Abstract
There is a lack of evidence about the ways in which balance ability influences the kinematic and kinetic parameters and muscle activities during gait among healthy individuals. The hypothesis is that balance ability would be associated with the lower limb kinematics, kinetics and muscle activities during gait. Twenty-nine healthy volunteers (Age 32.8 ± 9.1; 18 males and 11 females) performed a Star Excursion Balance test to measure their dynamic balance and walked for at least three trials in order to obtain a good quality of data. A Vicon® 3D motion capture system and AMTI® force plates were used for the collection of the movement data. The selected muscle activities were recorded using Delsys® Electromyography (EMG). The EMG activities were compared using the maximum values and root mean squared (RMS) values within the participants. The joint angle, moment, force and power were calculated using a Vicon Plug-in-Gait model. Descriptive analysis, correlation analysis and multivariate linear regression analysis were performed using SPSS version 23. In the muscle activities, positive linear correlations were found between the walking and balance test in all muscles, e.g., in the multifidus (RMS) (r = 0.800 p < 0.0001), vastus lateralis (RMS) (r = 0.639, p < 0.0001) and tibialis anterior (RMS) (r = 0.539, p < 0.0001). The regression analysis models showed that there was a strong association between balance ability (i.e., reaching distance) and the lower limb muscle activities (i.e., vastus medialis–RMS) (R = 0.885, p < 0.0001), and also between balance ability (i.e., reaching distance) and the lower limb kinematics and kinetics during gait (R = 0.906, p < 0.0001). In conclusion, the results showed that vastus medialis (RMS) muscle activity mainly contributes to balance ability, and that balance ability influences the lower limb kinetics and kinematics during gait.
1. Introduction
Gait is a fundamental functional task, and it is important for functional independence [1]. Gait is defined as a process of loading and unloading weight on the legs during the act of motion [2]. There are many reasons for gait disorders, including orthopedic problems, neurological conditions and medical conditions. In older age, osteoarthritis is one of the causes for gait disorders [3].
Understanding gait characteristics provides the potential for the development of a rehabilitation protocol for degenerative conditions, because gait analysis is a tool to quantitatively describe functional differences for patients [4]. The human gait comprises a qualitative and quantitative component. Gait analysis is performed in a calibrated laboratory or clinical environment, where sensors and force sensors are used in gait analysis. The data is captured using sensors while the subject walks on a clearly marked walkway. Force sensors measure the ground reaction force under foot and return a current or voltage proportional to the pressure measured. Electromyography (EMG) is used to record the muscle activities [5].
Joint loading can be affected by alterations in muscle activation patterns and decreased muscle strength. Resistance training restores muscle strength and joint mechanics [6]. However, hip abductor strengthening does not reduce knee joint loading [7]. A balance training programme is included in the rehabilitation protocol for many conditions. Balance and proprioception exercise programmes are widely used among people with osteoarthritis [8].
Balance and gait problems are common among elderly people due to advanced aging, and balance and gait disturbance can be seen at the same time [9]. Balance is generally defined as “the state of an object when the resultant force acting upon it is zero”. Human balance is defined as “a multidimensional concept, referring to the ability of a person not to fall” [10]. Balance control is related to the vestibular system, sight, proprioception, muscular strength and cognition [11]. A study conducted in 2001 revealed that the muscle activation of the vastus medialis oblique (VMO) and vastus lateralis (VL) are higher in the anterior direction; medial hamstring and biceps femoris (BF) activity are higher in the posterior direction during balance test [12]. Another study indicated that ankle muscle activity increased with different levels of stability [13].
Balance ability is assessed through different tests. A Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) is a highly dynamic balance test for physically active people [14]. It is a widely used dynamic test for clinical and research testing purposes [14]. It is considered a challenging dynamic test which requires adequate neuromuscular control of the stance leg to maintain balance. It is a reliable and a validated test for healthy participants [15]. This test can be administered quickly and easily to help the examiner determine dynamic balance [14], and it is considered a highly representative non-instrumented dynamic balance test for physically active people [14].
The distance a person can achieve along each reaching line while standing on a single limb is the outcome of SEBT. Limb length, height, foot types, sex differences and kinematic contribution, such as the ranges of motion available at each joint, are factors which influence the SEBT outcome [14,16].
Most studies have focused on patients’ gait during the latter stage of OA, or people in an early stage of OA. Some studies have been conducted to determine changes in balance ability and gait parameters after a progression of conditions. Different studies focus on muscle activities during balancing tasks and gait separately. There is a lack of literature about the association between balance ability and gait kinematics and kinetics parameters during gait in healthy individuals, nor is there an understanding of the muscle activation between balancing tasks and gait. This evidence would help in the better understanding of the disease process in degenerative arthritis in the lower limb. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the hypothesis that balance ability would be associated with the lower limb kinetics and kinematics and muscle activities during gait among a healthy population.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
Ethical approval was obtained. The participants were recruited by advertisements on the university notice board. All of the participants were informed of the benefits and risks of the investigation prior to signing an institutionally approved informed consent document. The participants were recruited for three months according to their availability. The participants were aged between 18 and 60; males and females were recruited. Participants without any recent injuries in the last 6 months, without any current injuries or without previous surgery in lower limbs, low back region, upper limb and no history of neuro-musculoskeletal conditions were included in this study if they were able to perform the star excursion tests. Furthermore, participants without any history of neurological, musculoskeletal and other degenerative conditions were included in this study.
2.2. Measurements
Basic anthropometric data was collected from the participants, e.g., body mass, height, leg length, knee and ankle width, in order to calculate the biomechanical parameters, such as joint angles. A Vicon® (Oxford, UK) 3D motion capture system (200 Hz), a set of four AMTI® (Watertown, MA, USA) force plates (1000 Hz) and a Delsys® EMG (2000 Hz) (Great Manchester, UK) were used in the data collection. The participants were asked to answer an interviewer-administered questionnaire before the tests in order to obtain some basic details, such as their dominant side and any history of injuries. The participants were asked to wear shorts and a short t-shirt in order to allow the investigator to place the Vicon® retro-reflective markers and EMG sensors. The T-shirt was folded to make sure that all of the markers were visible throughout the procedure. The markers were placed according to the Plug-in-Gait® (version 3.3.1) model, on the anterior and posterior superior iliac spines, lateral thigh, lateral femoral epicondyle, lateral shank, calcaneus, lateral malleolus and second metatarsal head for both sides (Figure 1). Double-sided adhesive tape was used to place the reflective markers. The skin preparation was performed prior to recording the muscle activities with the EMG. Excessive hair was removed and an alcohol swab was used to wipe the surface to remove oil and other contaminants. Double-sided adhesive tape was used to place the EMG sensors on the selected muscles in order to ensure minimum movement artefacts and strong skin adhesion. Surface EMG data were collected from the seven muscles during the walking and balancing tasks. The participants were asked to walk barefoot on a 20 m length walking way with reflective markers and EMG sensors attached to their body. They were also asked to walk at least three trials at their comfortable speed. For each participant, their dominant side was selected for the EMG placement. The EMG activities of multifidus (MF), rectus femoris (RF), VL, vastus medialis (VM), BF, gastrocnemius (Gastro) and tibialis anterior (TA) were recorded (Figure 1). The EMG signals of the evaluated muscles were recorded at a sampling frequency of 1000 Hz. The analog signal was converted to digital and filtered by bandwidth (12–450 Hz) with a fourth-order Butterworth filter. The raw EMG signals were then converted into root-mean-square (RMS) signals. In this study, the EMG data was compared within the subjects; therefore, the normalization of EMG data was not performed.
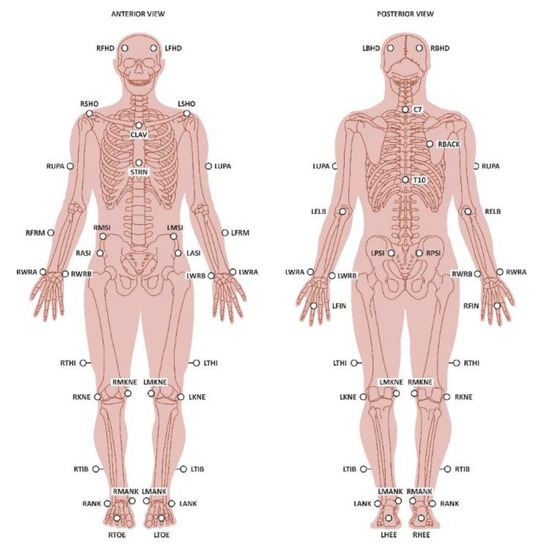
Figure 1.
Vicon markers and EMG placement.
The maximum value and RMS values were extracted from the EMG data. The EMG activities of the SEBT and gait were compared using the maximum value and RMS values within the participants. The ground reaction forces were collected using force plates during the movements. The participants were also asked to perform SEBT to assess their dynamic balance and postural stability while their standing leg was on the force plate. The SEBT was that a single leg stands in stance (the supporting leg) while another leg (the reaching leg) tries to reach eight different directions as far as possible according to the margin marked on the floor. The participants were given some practice trials to familiarize them with the balance test. The participants were instructed to perform a balance test on each (side) leg at least three times. If a participant was unable to maintain balance throughout the test, the balance test was repeated. A 5 min rest interval was given between the tests. The two markers on the lateral malleolus of the supporting and reaching legs were used to calculate the reaching distance. The reach distance was the maximum distance between the supporting and reaching legs in the eight directions. The average reach distance in the eight directions was calculated. The limb length was calculated by measuring from the anterior superior iliac spine to the medial malleolus of the leg. The Vicon® marker data were analysed using biomechanical models (Plug-In-Gait® model) to obtain the joint angles, forces, moments and powers.
2.3. Outcome Measures
Kinematics refer to the range of motion of each joint during gait. Kinetics refer to forces that cause the body to move [17]. Gait kinematics include the joint angle during walking. Gait kinetics include the force, moment, and power of each joint during walking. The outcomes used in the study were the joint angles (ROM), forces, moments and powers during balance and gait. The maximum value and RMS values were extracted from the EMG data for balance test and gait. The average reach distance in eight directions was calculated for the balance test, and the center of mass displacement data was extracted from the Plug-in Gait model for both balance and gait.
2.4. Data Analysis
All of the parameters were statistically analysed using SPSS version 23. Descriptive analysis, general linear model (estimated measure), correlation analysis and multivariate linear regression analysis were performed. The muscle activities during the gait and balance tasks were compared within the participants using the general linear model (repeated measure). A specific identifying number was used as a random factor when running the statistical analysis in order to consider the subject factors. The correlation of the muscle activities during the balance test and gait were analysed using the Pearson correlation coefficient. The multivariate-linear regression analysis model included the displacement of the centre of mass (COM) in the anterior–posterior (X), medial–lateral (Y) and vertical (Z) directions during the balance test, and the average normalised reach distance as the dependent variables, and the muscle activities of the whole phase maximum and the RMS value of the seven selected muscles as the independent variables in order to investigate the muscles’ contributions to the balance task. For the statistical test analysis purposes, the legs were considered as the standing leg and supporting leg. This approach was used because the muscle activities are different for the standing and supporting legs.
Between the dependent and independent variables, the regression model was performed with a stepwise or backward option to produce the R and related coefficients; if the collinearity diagnosis showed that the tolerance was too low and the variance inflation factor too high, the model was improved by using a zero-score transformation and factor reduction on the independent variables to produce the R and related coefficients again. In most of cases, it was found that the significant independent variables were similar between the first and second models, although the R was slightly changed. Therefore, the first set of models are still reported as results here, because the variables in the first models are easily identified, while the transformed factors in the second set of models are not easy to link with the original variables.
The second regression analysis model included the range of motion/displacement of the COM in the anterior–posterior, medial–lateral and vertical directions during the balance test and the reach distance during balance test as the dependent variables, and the gait kinematic and kinetic parameters as the independent variables to analyse the association between balance ability and gait kinematics and kinetics among healthy people. p < 0.05 was considered as the statistical significance value during the statistical analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Results
Twenty-nine-healthy volunteers (18 male participants and 11 female participants, BMI 23.69 ± 3.51 kg/m2, height 1.67 ± 0.087 m) participated in this study. The age range of the participants was 32.8 (±9.1) years. A descriptive analysis was performed in order to extract demographic and basic details of the participants (Table 1). The dominant side of the participants and the physical activity information were analysed. In total, 24 participants were right side dominant and only five participants were left side dominant. Therefore, the right-side data was analysed further in this study.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the participants.
The reach distances of the balance test were normalised by dividing them by the lower limb length. The average reach distance of all eight directions was 617.27 (±107.02) mm. The average duration for the test performance was recorded as 12.36 (±4.41) s.
3.2. Comparison of the Muscle Activities during the Balance Test and Gait
The EMG activities of the SEBT and gait were compared using the maximum value and RMS values within the participants. Figure 2 shows the comparison of the maximum values of the muscle activities (Figure 2a) and the RMS values (Figure 2b) between the tasks. All of the muscle activities showed a significant difference (p < 0.05) between the tasks, except for the VM between the supporting leg and gait (p > 0.05) in the whole phase maximum. All of the muscle activities showed a significant difference between the tasks (p < 0.0001) in the RMS values, except for BF between the supporting leg and gait (p > 0.05), and VM between the supporting leg and gait (p > 0.05).
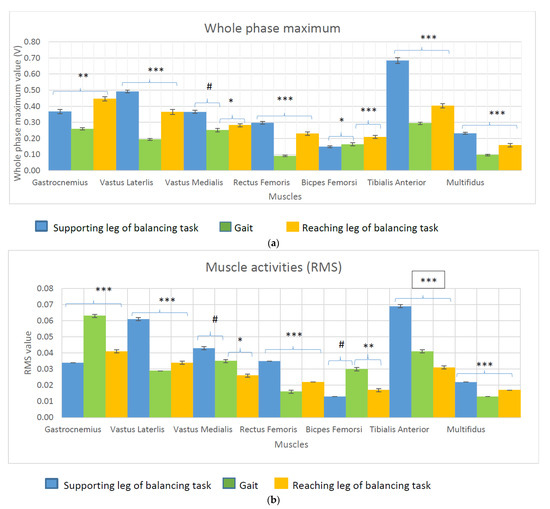
Figure 2.
(a): Whole phase maximum value during the balancing task and gait (#: p > 0.05; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.001; ***: p < 0.0001). (b): Root mean squared value during the balancing task and gait (#: p > 0.05; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.001; ***: p < 0.0001).
3.3. Correlation between the Balance Test Muscle Activities and Gait Muscle Activities
The correlations between the muscle activities between the balance test and gait were analysed. Table 2 illustrates the results of the correlation test. According to the results, a significant linear correlation was noticed in the MF (Max and RMS), VL (Max and RMS) and TA (Max and RMS) between the gait and the supporting leg of the balance task. Similarly, a significant linear correlation was noticed in the MF (Max and RMS), TA (Max and RMS) and VL (Max and RMS) between the balance test of the reaching leg and gait. The correlation coefficient values of the abovementioned results were between 0.5 and 0.85, while p < 0.05.

Table 2.
Correlation between the muscle activities during the balance ability test (supporting leg and reaching leg) and gait.
3.4. Association between Balance Ability and Muscle Activity
The contribution of the muscle activities of the seven selected muscles to balance ability in terms of the average reach distance in eight directions, and the displacement of CoM anterior–posterior (X), medial–lateral (Y) and vertical (Z) directions were analysed. The linear regression results were analysed. The regression analysis values for balance ability in terms of the total reach distance and muscle activity were R = 0.885, p < 0.0001, and the balance ability in terms of the medial–lateral displacement of COM and muscle activities was R = 0.912, p < 0.0001. Table 3 shows the results of the muscle contribution to balance ability. According to the results, VM (RMS) positively influences the average reach distance and BF (RMS), and MF (RMS) negatively influences the balance test reach distance. The displacement of CoM in the medial–lateral direction was positively influenced by VM (RMS) and VL (Max), and negatively influenced by BF (RMS), MF (RMS) and VL (RMS).

Table 3.
Balance ability and muscle activity.
3.5. Association between the Displacement of the Centre of Mass or the Total Reach Distance during the Balance Test and the Joint Kinematics and Kinetics during Gait
Table 4 illustrates the analysis results of the association between the balance ability and lower limb kinematics and kinetics during gait. According to the results, there is an association between the balance ability in terms of reach distance, the displacement of COM in the anterior–posterior direction, the displacement of COM in the vertical direction, the displacement of COM in the medial–lateral direction, and lower limb kinematics and kinetics during walking.

Table 4.
Linear regression analysis of the balance ability and gait kinematics and kinetics.
4. Discussion
This study analysed the influence of balance ability on muscle activities and the lower limb kinematics and kinetics during gait, and association between muscle activities during balancing task and gait. The present study shows that the muscle activation magnitude was different between the balance test and gait according to the EMG readings. This finding is similar to a study conducted in 2013 [18] which examined muscle activities during multidirectional support-surface perturbations during standing and walking. The study results showed that the muscle activation is similar in standing and walking, but the activation magnitude vary greatly. However, the present study results show that there is a linear correlation (mild to strong) between the MF, VL and TA muscle activities between both the balance test reaching and the supporting leg and gait. These results suggest that only specific muscles’ activations are similar in both gait and balance task compared to other lower limb muscles.
In this study, 18 male participants and 11 female participants were recruited. According to a study conducted in 2018, there was no significant difference in balance ability between genders even though there is a significant difference between leg lengths [19]. Furthermore, in the present study, the normalized reach distance was used to minimize the influence of leg length.
According to the present study, all of the maximum values were higher in the balance test supporting leg compared to the balance test reaching leg and gait (above two times compared to gait) except for the gastro muscle activities, which were higher in the reaching leg. This can be explained by the fact that the biomechanical challenges associated with balancing tasks are higher compared to gait. However, the BF and gastro RMSs were higher in gait. This can be explained by the fact that the gastro contribution is higher during the gait compared to balance task, as there are heel off and toe off phases where the plantarflexor facilitates foot clearance from the floor. During the gait cycle, in the swing phase, a higher degree of knee flexion was recorded compared to the balance task [3]. Therefore, the knee flexors’ contribution is higher for gait compared to the balancing task reaching task. However, a study conducted to examine the effect of balance task difficulty on the muscle activities among health adolescents concluded that the ankle muscles contribute to balance ability for a continuously increasing balance task difficulty [14]. Their study methodology is different from the present study, as muscle activities were compared within the balance task, but for six levels of increasing task difficulty.
The present study suggests that VM (RMS) positively influences the balance ability. Changes in the quadriceps’ muscle strength, decreased proprioception and increased postural sway were noticed in the patients in the knee OA group [11], and quadriceps strengthening is widely used during osteoarthritis physiotherapy management [20,21]. However, it should be analysed whether early changes in the muscle strength in the VM [21] due to pain are associated with changes in the balance ability of patients with knee osteoarthritis.
According to the study results, BF (RMS) activity negatively influences balance ability. The co-activation of the quadriceps and hamstrings is present during balancing tasks. The co-activation of the (hamstring) muscle decreases by nearly 20% with balance training. This provides less opposing force to the contracting quadriceps during balancing tasks [22]. Furthermore, the stance leg range of motion and muscle activation patterns differ in different reach directions. The hamstring muscle is more active in the posterior reach direction. The present study analysed a total of eight directions [23]. The following reasons could be used to explain the negative influence of hamstring muscle activity on balance ability.
MF (RMS) shows a negative influence on balance ability. A study indicated that SEBT performance did not improve with a 6-week core strength training programme [24]. Furthermore, a study indicated that neuromuscular training programmes focusing on lower limb muscle and core muscle improved only the posterolateral and posteromedial reaching distance of SEBT [24]. In this study, the overall score for reach distance was considered. This might be the possible reason for the negative influence on balance ability shown.
These results suggest that balance ability is associated with lower limb biomechanics during gait. The hypothesis of the study was accepted. Therefore, the findings of the study suggest that changes in balance ability after an injury or a disease condition would alter the joint biomechanics during gait. However, this a cross sectional study and only healthy volunteers were recruited to analyse the association between balance ability and joint kinematics and kinetics. Therefore, a longitudinal study should be conducted in order to confirm this association.
4.1. Application
This study investigated the influence of balance ability on joint kinematics and kinetics during gait among healthy adults. This study showed that there is an association between balance ability and gait kinematic and kinetic parameters. It is important to conduct follow-up studies among people who are prone to have poor balance. This would help to identify early changes in gait kinematics and kinetics among people with poor balance.
4.2. Limitations of the Study
This is a cross sectional study in which healthy participants’ gaits were analysed. The pathological gait pattern of people with poor balance was not analysed. In this study, specific events during the gait cycle were not compared. Potential confounders were not matched between the participants, such as gait speed and posture. There was a possibility of skin vibration during the tasks even after stabilization with double-sided adhesive tape, which might affect the stability of Vicon markers and EMG probes. Therefore, the data quality could be affected.
4.3. In Future
The center of pressure could be used in future to determine the balance ability among healthy individuals. The participants were asked to walk at their normal comfortable speed in this study. A future study should be carried out for the comfortable, high and slow speeds as well. Furthermore, if a wearable sensor would be available in future, this could be used to analyse the gait and influence of balance ability.
5. Conclusions
The present study examined the association of balance ability with muscle activities and gait biomechanics. These results suggest that the VM contribution is higher compared to the other muscle activities in the balance ability of healthy individuals. A linear correlation is seen in the MF, VL, TA muscle activities in the gait and balance ability (supporting and reaching leg) of healthy individuals. Furthermore, the results showed that the balance ability during balance test is associated with the lower limb kinetics and kinematics during the gait of healthy individuals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C. and W.W.; methodology, P.C. and W.W.; software, P.C., G.A. and W.W.; validation P.C., G.A. and W.W.; formal analysis, P.C. and W.W.; investigation, P.C., G.A. and W.W.; resources, G.A. and R.J.A.; writing—original P.C. and W.W.; preparation, P.C. and W.W.; writing—review and editing, P.C., R.J.A. and W.W.; visualization, W.W.; supervision, W.W.; project administration, G.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all of the subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request due to restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mirelman, A.; Shema, S.; Maidan, I.; Hausdorff, J. Gait. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 159, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sciencedirect, Gait. 2019. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/gait (accessed on 11 August 2019).
- Pirker, W.; Katzenschlager, R. Gait disorders in adults and the elderly. A clinical guide. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2017, 129, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landry, S.C.; McKean, K.A.; Hubley-Kozey, C.L.; Stanish, W.D.; Deluzio, K.J. Knee biomechanics of moderate OA patients measured during gait at a self-selected and fast walking speed. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro-de-la-Herran, A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; Mendez-Zorrilla, A. Gait analysis methods: An overview of wearable and non-wearable systems, highlighting clinical applications. Sensors 2014, 14, 3362–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, K.R.; Vincent, H.K. Resistance exercise for knee osteoarthritis. PM R J. Inj. Funct. Rehabil. 2012, 4 (Suppl. S5), S45–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sled, E.A.; Khoja, L.; Deluzio, K.J.; Olney, S.J.; Culham, E.G. Effect of a home program of hip abductor exercises on knee joint loading, strength, function, and pain in people with knee osteoarthritis. a clinical trial. Phys. Ther. 2010, 90, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, J. Propriocpetion and Balance Training in Osteoarthrits of the Knee Joint; Longdom Publishing: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Viswananthan, A.; Sudarsky, L. Balance and gait problems in the elderly. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2012, 103, 623–634. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, A.; Durward, B.; Rowe, P.; Paul, J. What is balance? Clin. Rehabil. 2000, 14, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Yun, D.H.; Yoo, S.D.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, Y.S.; Yun, J.-S.; Hwang, D.G.; Jung, P.K.; Choi, S.H.C. Balance control and knee osteoarthritis severity. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 35, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earl, J.; Hertel, J. Lower-Extremity muscle activation during the star excursion balance tests. J. Sport Rehabil. 2001, 10, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebel, A.; Luder, B.; Granacher, U. Effects of increasing balance task difficulty on postural sway and muscle activity in healthy adolescents. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J.; Plisky, P. Using the star excursion balance test to assess dynamic postural-control deficits and outcomes in lower extremity injury: A literature and systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanko, L.; Birmingham, T.; Bryant, D.; Gillanders, K.; Lemmon, K.; Chan, R.; Postic, M.; Giffin, J.R. The star excursion balance test is a reliable and valid outcome measure for patients with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillip, A.G.; Hertel, J. Considerations for normalising measures of the star excursion balance test. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2003, 7, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Dicharry, J. Kinematics and kinetics of gait: From lab to clinic. Clin. Sports Med. 2010, 29, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chvatal, S.; Ting, L.H. Common Muscle synergies for balance and walking. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 48, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrone, B.F.; Spaccarotella, K. Comparison of balance between genders of crossfit athletes. Grad. J. Sport Exerc. Phys. Educ. Res. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Imoto, A.; Peccin, M.; Trevisani, V. Quadriceps strengthening exercises are effective in improving pain, function and quality of life in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Acta Ortop. Bras. 2012, 20, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokaeian, H.R.; Bakhtiary, H.; Mirmohammadkhani, M.; Moghimi, J. Quadriceps strengthening exercises may not change pain and function in knee osteoarthritis. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2018, 22, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, C.O.; Behm, D.G.; Young, W.B. Fixed foot balance training increases rectus femoris activation during landing and jump height in recreationally active women. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2006, 5, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.; Gribble, P. Kinematic predictors of performance on the star excursion balance test. J. Sport Rehabil. 2008, 17, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipa, A.; Byrnes, R.; Paterno, M.V.; Myer, G.D.; Hewett, T.E. Neuromuscular training improves performance on the star excursion balance test in young female athletes. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 40, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).