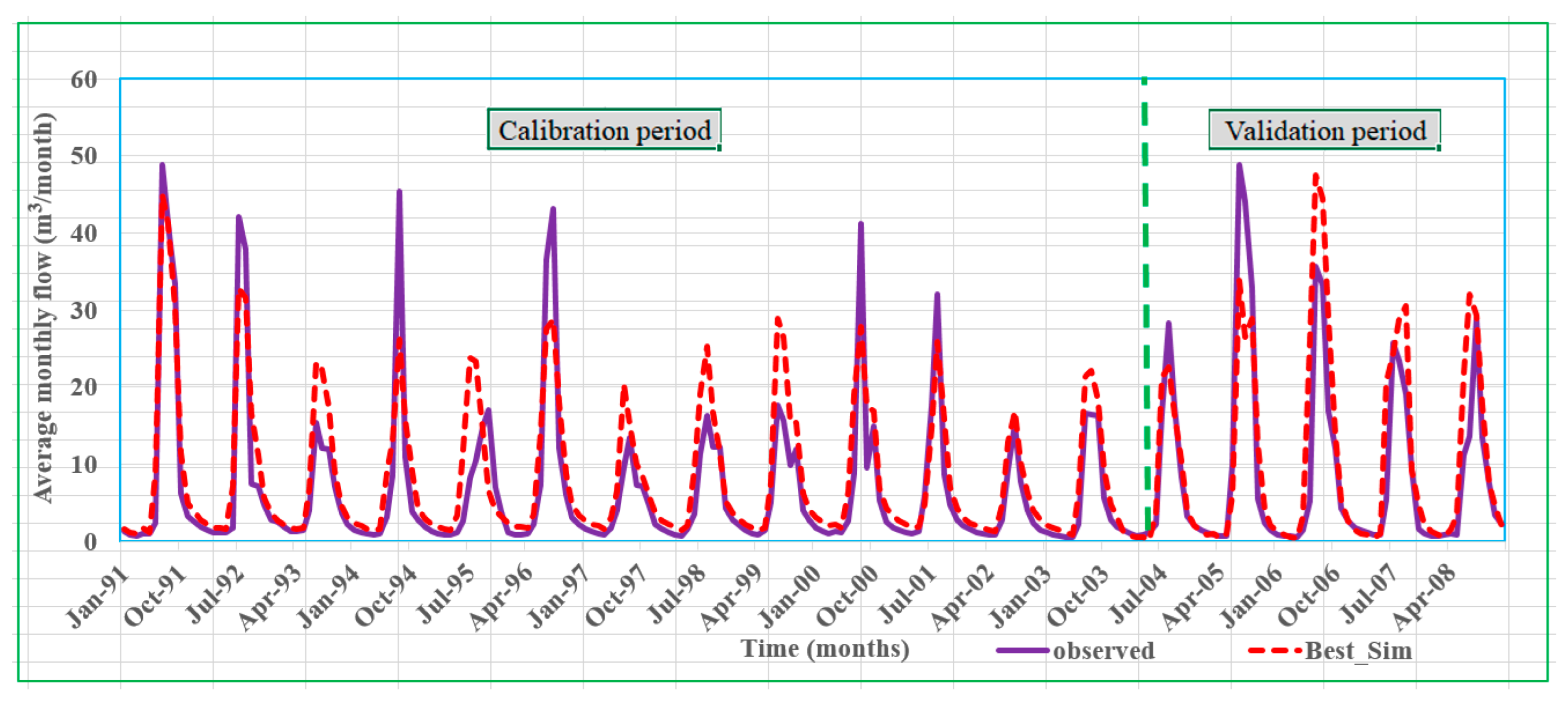
The SWAT Model Calibration and Validation
3.5. The Effects of Land Use/Cover Change on the Streamflow
3.6. Land Use/Cover Change Effects on the Sediment Yield
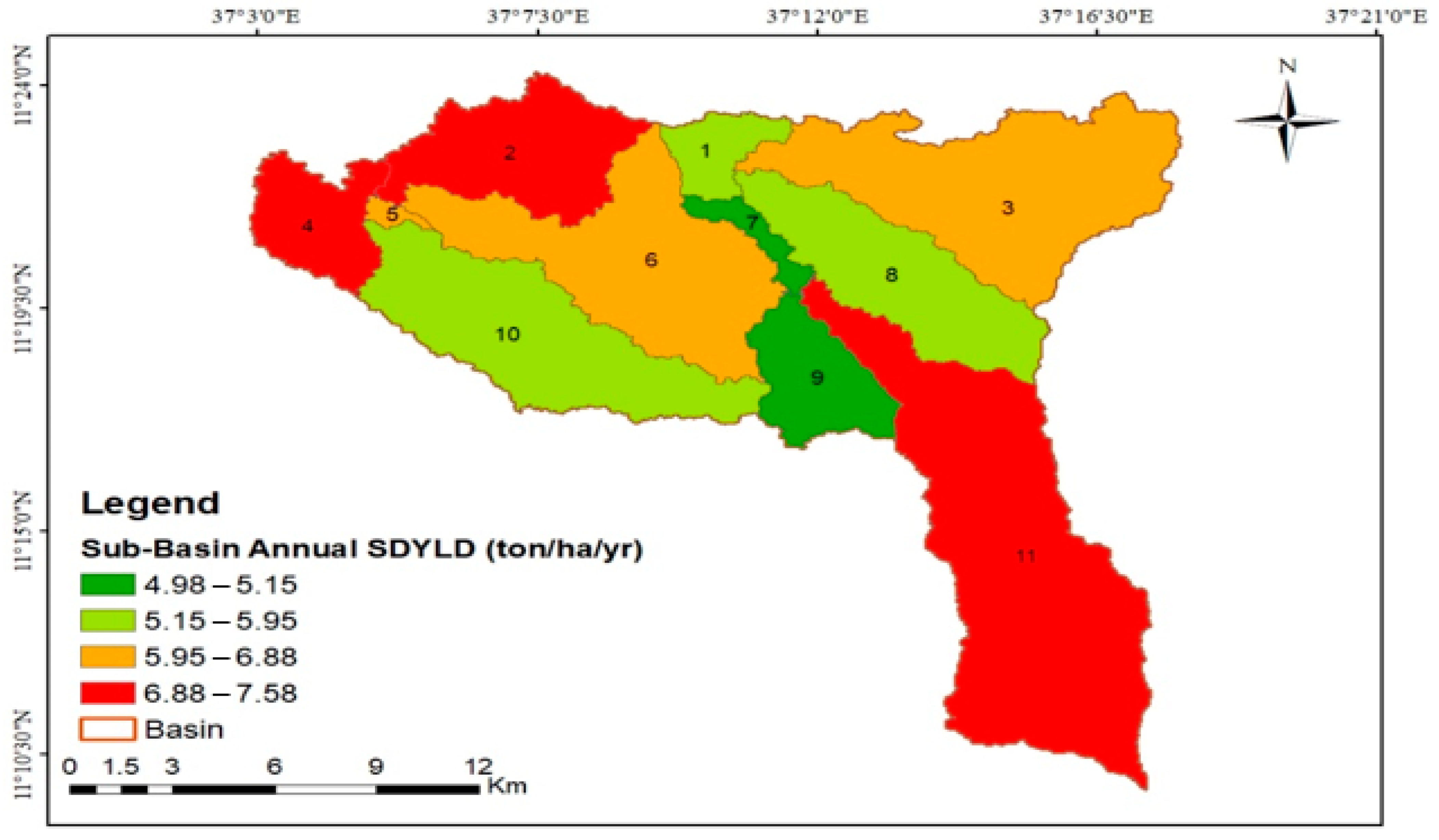
3.7. The Spatial Distribution of Sediments in the Watershed
3.8. Seasonal Variation of Sediment Yield in the Watershed
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kılıç, Z. The Importance of Water and Conscious Use of Water. Int. J. Hydrol. 2020, 4, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, A. Impact of Land Use Land Cover Change on Stream Flow (CASE STUDY GILGEL GIBE III). Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa Institute of Technology, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bogale, A. Review, Impact of Land Use/Cover Change on Soil Erosion in the Lake Tana Basin, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sui, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ge, D.; Kang, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Economic Globalization Impacts on the Ecological Environment of Inland Developing Countries: A Case Study of Laos from the Perspective of the Land Use/Cover Change. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, L.M.; Melesse, A.M.; McClain, M.E.; Gann, D.; Setegn, S.G. Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on the Hydrology of the Upper Mara River Basin, Kenya: Results of a Modeling Study to Support Better Resource Management. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2245–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyatuame, M.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Agodzo, S.K. Assessing the Land Use/Land Cover and Climate Change Impact on Water Balance on Tordzie Watershed. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Vanacker, V.; Balthazar, V.; Mora, D.; Govers, G. Complex Land Cover Change, Water and Sediment Yield in a Degraded Andean Environment. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472–473, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghsaei, H.; Mobarghaee Dinan, N.; Moridi, A.; Asadolahi, Z.; Delavar, M.; Fohrer, N.; Wagner, P.D. Effects of Dynamic Land Use/Land Cover Change on Water Resources and Sediment Yield in the Anzali Wetland Catchment, Gilan, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefay, T.; Abdisa, T.; Chelkeba Tumsa, B. Prioritization of Susceptible Watershed to Sediment Yield and Evaluation of Best Management Practice: A Case Study of Awata River, Southern Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, e1460945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechasa, A.; Aga, A.O.; Dufera, T. Erosion Risk Assessment for Prioritization of Conservation Measures in the Watershed of Genale Dawa-3 Hydropower Dam, Ethiopia. Quaternary 2022, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenea, U.; Adeba, D.; Regasa, M.S.; Nones, M. Hydrological Responses to Land Use Land Cover Changes in the Fincha’a Watershed, Ethiopia. Land 2021, 10, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolessa, T.; Senbeta, F.; Kidane, M. The Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Ecosystem Services in the Central Highlands of Ethiopia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 23, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, S.; Ahmed, F. Modelling Historic and Future Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Their Impact on Wetland Area in Shashe Sub-Catchment, Zimbabwe. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Rai, P.; Mohan, K. Prediction of Land Use Changes Based on Land Change Modeler (LCM) Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Muzaffarpur (Bihar), India. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 2014, 64, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamud, M.A.; Samat, N.; Tan, M.L.; Chan, N.W.; Tew, Y.L. Prediction Of Future Land Use Land Cover Changes Of Kelantan, Malaysia. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-4/W16, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, Y.S.; HAJ, V.L. Assessing the Impacts of Land Use-Cover Change on Hydrology of Melka Kuntrie Subbasin in Ethiopia, Using a Conceptual Hydrological Model. J. Waste Water Treat. Anal. 2015, 6, 1000210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailemariam, S.N.; Soromessa, T.; Teketay, D. Land Use and Land Cover Change in the Bale Mountain Eco-Region of Ethiopia during 1985 to 2015. Land 2016, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, M. The Ethiopian Forest from Ancient Time to 1900: A Brief Account. Walia 1989, 1998, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Angassa, A. Effects of Grazing Intensity and Bush Encroachment on Herbaceous Species and Rangeland Condition in Southern Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rientjes, T.H.M.; Haile, A.T.; Kebede, E.; Mannaerts, C.M.M.; Habib, E.; Steenhuis, T.S. Changes in Land Cover, Rainfall and Stream Flow in Upper Gilgel Abbay Catchment, Blue Nile Basin—Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidane, D.; Alemu, B. The Effect of Upstream Land Use Practices on Soil Erosion and Sedimentation in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Res. J. Agric. Environ. Manag. 2015, 4, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; Deckers, J.; Haile, M.; Lang, A. Human Impact on the Environment in the Ethiopian and Eritrean Highlands—A State of the Art. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 64, 273–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endalamaw, N.T.; Moges, M.A.; Kebede, Y.S.; Alehegn, B.M.; Sinshaw, B.G. Potential Soil Loss Estimation for Conservation Planning, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Koike, T.; Musiake, K. Global Potential Soil Erosion with Reference to Land Use and Climate Changes. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2913–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, K.; Sheleme, B.; Schoenau, J. Characterization of Problem Soils in and around the South Central Ethiopian Rift Valley. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2016, 7, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayneh, L.; Dewitte, O.; Gulie, G.; Poesen, J.; O’Hara, D.; Kassaye, A.; Endale, T.; Kervyn, M. Landslides and Gullies Interact as Sources of Lake Sediments in a Rifting Context: Insights from a Highly Degraded Mountain Environment. Geosciences 2022, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayneh, L.; Bantider, A.; Moges, A. Road Construction and Gully Development in Hadero Tunto—Durgi Road Project, Southern Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Environ. Stud. Manag. 2014, 7, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnez, E.; Sagir, H.; Gavan, M.; SaidGolpinar, M.; Cetin, M.; Akgul, M.A.; Ibrikci, H.; Pintar, M. Modeling Agricultural Land Management to Improve Understanding of Nitrogen Leaching in an Irrigated Mediterranean Area in Southern Turkey; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-2882-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dananto, M.; Aga, A.O.; Yohannes, P.; Shura, L. Assessing the Water-Resources Potential and Soil Erosion Hotspot Areas for Sustainable Land Management in the Gidabo Watershed, Rift Valley Lake Basin of Ethiopia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, A.O.; Melesse, A.M.; CHANE, B. An Alternative Empirical Model to Estimate Watershed Sediment Yield Based on Hydrology and Geomorphology of the Basin in Data-Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Geosciences 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, A.O.; Melesse, A.M.; Chane, B. Estimating the Sediment Flux and Budget for a Data Limited Rift Valley Lake in Ethiopia. Hydrology 2019, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliye, M.A.; Aga, A.O.; Tadesse, T.; Yohannes, P. Evaluating the Performance of HEC-HMS and SWAT Hydrological Models in Simulating the Rainfall-Runoff Process for Data Scarce Region of Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin. OJMH 2020, 10, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, A.O. Modeling Sediment Yield, Transport and Deposition in The Data Scarce Region of Ethiopian Rift Valley Lake Basin. Ph.D. Dissertation, Addis Ababa Institute of Technology, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aga, A.O.; Chane, B.; Melesse, A.M. Soil Erosion Modelling and Risk Assessment in Data Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andualem, T.G.; Gebremariam, B. Impact Of Land Use Land Cover Change On Stream Flow And Sediment Yield: A Case Study Of Gilgel Abay Watershed, Lake Tana Sub-Basin, Ethiopia. Int. J. Technol. Enhanc. Emerg. Eng. Res. 2015, 3, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Bekele, T. Effect of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Soil Erosion in Ethiopia. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Food Technol. 2019, 5, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, C.; Aggett, G. Land-Use Forecasting and Hydrologic Model Integration for Improved Land-Use Decision Support. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 84, 494–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemma, E. Sedimentation Problem and Mitigation Measure of Koga Reservoir. Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, T.T.; Jha, M.K.; Tilahun, S.A.; Yetbarek, E.; Adem, A.A.; Wale, A. Identification of Erosion Hotspot Area Using GIS and MCE Technique for Koga Watershed in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 11, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, G.T.; Kuriqi, A.; Jemberrie, M.A.; Saia, S.M.; Seka, A.M.; Teshale, E.Z.; Daba, M.H.; Ahmad Bhat, S.; Demissie, S.S.; Jeong, J.; et al. Sediment Yield and Reservoir Sedimentation in Highly Dynamic Watersheds: The Case of Koga Reservoir, Ethiopia. Water 2021, 13, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andualem, Y. Water Delivery Performance Evaluation of Koga Irrigation Scheme. Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tewabe, D.; Dessie, M. Enhancing Water Productivity of Different Field Crops Using Deficit Irrigation in the Koga Irrigation Project, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1757226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Lu, X.X.; Xin, Z.; Yang, X. Cumulative Sediment Trapping by Reservoirs in Large River Basins: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 100, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunderlik, M.J. Hydrologic Model Selection Fort the CFCAS Project: Assessment of Water Resources Risk and Vulnerability to Changing Climatic Conditions. In Project Report I By University of Western Ontario; University of Waterloo and Upper Thames River Conservation Authority: Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, B.A.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.; Rewerts, C.; Brown, S.J. Nonpoint Source (NPS) Pollution Modeling Using Models Integrated with Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulatu, C.A. Analysis of Reservoir Sedimentation Process Using Empirical and Mathematical Method: Case Study—Koga Irrigation and Watershed Management Project; Ethiopia. Main 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, G.G.; Kanellopoulos, I.; Liu, Z.K.; Folving, S. Integrated Land-Cover Mapping from Satellite Imagery Using Artificial Neural Networks. Ground Sens. 1993, 1941, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abburu, S.; Babu Golla, S. Satellite Image Classification Methods and Techniques: A Review. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 119, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M.; Worqlul, A.W. Evaluation and Prediction of Land Use/Land Cover Changes in the Andassa Watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibs, H.; Hasab, H.A.; Al-Rifaie, J.K.; Al-Ansari, N. An Optimal Approach for Land-Use/Land-Cover Mapping by Integration and Fusion of Multispectral Landsat OLI Images: Case Study in Baghdad, Iraq. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, H.; Dondeyne, S.; Poesen, J.; Frankl, A.; Nyssen, J. Transition from Forest-Based to Cereal-Based Agricultural Systems: A Review of the Drivers of Land Use Change and Degradation in Southwest Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Bantider, A.; Mahari, A. Evaluations of Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Land Degradation in Dera District, Ethiopia: GIS and Remote Sensing Based Analysis. Int. J. Sci. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Jaber, H.S. Accuracy Assessment of Supervised Classification Methods for Extraction Land Use Maps Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 745, 012166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, R.; Odehi, I.O.A.; Ancevt, T. Improving the Accuracy of Land Use and Land Cover Classification of Landsat Data Using Post-Classification Enhancement. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserud, R.A.; Leemans, R. Comparing Global Vegetation Maps with the Kappa Statistic. Ecol. Model. 1992, 62, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubbs, F.E. Procedures for Detecting Outlying Observations in Samples. Technometrics 1969, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling and Assessment Part I: Model Development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkodjo, T.P. Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Catchment Hydrology (A Case Study of Awassa Catchment) by : Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Catchment Hydrology (A Case Study of Awassa Catchment). Master’s Thesis, Arba Minch University, Arba Minch, Ethiopia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Geremew, A.A. Assessing the Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover Change on Hydrology of Watershed: A Case Study on Gilgel—Abbay Watershed, Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Jaume I University, Castelló de la Plana, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sith, R.; Nadaoka, K. Comparison of SWAT and GSSHA for High Time Resolution Prediction of Stream Flow and Sediment Concentration in a Small Agricultural Watershed. Hydrology 2017, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, E.I.; Fleifle, A.; Ludwig, R.; Disse, M. Improving SWAT Model Performance in the Upper Blue Nile River Basin Using Meteorological Data Integration and Catchment Scaling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 21, 4907–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Ma, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, S.; Chen, C.; Cai, T.; Fang, X. Effects of Land-Use and Climate Change on Hydrological Processes in the Upstream of Huai River, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Cui, Y. Development and Test of SWAT for Modeling Hydrological Processes in Irrigation Districts with Paddy Rice. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arekhi, S.; Shabani, A.; Rostamizad, G. Application of the Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation (MUSLE) in Prediction of Sediment Yield (Case Study: Kengir Watershed, Iran). Arab. J. Geosci. 2012, 5, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Srinivasan, R. A Guideline for Successful Calibration and Uncertainty Analysis for Soil and Water Assessment: A Review of Papers from the 2016 International SWAT Conference. Water 2017, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Wu, J. The Accuracy of Landscape Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing Data. Landsc. Ecol. 2008, 23, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewnet, A.; Abebe, G. Land Use and Land Cover Change and Implication to Watershed Degradation by Using GIS and Remote Sensing in the Koga Watershed, North Western Ethiopia. Earth Sci. Inform. 2018, 11, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agidew, A.A.; Singh, K.N. The Implications of Land Use and Land Cover Changes for Rural Household Food Insecurity in the Northeastern Highlands of Ethiopia: The Case of the Teleyayen Sub-Watershed. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getu Engida, T.; Nigussie, T.A.; Aneseyee, A.B.; Barnabas, J. Land Use/Land Cover Change Impact on Hydrological Process in the Upper Baro Basin, Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2021, 2021, e6617541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhay, W. Modeling the Impacts of Land Use/Land Cover Changes on the Hydrological Processes of Upper Gilgel Abay Watershed, Abbay River Basin, Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Hossain, F. Tracing Hydrologic Model Simulation Error as a Function of Satellite Rainfall Estimation Bias Components and Land Use and Land Cover Conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, H. The Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Hydrological Components Due to Resettlement Activity: SWAT Model Approach The Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Hydrological Components Due to Resettlement Activity: SWAT Model Approach. Int. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 37, 48–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tesfahunegn, G.B.; Mekonnen, K. Estimating Soil Loss Using Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) for Soil Conservation Planning at Medego Watershed, Northern Ethiopia. J. Am. Sci. 2009, 5, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Teklie, N.; Ashenafi, Y. Effect Of Land Use/Land Cover Management on Koga Reservoir Sedimentation. Nile Basin Capacit. Build. Netw. 2010, 1–60. Available online: https://www.nbcbn.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/ethiopia-local.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Gashaw, T.; Dile, Y.T.; Worqlul, A.W.; Bantider, A.; Zeleke, G.; Bewket, W.; Alamirew, T. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Best Management Practices On Soil Erosion Reduction Using the SWAT Model: For the Case of Gumara Watershed, Abbay (Upper Blue Nile) Basin. Environ. Manag. 2021, 68, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, G.T.; Teshale, E.Z.; Yu, B.; Rutherfurd, I.D.; Jeong, J. Streamflow and Sediment Yield Prediction for Watershed Prioritization in the Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2017, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Station | Adet | Bahir Dar (met) | Bahir Dar (AP) | Dangila | Merawi | Sekela | Wetet Abbay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lat | 11.600 | 11.603 | 11.434 | 11.275 | 11.411 | 10.980 | 11.370 |
| Long | 37.417 | 37.322 | 36.846 | 37.493 | 37.164 | 37.210 | 37.040 |
| Elev | 1770 | 1827 | 2116 | 2179 | 2000 | 2690 | 1920 |
| PCP | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| TMP | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| HMD | √ | √ | √ | √ | X | X | X |
| SLR | X | √ | √ | √ | X | X | X |
| WND | √ | √ | √ | √ | X | X | X |
| Kappa Coefficient Range | Remark |
|---|---|
| <0.00 | Poor |
| 0.00–0.20 | Slight |
| 0.21–0.40 | Fair |
| 0.41–0.60 | Moderate |
| 0.61–0.80 | Substantial |
| 0.81–1.00 | Almost perfect |
| Rank | Parameter Name | Parameter Description | Fitted Value | Range Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | ||||
| 1 | CN2 | Initial SCS CN II value (%) | 50.77 | 35.00 | 98.00 |
| 2 | SOL_BD | Moist bulk density | 0.91 | 0.00 | 2.50 |
| 3 | GW_REVAP | Groundwater “revap” coefficient | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.20 |
| 4 | GW_DELAY | Groundwater delay (day) | 271.60 | 0.00 | 500 |
| 5 | SOL_K | Soil conductivity (mm/h) | 148.28 | 0.00 | 2000 |
| 6 | CH_N2 | Manning’s primary channel n value | 0.10 | −0.01 | 0.30 |
| 7 | SOL_AWC | Water supply capacity | 0.53 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 8 | RCHRG_DP | Aquifer percolation coefficient | 0.47 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 9 | ALPHA_BNK | Bank storage base flow alpha factor | 0.77 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 10 | DEP_IMP | Depth in the perched water level | 2786.95 | 0.00 | 6000 |
| 11 | GWQMN | Water depth in an unconfined aquifer | 653.22 | 0.00 | 5000 |
| 12 | SOL_ALB | Moist soil albedo | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.25 |
| 13 | SURLAG | Surface runoff lag time | 3.25 | 0.05 | 24.00 |
| 14 | ALPHA_BF | Alpha base flow recession constant | 0.46 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| Rank | Parameter Name | Parameter Description | Fitted Value | Range Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | ||||
| 1 | USLE_K | USLE equation soil erodibility (K) factor | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.65 |
| 2 | USLE_P | USLE support practice factor | 0.15 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 3 | LAT_SED | Sed. conc. in lateral and G.W flow | 786.5 | 0.00 | 5000 |
| 4 | USLE_C (AGRC) | Min. value of USLE land cover for Agri. area | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.50 |
| 5 | USLE_C (RNGE) | Min. value of USLE land cover for grassland | 0.48 | 0.003 | 0.50 |
| 6 | CH_ERODMO | Jan. channel erodability factor | 0.56 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| 7 | CH_COV2 | Channel cover factor | 0.80 | −0.001 | 1.00 |
| 8 | CH_COV1 | Channel erodibility factor | 0.33 | −0.05 | 0.6 |
| 9 | ADJ_PKR | Silt routing height free association component in sub-watersheds | 0.94 | 0.50 | 2.00 |
| 10 | SPEXP | Exponent re-entrainment parameter in sediment routing | 1.23 | 1.00 | 1.50 |
| Evaluation Criteria | Streamflow | Sediment Yield | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration (1991–2003) | Validation (2004–2008) | Calibration (1991–2003) | Validation (2004–2008) | |
| R2 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.85 |
| NSE | 0.80 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.82 |
| PBIAS | −22.00 | −19.20 | −21.70 | −23.00 |
| RSR | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.42 |
| Flow Seasons | Years of Simulation | 1991–2008 | % of Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 2008 | |||
| Wet season (m3/s) | 15.81 | 15.92 | +0.11 | 0.76 |
| Dry season (m3/s) | 1.75 | 1.73 | −0.02 | 0.95 |
| Mean monthly flow (m3/s) | 8.78 | 8.83 | +0.05 | 0.57 |
| Years of Simulation | Sediment Yield Change Detection | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 2008 | 1991–2008 | |
| Annual Avg. Sed. Yield (t/ha/yr) | 6.23 | 6.31 | +0.08 |
| Sub-Basins in the Koga Watershed | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| Sed. Yield (tons/hectare/year) | 5.95 | 7.24 | 6.48 | 7.29 | 6.88 | 6.68 | 5.15 | 5.48 | 4.98 | 5.67 | 7.58 |
| Months | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Sed. load (tons/hectare/month) | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.201 | 0.677 | 0.639 | 0.343 | 0.131 | 0.033 | 0.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayele, H.A.; Aga, A.O.; Belayneh, L.; Wanjala, T.W. Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Koga Watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Geographies 2023, 3, 60-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3010004
Ayele HA, Aga AO, Belayneh L, Wanjala TW. Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Koga Watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Geographies. 2023; 3(1):60-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyele, Habitamu Alesew, Alemu O. Aga, Liuelsegad Belayneh, and Tilahun Wankie Wanjala. 2023. "Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Koga Watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia" Geographies 3, no. 1: 60-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3010004
APA StyleAyele, H. A., Aga, A. O., Belayneh, L., & Wanjala, T. W. (2023). Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Koga Watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Geographies, 3(1), 60-81. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies3010004





