Critical Effect of Oxygen Concentration and Acidity on the Efficiency of Photodegradation of Levofloxacin with Solar UVB Light; Cytotoxicity on Mammalian Cells of the Photoproducts and Its Activity on Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Levofloxacin Photolysis Experiments
2.2.2. In Vitro Bioassays on Bacteria
2.2.3. In Vitro Bioassays on Mammalian Cell
3. Results and Discussion
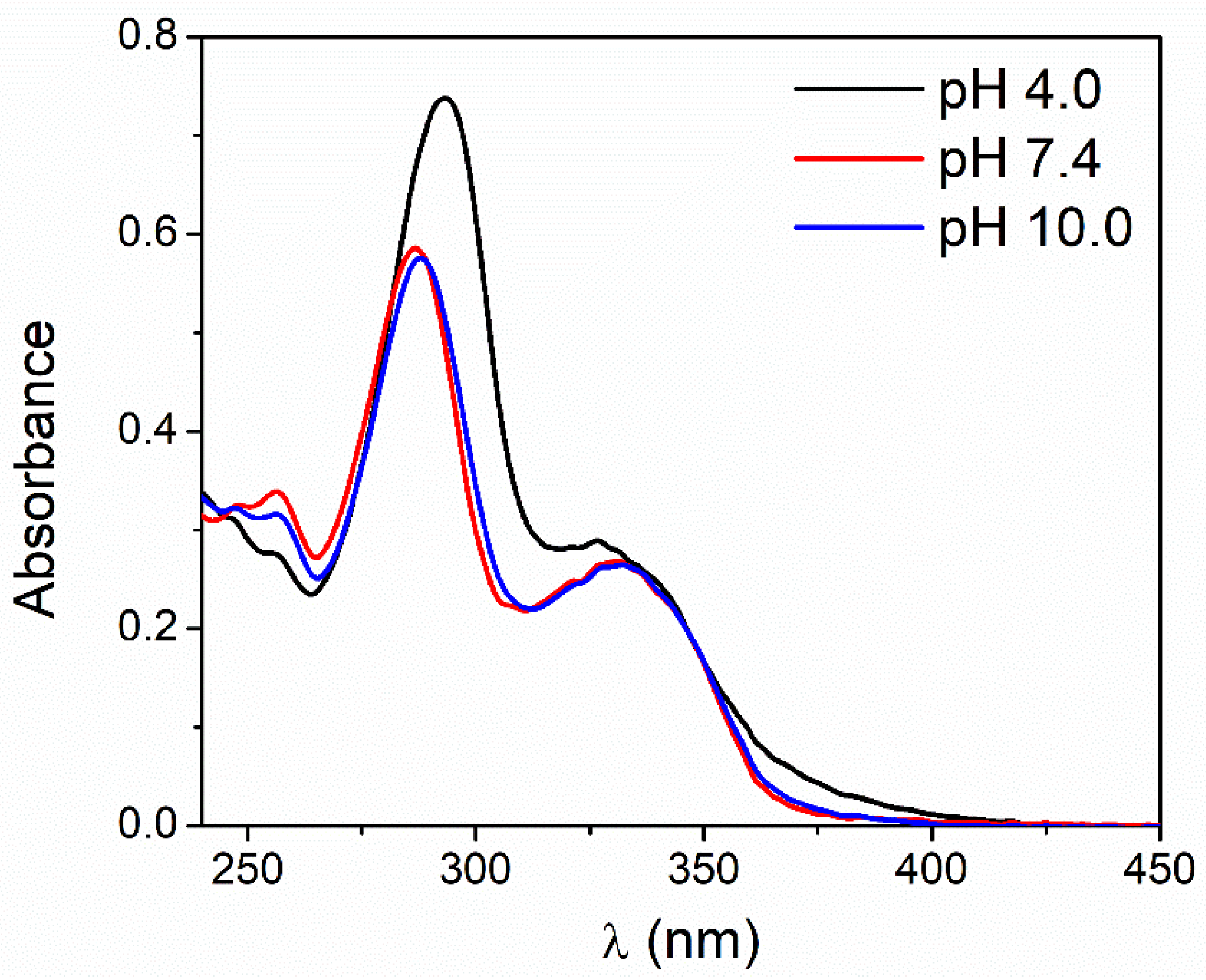
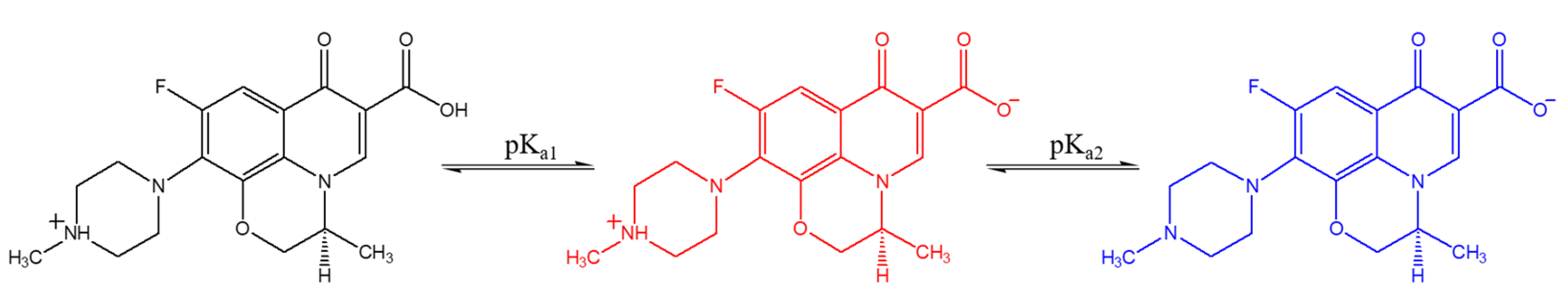
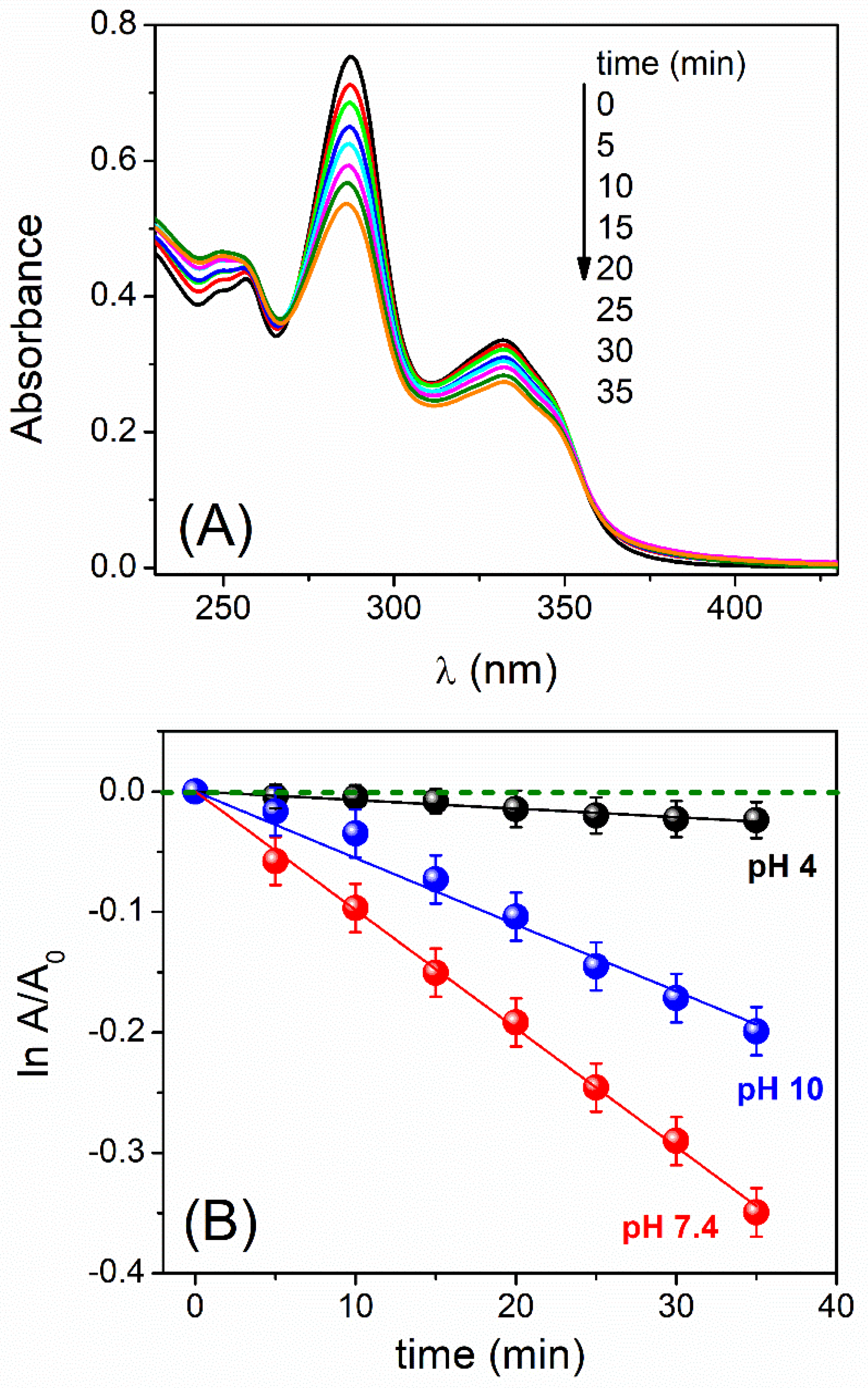
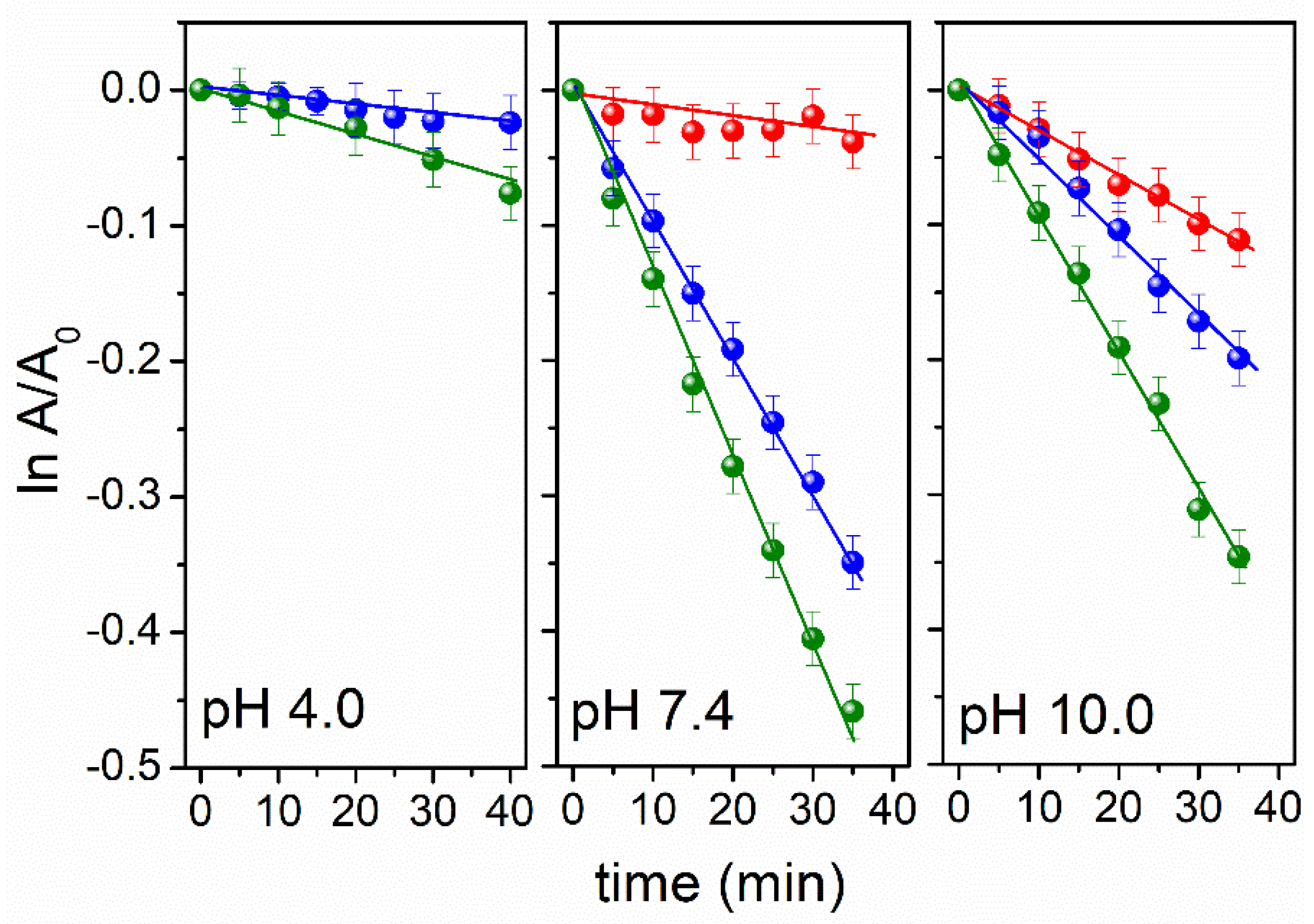
3.1. pH and Dissolved-Oxygen-Concentration Effect on Lev Photolysis
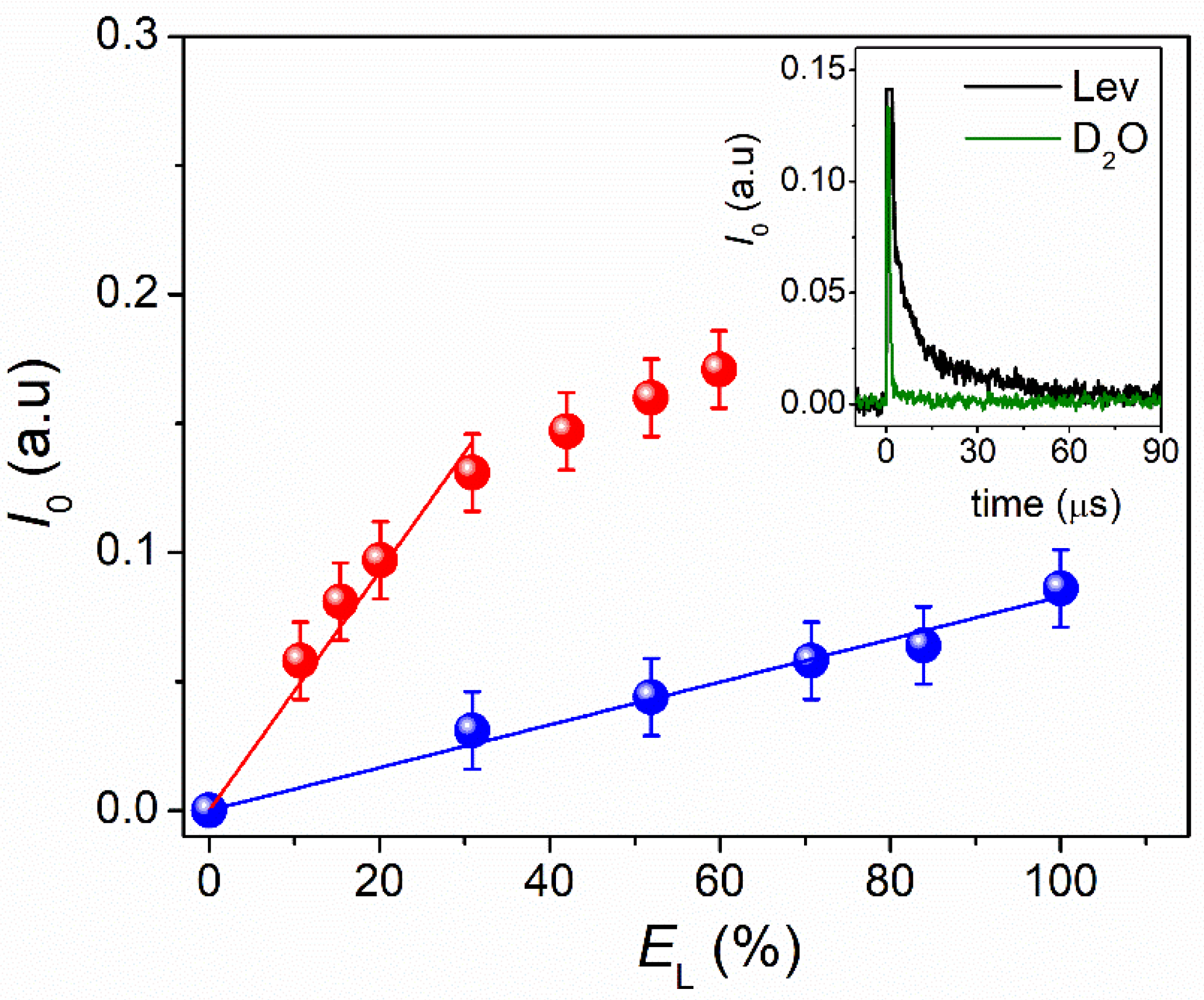
3.2. ROS Photogenerated and Singlet Oxygen Quantum Yield
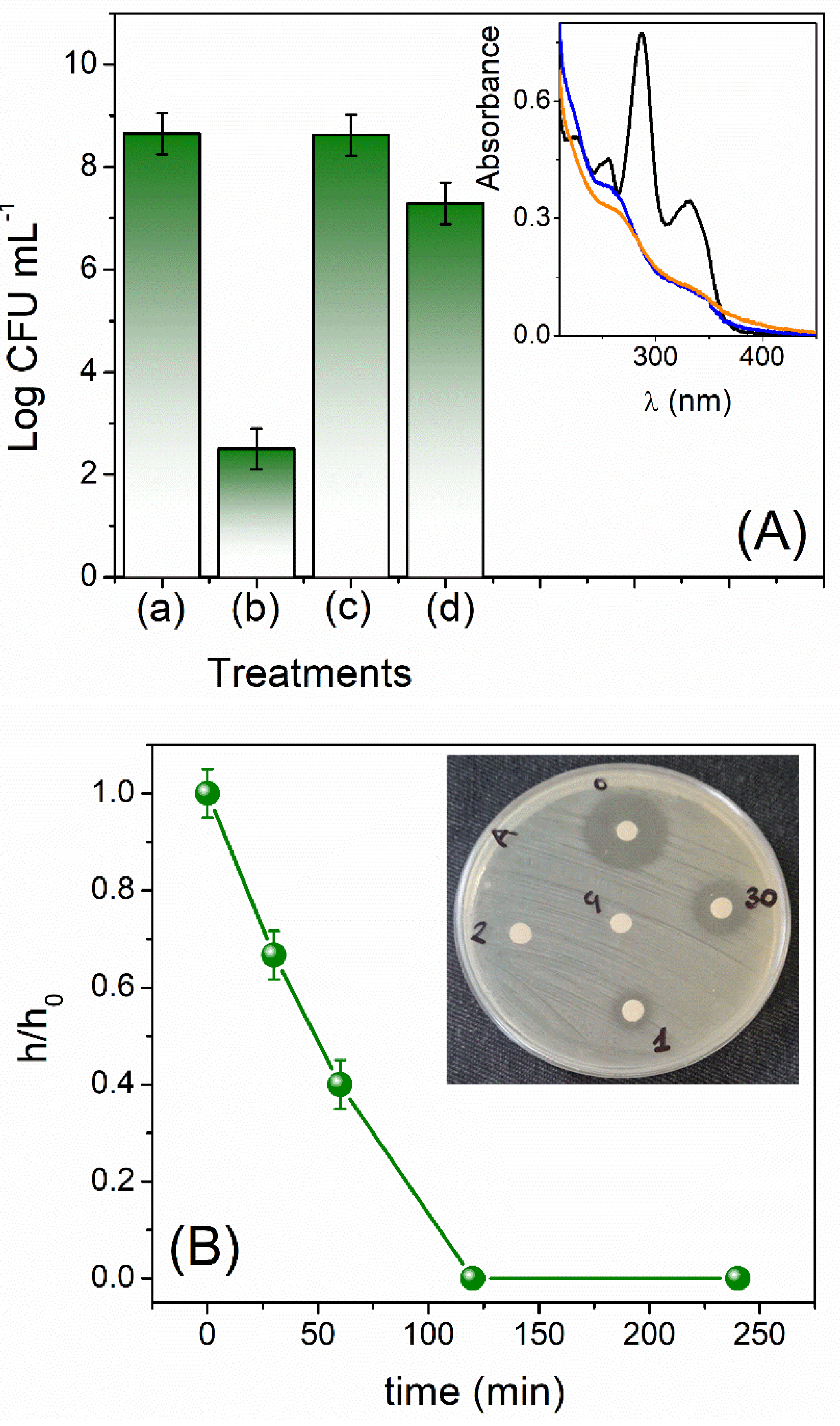
3.3. Activity of Levofloxacin and Its Photodegradation Products on Escherichia Coli
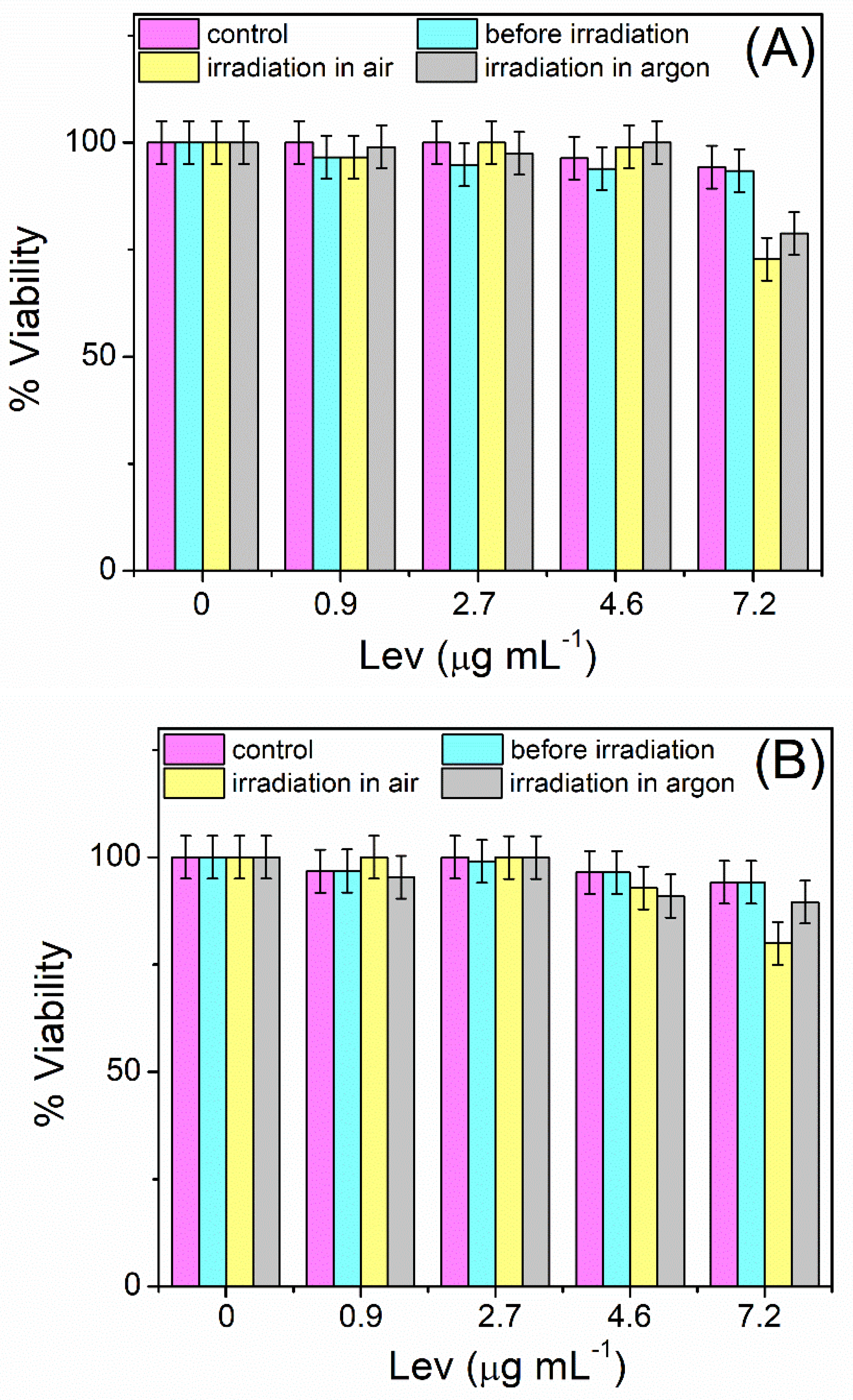
3.4. Toxicity of Levofloxacin and Its Photodegradation Products on Mammalian Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, N.; Khan, M.D.; Shahane, S.; Rai, D.; Chauhan, D.; Kant, C.; Chaudhary, V.K. Emerging pollutants in aquatic environment: Source, effect, and challenges in biomonitoring and bioremediation—A review. Pollution 2020, 6, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.Á.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottoni, P.; Caroli, S.; Caracciolo, A.B. Pharmaceuticals as priority water contaminants. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2010, 92, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M. Persistence, environmental hazards, and mitigation of pharmaceutically active residual contaminants from water matrices. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, M.; Watts, J.E.; Williams, J.B.; Joshi, H. An evaluation of conventional and nature-based technologies for controlling antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic-resistant genes in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Tripathi, G.; Mishra, V.; Ilyas, T.; Firdaus, S.; Ahmad, S.; Farooqui, A.; Yadav, N.; Rustagi, S.; Shreaz, S.; et al. Antibiotic contamination in wastewater treatment plant effluents: Current research and future perspectives. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2025, 23, 101047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, B.L.; Ong, C.C.; Saheed, M.S.M.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C.; Lam, S.S.; Juan, J.C. Conventional and emerging technologies for removal of antibiotics from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 122961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Qian, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, G.; Khan, E.; Ng, Y.H.; Ok, Y.S. Recent advances in photodegradation of antibiotic residues in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ilurdoz, M.S.; Sadhwani, J.J.; Reboso, J.V. Antibiotic removal processes from water & wastewater for the protection of the aquatic environment-a review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialaton, D.; Richard, C. Phototransformation of aromatic pollutants in solar light: Photolysis versus photosensitized reactions under natural water conditions. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Raffaele, M.; Nicklas, P. Pharmaceuticals in STP effluents and their solar photodegradation in aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.Y.C.; Reinhard, M. Photodegradation of common environmental pharmaceuticals and estrogens in river water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, J.; Prevot, A.B.; Montoneri, E.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Amat, A.M.; Martire, D.O.; Arques, A.; Carlos, L. Waste sourced bio-based substances for solar-driven wastewater remediation: Photodegradation of emerging pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Biondi, M.A.; Cacciari, R.D.; Sabini, M.C.; Spesia, M.B.; Biasutti, M.A.; Reynoso, E.; Montejano, H.A. Natural degradation of ceftriaxone promoted by direct UVB light in aqueous media. Mechanistic analysis and cytotoxic effects on a eukaryotic cell line and on bacteria. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 17799–17809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, J.K.; Hanson, M.L.; Friesen, K.J.; Wong, C.S. A critical assessment of the photodegradation of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environments: Defining our current understanding and identifying knowledge gaps. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 672–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, A.; Monti, S. Photophysics and photochemistry of fluoroquinolones. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, G.; Facciolo, L.; Canton, M.; Vedaldi, D.; Dall’Acqua, F.; Aloisi, G.G.; Amelia, M.; Barbafina, A.; Elisei, F.; Latterini, L. Photophysical and phototoxic properties of the antibacterial fluoroquinolones levofloxacin and moxifloxacin. Chem. Biodivers. 2004, 1, 782–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.; Mujtaba, S.F.; Kushwaha, H.N.; Ali, D.; Yadav, N.; Singh, S.K.; Ray, R.S. Photosensitizing mechanism and identification of levofloxacin photoproducts at ambient UV radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturini, M.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Profumo, A.; Pretali, L.; Irastorza, E.A.; Fasani, E.; Albini, A. Photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of fluoroquinolones in untreated river water under natural sunlight. Appl. Cat. B Environ. 2012, 119, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturini, M.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Pretali, L.; Profumo, A.; Fasani, E.; Albini, A.; Migliavacca, R.; Nucleo, E. Photodegradation of fluoroquinolones in surface water and antimicrobial activity of the photoproducts. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5575–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Bano, R.; Sheraz, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Mirza, T.; Ansari, S.A. Photodegradation of levofloxacin in aqueous and organic solvents: A kinetic study. Acta Pharm. 2013, 63, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wammer, K.H.; Korte, A.R.; Lundeen, R.A.; Sundberg, J.E.; McNeill, K.; Arnold, W.A. Direct photochemistry of three fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin. Water Res. 2013, 47, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturini, M.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Pretali, L.; Ferri, E.N.; Profumo, A. Sunlight-induced degradation of fluoroquinolones in wastewater effluent: Photoproducts identification and toxicity. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Na, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Zhang, P.; Ren, H.; Yao, Z. New insights into the aquatic photochemistry of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Direct photodegradation, hydroxyl-radical oxidation, and antibacterial activity changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckowiak, A.; Kamiński, B.; Urbaniak, B.; Dereziński, P.; Klupczyńska, A.; Darul-Duszkiewicz, M.; Kokot, Z.J. A study of ofloxacin and levofloxacin photostability in aqueous solutions. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 85, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Halsall, C.; Chen, C.E.; Zhang, P.; Dong, Q.; Yao, Z. Exploring the aquatic photodegradation of two ionisable fluoroquinolone antibiotics–gatifloxacin and balofloxacin: Degradation kinetics, photobyproducts and risk to the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyrski, A.; Anusiak, K.; Teżyk, A. The degradation of levofloxacin in infusions exposed to daylight with an identification of a degradation product with HPLC-MS. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Tang, Y.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Insights into the effects of acidification on sewage sludge dewaterability through pH repeated adjustment. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczkaj, G.; Fernandes, A. Wastewater treatment by means of advanced oxidation processes at basic pH conditions: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 608–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, M.R.; Pauer, J.J.; Mihelcic, J.R. Biochemical oxygen demand. Environ. Ecol. Chem. 2009, 2, 278–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; Volume 85. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciari, R.D.; Reynoso, E.; Spesia, M.B.; Criado, S.; Biasutti, M.A. Vancomycin-sensitized photooxidation in the presence of the natural pigment vitamin B2: Interaction with excited states and photogenerated ROS. Redox Rep. 2017, 22, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.H.; He, C.S.; Pei, D.N.; Dong, Y.; Yang, S.R.; Xiong, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, Z.-C.; Yao, G.; Lai, B. Review of characteristics, generation pathways and detection methods of singlet oxygen generated in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, C.; Schmidt, R. Physical mechanisms of generation and deactivation of singlet oxygen. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1685–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurlock, R.D.; Nonell, S.; Braslavsky, S.E.; Ogilby, P.R. Effect of solvent on the radiative decay of singlet molecular oxygen (1Δg). J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spesia, M.B.; Rovera, M.; Durantini, E.N. Photodynamic inactivation of Escherichia coli and Streptococcus mitis by cationic zinc (II) phthalocyanines in media with blood derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Guo, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ji, T.; Lin, Z.; Wang, W. Effect of C-5 position on the photochemical properties and phototoxicity of antofloxacin and levofloxacin: A stable and transient study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 155, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, A.; Emelina, T.; Karaseva, E.; Cramariuc, O.; Chukharev, V.; Karasev, V. Photochemical behavior and photolysis of protonated forms of levofloxacin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2014, 90, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murov, S.L.; Carmichael, I.; Hug, G.L. Handbook of Photochemistry; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Ji, Y.; Chovelon, J.M.; Lu, J. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics sensitized photodegradation of isoproturon. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciari, R.D.; Reynoso, E.; Montejano, H.A.; Biasutti, M.A. Photodegradation of prednisolone under UVB solar irradiation. Role of photogenerated ROS in the degradation mechanism. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2017, 16, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Biological chemistry of superoxide radicals. ChemTexts 2020, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.W.; Mabury, S.A. Photodegradation of the pharmaceuticals atorvastatin, carbamazepine, levofloxacin, and sulfamethoxazole in natural waters. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 67, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.Z.; Busetti, F.; Langsa, M.; Croué, J.P. Roles of singlet oxygen and dissolved organic matter in self-sensitized photo-oxidation of antibiotic norfloxacin under sunlight irradiation. Water Res. 2016, 106, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; Lebedev, A.T.; Zhang, Y. Singlet oxygen presenting a higher detoxification potential on enrofloxacin than sulfate and hydroxyl radicals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Liang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, C.; Du, J.; Wang, C. Energy-saving photo-degradation of three fluoroquinolone antibiotics under VUV/UV irradiation: Kinetics, mechanism, and antibacterial activity reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.D.; Maniero, M.G.; Guimaraes, J.R. Lomefloxacin degradation: Antimicrobial activity, toxicity and byproducts. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2015, 18, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
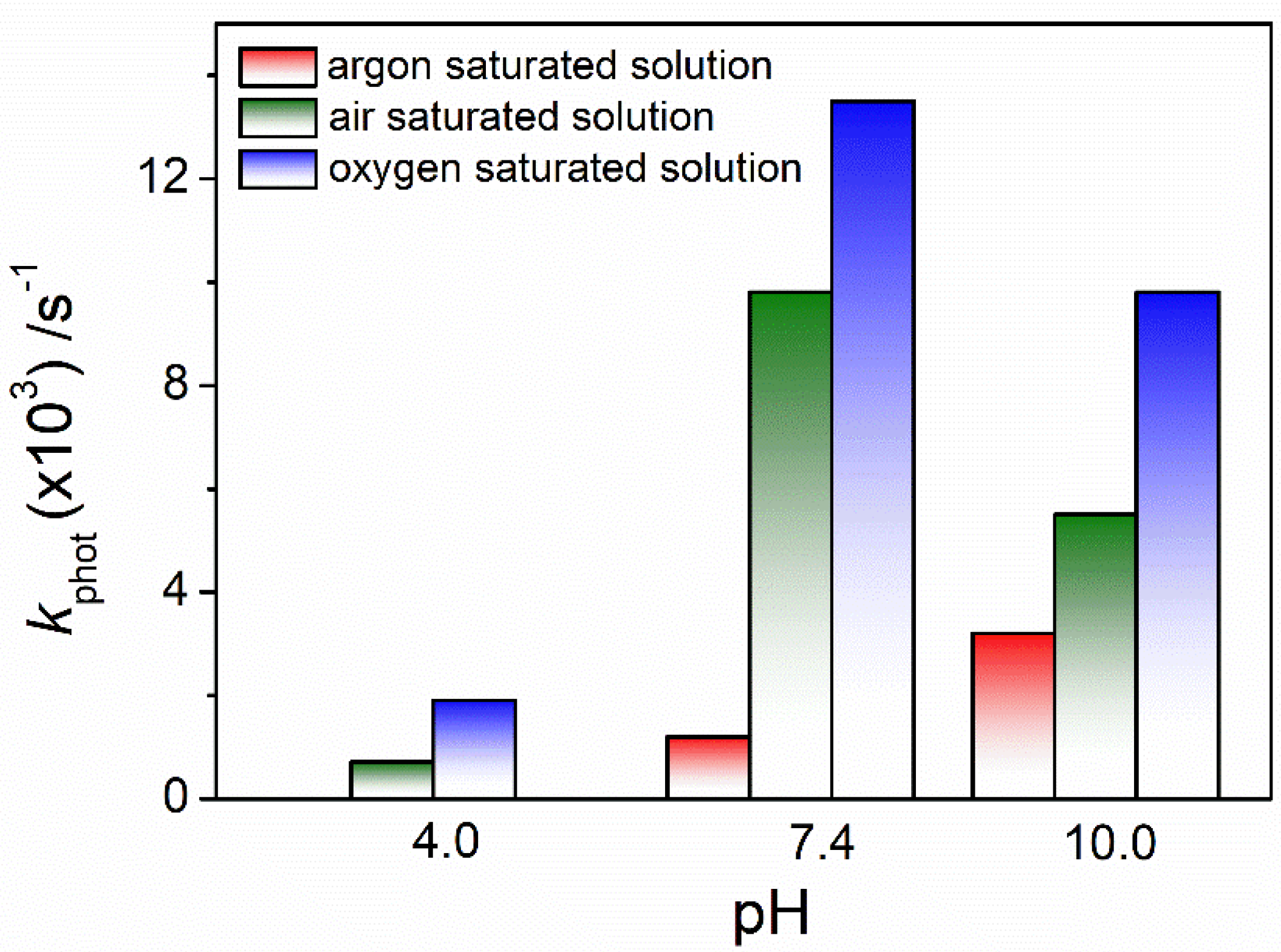

| kphot (×103)/s−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Argon | Air | Oxygen | |
| pH | ||||
| 4.0 | ~0 | 0.71 ± 0.03 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | |
| 7.4 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 9.8 ± 0.1 | 13.5 ± 0.1 | |
| 10.0 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 9.8 ± 0.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biondi, M.A.; Spesia, M.B.; Sabini, M.C.; Biasutti, M.A.; Montejano, H.A.; Reynoso, E. Critical Effect of Oxygen Concentration and Acidity on the Efficiency of Photodegradation of Levofloxacin with Solar UVB Light; Cytotoxicity on Mammalian Cells of the Photoproducts and Its Activity on Pathogenic Bacteria. Compounds 2025, 5, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5020023
Biondi MA, Spesia MB, Sabini MC, Biasutti MA, Montejano HA, Reynoso E. Critical Effect of Oxygen Concentration and Acidity on the Efficiency of Photodegradation of Levofloxacin with Solar UVB Light; Cytotoxicity on Mammalian Cells of the Photoproducts and Its Activity on Pathogenic Bacteria. Compounds. 2025; 5(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiondi, Macarena Agostina, Mariana Belén Spesia, María Carola Sabini, María Alicia Biasutti, Hernán Alfredo Montejano, and Eugenia Reynoso. 2025. "Critical Effect of Oxygen Concentration and Acidity on the Efficiency of Photodegradation of Levofloxacin with Solar UVB Light; Cytotoxicity on Mammalian Cells of the Photoproducts and Its Activity on Pathogenic Bacteria" Compounds 5, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5020023
APA StyleBiondi, M. A., Spesia, M. B., Sabini, M. C., Biasutti, M. A., Montejano, H. A., & Reynoso, E. (2025). Critical Effect of Oxygen Concentration and Acidity on the Efficiency of Photodegradation of Levofloxacin with Solar UVB Light; Cytotoxicity on Mammalian Cells of the Photoproducts and Its Activity on Pathogenic Bacteria. Compounds, 5(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds5020023








