Synthesis of Acetylated Phenolic Compounds with Promising Antifouling Applications: An Approach to Marine and Freshwater Mussel Settlement Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Procedures and Statements
2.2. Catalyst Preparation
2.2.1. Bulk Catalysts
2.2.2. Supported Catalyst, PWMo10SiO2
2.3. General Procedure for the Acetylation of Phenols
2.4. Melting Point and NMR Spectra of Synthesized Compounds
2.5. Biological Assays
2.5.1. Mussel Specimens
2.5.2. Settlement Assay
2.5.3. Recovery Tests
2.5.4. Ecotoxicity Assays
2.5.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Acetylation of Phenols
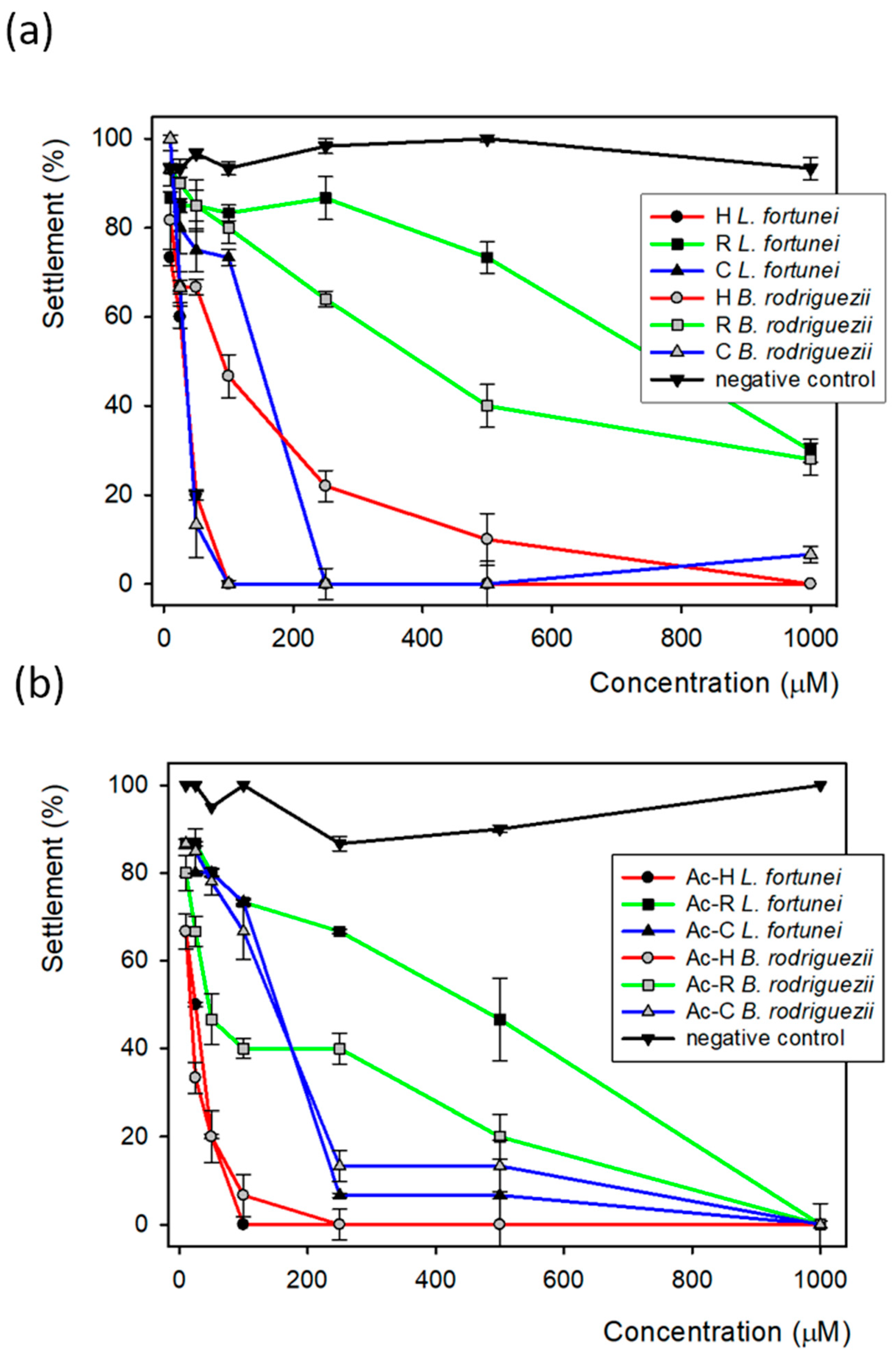
3.2. Biological Assays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abarzua, S.; Jakubowski, S. Biotechnological investigation for the prevention of biofouling. I. Biological and biochemical principles for the prevention of biofouling. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 123, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.R.; Targett, N.M.; Mcconnell, O.J.; Young, C.M. Epibiosis of marine algae and benthic invertebrates: Natural products chemistry and other mechanisms inhibiting settlement and overgrowth. In Bioorganic Marine Chemistry; Scheuer, P.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 86–114. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, M.; Bendick, J.; Holm, E.; Hertel, W. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship. Biofouling 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Pis Diez, C.; Valdez, M.; García, M.; Paola, A.; Avigliano, E.; Palermo, J.; Blustein, G. Isolation and antimacrofouling activity of indole and furoquinoline alkaloids from ‘guatambú’ trees (Aspidosperma australe and Balfourodendron riedelianum). Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatayev, A.Y.; Burlakova, L.E. What we know and don’t know about the invasive zebra (Dreissena polymorpha) and quagga (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis) mussels. Hydrobiologia 2022, 852, 1029–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltovskoy, D.; Xu, M.; Nakano, D. Impacts of Limnoperna Fortunei on Man-Made Structures and Control Strategies: General Overview. In Limnoperna fortunei: The Ecology, Distribution and Control of a Swiftly Spreading Invasive Fouling Mussel; Boltovskoy, D., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 375–393. [Google Scholar]
- Darrigran, G. Summary of the distribution and impact of the golden mussel in Argentina and neighboring countries. In Monitoring and Control of Macrofouling Mollusks in Freshwater Systems, 2nd ed.; Mackie, G.L., Claudi, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Rolla, M.E.; Mota, H.R. Response of a Major Brazilian Utility to the Golden Mussel Invasion. In Monitoring and Control of Macrofouling Mollusks in Freshwater Systems, 2nd ed.; Mackie, G.L., Claudi, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 396–403. [Google Scholar]
- Brankevich, G.; Bastida, R.; Lemmi, C. A comparative study of biofouling settlements in different sections of Necochea Power Plant (Quequen port, Argentina). Biofouling 1988, 1, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Venugopalan, V.; van der Velde, G.; Jenner, H. Mussel colonization of a high flow artificial benthic habitat: Byssogenesis holds the key. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 62, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, K.K.; Kumar, A.; Sahu, G.; Biswas, S.; Prasad, M.V.R.; Slvanayagam, M. Biofouling and its control in seawater cooled power plant cooling water system—A review. In Nuclear Power; Tsvetkov, P., Ed.; SCIYO: Rijeka, Croatia, 2010; pp. 191–242. [Google Scholar]
- Llanos, E.; Becherucci, M.; Garaffo, G.; Vallarino, E.A. A shift of ecosystem engineers during the succession of an intertidal benthic community associated with natural and anthropogenic disturbances. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 31, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, M.; Torroglosa, M.; Cremonte, F.; Yuvero, C.; Giménez, J. Pathological conditions of the sentinel bivalve, the little mussel Brachidontes rodriguezii, from contaminated intertidal sites in the Southwestern Atlantic coast. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 184, 107654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Van der Velde, G.; Van der Gaag, M.; Jenner, H.A. How effective is intermittent chlorination to control adult mussel fouling in cooling water systems? Water Res. 2003, 37, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, R.; Vicente, M.; Peribáñez, M.; Arques, A.; Amat, A. Exploring the applicability of solar driven photocatalytic processes to control infestation by zebra mussel. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, I.; Miled, W.; Ben Slama, R.; Ladhari, N. Antifouling processes and toxicity efects of antifouling paints on marine environment. A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 57, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedó, J.; Saiz-Poseu, J.; Busqué, F.; Ruiz-Molina, D. Catechol-Based Biomimetic Functional Materials. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 653–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, S. Hydroquinone. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 4th ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S.; Fan, P.; Wang, W.; Xia, C. Allelochemical induces growth and photosynthesis inhibition, oxidative damage in marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 444, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.K.; Mishra, N.; Singh, P. Relative phytotoxicity of hydroquinone on rice (Oryza sativa L.) and associated aquatic weed green musk Chara (Chara zeylanica Willd). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 83, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaçalişkan, I.; Talan, I.; Terzi, I. Antimicrobial Activity of Catechol and Pyrogallol as Allelochemicals. Z. Naturforschung Sect. C-J. Biosci. 2006, 61, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrouf, Z.; Guillaume, D. Phenols and polyphenols from Argania spinosa. Am. J. Food Technol. 2007, 2, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütfeld, R.; Petereit, F.; Nahrstedt, A. Resorcinol in exudates of Nuphar lutea. J. Chem. Ecol. 1996, 22, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, A.; Vilas Boas, C.; Gonçalves, C.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Silva, E.R.; Sousa, E.; Almeida, J.R.; Correia-Da-Silva, M. Gallic acid derivatives as inhibitors of mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) larval settlement: Lead optimization, biological evaluation and use in antifouling coatings. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 126, 105911. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Yu, L.; Mou, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, M.; Zhou, P.; Ren, Y. Research Strategies to Develop Environmentally Friendly Marine Antifouling Coatings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.; Lu, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. Terpolymer Resin Containing Bioinspired Borneol and Controlled Release of Camphor: Synthesis and Antifouling Coating Application. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fusetani, N. Mini-Review: Marine Natural Products and Their Synthetic Analogs as Antifouling Compounds: 2009−2014. Biofouling 2015, 31, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellio, C.; Tsoukatou, M.; Maréchal, J.; Aldred, N.; Beaupoil, C.; Clare, A.S.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Inhibitory effects of mediterranean sponge extracts and metabolites on larval settlement of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portilla-Zuñiga, O.; Sathicq, G.; Martínez, J.; Fernandes, S.A.; Rezende, T.R.; Romanelli, G.P. Synthesis of Biginelli adducts using a Preyssler heteropolyacid in silica matrix from biomass building block. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 10, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, D.; Romanelli, G.; Vázquez, P.; Autino, J.C. Preyssler catalyst: An efficient catalyst for esterification of cinnamic acids with phenols and amidoalcohols. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 374, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, G.; Shrestha, S. Unprecedented acetylation of phenols using a catalytic amount of magnesium powder. Synth. Commun. 2018, 48, 1688–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, X. Na2CO3-Catalyzed O-Acylation of Phenols for the Synthesis of Aryl Carboxylates with Use of Alkenyl Carboxylates. Synlett 2018, 29, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.; Clauser, C.; Lozano, V.; Cataldo, D.; Pizarro, H. An invasive mussel is in trouble: How do glyphosate, 2,4-D and its mixture affect Limnoperna fortuneiʹs survival? Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 239, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas, P.; Arias, A.; Oliva, A.; Domini, C.; Alvarez, M.; Garrido, M.; Marcovecchio, J. Organotin compounds in Brachidontes rodriguezii mussels from the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrighetti, F.; Landro, S.; Lambre, M.; Penchaszadeh, P.; Teso, V. Multiple-biomarker approach in the assessment of the health status of a novel sentinel mussel Brachidontes rodriguezii in a harbor area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1141–98 (Reapproved 2021); Standard Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Wilsanand, V.; Wagh, A.; Bapuji, M. Antifouling activities of marine sedentary invertebrates on some macrofoulers. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 1999, 28, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, M.; Sánchez, M.; García, M.; Patiño C., L.P.; Blustein, G.; Palermo, J.A. Antifouling activity of peracetylated cholic acid, a natural bile acid derivative. Steroids 2019, 149, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, C.; Costa, E.; Piazza, V.; Fabbrocini, A.; Magi, E.; Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F. Effect of silver nanoparticles on marine organisms belonging to different trophic levels. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Li, S.; AlMasoud, N.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Yin, C.; Jie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Alomar, T.; Li, X.; et al. Nature-inspired silicone-polythiourethane coatings based on capsaicin analogue for marine biofouling control. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 518, 164362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Gonçalves, C.; Martins, B.; Palmeira, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Almeida, J.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Cidade, H. Flavonoid glycosides with a triazole moiety for marine antifouling applications: Synthesis and biological activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuts, P.; Greene, T.H. Protection for Phenols and Catechols. In Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 4th ed.; Wuts, P., Greene, T.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 367–430. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, A.K.; Gulhane, R. Perchloric acid adsorbed on silica gel as a new, highly efficient, and versatile catalyst for acetylation of phenols, thiols, alcohols, and amines. Chem. Commun. 2003, 15, 1896–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Sun, J.; Xiang, H.; Zeng, Y.-Y.; Li, X.-B.; Xiao, H.; Chen, D.-Y.; Ma, R.-L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new flavonoid fatty acid esters with anti-adipogenic and enhancing glucose consumption activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 3192–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Zareisahamieh, R.; Zaidi, M. H6GeMo10V2O40·16H2O nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method: A new and reusable heteropoly acid catalyst for highly efficient acetylation of alcohols and phenols under solvent-free conditions. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, G.; Bennardi, D.; Autino, J.; Baronetti, G.T.; Thomas, H.J. A simple and mild acylation of alcohols, phenols, amines, and thiols with a reusable heteropolyacid catalyst (H6P2W18O62·24 H2O). J. Chem. 2008, 5, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, G.; Ruiz, D.; Vázquez, P.; Thomas, H.; Autino, J.C. Preyssler heteropolyacids H14[NaP5W29MoO110]: A heterogeneous, green and recyclable catalyst used for the protection of functional groups in organic synthesis. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 161, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathicq, A.; Ruiz, D.; Constantieux, T.; Rodriguez, J. Preyssler heteropolyacids encapsulated in a silica framework for an efficient preparation of fluorinated hexahydropyrimidine derivatives in solvent-free conditions. Synlett 2014, 25, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, S.; Inoue, Y.; Hosomi, M. Algal growth inhibition effects and inducement modes by plant-producing phenols. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapór, L. Toxicity of Some Phenolic Derivatives-In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2004, 10, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, D. Sources of Firewater Pump Supply. In Fire Pump Arrangements at Industrial Facilities, 3rd ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Latkar, M.; Chakrabarti, T. Resorcinol, catechol and hydroquinone biodegradation in mono and binary substrate matrices in upflow anaerobic fixed-film fixed-bed reactors. Water Res. 1994, 28, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enguita, F.; Leitão, A. Hydroquinone: Environmental Pollution, Toxicity, and Microbial Answers. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 1, 542168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, N.; Shirzad, N.; Farzi, A.; Salouti, M.; Momeni, A. Biodegradation of resorcinol by Pseudomonas sp. J. Coast. Life Med. 2016, 4, 932–934. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J. Biodegradation of Dihydroxybenzenes (Hydroquinone, Catechol and Resorcinol) by Granules Enriched with Phenol in an Aerobic Granular Sequencing Batch Reactor. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of the Graduate School of Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S.; Srivastava, V.; Mishra, I. Adsorption of catechol, resorcinol, hydroquinone, and their derivatives: A review. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2012, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


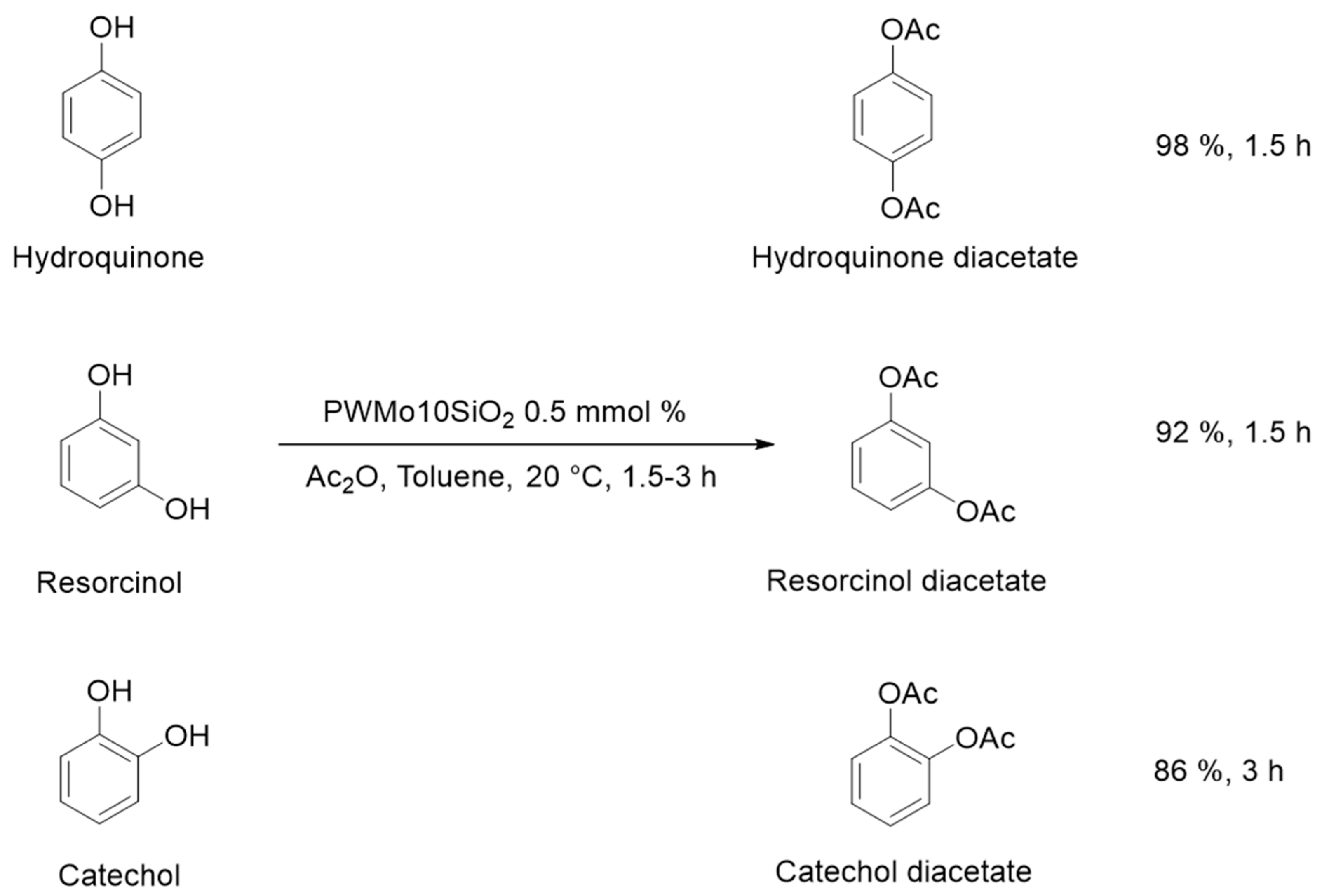
| Entry | Substrate | Temp (°C) | Time (h) | Catalysts Mass (mmol %) | Ratio Substrate/Ac2O | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydroquinone | 50 | 1 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 90 |
| 2 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 98 | |
| 3 | 20 | 2 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 97 | |
| 4 | 20 | 1 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 88 | |
| 5 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.25 | 2.4 | 72 | |
| 6 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.75 | 2.4 | 96 | |
| 7 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 98 | |
| 8 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2 | 79 | |
| 9 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 a | 2.4 | 97 | |
| 10 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 a | 2.4 | 96 | |
| 11 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 a | 2.4 | 96 | |
| 12 | Resorcinol | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 92 |
| 13 | 50 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 89 | |
| 14 | 20 | 2 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 92 | |
| 15 | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 91 | |
| 16 | Catechol | 20 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 75 |
| 17 | 20 | 2 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 79 | |
| 18 | 20 | 3 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 86 | |
| 19 | 20 | 3 | 0.5 | 3 | 85 |
| EC50 (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound | Limnoperna fortunei | Brachidontes rodriguezii |
| Hydroquinone | 22 | 63 |
| Resorcinol | 514 | 320 |
| Catechol | 110 | 145 |
| Acetylated hydroquinone | 36 | 25 |
| Acetylated resorcinol | 268 | 91 |
| Acetylated catechol | 121 | 120 |
| Compound | Mortality (%) |
|---|---|
| Negative control (artificial seawater) | 2.2 |
| Hydroquinone | 6.0 |
| Resorcinol | 29.4 |
| Catechol | 4.9 |
| Acetylated hydroquinone | 5.9 |
| Acetylated resorcinol | 39.6 |
| Acetylated catechol | 5.7 |
| Positive control (K2Cr2O7 13.6 μM) | 92.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez, M.C.; García, M.; Pasquale, G.; Laitano, M.V.; Romanelli, G.; Blustein, G. Synthesis of Acetylated Phenolic Compounds with Promising Antifouling Applications: An Approach to Marine and Freshwater Mussel Settlement Control. Compounds 2025, 5, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040045
Pérez MC, García M, Pasquale G, Laitano MV, Romanelli G, Blustein G. Synthesis of Acetylated Phenolic Compounds with Promising Antifouling Applications: An Approach to Marine and Freshwater Mussel Settlement Control. Compounds. 2025; 5(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040045
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez, Míriam C., Mónica García, Gustavo Pasquale, María V. Laitano, Gustavo Romanelli, and Guillermo Blustein. 2025. "Synthesis of Acetylated Phenolic Compounds with Promising Antifouling Applications: An Approach to Marine and Freshwater Mussel Settlement Control" Compounds 5, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040045
APA StylePérez, M. C., García, M., Pasquale, G., Laitano, M. V., Romanelli, G., & Blustein, G. (2025). Synthesis of Acetylated Phenolic Compounds with Promising Antifouling Applications: An Approach to Marine and Freshwater Mussel Settlement Control. Compounds, 5(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5040045






