Feline Parasitic Infections, Risk Factors, and Their Association with Parasitic Treatment in Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
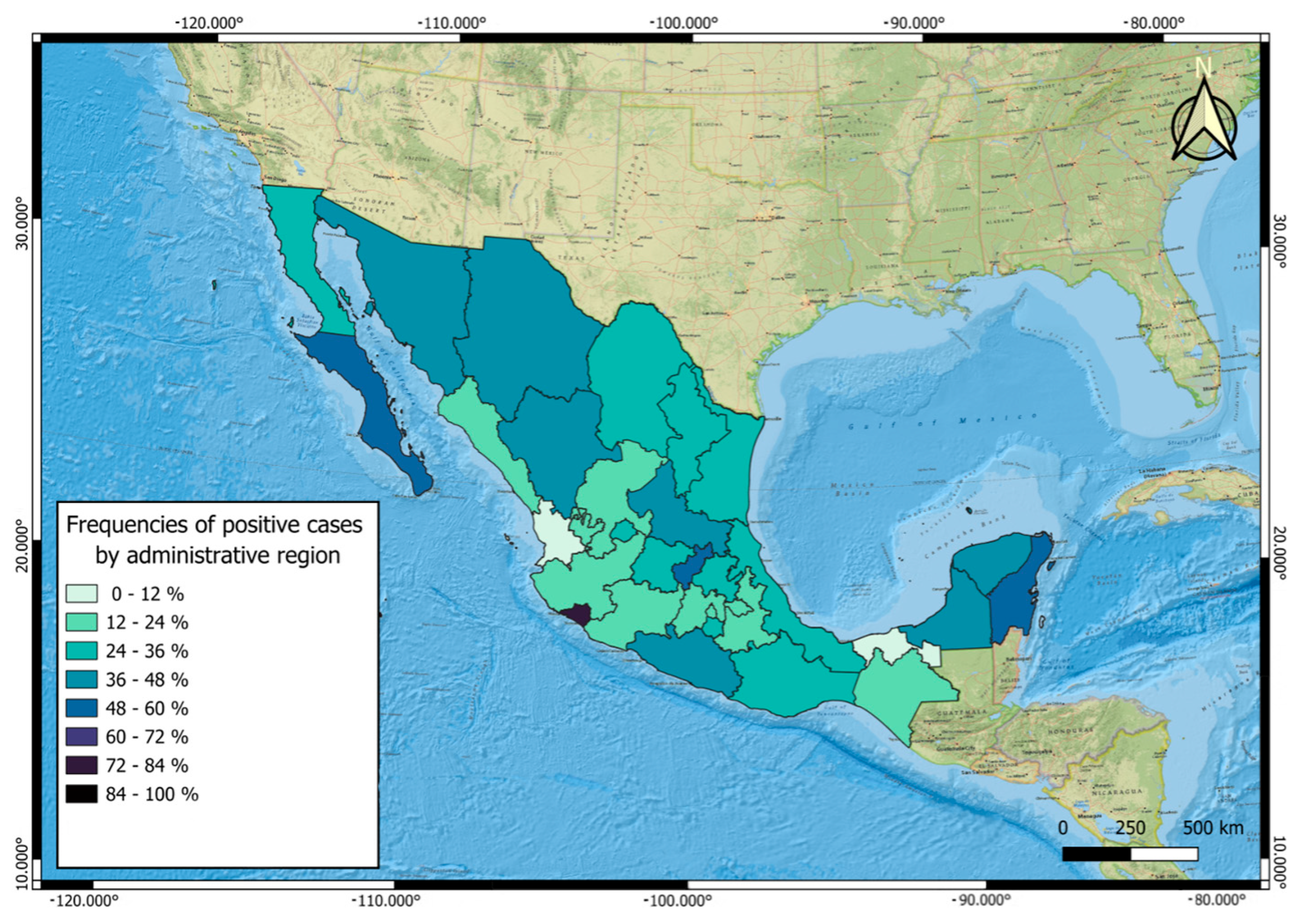
2.2. Georeferencing of Sampling Sites
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Parasite Detection
2.4.1. Macroscopic Technique
2.4.2. Microscopic Technique
2.4.3. Fecal Flotation Technique
2.4.4. Faust Technique
2.4.5. Sedimentation Technique
2.4.6. Graham Technique
2.4.7. Kinyoun Technique
2.4.8. Ectoparasite Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics Statement
2.7. Data Availability Statement
3. Results
3.1. Study Population Data
3.2. Parasite Positivity Frequencies
3.3. Coinfections
3.4. Risk Factors
3.4.1. Overall Parasitism
3.4.2. Endoparasites
3.4.3. Ectoparasites
3.5. Antiparasitic Treatments
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morchón, R.; Gabrielli, S.; Ciuca, L.; Napoli, E.; Carretón, E. Editorial: Advancements in understanding zoonotic parasitic diseases. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1539556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.G.; Fanelli, A.; Carvalho, J.; Serrano, E.; Domenech, G.; Alonso, F.; Martínez-Carrasco, C. Urban landscape and infection risk in free-roaming cats. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevins, S.N.; Carver, S.; Boydston, E.E.; Lyren, L.M.; Alldredge, M.; Logan, K.A.; Riley, S.P.D.; Fisher, R.N.; Vickers, T.W.; Boyce, W. Three pathogens in sympatric populations of pumas, bobcats, and domestic cats: Implications for infectious disease transmission. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, J.; Magnusson, U. Zoonotic pathogens in urban animals: Enough research to protect the health of the urban population? Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2020, 21, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.S.; de Souza Machado, D.; Caçador, M.E.; Ferreira, G.A.; Dickman, C.R.; Ceballos, M.C.; Prezoto, F.; Sant’Anna, A.C. The Wildcat That Lives in Me: A Review on Free-Roaming Cats (Felis catus) in Brazil, Focusing on Research Priorities, Management, and Their Impacts on Cat Welfare. Animals 2025, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baneth, G.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Otranto, D.; Guillot, J.; Blaga, R.; Deplazes, P.; Solano-Gallego, L. Major Parasitic Zoonoses Associated with Dogs and Cats in Europe. J. Comp. Pathol. 2016, 155, S54–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkes, A.H.; Bessant, C.; Cope, K.; Ellis, S.L.H.; Finka, L.; Halls, V.; Hiestand, K.; Horsford, K.; Laurence, C.; MacFarlaine, I. ISFM guidelines on population management and welfare of unowned domestic cats (Felis catus). J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESCCAP. Worm control in dogs and cats. In Guideline 01; European Scientific Counsel Companion Animal Parasites: Malvern, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, M.; Vismarra, A.; Zanet, S.; Morelli, S.; Galuppi, R.; Cringoli, G.; Lia, R.; Diaferia, M.; Frangipane di Regalbono, A.; Venegoni, G.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with cat parasites in Italy: A multicenter study. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Roldan, J.A.; Otranto, D. Zoonotic parasites associated with predation by dogs and cats. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.B.; Dhakal, M.A.; Ale, P.B.; Regmi, G.R.; Ghimire, T.R. Survey on the prevalence of intestinal parasites in domestic cats (Felis catus Linnaeus, 1758) in central Nepal. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Guerrero, R.E. Desarrollo y Análisis de Una Base de Datos de Los Parásitos de Los Gatos en la Ciudad de México y Área Metropolitana. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Giles, V.; Hortelano-Moncada, Y.; Torres-Carrera, G.; Gil-Alarcón, G.; Oceguera-Figueroa, A.; García-Prieto, L.; Osorio-Sarabia, D.; Cervantes, F.A.; Arenas, P. Helminths of free-ranging dogs and cats in an urban natural reserve in Mexico City and their potential risk as zoonotic agents. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baak-Baak, C.; Garcia-Rejon, J.; Tzuc-Dzul, J.; Nuñez-Corea, D.; Arana-Guardia, R.; Cetina-Trejo, R.; Machain-Williams, C.; Jimenez-Coello, M.; Acosta-Viana, K.; Torres-Chable, O.; et al. Four Species of Under-Reported Parasitic Arthropods in Mexico and Their Potential Role as Vectors of Pathogens. J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantó, G.J.; Guerrero, R.I.; Olvera-Ramírez, A.M.; Milian, F.; Mosqueda, J.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G. Prevalence of fleas and gastrointestinal parasites in free-roaming cats in central Mexico. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Arriaga, F. The temperature and regional climate effects on communitarian COVID-19 contagion in Mexico throughout phase 1. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naing, L.; Winn, T.; Rusli, B.N. Practical issues in calculating the sample size for prevalence studies. Arch. Orofac. Sci. 2006, 1, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.K. How to choose a sampling technique and determine sample size for research: A simplified guide for researchers. Oral Oncol. Rep. 2024, 12, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Corona, S.I.; Gomez-Vazquez, J.P.; López-Flores, E.A.; Vargas Estrada, D.; Arvizu-Tovar, L.O.; Pérez-Rivero, J.J.; Juárez Rodríguez, I.; Sierra Resendiz, A.; Soberanis-Ramos, O. Use of an extrapolation method to estimate the population of cats and dogs living at homes in Mexico in 2022. Vet. México OA 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Estadísticas Sobre Disponibilidad y Características de Animales de Compañía en los Hogares de México. 2023. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Allies, A.C. How to Help Community Cats: A Step-by-Step Guide to Trap-Neuter Return. 2019. Available online: https://www.alleycat.org/resources/how-to-help-community-cats-a-step-by-step-guide-to-trap-neuter-return/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Figueroa, C.J.A.; Jasso, V.C.; Liébano, H.E.; Martínez, L.P.; Rodríguez, V.R.I.; Zárate, R.J.J. Examen Coproparasitoscópico. In Técnicas Para el Diagnóstico de Parásitos Con Importancia en Salud Pública y Veterinaria; Rodríguez Vivas, R.I.e., Ed.; AMPAVE-CONASA: Mexico City, Mexico, 2015; p. 517. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, M.M.C.; Cruz, V.C.; Cruz, M.I.; Escutia, S.I. Muestras biológicas y muestreos para estudios parasitológicos. In Técnicas Para el Diagnóstico de Parásitos Con Importancia en Salud Pública y Veterinaria. México; Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I., Ed.; AMPAVE-CONASA: Mexico City, Mexico, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Guía Para la Interpretación de Cartografía Climática. 2017. Available online: http://internet.contenidos.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/productos/prod_serv/contenidos/espanol/bvinegi/productos/geografia/publicaciones/guias-carto/clima/CLIMATIII.pdf#page=1&zoom=auto,-102,792 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Nagamori, Y.; Payton, M.E.; Duncan-Decocq, R.; Johnson, E.M. Fecal survey of parasites in free-roaming cats in northcentral Oklahoma, United States. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 14, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamori, Y.; Payton, M.E.; Looper, E.; Apple, H.; Johnson, E.M. Retrospective survey of parasitism identified in feces of client-owned cats in North America from 2007 through 2018. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 277, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowska, I.A.; Kornaś, S.; Piontek, A.M.; Rola, K. The Prevalence of Endoparasites of Free Ranging Cats. Animals 2020, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poglayen, G.; Gelati, A.; Scala, A.; Naitana, S.; Musella, V.; Nocerino, M.; Cringoli, G.; Frangipane di Regalbono, A.; Habluetzel, A. Do natural catastrophic events and exceptional climatic conditions also affect parasites? Parasitology 2023, 150, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbe Cossío, T.L.; Montes Luna, A.D.; Ruiz Mejia, M.; Flores Ortega, A.; Heredia Cárdenas, R.; Romero Núñez, C. Risk factors associated with cat parasites in a feline medical center. JFMS Open Rep. 2021, 7, 20551169211033183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugnet, F.; Bourdeau, P.; Chalvet-Monfray, K.; Cozma, V.; Farkas, R.; Guillot, J.; Halos, L.; Joachim, A.; Losson, B.; Miró, G.; et al. Parasites of domestic owned cats in Europe: Co-infestations and risk factors. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcedo-Jiménez, J.; Alcala-Canto, Y.; Segura-Tinoco, J.; Valadez-Moctezuma, E.; Pérez-Rivero, J.J. Identifying Zoonotic Parasites in Domiciled and Non-Domiciled Dogs (Canis lupus familiaris) Within an Urban Zone of the Eastern State of Mexico. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e70059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesołowska, A. Sex—The most underappreciated variable in research: Insights from helminth-infected hosts. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugnet, F.; Taweethavonsawat, P.; Traversa, D.; Fourie, J.; McCall, J.; Tielemans, E.; Geurden, T. World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology (WAAVP): Second edition of guidelines for evaluating the efficacy of anthelmintics for dogs and cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2022, 312, 109815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, B.J.; Hoopes, J.; Cumming, B. Cutaneous Larva Migrans Refractory to Therapy with Ivermectin: Case Report and Review of Implicated Zoonotic Pathogens, Epidemiology, Anthelmintic Drug Resistance and Therapy. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez Castro, P.D.; Howell, S.B.; Schaefer, J.J.; Avramenko, R.W.; Gilleard, J.S.; Kaplan, R.M. Multiple drug resistance in the canine hookworm Ancylostoma caninum: An emerging threat? Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Rodríguez, D.; Seco-Hidalgo, V.; Lopez, A.; Romero-Sandoval, N.; Calvopiña, M.; Guevara, A.; Baldeón, L.; Rodríguez, A.; Mejia, R.; Nutman, T.B.; et al. Geographic Distribution of Human Infections with Zoonotic Ancylostoma ceylanicum and Anthropophilic Hookworms in Ecuador: A Retrospective Analysis of Archived Stool Samples. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 110, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Candelas, L.A.; Aguilar-Castro, J.; Buendía-González, F.O.; Fernández-Rivera, O.; Nolasco-Pérez, T.d.J.; López-Padilla, M.S.; Chavira-Ramírez, D.R.; Legorreta-Herrera, M. 17β-Estradiol is involved in the sexual dimorphism of the immune response to malaria. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 643851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.O.; André, M.R.; Šlapeta, J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Vector biology of the cat flea Ctenocephalides felis. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.; Helps, C.; Tasker, S.; Newbury, H.; Wall, R. Pathogens in fleas collected from cats and dogs: Distribution and prevalence in the UK. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bett, B.; Kiunga, P.; Gachohi, J.; Sindato, C.; Mbotha, D.; Robinson, T.; Lindahl, J.; Grace, D. Effects of climate change on the occurrence and distribution of livestock diseases. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 137, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beugnet, F.; Labuschagne, M.; Vos, C.; Crafford, D.; Fourie, J. Analysis of Dipylidium caninum tapeworms from dogs and cats, or their respective fleas—Part 2. Distinct canine and feline host association with two different Dipylidium caninum genotypes. Parasite 2018, 25, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, C.; Drake, J.; Ariza, J.M. French national survey of dog and cat owners on the deworming behaviour and lifestyle of pets associated with the risk of endoparasites. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAPC. Companion Animal Parasite Council. 2025. Available online: https://capcvet.org/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Ketzis, J.; Mihalca, A.D.; Baneth, G.; Otranto, D.; Tort, G.P.; Watanabe, M.; Linh, B.K.; Inpankaew, T.; Jimenez Castro, P.D.; et al. TroCCAP recommendations for the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of parasitic infections in dogs and cats in the tropics. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESCCAP. European Scientific Counsel Companion Animal Parasites. Control of Ectoparasites in Dogs and Cats. 2025. Available online: https://www.esccap.org/guidelines/gl3/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Beugnet, F.; Halos, L.; Guillot, J. Textbook of Clinical Parasitology in Dogs and Cats; Servet Editorial—Grupo Asís Biomedia, S.L.: Zaragoza, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ydsten, K.A.; Öhd, J.N.; Hellgren, U.; Asgeirsson, H. Prevalence of Nitroimidazole-Refractory Giardiasis Acquired in Different World Regions, Sweden, 2008–2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2025, 31, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | Subcategory | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parasitism | Positive | 829 | 30.1 |
| Negative | 1929 | 69.9 | |
| Sex | Female | 2091 | 75.8 |
| Male | 484 | 17.5 | |
| Not determined | 183 | 6.6 | |
| Age | Kittens (0–6 months) | 1236 | 44.8 |
| Young (6–12 months) | 418 | 15.2 | |
| Adults (1–7 years) | 862 | 31.3 | |
| Senior (>7 years) | 242 | 8.8 | |
| Lifestyle | Domesticated | 1840 | 66.7 |
| Feral | 918 | 33.3 | |
| Climate | Tropical (A) | 734 | 39.0 |
| Arid (B) | 683 | 19.8 | |
| Temperate (C) | 1341 | 30.4 |
| Parasite | n | % | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endoparasites | |||
| Ancylostoma | 448 | 16.2 | 14.9–17.6 |
| Dipylidium | 309 | 11.2 | 10.0–12.4 |
| Cryptosporidium | 205 | 7.4 | 6.5–8.4 |
| Cystoisospora | 184 | 6.7 | 5.7–7.6 |
| Toxocara | 94 | 3.4 | 2.7–4.1 |
| Giardia | 72 | 2.6 | 2.0–3.2 |
| Ectoparasites | |||
| Ctenocephalides | 495 | 17.9 | 16.5–19.4 |
| Notoedres | 53 | 1.9 | 1.4–2.4 |
| Felicola | 50 | 1.8 | 1.3–2.3 |
| Otodectes | 46 | 1.7 | 1.2–2.1 |
| Rhipicephalus | 4 | 0.1 | 0.0–0.3 |
| Number of Genera | n (Cats) | % | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 genus | 1372 | 49.8 | 47.9–51.7 |
| 2 genera | 692 | 25.1 | 23.5–26.8 |
| 3 genera | 386 | 14.0 | 12.8–15.4 |
| 4 genera | 188 | 6.8 | 5.9–7.8 |
| 5 genera | 77 | 2.8 | 2.2–3.5 |
| 6 genera | 31 | 1.1 | 0.7–1.6 |
| 7 genera | 10 | 0.4 | 0.2–0.7 |
| 8 genera | 2 | 0.1 | 0.0–0.3 |
| Category | n | % | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treated 3 months prior | 454 | 16.5 | 15.1–17.9 |
| Treated 6 months prior | 264 | 9.6 | 8.5–10.7 |
| Treated 1 year prior | 164 | 5.9 | 5.1–6.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segura-Tinoco, J.C.; Morales-Guerrero, R.E.; Pérez-Rivero, J.J.; Rico-Chávez, O.; Del Río-Araiza, V.H.; Alcala-Canto, Y. Feline Parasitic Infections, Risk Factors, and Their Association with Parasitic Treatment in Mexico. Parasitologia 2025, 5, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030048
Segura-Tinoco JC, Morales-Guerrero RE, Pérez-Rivero JJ, Rico-Chávez O, Del Río-Araiza VH, Alcala-Canto Y. Feline Parasitic Infections, Risk Factors, and Their Association with Parasitic Treatment in Mexico. Parasitologia. 2025; 5(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegura-Tinoco, Julio César, Rocío Estefanía Morales-Guerrero, Juan José Pérez-Rivero, Oscar Rico-Chávez, Victor Hugo Del Río-Araiza, and Yazmin Alcala-Canto. 2025. "Feline Parasitic Infections, Risk Factors, and Their Association with Parasitic Treatment in Mexico" Parasitologia 5, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030048
APA StyleSegura-Tinoco, J. C., Morales-Guerrero, R. E., Pérez-Rivero, J. J., Rico-Chávez, O., Del Río-Araiza, V. H., & Alcala-Canto, Y. (2025). Feline Parasitic Infections, Risk Factors, and Their Association with Parasitic Treatment in Mexico. Parasitologia, 5(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia5030048






