Cytotoxic Effects of Water-Soluble N-Heterocyclic Carbene Platinum(II) Complexes on Prostatic Tumor PC3 and Leukemia NB4 Human Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
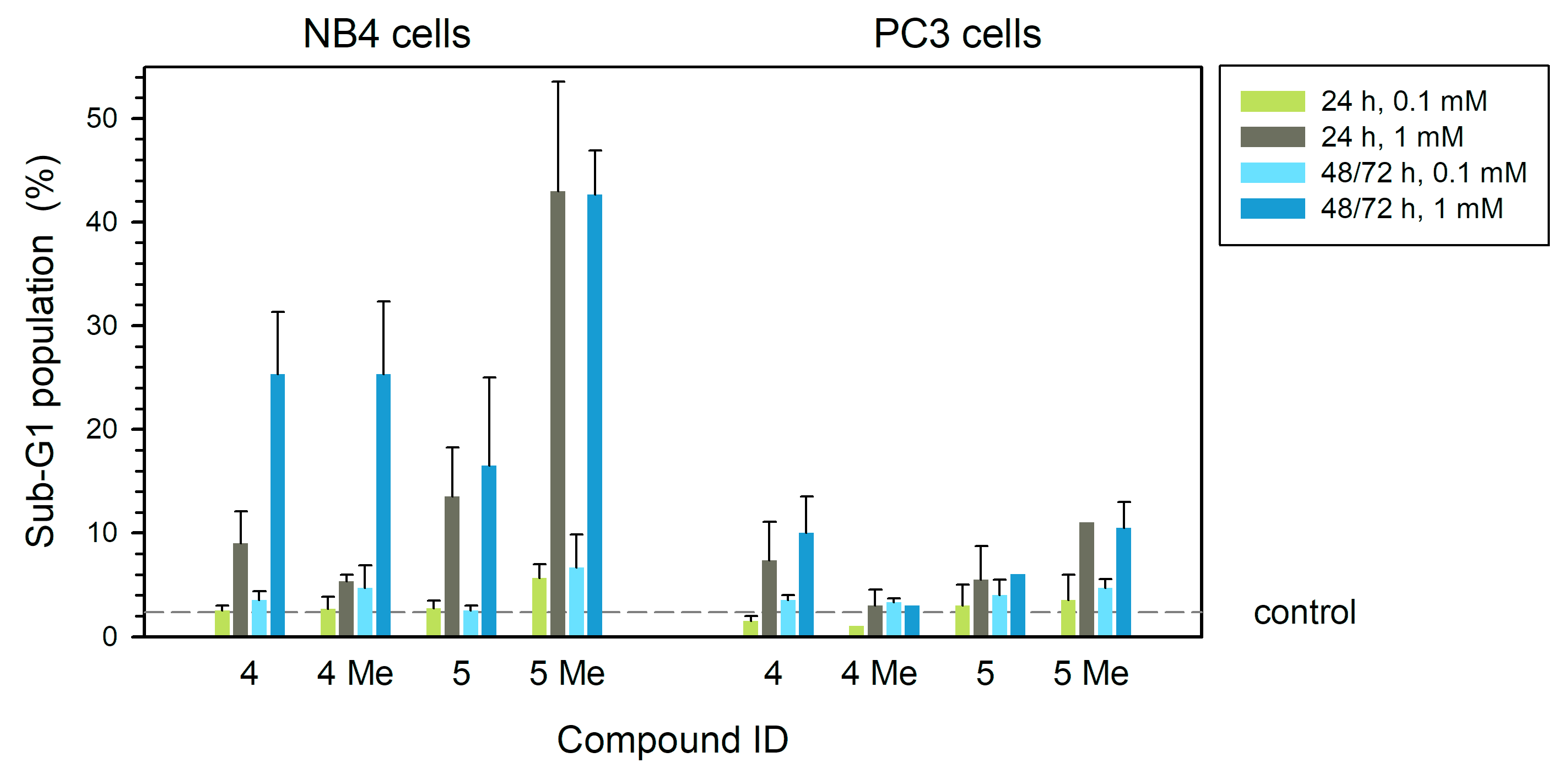
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
References
- Lanotte, M.; Martin-Thouvenin, V.; Najman, S.; Balerini, P.; Valensi, F.; Berger, R. NB4, a maturation inducible cell line with t(15;17) marker isolated from a human acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3). Blood 1991, 77, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; García-Pérez, A.I.; Tejedor, M.C.; Herráez, A.; Diez, J.C. Esculetin neutralises cytotoxicity of t-BHP but not of H2O2 on human leukaemia NB4 cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9491045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; García-Pérez, A.I.; Herráez, A.; Tejedor, M.C.; Diez, J.C. Esculetin modulates cytotoxicity induced by oxidants in NB4 human leukemia cells. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 69, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; García-Pérez, A.I.; Herráez, A.; Diez, J.C. Different roles of Nrf2 and NFκB in the antioxidant imbalance produced by esculetin or quercetin on NB4 leukemia cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 294, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavridi, F.; Karapanagiotou, E.M.; Syrigos, K.N. Targeted therapeutic approaches for hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2010, 36, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuu, C.P.; Kokontis, J.M.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Liao, S. Modulation of liver X receptor signalling as novel therapy for prostate cancer. J. Biomed. Sci. 2007, 14, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaighn, M.E.; Narayan, K.S.; Ohnuki, Y.; Lechner, J.F.; Jones, L.W. Establishment and characterization of a human prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC3). Investig. Urol. 1979, 17, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, B.; VanCamp, L.; Trosko, J.E.; Mansour, V.H. Platinum compounds: A new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature 1969, 222, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.K. A histochemical approach to the mechanism of action of cisplatin and its analogues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1993, 41, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, M.A.; Castilla, J.; Alonso, C.; Pérez, J.M. Cisplatin biochemical mechanism of action: From cytotoxicity to induction of cell death through interconnections between apoptotic and necrotic pathways, Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartalou, M.; Essigmann, J.M. Recognition of cisplatin adducts by cellular proteins. Mutat. Res. 2001, 478, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartalou, M.; Essigmann, J.M. Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin. Mutat. Res. 2001, 478, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, A.; Trombatore, G.; Triarico, S.; Arena, R.; Ferrara, P.; Scalzone, M.; Pierri, F.; Riccardi, R. Platinum compounds in children with cancer: Toxicity and clinical management. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.; Leung, N. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review of the literature. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, A.G.; Hernández-Sánchez, M.T.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Martínez-Salgado, C.; Prieto, M.; Vicente-Vicente, L.; Morales, A.I. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of clinically tested protectants of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleki, S.; Khaksar, S.; Aliabadi, A.; Panjehpour, A.; Motieiyan, E.; Marabello, D.; Faraji, M.H.; Beihaghi, M. Cytotoxicity and mechanism of action of metal complexes: An overview. Toxicology 2023, 492, 153516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.W.; Pouliot, L.M.; Hall, M.D.; Gottesman, M.M. Cisplatin resistance: A cellular self-defense mechanism resulting from multiple epigenetic and genetic changes. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breglio, A.M.; Rusheen, E.; Shide, D.; Fernandez, K.A.; Spielbauer, K.K.; McLachlin, K.M.; Hall, M.D.; Amable, L.; Cunningham, L.L. Cisplatin is retained in the cochlea indefinitely following chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanovska, V.; McQuade, R.; Rybalka, E.; Nurgali, K. Neurotoxicity associated with platinum-based anti-cancer agents: What are the implications of copper transporters? Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1520–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biersack, B.; Schobert, R. Current state of platinum complexes for the treatment of advanced and drug-resistant breast cancers. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1152, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Hashemi, F.; Moghadam, E.R.; Owrang, M.; Hashemi, F.; Makvandi, P.; Goharrizi, M.A.S.B.; Najafi, M.; et al. Lung cancer cells and their sensitivity/resistance to cisplatin chemotherapy: Role of microRNAs and upstream mediators. Cell. Signal. 2021, 78, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tendulkar, S.; Dodamani, S. Chemoresistance in ovarian cancer: Prospects for new drugs. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štarha, P.; Vančo, J.; Trávníček, Z.; Hošek, J.; Klusáková, J.; Dvořák, Z. Platinum(II) Iodido Complexes of 7-Azaindoles with Significant Antiproliferative Effects: An Old Story Revisited with Unexpected Outcomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.K.; Broomhead, J.A.; Fairlie, D.P.; Whithouse, M.W. Platinum drugs: Combined anti-lymphoproliferative and nephrotoxicity assays in rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1980, 4, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippard, S.J. New chemistry of an old molecule: Cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]. Science 1982, 218, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfgang, G.H.; Dominick, M.A.; Walsh, K.M.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Pegg, D.G. Comparative nephrotoxicity of a novel platinum compound, cisplatin, and carboplatin in male Wistar rats. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1994, 22, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, J.L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Deng, L. Metal-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as anti-tumor agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt(II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt(IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, R.G.; Marmion, C.J. Toward multi-targeted platinum and ruthenium drugs—A new paradigm in cancer drug treatment regimens? Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 1058–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, D.; Ivanova, S. Application of approved cisplatin derivatives in combination therapy against different cancer diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, D.; Canetta, R. Clinical development of platinum complexes in cancer therapy: An historical perspective and an update. Eur. J. Cancer 1998, 34, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilruba, S.; Kalayda, G.V. Platinum-based drugs: Past, present and future. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 1103–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treskes, M.; van der Vijgh, W.J. WR2721 as a modulator of cisplatin- and carboplatin-induced side effects in comparison with other chemoprotective agents: A molecular approach. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1993, 33, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, E.A.; Silbestri, G.F.; Gómez-Sal, P.; Flores, J.C.; de Jesús, E. Sulfonated water-soluble N-heterocyclic carbene silver(I) complexes: Behavior in aqueous medium and as NHC-transfer agents to platinum(II). Organometallics 2013, 32, 2814–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, E.A.; Flores, J.C.; Perles, J.; Gómez-Sal, P.; de Jesús, E. Water-soluble mono- and dimethyl N-heterocyclic carbene platinum(II) complexes: Synthesis and reactivity. Organometallics 2014, 33, 5470–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, E.; Nieto, E.; García-Pérez, A.I.; Delgado, M.D.; Pinilla, M.; Sancho, P. Effects of the antitumoural dequalinium on NB4 and K562 human leukemia cell lines. Mitochondrial implication in cell death. Leuk. Res. 2005, 29, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, P.; Galeano, E.; Nieto, E.; Delgado, M.D.; García-Pérez, A.I. Dequalinium induces cell death in human leukemia cells by early mitochondrial alterations which enhance ROS production. Leuk. Res. 2007, 31, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronina, T.; Bartmanska, A.; Popłonski, J.; Rychlicka, M.; Sordon, S.; Filip-Psurska, B.; Milczarek, M.; Wietrzyk, J.; Huszcza, E. Prenylated flavonoids with selective toxicity against human cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, C.; Gao, X.; Yao, Q. Platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy and anti-tumor strategies. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2115–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibas, A.; Howard, J.; Anwar, S.; Stewart, D.; Khan, A. Borato-1,2-diaminocyclohexane platinum (II), a novel anti-tumor drug. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2000, 270, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Singh, V.J.; Chawla, P.A. Advancements in the use of platinum complexes as anticancer agents. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahsavari, H.R.; Hu, J.; Chamyani, S.; Sakamaki, Y.; Aghakhanpour, R.B.; Salmon Ch Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Mojaddami, A.; Peyvasteh, P.; Beyzavi, H. Fluorinated cycloplatinated(II) complexes bearing bisphosphine ligands as potent anticancer agents. Organometallics 2021, 40, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman-Blanco, G.; Valdés, H.; Ramírez-Apan, M.T.; Cano-Sanchez, P.; Hernandez-Ortega, S.; Orjuela, A.L.; Alí-Torres, J.; Flores-Gaspar, A.; Reyes-Martínez, R.; Morales-Morales, D. Synthesis of Pt(II) complexes of the type [Pt(1,10-phenanthroline)(SArFn)2] (SArFn = SC6H3-3,4-F2; SC6F4-4-H.; SC6F5). Preliminary evaluation of their in vitro anticancer activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 211, 111206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P.; Alberts, I.; Patel, S.; Al Aameri, R.F.H.; Ramkumar, V. Effects of natural products on cisplatin ototoxicity and chemotherapeutic efficacy. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkinson, M.N.; Christian Richter, C.; Schedler, M.; Glorius, F. An overview of N-heterocyclic carbenes. Nature 2014, 510, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, V.; Reiter, D.; Bag, P.; Frisch, P.; Holzner, R.; Porzelt, A.; Inoue, S. NHCs in main group chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9678–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin cytotoxicity in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2025, 6, 40734–40746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafees, M.; Hanif, M.; Muhammad Asif Khan, R.; Faiz, F.; Yang, P. A dual action platinum(IV) complex with self-assembly property inhibits prostate cancer through mitochondrial stress pathway. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Nady, S.; Shafaa, M.W.; Khalil, M.M. Radiation and chemotherapy variable response induced by tumor cell hypoxia: Impact of radiation dose, anticancer drug, and type of cancer. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2022, 61, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang Ch Li, S. Reduced pim-1 expression increases chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human androgen-independent prostate cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.-C.; Chang, S.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, J.-S.; Tsao, C.-J. Comparison of in vitro growth-inhibitory activity of carboplatin and cisplatin on leukemic cells and hematopoietic progenitors: The myelosuppressive activity of carboplatin may be greater than its antileukemic effect. Jap. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 30, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diez, J.C.; Baquero, E.A.; Rubio, V.; Flores, J.C.; Herráez, A.; Tejedor, M.C.; Jesús, E.d.; García-Pérez, A.I. Cytotoxic Effects of Water-Soluble N-Heterocyclic Carbene Platinum(II) Complexes on Prostatic Tumor PC3 and Leukemia NB4 Human Cells. Compounds 2025, 5, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040053
Diez JC, Baquero EA, Rubio V, Flores JC, Herráez A, Tejedor MC, Jesús Ed, García-Pérez AI. Cytotoxic Effects of Water-Soluble N-Heterocyclic Carbene Platinum(II) Complexes on Prostatic Tumor PC3 and Leukemia NB4 Human Cells. Compounds. 2025; 5(4):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040053
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiez, José C., Edwin A. Baquero, Virginia Rubio, Juan C. Flores, Angel Herráez, M. Cristina Tejedor, Ernesto de Jesús, and Ana I. García-Pérez. 2025. "Cytotoxic Effects of Water-Soluble N-Heterocyclic Carbene Platinum(II) Complexes on Prostatic Tumor PC3 and Leukemia NB4 Human Cells" Compounds 5, no. 4: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040053
APA StyleDiez, J. C., Baquero, E. A., Rubio, V., Flores, J. C., Herráez, A., Tejedor, M. C., Jesús, E. d., & García-Pérez, A. I. (2025). Cytotoxic Effects of Water-Soluble N-Heterocyclic Carbene Platinum(II) Complexes on Prostatic Tumor PC3 and Leukemia NB4 Human Cells. Compounds, 5(4), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040053





